此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
CLI Reference
OpenShift Container Platform 3.5 CLI Reference
Abstract
Chapter 1. Overview
With the OpenShift Container Platform command line interface (CLI), you can create applications and manage OpenShift Container Platform projects from a terminal. The CLI is ideal in situations where you are:
- Working directly with project source code.
- Scripting OpenShift Container Platform operations.
- Restricted by bandwidth resources and cannot use the web console.
The CLI is available using the oc command:
oc <command>
$ oc <command>See Get Started with the CLI for installation and setup instructions.
Chapter 2. Get Started with the CLI
2.1. Overview
The OpenShift Container Platform CLI exposes commands for managing your applications, as well as lower level tools to interact with each component of your system. This topic guides you through getting started with the CLI, including installation and logging in to create your first project.
2.2. Prerequisites
Certain operations require Git to be locally installed on a client. For example, the command to create an application using a remote Git repository:
oc new-app https://github.com/<your_user>/<your_git_repo>
$ oc new-app https://github.com/<your_user>/<your_git_repo>Before proceeding, install Git on your workstation. See the official Git documentation for instructions per your workstation’s operating system.
2.3. Installing the CLI
The easiest way to download the CLI is by accessing the About page on the web console if your cluster administrator has enabled the download links:
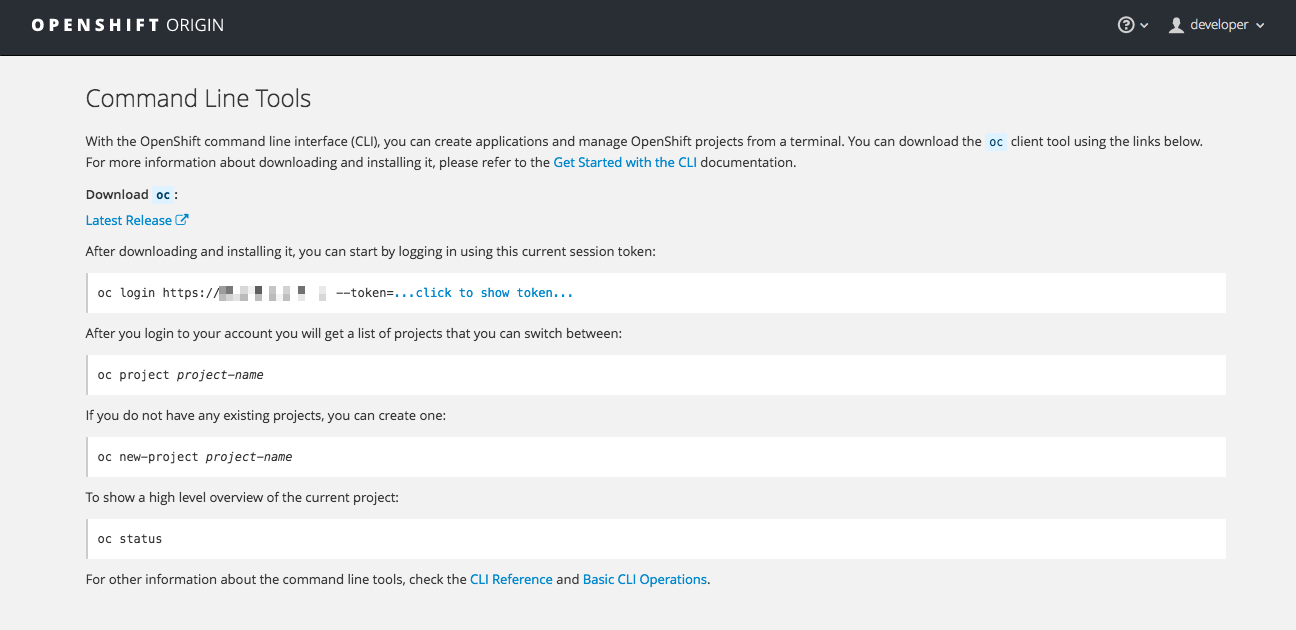
Installation options for the CLI vary depending on your operating system.
To log in using the CLI, collect your token from the web console’s Command Line page, which is accessed from Command Line Tools in the Help menu. The token is hidden, so you must click the copy to clipboard button at the end of the oc login line on the Command Line Tools page, then paste the copied contents to show the token.
2.3.1. For Windows
The CLI for Windows is provided as a zip archive; you can download it from the Red Hat Customer Portal. After logging in with your Red Hat account, you must have an active OpenShift Enterprise subscription to access the downloads page:
Download the CLI from the Red Hat Customer Portal
Alternatively, if the cluster administrator has enabled it, you can download and unpack the CLI from the About page on the web console.
Tutorial Video:
The following video walks you through this process: Click here to watch
Then, unzip the archive with a ZIP program and move the oc binary to a directory on your PATH. To check your PATH, open the Command Prompt and run:
path
C:\> path2.3.2. For Mac OS X
The CLI for Mac OS X is provided as a tar.gz archive; you can download it from the Red Hat Customer Portal. After logging in with your Red Hat account, you must have an active OpenShift Enterprise subscription to access the downloads page:
Download the CLI from the Red Hat Customer Portal
Alternatively, if the cluster administrator has enabled it, you can download and unpack the CLI from the About page on the web console.
Tutorial Video:
The following video walks you through this process: Click here to watch
Then, unpack the archive and move the oc binary to a directory on your PATH. To check your PATH, open a Terminal window and run:
echo $PATH
$ echo $PATH2.3.3. For Linux
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7, you can install the CLI as an RPM using Red Hat Subscription Management (RHSM) if you have an active OpenShift Enterprise subscription on your Red Hat account:
subscription-manager register subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_ID> subscription-manager repos --enable="rhel-7-server-ose-3.5-rpms" yum install atomic-openshift-clients
# subscription-manager register
# subscription-manager attach --pool=<pool_ID>
# subscription-manager repos --enable="rhel-7-server-ose-3.5-rpms"
# yum install atomic-openshift-clients- 1
- Pool ID for an active OpenShift Enterprise subscription
For RHEL, Fedora, and other Linux distributions, you can also download the CLI directly from the Red Hat Customer Portal as a tar.gz archive. After logging in with your Red Hat account, you must have an active OpenShift Enterprise subscription to access the downloads page.
Download the CLI from the Red Hat Customer Portal
Tutorial Video:
The following video walks you through this process: Click here to watch
Alternatively, if the cluster administrator has enabled it, you can download and unpack the CLI from the About page on the web console.
Then, unpack the archive and move the oc binary to a directory on your PATH. To check your path, run:
echo $PATH
$ echo $PATHTo unpack the archive:
tar -xf <file>
$ tar -xf <file>If you do not use RHEL or Fedora, ensure that libc is installed and on your library path. If libc is not available, you might see the following error when you run CLI commands:
oc: No such file or directory
oc: No such file or directory2.4. Basic Setup and Login
The oc login command is the best way to initially set up the CLI, and it serves as the entry point for most users. The interactive flow helps you establish a session to an OpenShift Container Platform server with the provided credentials. The information is automatically saved in a CLI configuration file that is then used for subsequent commands.
The following example shows the interactive setup and login using the oc login command:
Example 2.1. Initial CLI Setup
When you have completed the CLI configuration, subsequent commands use the configuration file for the server, session token, and project information.
You can log out of CLI using the oc logout command:
oc logout User, alice, logged out of https://openshift.example.com
$ oc logout
User, alice, logged out of https://openshift.example.comIf you log in after creating or being granted access to a project, a project you have access to is automatically set as the current default, until switching to another one:
Additional options are also available for the oc login command.
If you have access to administrator credentials but are no longer logged in as the default system user system:admin, you can log back in as this user at any time as long as the credentials are still present in your CLI configuration file. The following command logs in and switches to the default project:
oc login -u system:admin -n default
$ oc login -u system:admin -n default2.5. CLI Configuration Files
A CLI configuration file permanently stores oc options and contains a series of authentication mechanisms and OpenShift Container Platform server connection information associated with nicknames.
As described in the previous section, the oc login command automatically creates and manages CLI configuration files. All information gathered by the command is stored in a configuration file located in ~/.kube/config. The current CLI configuration can be viewed using the following command:
Example 2.2. Viewing the CLI Configuration
CLI configuration files can be used to setup multiple CLI profiles using various OpenShift Container Platform servers, namespaces, and users so that you can switch easily between them. The CLI can support multiple configuration files; they are loaded at runtime and merged together along with any override options specified from the command line.
2.6. Projects
A project in OpenShift Container Platform contains multiple objects to make up a logical application.
Most oc commands run in the context of a project. The oc login selects a default project during initial setup to be used with subsequent commands. Use the following command to display the project currently in use:
oc project
$ oc projectIf you have access to multiple projects, use the following syntax to switch to a particular project by specifying the project name:
oc project <project_name>
$ oc project <project_name>For example:
The oc status command shows a high level overview of the project currently in use, with its components and their relationships, as shown in the following example:
2.7. What’s Next?
After you have logged in, you can create a new application and explore some common CLI operations.
Chapter 3. Managing CLI Profiles
3.1. Overview
A CLI configuration file allows you to configure different profiles, or contexts, for use with the OpenShift CLI. A context consists of user authentication and OpenShift Container Platform server information associated with a nickname.
3.2. Switching Between CLI Profiles
Contexts allow you to easily switch between multiple users across multiple OpenShift Container Platform servers, or clusters, when using issuing CLI operations. Nicknames make managing CLI configuration easier by providing short-hand references to contexts, user credentials, and cluster details.
After logging in with the CLI for the first time, OpenShift Container Platform creates a ~/.kube/config file if one does not already exist. As more authentication and connection details are provided to the CLI, either automatically during an oc login operation or by setting them explicitly, the updated information is stored in the configuration file:
Example 3.1. CLI Configuration File
- 1
- The
clusterssection defines connection details for OpenShift Container Platform clusters, including the address for their master server. In this example, one cluster is nicknamed openshift1.example.com:8443 and another is nicknamed openshift2.example.com:8443. - 2
- This
contextssection defines two contexts: one nicknamed alice-project/openshift1.example.com:8443/alice, using the alice-project project, openshift1.example.com:8443 cluster, and alice user, and another nicknamed joe-project/openshift1.example.com:8443/alice, using the joe-project project, openshift1.example.com:8443 cluster and alice user. - 3
- The
current-contextparameter shows that the joe-project/openshift1.example.com:8443/alice context is currently in use, allowing the alice user to work in the joe-project project on the openshift1.example.com:8443 cluster. - 4
- The
userssection defines user credentials. In this example, the user nickname alice/openshift1.example.com:8443 uses an access token.
The CLI can support multiple configuration files; they are loaded at runtime and merged together along with any override options specified from the command line.
After you are logged in, you can use the oc status command or the oc project command to verify your current working environment:
Example 3.2. Verifying the Current Working Environment
oc project Using project "joe-project" from context named "joe-project/openshift1.example.com:8443/alice" on server "https://openshift1.example.com:8443".
$ oc project
Using project "joe-project" from context named "joe-project/openshift1.example.com:8443/alice" on server "https://openshift1.example.com:8443".
To log in using any other combination of user credentials and cluster details, run the oc login command again and supply the relevant information during the interactive process. A context is constructed based on the supplied information if one does not already exist.
If you are already logged in and want to switch to another project the current user already has access to, use the oc project command and supply the name of the project:
oc project alice-project Now using project "alice-project" on server "https://openshift1.example.com:8443".
$ oc project alice-project
Now using project "alice-project" on server "https://openshift1.example.com:8443".
At any time, you can use the oc config view command to view your current, full CLI configuration, as seen in the above output.
Additional CLI configuration commands are also available for more advanced usage.
If you have access to administrator credentials but are no longer logged in as the default system user system:admin, you can log back in as this user at any time as long as the credentials are still present in your CLI configuration file. The following command logs in and switches to the default project:
oc login -u system:admin -n default
$ oc login -u system:admin -n default3.3. Manually Configuring CLI Profiles
This section covers more advanced usage of CLI configurations. In most situations, you can simply use the oc login and oc project commands to log in and switch between contexts and projects.
If you want to manually configure your CLI configuration files, you can use the oc config command instead of modifying the files themselves. The oc config command includes a number of helpful subcommands for this purpose:
| Subcommand | Usage |
|---|---|
|
| Sets a user entry in the CLI configuration file. If the referenced user nickname already exists, the specified information is merged in. oc config set-credentials <user_nickname> [--client-certificate=<path/to/certfile>] [--client-key=<path/to/keyfile>] [--token=<bearer_token>] [--username=<basic_user>] [--password=<basic_password>] |
|
| Sets a cluster entry in the CLI configuration file. If the referenced cluster nickname already exists, the specified information is merged in. oc config set-cluster <cluster_nickname> [--server=<master_ip_or_fqdn>] [--certificate-authority=<path/to/certificate/authority>] [--api-version=<apiversion>] [--insecure-skip-tls-verify=true] |
|
| Sets a context entry in the CLI configuration file. If the referenced context nickname already exists, the specified information is merged in. oc config set-context <context_nickname> [--cluster=<cluster_nickname>] [--user=<user_nickname>] [--namespace=<namespace>] |
|
| Sets the current context using the specified context nickname. oc config use-context <context_nickname> |
|
| Sets an individual value in the the CLI configuration file. oc config set <property_name> <property_value>
The |
|
| Unsets individual values in the CLI configuration file. oc config unset <property_name>
The |
|
| Displays the merged CLI configuration currently in use. oc config view Displays the result of the specified CLI configuration file. oc config view --config=<specific_filename> |
Example Usage
Consider the following configuration workflow. First, set credentials for a user nickname alice that uses an access token:
oc config set-credentials alice --token=NDM2N2MwODgtNjI1Yy10N3VhLTg1YmItYzI4NDEzZDUyYzVi
$ oc config set-credentials alice --token=NDM2N2MwODgtNjI1Yy10N3VhLTg1YmItYzI4NDEzZDUyYzViSet a cluster entry named openshift1:
oc config set-cluster openshift1 --server=https://openshift1.example.com
$ oc config set-cluster openshift1 --server=https://openshift1.example.comSet a context named alice that uses the alice user and the openshift1 cluster:
oc config set-context alice --cluster=openshift1 --user=alice
$ oc config set-context alice --cluster=openshift1 --user=aliceNow that the alice context has been created, switch to that context:
oc config use-context alice
$ oc config use-context aliceSet the aliceproject namespace for the alice context:
oc config set contexts.alice.namespace aliceproject
$ oc config set contexts.alice.namespace aliceprojectYou can now view the configuration that has been created:
- 1
- The current context is set to alice.
All subsequent CLI operations will use the alice context, unless otherwise specified by overriding CLI options or until the context is switched.
3.4. Loading and Merging Rules
When issuing CLI operations, the loading and merging order for the CLI configuration follows these rules:
CLI configuration files are retrieved from your workstation, using the following hierarchy and merge rules:
-
If the
--configoption is set, then only that file is loaded. The flag may only be set once and no merging takes place. -
If
$KUBECONFIGenvironment variable is set, then it is used. The variable can be a list of paths, and if so the paths are merged together. When a value is modified, it is modified in the file that defines the stanza. When a value is created, it is created in the first file that exists. If no files in the chain exist, then it creates the last file in the list. -
Otherwise, the ~/.kube/config file is used and no merging takes place.
-
If the
The context to use is determined based on the first hit in the following chain:
-
The value of the
--contextoption. -
The
current-contextvalue from the CLI configuration file. -
An empty value is allowed at this stage.
-
The value of the
The user and cluster to use is determined. At this point, you may or may not have a context; they are built based on the first hit in the following chain, which is run once for the user and once for the cluster:
-
The value of the
--useroption for user name and the--clusteroption for cluster name. -
If the
--contextoption is present, then use the context’s value. -
An empty value is allowed at this stage.
-
The value of the
The actual cluster information to use is determined. At this point, you may or may not have cluster information. Each piece of the cluster information is built based on the first hit in the following chain:
The values of any of the following command line options:
-
--server, -
--api-version -
--certificate-authority -
--insecure-skip-tls-verify
-
- If cluster information and a value for the attribute is present, then use it.
-
If you do not have a server location, then there is an error.
The actual user information to use is determined. Users are built using the same rules as clusters, except that you can only have one authentication technique per user; conflicting techniques cause the operation to fail. Command line options take precedence over configuration file values. Valid command line options are:
-
--auth-path -
--client-certificate -
--client-key -
--token
-
- For any information that is still missing, default values are used and prompts are given for additional information.
Chapter 4. Developer CLI Operations
4.1. Overview
This topic provides information on the developer CLI operations and their syntax. You must setup and login with the CLI before you can perform these operations.
The developer CLI uses the oc command, and is used for project-level operations. This differs from the administrator CLI, which uses the oc adm command for more advanced, administrator operations.
4.2. Common Operations
The developer CLI allows interaction with the various objects that are managed by OpenShift Container Platform. Many common oc operations are invoked using the following syntax:
oc <action> <object_type> <object_name>
$ oc <action> <object_type> <object_name>This specifies:
-
An
<action>to perform, such asgetordescribe. -
The
<object_type>to perform the action on, such asserviceor the abbreviatedsvc. -
The
<object_name>of the specified<object_type>.
For example, the oc get operation returns a complete list of services that are currently defined:
oc get svc NAME LABELS SELECTOR IP PORT(S) docker-registry docker-registry=default docker-registry=default 172.30.78.158 5000/TCP kubernetes component=apiserver,provider=kubernetes <none> 172.30.0.2 443/TCP kubernetes-ro component=apiserver,provider=kubernetes <none> 172.30.0.1 80/TCP
$ oc get svc
NAME LABELS SELECTOR IP PORT(S)
docker-registry docker-registry=default docker-registry=default 172.30.78.158 5000/TCP
kubernetes component=apiserver,provider=kubernetes <none> 172.30.0.2 443/TCP
kubernetes-ro component=apiserver,provider=kubernetes <none> 172.30.0.1 80/TCP
The oc describe operation can then be used to return detailed information about a specific object:
Versions of oc prior to 3.0.2.0 did not have the ability to negotiate API versions against a server. So if you are using oc up to endif::openshift-origin[][]
Legal Notice
Copyright © Red Hat
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of the OpenJS Foundation.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.