Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Configuring SAP HANA Scale-Up Multitarget System Replication for disaster recovery
Abstract
Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code and documentation. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Due to the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be gradually implemented over upcoming releases. For more details on making our language more inclusive, see our CTO Chris Wright’s message.
Providing feedback on Red Hat documentation
We appreciate your feedback on our documentation. Let us know how we can improve it.
Submitting feedback through Jira (account required)
- Make sure you are logged in to the Jira website.
- Provide feedback by clicking on this link.
- Enter a descriptive title in the Summary field.
- Enter your suggestion for improvement in the Description field. Include links to the relevant parts of the documentation.
- If you want to be notified about future updates, please make sure you are assigned as Reporter.
- Click Create at the bottom of the dialogue.
Chapter 1. Overview
Due to the growing demands on availability, one copy of data is not enough.
To ensure business continuity, a reliable and highly available architecture must replicate data across more than just one system. Using multitarget system replication, the primary system can replicate data changes to more than one secondary system. For more information, see SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication.
This document describes how to configure a replication site for disaster recovery using SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication on a 2-node cluster, installed as described in Automating SAP HANA Scale-Up System Replication using the RHEL HA Add-On.
A sample configuration looks like this:
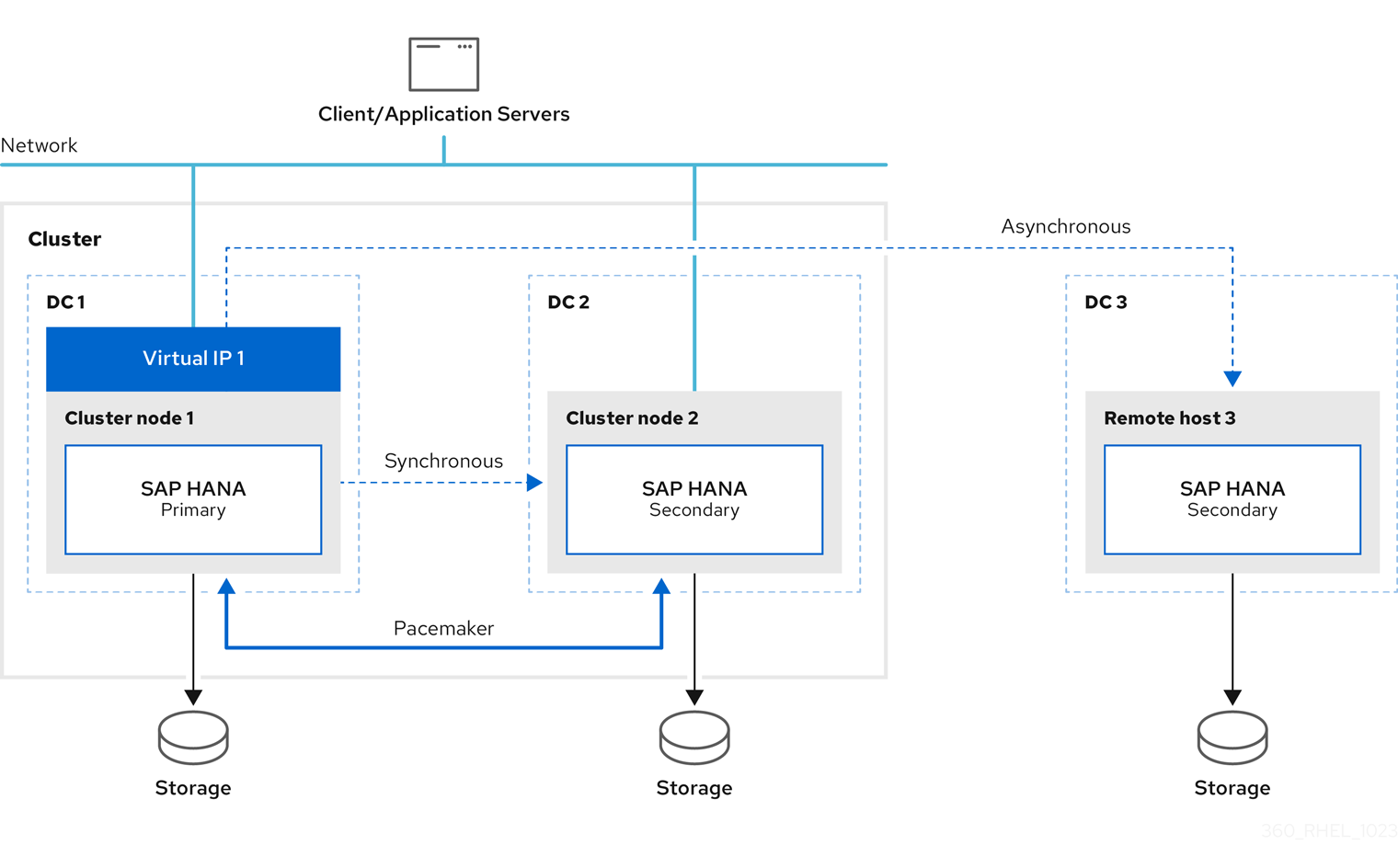
The initial setup is as follows:
- Replicate Primary site 1 (DC1) to Secondary site 2 (DC2)
- Replicate Primary site 1 (DC1) to Secondary site 3 (DC3)
If the primary fails, the primary switches to secondary site 2 (DC2) and the former primary site 1 (DC1) will become the secondary site.
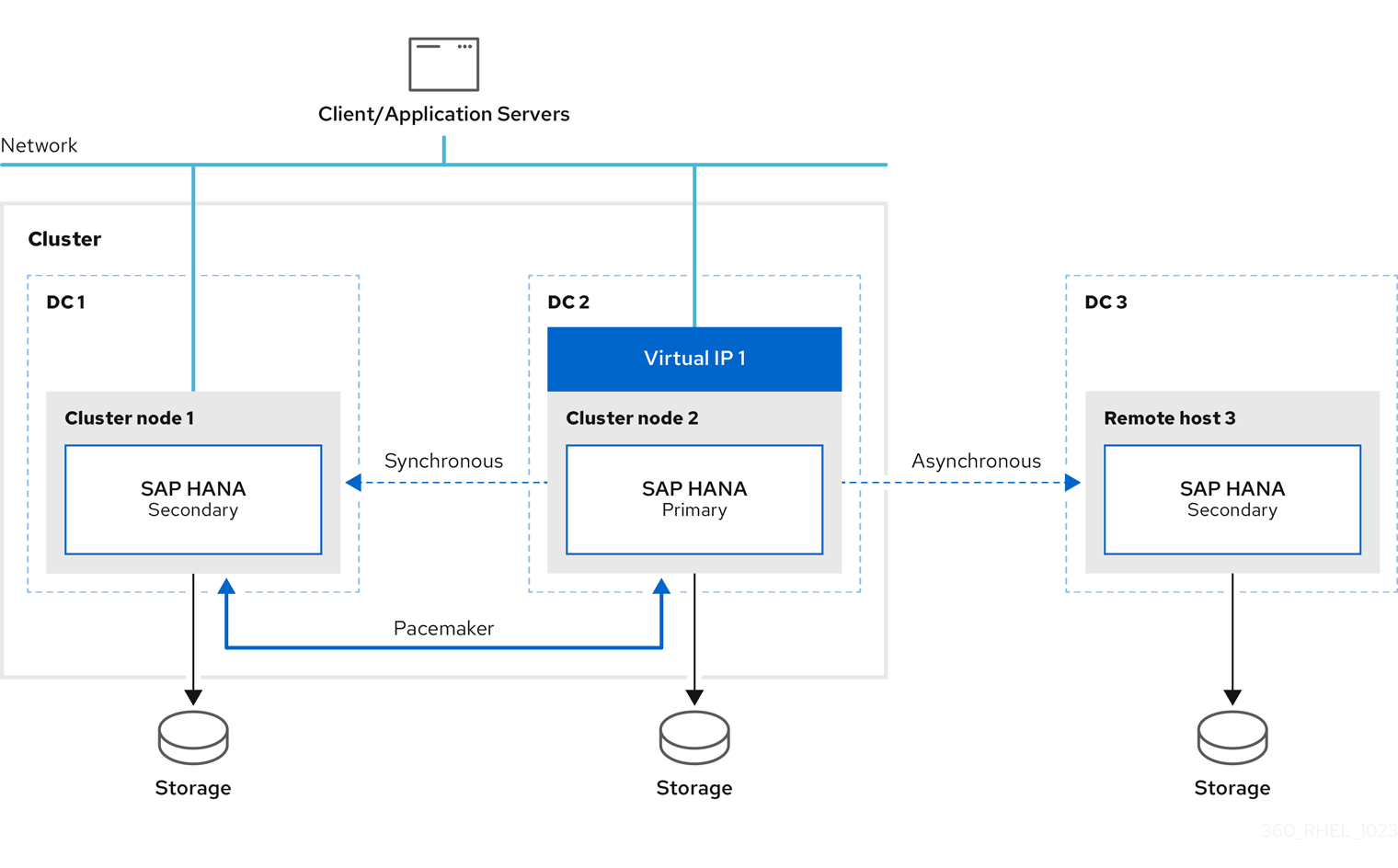
When failover occurs, this solution ensures that the configured primary site is switched at the third DR site as well. The configuration after failover is as follows:
- Primary running on DC2
- Secondary running on DC1 (synced from DC2)
- Secondary running on DC3 (synced from DC2)
The SAP HANA instance on remotehost3 will be automatically re-registered to the new primary as long as this instance is up and running during the failover.
This document also describes the example of switching the primary database to the third site.
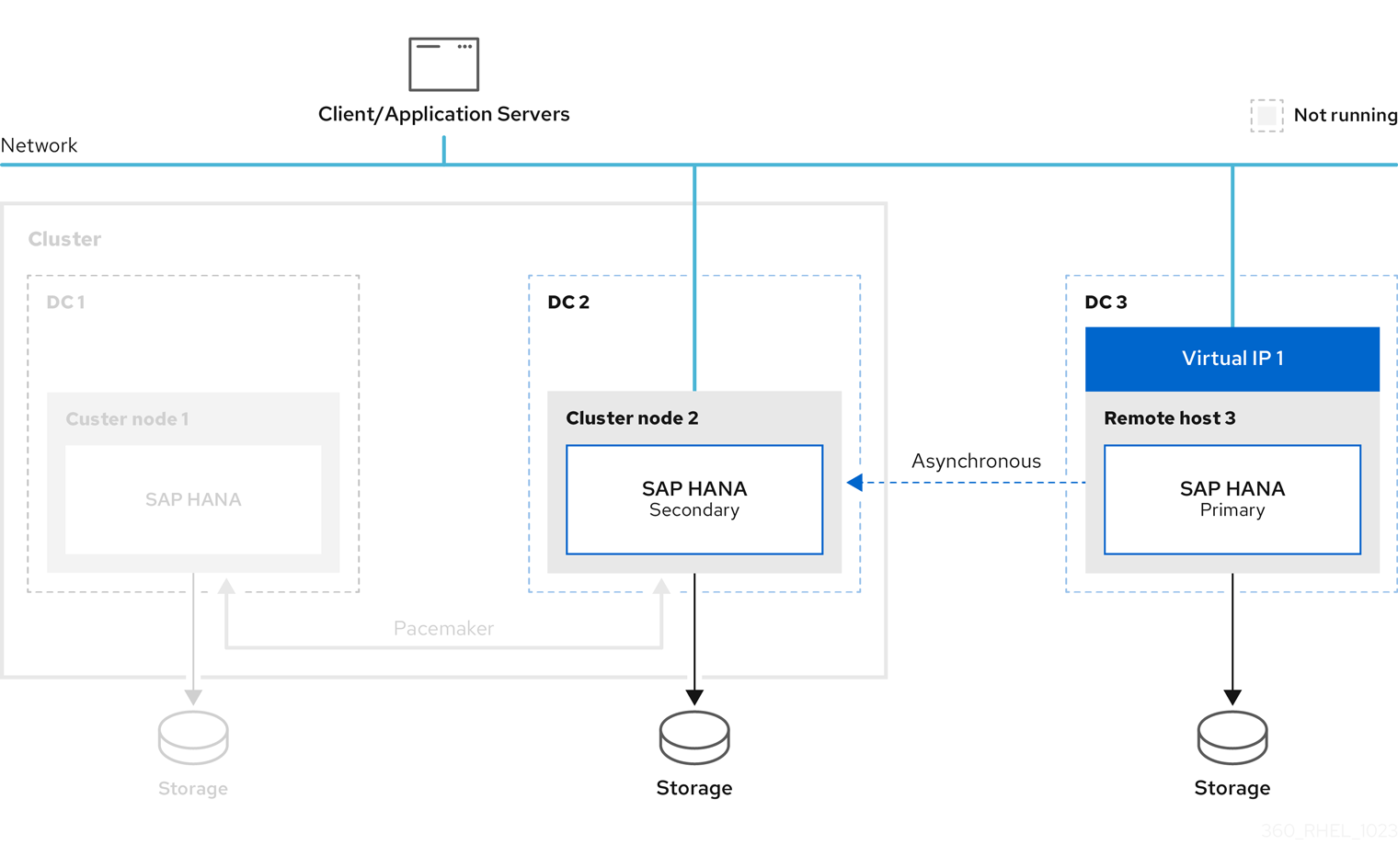
Please note that further network configuration is required for the connection of the clients to the database. This is not within the scope of this document.
For further information, please check the following:
Chapter 2. Parameters
These parameters of an existing two-node cluster are used to setup the third site:
| Parameter | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SID | RH2 | System ID of the HANA Database |
| First SITE | DC1 | Name of the first datacenter /site |
| Second SITE | DC2 | Name of the second datacenter / site |
| Third SITE | DC3 | Name of the third datacenter / site |
| InstanceNr | 02 | HANA Instance Number |
| <sid>adm uid | 1000 | User-ID of sidadm user |
| sapsys gid | 980 | Group ID of sapsys |
It is required that all three HANA instances use the same values for the following:
- SID
- InstanceNr
- <sid>adm uid
- sapsys gid
Chapter 3. Prerequisite
For the solution to work, the following requirements must be met.
All nodes must have the same:
- number of CPUs and RAM
- software configuration
- RHEL release
- firewall settings
- SAP HANA release (SAP HANA 2.0 SPS04 or later)
The pacemaker packages are only installed on the cluster nodes and must use the same version of resource-agents-sap-hana (0.162.1 or later).
To be able to support SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication, refer to Add SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication autoregister support. Also, set the following:
-
use
register_secondaries_on_takeover=true -
use
log_mode=normal
The initial setup is based on the installation guide, Automating SAP HANA Scale-Up System Replication using the RHEL HA Add-On.
The system replication configuration of all SAP HANA instances is based on SAP requirements. For more information, refer to the guidelines from SAP based on the SAP HANA Administration Guide .
Chapter 4. Installation
This chapter describes the installation of the additional SAP HANA instance.
4.1. Check the 2-node Base Installation with a failover test
Verify that the installation is done based on Automating SAP HANA Scale-Up System Replication using the RHEL HA Add-On.
To be able to use SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication, the version of resource-agents-sap-hana must be 0.162.1 or later. This can be checked, as shown below:
rpm -q resource-agents-sap-hana
# rpm -q resource-agents-sap-hana
resource-agents-sap-hana-0.162.1-0.el8_6.1.noarchYou can run a failover test to ensure that the environment is working. You can move the SAPHana resource, which is also described in Failover the SAPHana Resource using Move.
4.2. Install SAP HANA on third site
On the third site, you also need to install SAP HANA using the same version and parameters as for the SAP HANA instances on the two-node Pacemaker cluster, as shown below:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | RH2 |
| InstanceNumber | 02 |
| <sid>adm user ID | rh2adm 999 |
| sapsys group ID | sapsys 999 |
The SAP HANA installation is done using hdblcm. For more details, see SAP HANA Installation using hdbclm. Optionally, the installation can also be done using Ansible.
In the examples in this chapter, we are using:
- hosts: clusternode1 on site DC1, clusternode2 on site DC2, and remotehost3 on site DC3
- SID RH2
- adminuser rh2adm
4.3. Setup SAP HANA System Replication on the third node
In the existing installation, there is already SAP HANA system replication configured between the primary and secondary SAP HANA instances in a two-node cluster. SAP HANA System Replication is enabled on the up-and-running primary SAP HANA database instance.
This chapter describes how to register the third SAP HANA instance as an additional secondary HANA System Replication site on node remotehost3 at site DC3. This step is similar to the registration of the original secondary HANA instance (DC2) on node clusternode2. More details are described in the following chapters. If you need further information, you can also check General Prerequisites for Configuring SAP HANA System Replication.
4.3.1. Check the primary database
You must check that the other databases are running and the system replication is working properly. Please refer to:
You can discover the primary HANA instance with:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode" mode: primary
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode"
mode: primary4.3.2. Copy database keys
Before you are able to register a new secondary HANA instance, the database keys of the primary HANA instance need to be copied to the new additional HANA replication site. In our example, the hostname of the third site is remotehost3.
For example, on the primary node clusternode1, run:
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY4.3.3. Register the third site as secondary
You need to know the name of the node that is running the primary database.
To monitor the registration, you can run the following command in a separate terminal on the primary node:
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch python
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch python
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.pyThis will show you the progress and any errors if they occur.
To register the HANA instance on the third site (DC3) as an additional secondary SAP HANA instance, run the following command on the third site host remotehost3:
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --name=DC3
--remoteHost=clusternode1 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE}
--replicationMode=async --operationMode=logreplay --online
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --name=DC3
--remoteHost=clusternode1 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE}
--replicationMode=async --operationMode=logreplay --onlineIn this example, DC3 is the name of the third site, clusternode1 is the name of the primary node.
If the database instance is already running, you don’t have to stop it, you can use the option --online, which will register the instance while it is online. The necessary restart (stop and start) of the instance will then be initiated by hdbnsutil itself.
The option --online works in any case, both when the HANA instance is online and offline (this option is available with SAP HANA 2.0 SPS04 and later).
If the HANA instance is offline, you have to start it after the third node is registered. You can find additional information in SAP HANA System Replication.
4.3.4. Add SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication autoregister support
We are using a SAP HANA System Replication option called register_secondaries_on_takeover = true. This will automatically re-register with the new primary site in case of a failover between the previous primary site and the other secondary site. This option must be added to the global.ini file on all potential primary sites.
All HANA instances should have this entry in their global.ini:
[system_replication] register_secondaries_on_takeover = true
[system_replication]
register_secondaries_on_takeover = true
The following two chapters describe the global.ini configuration in detail.
Despite the parameter, if the third database is down when the failover is initiated, the third instance needs to be re-registered manually.
4.3.5. Configure global.ini on the pacemaker nodes
The option register_secondaries_on_takeover = true needs to be added to the [system_replication] section in global.ini of the SAP HANA nodes of site 1 and site 2, which are managed by the pacemaker cluster. Please edit the file global.ini always on the respective node, and do not copy the file from another node.
The global.ini file should only be edited if the HANA instance of a site has stopped processing.
Edit the global.ini as the rh2adm user:
clusternode1:rh2adm> vim
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini
clusternode1:rh2adm> vim
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.iniExample:
This option is active as soon as the SAP HANA database instance is started.
4.3.6. Configure global.ini on remotehost3
Edit the global.ini as a <sid>adm user:
% vim /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini
% vim /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini
On remotehost3, the ha_dr_provider_SAPHanaSR section is not used.
Example of global.ini on remotehost3:
4.3.7. Verify installation
After the installation, you have to check if all HANA instances are up and running and that HANA System Replication is working between them. The easiest way is to check the systemReplicationStatus, as described in more detail in Check the System Replication status. Please also refer to the Check Database for further information.
For HANA System Replication to work correctly, please ensure that the “log_mode” parameter is set to “normal”. Please refer to Checking the log_mode of the SAP HANA database for more information.
To verify that the setup is working as expected, please run the Test cases as described in the following chapter.
Chapter 5. Test cases
After finishing the installation, it is recommended to run some basic tests to check the installation and verify how SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication is working and how it recovers from a failure. It is always a good practice to run these test cases before starting production. If possible, you can also prepare a test environment to verify the changes before applying them in production.
All cases will describe:
- Subject of the test
- Test preconditions
- Test steps
- Monitoring the test
- Starting the test
- Expected result(s)
- Ways to return to an initial state
To automatically register a former primary HANA replication site as a new secondary HANA replication site on the HANA instances that are managed by the cluster, you can use the option AUTOMATED_REGISTER=true in the SAPHana resource. For more details, refer to AUTOMATED_REGISTER.
The names of the HA cluster nodes and the HANA replication sites (in brackets) used in the examples are:
- clusternode1 (DC1)
- clusternode2 (DC2)
- remotehost3 (DC3)
The following parameters are used for configuring the HANA instances and the cluster:
- SID=RH2
- INSTANCENUMBER=02
- CLUSTERNAME=cluster1
You can use clusternode1-2, remotehost3 also as alias in the /etc/hosts in your test environment.
The tests are described in more detail, including examples and additional checks of preconditions. At the end, there are examples of how to clean up the environment to be prepared for further testing.
In some cases, if the distance between clusternode1-2 and remotehost3 is too long, you should use –replcationMode=async instead of –replicationMode=syncmem. Please also ask your SAP HANA administrator before choosing the right option.
5.1. Prepare the tests
Before we run a test, the complete environment needs to be in a correct and healthy state. We have to check the cluster and the database via:
-
pcs status --full -
python systemReplicationStatus.py -
df -h
An example for pcs status --full can be found in Check cluster status with pcs status. If there are warnings or previous failures in the "Migration Summary", you should clean up the cluster before you start your test.
pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-cloneCluster Cleanup describes some more ways to do it. It is important that the cluster and all the resources be started.
Besides the cluster, the database should also be up and running and in sync. The easiest way to verify the proper status of the database is to check the system replication status. See also Replication Status. This should be checked on the primary database.
To discover the primary node, you can check Discover Primary Database or use:
-
pcs status | grep -E "Promoted|Master" -
hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration
Check if there is enough space on the file systems by running:
df -h
# df -hPlease also follow the guidelines for a system check before you continue. If the environment is clean, it is ready to run the tests. During the test, monitoring is helpful to observe progress.
5.2. Monitor the environment
In this section, we are focusing on monitoring the environment during the tests. This section will only cover the necessary monitors to see the changes. It is recommended to run the monitors from a dedicated terminal. To be able to detect changes during the test, it is recommended to start monitoring before starting the test.
In the Useful Commands section, more examples are shown.
5.2.1. Discover the primary node
You need to discover the primary node to monitor a failover or run certain commands that only provide information about the replication status when executed on the primary node.
To discover the primary node, you can run the following commands as the <sid>adm user:
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode"'
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode"'Output example, when clusternode2 is the primary database:
mode: syncmem primary masters: clusternode2
mode: syncmem
primary masters: clusternode2A second way to identify the primary node is to run the following command as root on a cluster node:
watch -n 5 'pcs status --full'
# watch -n 5 'pcs status --full'Output on the node that runs the primary database is:
mode: primary
mode: primary5.2.2. Check the Replication status
The replication status shows the relationship between primary and secondary database nodes and the current status of the replication.
To discover the replication status, you can run as the <sid>adm user:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfigurationIf you want to permanently monitor changes in the system replication status, please run the following command:
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'
This example repeatedly captures the replication status and also determines the current return code.
As long as the return code (status) is 15, the replication status is fine. The other return codes are:
- 10: NoHSR
- 11: Error
- 12: Unknown
- 13: Initializing
- 14: Syncing
- 15: Active
If you register a new secondary, you can run it in a separate window on the primary node, and you will see the progress of the replication. If you want to monitor a failover, you can run it in parallel on the old primary as well as on the new primary database server. For more information, please read Check SAP HANA System Replication Status.
5.2.3. Check /var/log/messages entries
Pacemaker is writing a lot of information into the /var/log/messages file. During a failover, a huge number of messages are written into this message file. To be able to follow only the important messages depending on the SAP HANA resource agent, it is useful to filter the detailed activities of the pacemaker SAP resources. It is enough to check the message file on a single cluster node.
For example, you can use this alias:
alias tmsl='tail -1000f /var/log/messages | egrep -s "Setting master-rsc_SAPHana_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}_HDB${TINSTANCE}|sr_register|WAITING4LPA|PROMOTED|DEMOTED|UNDEFINED|master_walk|SWAIT|WaitforStopped|FAILED|LPT"'
# alias tmsl='tail -1000f /var/log/messages | egrep -s "Setting master-rsc_SAPHana_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}_HDB${TINSTANCE}|sr_register|WAITING4LPA|PROMOTED|DEMOTED|UNDEFINED|master_walk|SWAIT|WaitforStopped|FAILED|LPT"'Run this alias in a separate window to monitor the progress of the test. Please also check the example Monitor failover and sync state.
5.2.4. Cluster status
There are several ways to check the cluster status.
Check if the cluster is running:
-
pcs cluster status
-
Check the cluster and all resources:
-
pcs status
-
Check the cluster, all resources and all node attributes:
-
pcs status --full
-
Check the resources only:
-
pcs resource
-
The pcs status --full command will give you all the necessary information. To monitor changes, you can run this command together with watch.
pcs status --full
# pcs status --full
If you want to see changes, you can run, in a separate window, the command watch:
watch pcs status --full
# watch pcs status --fullAn output example and further options can be found in Check cluster status.
5.2.5. Discover leftovers
To ensure that your environment is ready to run the next test, leftovers from previous tests need to be fixed or removed.
stonithis used to fence a node in the cluster:-
Detect:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs stonith history -
Fix:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs stonith cleanup
-
Detect:
Multiple primary databases:
Detect:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration | grep -i primaryAll nodes with the same primary need to be identified.
-
Fix: clusternode1:rh2adm> re-register the wrong primary with option
--force_full_replica
Location Constraints caused by move:
Detect:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs constraint locationCheck the warning section.
-
Fix:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource clear <clone-resource-which was moved>
Secondary replication relationship:
-
Detect: on the primary database run
clusternode1:rh2adm> python ${DIR_EXECUTABLES}/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py - Fix: unregister and re-register the secondary databases.
-
Detect: on the primary database run
Check siteReplicationMode (same output on all SAP HANA nodes
-
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep site.*Mode
-
Pcs property:
-
Detect:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property config -
Fix:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set <key=value> -
Clear
maintenance_mode -
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
-
Detect:
log_mode:Detect:
clusternode1:rh2adm> python systemReplicationStatus.pyWill respond in the replication status that
log_modenormally is required.log_modecan be detected as described in Usinghdbsqlto checkInifilecontents.-
Fix: change the
log_modeto normal and restart the primary database.
CIB entries:
Detect: SFAIL entries in the cluster information base.
Please refer to Check cluster consistency, to find and remove CIB entries.
Cleanup/clear:
Detect:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs status --fullSometimes it shows errors or warnings. You can cleanup/clear resources and if everything is fine, nothing happens. Before running the next test, you can cleanup your environment.
Examples to fix:
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource clear <name-of-the-clone-resource>[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource cleanup <name-of-the-clone-resource>
This is also useful if you want to check if there is an issue in an existing environment. For more information, please refer to Useful commands.
5.3. Test 1:Failover of the primary node with an active third site
| Subject of the test | Automatic re-registration of the third site. Sync state changes to SOK after clearing. |
| Test preconditions |
|
| Test steps |
Move the SAPHana resource using the |
| Monitoring the test |
On the third site run as
On the secondary node run as root: |
| Starting the test | Execute the cluster command:
|
| Expected result | In the monitor command on site 3 the primary master changes from clusternode1 to clusternode2.
After clearing the resource the sync state will change from |
| Ways to return to an initial state | Run the test twice. |
(*)
remotehost3:rh2adm> watch hdbnsutil -sr_state [root@clusternode1]# tail -1000f /var/log/messages |egrep -e ‘SOK|SWAIT|SFAIL’
remotehost3:rh2adm>
watch hdbnsutil -sr_state
[root@clusternode1]# tail -1000f /var/log/messages |egrep -e ‘SOK|SWAIT|SFAIL’Detailed description
Check the initial state of your cluster as root on clusternode1 or clusternode2:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This output shows you that HANA is promoted on clusternode1 which is the primary SAP HANA server, and that the name of the clone resource is SAPHana_RH2_02-clone, which is promotable.
You can run this in a separate window during the test to see the changes.
watch pcs status --full
[root@clusternode1]# watch pcs status --fullCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Another way to identify the name of the SAP HANA clone resource is:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To see the change of the primary server start monitoring on remotehost3 on a separate terminal window before you start the test.
remotehost3:rh2adm> watch 'hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep "primary masters"
remotehost3:rh2adm> watch 'hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep "primary masters"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will look like:
Every 2.0s: hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep "primary masters" remotehost3: Mon Sep 4 08:47:21 2023 primary masters: clusternode1
Every 2.0s: hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep "primary masters" remotehost3: Mon Sep 4 08:47:21 2023 primary masters: clusternode1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow During the test the expected output will change to clusternode2.
Start the test by moving the clone resource discovered above to clusternode2:
pcs resource move SAPhana_RH2_02-clone clusternode2
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource move SAPhana_RH2_02-clone clusternode2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output of the monitor on remotehost3 will change to:
Every 2.0s: hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep "primary masters" remotehost3: Mon Sep 4 08:50:31 2023 primary masters: clusternode2
Every 2.0s: hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep "primary masters" remotehost3: Mon Sep 4 08:50:31 2023 primary masters: clusternode2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Pacemaker creates a location constraint for moving the clone resource. This needs to be manually removed. You can see the constraint using:
pcs constraint location
[root@clusternode1]# pcs constraint locationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This constraint needs to be removed by executing the following steps.
Clear the clone resource to remove the location constraint:
pcs resource clear SAPhana_RH2_02-clone
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource clear SAPhana_RH2_02-clone Removing constraint: cli-prefer-SAPHana_RH2_02-cloneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Cleanup the resource:
pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_RH2_02-clone Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:0 on clusternode2 Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:1 on clusternode1 Waiting for 1 reply from the controller ... got reply (done)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Result of the test
- The “primary masters” monitor on remotehost3 should show an immediate switch to the new primary node.
-
If you check the cluster status, the former secondary will be promoted, the former primary gets re-registered, and the
Clone_Statechanges fromPromotedtoUndefinedtoWAITINGFORLPAtoDEMOTED. -
The secondary will change the
sync_statetoSFAILwhen theSAPHanamonitor is started for the first time after the failover. Because of existing location constraints, the resource needs to be cleared, and after a short time, thesync_stateof the secondary will change toSOKagain. - Secondary gets promoted.
To restore the initial state you can simply run the next test. After finishing the tests please run a Cluster Cleanup.
5.4. Test 2:Failover of the primary node with passive third site
| Subject of the test | No registration of the third site. Failover works even if the third site is down. |
| Test preconditions |
|
| Test steps |
Move the SAPHana resource using the |
| Starting the test | Execute the cluster command:
|
| Monitoring the test |
On the third site run as
On the cluster nodes run as root: |
| Expected result | No change on DC3. Replication stays on old relationship. |
| Ways to return to an initial state | Re-register DC3 on new primary and start SAP HANA. |
Detailed description
Check the initial state of your cluster as root on clusternode1 or clusternode2:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This output of this example shows you that HANA is promoted on clusternode1, which is the primary SAP HANA server, and that the name of the clone resource is
SAPHana_RH2_02-clone, which is promotable. If you run test 3 before HANA, it might be promoted on clusternode2.Stop the database on remotehost3:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the primary database on remotehost3:
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration| grep -i "primary masters" primary masters: clusternode2
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration| grep -i "primary masters" primary masters: clusternode2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the current primary in the cluster on a cluster node:
pcs resource | grep Masters
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource | grep Masters * Masters: [ clusternode2 ]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the
sr_stateto see the SAP HANA System Replication relationships:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The SAP HANA System Replication relations still have one primary (DC1), which is replicated to DC2 and DC3.
The replication relationship on remotehost3, which is down, can be displayed using:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The database on remotehost3 which is offline checks the entries in the
global.inifile.Starting the test: Initiate a failover in the cluster, moving the
SAPHana-clone-resourceexample:pcs resource move SAPHana_RH2_02-clone clusternode2
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource move SAPHana_RH2_02-clone clusternode2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf SAPHana is promoted on clusternode2, you have to move the clone resource to clusternode1. The example expects that SAPHana is promoted on clusternode1.
There will be no output. Similar to the former test, a location constraint will be created, which can be displayed with:
pcs constraint location
[root@clusternode1]# pcs constraint location Location Constraints: Resource: SAPHana_RH2_02-clone Enabled on: Node: clusternode1 (score:INFINITY) (role:Started)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Even if the cluster looks fine again, this constraint avoids another failover unless the constraint is removed. One way is to clear the resource.
Clear the resource:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Cleanup the resource:
pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_RH2_02-clone Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:0 on clusternode2 Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:1 on clusternode1 Waiting for 1 reply from the controller ... got reply (done)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the current status.
There are three ways to display the replication status, which needs to be in sync. Starting with the primary on remotehost3:
remotehost3clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration| grep -i primary active primary site: 1 primary masters: clusternode1
remotehost3clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration| grep -i primary active primary site: 1 primary masters: clusternode1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows site 1 or clusternode1, which was the primary before starting the test to move the primary to clusternode2.
Next check the system replication status on the new primary.
First detect the new primary:
pcs resource | grep Master
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource | grep Master * Masters: [ clusternode2 ]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Here we have an inconsistency, which requires us to re-register remotehost3. You might think that if we run the test again, we might switch the primary back to the original clusternode1. In this case, we have a third way to identify if system replication is working. On the primary node run:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you don’t see remotehost3 in this output, you have to re-register remotehost3. Before registering, please run the following on the primary node to watch the progress of the registration:
clusternode2:rh2adm> watch python ${DIR_EXECUTABLES}/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.pyclusternode2:rh2adm> watch python ${DIR_EXECUTABLES}/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.pyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now you can re-register remotehost3 using this command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Even if the database on remotehost3 is not started yet, you are able to see the third site in the system replication status output. The registration can be finished by starting the database on remotehost3:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The monitor started above will immediately show the synchronization of remotehost3.
-
To switch back, run the test again. One optional test is to switch the primary to the node, which is configured on the
global.inion remotehost3 and then starting the database. The database might come up, but it will never be shown in the output of the system replication status unless it is re-registered. - The missing entry will be immediately created, and the system replication will start as soon as the SAP HANA database is started.
You can check this by executing:
sidadm@clusternode1% hdbnsutil -sr_state sidadm@clusternode1% python systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo $?
sidadm@clusternode1% hdbnsutil -sr_state sidadm@clusternode1% python systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo $?Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You can find more information in Check SAP HANA System Replication status.
5.5. Test 3:Failover of the primary node to the third site
| Subject of the test | Failover the primary to the third site.. Third site becomes primary. Secondary will be re-registered to third site. |
| Test preconditions |
|
| Test steps |
Put the cluster into
Takeover the HANA database form the third node using: |
| Starting the test |
Execute the SAP HANA command on remotehost3:rh2adm>: |
| Monitoring the test |
On the third site run as |
| Expected result |
|
| Ways to return to an initial state |
Detailed description
Check if the databases are running using Check database and check the replication status:
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters"
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output is, for example:
mode: syncmem primary masters: clusternode1
mode: syncmem primary masters: clusternode1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this case, the primary database is clusternode1. If you run this command on clusternode1, you will get:
mode: primary
mode: primaryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On this primary node, you can also display the system replication status. It should look like this:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now we have a proper environment, and we can start monitoring the system replication status on all 3 nodes in separate windows. The 3 monitors should be started before the test is started. The output will change when the test is executed. So keep them running as long as the test is not completed.
On the old primary node, clusternode1 ran in a separate window during the test:
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'clusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output on clusternode1 will be:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On remotehost3, run the same command:
remotehost3:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'remotehost3:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The response will be:
this system is either not running or is not primary system replication site
this system is either not running or is not primary system replication siteCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This will change after the test initiates the failover. The output looks similar to the example of the primary node before the test was started.
On the second node, start:
clusternode2:rh2adm> watch -n 10 'hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep masters'
clusternode2:rh2adm> watch -n 10 'hdbnsutil -sr_state | grep masters'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This will show the current master clusternode1 and will switch immediately after the failover is initiated.
-
To ensure that everything is configured correctly, please also check the
global.ini. Check
global.inion DC1, DC2, and DC3:On all three nodes, the
global.inishould contain:[persistent] log_mode=normal [system_replication] register_secondaries_on_takeover=true
[persistent] log_mode=normal [system_replication] register_secondaries_on_takeover=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can edit the
global.iniwith:clusternode1:rh2adm>vim /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.iniclusternode1:rh2adm>vim /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.iniCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow [Optional] Put the cluster into
maintenance-mode:pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set maintenance-mode=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow During the tests, you will find out that the failover will work with and without setting the
maintenance-mode. So you can run the first test without it. While recovering, it should be done; I just want to show you that it works with and without. This is an option if the primary is not accessible.Start the test: Failover to DC3. On remotehost3, please run:
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_takeover done.
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_takeover done.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The test has started, and now please check the output of the previously started monitors. On the clusternode1, the system replication status will lose its relationship to remotehost3 and clusternode2 (DC2):
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The cluster still doesn’t notice this behavior. If you check the return code of the system replication status, Returncode 11 means error, which tells you something is wrong. If you have access, it is a good idea to enter
maintenance-modenow.The remotehost3 becomes the new primary, and clusternode2 (DC2) gets automatically registered as the new primary on the remotehost3.
Example output of the system replication state of remotehost3:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The returncode 15 also says everything is okay, but clusternode1 is missing. This must be re-registered manually. The former primary clusternode1 is not listed, so the replication relationship is lost.
Set
maintenance-mode.If not already done before, set
maintenance-modeon the cluster on one node of the cluster with the command:pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set maintenance-mode=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can check if the
maintenance-modeis active by running this command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The resources are displaying unmanaged, this indicates that the cluster is in
maintenance-mode=true. The virtual IP address is still started on clusternode1. If you want to use this IP on another node, please disablevip_RH2_02_MASTERbefore you set maintanence-mode=true.pcs resource disable vip_RH2_02_MASTER
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource disable vip_RH2_02_MASTERCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Re-register clusternode1.
When we check the
sr_stateon clusternode1, you will see a relationship only to DC2:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow But when we check DC2, the primary database server is DC3. So the information from DC1 is not correct.
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If we check the system replication status on DC1, the returncode is 12, which is unknown. So DC1 needs to be re-registered.
You can use this command to register the former primary clusternode1 as a new secondary of remotehost3.
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=remotehost3 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=asyncsyncmem --name=DC1 --remoteName=DC3 --operationMode=logreplay --onlineclusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=remotehost3 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=asyncsyncmem --name=DC1 --remoteName=DC3 --operationMode=logreplay --onlineCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the registration is done, you will see on remotehost3 all three sites replicated, and the status (return code) will change to 15.
If this fails, you have to manually remove the replication relationships on DC1 and DC3. Please follow the instructions described in Register Secondary.
For example, list the existing relationships with:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the existing relationships you can use:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_unregister --name=DC2`
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_unregister --name=DC2`Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This may not usually be necessary. We assume that test 4 will be performed after test 3. So the recovery step is to run test 4.
5.6. Test 4:Failback of the primary node to the first site
| Subject of the test | Primary switch back to a cluster node. Failback and enable the cluster again. Re-register the third site as secondary. |
| Test preconditions |
|
| Test steps | Check the expected primary of the cluster. Failover from the DC3 node to the DC1 node. Check if the former secondary has switched to the new primary. Re-register remotehost3 as a new secondary.
Set cluster |
| Monitoring the test | On the new primary start:
On the secondary start:
|
| Starting the test |
Check the expected primary of the cluster: VIP and promoted SAP HANA resources should run on the same node which is the potential new primary.
On this potential primary run as Re-register the former primary as new secondary:
Cluster continues to work after setting the |
| Expected result | New primary is starting SAP HANA. The replication status will show all 3 sites replicated. Second cluster site gets automatically re-registered to the new primary. DR site becomes an additional replica of the database. |
| Ways to return to an initial state | Run test 3. |
Detailed description
Check if the cluster is put into
maintenance-mode:pcs property config maintenance-mode
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property config maintenance-mode Cluster Properties: maintenance-mode: trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the
maintenance-modeis not true you can set it with:pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set maintenance-mode=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the system replication status and discover the primary database on all nodes.
First of all, discover the primary database using:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters"
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should be as follows:
On clusternode1:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters" mode: syncmem primary masters: remotehost3
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters" mode: syncmem primary masters: remotehost3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On clusternode2:
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters" mode: syncmem primary masters: remotehost3
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters" mode: syncmem primary masters: remotehost3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On remotehost3:
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters" mode: primary
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "^mode:|primary masters" mode: primaryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On all three nodes, the primary database is remotehost3.
On this primary database, you have to ensure that the system replication status is active for all three nodes and the return code is 15:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check if all three
sr_statesare consistent.Please run on all three nodes,
hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep site.*Mode:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should be the same on all nodes:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start monitoring in separate windows.
On clusternode1, start:
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch "python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py; echo \$?"clusternode1:rh2adm> watch "python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py; echo \$?"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On remotehost3, start:
remotehost3:rh2adm>watch "python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py; echo \$?"remotehost3:rh2adm>watch "python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py; echo \$?"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On clusternode2, start:
clusternode2:rh2adm> watch "hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep siteReplicationMode"
clusternode2:rh2adm> watch "hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep siteReplicationMode"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the test.
To failover to clusternode1, start on clusternode1:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_takeover done.
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_takeover done.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the output of the monitors.
The monitor on clusternode1 will change to:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important is also the return code 15.
The monitor on clusternode2 will change to:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow DC3 is gone and needs to be re-registered.
On remotehost3, the
systemReplicationStatusreports an error, and the returncode changes to 11.Check if cluster nodes get re-registered:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Site Mapping shows that clusternode2 (DC2) was re-registered.
Check or enable the vip resource:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The vip resource
vip_RH2_02_MASTERis stopped.To start it again run:
pcs resource enable vip_RH2_02_MASTER
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource enable vip_RH2_02_MASTER Warning: 'vip_RH2_02_MASTER' is unmanagedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The warning is right because the cluster will not start any resources unless
maintenance-mode=false.Stop cluster
maintenance-mode.Before we stop the
maintenance-mode, we should start two monitors in separate windows to see the changes.On clusternode2, run:
watch pcs status --full
[root@clusternode2]# watch pcs status --fullCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On clusternode1, run:
clusternode1:rh2adm> watch "python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py; echo $?"clusternode1:rh2adm> watch "python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py; echo $?"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now you can unset the
maintenance-modeon clusternode1 by running:pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set maintenance-mode=falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The monitor on clusternode1 should show you that everything is running now as expected:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After manual interaction, it is always good advice to cleanup the cluster, as described in Cluster Cleanup.
Re-register remotehost3 to the new primary on clusternode1.
Remotehost3 needs to be re-registered. To monitor the progress, please start on clusternode1:
con_cluster_cleanupclusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'con_cluster_cleanupclusternode1:rh2adm> watch -n 5 'python /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py ; echo Status $?'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On remotehost3, please start:
remotehost3:rh2adm> watch 'hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep siteReplicationMode'
remotehost3:rh2adm> watch 'hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep siteReplicationMode'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now you can re-register remotehost3 with this command:
remotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=clusternode1 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=async --name=DC3 --remoteName=DC1 --operationMode=logreplay --onlineremotehost3:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=clusternode1 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=async --name=DC3 --remoteName=DC1 --operationMode=logreplay --onlineCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The monitor on clusternode1 will change to:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow And the monitor of remotehost3 will change to:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now we have again 3 entries, and remotehost3 (DC3) is again a secondary site replicated from clusternode1 (DC1).
Check if all nodes are part of the system replication status on clusternode1.
Please run on all three nodes,
hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 |grep site.*Mode:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On all nodes, we should get the same output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check pcs status --full and SOK.
Run:
pcs status --full| grep sync_state
[root@clusternode1]# pcs status --full| grep sync_stateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output should be either PRIM or SOK:
* hana_rh2_sync_state : PRIM * hana_rh2_sync_state : SOK* hana_rh2_sync_state : PRIM * hana_rh2_sync_state : SOKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Finally, the cluster status should look like this, including the
sync_statePRIM and SOK:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Refer to Check cluster status and Check database to verify that all works fine again.
Chapter 6. Useful commands
Below are 3 sections of useful commands. In most cases, it should help to verify successful operation or configuration. Examples are listed together with the response. In some cases, the output has been adjusted for formatting reasons.
-
All commands listed in this document when executed by the
<sid>admuser start with>. -
All commands run by the
root userstart with a#. -
To execute the commands, omit the prefix
>or#.
6.1. SAP HANA commands
The SAP HANA commands are executed by the <sid>adm user. Example:
6.1.1. SAP HANA installation using hdbclm
The installation of the third site is similar to the installation of the second site. The installation can be done with hdblcm as user root. To ensure that nothing is installed before, run hdbuninst to check if SAP HANA is not already installed on this node.
Example output of HANA uninstallation:
cd /software/DATA_UNITS/HDB_SERVER_LINUX_X86_64
[root@remotehost3]# cd /software/DATA_UNITS/HDB_SERVER_LINUX_X86_64
root@DC3/software/DATA_UNITS/HDB_SERVER_LINUX_X86_64# ./hdbuninst
Option 0 will remove an already existing HANA Installation
No SAP HANA Installation found is the expected answerExample output of HANA installation on DC3:
Before the installation starts, a summary is listed:
Enter y to start the installation.
6.1.2. Using hdbsql to check Inifile contents
6.1.3. Check database
Check if the database is running and discover the current primary node.
List database instances
If the output is green the instance is running.
List database processes
Usually, all database processes have the status GREEN.
List SAP HANA processes
Display SAP HANA landscape configuration
Returncodes:
- 0: Fatal
- 1: Error
- 2: Warning
- 3: Info
- 4: OK
Discover primary database
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode"
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode"Example of check on a secondary:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode" mode: syncmem primary masters: clusternode1
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state | egrep -e "primary masters|^mode"
mode: syncmem
primary masters: clusternode1Example of check on the current primary:
Display the database version
Example using SQL query:
hdbsql RH2=> select * from m_database SYSTEM_ID,DATABASE_NAME,HOST,START_TIME,VERSION,USAGE "RH2","RH2","node1","2023-06-22 15:33:05.235000000","2.00.059.02.1647435895","CUSTOM" 1 row selected (overall time 29.107 msec; server time 927 usec)
hdbsql RH2=> select * from m_database
SYSTEM_ID,DATABASE_NAME,HOST,START_TIME,VERSION,USAGE
"RH2","RH2","node1","2023-06-22 15:33:05.235000000","2.00.059.02.1647435895","CUSTOM"
1 row selected (overall time 29.107 msec; server time 927 usec)
Example using systemOverview.py:
6.1.4. Start and stop SAP HANA
Option 1: HDB command
clusternode1:rh2adm> HDB help
Usage: /usr/sap/RH2/HDB02/HDB { start|stop|reconf|restart|version|info|proc|admin|kill|kill-<sig>|term }
kill or kill-9 should never be used in a productive environment!
clusternode1:rh2adm> HDB help
Usage: /usr/sap/RH2/HDB02/HDB { start|stop|reconf|restart|version|info|proc|admin|kill|kill-<sig>|term }
kill or kill-9 should never be used in a productive environment!Start the Database
clusternode1:rh2adm> HDB start
clusternode1:rh2adm> HDB startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop the database
clusternode1:rh2adm> HDB stop
clusternode1:rh2adm> HDB stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Option 2 (recommended): Use sapcontrol
clusternode1:rh2adm> sapcontrol -nr ${TINSTANCE} -function StartSystem HDB
03.07.2023 14:08:30
StartSystem
OK
clusternode1:rh2adm> sapcontrol -nr ${TINSTANCE} -function StartSystem HDB
03.07.2023 14:08:30
StartSystem
OKclusternode1:rh2adm> sapcontrol -nr ${TINSTANCE} -function StopSystem HDB
03.07.2023 14:09:33
StopSystem
OK
clusternode1:rh2adm> sapcontrol -nr ${TINSTANCE} -function StopSystem HDB
03.07.2023 14:09:33
StopSystem
OKUse the GetProcessList to monitor the starting and stopping of HANA services:
clusternode1:rh2adm> sapcontrol -nr ${TINSTANCE} -function GetProcessList
clusternode1:rh2adm> sapcontrol -nr ${TINSTANCE} -function GetProcessList6.1.5. Check SAP HANA System Replication status
There are many ways to check the SAP HANA System Replication status:
- `clusternode1:rh2adm> python systemReplicationStatus.py ` on the primary node
-
clusternode1:rh2adm> echo $? #(Return code of systemReplicationStatus) -
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_state -
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration
Example of systemReplicationStatus.py output running as a monitor:
The expected results for the return codes are:
- 10: NoHSR
- 11: Error
- 12: Unknown
- 13: Initializing
- 14: Syncing
- 15: Active
In most cases the System Replication check will return with return code 15. Another display option is to use -t (printLandscapeTree).
Example for the output on the current primary:
clusternode1:rh2adm> python systemReplicationStatus.py -t
HANA System Replication landscape:
DC1 ( primary )
| --- DC3 ( syncmem )
| --- DC2 ( syncmem )
clusternode1:rh2adm> python systemReplicationStatus.py -t
HANA System Replication landscape:
DC1 ( primary )
| --- DC3 ( syncmem )
| --- DC2 ( syncmem )
Example of hdbnsutil -sr_state:
Example of sr_stateConfiguation on the primary:
Example of sr_stateConfiguration on the secondary:
You can also check in the secondary database which node is the current primary. During the failover it happens to have two primary databases and this information is needed to decide which potential primary database is wrong and needs to be re-registered as secondary.
For additional information, refer to Example: Checking the Status on the Primary and Secondary Systems.
6.1.6. Register secondary node
Preconditions to register a secondary database for a SAP HANA System Replication environment:
- Create SAP HANA backup
- Enable SAP HANA System Replication on the primary node
- Copy database keys
- Register Secondary Node
Registration example:
With the registration the global.ini file will be automatically updated
… from:
… to:
6.1.7. sapcontrol GetProcessList
Check the processes of an active SAP HANA database
6.1.8. sapcontrol GetInstanceList
This will list the status of instances of a SAP HANA database. It will also show the ports. There are three different status names:
- GREEN (running)
- GRAY (stopped)
- YELLOW ( status is currently changing)
Example of an active instance:
Example of a stopped instance:
6.1.9. hdbcons examples
You can also use the HDB Console to display information about the database:
-
hdbcons -e hdbindexserver 'replication info' -
hdbcons -e hdbindexserver helpfor more options
Example of ‘replication info’:
Example of help:
6.1.10. Create SAP HANA backup
If you want to use SAP HANA System Replication, a backup must first be created on the primary system.
Example of how to perform this is as user <sid>adm:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbsql -i ${TINSTANCE} -u system -d SYSTEMDB "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('/hana/backup/')"
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbsql -i ${TINSTANCE} -u system -d ${SAPSYSTEMNAME} "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('/hana/backup/')"
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbsql -i ${TINSTANCE} -u system -d SYSTEMDB "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('/hana/backup/')"
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbsql -i ${TINSTANCE} -u system -d ${SAPSYSTEMNAME} "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('/hana/backup/')"6.1.11. Enable SAP HANA System Replication on the primary database
SAP HANA System Replication has to be enabled on the primary node. This requires a backup to be done first.
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_enable --name=DC1 nameserver is active, proceeding ... successfully enabled system as system replication source site done.
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_enable --name=DC1
nameserver is active, proceeding ...
successfully enabled system as system replication source site
done.6.1.12. Copy database keys to the secondary nodes
The database keys need to be copied from the primary to the secondary database before it can be registered as a secondary.
For example:
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.DAT
clusternode1:rh2adm> scp -rp /usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY remotehost3:/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}.KEY6.1.13. Register a secondary node for SAP HANA System Replication
Please ensure that the database keys have been copied to the secondary nodes first. Then run the registration command:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=remotehost3 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=syncmem --name=DC1 --remoteName=DC3 --operationMode=logreplay --online
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=remotehost3 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=syncmem --name=DC1 --remoteName=DC3 --operationMode=logreplay --onlineParameter description:
-
remoteHost: hostname of the active node running the source (primary) database -
remoteInstance: the instance number of the database replicationMode: one of the following options-
sync: hard disk synchronization -
async: asynchronous replication -
syncmem: memory synchronization
-
-
name: this is an alias for this replication site -
remoteName: alias name of the source database operationMode: one of the following options-
delta_datashipping: data is periodically transmitted. Takeovers take a little bit longer. -
logreplay: logs are redone immediately on the remote site. Takeover is faster. -
logreplay_readaccess: additional logreplay read-only access to the second site is possible.
-
6.1.14. Check the log_mode of the SAP HANA database
There are two options for setting the log_mode:
-
log_mode=overwrite -
log_mode=normal: This is the default value and is also required when the database instance is running as primary. Using SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication, you have to uselog_mode=normal. The best way to check thelog_modeis by usinghdbsql:
Example including a wrong overwrite entry:
In this case, we have two global.ini files:
DEFAULT-
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/SYS/global/hdb/custom/config/global.ini
-
HOST-
/hana/shared/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/${HOSTNAME}/global.iniTheHOSTvalues overwrite theDEFAULTvalues. You can also check both files before the database is started and then usehdbsqlagain to verify the right settings. You can change thelog_modeby editing theglobal.inifile.
-
Example:
clusternode1:rh2adm> vim /hana/shared/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/${HOSTNAME}/global.ini
# global.ini last modified 2023-04-06 16:15:03.521715 by hdbnameserver
[persistence]
log_mode = overwrite
clusternode1:rh2adm> vim /hana/shared/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/${HOSTNAME}/global.ini
# global.ini last modified 2023-04-06 16:15:03.521715 by hdbnameserver
[persistence]
log_mode = overwriteglobal.ini last modified 2023-04-06 16:15:03.521715 by hdbnameserver
# global.ini last modified 2023-04-06 16:15:03.521715 by hdbnameserver
[persistence]
log_mode = normal
After having checked or updated the global.ini file(s), verify the log_mode values:
The section also shows that this parameter needs to be set in the [persistence] section. When you change the log mode from overwrite to normal, it is recommended that you create a full data backup to ensure that the database can be recovered.
6.1.15. Discover primary database
There are several ways to identify the primary node, for instance:
-
pcs status | grep Promoted -
hdbnsutil -sr_stateConfiguration -
systemReplicationStatus.py
Option 1 - The following example of the systemReplicationStatus.py script and filter will return the primary database location on all nodes:
clusternode1:rh2adm>
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/Python/bin/python
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py --sapcontrol=1 | egrep -e
"3${TINSTANCE}01/HOST|PRIMARY_MASTERS"| head -1 | awk -F"=" '{ print $2 }'
clusternode1:rh2adm>
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/Python/bin/python
/usr/sap/${SAPSYSTEMNAME}/HDB${TINSTANCE}/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py --sapcontrol=1 | egrep -e
"3${TINSTANCE}01/HOST|PRIMARY_MASTERS"| head -1 | awk -F"=" '{ print $2 }'Output:
clusternode2
clusternode2
Option 2 - The following example displays the systemReplicationStatus in a similar way for all nodes:
rh2adm>hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 | grep site.*Mode
rh2adm>hdbnsutil -sr_state --sapcontrol=1 | grep site.*ModeOutput:
6.1.16. Takeover primary
Please refer to Check the Replication status section for check on the primary and the secondary nodes. Also:
-
Put cluster into
maintenance-mode - Initiate the takeover on the secondary node
Example for enabling maintenance-mode for the cluster:
pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
[root@clusternode1]# pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
On the secondary that is to become the new primary, run as <sidadm> user:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_takeover
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_takeoverThis secondary becomes the primary, other active secondary databases get re-registered to the new primary and the old primary needs to be manually re-registered as secondary.
6.1.17. Re-register former primary as secondary
Please ensure that the cluster is stopped or put in maintenance-mode. Example:
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=remotehost3 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=syncmem --name=DC2 --online --remoteName=DC3 --operationMode=logreplay --force_full_replica --online
clusternode2:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=remotehost3 --remoteInstance=${TINSTANCE} --replicationMode=syncmem --name=DC2 --online --remoteName=DC3 --operationMode=logreplay --force_full_replica --onlineIn our examples, we are using full replication. Your SAP HANA system administrator should know when full replication is required.
6.1.18. Recover from failover
Please refer to Check the SAP HANA System Replication status and Discover the primary node. It is important that the information is consistent. If a node is not part of the systemReplicationStatus.py output and has a different system replication state, please check with your database administrator if this node needs to be re-registered.
One way of solving this is to re-register this site as a new secondary.
Sometimes a secondary instance will still not come up. Then unregister this site before you re-register it again. Example of unregistering the secondary DC1:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_unregister --name=DC1
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_unregister --name=DC1Example of re-registering DC1:
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --name=DC1 --remoteHost=node2 --remoteInstance=02 --replicationMode=sync --operationMode=logreplay --online
clusternode1:rh2adm> hdbnsutil -sr_register --name=DC1 --remoteHost=node2 --remoteInstance=02 --replicationMode=sync --operationMode=logreplay --onlineThe database needs to be started and checked if it is running. Finally check the replication status.
6.2. Pacemaker commands
6.2.1. Start and stop the cluster
To start the cluster on all nodes execute the following command:
pcs cluster start -all
# pcs cluster start -allAfter a reboot, the cluster will be started automatically only if the service is enabled. The command will help to know if the cluster has started and if the daemons are enabled to be autostarted.
pcs cluster status
# pcs cluster statusThe cluster auto-start can be enabled with:
pcs cluster enable --all
# pcs cluster enable --allOther options are:
- Stop the cluster.
- Put a node into standby.
-
Put the cluster into
maintenance-mode.
For more details, please check the pcs cluster help:
pcs cluster stop --all pcs cluster help
# pcs cluster stop --all
# pcs cluster help6.2.2. Put the cluster into maintenance-mode
If you want to make changes and you want to avoid interference bythe pacemaker cluster, you can "freeze" the cluster by putting it into maintenance-mode:
pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
# pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
An easy way to verify maintenance-mode is to check if the resources are unmanaged:
Refresh cluster resources to detect the resource state while the cluster is in maintenance-mode and does not update resource status changes:
pcs resource refresh
# pcs resource refresh
This will indicate if anything is not yet correct and will cause remediation action by the cluster, as soon as it is taken out of maintenance-mode.
Remove the maintenance-mode by running:
pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
# pcs property set maintenance-mode=falseNow the cluster will continue to work. If something is configured wrong, it will react now.
6.2.3. Check cluster status
Following are several ways to check the cluster status:
Check if the cluster is running:
pcs cluster status
# pcs cluster statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the cluster and all resources:
pcs status
# pcs statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the cluster, all resources and all node attributes:
pcs status --full
# pcs status --fullCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the resources only:
pcs resource status --full
# pcs resource status --fullCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check
Stonithhistory:pcs stonith history
# pcs stonith historyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check location constraints:
pcs constraint location
# pcs constraint locationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Fencing must be configured and tested. In order to obtain a solution that is as automated as possible, the cluster must be constantly activated, which will then enable the cluster to automatically start after a reboot. In a production environment, disabling the restart allows manual intervention, for instance after a crash. Please also check the daemon status.
Example:
6.2.4. Check resource states
Use pcs resource to check the status of all resources. This prints the list and the current status of the resources.
Example:
6.2.5. Check resource config
The following displays the current resource configuration:
This lists all the parameters which are used to configure the installed and configured resource agent.
6.2.6. SAPHana resource option AUTOMATED_REGISTER=true
If this option is used in the SAPHana resource, pacemaker will automatically re-register the secondary database.
It is recommended to use this option for the first tests. When using AUTOMATED_REGISTER=false the administrator needs to re-register the secondary node manually.
6.2.7. Resource handling
There are several options for managing resources. For more information, please check out the help available:
pcs resource help
# pcs resource helpList the used resource agents:
pcs resource config | grep "type=" | awk -F"type=" '{ print $2 }' | sed -e "s/)//g"
# pcs resource config | grep "type=" | awk -F"type=" '{ print $2 }' | sed -e "s/)//g"Example output:
IPaddr2 SAPHanaTopology SAPHana
IPaddr2
SAPHanaTopology
SAPHanaDisplay specific resource agent description and configuration parameters:
pcs resource describe <resource agent>
# pcs resource describe <resource agent>Example (without output):
pcs resource describe IPaddr2
# pcs resource describe IPaddr2
Example of resource agent IPaddr2 (with output):
If the cluster is stopped, all the resources will be stopped as well; if the cluster is put into maintenance-mode, all resources remain in their current status but will not be monitored or managed.
6.2.8. Cluster property handling for maintenance-mode
List all defined properties:
To reconfigure the database, the cluster must be instructed to ignore any changes until the configuration is complete. You can put the cluster into maintenance-mode using:
pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
# pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
Check the maintenance-mode:
Verify that all resources are "unmanaged":
The resources will switch back to managed if you unset the maintenance-mode:
pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
# pcs property set maintenance-mode=false6.2.9. Failover the SAPHana resource using Move
A simple example of how to failover the SAP HANA database is to use the pcs resource move command. You need to use the clone resource name and move the resource as shown below:
pcs resource move <SAPHana-clone-resource>
# pcs resource move <SAPHana-clone-resource>
In this example, the clone resource is SAPHana_RH2_02-clone:
Move the resource:
Check if there are remaining constraints:
pcs constraint location
# pcs constraint locationYou can remove those location constraints created during the failover by clearing the resource. Example:
pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
[root@clusternode1]# pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-cloneCheck if there are any remaining warnings or entries in the "Migration Summary":
pcs status --full
# pcs status --full
Check the stonith history:
pcs stonith history
# pcs stonith historyIf desired, clear the stonith history:
pcs stonith history cleanup
# pcs stonith history cleanupIf you are using a pacemaker version earlier than 2.1.5, please refer to Is there a way to manage constraints when running pcs resource move? and check the remaining constraints.
6.2.10. Monitor failover and sync state
All pacemaker activities are logged in the /var/log/messages file on the cluster nodes. Since there are many other messages, it is sometimes difficult to read the messages related to the SAP resource agent. You can configure a command alias that filters out only the messages related to SAP resource agent.
Example alias tmsl:
alias tmsl='tail -1000f /var/log/messages | egrep -s "Setting master-rsc_SAPHana_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}_HDB${TINSTANCE}|sr_register|WAITING4LPA|PROMOTED|DEMOTED|UNDEFINED|master_walk|SWAIT|WaitforStopped|FAILED|LPT"'
# alias tmsl='tail -1000f /var/log/messages | egrep -s "Setting master-rsc_SAPHana_${SAPSYSTEMNAME}_HDB${TINSTANCE}|sr_register|WAITING4LPA|PROMOTED|DEMOTED|UNDEFINED|master_walk|SWAIT|WaitforStopped|FAILED|LPT"'
Example output of tsml:
The filter makes it easier to understand what status changes are happening. If details are missing, you can open the whole message file to read all the information.
After a failover, you can clear the resource. Please also check that there are no remaining location constraints.
6.2.11. Check cluster consistency
During the installation the resources are sometimes started before the configuration is finally completed. This can lead to entries in the Cluster Information Base (CIB), which can result in incorrect behavior. This can easily be checked and also manually corrected after the configuration has been completed.
If you start the SAPHana resources the missing entries will be recreated. Wrong entries cannot be addressed by pcs commands and need to be removed manually.
Check CIB entries:
cibadmin --query
# cibadmin --queryDC3 and SFAIL are entries that should not be present in the Cluster Information Base, when the cluster members are DC1 and DC2, and when the sync state between the nodes is reported as SOK.
Example to check for corresponding entries:
cibadmin --query |grep '"DC3"' cibadmin --query |grep '"SFAIL"'
# cibadmin --query |grep '"DC3"'
# cibadmin --query |grep '"SFAIL"'The command can be executed on any node in the cluster as user root. Usually the output of the command is empty. If there is still an error in the configuration the output could look like this:
<nvpair id="SAPHanaSR-hana_rh1_glob_sec" name="hana_rh1_glob_sec" value="DC3"/>
<nvpair id="SAPHanaSR-hana_rh1_glob_sec" name="hana_rh1_glob_sec" value="DC3"/>These entries can be removed with the following command:
cibadmin --delete --xml-text '<...>'
# cibadmin --delete --xml-text '<...>'To remove the entries in the example above you have to enter the following. Please note that the output contains double quotes, so the text must be embedded in single quotes:
cibadmin --delete --xml-text ' <nvpair id="SAPHanaSR-hana_rh1_glob_sec" name="hana_rh1_glob_sec" value="DC3"/>'
# cibadmin --delete --xml-text ' <nvpair id="SAPHanaSR-hana_rh1_glob_sec" name="hana_rh1_glob_sec" value="DC3"/>'Verify the absence of the removed CIB entries. The returned output should be empty.
cibadmin --query |grep 'DC3"'
# cibadmin --query |grep 'DC3"'6.2.12. Cluster cleanup
During the failover tests there might be left behind constraints and other remains from previous tests. The cluster needs to be cleared from these before starting the next test.
Check the cluster status for failure events:
pcs status --full
# pcs status --fullIf you see cluster warnings or entries in the "Migration Summary", you should clear and cleanup the resources:
pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-clone pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
# pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
# pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_RH2_02-cloneOutput:
Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:0 on clusternode1 Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:1 on clusternode2
Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:0 on clusternode1
Cleaned up SAPHana_RH2_02:1 on clusternode2Check if there are unwanted location constraints, for example from a previous failover:
pcs constraint location
# pcs constraint locationCheck the existing constraints in more detail:
pcs constraint --full
# pcs constraint --fullExample of a location constraint after a resource move:
Node: hana08 (score:-INFINITY) (role:Started) (id:cli-ban-SAPHana_RH2_02-clone-on-hana08)
Node: hana08 (score:-INFINITY) (role:Started) (id:cli-ban-SAPHana_RH2_02-clone-on-hana08)Clear this location constraint:
pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-clone
# pcs resource clear SAPHana_RH2_02-cloneVerify the constraint is gone from the constraints list. If it persists, explicitly delete it using its constraint id:
pcs constraint delete cli-ban-SAPHana_RH2_02-clone-on-hana08
# pcs constraint delete cli-ban-SAPHana_RH2_02-clone-on-hana08
If you run several tests with fencing you might also clear the stonith history:
pcs stonith history cleanup
# pcs stonith history cleanupAll pcs commands are executed as user root. Please also check Discover leftovers.
6.2.13. Other cluster commands
Various cluster command examples
6.3. RHEL and general commands
6.3.1. Discover current status
You have to follow several steps to know what the current status of the environment is. Please refer to Monitor the environment. Also, we recommend to do the following:
-
Check
/var/log/messages, use Aliases for monitoring for easier log reviews. - Sometimes a cluster must be cleaned up from previous activity to continue proper operation. Discover leftovers and clear them if necessary.
6.3.2. yum info
6.3.3. RPM display version
rpm -q resource-agents-sap-hana
# rpm -q resource-agents-sap-hana
resource-agents-sap-hana-0.162.1-2.el9_2.noarch6.3.4. Aliases for monitoring
You can add this to your shell profile. In the example the root aliases depend on the <sid>adm aliases, which must therefore also already be defined.
root ( add to
~/.bashrc):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow <sid>adm( add to~/.customer.sh):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 7. References
7.1. Red Hat
7.2. SAP
- SAP HANA Administration Guide for SAP HANA Platform
- Disaster Recovery Scenarios for Multitarget System Replication
- SAP HANA System Replication Configuration Parameter
- Example: Checking the Status on the Primary and Secondary Systems
- General Prerequisites for Configuring SAP HANA System Replication
- Change Log Modes
- Failed to re-register former primary site as new secondary site due to missing log
- Checking the Status with landscapeHostConfiguration.py
- How to Setup SAP HANA Multi-Target System Replication
- SAP HANA Multitarget System Replication