Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Developer Guide
A guide to development using Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 6.
Edition 1
Abstract
Preface
Chapter 1. JBoss Data Grid
1.1. About JBoss Data Grid
- Schemaless key-value store – Red Hat JBoss Data Grid is a NoSQL database that provides the flexibility to store different objects without a fixed data model.
- Grid-based data storage – Red Hat JBoss Data Grid is designed to easily replicate data across multiple nodes.
- Elastic scaling – Adding and removing nodes is achieved simply and is non-disruptive.
- Multiple access protocols – It is easy to access to the data grid using REST, Memcached, Hot Rod, or simple map-like API.
1.2. JBoss Data Grid Usage Modes
- Remote Client-Server mode
- Remote Client-Server mode provides a managed, distributed and clusterable data grid server. Applications can remotely access the data grid server using Hot Rod, Memcached or REST client APIs.
- Library mode
- Library mode provides all the binaries required to build and deploy a custom runtime environment. The library usage mode allows local access to a single node in a distributed cluster. This usage mode gives the application access to data grid functionality within a virtual machine in the container being used. Supported containers include Tomcat 7 and JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6.
1.3. JBoss Data Grid Benefits
Benefits of JBoss Data Grid
- Massive Heap and High Availability
- In JBoss Data Grid, applications no longer need to delegate the majority of their data lookup processes to a large single server database for performance benefits. JBoss Data Grid completely removes the bottleneck that exists in the vast majority of current enterprise applications.
Example 1.1. Massive Heap and High Availability Example
In a sample grid with one hundred blade servers, each node has 2 GB storage space dedicated for a replicated cache. In this case, all the data in the grid is copies of the 2 GB data. In contrast, using a distributed grid (assuming the requirement of one copy per data item) the resulting memory backed virtual heap contains 100 GB data. This data can now be effectively accessed from anywhere in the grid. In case of a server failure, the grid promptly creates new copies of the lost data and places them on operational servers in the grid. - Scalability
- Due to the even distribution of data in JBoss Data Grid, the only upper limit for the size of the grid is the group communication on the network. The network's group communication is minimal and restricted only to the discovery of new nodes. Nodes are permitted by all data access patterns to communicate directly via peer-to-peer connections, facilitating further improved scalability. JBoss Data Grid clusters can be scaled up or down in real time without requiring an infrastructure restart. The result of the real time application of changes in scaling policies results in an exceptionally flexible environment.
- Data Distribution
- JBoss Data Grid uses consistent hash algorithms to determine the locations for keys in clusters. Benefits associated with consistent hashing include:Data distribution ensures that sufficient copies exist within the cluster to provide durability and fault tolerance, while not an abundance of copies, which would reduce the environment's scalability.
- cost effectiveness.
- speed.
- deterministic location of keys with no requirements for further metadata or network traffic.
- Persistence
- JBoss Data Grid exposes a
CacheStoreinterface and several high-performance implementations, including the JDBC Cache stores and file system based cache stores. Cache stores can be used to seed the cache and to ensure that the relevant data remains safe from corruption. The cache store also overflows data to the disk when required if a process runs out of memory. - Language bindings
- JBoss Data Grid supports both the popular Memcached protocol, with existing clients for a large number of popular programming languages, as well as an optimized JBoss Data Grid specific protocol called Hot Rod. As a result, instead of being restricted to Java, JBoss Data Grid can be used for any major website or application.
- Management
- In a grid environment of several hundred or more servers, management is an important feature. JBoss Operations Network, the enterprise network management software, is the best tool to manage multiple JBoss Data Grid instances. JBoss Operations Network's features allow easy and effective monitoring of the Cache Manager and cache instances.
1.4. JBoss Data Grid Prerequisites
1.5. JBoss Data Grid Version Information
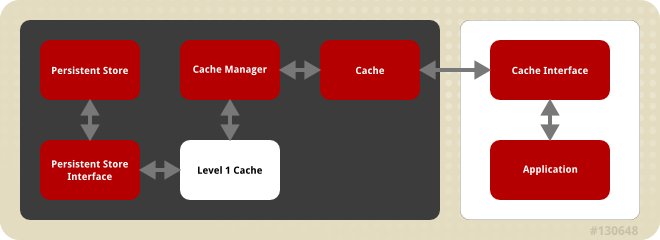
1.6. JBoss Data Grid Cache Architecture
Figure 1.1. JBoss Data Grid Cache Architecture
- Elements that a user cannot directly interact with (depicted within a dark box), which includes the Cache, Cache Manager, Level 1 Cache, Persistent Store Interfaces and the Persistent Store.
- Elements that a user can interact directly with (depicted within a white box), which includes Cache Interfaces and the Application.
JBoss Data Grid's cache architecture includes the following elements:
- The Persistent Store permanently houses cache instances and entries.
- JBoss Data Grid offers two Persistent Store Interfaces to access the persistent store. Persistent store interfaces can be either:
- A cache loader is a read only interface that provides a connection to a persistent data store. A cache loader can locate and retrieve data from cache instances and from the persistent store.
- A cache store extends the cache loader functionality to include write capabilities by exposing methods that allow the cache loader to load and store states.
- The Level 1 Cache (or L1 Cache) stores remote cache entries after they are initially accessed, preventing unnecessary remote fetch operations for each subsequent use of the same entries.
- The Cache Manager is the primary mechanism used to retrieve a Cache instance in JBoss Data Grid, and can be used as a starting point for using the Cache.
- The Cache houses cache instances retrieved by a Cache Manager.
- Cache Interfaces use protocols such as Memcached and Hot Rod, or REST to interface with the cache. For details about the remote interfaces, refer to the Developer Guide.
- Memcached is a distributed memory object caching system used to store key-values in-memory. The Memcached caching system defines a text based, client-server caching protocol called the Memcached protocol.
- Hot Rod is a binary TCP client-server protocol used in JBoss Data Grid. It was created to overcome deficiencies in other client/server protocols, such as Memcached. Hot Rod enables clients to do smart routing of requests in partitioned or distributed JBoss Data Grid server clusters.
- The REST protocol eliminates the need for tightly coupled client libraries and bindings. The REST API introduces an overhead, and requires a REST client or custom code to understand and create REST calls.
- An application allows the user to interact with the cache via a cache interface. Browsers are a common example of such end-user applications.
Part I. Programmable APIs
- Cache
- Batching
- Grouping
- CacheStore
- Externalizable
Chapter 2. The Cache API
2.1. About the Cache API
ConcurrentMap interface. How entries are stored depends on the cache mode in use. For example, an entry may be replicated to a remote node or an entry may be looked up in a cache store.
Note
2.2. Using the ConfigurationBuilder API to Configure the Cache API
ConfigurationBuilder helper object.
An explanation of each line of the provided configuration is as follows:
- In the first line of the configuration, a new cache configuration object (named
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.REPL_SYNC).build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.REPL_SYNC).build();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow c) is created using theConfigurationBuilder. Configurationcis assigned the default values for all cache configuration options except the cache mode, which is overridden and set to synchronous replication (REPL_SYNC). - In the second line of the configuration, a new variable (of type
String newCacheName = "repl";
String newCacheName = "repl";Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow String) is created and assigned the valuerepl. - In the third line of the configuration, the cache manager is used to define a named cache configuration for itself. This named cache configuration is called
manager.defineConfiguration(newCacheName, c);
manager.defineConfiguration(newCacheName, c);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow repland its configuration is based on the configuration provided for cache configurationcin the first line. - In the fourth line of the configuration, the cache manager is used to obtain a reference to the unique instance of the
Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);
Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow replthat is held by the cache manager. This cache instance is now ready to be used to perform operations to store and retrieve data.
2.3. Per-Invocation Flags
2.3.1. About Per-Invocation Flags
2.3.2. Per-Invocation Flag Functions
putForExternalRead() method in JBoss Data Grid's Cache API uses flags internally. This method can load a JBoss Data Grid cache with data loaded from an external resource. To improve the efficiency of this call, JBoss Data Grid calls a normal put operation passing the following flags:
- The
ZERO_LOCK_ACQUISITION_TIMEOUTflag: JBoss Data Grid uses an almost zero lock acquisition time when loading data from an external source into a cache. - The
FAIL_SILENTLYflag: If the locks cannot be acquired, JBoss Data Grid fails silently without throwing any lock acquisition exceptions. - The
FORCE_ASYNCHRONOUSflag: If clustered, the cache replicates asynchronously, irrespective of the cache mode set. As a result, a response from other nodes is not required.
putForExternalRead calls of this type are used because the client can retrieve the required data from a persistent store if the data cannot be found in memory. If the client encounters a cache miss, it should retry the operation.
2.3.3. Configure Per-Invocation Flags
withFlags() method call. For example:
Cache cache = ...
cache.getAdvancedCache()
.withFlags(Flag.SKIP_CACHE_STORE, Flag.CACHE_MODE_LOCAL)
.put("local", "only");
Cache cache = ...
cache.getAdvancedCache()
.withFlags(Flag.SKIP_CACHE_STORE, Flag.CACHE_MODE_LOCAL)
.put("local", "only");Note
withFlags() method for each invocation. If the cache operation must be replicated onto another node, the flags are also carried over to the remote nodes.
2.3.4. Per-Invocation Flags Example
put(), should not return the previous value, two flags are used. The two flags prevent a remote lookup (to get the previous value) in a distributed environment, which in turn prevents the retrieval of the undesired, potential, previous value. Additionally, if the cache is configured with a cache loader, the two flags prevent the previous value from being loaded from its cache store.
Cache cache = ...
cache.getAdvancedCache()
.withFlags(Flag.SKIP_REMOTE_LOOKUP, Flag.SKIP_CACHE_LOAD)
.put("local", "only")
Cache cache = ...
cache.getAdvancedCache()
.withFlags(Flag.SKIP_REMOTE_LOOKUP, Flag.SKIP_CACHE_LOAD)
.put("local", "only")
2.4. The AdvancedCache Interface
2.4.1. About the AdvancedCache Interface
AdvancedCache interface, geared towards extending JBoss Data Grid, in addition to its simple Cache Interface. The AdvancedCache Interface can:
- Inject custom interceptors.
- Access certain internal components.
- Apply flags to alter the behavior of certain cache methods.
AdvancedCache:
AdvancedCache advancedCache = cache.getAdvancedCache();
AdvancedCache advancedCache = cache.getAdvancedCache();
2.4.2. Flag Usage with the AdvancedCache Interface
AdvancedCache.withFlags() to apply any number of flags to a cache invocation, for example:
advancedCache.withFlags(Flag.CACHE_MODE_LOCAL, Flag.SKIP_LOCKING)
.withFlags(Flag.FORCE_SYNCHRONOUS)
.put("hello", "world");
advancedCache.withFlags(Flag.CACHE_MODE_LOCAL, Flag.SKIP_LOCKING)
.withFlags(Flag.FORCE_SYNCHRONOUS)
.put("hello", "world");
2.4.3. Custom Interceptors and the AdvancedCache Interface
AdvancedCache Interface provides a mechanism that allows advanced developers to attach custom interceptors. Custom interceptors can alter the behavior of the Cache API methods and the AdvacedCache Interface can be used to attach such interceptors programmatically at run time.
2.4.4. Custom Interceptors
2.4.4.1. About Custom Interceptors
2.4.4.2. Custom Interceptor Design
- A custom interceptor must extend the
CommandInterceptor. - A custom interceptor must declare a public, empty constructor to allow for instantiation.
- A custom interceptor must have JavaBean style setters defined for any property that is defined through the
propertyelement.
2.4.4.3. Add Custom Interceptors
2.4.4.3.1. Adding Custom Interceptors Declaratively
Note
2.4.4.3.2. Adding Custom Interceptors Programmatically
AdvancedCache.
CacheManager cm = getCacheManager();
Cache aCache = cm.getCache("aName");
AdvancedCache advCache = aCache.getAdvancedCache();
CacheManager cm = getCacheManager();
Cache aCache = cm.getCache("aName");
AdvancedCache advCache = aCache.getAdvancedCache();
addInterceptor() method to add the interceptor.
advCache.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor(), 0);
advCache.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor(), 0);Chapter 3. The Batching API
3.1. About the Batching API
Note
3.2. About Java Transaction API Transactions
- First, it retrieves the transactions currently associated with the thread.
- If not already done, it registers
XAResourcewith the transaction manager to receive notifications when a transaction is committed or rolled back.
3.3. Batching and the Java Transaction API (JTA)
- Locks acquired during an invocation are retained until the transaction commits or rolls back.
- All changes are replicated in a batch on all nodes in the cluster as part of the transaction commit process. Ensuring that multiple changes occur within the single transaction, the replication traffic remains lower and improves performance.
- When using synchronous replication or invalidation, a replication or invalidation failure causes the transaction to roll back.
- If a
CacheLoaderthat is compatible with a JTA resource, for example a JTADataSource, is used for a transaction, the JTA resource can also participate in the transaction. - All configurations related to a transaction apply for batching as well.
<transaction syncRollbackPhase="false" syncCommitPhase="false" useEagerLocking="true" eagerLockSingleNode="true" />
<transaction syncRollbackPhase="false"
syncCommitPhase="false"
useEagerLocking="true"
eagerLockSingleNode="true" />Note
3.4. Using the Batching API
3.4.1. Enable the Batching API
<distributed-cache name="default" batching="true"> ... </distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache name="default" batching="true">
...
</distributed-cache>
3.4.2. Configure the Batching API
To configure the Batching API in the XML file:
<invocationBatching enabled="true" />
<invocationBatching enabled="true" />
To configure the Batching API programmatically use:
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().invocationBatching().enable().build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().invocationBatching().enable().build();3.4.3. Use the Batching API
startBatch() and endBatch() on the cache as follows to use batching:
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache();
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache();Example 3.1. Without Using Batch
cache.put("key", "value");
cache.put("key", "value"); cache.put(key, value); line executes, the values are replaced immediately.
Example 3.2. Using Batch
cache.endBatch(true); executes, all modifications made since the batch started are replicated.
cache.endBatch(false); executes, changes made in the batch are discarded.
3.4.4. Batching API Usage Example
Example 3.3. Batching API Usage Example
3.5. Transactions
3.5.1. Transactions Spanning Multiple Cache Instances
3.5.2. Transaction/Batching and Invalidation Messages
3.5.3. The Transaction Manager
3.5.3.1. About JTA Transaction Manager Lookup Classes
TransactionManagerLookup interface. When initialized, the cache creates an instance of the specified class and invokes its getTransactionManager() method to locate and return a reference to the Transaction Manager.
- The
DummyTransactionManagerLookupprovides a transaction manager for testing purposes. This testing transaction manager is not for use in a production environment and is severely limited in terms of functionality, specifically for concurrent transactions and recovery. - The
JBossStandaloneJTAManagerLookupis the default transaction manager when JBoss Data Grid runs in a standalone environment. It is a fully functional JBoss Transactions based transaction manager that overcomes the functionality limits of theDummyTransactionManagerLookup. - The
GenericTransactionManagaerLookupis a lookup class used to locate transaction managers in most Java EE application servers. If no transaction manager is located, it defaults toDummyTransactionManagerLookup. - The
JBossTransactionManagerLookupis a lookup class that locates a transaction manager within a JBoss Application Server instance.
Note
3.5.3.2. About DummyTransactionManagerLookup
DummyTransactionManagerLookup provides a transaction manager for testing purposes. This testing transaction manager is not for use in a production environment and is severely limited in terms of functionality, specifically for concurrent transactions and recovery.
Note
3.5.3.3. About JBossStandaloneJTAManagerLookup
JBossStandaloneJTAManagerLookup is the default transaction manager when JBoss Data Grid runs in a standalone environment. It is a fully functional JBoss Transactions based transaction manager that overcomes the functionality limits of the DummyTransactionManagerLookup.
Note
3.5.3.4. About GenericTransactionManagerLookup
GenericTransactionManagerLookup is a lookup class used to locate transaction managers in most Java EE application servers. If no transaction manager is located, it defaults to DummyTransactionManagerLookup.
Note
3.5.3.5. About JBossTransactionManagerLookup
JBossTransactionManagerLookup is a lookup class that locates a transaction manager within a JBoss Application Server instance.
Note
3.5.3.6. Use the Transaction Manager
3.5.3.6.1. Obtain the Transaction Manager From the Cache
Procedure 3.1. Obtain the Transaction Manager from the Cache
- Define a
transactionManagerLookupClassby adding the following property to yourBasicCacheContainer's configuration location properties:Configuration config = new ConfigurationBuilder() ... .transaction().transactionManagerLookup(new GenericTransactionManagerLookup())
Configuration config = new ConfigurationBuilder() ... .transaction().transactionManagerLookup(new GenericTransactionManagerLookup())Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Call
TransactionManagerLookup.getTransactionManageras follows:TransactionManager tm = cache.getAdvancedCache().getTransactionManager();
TransactionManager tm = cache.getAdvancedCache().getTransactionManager();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.5.3.6.2. Transaction Configuration
- The
modeattribute sets the cache transaction mode. Valid values for this attribute areNONE(default),NON_XA,NON_DURABLE_XA,FULL_XA. - The
stop-timeoutattribute indicates the number of milliseconds JBoss Data Grid waits for ongoing remote and local transactions to conclude when the cache is stopped. - The
lockingattribute specifies the locking mode used for the cache. Valid values for this attribute areOPTIMISTIC(default) andPESSIMISTIC.
3.5.3.6.3. Transaction Manager and XAResources
XAResource implementation to run XAResource.recover on it.
3.5.3.6.4. Obtain a XAResource Reference
XAResource, use the following API:
XAResource xar = cache.getAdvancedCache().getXAResource();
XAResource xar = cache.getAdvancedCache().getXAResource();
3.5.3.6.5. Default Distributed Transaction Behavior
XAResource. In situations where JBoss Data Grid does not need to be a participant in a transaction, it can be notified about the lifecycle status (for example, prepare, complete, etc.) of the transaction via a synchronization.
3.5.4. Transaction Synchronization
3.5.4.1. About Transaction (JTA) Synchronizations
XAResource. As a result, the Transaction Manager optimizes transaction operations so that they require the one phase commit (1PC) algorithm instead of the two phase commit (2PC) algorithm.
3.5.4.2. Enable Synchronization
NONE(synchronous), or;NO_XA(synchronous).
Note
3.5.5. State Reconciliation
3.5.5.1. About State Reconciliation
3.5.5.2. About Transaction Recovery
3.5.5.3. Enable Transaction Recovery
Enable transaction recovery using XML configuration as follows:
<transaction useEagerLocking="true" eagerLockSingleNode="true">
<recovery enabled="true" recoveryInfoCacheName="noRecovery"/>
</transaction>
<transaction useEagerLocking="true" eagerLockSingleNode="true">
<recovery enabled="true" recoveryInfoCacheName="noRecovery"/>
</transaction>
recoveryInfoCacheName attribute is optional.
Alternatively, enable transaction recovery through the fluent configuration API as follows:
Procedure 3.2. Configure Transaction Recovery Programmatically
- To enable JBoss Data Grid's Transaction Recovery, call
.recovery:configuration.fluent().transaction().recovery();
configuration.fluent().transaction().recovery();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To check Transactions Recovery's status, use the following programmatic configuration:
boolean isRecoveryEnabled = configuration.isTransactionRecoveryEnabled();
boolean isRecoveryEnabled = configuration.isTransactionRecoveryEnabled();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To disable JBoss Data Grid's Transaction recovery, use the following programmatic configuration:
configuration.fluent().transaction().recovery().disable();
configuration.fluent().transaction().recovery().disable();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.5.5.4. Transaction Recovery Process
Procedure 3.3. The Transaction Recovery Process
- The Transaction Manager creates a list of transactions that require intervention.
- The system administrator, connected to JBoss Data Grid using JMX, is presented with the list of transactions (including transaction IDs) using email or logs. The status of each transaction is either
COMMITTEDorPREPARED. If some transactions are in bothCOMMITTEDandPREPAREDstates, it indicates that the transaction was committed on some nodes while in the preparation state on others. - The System Administrator visually maps the XID received from the Transaction Manager to a JBoss Data Grid internal ID. This step is necessary because the XID (a byte array) cannot be conveniently passed to the JMX tool and then reassembled by JBoss Data Grid without this mapping.
- The system administrator forces the commit or rollback process for a transaction based on the mapped internal ID.
3.5.5.5. Transaction Recovery Example
Example 3.4. Money Transfer from an Account Stored in a Database to an Account in JBoss Data Grid
- The
TransactionManager.commit()method is invoked to to run the two phase commit protocol between the source (the database) and the destination (JBoss Data Grid) resources. - The
TransactionManagertells the database and JBoss Data Grid to initiate the prepare phase (the first phase of a Two Phase Commit).
3.5.5.6. Transaction Memory and JMX Support
3.5.5.7. Forced Commit and Rollback Operations
3.5.5.8. Transactions and Exceptions
CacheException (or a subclass of the CacheException) within the scope of a JTA transaction, the transaction is automatically marked to be rolled back.
3.5.6. Deadlock Detection
3.5.6.1. About Deadlock Detection
disabled by default.
3.5.6.2. Enable Deadlock Detection
disabled by default but can be enabled and configured for each cache using the namedCache configuration element by adding the following:
<deadlockDetection enabled="true" spinDuration="1000"/>
<deadlockDetection enabled="true" spinDuration="1000"/>
Note
Chapter 4. The Grouping API
4.1. About the Grouping API
4.2. Grouping API Operations
- Intrinsic to the entry, which means it was generated by the key class.
- Extrinsic to the entry, which means it was generated by an external function.
4.3. Grouping API Configuration
To configure JBoss Data Grid using the programmatic API, call the following:
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().hash().groups().enabled().build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().hash().groups().enabled().build();To configure JBoss Data Grid using XML, use the following:
<clustering>
<hash>
<groups enabled="true" />
</hash>
</clustering>
<clustering>
<hash>
<groups enabled="true" />
</hash>
</clustering>@Group annotation within the method to specify the intrinsic group. For example:
Note
String.
Grouper interface. The computeGroup method within the Grouper interface returns the group.
Grouper operates as an interceptor and passes previously computed values to the computeGroup() method. If defined, @Group determines which group is passed to the first Grouper, providing improved group control when using intrinsic groups.
grouper to determine a key's group, its keyType must be assignable from the target key.
Grouper:
grouper uses the key class to extract the group from a key using a pattern. Information specified on the key class is ignored. Each grouper must be registered to be used.
When configuring JBoss Data Grid programmatically:
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().hash().groups().addGrouper(new KXGrouper()).build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().hash().groups().addGrouper(new KXGrouper()).build();Or when configuring JBoss Data Grid using XML:
Chapter 5. The CacheStore API
5.1. About the CacheStore API
5.2. The ConfigurationBuilder API
5.2.1. About the ConfigurationBuilder API
- Chain coding of configuration options in order to make the coding process more efficient
- Improve the readability of the configuration
5.2.2. Using the ConfigurationBuilder API
5.2.2.1. Programmatically Create a CacheManager and Replicated Cache
Procedure 5.1. Steps for Programmatic Configuration in JBoss Data Grid
- Create a CacheManager as a starting point in an XML file. If required, this CacheManager can be programmed in runtime to the specification that meets the requirements of the use case. The following is an example of how to create a CacheManager:
EmbeddedCacheManager manager = new DefaultCacheManager("my-config-file.xml"); Cache defaultCache = manager.getCache();EmbeddedCacheManager manager = new DefaultCacheManager("my-config-file.xml"); Cache defaultCache = manager.getCache();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a new synchronously replicated cache programmatically.
- Create a new configuration object instance using the ConfigurationBuilder helper object:
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.REPL_SYNC).build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.REPL_SYNC).build();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Set the cache mode to synchronous replication:
String newCacheName = "repl";
String newCacheName = "repl";Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define or register the configuration with a manager:
manager.defineConfiguration(newCacheName, c); Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);
manager.defineConfiguration(newCacheName, c); Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.2.2. Create a Customized Cache Using the Default Named Cache
infinispan-config-file.xml specifies the configuration for a replicated cache as a default and a distributed cache with a customized lifespan value is required. The required distributed cache must retain all aspects of the default cache specified in the infinispan-config-file.xml file except the mentioned aspects.
Procedure 5.2. Customize the Default Cache
- Read an instance of a default Configuration object to get the default configuration:
EmbeddedCacheManager manager = new DefaultCacheManager("infinispan-config-file.xml"); Configuration dcc = cacheManager.getDefaultCacheConfiguration();EmbeddedCacheManager manager = new DefaultCacheManager("infinispan-config-file.xml"); Configuration dcc = cacheManager.getDefaultCacheConfiguration();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Use the ConfigurationBuilder to construct and modify the cache mode and L1 cache lifespan on a new configuration object:
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().read(dcc).clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.DIST_SYNC).l1().lifespan(60000L).build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().read(dcc).clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.DIST_SYNC).l1().lifespan(60000L).build();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Register/define your cache configuration with a cache manager:
Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);
Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.2.3. Create a Customized Cache Using a Non-Default Named Cache
replicatedCache as the base instead of the default cache.
Procedure 5.3. Create a Customized Cache Using a Non-Default Named Cache
- Read the
replicatedCacheto get the default configuration:EmbeddedCacheManager manager = new DefaultCacheManager("infinispan-config-file.xml"); Configuration rc = cacheManager.getCacheConfiguration("replicatedCache");EmbeddedCacheManager manager = new DefaultCacheManager("infinispan-config-file.xml"); Configuration rc = cacheManager.getCacheConfiguration("replicatedCache");Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Use the ConfigurationBuilder to construct and modify the desired configuration on a new configuration object:
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().read(rc).clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.DIST_SYNC).l1().lifespan(60000L).build();
Configuration c = new ConfigurationBuilder().read(rc).clustering().cacheMode(CacheMode.DIST_SYNC).l1().lifespan(60000L).build();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Register/define your cache configuration with a cache manager:
Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);
Cache<String, String> cache = manager.getCache(newCacheName);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.2.4. Using the Configuration Builder to Create Caches Programmatically
5.2.2.5. Global Configuration Examples
5.2.2.5.1. Globally Configure the Transport Layer
GlobalConfiguration globalConfig = new GlobalConfigurationBuilder() .globalJmxStatistics() .build();
GlobalConfiguration globalConfig = new GlobalConfigurationBuilder()
.globalJmxStatistics()
.build();
5.2.2.5.2. Globally Configure the Cache Manager Name
5.2.2.5.3. Globally Customize Thread Pool Executors
5.2.2.6. Cache Level Configuration Examples
5.2.2.6.1. Cache Level Configuration for the Cluster Mode
5.2.2.6.2. Cache Level Eviction and Expiration Configuration
5.2.2.6.3. Cache Level Configuration for JTA Transactions
5.2.2.6.4. Cache Level Configuration Using Chained Persistent Stores
Configuration config = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.loaders()
.shared(false).passivation(false).preload(false)
.addFileCacheStore().location("/tmp").streamBufferSize(1800).async().enable().threadPoolSize(20).build();
Configuration config = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.loaders()
.shared(false).passivation(false).preload(false)
.addFileCacheStore().location("/tmp").streamBufferSize(1800).async().enable().threadPoolSize(20).build();
5.2.2.6.5. Cache Level Configuration for Advanced Externalizers
5.2.2.6.6. Cache Level Configuration for Custom Interceptors
Chapter 6. The Externalizable API
6.1. About Externalizer
Externalizer is a class that can:
- Marshall a given object type to a byte array.
- Unmarshall the contents of a byte array into an instance of the object type.
6.2. About the Externalizable API
6.3. Using the Externalizable API
6.3.1. The Externalizable API Usage
- Transform an object class into a serialized class
- Read an object class from an output.
readObject() implementations create object instances of the target class. This provides flexibility in the creation of instances and allows target classes to persist immutably.
Note
6.3.2. The Externalizable API Configuration Example
- Provide an
externalizerimplementation for the type of object to be marshalled/unmarshalled. - Annotate the marshalled type class using {@link SerializeWith} to indicate the
externalizerclass.
- The payload size generated using this method can be inefficient due to constraints within the model.
- An Externalizer can be required for a class for which the source code is not available, or the source code cannot be modified.
- The use of annotations can limit framework developers or service providers attempting to abstract lower level details, such as marshalling layer.
6.3.3. Linking Externalizers with Marshaller Classes
readObject() and writeObject() methods link with the type classes they are configured to externalize by providing a getTypeClasses() implementation.
6.4. The AdvancedExternalizer
6.4.1. About the AdvancedExternalizer
6.4.2. AdvancedExternalizer Example Configuration
6.4.3. Externalizer Identifiers
getId()implementations.- Declarative or Programmatic configuration that identifies the externalizer when unmarshalling a payload.
GetId() will either return a positive integer or a null value:
- A positive integer allows the externalizer to be identified when read and assigned to the correct Externalizer capable of reading the contents.
- A null value indicates that the identifier of the AdvancedExternalizer will be defined via declarative or programmatic configuration.
6.4.4. Registering Advanced Externalizers
The following is an example of a declarative configuration for an advanced Externalizer implementation:
The following is an example of a programmatic configuration for an advanced Externalizer implementation:
GlobalConfigurationBuilder builder = ... builder.serialization() .addAdvancedExternalizer(new Person.PersonExternalizer());
GlobalConfigurationBuilder builder = ...
builder.serialization()
.addAdvancedExternalizer(new Person.PersonExternalizer());
The following is a declarative configuration for the location of the identifier definition during registration:
The following is a programmatic configuration for the location of the identifier definition during registration:
GlobalConfigurationBuilder builder = ... builder.serialization() .addAdvancedExternalizer(123, new Person.PersonExternalizer());
GlobalConfigurationBuilder builder = ...
builder.serialization()
.addAdvancedExternalizer(123, new Person.PersonExternalizer());
6.4.5. Register Multiple Externalizers Programmatically
@Marshalls annotation.
builder.serialization()
.addAdvancedExternalizer(new Person.PersonExternalizer(),
new Address.AddressExternalizer());
builder.serialization()
.addAdvancedExternalizer(new Person.PersonExternalizer(),
new Address.AddressExternalizer());
6.5. Internal Externalizer Implementation Access
6.5.1. Internal Externalizer Implementation Access
Part II. Remote Client-Server Mode Interfaces
- The Asynchronous API (can only be used in conjunction with the Hot Rod Client in Remote Client-Server Mode)
- The REST Interface
- The Memcached Interface
- The Hot Rod Interface
- The RemoteCache API
Chapter 7. The Asynchronous API
7.1. About the Asynchronous API
Async appended to each method name. Asynchronous methods return a Future that contains the result of the operation.
Cache(String, String), Cache.put(String key, String value) returns a String, while Cache.putAsync(String key, String value) returns a Future(String).
7.2. Asynchronous API Benefits
- The guarantee of synchronous communication, with the added ability to handle failures and exceptions.
- Not being required to block a thread's operations until the call completes.
Set<Future<?>> futures = new HashSet<Future<?>>();
futures.add(cache.putAsync("key1", "value1"));
futures.add(cache.putAsync("key2", "value2"));
futures.add(cache.putAsync("key3", "value3"));
Set<Future<?>> futures = new HashSet<Future<?>>();
futures.add(cache.putAsync("key1", "value1"));
futures.add(cache.putAsync("key2", "value2"));
futures.add(cache.putAsync("key3", "value3"));futures.add(cache.putAsync(key1, value1));futures.add(cache.putAsync(key2, value2));futures.add(cache.putAsync(key3, value3));
7.3. About Asynchronous Processes
- Network calls
- Marshalling
- Writing to a cache store (optional)
- Locking
7.4. Return Values and the Asynchronous API
Future or the NotifyingFuture in order to query the previous value.
Note
Future.get()
Future.get()Chapter 8. The REST Interface
8.1. About the REST Interface in JBoss Data Grid
8.2. Ruby Client Code
8.3. Using JSON with Ruby Example
To use JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) with ruby to interact with JBoss Data Grid's REST Interface, declare the requirement using the following code:
data = {:name => "michael", :age => 42 }
http.put('/infinispan/rest/Users/data/0', data.to_json, {"Content-Type" => "application/json"})
data = {:name => "michael", :age => 42 }
http.put('/infinispan/rest/Users/data/0', data.to_json, {"Content-Type" => "application/json"})
The following code is an example of how to use JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) in conjunction with Ruby to send specific data, in this case the name and age of an individual, using the PUT function.
data = {:name => "michael", :age => 42 }
http.put('/infinispan/rest/Users/data/0', data.to_json, {"Content-Type" => "application/json"})
data = {:name => "michael", :age => 42 }
http.put('/infinispan/rest/Users/data/0', data.to_json, {"Content-Type" => "application/json"})8.4. Python Client Code
8.5. Java Client Code
Define imports as follows:
import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.HttpURLConnection;import java.net.URL;
import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;import java.net.URL;
The following is an example of using Java to add a string value to a cache:
The following code is an example of a method used that reads a value specified in a URL using Java to interact with the JBoss Data Grid REST Interface.
8.6. Configure the REST Interface
8.6.1. Configure REST Connectors
rest-connector element in JBoss Data Grid's Remote Client-Server mode.
8.6.2. REST Connector Attributes
- The
rest-connectorelement specifies the configuration information for the REST connector.- The
virtual-serverparameter specifies the virtual server used by the REST connector. The default value for this parameter isdefault-host. This is an optional parameter. - The
cache-containerparameter names the cache container used by the REST connector. This is a mandatory parameter. - The
context-pathparameter specifies the context path for the REST connector. The default value for this parameter is an empty string (""). This is an optional parameter. - the
security-domainparameter specifies that the specified domain, declared in the security subsystem, should be used to authenticate access to the REST endpoint. This is an optional parameter. If this parameter is omitted, no authentication is performed. - The
auth-methodparameter specifies the method used to retrieve credentials for the end point. The default value for this parameter isBASIC. Supported alternate values includeDIGEST,CLIENT-CERTandSPNEGO. This is an optional parameter. - The
security-modeparameter specifies whether authentication is required only for write operations (such as PUT, POST and DELETE) or for read operations (such as GET and HEAD) as well. Valid values for this parameter areWRITEfor authenticating write operations only, orREAD_WRITEto authenticate read and write operations.
8.7. Using the REST Interface
8.7.1. REST Interface Operations
- Adding data.
- Retrieving data.
- Removing data.
8.7.2. Adding Data
8.7.2.1. Adding Data Using the REST Interface
- HTTP
PUTmethod - HTTP
POSTmethod
PUT and POST methods are used, the body of the request contains this data, which includes any information added by the user.
PUT and POST methods require a Content-Type header.
8.7.2.2. About PUT /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}
PUT request from the provided URL form places the payload, (from the request body) in the targeted cache using the provided key. The targeted cache must exist on the server for this task to successfully complete.
hr is the cache name and payRoll%2F3 is the key. The value %2F indicates that a / was used in the key.
http://someserver/rest/hr/payRoll%2F3
http://someserver/rest/hr/payRoll%2F3Time-To-Live and Last-Modified values are updated, if an update is required.
Note
%2F to represent a / in the key (as in the provided example) can be successfully run if the server is started using the following argument:
-Dorg.apache.tomcat.util.buf.UDecoder.ALLOW_ENCODED_SLASH=true
-Dorg.apache.tomcat.util.buf.UDecoder.ALLOW_ENCODED_SLASH=true8.7.2.3. About POST /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}
POST method from the provided URL form places the payload (from the request body) in the targeted cache using the provided key. However, in a POST method, if a value in a cache/key exists, a HTTP CONFLICT status is returned and the content is not updated.
8.7.3. Retrieving Data
8.7.3.1. Retrieving Data Using the REST Interface
- HTTP
GETmethod. - HTTP
HEADmethod.
8.7.3.2. About GET /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}
GET method returns the data located in the supplied cacheName, matched to the relevant key, as the body of the response. The Content-Type header provides the type of the data. A browser can directly access the cache.
8.7.3.3. About HEAD /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}
HEAD method operates in a manner similar to the GET method, however returns no content (header fields are returned).
8.7.4. Removing Data
8.7.4.1. Removing Data Using the REST Interface
DELETE method to retrieve data from the cache. The DELETE method can:
- Remove a cache entry/value. (
DELETE /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}) - Remove a cache. (
DELETE /{cacheName})
8.7.4.2. About DELETE /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}
DELETE /{cacheName}/{cacheKey}), the DELETE method removes the key/value from the cache for the provided key.
8.7.4.3. About DELETE /{cacheName}
DELETE /{cacheName}), the DELETE method removes all entries in the named cache. After a successful DELETE operation, the HTTP status code 200 is returned.
8.7.4.4. Background Delete Operations
performAsync header to true to ensure an immediate return while the removal operation continues in the background.
8.7.5. REST Interface Operation Headers
8.7.5.1. Headers
| Headers | Mandatory/Optional | Values | Default Value | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Type | Mandatory | - | - | If the Content-Type is set to application/x-java-serialized-object, it is stored as a Java object. |
| performAsync | Optional | True/False | - | If set to true, an immediate return occurs, followed by a replication of data to the cluster on its own. This feature is useful when dealing with bulk data inserts and large clusters. |
| timeToLiveSeconds | Optional | Numeric (positive and negative numbers) | -1 (This value prevents expiration as a direct result of timeToLiveSeconds. Expiration values set elsewhere override this default value.) | Reflects the number of seconds before the entry in question is automatically deleted. Setting a negative value for timeToLiveSeconds provides the same result as the default value. |
| maxIdleTimeSeconds | Optional | Numeric (positive and negative numbers) | -1 (This value prevents expiration as a direct result of maxIdleTimeSeconds. Expiration values set elsewhere override this default value.) | Contains the number of seconds after the last usage when the entry will be automatically deleted. Passing a negative value provides the same result as the default value. |
timeToLiveSeconds and maxIdleTimeSeconds headers:
- If both the
timeToLiveSecondsandmaxIdleTimeSecondsheaders are assigned the value0, the cache uses the defaulttimeToLiveSecondsandmaxIdleTimeSecondsvalues configured either using XML or programatically. - If only the
maxIdleTimeSecondsheader value is set to0, thetimeToLiveSecondsvalue should be passed as the parameter (or the default-1, if the parameter is not present). Additionally, themaxIdleTimeSecondsparameter value defaults to the values configured either using XML or programatically. - If only the
timeToLiveSecondsheader value is set to0, expiration occurs immediately and themaxIdleTimeSecondsvalue is set to the value passed as a parameter (or the default-1if no parameter was supplied).
ETags (Entity Tags) are returned for each REST Interface entry, along with a Last-Modified header that indicates the state of the data at the supplied URL. ETags are used in HTTP operations to request data exclusively in cases where the data has changed to save bandwidth. The following headers support ETags (Entity Tags) based optimistic locking:
| Header | Algorithm | Example | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| If-Match | If-Match = "If-Match" ":" ( "*" | 1#entity-tag ) | - | Used in conjunction with a list of associated entity tags to verify that a specified entity (that was previously obtained from a resource) remains current. |
| If-None-Match | - | Used in conjunction with a list of associated entity tags to verify that none of the specified entities (that was previously obtained from a resource) are current. This feature facilitates efficient updates of cached information when required and with minimal transaction overhead. | |
| If-Modified-Since | If-Modified-Since = "If-Modified-Since" ":" HTTP-date | If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 1994 19:43:31 GMT | Compares the requested variant's last modification time and date with a supplied time and date value. If the requested variant has not been modified since the specified time and date, a 304 (not modified) response is returned without a message-body instead of an entity. |
| If-Unmodified-Since | If-Unmodified-Since = "If-Unmodified-Since" ":" HTTP-date | If-Unmodified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 1994 19:43:31 GMT | Compares the requested variant's last modification time and date with a supplied time and date value. If the requested resources has not been modified since the supplied date and time, the specified operation is performed. If the requested resource has been modified since the supplied date and time, the operation is not performed and a 412 (Precondition Failed) response is returned. |
8.8. REST Interface Security
8.8.1. Publish REST Endpoints as a Public Interface
interface parameter in the socket-binding element from management to public as follows:
<socket-binding name="http" interface="public" port="8080"/>
<socket-binding name="http" interface="public" port="8080"/>
8.8.2. Enable Security for the REST Endpoint
JBoss Data Grid includes an example standalone-rest-auth.xml file located within the JBoss Data Grid directory at the location /docs/examples/configs).
$JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration directory to use the configuration. From the $JDG_HOME location, enter the following command to create a copy of the standalone-rest-auth.xml in the appropriate location:
cp docs/examples/configs/standalone-rest-auth.xml standalone/configuration/standalone.xml
$ cp docs/examples/configs/standalone-rest-auth.xml standalone/configuration/standalone.xml
standalone-rest-auth.xml to start with a new configuration template.
Procedure 8.1. Enable Security for the REST Endpoint
standalone.xml:
Specify Security Parameters
Ensure that the rest endpoint specifies a valid value for thesecurity-domainandauth-methodparameters. Recommended settings for these parameters are as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check Security Domain Declaration
Ensure that the security subsystem contains the corresponding security-domain declaration. For details about setting up security-domain declarations, refer to the JBoss Application Server 7 or JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6 documentation.Add an Application User
Run the relevant script and enter the configuration settings to add an application user.- Run the
adduser.shscript (located in$JDG_HOME/bin).- On a Windows system, run the
adduser.batfile (located in$JDG_HOME/bin) instead.
- When prompted about the type of user to add, select
Application User (application-users.properties)by enteringb. - Accept the default value for realm (
ApplicationRealm) by pressing the return key. - Specify a username and password.
- When prompted for a role for the created user, enter
REST. - Ensure the username and application realm information is correct when prompted and enter "yes" to continue.
Verify the Created Application User
Ensure that the created application user is correctly configured.- Check the configuration listed in the
application-users.propertiesfile (located in$JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration/). The following is an example of what the correct configuration looks like in this file:user1=2dc3eacfed8cf95a4a31159167b936fc
user1=2dc3eacfed8cf95a4a31159167b936fcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check the configuration listed in the
application-roles.propertiesfile (located in$JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration/). The following is an example of what the correct configuration looks like in this file:user1=REST
user1=RESTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Test the Server
Start the server and enter the following link in a browser window to access the REST endpoint:http://localhost:8080/rest/namedCache
http://localhost:8080/rest/namedCacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
If testing using a GET request, a405response code is expected and indicates that the server was successfully authenticated.
Chapter 9. The Memcached Interface
9.1. About the Memcached Protocol
9.2. About Memcached Servers in JBoss Data Grid
- Standalone, where each server acts independently without communication with any other memcached servers.
- Clustered, where servers replicate and distribute data to other memcached servers.
9.3. Using the Memcached Interface
9.3.1. Memcached Statistics
| Statistic | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| uptime | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the time (in seconds) that the memcached instance has been available and running. |
| time | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the current time. |
| version | String | Contains the current version. |
| curr_items | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the number of items currently stored by the instance. |
| total_items | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the total number of items stored by the instance during its lifetime. |
| cmd_get | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of get operation requests (requests to retrieve data). |
| cmd_set | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of set operation requests (requests to store data). |
| get_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys that are present from the keys requested. |
| get_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys that were not found from the keys requested. |
| delete_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be deleted that were located and successfully deleted. |
| delete_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be deleted that were not located and therefore could not be deleted. |
| incr_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be incremented that were located and successfully incremented |
| incr_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be incremented that were not located and therefore could not be incremented. |
| decr_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be decremented that were located and successfully decremented. |
| decr_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be decremented that were not located and therefore could not be decremented. |
| cas_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be compared and swapped that were found and successfully compared and swapped. |
| cas_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be compared and swapped that were not found and therefore not compared and swapped. |
| cas_badvalue | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys where a compare and swap occurred but the original value did not match the supplied value. |
| evictions | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of eviction calls performed. |
| bytes_read | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of bytes read by the server from the network. |
| bytes_written | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of bytes written by the server to the network. |
9.4. Configure the Memcached Interface
9.4.1. About JBoss Data Grid Connectors
- The
hotrod-connectorelement, which defines the configuration for a Hot Rod based connector. - The
memcached-connectorelement, which defines the configuration for a memcached based connector. - The
rest-connectorelement, which defines the configuration for a REST interface based connector.
9.4.2. Configure Memcached Connectors
memcached-connector element in JBoss Data Grid's Remote Client-Server Mode.
9.4.3. Memcached Connector Attributes
- The following is a list of attributes used to configure the memcached connector within the
connectorselement in JBoss Data Grid's Remote Client-Server Mode.- The
memcached-connectorelement defines the configuration elements for use with memcached.- The
socket-bindingparameter specifies the socket binding port used by the memcached connector. This is a mandatory parameter. - The
cache-containerparameter names the cache container used by the memcached connector. This is a mandatory parameter. - The
worker-threadsparameter specifies the number of worker threads available for the memcached connector. The default value for this parameter is the number of cores available multiplied by two. This is an optional parameter. - The
idle-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) the connector can remain idle before the connection times out. The default value for this parameter is-1, which means that no timeout period is set. This is an optional parameter. - The
tcp-nodelayparameter specifies whether TCP packets will be delayed and sent out in batches. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. The default value for this parameter istrue. This is an optional parameter. - The
send-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the send buffer for the memcached connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter. - The
receive-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the receive buffer for the memcached connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter.
9.5. Memcached Interface Security
9.5.1. Publish Memcached Endpoints as a Public Interface
interface parameter in the socket-binding element from management to public as follows:
<socket-binding name="memcached" interface="public" port="11211" />
<socket-binding name="memcached" interface="public" port="11211" />
Chapter 10. The Hot Rod Interface
10.1. About Hot Rod
10.2. About Hot Rod Servers in JBoss Data Grid
10.3. Hot Rod Hash Functions
Integer.MAX_INT. This value is returned to the client using the Hot Rod protocol each time a hash-topology change is detected to prevent Hot Rod clients assuming a specific hash space as a default. The hash space can only contain positive numbers ranging from 0 to Integer.MAX_INT.
10.4. Hot Rod Server Nodes
10.4.1. About Server Node Hash Calculation
hash ID or the hash code for each server. This information is used to calculate the real hash position of each server, whether virtual nodes are configured or not.
10.4.2. About Consistent Hashing Algorithms
10.4.3. Hash Code Calculation Rules for Clients
When clients receive the base hash code of a server, it must be normalized to locate the exact position on the hash wheel. This normalization process includes:
- Passing the base hash code to the hash function.
- Calculations to avoid negative values.
public static int getNormalizedHash(int nodeBaseHashCode, Hash hashFct) {
return hashFct.hash(nodeBaseHashCode) & Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public static int getNormalizedHash(int nodeBaseHashCode, Hash hashFct) {
return hashFct.hash(nodeBaseHashCode) & Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
Each node represents N different virtual modes. Therefore, to calculate the hash code for each virtual node, use the numbers between 0 and N-1 and apply the following process:
Procedure 10.1. Hash Code Calculation with Virtual Nodes
- For the virtual node with the ID "0", use the following code to obtain the hash code:
public static int getNormalizedHash(int nodeBaseHashCode, Hash hashFct) { return hashFct.hash(nodeBaseHashCode) & Integer.MAX_VALUE; }public static int getNormalizedHash(int nodeBaseHashCode, Hash hashFct) { return hashFct.hash(nodeBaseHashCode) & Integer.MAX_VALUE; }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For all subsequent virtual nodes (with IDs from "1" to "N-1"), execute the following code:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.4.4. The hotrod.properties File
infinispan.client.hotrod.server_list=remote-server:11222
infinispan.client.hotrod.server_list=remote-server:11222infinispan.client.hotrod.request_balancing_strategy- For replicated (vs distributed) Hot Rod server clusters, the client balances requests to the servers according to this strategy.The default value for this property is
org.infinispan.client.hotrod.impl.transport.tcp.RoundRobinBalancingStrategy. infinispan.client.hotrod.server_list- This is the initial list of Hot Rod servers to connect to, specified in the following format: host1:port1;host2:port2... At least one host:port must be specified.The default value for this property is
127.0.0.1:11222. infinispan.client.hotrod.force_return_values- Whether or not to implicitly Flag.FORCE_RETURN_VALUE for all calls.The default value for this property is
false. infinispan.client.hotrod.tcp_no_delay- Affects TCP NODELAY on the TCP stack.The default value for this property is
true. infinispan.client.hotrod.ping_on_startup- If true, a ping request is sent to a back end server in order to fetch cluster's topology.The default value for this property is
true. infinispan.client.hotrod.transport_factory- Controls which transport will be used. Currently only the TcpTransport is supported.The default value for this property is
org.infinispan.client.hotrod.impl.transport.tcp.TcpTransportFactory. infinispan.client.hotrod.marshaller- Allows you to specify a custom Marshaller implementation to serialize and deserialize user objects.The default value for this property is
org.infinispan.marshall.jboss.GenericJBossMarshaller. infinispan.client.hotrod.async_executor_factory- Allows you to specify a custom asynchronous executor for async calls.The default value for this property is
org.infinispan.client.hotrod.impl.async.DefaultAsyncExecutorFactory. infinispan.client.hotrod.default_executor_factory.pool_size- If the default executor is used, this configures the number of threads to initialize the executor with.The default value for this property is
10. infinispan.client.hotrod.default_executor_factory.queue_size- If the default executor is used, this configures the queue size to initialize the executor with.The default value for this property is
100000. infinispan.client.hotrod.hash_function_impl.1- This specifies the version of the hash function and consistent hash algorithm in use, and is closely tied with the Hot Rod server version used.The default value for this property is the
Hash function specified by the server in the responses as indicated in ConsistentHashFactory. infinispan.client.hotrod.key_size_estimate- This hint allows sizing of byte buffers when serializing and deserializing keys, to minimize array resizing.The default value for this property is
64. infinispan.client.hotrod.value_size_estimate- This hint allows sizing of byte buffers when serializing and deserializing values, to minimize array resizing.The default value for this property is
512. infinispan.client.hotrod.socket_timeout- This property defines the maximum socket read timeout before giving up waiting for bytes from the server.The default value for this property is
60000 (equals 60 seconds). infinispan.client.hotrod.protocol_version- This property defines the protocol version that this client should use. Other valid values include 1.0.The default value for this property is
1.1. infinispan.client.hotrod.connect_timeout- This property defines the maximum socket connect timeout before giving up connecting to the server.The default value for this property is
60000 (equals 60 seconds).
10.5. Hot Rod Headers
10.5.1. Hot Rod Header Data Types
| Data Type | Size | Details |
|---|---|---|
| vInt | Between 1-5 bytes. | Unsigned variable length integer values. |
| vLong | Between 1-9 bytes. | Unsigned variable length long values. |
| string | - | Strings are always represented using UTF-8 encoding. |
10.5.2. Request Header
| Field Name | Data Type/Size | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Magic | 1 byte | Indicates whether the header is a request header or response header. |
| Message ID | vLong | Contains the message ID. Responses use this unique ID when responding to a request. This allows Hot Rod clients to implement the protocol in an asynchronous manner. |
| Version | 1 byte | Contains the Hot Rod server version. |
| Opcode | 1 byte | Contains the relevant operation code. In a request header, opcode can only contain the request operation codes. |
| Cache Name Length | vInt | Stores the length of the cache name. If Cache Name Length is set to 0 and no value is supplied for Cache Name, the operation interacts with the default cache. |
| Cache Name | string | Stores the name of the target cache for the specified operation. This name must match the name of a predefined cache in the cache configuration file. |
| Flags | vInt | Contains a numeric value of variable length that represents flags passed to the system. Each bit represents a flag, except the most significant bit, which is used to determine whether more bytes must be read. Using a bit to represent each flag facilitates the representation of flag combinations in a condensed manner. |
| Client Intelligence | 1 byte | Contains a value that indicates the client capabilities to the server. |
| Topology ID | vInt | Contains the last known view ID in the client. Basic clients supply the value 0 for this field. Clients that support topology or hash information supply the value 0 until the server responds with the current view ID, which is subsequently used until a new view ID is returned by the server to replace the current view ID. |
| Transaction Type | 1 byte | Contains a value that represents one of two known transaction types. Currently, the only supported value is 0. |
| Transaction ID | byte-array | Contains a byte array that uniquely identifies the transaction associated with the call. The transaction type determines the length of this byte array. If the value for Transaction Type was set to 0, no Transaction ID is present. |
10.5.3. Response Header
| Field Name | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Magic | 1 byte | Indicates whether the header is a request or response header. |
| Message ID | vLong | Contains the message ID. This unique ID is used to pair the response with the original request. This allows Hot Rod clients to implement the protocol in an asynchronous manner. |
| Opcode | 1 byte | Contains the relevant operation code. In a response header, opcode can only contain the response operation codes. |
| Status | 1 byte | Contains a code that represents the status of the response. |
| Topology Change Marker | 1 byte | Contains a marker byte that indicates whether the response is included in the topology change information. |
10.5.4. Topology Change Headers
10.5.4.1. About Topology Change Headers
topology ID and the topology ID sent by the client and, if the two differ, it returns a new topology ID.
10.5.4.2. Topology Change Marker Values
Topology Change Marker field in a response header:
| Value | Details |
|---|---|
| 0 | No topology change information is added. |
| 1 | Topology change information is added. |
10.5.4.3. Topology Change Headers for Topology-Aware Clients
| Response Header Fields | Data Type/Size | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Response Header with Topology Change Marker | - | - |
| Topology ID | vInt | - |
| Num Servers in Topology | vInt | Contains the number of Hot Rod servers running in the cluster. This value can be a subset of the entire cluster if only some nodes are running Hot Rod servers. |
| mX: Host/IP Length | vInt | Contains the length of the hostname or IP address of an individual cluster member. Variable length allows this element to include hostnames, IPv4 and IPv addresses. |
| mX: Host/IP Address | string | Contains the hostname or IP address of an individual cluster member. The Hot Rod client uses this information to access the individual cluster member. |
| mX: Port | Unsigned Short. 2 bytes | Contains the port used by Hot Rod clients to communicate with the cluster member. |
mX, are repeated for each server in the topology. The first server in the topology's information fields will be prefixed with m1 and the numerical value is incremented by one for each additional server till the value of X equals the number of servers specified in the num servers in topology field.
10.5.4.4. Topology Change Headers for Hash Distribution-Aware Clients
| Field | Data Type/Size | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Response Header with Topology Change Marker | - | - |
| Topology ID | vInt | - |
| Number Key Owners | Unsigned short. 2 bytes. | Contains the number of globally configured copies for each distributed key. Contains the value 0 if distribution is not configured on the cache. |
| Hash Function Version | 1 byte | Contains a pointer to the hash function in use. Contains the value 0 if distribution is not configured on the cache. |
| Hash Space Size | vInt | Contains the modulus used by JBoss Data Grid for all module arithmetic related to hash code generation. Clients use this information to apply the correct hash calculations to the keys. Contains the value 0 if distribution is not configured on the cache. |
| Number servers in topology | vInt | Contains the number of Hot Rod servers running in the cluster. This value can be a subset of the entire cluster if only some nodes are running Hot Rod servers. This value also represents the number of host to port pairings included in the header. |
| Number Virtual Nodes Owners | vInt | Contains the number of configured virtual nodes. Contains the value 0 if no virtual nodes are configured or if distribution is not configured on the cache. |
| mX: Host/IP Length | vInt | Contains the length of the hostname or IP address of an individual cluster member. Variable length allows this element to include hostnames, IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. |
| mX: Host/IP Address | string | Contains the hostname or IP address of an individual cluster member. The Hot Rod client uses this information to access the individual cluster member. |
| mX: Port | Unsigned short. 2 bytes. | Contains the port used by Hot Rod clients to communicate with the cluster member. |
| mX: Hashcode | 4 bytes. |
mX, are repeated for each server in the topology. The first server in the topology's information fields will be prefixed with m1 and the numerical value is incremented by one for each additional server till the value of X equals the number of servers specified in the num servers in topology field.
10.6. Hot Rod Operations
10.6.1. Hot Rod Operations
- Get
- BulkGet
- GetWithVersion
- Put
- PutIfAbsent
- Remove
- RemoveIfUnmodified
- Replace
- ReplaceIfUnmodified
- Clear
- ContainsKey
- Ping
- Stats
10.6.2. Hot Rod Get Operation
Get operation uses the following request format:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. The vInt data type is used because of its size (up to 6 bytes), which is larger than the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. However, Java disallows single array sizes to exceed the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. As a result, this vInt is also limited to the maximum size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains a key, the corresponding value of which is requested. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Successful operation. |
| 0x02 | The key does not exist. |
get operation's response when the key is found is as follows:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | Byte array | Contains the requested value. |
10.6.3. Hot Rod BulkGet Operation
BulkGet operation uses the following request format:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Entry Count | vInt | Contains the maximum number of JBoss Data Grid entries to be returned by the server. The entry count value equals the sum of the key and the associated value. |
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| More | vInt | Represents if more entries must be read from the stream. While More is set to 1, additional entries follow until the value of More is set to 0, which indicates the end of the stream. |
| Key Size | - | Contains the size of the key. |
| Key | - | Contains the key value. |
| Value Size | - | Contains the size of the value. |
| Value | - | Contains the value. |
More, Key Size, Key, Value Size and Value entry is appended to the response.
10.6.4. Hot Rod GetWithVersion Operation
GetWithVersion operation uses the following request format:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. The vInt data type is used because of its size (up to 6 bytes), which is larger than the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. However, Java disallows single array sizes to exceed the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. As a result, this vInt is also limited to the maximum size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains a key, the corresponding value of which is requested. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Successful operation. |
| 0x02 | The key does not exist. |
| Field | Data Type/Size | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Entry Version | 8 bytes | Contains the unique value of an existing entry's modification. |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | Byte array | Contains the requested value. |
10.6.5. Hot Rod Put Operation
put operation request format includes the following:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | - | Contains the length of the key. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains the key value. |
| Lifespan | vInt | Contains the number of seconds before the entry expires. If the number of seconds exceeds thirty days, the value is treated as UNIX time (i.e. the number of seconds since the date 1/1/1970) as the entry lifespan. When set to the value 0, the entry will never expire. |
| Max Idle | vInt | Contains the number of seconds an entry is allowed to remain idle before it is evicted from the cache. If this entry is set to 0, the entry is allowed to remain idle indefinitely without being evicted due to the max idle value. |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | Byte array | The requested value. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | The value was successfully stored. |
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed, the previous value and key are returned. If the previous key and value do not exist, the value length would contain the value 0.
10.6.6. Hot Rod PutIfAbsent Operation
putIfAbsent operation request format includes the following:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains the key value. |
| Lifespan | vInt | Contains the number of seconds before the entry expires. If the number of seconds exceeds thirty days, the value is treated as UNIX time (i.e. the number of seconds since the date 1/1/1970) as the entry lifespan. When set to the value 0, the entry will never expire. |
| Max Idle | vInt | Contains the number of seconds an entry is allowed to remain idle before it is evicted from the cache. If this entry is set to 0, the entry is allowed to remain idle indefinitely without being evicted due to the max idle value. |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | Byte array | Contains the requested value. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | The value was successfully stored. |
| 0x01 | The value was not stored because the key was not present. |
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed, the previous value and key are returned. If the previous key and value do not exist, the value length would contain the value 0.
10.6.7. Hot Rod Remove Operation
Hot Rod Remove operation uses the following request format:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. The vInt data type is used because of its size (up to 6 bytes), which is larger than the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. However, Java disallows single array sizes to exceed the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. As a result, this vInt is also limited to the maximum size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains a key, the corresponding value of which is requested. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Successful operation. |
| 0x02 | The key does not exist. |
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed, the response header contains either:
- The value and length of the previous key.
- The value length
0and the response status0x02to indicate that the key does not exist.
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed. If the key does not exist or the previous value was null, the value length is 0.
10.6.8. Hot Rod RemoveIfUnmodified Operation
RemoveIfUnmodified operation request format includes the following:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains the key value. |
| Entry Version | 8 bytes | Uses the value returned by the GetWithVersion operation. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Returned status if the entry was replaced or removed. |
| 0x01 | Returns status if the entry replace or remove was unsuccessful because the key was modified. |
| 0x02 | Returns status if the key does not exist. |
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed, the previous value and key are returned. If the previous key and value do not exist, the value length would contain the value 0.
10.6.9. Hot Rod Replace Operation
replace operation request format includes the following:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains the key value. |
| Lifespan | vInt | Contains the number of seconds before the entry expires. If the number of seconds exceeds thirty days, the value is treated as UNIX time (i.e. the number of seconds since the date 1/1/1970) as the entry lifespan. When set to the value 0, the entry will never expire. |
| Max Idle | vInt | Contains the number of seconds an entry is allowed to remain idle before it is evicted from the cache. If this entry is set to 0, the entry is allowed to remain idle indefinitely without being evicted due to the max idle value. |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | Byte array | Contains the requested value. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | The value was successfully stored. |
| 0x01 | The value was not stored because the key does not exist. |
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed, the previous value and key are returned. If the previous key and value do not exist, the value length would contain the value 0.
10.6.10. Hot Rod ReplaceIfUnmodified Operation
ReplaceIfUnmodified operation request format includes the following:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains the key value. |
| Lifespan | vInt | Contains the number of seconds before the entry expires. If the number of seconds exceeds thirty days, the value is treated as UNIX time (i.e. the number of seconds since the date 1/1/1970) as the entry lifespan. When set to the value 0, the entry will never expire. |
| Max Idle | vInt | Contains the number of seconds an entry is allowed to remain idle before it is evicted from the cache. If this entry is set to 0, the entry is allowed to remain idle indefinitely without being evicted due to the max idle value. |
| Entry Version | 8 bytes | Uses the value returned by the GetWithVersion operation. |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | Byte array | Contains the requested value. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Returned status if the entry was replaced or removed. |
| 0x01 | Returns status if the entry replace or remove was unsuccessful because the key was modified. |
| 0x02 | Returns status if the key does not exist. |
ForceReturnPreviousValue is passed, the previous value and key are returned. If the previous key and value do not exist, the value length would contain the value 0.
10.6.11. Hot Rod Clear Operation
clear operation format includes only a header.
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | JBoss Data Grid was successfully cleared. |
10.6.12. Hot Rod ContainsKey Operation
ContainsKey operation uses the following request format:
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Key Length | vInt | Contains the length of the key. The vInt data type is used because of its size (up to 6 bytes), which is larger than the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. However, Java disallows single array sizes to exceed the size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. As a result, this vInt is also limited to the maximum size of Integer.MAX_VALUE. |
| Key | Byte array | Contains a key, the corresponding value of which is requested. |
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Successful operation. |
| 0x02 | The key does not exist. |
10.6.13. Hot Rod Ping Operation
ping is an application level request to check for server availability.
| Response Status | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | Successful ping without any errors. |
10.6.14. Hot Rod Stats Operation
| Name | Details |
|---|---|
| timeSinceStart | Contains the number of seconds since Hot Rod started. |
| currentNumberOfEntries | Contains the number of entries that currently exist in the Hot Rod server. |
| totalNumberOfEntries | Contains the total number of entries stored in the Hot Rod server. |
| stores | Contains the number of put operations attempted. |
| retrievals | Contains the number of get operations attempted. |
| hits | Contains the number of get hits. |
| misses | Contains the number of get misses. |
| removeHits | Contains the number of remove hits. |
| removeMisses | Contains the number of removal misses. |
| Name | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - |
| Number of Stats | vInt | Contains the number of individual statistics returned. |
| Name Length | vInt | Contains the length of the named statistic. |
| Name | string | Contains the name of the statistic. |
| Value Length | vInt | Contains the length of the value. |
| Value | string | Contains the statistic value. |
Name Length, Name, Value Length and Value recur for each statistic requested.
10.6.15. Hot Rod Operation Values
10.6.15.1. Opcode Request and Response Values
opcode values for a request header and their corresponding response header values:
| Operation | Request Operation Code | Response Operation Code |
|---|---|---|
| put | 0x01 | 0x02 |
| get | 0x03 | 0x04 |
| putIfAbsent | 0x05 | 0x06 |
| replace | 0x07 | 0x08 |
| replaceIfUnmodified | 0x09 | 0x0A |
| remove | 0x0B | 0x0C |
| removeIfUnmodified | 0x0D | 0x0E |
| containsKey | 0x0F | 0x10 |
| getWithVersion | 0x11 | 0x12 |
| clear | 0x13 | 0x14 |
| stats | 0x15 | 0x16 |
| ping | 0x17 | 0x18 |
| bulkGet | 0x19 | 0x1A |
opcode value is 0x50, it indicates an error response.
10.6.15.2. Magic Values
Magic field in request and response headers:
| Value | Details |
|---|---|
| 0xA0 | Cache request marker. |
| 0xA1 | Cache response marker. |
10.6.15.3. Status Values
Status field in a response header:
| Value | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x00 | No error. |
| 0x01 | Not put/removed/replaced. |
| 0x02 | Key does not exist. |
| 0x81 | Invalid Magic value or Message ID. |
| 0x82 | Unknown command. |
| 0x83 | Unknown version. |
| 0x84 | Request parsing error. |
| 0x85 | Server error. |
| 0x86 | Command timed out. |
10.6.15.4. Transaction Type Values
Transaction Type in a request header:
| Value | Details |
|---|---|
| 0 | Indicates a non-transactional call or that the client does not support transactions. If used, the TX_ID field is omitted. |
| 1 | Indicates X/Open XA transaction ID (XID). This value is currently not supported. |
10.6.15.5. Client Intelligence Values
Client Intelligence in a request header:
| Value | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x01 | Indicates a basic client that does not require any cluster or hash information. |
| 0x02 | Indicates a client that is aware of topology and requires cluster information. |
| 0x03 | Indicates a client that is aware of hash and distribution and requires both the cluster and hash information. |
10.6.15.6. Flag Values
flag values in the request header:
| Value | Details |
|---|---|
| 0x0001 | ForceReturnPreviousValue |
10.6.15.7. Hot Rod Error Handling
| Field | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Error Opcode | - | Contains the error operation code. |
| Error Status Number | - | Contains a status number that corresponds to the error opcode. |
| Error Message Length | vInt | Contains the length of the error message. |
| Error Message | string | Contains the actual error message. If an 0x84 error code returns, which indicates that there was an error in parsing the request, this field contains the latest version supported by the Hot Rod server. |
10.7. Examples
10.7.1. Put Request Example
put request using Hot Rod:
| Byte | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0xA0 | 0x09 | 0x41 | 0x01 | 0x07 | 0x4D ('M') | 0x79 ('y') | 0x43 ('C') |
| 16 | 0x61 ('a') | 0x63 ('c') | 0x68 ('h') | 0x65 ('e') | 0x00 | 0x03 | 0x00 | 0x00 |
| 24 | 0x00 | 0x05 | 0x48 ('H') | 0x65 ('e') | 0x6C ('l') | 0x6C ('l') | 0x6F ('o') | 0x00 |
| 32 | 0x00 | 0x05 | 0x57 ('W') | 0x6F ('o') | 0x72 ('r') | 0x6C ('l') | 0x64 ('d') | - |
| Field Name | Byte | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Magic | 0 | 0xA0 |
| Version | 2 | 0x41 |
| Cache Name Length | 4 | 0x07 |
| Flag | 12 | 0x00 |
| Topology ID | 14 | 0x00 |
| Transaction ID | 16 | 0x00 |
| Key | 18-22 | 'Hello' |
| Max Idle | 24 | 0x00 |
| Value | 26-30 | 'World' |
| Message ID | 1 | 0x09 |
| Opcode | 3 | 0x01 |
| Cache Name | 5-11 | 'MyCache' |
| Client Intelligence | 13 | 0x03 |
| Transaction Type | 15 | 0x00 |
| Key Field Length | 17 | 0x05 |
| Lifespan | 23 | 0x00 |
| Value Field Length | 25 | 0x05 |
put request:
| Byte | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0xA1 | 0x09 | 0x01 | 0x00 | 0x00 | - | - | - |
| Field Name | Byte | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Magic | 0 | 0xA1 |
| Opcode | 2 | 0x01 |
| Topology Change Marker | 4 | 0x00 |
| Message ID | 1 | 0x09 |
| Status | 3 | 0x00 |
10.8. Configure the Hot Rod Interface
10.8.1. About JBoss Data Grid Connectors
- The
hotrod-connectorelement, which defines the configuration for a Hot Rod based connector. - The
memcached-connectorelement, which defines the configuration for a memcached based connector. - The
rest-connectorelement, which defines the configuration for a REST interface based connector.
10.8.2. Configure Hot Rod Connectors
hotrod-connector element in JBoss Data Grid's Remote Client-Server Mode.
10.8.3. Hot Rod Connector Attributes
The hotrod-connector element defines the configuration elements for use with Hot Rod.
- The
socket-bindingparameter specifies the socket binding port used by the Hot Rod connector. This is a mandatory parameter. - The
cache-containerparameter names the cache container used by the Hot Rod connector. This is a mandatory parameter. - The
worker-threadsparameter specifies the number of worker threads available for the Hot Rod connector. The default value for this parameter is the number of cores available multiplied by two. This is an optional parameter. - The
idle-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) the connector can remain idle before the connection times out. The default value for this parameter is-1, which means that no timeout period is set. This is an optional parameter. - The
tcp-nodelayparameter specifies whether TCP packets will be delayed and sent out in batches. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. The default value for this parameter istrue. This is an optional parameter. - The
send-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the send buffer for the Hot Rod connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter. - The
receive-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the receive buffer for the Hot Rod connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter.
The Topology-State-Transfer ElementThe
topology-state-transferelement specifies the topology state transfer configurations for the Hot Rod connector. This element can only occur once within ahotrod-connectorelement.- The
lock-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) after which the operation attempting to obtain a lock times out. The default value for this parameter is10seconds. This is an optional parameter. - The
replication-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) after which the replication operation times out. The default value for this parameter is10seconds. This is an optional parameter. - The
update-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) after which the update operation times out. The default value for this parameter is30seconds. This is an optional parameter. - The
external-hostparameter specifies the hostname sent by the Hot Rod server to clients listed in the topology information. The default value for this parameter is the host address. This is an optional parameter. - The
external-portparameter specifies the port sent by the Hot Rod server to clients listed in the topology information. The default value for this parameter is the configured port. This is an optional parameter. - The
lazy-retrievalparameter indicates whether the Hot Rod connector will carry out retrieval operations lazily. The default value for this parameter istrue. This is an optional parameter.
10.9. Hot Rod Interface Security
10.9.1. Publish Hot Rod Endpoints as a Public Interface
interface parameter in the socket-binding element from management to public as follows:
<socket-binding name="hotrod" interface="public" port="11222" />
<socket-binding name="hotrod" interface="public" port="11222" />
Chapter 11. The RemoteCache Interface
11.1. About the RemoteCache Interface
11.2. Create a New RemoteCacheManager
RemoteCacheManager:
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("infinispan.client.hotrod.server_list", "127.0.0.1:11222");
RemoteCacheManager manager = new RemoteCacheManager(props);
RemoteCache defaultCache = manager.getCache();
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("infinispan.client.hotrod.server_list", "127.0.0.1:11222");
RemoteCacheManager manager = new RemoteCacheManager(props);
RemoteCache defaultCache = manager.getCache();
Note
Hot Rod with JBoss Data Grid, refer to the Developer Guide's Hot Rod Chapter.
Appendix A. Revision History
| Revision History | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revision 0.0-3.400 | 2013-10-31 | |||
| ||||
| Revision 0.0-3 | Tue Aug 06 2013 | |||
| ||||
| Revision 0.0-2 | Mon Sep 17 2012 | |||
| ||||