End-user Guide
Using Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces 2.4
Abstract
Chapter 2. Che-Theia IDE basics
This section describes basics workflows and commands for Che-Theia: the native integrated development environment for Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.
2.1. Defining custom commands for Che-Theia
The Che-Theia IDE allows users to define custom commands in a devfile that are then available when working in a workspace.
This is useful, for example, for:
- Simplifying building, running, and debugging projects.
- Allowing lead developers to customize workspaces based on team requirements.
- Reducing time needed to onboard new team members.
See also Section 3.1, “Configuring a workspace using a devfile”.
2.1.1. Che-Theia task types
The following is an example of the commands section of a devfile.
- CodeReady Workspaces commands
Package Native AppandStart Native AppThe CodeReady Workspaces commands are to be used to define tasks that will be executed in the workspace container.
-
The
exectype implies that the CodeReady Workspaces runner is used for command execution. The user can specify the component in whose container the command is executed. -
The
commandfield contains the command line for execution. -
The
workdiris the working directory in which the command is executed. -
The
componentfield refers to the container where the command will be executed. The field contains the componentaliaswhere the container is defined.
-
The
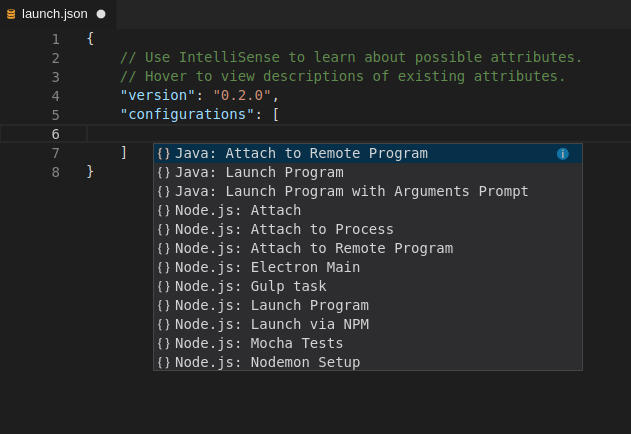
- VS Code launch configurations
Attach remote debuggerVS Code launch configurations are usually used to define debugging configuration. To trigger these configurations, press or choose Start Debugging from the Debug menu. The configurations provide information to the debugger, such as the port to connect to for debugging or the type of the application to debug (Node.js, Java, and others.).
-
The type is
vscode-launch. - It contains the launch configurations in the VS Code format.
- For more information about VS Code launch configurations, see the Debugging section on the Visual Studio documentation page.
-
The type is
Tasks of type che, also known as exec commands, can be executed from the Terminal→Run Task menu or by selecting them in the My Workspace panel. Other tasks are only available from Terminal→Run Task. Launch configurations are available in the Che-Theia debugger.
Additional examples
2.1.2. Running and debugging
Che-Theia supports the Debug Adapter Protocol. This protocol defines a generic way for how a development tool can communicate with a debugger. It means Che-Theia works with all implementations.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
To debug an application:
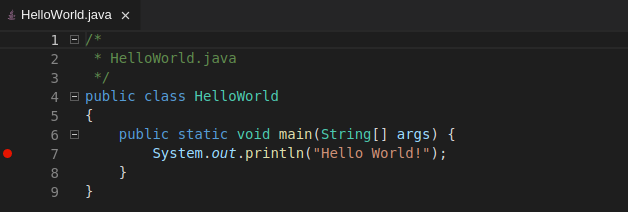
Click Debug → Add Configuration to add debugging or launch configuration to the project.
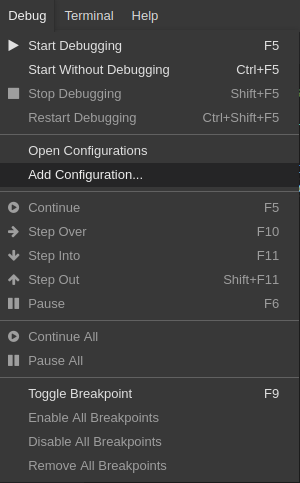
From the pop-up menu, select the appropriate configuration for the application that you want to debug.
Update the configuration by modifying or adding attributes.
Breakpoints can be toggled by clicking the editor margin.
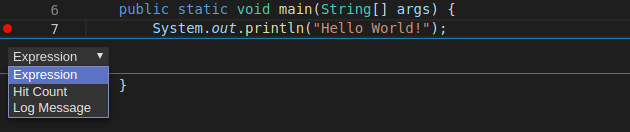
After opening a context menu, use the Edit Breakpoint command to add conditions.
The IDE then displays the
Expresioninput field.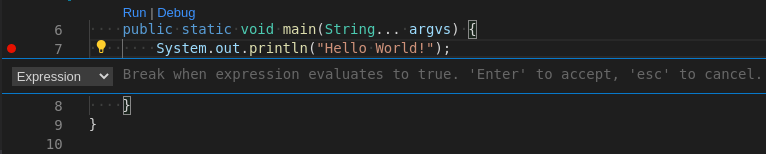
To start debugging, click View→Debug.
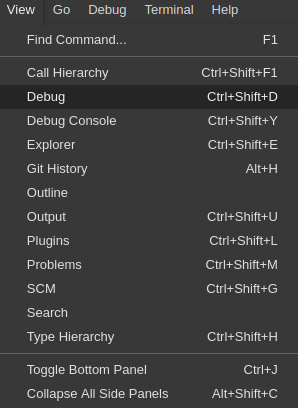
In the Debug view, select the configuration and press F5 to debug the application. Or, start the application without debugging by pressing Ctrl+F5.
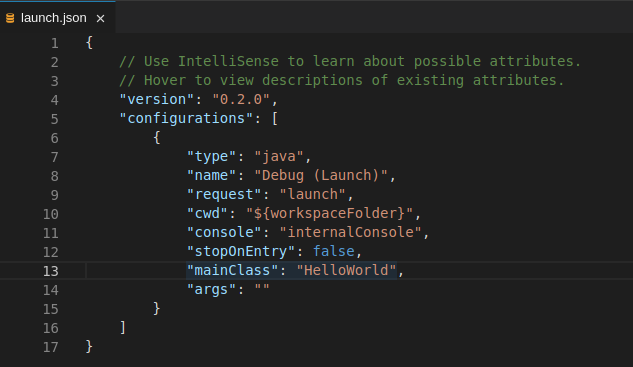
2.1.3. Editing a task and launch configuration
Procedure
To customize the configuration file:
-
Edit the
tasks.jsonorlaunch.jsonconfiguration files. Add new definitions to the configuration file or modify the existing ones.
NoteThe changes are stored in the configuration file.
-
To customize the task configuration provided by plug-ins, select the Terminal → Configure Tasks menu option, and choose the task to configure. The configuration is then copied to the
tasks.jsonfile and is available for editing.
2.2. Version Control
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces natively supports the VS Code SCM model. By default, Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces includes the native VS Code Git extension as a Source Code Management (SCM) provider.
2.2.1. Managing Git configuration: identity
The first thing to do before starting to use Git is to set a user name and email address. This is important because every Git commit uses this information.
Prerequisites
- The Visual Studio Code Git extension installed.
Procedure
To configure Git identity using the CodeReady Workspaces user interface, go to in Preferences.
Open File > Settings > Open Preferences:
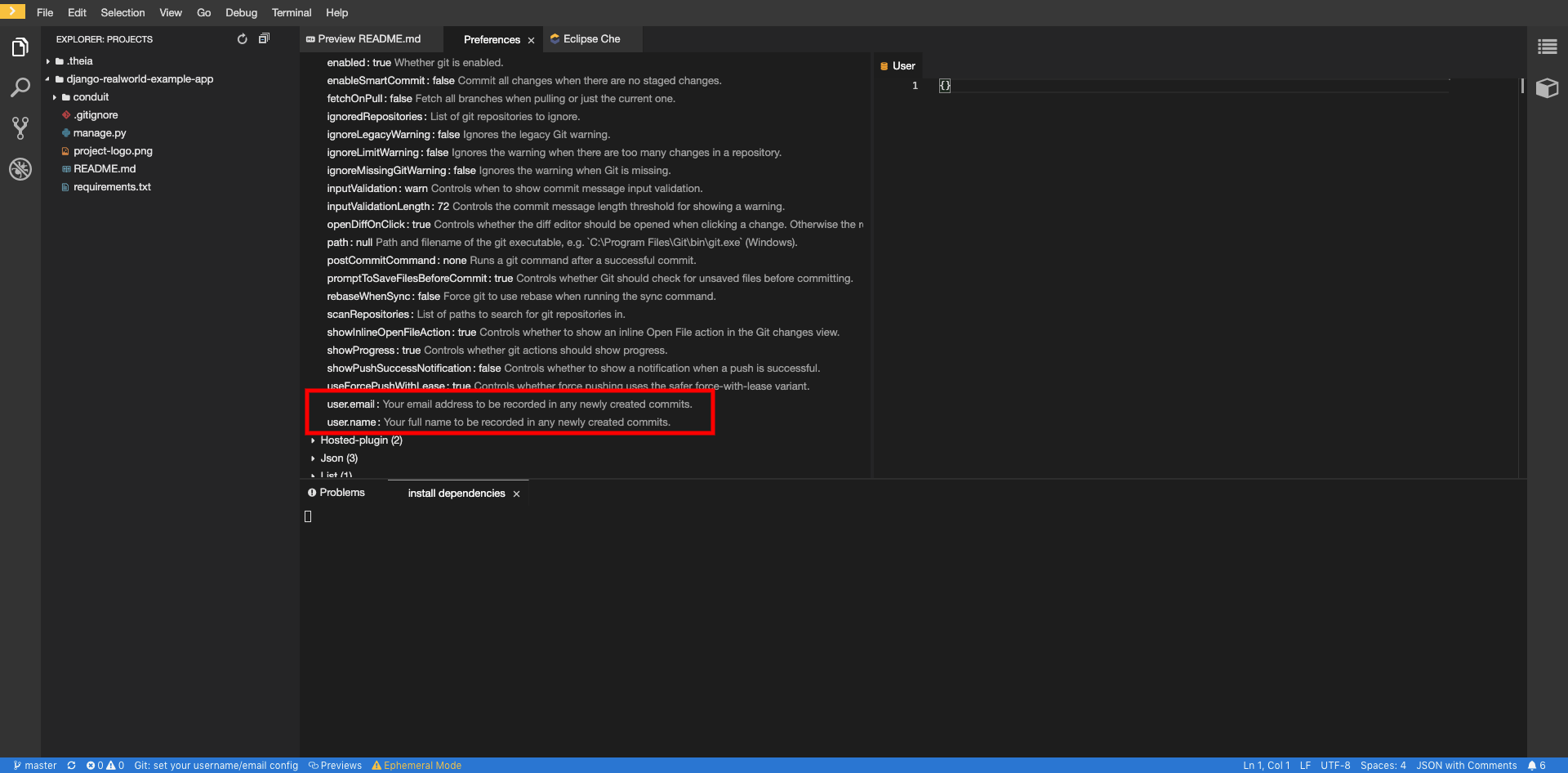
In the opened window, navigate to the Git section, and find:
user.name user.email
user.name user.emailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the identity.
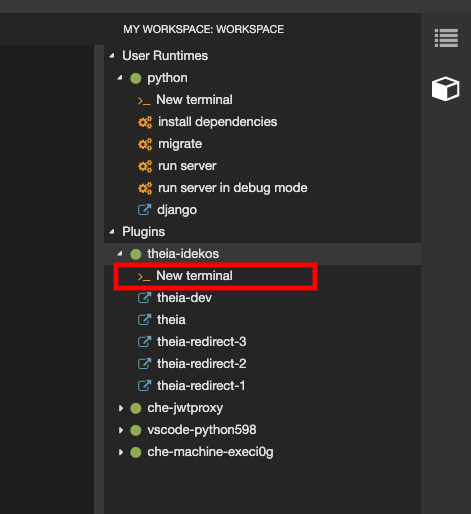
To configure Git identity using the command line, open the terminal of the Che-Theia container.
Navigate to the My Workspace view, and open Plugins > theia-ide… > New terminal:
Execute the following commands:
git config --global user.name "John Doe" git config --global user.email johndoe@example.com
$ git config --global user.name "John Doe" $ git config --global user.email johndoe@example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Che-Theia permanently stores this information and restores it on future workspace starts.
2.2.2. Accessing a Git repository using HTTPS
Prerequisites
-
The
gittool is available. See: Getting Started - Installing Git.
Procedure
To clone a repository using HTTPS:
- Use the clone command provided by the Visual Studio Code Git extension.
Alternatively, use the native Git commands in the terminal to clone a project.
-
Navigate to destination folder using the
cdcommand. Use
git cloneto clone a repository:git clone <link>
$ git clone <link>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces supports Git self-signed TLS certificates. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#deploying-codeready-workspaces-with-support-for-git-repositories-with-self-signed-certificates_crw to learn more.
2.2.3. Accessing a Git repository using a generated SSH key pair
2.2.3.1. Generating an SSH key using the CodeReady Workspaces command palette
The following section describes a generation of an SSH key using the CodeReady Workspaces command palette and its further use in Git provider communication. This SSH key restricts permissions for the specific Git provider; therefore, the user has to create a unique SSH key for each Git provider in use.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
- Personal GitHub account or other Git provider account created.
Procedure
A common SSH key pair that works with all the Git providers is present by default. To start using it, add the public key to the Git provider.
Generate an SSH key pair that only works with a particular Git provider:
In the CodeReady Workspaces IDE, press F1 to open the Command Palette, or navigate to View → Find Command in the top menu.
The command palette can be also activated by pressing Ctrl+Shift+p (or Cmd+Shift+p on macOS).
-
Search for SSH: generate key pair for particular host by entering
generateinto the search box and pressing Enter once filled. Provide the hostname for the SSH key pair such as, for example,
github.com.The SSH key pair is generated.
Click the button and copy the public key from the editor and add it to the Git provider.
Because of this action, the user can now use another command from the command palette: Clone git repository by providing an SSH secured URL.
2.2.3.2. Adding the associated public key to a repository or account on GitHub
To add the associated public key to a repository or account on GitHub:
- Navigate to github.com.
- Click the drop-down arrow next to the user icon in the upper right corner of the window.
- Click Settings → SSH and GPG keys and then click the button.
- In the Title field, type a title for the key, and in the Key field, paste the public key copied from CodeReady Workspaces.
- Click the button.
2.2.3.3. Adding the associated public key to a Git repository or account on GitLab
To add the associated public key to a Git repository or account on GitLab:
- Navigate to gitlab.com.
- Click the user icon in the upper right corner of the window.
- Click Settings → SSH Keys.
- In the Title field, type a title for the key and in the Key field, paste the public key copied from CodeReady Workspaces.
- Click the button.
2.2.4. Managing pull requests using the GitHub PR plug-in
To manage GitHub pull requests, the VS Code GitHub Pull Request plug-in is available in the list of plug-ins of the workspace.
2.2.4.1. Using the GitHub Pull Requests plug-in
Prerequisites
- GitHub OAuth is configured. See Section 5.1, “Configuring GitHub OAuth”.
Procedure
- Authenticate by running the GitHub authenticate command.
- You will be redirected to GitHub to authorize CodeReady Workspaces.
- When CodeReady Workspaces is authorized, refresh the browser page where CodeReady Workspaces is running to update the plug-in with the GitHub token.
Alternatively, manually fetch the GitHub token and paste it to the plug-in by running the GitHub Pull Requests: Manually Provide Authentication Response command.
2.2.4.2. Creating a new pull request
- Open the GitHub repository. To be able to execute remote operations, the repository must have a remote with an SSH URL.
- Checkout a new branch and make changes that you want to publish.
- Run the GitHub Pull Requests: Create Pull Request command.
2.3. Che-Theia Troubleshooting
This section describes some of the most frequent issues with the Che-Theia IDE.
- Che-Theia shows a notification with the following message:
Plugin runtime crashed unexpectedly, all plugins are not working, please reload the page. Probably there is not enough memory for the plugins. This means that one of the Che-Theia plug-ins that are running in the Che-Theia IDE container requires more memory than the container has. To fix this problem, increase the amount of memory for the Che-Theia IDE container:
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard.
- Select the workspace in which the problem happened.
- Switch to the Devfile tab.
-
In the
componentssection of the devfile, find a component of thecheEditortype. -
Add a new property,
memoryLimit: 1024M(or increase the value if it already exists). - Save changes and restart the workspace.
Additional resources
- Asking the community for help: Mattermost channel dedicated to Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.
- Reporting a bug: Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces repository issues.
Chapter 3. Developer workspaces
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces provides developer workspaces with everything needed to a code, build, test, run, and debug applications. To allow that, the developer workspaces provide four main components:
- The source code of a project.
- A web-based IDE.
- Tool dependencies, needed by developers to work on a project
- Application runtime: a replica of the environment where the application runs in production
Pods manage each component of a CodeReady Workspaces workspace. Therefore, everything running in a CodeReady Workspaces workspace is running inside containers. This makes a CodeReady Workspaces workspace highly portable.
The embedded browser-based IDE is the point of access for everything running in a CodeReady Workspaces workspace. This makes a CodeReady Workspaces workspace easily shareable.
By default, it is possible to run only one workspace at a time. To change the default value, see: Users workspace limits.
| Features | Traditional IDE workspaces | Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspaces |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration and installation required | Yes. | No. |
| Embedded tools | Partial. IDE plug-ins need configuration. Dependencies need installation and configuration. Example: JDK, Maven, Node. | Yes. Plug-ins provide their dependencies. |
| Application runtime provided | No. Developers have to manage that separately. | Yes. Application runtime is replicated in the workspace. |
| Shareable | No. Or not easily | Yes. Developer workspaces are shareable with a URL. |
| Versionable | No | Yes. Devfiles exist with project source code. |
| Accessible from anywhere | No. Installation is needed. | Yes. Only requires a browser. |
To start a CodeReady Workspaces workspace, following options are available:
Use the Dashboard to discover CodeReady Workspaces 2.4:
Use a devfile as the preferred way to start a CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace:
Use the browser-based IDE as the preferred way to interact with a CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace. For an alternative way to interact with a CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace, see: Section 3.5, “Remotely accessing workspaces”.
3.1. Configuring a workspace using a devfile
To quickly and easily configure a CodeReady Workspaces workspace, use a devfile. For an introduction to devfiles and instructions for their use, see the instructions in this section.
3.1.1. What is a devfile
A devfile is a file that describes and define a development environment:
- the source code
- the development components, such as browser IDE tools and application runtimes
- a list of pre-defined commands
- projects to clone
Devfiles are YAML files that CodeReady Workspaces consumes and transforms into a cloud workspace composed of multiple containers. The devfile can be saved in the root folder of a Git repository, a feature branch of a Git repository, a publicly accessible destination, or as a separate, locally stored artifact. Devfiles saved in Git repository can use multiple names, such as devfile.yaml or .devfile.yaml.
When creating a workspace, CodeReady Workspaces uses that definition to initiate everything and run all the containers for the required tools and application runtimes. CodeReady Workspaces also mounts file-system volumes to make source code available to the workspace.
Devfiles can be versioned with the project source code. When there is a need for a workspace to fix an old maintenance branch, the project devfile provides a definition of the workspace with the tools and the exact dependencies to start working on the old branch. Use it to instantiate workspaces on demand.
CodeReady Workspaces maintains the devfile up-to-date with the tools used in the workspace:
- Projects of the workspace (path, Git location, branch)
- Commands to perform daily tasks (build, run, test, debug)
- Runtime environment (container images to run the application)
- Che-Theia plug-ins with tools, IDE features, and helpers that a developer would use in the workspace (Git, Java support, SonarLint, Pull Request)
3.1.2. Creating a workspace from the default branch of a Git repository
A CodeReady Workspaces workspace can be created by pointing to a devfile that is stored in a Git source repository. The CodeReady Workspaces instance then uses the discovered devfile.yaml file to build a workspace using the /f?url= API.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
-
The
devfile.yamlor.devfile.yamlfile is located in the root folder of a Git repository that is available over HTTPS. See Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile” for detailed information about creating and using devfiles.
Procedure
Run the workspace by opening the following URL: https://codeready-<openshift_deployment_name>.<domain_name>/f?url=https://<GitRepository>
Example
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://github.com/eclipse/che
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://github.com/eclipse/che3.1.3. Creating a workspace from a feature branch of a Git repository
A CodeReady Workspaces workspace can be created by pointing to devfile that is stored in a Git source repository on a feature branch of the user’s choice. The CodeReady Workspaces instance then uses the discovered devfile to build a workspace.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
-
The
devfile.yamlor.devfile.yamlfile is located in the root folder of a Git repository, on a specific branch of the user’s choice that is accessible over HTTPS. See Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile” for detailed information about creating and using devfiles.
Procedure
Execute the workspace by opening the following URL: https://codeready-<openshift_deployment_name>.<domain_name>/f?url=<GitHubBranch>
Example
Use following URL format to open an experimental quarkus-quickstarts branch hosted on che.openshift.io.
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://github.com/maxandersen/quarkus-quickstarts/tree/che
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://github.com/maxandersen/quarkus-quickstarts/tree/che3.1.4. Creating a workspace from a publicly accessible standalone devfile using HTTP
A workspace can be created using a devfile, the URL of which is pointing to the raw content of the devfile. The CodeReady Workspaces instance then uses the discovered devfile to build a workspace.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
-
The publicly-accessible standalone
devfile.yamlfile. See Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile” for detailed information about creating and using devfiles.
Procedure
-
Execute the workspace by opening the following URL:
https://codeready-<openshift_deployment_name>.<domain_name>/f?url=https://<yourhosturl>/devfile.yaml
Example
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml3.1.5. Overriding devfile values using factory parameters
Values in the following sections of a remote devfile can be overridden using specially constructed additional factory parameters:
-
apiVersion -
metadata -
projects -
attributes
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
-
A publicly accessible standalone
devfile.yamlfile. See Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile” for detailed information about creating and using devfiles.
Procedure
-
Open the workspace by navigating to the following URL:
https://codeready-<openshift_deployment_name>.<domain_name>/f?url=https://<hostURL>/devfile.yaml&override.<parameter.path>=<value>
Example of overriding the generateName property
Consider the following initial devfile:
To add or override generateName value, use the following factory URL:
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.metadata.generateName=myprefix
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.metadata.generateName=myprefixThe resulting workspace has the following devfile model:
Example of overriding project source branch property
Consider the following initial devfile:
To add or override source branch value, use the following factory URL:
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.projects.web-java-spring-petclinic.source.branch=1.0.x
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.projects.web-java-spring-petclinic.source.branch=1.0.xThe resulting workspace has the following devfile model:
Example of overriding or creating an attribute value
Consider the following initial devfile:
To add or override persistVolumes attribute value, use the following factory URL:
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.attributes.persistVolumes=true
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.attributes.persistVolumes=trueThe resulting workspace has the following devfile model:
When overriding attributes, everything that follows the attributes keyword is interpreted as an attribute name, so you can use dot-separated names:
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.attributes.dot.name.format.attribute=true
https://che.openshift.io/f?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/themr0c/ef8e59a162748a8be07e900b6401e6a8/raw/8802c20743cde712bbc822521463359a60d1f7a9/devfile.yaml&override.attributes.dot.name.format.attribute=trueThe resulting workspace has the following devfile model:
3.1.6. Creating a workspace using crwctl and a local devfile
A CodeReady Workspaces workspace can be created by pointing the crwctl tool to a locally stored devfile. The CodeReady Workspaces instance then uses the discovered devfile to build a workspace.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- The CodeReady Workspaces CLI management tool. See CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 Installation Guide.
The devfile is available on the local filesystem in the current working directory. See Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile” for detailed information about creating and using devfiles.
Example
Download the
devfile.yamlfile from the GitHub repository to the current working directory.
Procedure
-
Run a workspace from a devfile using the
workspace:startparameter with thecrwctltool as follows:
crwctl workspace:start --devfile=devfile.yaml
$ crwctl workspace:start --devfile=devfile.yamlAdditional resources
3.2. Making a workspace portable using a devfile
To transfer a configured CodeReady Workspaces workspace, create and export the devfile of the workspace and load the devfile on a different host to initialize a new instance of the workspace. For detailed instructions on how to create such a devfile, see below.
3.2.1. A minimal devfile
The following is the minimum content required in a devfile:
apiVersion: 1.0.0 metadata: name: crw-in-crw-out
apiVersion: 1.0.0
metadata:
name: crw-in-crw-outFor a complete devfile example, see Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces in CodeReady Workspaces devfile.yaml.
name or generateName must be defined
Both name and generateName are optional parameters, but at least one of them must be defined. See Section 3.2.2, “Generating workspace names”.
3.2.2. Generating workspace names
To specify a prefix for automatically generated workspace names, set the generateName parameter in the devfile:
apiVersion: 1.0.0 metadata: generateName: crw-
apiVersion: 1.0.0
metadata:
generateName: crw-
The workspace name will be in the <generateName>YYYYY format (for example, che-2y7kp). Y is random [a-z0-9] character.
The following naming rules apply when creating workspaces:
-
When
nameis defined, it is used as the workspace name:<name> -
When only
generateNameis defined, it is used as the base of the generated name:<generateName>YYYYY
For workspaces created using a factory, defining name or generateName has the same effect. The defined value is used as the name prefix: <name>YYYYY or <generateName>YYYYY. When both generateName and name are defined, generateName takes precedence.
3.2.3. Writing a devfile for a project
This section describes how to create a minimal devfile for your project and how to include more than one projects in a devfile.
3.2.3.1. Preparing a minimal devfile
A minimal devfile sufficient to run a workspace consists of the following parts:
- Specification version
- Name
Example of a minimal devfile with no project
apiVersion: 1.0.0 metadata: name: minimal-workspace
apiVersion: 1.0.0
metadata:
name: minimal-workspaceWithout any further configuration, a workspace with the default editor is launched along with its default plug-ins, which are configured on the CodeReady Workspaces Server. Che-Theia is configured as the default editor along with the CodeReady Workspaces Machine Exec plug-in. When launching a workspace within a Git repository using a factory, the project from the given repository and branch is be created by default. The project name then matches the repository name.
Add the following parts for a more functional workspace:
- List of components: Development components and user runtimes
- List of projects: Source code repositories
- List of commands: Actions to manage the workspace components, such as running the development tools, starting the runtime environments, and others
Example of a minimal devfile with a project
3.2.3.2. Specifying multiple projects in a devfile
A single devfile can specify multiple projects. For each project, specify the type of the source repository, its location, and, optionally, the directory the project is cloned to.
Example of a devfile with two projects
In the preceding example, there are two projects defined, frontend and backend. Each project is located in its own repository. The backend project has a specific requirement to be cloned into the src/github.com/acmecorp/backend/ directory under the source root (implicitly defined by the CodeReady Workspaces runtime) while the frontend project will be cloned into the frontend/ directory under the source root.
Additional resources
For a detailed explanation of all devfile component assignments and possible values, see:
These sample devfiles are a good source of inspiration:
3.2.4. Devfile reference
This section contains devfile reference and instructions on how to use the various elements that devfiles consist of.
3.2.4.1. Adding projects to a devfile
Usually a devfile contains one or more projects. A workspace is created to develop those projects. Projects are added in the projects section of devfiles.
Each project in a single devfile must have:
- Unique name
- Source specified
Project source consists of two mandatory values: type and location.
type- The kind of project-source provider.
location- The URL of project source.
CodeReady Workspaces supports the following project types:
git- Projects with sources in Git. The location points to a clone link.
github-
Same as
gitbut for projects hosted on GitHub only. Usegitfor projects that do not use GitHub-specific features. zip- Projects with sources in a ZIP archive. Location points to a ZIP file.
3.2.4.1.1. Project-source type: git
- 1
startPointis the general value fortag,commitId, andbranch. ThestartPoint,tag,commitId, andbranchparameters are mutually exclusive. When more than one is supplied, the following order is used:startPoint,tag,commitId,branch.- 2
sparseCheckoutDirthe template for the sparse checkout Git feature. This is useful when only a part of a project (typically only a single directory) is needed.
Example 3.1. sparseCheckoutDir parameter settings
-
Set to
/my-module/to create only the rootmy-moduledirectory (and its content). Omit the leading slash (
my-module/) to create allmy-moduledirectories that exist in the project. Including, for example,/addons/my-module/.The trailing slash indicates that only directories with the given name (including their content) are created.
-
Use wildcards to specify more than one directory name. For example, setting
module-*checks out all directories of the given project that start withmodule-.
For more information, see Sparse checkout in Git documentation.
3.2.4.1.2. Project-source type: zip
source:
type: zip
location: http://host.net/path/project-src.zip
source:
type: zip
location: http://host.net/path/project-src.zip3.2.4.1.3. Project clone-path parameter: clonePath
The clonePath parameter specifies the path into which the project is to be cloned. The path must be relative to the /projects/ directory, and it cannot leave the /projects/ directory. The default value is the project name.
Example devfile with projects
3.2.4.2. Adding components to a devfile
Each component in a single devfile must have a unique name.
3.2.4.2.1. Component type: cheEditor
Describes the editor used in the workspace by defining its id. A devfile can only contain one component of the cheEditor type.
components:
- alias: theia-editor
type: cheEditor
id: eclipse/che-theia/next
components:
- alias: theia-editor
type: cheEditor
id: eclipse/che-theia/next
When cheEditor is missing, a default editor is provided along with its default plug-ins. The default plug-ins are also provided for an explicitly defined editor with the same id as the default one (even if it is a different version). Che-Theia is configured as default editor along with the CodeReady Workspaces Machine Exec plug-in.
To specify that a workspace requires no editor, use the editorFree:true attribute in the devfile attributes.
3.2.4.2.2. Component type: chePlugin
Describes plug-ins in a workspace by defining their id. It is allowed to have several chePlugin components.
components:
- alias: exec-plugin
type: chePlugin
id: eclipse/che-machine-exec-plugin/0.0.1
components:
- alias: exec-plugin
type: chePlugin
id: eclipse/che-machine-exec-plugin/0.0.1Both types above use an ID, which is slash-separated publisher, name and version of plug-in from the CodeReady Workspaces Plug-in registry.
List of available Eclipse Che plug-ins and more information about registry can be found in the Eclipse Che plug-in registry GitHub repository.
3.2.4.2.3. Specifying an alternative component registry
To specify an alternative registry for the cheEditor and chePlugin component types, use the registryUrl parameter:
components:
- alias: exec-plugin
type: chePlugin
registryUrl: https://my-customregistry.com
id: eclipse/che-machine-exec-plugin/0.0.1
components:
- alias: exec-plugin
type: chePlugin
registryUrl: https://my-customregistry.com
id: eclipse/che-machine-exec-plugin/0.0.13.2.4.2.4. Specifying a component by linking to its descriptor
An alternative way of specifying cheEditor or chePlugin, instead of using the editor or plug-in id (and optionally an alternative registry), is to provide a direct link to the component descriptor (typically named meta.yaml) by using the reference field:
components:
- alias: exec-plugin
type: chePlugin
reference: https://raw.githubusercontent.com.../plugin/1.0.1/meta.yaml
components:
- alias: exec-plugin
type: chePlugin
reference: https://raw.githubusercontent.com.../plugin/1.0.1/meta.yaml
It is impossible to mix the id and reference fields in a single component definition; they are mutually exclusive.
3.2.4.2.5. Tuning chePlugin component configuration
A chePlugin component may need to be precisely tuned, and in such case, component preferences can be used. The example shows how to configure JVM using plug-in preferences.
id: redhat/java/0.38.0
type: chePlugin
preferences:
java.jdt.ls.vmargs: '-noverify -Xmx1G -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+UseStringDeduplication'
id: redhat/java/0.38.0
type: chePlugin
preferences:
java.jdt.ls.vmargs: '-noverify -Xmx1G -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+UseStringDeduplication'Preferences may also be specified as an array:
id: redhat/java/0.38.0
type: chePlugin
preferences:
go.lintFlags: ["--enable-all", "--new"]
id: redhat/java/0.38.0
type: chePlugin
preferences:
go.lintFlags: ["--enable-all", "--new"]3.2.4.2.6. Component type: kubernetes
A complex component type that allows to apply configuration from a list of OpenShift components.
The content can be provided through the reference attribute, which points to the file with the component content.
Alternatively, to post a devfile with such components to REST API, the contents of the OpenShift List object can be embedded into the devfile using the referenceContent field:
3.2.4.2.7. Overriding container entrypoints
As with the understood by OpenShift).
There can be more containers in the list (contained in Pods or Pod templates of deployments). To select which containers to apply the entrypoint changes to.
The entrypoints can be defined as follows:
The entrypoints list contains constraints for picking the containers along with the command and args parameters to apply to them. In the example above, the constraint is parentName: mysqlServer, which will cause the command to be applied to all containers defined in any parent object called mysqlServer. The parent object is assumed to be a top level object in the list defined in the referenced file, which is app-deployment.yaml in the example above.
Other types of constraints (and their combinations) are possible:
containerName- the name of the container
parentName- the name of the parent object that (indirectly) contains the containers to override
parentSelector- the set of labels the parent object needs to have
A combination of these constraints can be used to precisely locate the containers inside the referenced OpenShift List.
3.2.4.2.8. Overriding container environment variables
To provision or override entrypoints in a OpenShift component, configure it in the following way:
This is useful for temporary content or without access to editing the referenced content. The specified environment variables are provisioned into each init container and containers inside all Pods and Deployments.
3.2.4.2.9. Specifying mount-source option
To specify a project sources directory mount into container(s), use the mountSources parameter:
components:
- alias: appDeployment
type: kubernetes
reference: app-deployment.yaml
mountSources: true
components:
- alias: appDeployment
type: kubernetes
reference: app-deployment.yaml
mountSources: true
If enabled, project sources mounts will be applied to every container of the given component. This parameter is also applicable for chePlugin type components.
3.2.4.2.10. Component type: dockerimage
A component type that allows to define a container image-based configuration of a container in a workspace. A devfile can only contain one component of the dockerimage type. The dockerimage type of component brings in custom tools into the workspace. The component is identified by its image.
Example of a minimal dockerimage component
It specifies the type of the component, dockerimage and the image attribute names the image to be used for the component using the usual Docker naming conventions, that is, the above type attribute is equal to docker.io/library/golang:latest.
A dockerimage component has many features that enable augmenting the image with additional resources and information needed for meaningful integration of the tool provided by the image with Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.
3.2.4.2.11. Mounting project sources
For the dockerimage component to have access to the project sources, you must set the mountSources attribute to true.
The sources is mounted on a location stored in the CHE_PROJECTS_ROOT environment variable that is made available in the running container of the image. This location defaults to /projects.
3.2.4.2.12. Container Entrypoint
The command attribute of the dockerimage along with other arguments, is used to modify the entrypoint command of the container created from the image. In Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces the container is needed to run indefinitely so that you can connect to it and execute arbitrary commands in it at any time. Because the availability of the sleep command and the support for the infinity argument for it is different and depends on the base image used in the particular images, CodeReady Workspaces cannot insert this behavior automatically on its own. However, you can take advantage of this feature to, for example, start necessary servers with modified configurations, etc.
3.2.4.2.13. Persistent Storage
Components of any type can specify the custom volumes to be mounted on specific locations within the image. Note that the volume names are shared across all components and therefore this mechanism can also be used to share file systems between components.
Example specifying volumes for dockerimage type:
Example specifying volumes for cheEditor/chePlugin type:
Example specifying volumes for kubernetes/openshift type:
3.2.4.2.14. Specifying container memory limit for components
To specify a container(s) memory limit for dockerimage, chePlugin, cheEditor, use the memoryLimit parameter:
This limit will be applied to every container of the given component.
For the cheEditor and chePlugin component types, RAM limits can be described in the plug-in descriptor file, typically named meta.yaml.
If none of them are specified, system-wide defaults will be applied (see description of CHE_WORKSPACE_SIDECAR_DEFAULT__MEMORY__LIMIT__MB system property).
3.2.4.2.15. Specifying container memory request for components
To specify a container(s) memory request for chePlugin or cheEditor, use the memoryRequest parameter:
This limit will be applied to every container of the given component.
For the cheEditor and chePlugin component types, RAM requests can be described in the plug-in descriptor file, typically named meta.yaml.
If none of them are specified, system-wide defaults are applied (see description of CHE_WORKSPACE_SIDECAR_DEFAULT__MEMORY__REQUEST__MB system property).
3.2.4.2.16. Specifying container CPU limit for components
To specify a container(s) CPU limit for chePlugin, cheEditor or dockerimage use the cpuLimit parameter:
This limit will be applied to every container of the given component.
For the cheEditor and chePlugin component types, CPU limits can be described in the plug-in descriptor file, typically named meta.yaml.
If none of them are specified, system-wide defaults are applied (see description of CHE_WORKSPACE_SIDECAR_DEFAULT__CPU__LIMIT__CORES system property).
3.2.4.2.17. Specifying container CPU request for components
To specify a container(s) CPU request for chePlugin, cheEditor or dockerimage use the cpuRequest parameter:
This limit will be applied to every container of the given component.
For the cheEditor and chePlugin component types, CPU requests can be described in the plug-in descriptor file, typically named meta.yaml.
If none of them are specified, system-wide defaults are applied (see description of CHE_WORKSPACE_SIDECAR_DEFAULT__CPU__REQUEST__CORES system property).
3.2.4.2.18. Environment variables
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces allows you to configure Docker containers by modifying the environment variables available in component’s configuration. Environment variables are supported by the following component types: dockerimage, chePlugin, cheEditor, kubernetes, openshift. In case component has multiple containers, environment variables will be provisioned to each container.
- The variable expansion works between the environment variables, and it uses the Kubernetes convention for the variable references.
- The predefined variables are available for use in custom definitions.
The following environment variables are pre-set by the CodeReady Workspaces server:
-
CHE_PROJECTS_ROOT: The location of the projects directory (note that if the component does not mount the sources, the projects will not be accessible). -
CHE_WORKSPACE_LOGS_ROOT__DIR: The location of the logs common to all the components. If the component chooses to put logs into this directory, the log files are accessible from all other components. -
CHE_API_INTERNAL: The URL to the CodeReady Workspaces server API endpoint used for communication with the CodeReady Workspaces server. -
CHE_WORKSPACE_ID: The ID of the current workspace. -
CHE_WORKSPACE_NAME: The name of the current workspace. -
CHE_WORKSPACE_NAMESPACE: The CodeReady Workspaces project of the current workspace. This environment variable is the name of the user or organization that the workspace belongs to. Note that this is different from the OpenShift project to which the workspace is deployed. -
CHE_MACHINE_TOKEN: The token used to authenticate the request against the CodeReady Workspaces server. -
CHE_MACHINE_AUTH_SIGNATUREPUBLICKEY: The public key used to secure the communication with the CodeReady Workspaces server. -
CHE_MACHINE_AUTH_SIGNATURE__ALGORITHM: The encryption algorithm used in the secured communication with the CodeReady Workspaces server.
A devfiles may only need the CHE_PROJECTS_ROOT environment variable to locate the cloned projects in the component’s container. More advanced devfiles might use the CHE_WORKSPACE_LOGS_ROOT__DIR environment variable to read the logs (for example as part of a devfile command). The environment variables used to securely access the CodeReady Workspaces server are mostly out of scope for devfiles and are present only for advanced use cases that are usually handled by the CodeReady Workspaces plug-ins.
3.2.4.2.19. Endpoints
Components of any type can specify the endpoints that the Docker image exposes. These endpoints can be made accessible to the users if the CodeReady Workspaces cluster is running using a Kubernetes ingress or an OpenShift route and to the other components within the workspace. You can create an endpoint for your application or database, if your application or database server is listening on a port and you want to be able to directly interact with it yourself or you want other components to interact with it.
Endpoints have several properties as shown in the following example:
Here, there are two Docker images, each defining a single endpoint. Endpoint is an accessible port that can be made accessible inside the workspace or also publicly (example, from the UI). Each endpoint has a name and port, which is the port on which certain server running inside the container is listening. The following are a few attributes that you can set on the endpoint:
-
discoverable: If an endpoint is discoverable, it means that it can be accessed using its name as the host name within the workspace containers (in the OpenShift terminology, a service is created for it with the provided name). 55 -
public: The endpoint will be accessible outside of the workspace, too (such endpoint can be accessed from the CodeReady Workspaces user interface). Such endpoints are publicized always on port80or443(depending on whethertlsis enabled in CodeReady Workspaces). -
protocol: For public endpoints the protocol is a hint to the UI on how to construct the URL for the endpoint access. Typical values arehttp,https,ws,wss. secure: A boolean (defaulting tofalse) specifying whether the endpoint is put behind a JWT proxy requiring a JWT workspace token to grant access. The JWT proxy is deployed in the same Pod as the server and assumes the server listens solely on the local loopback interface, such as127.0.0.1.WarningListening on any other interface than the local loopback poses a security risk because such server is accessible without the JWT authentication within the cluster network on the corresponding IP addresses.
-
path: The URL of the endpoint. -
unsecuredPaths: A comma-separated list of endpoint paths that are to stay unsecured even if thesecureattribute is set totrue. cookiesAuthEnabled: When set totrue(the default isfalse), the JWT workspace token is automatically fetched and included in a workspace-specific cookie to allow requests to pass through the JWT proxy.WarningThis setting potentially allows a CSRF attack when used in conjunction with a server using POST requests.
When starting a new server within a component, CodeReady Workspaces autodetects this, and the UI offers to automatically expose this port as a public port. This is useful for debugging a web application, for example. It is impossible to do this for servers that autostart with the container (for example, a database server). For such components, specify the endpoints explicitly.
Example specifying endpoints for kubernetes/openshift and chePlugin/cheEditor types:
3.2.4.2.20. OpenShift resources
To describe complex deployments, include references to OpenShift resource lists in the devfile. The OpenShift resource lists become a part of the workspace.
- CodeReady Workspaces merges all resources from the OpenShift resource lists into a single deployment.
- Be careful when designing such lists to avoid name conflicts and other problems.
| Platform | Supported resources |
|---|---|
| OpenShift |
|
The preceding component references a file that is relative to the location of the devfile itself. Meaning, this devfile is only loadable by a CodeReady Workspaces factory to which you supply the location of the devfile and therefore it is able to figure out the location of the referenced OpenShift resource list.
The following is an example of the postgres.yaml file.
For a basic example of a devfile with an associated OpenShift list, see web-nodejs-with-db-sample on redhat-developer GitHub.
If you use generic or large resource lists from which you will only need a subset of resources, you can select particular resources from the list using a selector (which, as the usual OpenShift selectors, works on the labels of the resources in the list).
Additionally, it is also possible to modify the entrypoints (command and arguments) of the containers present in the resource list. For details of the advanced use case, see Defining specific container images.
3.2.4.3. Adding commands to a devfile
A devfile allows to specify commands to be available for execution in a workspace. Every command can contain a subset of actions, which are related to a specific component in whose container it will be executed.
You can use commands to automate the workspace. You can define commands for building and testing your code, or cleaning the database.
The following are two kinds of commands:
- CodeReady Workspaces specific commands: You have full control over what component executes the command.
-
Editor specific commands: You can use the editor-specific command definitions (example:
tasks.jsonandlaunch.jsonin Che-Theia, which is equivalent to how these files work in VS Code).
3.2.4.3.1. CodeReady Workspaces-specific commands
Each CodeReady Workspaces-specific command features:
-
An
actionattribute that is a command to execute. -
A
componentattribute that specifies the container in which to execute the command.
The commands are run using the default shell in the container.
+
-
If a component to be used in a command must have an alias. This alias is used to reference the component in the command definition. Example:
alias: go-cliin the component definition andcomponent: go-cliin the command definition. This ensures that Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces can find the correct container to run the command in. - A command can have only one action.
3.2.4.3.2. Editor-specific commands
If the editor in the workspace supports it, the devfile can specify additional configuration in the editor-specific format. This is dependent on the integration code present in the workspace editor itself and so is not a generic mechanism. However, the default Che-Theia editor within Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces is equipped to understand the tasks.json and launch.json files provided in the devfile.
This example shows association of a tasks.json file with a devfile. Notice the vscode-task type that instructs the Che-Theia editor to interpret this command as a tasks definition and referenceContent attribute that contains the contents of the file itself. You can also save this file separately from the devfile and use reference attribute to specify a relative or absolute URL to it.
In addition to the vscode-task commands, the Che-Theia editor understands vscode-launch type using which you can specify the launch configurations.
3.2.4.3.3. Command preview URL
It is possible to specify a preview URL for commands that expose web UI. This URL is offered for opening when the command is executed.
The example above opens http://__<server-domain>__/myweb, where <server-domain> is the URL to the dynamically created OpenShift Route.
3.2.4.3.3.1. Setting the default way of opening preview URLs
By default, a notification that asks the user about the URL opening preference is displayed.
To specify the preferred way of previewing a service URL:
-
Open CodeReady Workspaces preferences in File → Settings → Open Preferences and find
che.task.preview.notificationsin the CodeReady Workspaces section. Choose from the list of possible values:
-
on— enables a notification for asking the user about the URL opening preferences -
alwaysPreview— the preview URL opens automatically in the Preview panel as soon as a task is running -
alwaysGoTo— the preview URL opens automatically in a separate browser tab as soon as a task is running -
off— disables opening the preview URL (automatically and with a notification)
-
3.2.4.4. Devfile attributes
Devfile attributes can be used to configure various features.
3.2.4.4.1. Attribute: editorFree
When an editor is not specified in a devfile, a default is provided. When no editor is needed, use the editorFree attribute. The default value of false means that the devfile requests the provisioning of the default editor.
Example of a devfile without an editor
3.2.4.4.2. Attribute: persistVolumes (ephemeral mode)
By default, volumes and PVCs specified in a devfile are bound to a host folder to persist data even after a container restart. To disable data persistence to make the workspace faster, such as when the volume back end is slow, modify the persistVolumes attribute in the devfile. The default value is true. Set to false to use emptyDir for configured volumes and PVC.
Example of a devfile with ephemeral mode enabled
3.2.4.4.3. Attribute: asyncPersist (asynchronous storage)
When persistVolumes is set to false (see above), the additional attribute asyncPersist can be set to true to enable asynchronous storage. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#configuring-storage-types_crw for more details.
Example of a devfile with asynchronous storage enabled
3.2.4.4.4. Attribute: mergePlugins
This property can be set to manually control how plugins are included in the workspace. When the property mergePlugins is set to true, Che will attempt to avoid running multiple instances of the same container by combining plugins. The default value when this property is not included in a devfile is governed by the Che configuration property che.workspace.plugin_broker.default_merge_plugins; adding the mergePlugins: false attribute to a devfile will disable plugin merging for that workspace.
Example of a devfile with plugin merging disabled
3.2.5. Objects supported in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces 2.4
The following table lists the objects that are partially supported in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces 2.4:
| Object | API | Kubernetes Infra | OpenShift Infra | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pod | Kubernetes | Yes | Yes | - |
| Deployment | Kubernetes | Yes | Yes | - |
| ConfigMap | Kubernetes | Yes | Yes | - |
| PVC | Kubernetes | Yes | Yes | - |
| Secret | Kubernetes | Yes | Yes | - |
| Service | Kubernetes | Yes | Yes | - |
| Ingress | Kubernetes | Yes | No |
Minishift allows you to create Ingress and it works when the host is specified (OpenShift creates a route for it). But, the |
| Route | OpenShift | No | Yes | The OpenShift recipe must be made compatible with the Kubernetes Infrastructure and, instead of the provided route, generate Ingress. |
| Template | OpenShift | Yes | Yes | The Kubernetes API does not support templates. A workspace with a template in the recipe starts successfully and the default parameters are resolved. |
Additional resources
3.3. Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace
3.3.1. Creating a new workspace from the dashboard
This procedure describes how to create and edit a new CodeReady Workspaces devfile using the Dashboard.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
To edit the devfile:
- In the Workspaces window, click the button. The Custom Workspace page should be opened.
Scroll down to the Devfile section. In the Devfile editor, add necessary changes.
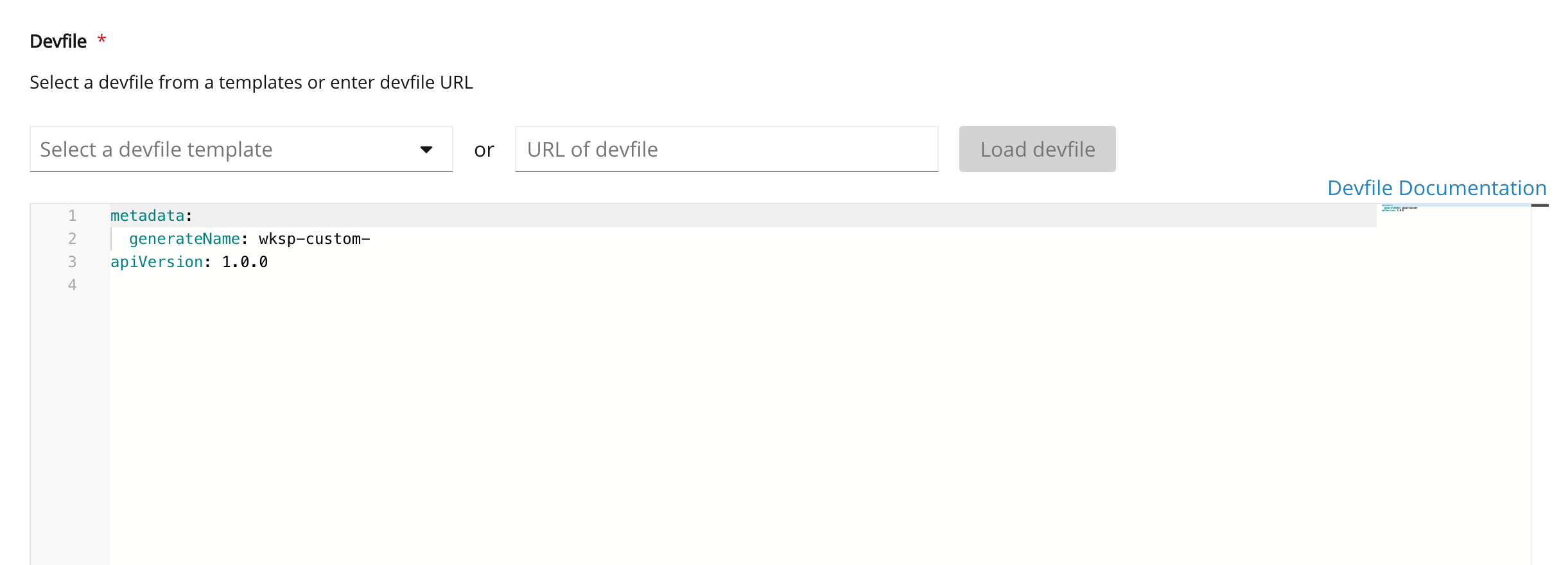 Example: add a project
Example: add a projectTo add a project into the workspace, add or edit the following section:
projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See the Section 3.2.4, “Devfile reference”.
3.3.2. Adding projects to your workspace
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
To add a project to your workspace:
Navigate to Workspaces page and click the workspace you want to update.
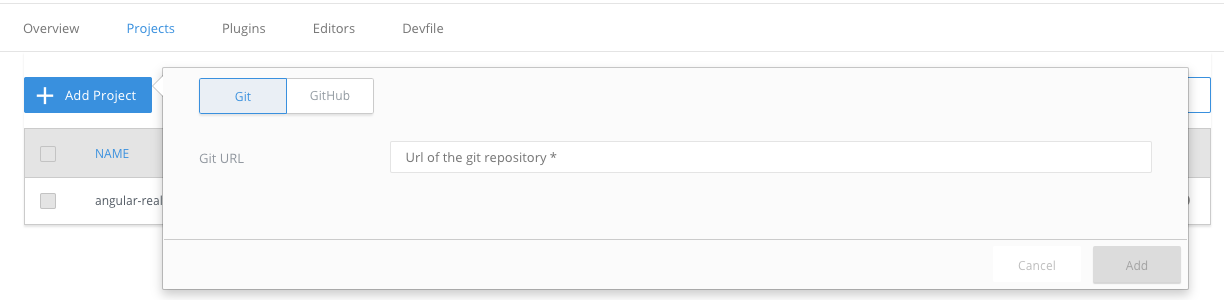
Here you have two ways to add a project to your workspace:
From the Projects tab.
- Open the Projects tab, and then click the button.
Choose if you want to import the project by Git URL or from your GitHub account.
From the Devfile tab.
- Open the Devfile tab.
In the Devfile editor, add
projectssection with desired project.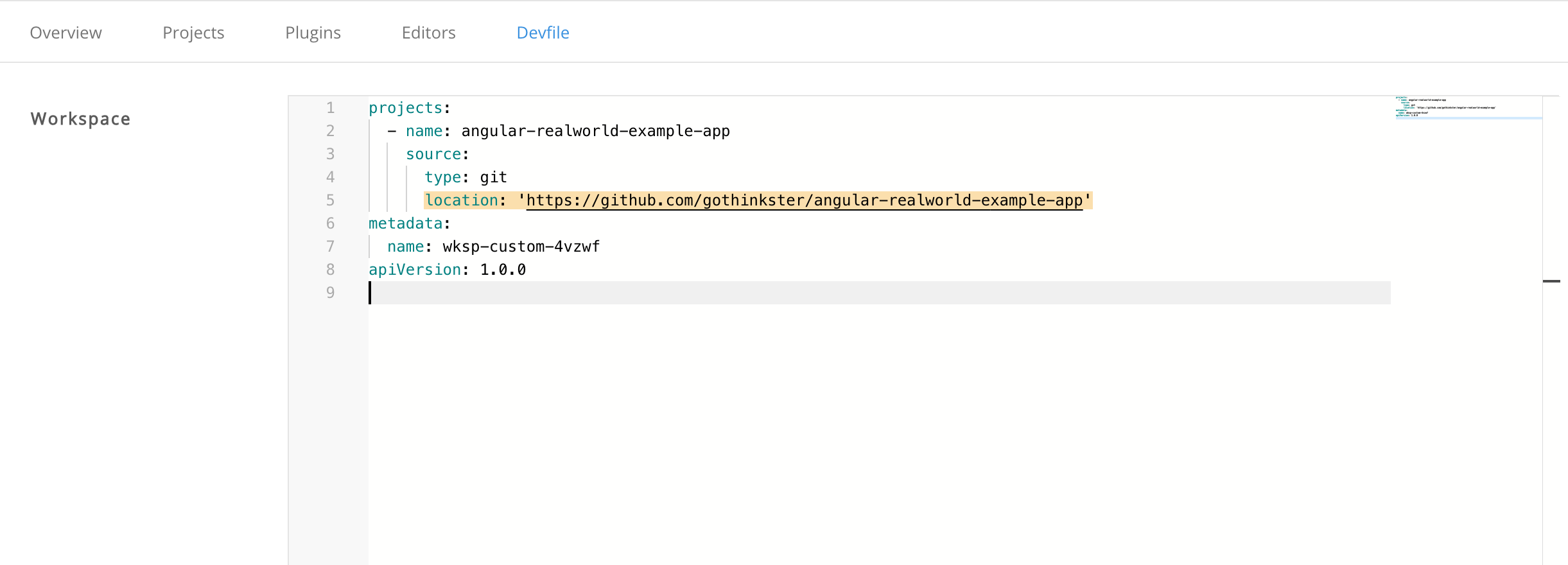 Example: add a project
Example: add a projectTo add a project into the workspace, add or edit the following section:
projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See the Section 3.2.4, “Devfile reference”.
Once the project is added, click button to save this workspace configuration, or click button to apply changes to the running workspace.
3.3.3. Configuring the workspace and adding tools
3.3.3.1. Adding plug-ins
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
To add plug-ins to your workspace:
- Click the Plugins tab.
- Enable the plug-in that you want to add and click the button.
3.3.3.2. Defining the workspace editor
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
To define the editor to use with the workspace:
Click the Editors tab.
NoteThe recommended editor for CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 is Che-Theia.
- Enable the editor to add and click the button.
Click the Devfile tab to view the changes.
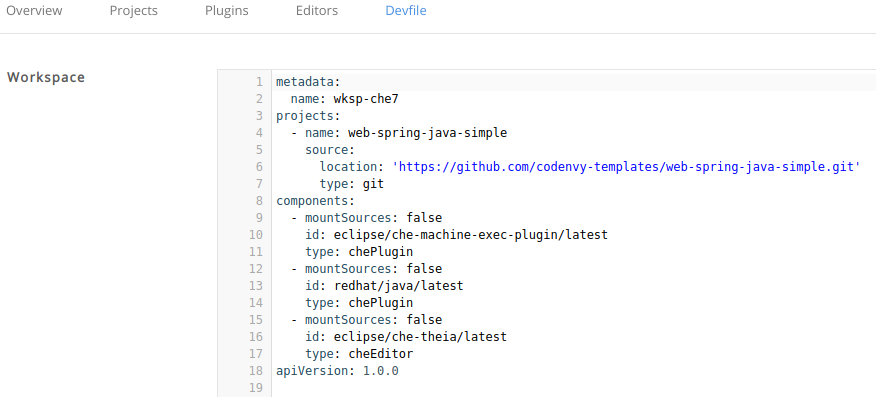
3.3.3.3. Defining specific container images
Procedure
To add a new container image:
In the Devfile tab, add the following section under the components property:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a CodeReady Workspaces 2.3 recipe content to the CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 devfile as
referenceContent: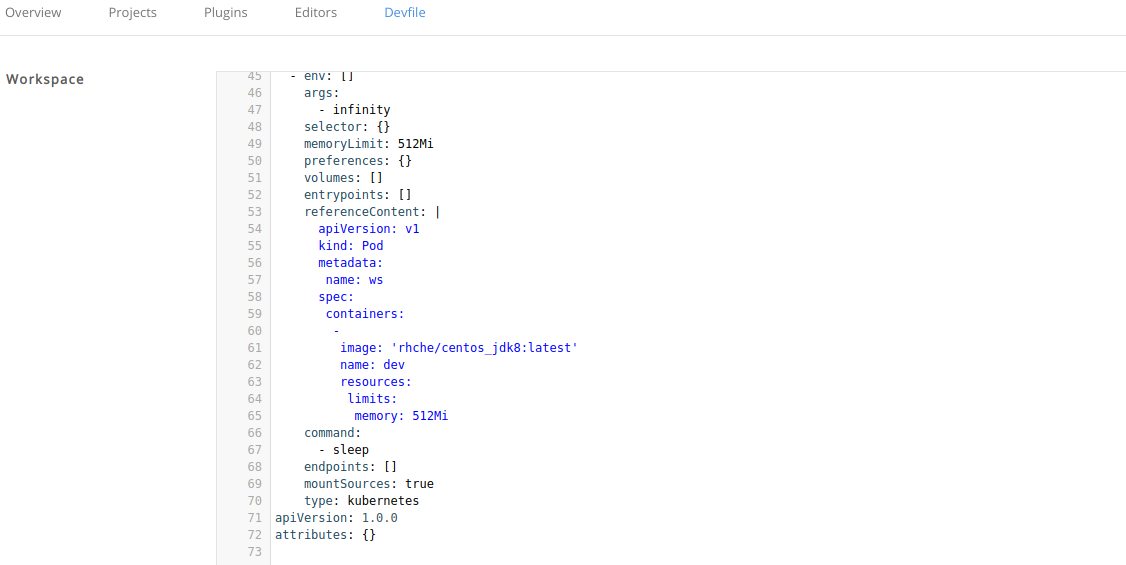
Set the type from the original CodeReady Workspaces 2.3 configuration. The following is an example of the resulting file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Copy the required fields from the old workspace (
image,volumes,endpoints). For example: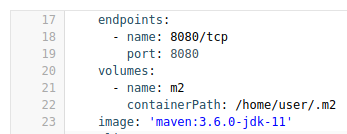
Change the
memoryLimitandaliasvariables, if needed. Here, the fieldaliasis used to set a name for the component. It is generated automatically from theimagefield, if not set.image: 'maven:3.6.0-jdk-11' alias: maven3-jdk11
image: 'maven:3.6.0-jdk-11' alias: maven3-jdk11Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change the
memoryLimit,memoryRequest, or both fields to specify theRAMrequired for the component.alias: maven3-jdk11 memoryLimit: 256M memoryRequest: 128M
alias: maven3-jdk11 memoryLimit: 256M memoryRequest: 128MCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Repeat the steps to add additional container images.
3.3.3.4. Adding commands to your workspace
The following is a comparison between workspace configuration commands in CodeReady Workspaces 2.3 (Figure 1) and CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 (Figure 2):
Figure 3.1. An example of the Workspace configuration commands in CodeReady Workspaces 2.4

Procedure
To define commands to your workspace, edit the workspace devfile:
Add (or replace) the
commandssection with the first command. Change thenameand thecommandfields from the original workspace configuration (see the preceding equivalence table).commands: - name: build actions: - type: exec command: mvn clean installcommands: - name: build actions: - type: exec command: mvn clean installCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the following YAML code into the
commandssection to add a new command. Change thenameand thecommandfields from the original workspace configuration (see the preceding equivalence table).- name: build and run actions: - type: exec command: mvn clean install && java -jar- name: build and run actions: - type: exec command: mvn clean install && java -jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Optionally, add the
componentfield intoactions. This indicates the component alias where the command will be performed. - Repeat step 2 to add more commands to the devfile.
Click the Devfile tab to view the changes.

Save changes and start the new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace.
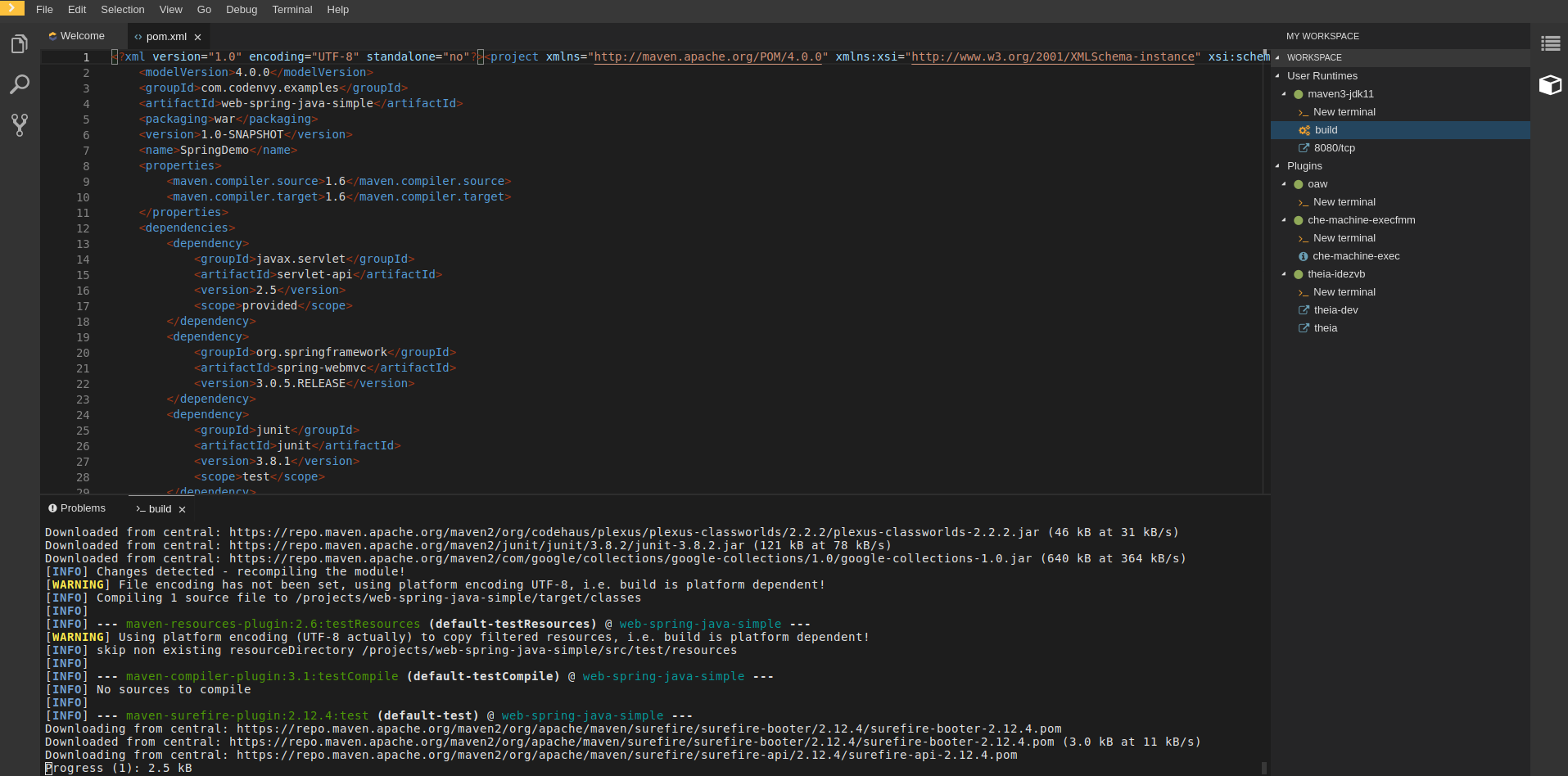
3.4. Importing a OpenShift application into a workspace
This section describes how to import a OpenShift application into a CodeReady Workspaces workspace.
For demonstration purposes, the section uses a sample OpenShift application having the following two Pods:
- A Node.js application specified by this nodejs-app.yaml
- A MongoDB Pod specified by this mongo-db.yaml
To run the application on a OpenShift cluster:
node=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redhat-developer/devfile/master/samples/web-nodejs-with-db-sample/nodejs-app.yaml && \
mongo=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redhat-developer/devfile/master/samples/web-nodejs-with-db-sample/mongo-db.yaml && \
oc apply -f ${mongo} && \
oc apply -f ${node}
$ node=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redhat-developer/devfile/master/samples/web-nodejs-with-db-sample/nodejs-app.yaml && \
mongo=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redhat-developer/devfile/master/samples/web-nodejs-with-db-sample/mongo-db.yaml && \
oc apply -f ${mongo} && \
oc apply -f ${node}To deploy a new instance of this application in a CodeReady Workspaces workspace, use one of the following three scenarios:
- Starting from scratch: Writing a new devfile
- Modifying an existing workspace: Using the Dashboard user interface
-
From a running application: Generating a devfile with
crwctl
3.4.1. Including a OpenShift application in a workspace devfile definition
This procedure describes how to define a CodeReady Workspaces workspace devfile to include a OpenShift application.
The devfile format is used to define a CodeReady Workspaces workspace, and its format is described in the Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile” section.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the cluster with a running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
-
crwctlmanagement tool is available. See CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 Installation Guide.
Procedure
Create the simplest devfile:
apiVersion: 1.0.0 metadata: name: minimal-workspace
apiVersion: 1.0.0 metadata: name: minimal-workspace1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Only the name
minimal-workspaceis specified. After the CodeReady Workspaces server processes this devfile, the devfile is converted to a minimal CodeReady Workspaces workspace that only has the default editor (Che-Theia) and the default editor plug-ins, including, for example, the terminal.
To add OpenShift applications to a workspace, modify the devfile and add the
OpenShiftcomponent type.For example, to embed the NodeJS-Mongo application in the
minimal-workspace:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
sleep infinitycommand is added as the entrypoint of the Node.js application. The command prevents the application from starting at the workspace start phase. This configuration allows the user to start the application when needed for testing or debugging purposes.
Add the commands in the devfile to make it easier for a developer to test the application:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
runcommand added to the devfile is available as a task in Che-Theia from the command palette. When executed, the command starts the Node.js application.
Use the devfile to create and start a workspace:
crwctl worspace:start --devfile <devfile-path>
$ crwctl worspace:start --devfile <devfile-path>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.4.2. Adding a OpenShift application to an existing workspace using the dashboard
This procedure demonstrates how to modify an existing workspace and import the OpenShift application using the newly created devfile.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
After the creation of a workspace, use the Workspace menu and then the Configure workspace icon to manage the workspace.

To modify the workspace details, use the Devfile tab. The workspace details are displayed in this tab in the devfile format.
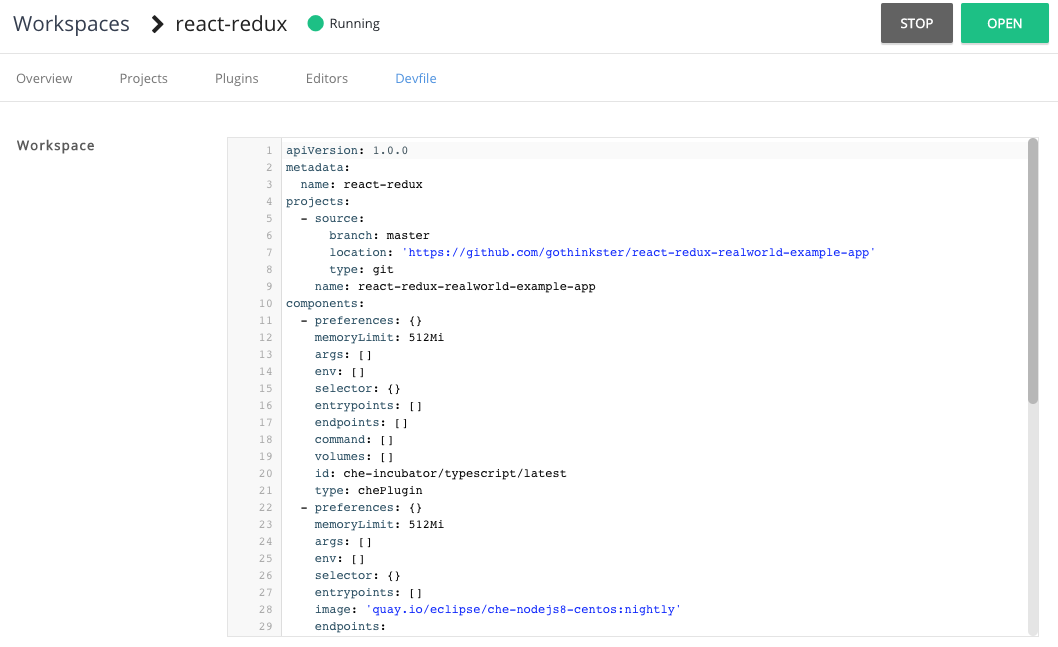
- To add a OpenShift component, use the Devfile editor on the dashboard.
- For the changes to take effect, save the devfile and restart the CodeReady Workspaces workspace.
3.4.3. Generating a devfile from an existing OpenShift application
This procedure demonstrates how to generate a devfile from an existing OpenShift application using the crwctl tool.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
-
The
crwctlmanagement tool is available. See CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 Installation Guide.
Procedure
Use the
crwctl devfile:generatecommand to generate a devfile:crwctl devfile:generate
$ crwctl devfile:generateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The user can also use the
crwctl devfile:generatecommand to generate a devfile from, for example, theNodeJS-MongoDBapplication.The following example generates a devfile that includes the
NodeJScomponent:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The Node.js application YAML definition is available in the devfile, inline, using the
referenceContentattribute.To include support for a language, use the
--languageparameter:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Use the generated devfile to start a CodeReady Workspaces workspace with
crwctl.
3.5. Remotely accessing workspaces
This section describes how to remotely access CodeReady Workspaces workspaces outside of the browser.
CodeReady Workspaces workspaces exist as containers and are, by default, modified from a browser window. In addition to this, there are the following methods of interacting with a CodeReady Workspaces workspace:
-
Opening a command line in the workspace container using the OpenShift command-line tool,
oc -
Uploading and downloading files using the
octool
3.5.1. Remotely accessing workspaces using oc
To access CodeReady Workspaces workspaces remotely using OpenShift command-line tool (oc), follow the instructions in this section.
Prerequisites
-
The
octool is available. See Kubernetes website. Verify the installation of
ocusing theoc versioncommand:{orch-cli} version Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"15", GitVersion:"v1.15.0", GitCommit:"e8462b5b5dc2584fdcd18e6bcfe9f1e4d970a529", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-06-19T16:40:16Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"} Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"15", GitVersion:"v1.15.0", GitCommit:"e8462b5b5dc2584fdcd18e6bcfe9f1e4d970a529", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-06-19T16:32:14Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}$ {orch-cli} version Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"15", GitVersion:"v1.15.0", GitCommit:"e8462b5b5dc2584fdcd18e6bcfe9f1e4d970a529", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-06-19T16:40:16Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"} Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"15", GitVersion:"v1.15.0", GitCommit:"e8462b5b5dc2584fdcd18e6bcfe9f1e4d970a529", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2019-06-19T16:32:14Z", GoVersion:"go1.12.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For versions 1.5.0 or higher, proceed with the steps in this section.
Procedure
-
Use the
execcommand to open a remote shell. To find the name of the OpenShift project and the Pod that runs the CodeReady Workspaces workspace:
oc get pod -l che.workspace_id --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE che workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 4/4 Running 0 6m4s
$ oc get pod -l che.workspace_id --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE che workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 4/4 Running 0 6m4sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
In the example above, the Pod name is workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4, and the project is che.
To find the name of the container:
NAMESPACE=che POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 oc get pod ${POD} -o custom-columns=CONTAINERS:.spec.containers[*].name CONTAINERS maven,che-machine-execpau,theia-ide6dj,vscode-javaw92$ NAMESPACE=che $ POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 $ oc get pod ${POD} -o custom-columns=CONTAINERS:.spec.containers[*].name CONTAINERS maven,che-machine-execpau,theia-ide6dj,vscode-javaw92Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When you have the project, pod name, and the name of the container, use the `oc ` command to open a remote shell:
NAMESPACE=che POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 CONTAINER=maven oc exec -ti -n ${NAMESPACE} ${POD} -c ${CONTAINER} bash user@workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln $$ NAMESPACE=che $ POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 $ CONTAINER=maven $ oc exec -ti -n ${NAMESPACE} ${POD} -c ${CONTAINER} bash user@workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln $Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the container, execute the
buildandruncommands (as if from the CodeReady Workspaces workspace terminal):user@workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln $ mvn clean install [INFO] Scanning for projects... (...)
user@workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln $ mvn clean install [INFO] Scanning for projects... (...)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Additional resources
-
For more about
oc, see the Kubernetes documentation.
3.5.2. Downloading and uploading a file to a workspace using the command-line interface
This procedure describes how to use the `oc ` tool to download or upload files remotely from or to an Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspace.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- Remote access to the CodeReady Workspaces workspace you intend to modify. For instructions see Section 3.5, “Remotely accessing workspaces”.
- The `oc ` tool is available. See Installing `oc `.
-
Verify the installation of
oc ` using the `oc versioncommand:
Procedure
To download a local file named
downloadme.txtfrom a workspace container to the current home directory of the user, use the following in the CodeReady Workspaces remote shell.REMOTE_FILE_PATH=/projects/downloadme.txt NAMESPACE=che POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 CONTAINER=maven oc cp ${NAMESPACE}/${POD}:${REMOTE_FILE_PATH} ~/downloadme.txt -c ${CONTAINER}$ REMOTE_FILE_PATH=/projects/downloadme.txt $ NAMESPACE=che $ POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4 $ CONTAINER=maven $ oc cp ${NAMESPACE}/${POD}:${REMOTE_FILE_PATH} ~/downloadme.txt -c ${CONTAINER}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To upload a local file named
uploadme.txtto a workspace container in the/projectsdirectory:
LOCAL_FILE_PATH=./uploadme.txt
NAMESPACE=che
POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4
CONTAINER=maven
oc cp ${LOCAL_FILE_PATH} ${NAMESPACE}/${POD}:/projects -c ${CONTAINER}
$ LOCAL_FILE_PATH=./uploadme.txt
$ NAMESPACE=che
$ POD=workspace7b2wemdf3hx7s3ln.maven-74885cf4d5-kf2q4
$ CONTAINER=maven
$ oc cp ${LOCAL_FILE_PATH} ${NAMESPACE}/${POD}:/projects -c ${CONTAINER}Using the preceding steps, the user can also download and upload directories.
3.6. Creating a workspace from code sample
Every stack includes a sample codebase, which is defined by the devfile of the stack. This section explains how to create a workspace from this code sample in a sequence of three procedures.
Creating a workspace from the user dashboard:
- Using the Get Started view.
- Using the Custom Workspace view.
- Changing the configuration of the workspace to add code sample.
- Running an existing workspace from the user dashboard.
For more information about devfiles, see Section 3.1, “Configuring a workspace using a devfile”.
3.6.1. Creating a workspace from Get Started view of User Dashboard
This section describes how to create a workspace from the User Dashboard.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
Procedure
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
- In the left navigation panel, go to Get Started.
- Click the tab.
In the gallery, there is list of samples that may be used to build and run projects.
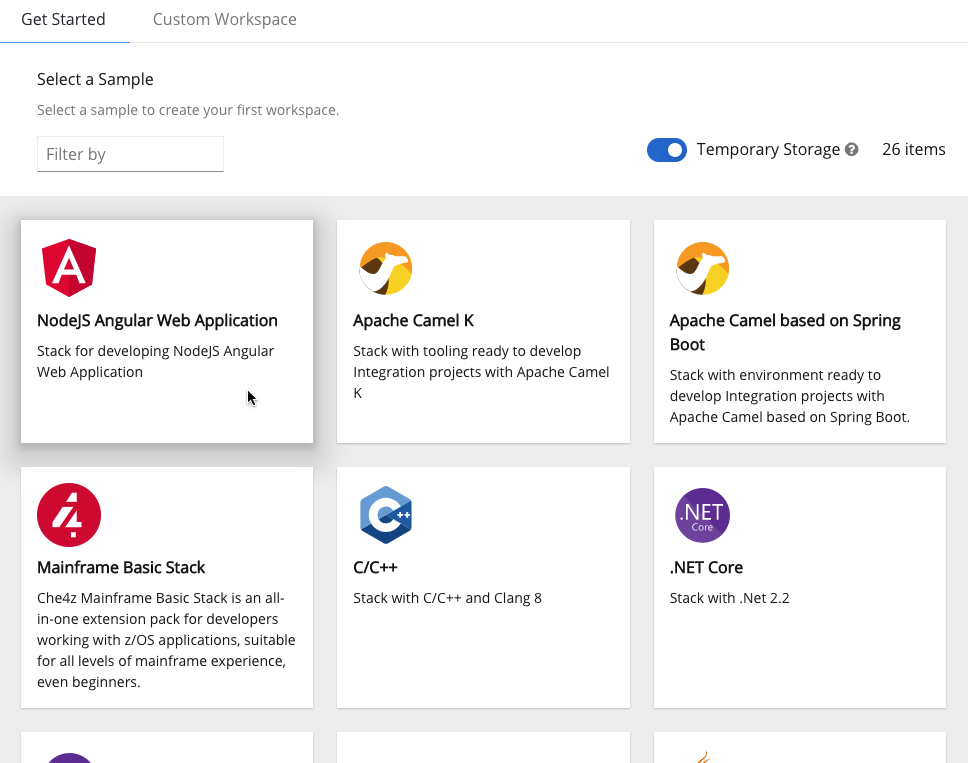 Changing resource limits
Changing resource limitsChanging the memory requirements is only possible from the devfile. See Section 3.6.3, “Changing the configuration of an existing workspace”.
Start the workspace: click the chosen stack card.

Workspace name can be auto-generated based on the underlying devfile of the stack. Generated names always consist of the devfile metadata.generateName property as the prefix and four random characters.
3.6.2. Creating a workspace from Custom Workspace view of User Dashboard
This section describes how to create a workspace from the User Dashboard.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
Procedure
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
- In the left navigation panel, go to Get Started.
- Click the tab.
Define a Name for the workspace.
New workspace nameWorkspace name can be auto-generated based on the underlying devfile of the stack. Generated names always consist of the devfile
metadata.generateNameproperty as the prefix and four random characters.In the Devfile section, select the devfile template that will be used to build and run projects.
 Changing resource limits
Changing resource limitsChanging the memory requirements is only possible from the devfile. See Section 3.6.3, “Changing the configuration of an existing workspace”.
Start the workspace: click the button at the bottom of the form:

3.6.3. Changing the configuration of an existing workspace
This section describes how to change the configuration of an existing workspace from the User Dashboard.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
- In the left navigation panel, go to Workspaces.
- Click the name of a workspace to navigate to the configuration overview page.
Click the Overview tab and execute following actions:
- Change the Workspace name.
- Select Storage Type.
- Export the workspace configuration to a file or private cloud.
Delete the workspace.
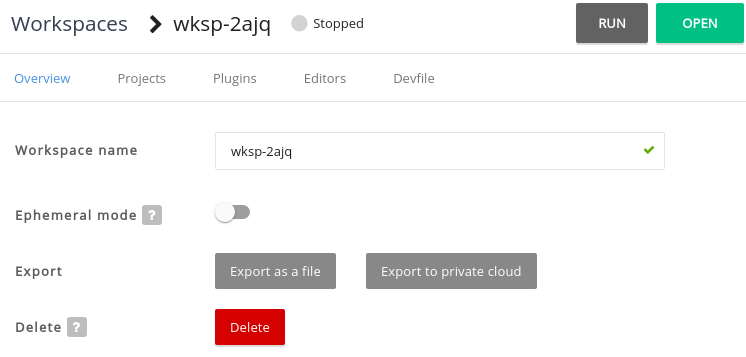
In the Projects section, choose the projects to integrate in the workspace.
Click the button and do one of the following:
Enter the project Git repository URL to integrate in the workspace:

Connect your GitHub account and select projects to integrate:
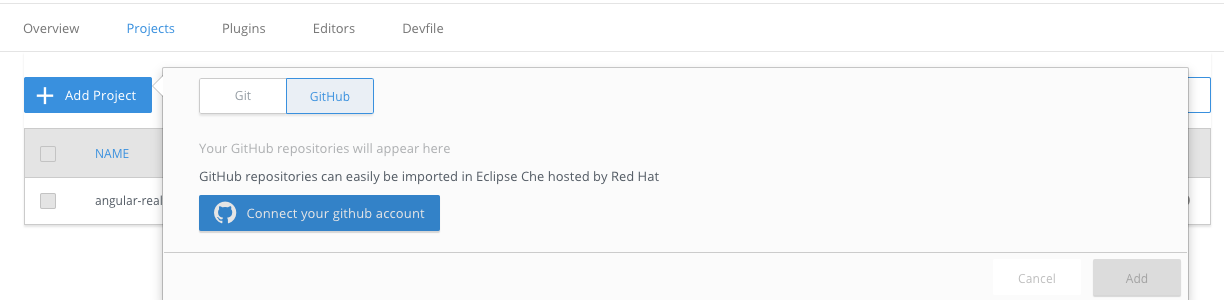
- Click the button.
In the Plugins section, choose the plug-ins to integrate in the workspace.
ExampleStart with a generic Java-based stack, then add support for Node.js or Python.
- In the Editors section, choose the editors to integrate in the workspace. The CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 editor is based on Che-Theia.
From the Devfile tab, edit YAML configuration of the workspace. See Section 3.2, “Making a workspace portable using a devfile”.
Example: add commands Example: add a project
Example: add a projectTo add a project into the workspace, add or edit the following section:
projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.6.4. Running an existing workspace from the User Dashboard
This section describes how to run an existing workspace from the User Dashboard.
3.6.4.1. Running an existing workspace from the User Dashboard with the Run button
This section describes how to run an existing workspace from the User Dashboard using the Run button.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
- In the left navigation panel, navigate to Workspaces.
- Click on the name of a non-running workspace to navigate to the overview page.
- Click on the button in the top right corner of the page.
- The workspace is started.
- The browser does not navigates to the workspace.
3.6.4.2. Running an existing workspace from the User Dashboard using the Open button
This section describes how to run an existing workspace from the User Dashboard using the Open button.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
- In the left navigation panel, navigate to Workspaces.
- Click on the name of a non-running workspace to navigate to the overview page.
- Click on the button in the top right corner of the page.
- The workspace is started.
- The browser navigates to the workspace.
3.6.4.3. Running an existing workspace from the User Dashboard using the Recent Workspaces
This section describes how to run an existing workspace from the User Dashboard using the Recent Workspaces.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
In the left navigation panel, in the Recent Workspaces section, right-click the name of a non-running workspace and click Run in the contextual menu to start it.
3.7. Creating a workspace by importing the source code of a project
This section describes how to create a new workspace to edit an existing codebase.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace with plug-ins related to your development environment defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
You can do it in two ways before starting a workspace:
To create a new workspace to edit an existing codebase, use one of the following three methods after you have started the workspace:
3.7.1. Select a sample from the Dashboard, then change the devfile to include your project
- In the left navigation panel, go to Get Started.
- Click the Custom Workspace tab if it’s not already selected.
In the Devfile section, select the devfile template that will be used to build and run projects.

In the Devfile editor, update
projectssection: Example: add a project
Example: add a projectTo add a project into the workspace, add or edit the following section:
projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'projects: - name: che source: type: git location: 'https://github.com/eclipse/che.git'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See the Section 3.2.4, “Devfile reference”.
- To open the workspace, click the button.
3.7.2. Importing from the Dashboard into an existing workspace
Import the project. There are at least two ways to import a project using the Dashboard.
- From the Dashboard, select Workspaces, then select your workspace by clicking on its name. This will link you to the workspace’s Overview tab.
- Or, use the gear icon. This will link to the Devfile tab where you can enter your own YAML configuration.
- Click the Projects tab.
- Click Add Project. You can then import project by a repository Git URL or from GitHub.

You can add a project to a non-running workspace, but you must start the workspace to delete it.
3.7.2.1. Editing the commands after importing a project
After you have a project in your workspace, you can add commands to it. Adding commands to your projects allows you to run, debug, or launch your application in a browser.
To add commands to the project:
Open the workspace configuration in the Dashboard, then select the Devfile tab.

- Open the workspace.
To run a command, select Terminal > Run Task from the main menu.
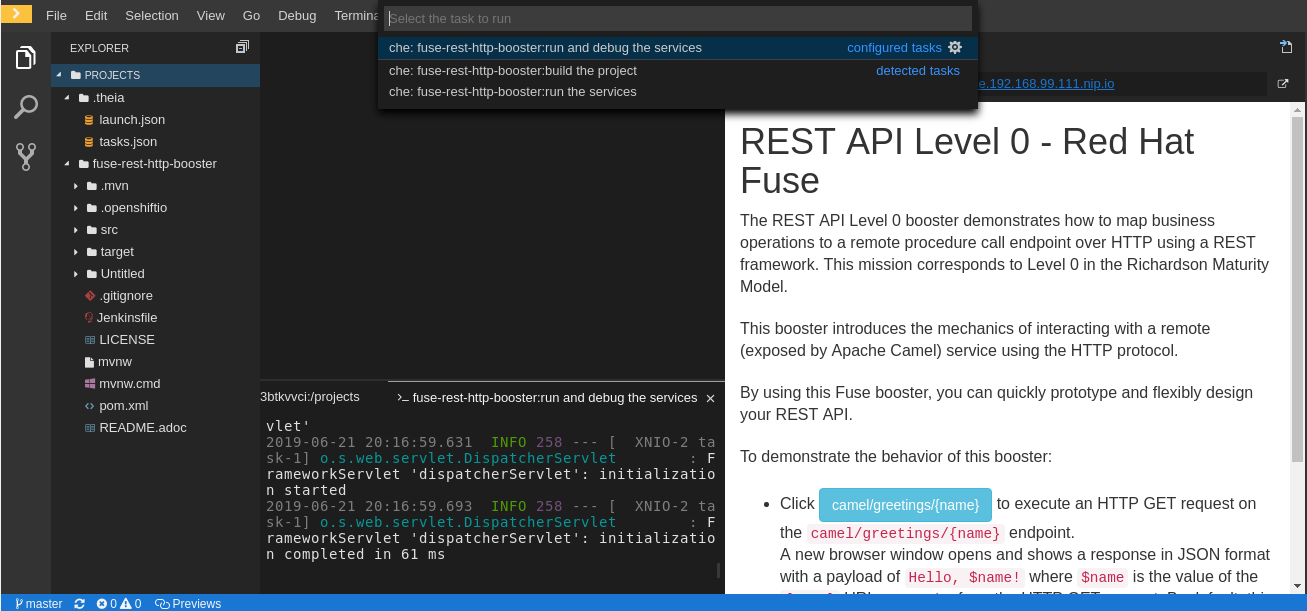
To configure commands, select Terminal > Configure Tasks from the main menu.
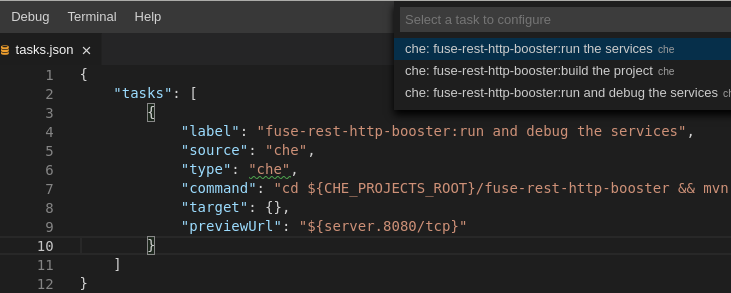
3.7.3. Importing to a running workspace using the Git: Clone command
To import to a running workspace using the Git: Clone command:
Start a workspace, then use the Git: Clone command from the command palette or the Welcome screen to import a project to a running workspace.
Open the command palette using
F1orCTRL-SHIFT-P, or from the link in the Welcome screen.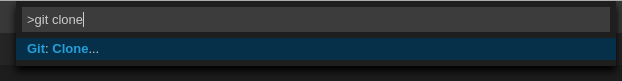
Enter the path to the project you want to clone.
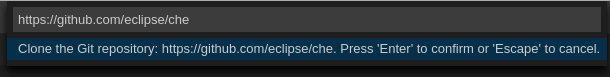
3.7.4. Importing to a running workspace with git clone in a terminal
In addition to the approaches above, you can also start a workspace, open a Terminal, and type git clone to pull code.

Importing or deleting workspace projects in the terminal does not update the workspace configuration, and the change is not reflected in the Project and Devfile tabs in the dashboard.
Similarly, if you add a project using the Dashboard, then delete it with rm -fr myproject, it may still appear in the Projects or Devfile tab.
3.8. Mounting a secret as a file or an environment variable into a workspace container
Secrets are OpenShift objects that store sensitive data such as user names, passwords, authentication tokens, and configurations in an encrypted form.
Users can mount a secret that contains sensitive data in a workspace container. This reapplies the stored data from the secret automatically for every newly created workspace. As a result, the user does not have to provide these credentials and configuration settings manually.
The following section describes how to automatically mount a OpenShift secret in a workspace container and create permanent mount points for components such as:
-
Maven configuration, the
settings.xmlfile - SSH key pairs
- AWS authorization tokens
- Git credentials store file
A OpenShift secret can be mounted into a workspace container as:
- A file - This creates automatically mounted Maven settings that will be applied to every new workspace with Maven capabilities.
An environment variable - This uses SSH key pairs and AWS authorization tokens for automatic authentication.
NoteSSH key pairs can also be mounted as a file, but this format is primarily aimed at the settings of the Maven configuration.
The mounting process uses the standard OpenShift mounting mechanism, but it requires additional annotations and labeling for a proper bound of a secret with the required CodeReady Workspaces workspace container.
3.8.1. Mounting a secret as a file into a workspace container
On OpenShift 3.11, secrets mounted as file overrides volume mounts defined in the devfile.
This section describes how to mount a secret from the user’s project as a file in single-workspace or multiple-workspace containers of CodeReady Workspaces.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
Create a new OpenShift secret in the OpenShift project where a CodeReady Workspaces workspace will be created.
-
The labels of the secret that is about to be created must match the set of labels configured in
che.workspace.provision.secret.labelsproperty of CodeReady Workspaces. The default labels are: -
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: che.eclipse.org app.kubernetes.io/component: workspace-secret:NoteNote that the following example describes variations in the usage of the
target-containerannotation in versions 2.1 and 2.2 of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.Example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Annotations must indicate the given secret is mounted as a file, provide the mount path, and, optionally, specify the name of the container in which the secret is mounted. If there is no target-container annotation, the secret will be mounted into all user containers of the CodeReady Workspaces workspace, but this is applicable only for the CodeReady Workspaces version 2.1.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Since the CodeReady Workspaces version 2.2, the
target-containerannotation is deprecated andautomount-workspace-secretannotation with Boolean values is introduced. Its purpose is to define the default secret mounting behavior, with the ability to be overridden in a devfile. Thetruevalue enables the automatic mounting into all workspace containers. In contrast, thefalsevalue disables the mounting process until it is explicitly requested in a devfile component using theautomountWorkspaceSecrets:trueproperty.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Data of the OpenShift secret may contain several items, whose names must match the desired file name mounted into the container.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This results in a file named
settings.xmlbeing mounted at the/home/jboss/.m2/path of all workspace containers.The secret-s mount path can be overridden for specific components of the workspace using devfile. To change mount path, an additional volume should be declared in a component of the devfile, with name matching overridden secret name, and desired mount path.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that for this kind of overrides, components must declare an alias to be able to distinguish containers which belong to them and apply override path exclusively for those containers.
-
The labels of the secret that is about to be created must match the set of labels configured in
3.8.2. Mounting a secret as an environment variable into a workspace container
The following section describes how to mount a OpenShift secret from the user’s project as an environment variable, or variables, into single-workspace or multiple-workspace containers of CodeReady Workspaces.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
Create a new OpenShift secret in the k8s project where a CodeReady Workspaces workspace will be created.
-
The labels of the secret that is about to be created must match the set of labels configured in
che.workspace.provision.secret.labelsproperty of CodeReady Workspaces. By default, it is a set of two labels: -
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: che.eclipse.org app.kubernetes.io/component: workspace-secret:NoteNote that the following example describes variations in the usage of the
target-containerannotation in versions 2.1 and 2.2 of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.Example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Annotations must indicate that the given secret is mounted as an environment variable, provides variable names, and optionally, specifies the container name where this mount will be applied. If there is no target-container annotation defined, the secret will be mounted into all user containers of the CodeReady Workspaces workspace, but this is applicable only for the CodeReady Workspaces version 2.1.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This results in the environment variable named
FOO_ENVand the valuemyvaluebeing provisioned into the container namedmaven.Since the CodeReady Workspaces version 2.2, the
target-containerannotation is deprecated andautomount-workspace-secretannotation with Boolean values is introduced. Its purpose is to define the default secret mounting behavior, with the ability to be overridden in a devfile. Thetruevalue enables the automatic mounting into all workspace containers. In contrast, thefalsevalue disables the mounting process until it is explicitly requested in a devfile component using theautomountWorkspaceSecrets:trueproperty.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This results in the environment variable named
FOO_ENVand the valuemyvaluebeing provisioned into all workspace containers.If the secret provides more than one data item, the environment variable name must be provided for each of the data keys as follows:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This results in two environment variables with names
FOO_ENV,OTHER_ENV, and valuesmyvalueandothervalue, being provisioned into all workpsace containers.NoteThe maximum length of annotation names in a OpenShift secret is 63 characters, where 9 characters are reserved for a prefix that ends with
/. This acts as a restriction for the maximum length of the key that can be used for the secret.
-
The labels of the secret that is about to be created must match the set of labels configured in
3.8.3. Mounting a git credentials store into a workspace container
This section describes how to mount git credentials store as secret from the user’s project into the file in single-workspace or multiple-workspace containers of CodeReady Workspaces.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
- Prepare git credential file in format https://git-scm.com/docs/git-credential-store#_storage_format.
- Encode content of the file to the base64 format.
Create a new OpenShift secret in the OpenShift project where a CodeReady Workspaces workspace will be created.
-
The labels of the secret that is about to be created must match the set of labels configured in
che.workspace.provision.secret.labelsproperty of CodeReady Workspaces. The default labels are: -
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: che.eclipse.org -
app.kubernetes.io/component: workspace-secret:
-
The labels of the secret that is about to be created must match the set of labels configured in
3.8.4. The use of annotations in the process of mounting a secret into a workspace container
Kubernetes annotations and labels are tools used by libraries, tools, and other clients, to attach arbitrary non-identifying metadata to OpenShift native objects.
Labels select objects and connect them to a collection that satisfies certain conditions, where annotations are used for non-identifying information that is not used by OpenShift objects internally.
This section describes OpenShift annotation values used in the process of OpenShift secret mounting in a CodeReady Workspaces workspace.
Annotations must contain items that help identify the proper mounting configuration. These items are:
-
che.eclipse.org/target-container: Valid till the version 2.1. The name of the mounting container. If the name is not defined, the secret mounts into all user’s containers of the CodeReady Workspaces workspace. -
che.eclipse.org/automount-workspace-secret: Introduced in the version 2.2.. The main mount selector. When set totrue, the secret mounts into all user’s containers of the CodeReady Workspaces workspace. When set tofalse, the secret does not mount into containers by default. The value of this attribute can be overridden in devfile components, using theautomountWorkspaceSecretsboolean property that gives more flexibility to workspace owners. This property requires analiasto be defined for the component that uses it. -
che.eclipse.org/env-name: The name of the environment variable that is used to mount a secret. -
che.eclipse.org/mount-as: This item describes if a secret will be mounted as an environmental variable or a file. Options:envorfile. -
che.eclipse.org/<mykeyName>-env-name: FOO_ENV: The name of the environment variable used when data contains multiple items.mykeyNameis used as an example.
Chapter 4. Customizing developer environments
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces is an extensible and customizable developer-workspaces platform.
You can extend Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces in three different ways:
- Alternative IDEs provide specialized tools for Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. For example, a Jupyter notebook for data analysis. Alternate IDEs can be based on Eclipse Theia or any other web IDE. The default IDE in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces is Che-Theia.
- Che-Theia plug-ins add capabilities to the Che-Theia IDE. They rely on plug-in APIs that are compatible with Visual Studio Code. The plug-ins are isolated from the IDE itself. They can be packaged as files or as containers to provide their own dependencies.
- Stacks are pre-configured CodeReady Workspaces workspaces with a dedicated set of tools, which cover different developer personas. For example, it is possible to pre-configure a workbench for a tester with only the tools needed for their purposes.
Figure 4.1. CodeReady Workspaces extensibility
A user can extend CodeReady Workspaces by using self-hosted mode, which CodeReady Workspaces provides by default.
4.1. What is a Che-Theia plug-in
A Che-Theia plug-in is an extension of the development environment isolated from the IDE. Plug-ins can be packaged as files or containers to provide their own dependencies.
Extending Che-Theia using plug-ins can enable the following capabilities:
- Language support: Extend the supported languages by relying on the Language Server Protocol.
- Debuggers: Extend debugging capabilities with the Debug Adapter Protocol.
- Development Tools: Integrate your favorite linters, and as testing and performance tools.
- Menus, panels, and commands: Add your own items to the IDE components.
- Themes: Build custom themes, extend the UI, or customize icon themes.
- Snippets, formatters, and syntax highlighting: Enhance comfort of use with supported programming languages.
- Keybindings: Add new keymaps and popular keybindings to make the environment feel natural.
4.1.1. Features and benefits of Che-Theia plug-ins
| Features | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Loading | Plug-ins are loaded at runtime and are already compiled. IDE is loading the plug-in code. | Avoid any compilation time. Avoid post-installation steps. |
| Secure Loading | Plug-ins are loaded separately from the IDE. The IDE stays always in a usable state. | Plug-ins do not break the whole IDE if it has bugs. Handle network issue. |
| Tools Dependencies | Dependencies for the plug-in are packaged with the plug-in in its own container. | No-installation for tools. Dependencies running into container. |
| Code Isolation | Guarantee that plug-ins cannot block the main functions of the IDE like opening a file or typing | Plug-ins are running into separate threads. Avoid dependencies mismatch. |
| VS Code Extension Compatibility | Extend the capabilities of the IDE with existing VS Code Extensions. | Target multiple platform. Allow easy discovery of Visual Studio Code Extension with required installation. |
4.1.2. Che-Theia plug-in concept in detail
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces provides a default web IDE for workspaces: Che-Theia. It is based on Eclipse Theia. It is a slightly different version than the plain Eclipse Theia one because there are functionalities that have been added based on the nature of the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspaces. This version of Eclipse Theia for CodeReady Workspaces is called Che-Theia.
You can extend the IDE provided with Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces by building a Che-Theia plug-in. Che-Theia plug-ins are compatible with any other Eclipse Theia-based IDE.
4.1.2.1. Client-side and server-side Che-Theia plug-ins
The Che-Theia editor plug-ins let you add languages, debuggers, and tools to your installation to support your development workflow. Plug-ins run when the editor completes loading. If a Che-Theia plug-in fails, the main Che-Theia editor continues to work.
Che-Theia plug-ins run either on the client side or on the server side. This is a scheme of the client and server-side plug-in concept:
Figure 4.2. Client and server-side Che-Theia plug-ins
The same Che-Theia plug-in API is exposed to plug-ins running on the client side (Web Worker) or the server side (Node.js).
4.1.2.2. Che-Theia plug-in APIs
For the purpose of providing tool isolation and easy extensibility in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, the Che-Theia IDE has a set of plug-in APIs. The APIs are compatible with Visual Studio Code extension APIs. Usually, Che-Theia can run VS Code extensions as its own plug-ins.
When developing a plug-in that depends on or interacts with components of CodeReady Workspaces workspaces (containers, preferences, factories), use the CodeReady Workspaces APIs embedded in Che-Theia.
4.1.2.3. Che-Theia plug-in capabilities
Che-Theia plug-ins have the following capabilities:
| Plug-in | Description | Repository |
|---|---|---|
| CodeReady Workspaces Extended Tasks | Handles the CodeReady Workspaces commands and provides the ability to start those into a specific container of the workspace. | |
| CodeReady Workspaces Extended Terminal | Allows to provide terminal for any of the containers of the workspace. | |
| CodeReady Workspaces Factory | Handles the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces Factories | |
| CodeReady Workspaces Container | Provides a container view that shows all the containers that are running in the workspace and allows to interact with them. | |
| Dashboard | Integrates the IDE with the Dashboard and facilitate the navigation. | |
| CodeReady Workspaces APIs | Extends the IDE APIs to allow interacting with CodeReady Workspaces-specific components (workspaces, preferences). |
4.1.2.4. VS Code extensions and Eclipse Theia plug-ins
A Che-Theia plug-in can be based on a VS Code extension or an Eclipse Theia plug-in.
- A Visual Studio Code extension
- To repackage a VS Code extension as a Che-Theia plug-in with its own set of dependencies, package the dependencies into a container. This ensures that Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces users do not need to install the dependencies when using the extension. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/administration_guide/index#using-a-visual-studio-code-extension-in-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- An Eclipse Theia plug-in
- You can build a Che-Theia plug-in by implementing an Eclipse Theia plug-in and packaging it to Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.
Additional resources
4.1.3. Che-Theia plug-in metadata
Che-Theia plug-in metadata is information about individual plug-ins for the plug-in registry.
The Che-Theia plug-in metadata, for each specific plug-in, is defined in a meta.yaml file.
Here is an overview of all fields that can be available in plugin meta YAML files. This document represents the Plugin meta YAML structure version 3.
The che-plugin-registry repository contains:
|
| Version 2 and higher where version is 1 supported for backwards compatibility |
|
|
Available: Category must be set to one of the followings: |
|
| Short description of plugin’s purpose |
|
| Name shown in user dashboard |
|
| Optional; section for deprecating plugins in favor of others * autoMigrate - boolean
* migrateTo - new org/plugin-id/version, for example |
|
| Not required to be present in YAML, as if not present, it will be generated during Plugin Registry dockerimage build |
|
| Not required to be present in YAML, as if not present, it will be generated during Plugin Registry dockerimage build |
|
| URL of an SVG or PNG icon |
|
| Name (no spaces allowed), must match [-a-z0-9] |
|
| Name of the publisher, must match [-a-z0-9] |
|
| URL for plugin repository, for example, GitHub |
|
| Plugin title (long) |
|
|
|
|
| Version information, for example: 7.5.1, [-.a-z0-9] |
|
| Specifications (see below) |
|
| Optional; plugin endpoint. See Section 3.2.4.2.19, “Endpoints” |
|
| Optional; sidecar containers for the plug-in. Che Plugin and VS Code extension supports only one container |
|
| Optional; sidecar init containers for the plug-in |
|
| Optional; environment variables for the workspace |
|
| Optional; Attribute that is required for VS Code and Che-Theia plug-ins in a form list of URLs to plug-in artefacts, such as .vsix or .theia files |
|
| Sidecar container name |
|
| Absolute or relative container image URL |
|
|
OpenShift memory limit string, for example |
|
|
OpenShift memory request string, for example |
|
|
OpenShift CPU limit string, for example |
|
|
OpenShift CPU request string, for example |
|
| List of environment variables to set in the sidecar |
|
| String array definition of the root process command in the container |
|
| String array arguments for the root process command in the container |
|
| Volumes required by the plug-in |
|
| Ports exposed by the plug-in (on the container) |
|
| Development commands available to the plug-in container |
|
|
Boolean flag to bound volume with source code |
|
| Optional; init containers for sidecar plugin |
|
|
Container lifecycle hooks. See |
|
| Environment variable name |
|
| Environment variable value |
|
| Path to the volume in the container |
|
| Volume name |
|
| If true, the volume is ephemeral, otherwise the volume is persisted |
|
| Exposed port |
|
| Command name |
|
| Command working directory |
|
| String array that defines the development command |
|
| Name (no spaces allowed), must match [-a-z0-9] |
|
|
|
|
| Target port |
|
| Endpoint attributes |
|
|
Protocol, example: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The
*
* |
|
|
The
*
* |
Example meta.yaml for a Che-Theia plug-in: the CodeReady Workspaces machine-exec Service
Example meta.yaml for a VisualStudio Code extension: the AsciiDoc support extension
4.1.4. Che-Theia plug-in lifecycle
When a user is starting a workspace, the following procedure is followed:
- CodeReady Workspaces master checks for plug-ins to start from the workspace definition.
- Plug-in metadata is retrieved, and the type of each plug-in is recognized.
- A broker is selected according to the plug-in type.
- The broker processes the installation and deployment of the plug-in (the installation process is different for each broker).
Different types of plug-ins exist. A broker ensures all installation requirements are met for a plug-in to deploy correctly.
Figure 4.3. Che-Theia plug-in lifecycle
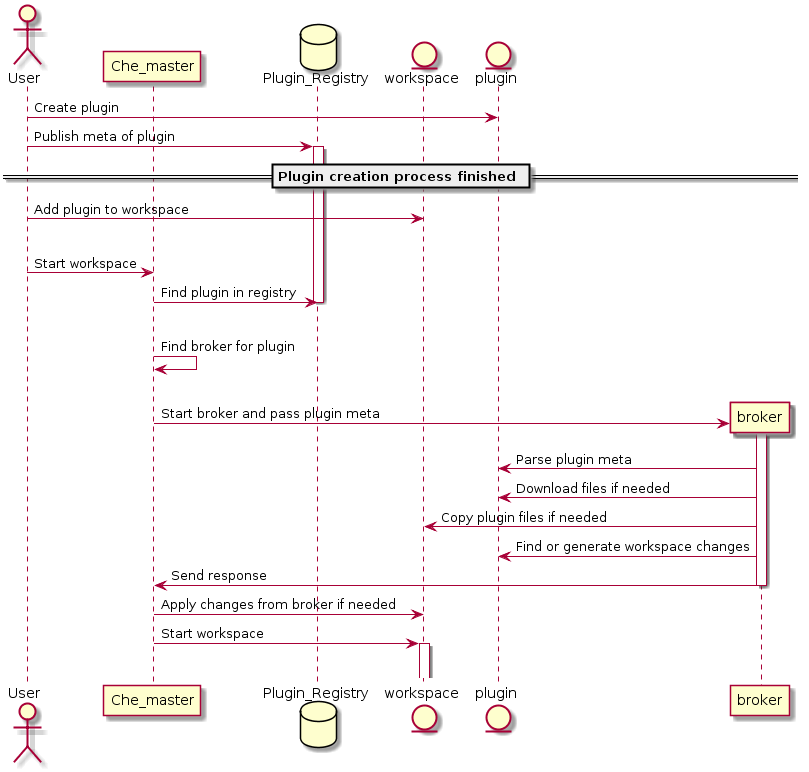
Before a CodeReady Workspaces workspace is launched, CodeReady Workspaces master starts containers for the workspace:
-
The Che-Theia plug-in broker extracts the plug-in (from the
.theiafile) to get the sidecar containers that the plug-in needs. - The broker sends the appropriate container information to CodeReady Workspaces master.
- The broker copies the Che-Theia plug-in to a volume to have it available for the Che-Theia editor container.
- CodeReady Workspaces workspace master then starts all the containers of the workspace.
- Che-Theia is started in its own container and checks the correct folder to load the plug-ins.
Che-Theia plug-in lifecycle:
-
When a user is opening a browser tab or window with Che-Theia, Che-Theia starts a new plug-in session (Web Worker for frontend or Node.js for backend). Every Che-Theia plug-in is notified that a new session has been started (the
start()function of the plug-in triggered). - A Che-Theia plug-in session is running and interacting with the Che-Theia backend and frontend.
-
When the user is closing the browser tab or there is a timeout, every plug-in is notified (the
stop()function of the plug-in triggered).
4.1.5. Embedded and remote Che-Theia plug-ins
Developer workspaces in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces provide all dependencies needed to work on a project. The application includes the dependencies needed by all the tools and plug-ins used.
Che-Theia plug-in can run in two different ways, based on the necessary dependencies: embedded (or local) and remote.
4.1.5.1. Embedded (or local) plug-ins
The plug-in does not have specific dependencies - it only uses a Node.js runtime, and it runs in the same container as the IDE. The plug-in is injected into the IDE.
Examples:
- Code linting
- New set of commands
- New UI components
To include a Che-Theia plug-in as embedded, define a URL to the plug-in binary file (the .theia archive) in the meta.yaml file. In the case of a VS Code extension, provide the extension ID from the Visual Studio Code marketplace (see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/administration_guide/index#using-a-visual-studio-code-extension-in-codeready-workspaces_crw).
When starting a workspace, CodeReady Workspaces downloads and unpacks the plug-in binaries and includes them in the Che-Theia editor container. The Che-Theia editor initializes the plug-ins when it starts.
Figure 4.4. Local Che-Theia plug-in
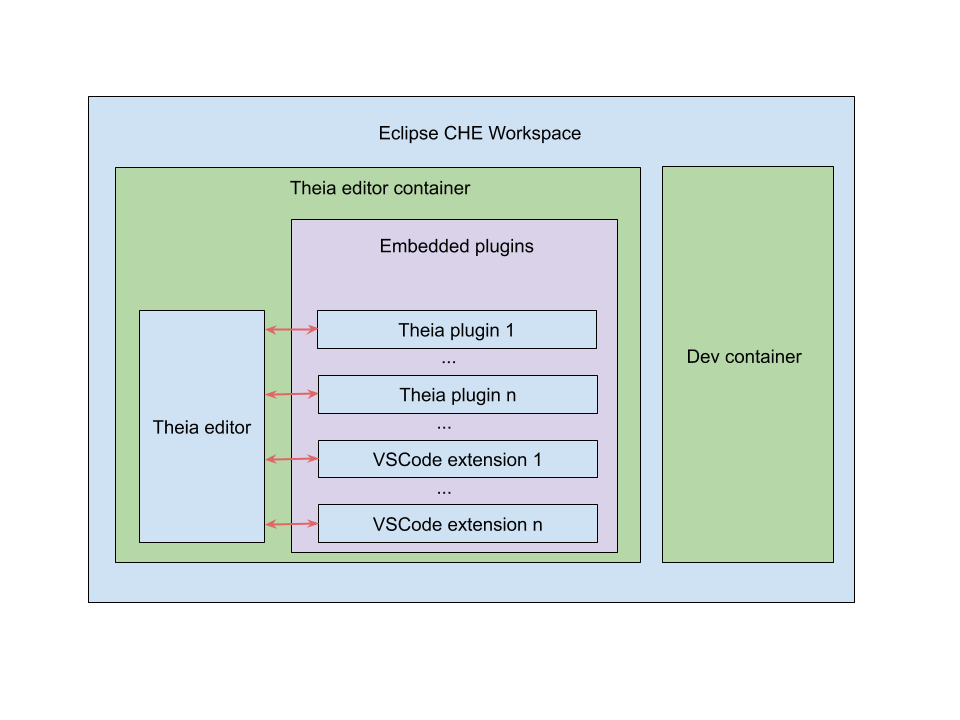
4.1.5.2. Remote plug-ins
The plug-in relies on dependencies or it has a back end. It runs in its own sidecar container, and all dependencies are packaged in the container.
A remote Che-Theia plug-in consist of two parts:
-
Che-Theia plug-in or VS Code extension binaries. The definition in the
meta.yamlfile is the same as for embedded plug-ins. -
Container image definition, for example,
eclipse/che-theia-dev:nightly. From this image, CodeReady Workspaces creates a separate container inside a workspace.
Examples:
- Java Language Server
- Python Language Server
When starting a workspace, CodeReady Workspaces creates a container from the plug-in image, downloads and unpacks the plug-in binaries, and includes them in the created container. The Che-Theia editor connects to the remote plug-ins when it starts.
Figure 4.5. Remote Che-Theia plug-in
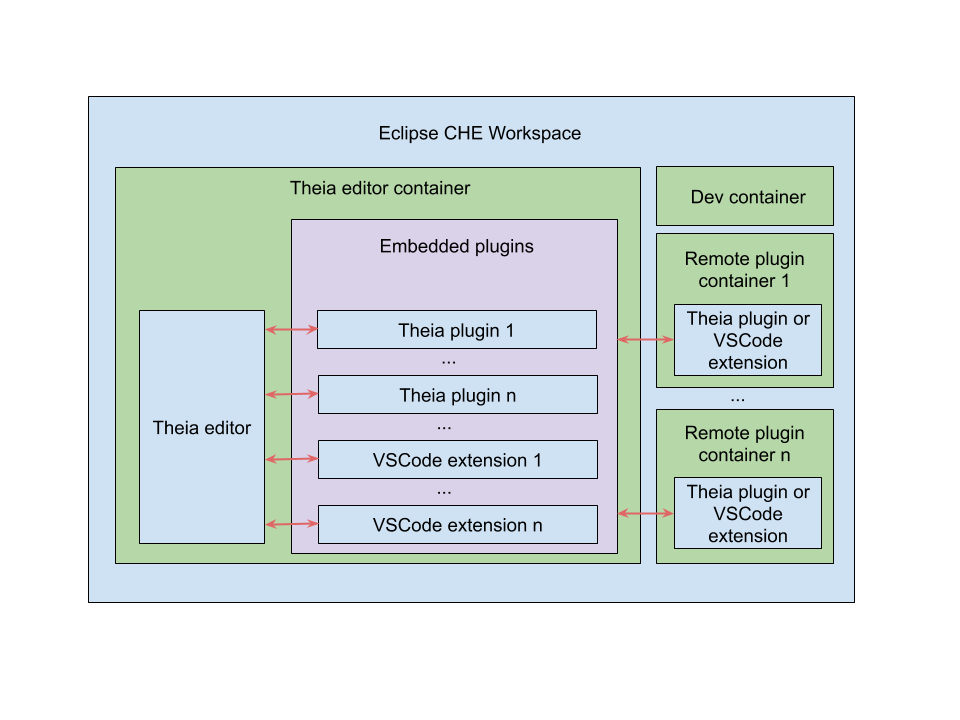
4.1.5.3. Comparison matrix
When a Che-Theia plug-in (or a VS Code extension) does not need extra dependencies inside its container, it is an embedded plug-in. A container with extra dependencies that includes a plug-in is a remote plug-in.
| Configure RAM per plug-in | Environment dependencies | Create separated container | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote | TRUE | Plug-in uses dependencies defined in the remote container. | TRUE |
| Embedded | FALSE (users can configure RAM for the whole editor container, but not per plug-in) | Plug-in uses dependencies from the editor container; if container does not include these dependencies, the plug-in fails or does not function as expected. | FALSE |
Depending on your use case and the capabilities provided by your plug-in, select one of the described running modes.
4.1.6. Remote plug-in endpoint
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces has a remote plug-in endpoint service to start VS Code Extensions and Che-Theia plug-ins in separate containers. Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces injects the remote plug-in endpoint binaries into each remote plug-in container. This service starts remote extensions and plug-ins defined in the plug-in meta.yaml file and connects them to the Che-Theia editor container.
The remote plug-in endpoint creates a plug-in API proxy between the remote plug-in container and the Che-Theia editor container. The remote plug-in endpoint is also an interceptor for some plug-in API parts, which it launches inside a remote sidecar container rather than an editor container. Examples: terminal API, debug API.
The remote plug-in endpoint executable command is stored in the environment variable of the remote plug-in container: PLUGIN_REMOTE_ENDPOINT_EXECUTABLE.
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces provides two ways to start the remote plug-in endpoint with a sidecar image:
- Defining a launch remote plug-in endpoint using a Dockerfile. To use this method, patch an original image and rebuild it.
-
Defining a launch remote plug-in endpoint in the plug-in
meta.yamlfile. Use this method to avoid patching an original image.
4.1.6.1. Defining a launch remote plug-in endpoint using Dockerfile
To start a remote plug-in endpoint, use the PLUGIN_REMOTE_ENDPOINT_EXECUTABLE environment variable in the Dockerfile.
Procedure
Start a remote plug-in endpoint using the
CMDcommand in the Dockerfile:Dockerfile example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start a remote plug-in endpoint using the
ENTRYPOINTcommand in the Dockerfile:Dockerfile example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.1.6.1.1. Using a wrapper script
Some images use a wrapper script to configure permissions. The script is defined it in the ENTRYPOINT command of the Dockerfile to configure permissions inside the container, and it script executes a main process defined in the CMD command of the Dockerfile.
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces uses such images with a wrapper script to provide permission configurations on different infrastructures with advanced security, for example on OpenShift.
Example of a wrapper script:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example of a Dockerfile with a wrapper script:
Dockerfile example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the container launches the
/entrypoint.shscript defined in theENTRYPOINTcommand of the Dockerfile. The script configures the permissions and executes the command usingexec $@.CMDis the argument forENTRYPOINT, and theexec $@command calls${PLUGIN_REMOTE_ENDPOINT_EXECUTABLE}. A remote plug-in endpoint then starts in the container after permission configuration.
4.1.6.2. Defining a launch remote plug-in endpoint in a meta.yaml file
Use this method to re-use images to start remote a plug-in endpoint without modifications.
Procedure
Modify the plug-in meta.yaml file properties command and args:
-
command- Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces uses to overrideDockerfile#ENTRYPOINT. -
args- Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces uses to overrideDockerfile#CMD. Example of a YAML file with the
commandandargsproperties modified:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify
argsinstead ofcommandto use an image with a wrapper script pattern and to keep a call of theentrypoint.shscript:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces calls the
entrypoint.shwrapper script defined in theENTRYPOINTcommand of the Dockerfile. The script executes[ ‘sh’, ‘-c”, ‘ ${PLUGIN_REMOTE_ENDPOINT_EXECUTABLE}’ ]using theexec “$@”command.
To execute a service when starting the container and also to start a remote plug-in endpoint, use meta.yaml with modified command and args properties. Start the service, detach the process, and start the remote plug-in endpoint, and they then work in parallel.
4.2. Using alternative IDEs in CodeReady Workspaces
Extending Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces developer workspaces using different IDEs (integrated development environments) enables:
- Re-purposing the environment for different use cases.
- Providing a dedicated custom IDE for specific tools.
- Providing different perspectives for individual users or groups of users.
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces provides a default web IDE to be used with the developer workspaces. This IDE is completely decoupled. You can bring your own custom IDE for Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces:
- Built from Eclipse Theia, which is a framework to build web IDEs. Example: Sirius on the web.
- Completely different web IDEs, such as Jupyter, Eclipse Dirigible, or others. Example: Jupyter in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspaces.
Bringing custom IDE built from Eclipse Theia
- Creating your own custom IDE based on Eclipse Theia.
- Adding CodeReady Workspaces-specific tools to your custom IDE.
- Packaging your custom IDE into the available editors for CodeReady Workspaces.
Bringing your completely different web IDE into CodeReady Workspaces
- Packaging your custom IDE into the available editors for CodeReady Workspaces.
4.3. Adding tools to CodeReady Workspaces after creating a workspace
When installed in a workspace, CodeReady Workspaces plug-ins bring new capabilities to CodeReady Workspaces. Plug-ins consist of a Che-Theia plug-in, metadata, and a hosting container. These plug-ins may provide the following capabilities:
- Integrating with other systems, including OpenShift.
- Automating some developer tasks, such as formatting, refactoring, and running automated tests.
- Communicating with multiple databases directly from the IDE.
- Enhanced code navigation, auto-completion and error highlighting.
This chapter provides basic information about installing, enabling, and using CodeReady Workspaces plug-ins in workspaces.
4.3.1. Additional tools in the CodeReady Workspaces workspace
CodeReady Workspaces plug-ins are extensions to the Che-Theia IDE that come bundled with a container image that contains their native prerequisites (for example, the OpenShift Connector plug-in needs the oc command installed). Plug-ins can also include metadata to define a description, categorization tags, and an icon. CodeReady Workspaces provides a registry of plug-ins available for installation into the user’s workspace.
The Che-Theia IDE is generally compatible with the VS Code extensions API. This means that many VS Code extensions are automatically compatible with Che-Theia, and can be packaged as CodeReady Workspaces plug-ins by combining them container that contains their dependencies. By default, CodeReady Workspaces includes a plug-in registry containing common plug-ins.
From the Dashboard, plug-ins in the registry can be added from the Plugin tab in the Workspace details page, or by adding them directly into a devfile. The devfile can also be used for further configuration of the plug-in, such defining memory or CPU usage. Alternatively, plug-ins can also be installed from within the Che-Theia IDE by pressing Ctrl+Shift+J or by navigating to View → Plugins.
Additional resources
4.3.2. Adding a language support plug-in to a CodeReady Workspaces workspace
This procedure describes adding a tool to an existing workspace by enabling a dedicated plug-in from the Dashboard.
To add tools that are available as plug-ins into a CodeReady Workspaces workspace, use one of the following methods:
This procedure uses the Java language support plug-in as an example.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
An existing workspace defined in this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces; see:
The workspace must be in a stopped state. To stop a workspace,
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard. See Section 1.1, “Navigating CodeReady Workspaces using the Dashboard”.
- In the Dashboard, click the Workspaces menu to open the workspaces list and locate the workspace.
- On the same row with the displayed workspace, on the right side of the screen, click the square button to stop the workspace.
- Wait a few seconds for the workspace to stop (the workspace’s icon on the list will turn grey), then configure the workspace by clicking on it.
Procedure
To add the plug-in from the Plug-in registry to an existing CodeReady Workspaces workspace, use one of the following methods:
Installing the plug-in from the Plugin tab.
- Navigate to the Plugin tab. The list of available plug-ins is displayed.
- Enable the desired plug-in, for example, the Language Support for Java 11, by using the Enable slide-toggle. This will add the plug-in’s ID to the workspace’s devfile, enabling the plug-in.
- On the bottom right side of the screen, save the changes by clicking the button. After changes are saved, the workspace can be restarted and will include the new plug-in.
Installing the plug-in by adding content to the devfile.
- Navigate to the Devfile tab. The devfile YAML is displayed.
Locate the
componentssection of the devfile and add the following lines to add the Java language plugin with Java 8 to the workspace:- id: redhat/java8/latest type: chePlugin
- id: redhat/java8/latest type: chePluginCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow An example of the final result:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On the bottom right side of the screen, save the changes by clicking the button. After changes are saved, the workspace can be restarted and will include the new plug-in.
Additional resources
Chapter 5. Configuring OAuth authorization
This section describes how to connect Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces as an OAuth application to supported OAuth providers.
5.1. Configuring GitHub OAuth
OAuth for GitHub allows for automatic SSH key upload to GitHub.
Procedure
Set up the GitHub OAuth client. The Authorization callback URL is filled in the next steps.
- Go to the RH-SSO administration console and select the Identity Providers tab.
- Select the GitHub identity provider in the drop-down list.
- Paste the Redirect URI to the Authorization callback URL of the GitHub OAuth application.
- Fill the Client ID and Client Secret from the GitHub oauth app.
- Enable Store Tokens.
- Save the changes of the Github Identity provider and click Register application in the GitHub oauth app page.
5.2. Configuring OpenShift OAuth
For users to interact with OpenShift, they must first authenticate to the OpenShift cluster. OpenShift OAuth is a process in which users prove themselves to a cluster through an API with obtained OAuth access tokens.
Authentication with the Chapter 8, OpenShift Connector overview is a possible way for CodeReady Workspaces users to authenticate with an OpenShift cluster.
The following section describes the OpenShift OAuth configuration options and its use with a CodeReady Workspaces.
Prerequisites
-
The
octool is available.
Procedure
-
To enable OpenShift OAuth automatically, deploy CodeReady Workspaces using the crwctl with the
--os-oauthoption. See thecrwctl server:startspecification chapter. For CodeReady Workspaces deployed in single-user mode:
Register CodeReady Workspaces OAuth client in OpenShift. See the Register an OAuth client in OpenShift chapter.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the OpenShift TLS certificate to the CodeReady Workspaces Java trust store.
Update the OpenShift deployment configuration.
CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_CLIENTID: <client-ID> CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_CLIENTSECRET: <openshift-secret> CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_OAUTH__ENDPOINT: <oauth-endpoint> CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_VERIFY__TOKEN__URL: <verify-token-url>
CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_CLIENTID: <client-ID> CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_CLIENTSECRET: <openshift-secret> CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_OAUTH__ENDPOINT: <oauth-endpoint> CHE_OAUTH_OPENSHIFT_VERIFY__TOKEN__URL: <verify-token-url>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
<client-ID>a name specified in the OpenShift OAuthClient. -
<openshift-secret>a secret specified in the OpenShift OAuthClient. <oauth-endpoint>the URL of the OpenShift OAuth service:- For OpenShift 3 specify the OpenShift master URL.
-
For OpenShift 4 specify the
oauth-openshiftroute.
-
<verify-token-url>request URL that is used to verify the token.<OpenShift master url>/apican be used for OpenShift 3 and 4. - See CodeReady Workspaces configMaps and their behavior.
-
Chapter 6. Using artifact repositories in a restricted environment
This section describes how to manually configure various technology stacks to work with artifacts from in-house repositories using self-signed certificates.
6.1. Using Maven artifact repositories
Maven downloads artifacts that are defined in two locations:
-
Artifact repositories defined in a
pom.xmlfile of the project. Configuring repositories inpom.xmlis not specific to Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. For more information, see the Maven documentation about the POM. -
Artifact repositories defined in a
settings.xmlfile. By default,settings.xmlis located at`~/.m2/settings.xml.
6.1.1. Defining repositories in settings.xml
To specify your own artifact repositories at example.server.org, use the settings.xml file. To do that, ensure, that settings.xml is present in all the containers that use Maven tools, in particular the Maven container and the Java plug-in container.
By default, settings.xml is located at the <home dir>/.m2 directory which is already on persistent volume in Maven and Java plug-in containers and you don’t need to re-create the file each time you restart the workspace if it isn’t in ephemeral mode.
In case you have another container that uses Maven tools and you want to share <home dir>/.m2 folder with this container, you have to specify the custom volume for this specific component in the devfile:
Procedure
Configure your
settings.xmlfile to use artifact repositories atexample.server.org:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.2. Defining Maven settings.xml file across workspaces
To use your own settings.xml file across all your workspaces, create a Secret object (with a name of your choice) in the same project as the workspace. Put the contents of the required settings.xml in the data section of the Secret (possibly along with other files that should reside in the same directory). Labelling and annotating this Secret according to Section 3.8.1, “Mounting a secret as a file into a workspace container” ensures that the contents of the Secret is mounted into the workspace Pod. Note that you need to restart any previously running workspaces for them to use this Secret.
Prerequisites
This is required to set your private credentials to a Maven repository. See the Maven documentation Settings.xml#Servers for additional information.
To mount this settings.xml:
Procedure
Convert
settings.xmlto base64:cat settings.xml | base64
$ cat settings.xml | base64Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the output to a new file,
secret.yaml, which also defines needed annotations and labels:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create this secret in the cluster:
oc apply -f secret.yaml
$ oc apply -f secret.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Start a new workspace. You will see
/home/jboss/.m2/settings.xmlwith your original content in themavencontainer.
6.1.2.1. Openshift 3.11 and OpenShift <1.13
On OpenShift 3.11 , it’s impossible to have multiple VolumeMounts at same path so having devfile with volume /home/jboss/.m2 and secret at /home/jboss/.m2/settings.xml would resolve into the conflict. On these clusters use /home/jboss/.m2/repository as a volume for maven repository in the devfile:
6.1.3. Using self-signed certificates in Maven projects
Internal artifact repositories often do not have a certificate signed by an authority that is trusted by default in Java. They are usually signed by an internal company authority or are self-signed. Configure your tools to accept these certificates by adding them to the Java truststore.
Procedure
Obtain a server certificate file from the repository server. It is often a file named
tls.crt.Create a Java truststore file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Upload the truststore file to
/projects/maven/truststore.jksto make it available for all containers.
Add the truststore file.
In the Maven container:
Add the
javax.net.sslsystem property to theMAVEN_OPTSenvironment variable:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the workspace.
In the Java plug-in container:
In the devfile, add the
javax.net.sslsystem property for the Java language server:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2. Using Gradle artifact repositories
6.2.1. Downloading different versions of Gradle
The recommended way to download any version of Gradle is by using the Gradle Wrapper script. If your project does not have a gradle/wrapper directory, run $ gradle wrapper to configure the Wrapper.
Prerequisites
- The Gradle Wrapper is present in your project.
Procedure
To download a Gradle version from a non-standard location, change your Wrapper settings in /projects/<your_project>/gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.properties:
Change the
distributionUrlproperty to point to a URL of the Gradle distribution ZIP file:properties distributionUrl=http://<url_to_gradle>/gradle-6.1-bin.zip
properties distributionUrl=http://<url_to_gradle>/gradle-6.1-bin.zipCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Alternatively, you may place a Gradle distribution zip file locally in /project/gradle in your workspace.
Change the
distributionUrlproperty to point to a local address of the Gradle distribution zip file:properties distributionUrl=file\:/projects/gradle/gradle-6.1-bin.zip
properties distributionUrl=file\:/projects/gradle/gradle-6.1-bin.zipCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.2. Configuring global Gradle repositories
Use an initialization script to configure global repositories for the workspace. Gradle performs extra configuration before projects are evaluated, and this configuration is used in each Gradle project from the workspace.
Procedure
To set global repositories for Gradle that could be used in each Gradle project in the workspace, create an init.gradle script in the ~/.gradle/ directory:
This file configures Gradle to use a local Maven repository with the given credentials.
The ~/.gradle directory does not persist in the current Java plug-in versions, so you must create the init.gradle script at each workspace start in the Java plug-in sidecar container.
6.2.3. Using self-signed certificates in Gradle projects
Internal artifact repositories often do not have a certificate signed by an authority that is trusted by default in Java. They are usually signed by an internal company authority or are self-signed. Configure your tools to accept these certificates by adding them to the Java truststore.
Procedure
Obtain a server certificate file from the repository server. It is often a file named
tls.crt.Create a Java truststore file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Upload the truststore file to
/projects/gradle/truststore.jksto make it available for all containers.
Add the truststore file in the Gradle container.
Add the
javax.net.sslsystem property to theJAVA_OPTSenvironment variable:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Additional resources
6.3. Using Python artifact repositories
6.3.1. Configuring Python to use a non-standard registry
To specify a non-standard repository for use by the Python pip tool, set the PIP_INDEX_URL environment variable.
Procedure
In your devfile, configure the
PIP_INDEX_URLenvironment variable for the language support and for the development container components:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.2. Using self-signed certificates in Python projects
Internal artifact repositories often do not have a self-signed TLS certificate signed by an authority that is trusted by default. They are usually signed by an internal company authority or are self-signed. Configure your tools to accept these certificates.
Python uses certificates from a file defined in the PIP_CERT environment variable.
Procedure
Obtain the certificate from the non-standard repository and place the certificate file in the
/projects/tls/rootCA.pemfile to make it accessible from all your containers.Notepip accepts certificates in the Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format only. Convert the certificate to the PEM format using OpenSSL if necessary.
Configure the devfile:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4. Using Go artifact repositories
To configure Go in a restricted environment, use the GOPROXY environment variable and the Athens module datastore and proxy.
6.4.1. Configuring Go to use a non-standard-registry
Athens is a Go module datastore and proxy with many configuration options. It can be configured to act only as a module datastore and not as a proxy. An administrator can upload their Go modules to the Athens datastore and have them available across their Go projects. If a project tries to access a Go module that is not in the Athens datastore, the Go build fails.
To work with Athens, configure the
GOPROXYenvironment variable in the devfile of your CLI container:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4.2. Using self-signed certificates in Go projects
Internal artifact repositories often do not have a self-signed TLS certificate signed by an authority that is trusted by default. They are usually signed by an internal company authority or are self-signed. Configure your tools to accept these certificates.
Go uses certificates from a file defined in the SSL_CERT_FILE environment variable.
Procedure
-
Obtain the certificate used by the Athens server in the Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format and place it in the
/projects/tls/rootCA.crtfile to make it accessible from all your containers. -
Right-click the project explorer and select Upload files to upload the
rootCA.crtcertificate file to your Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspace. Add the appropriate environment variables to your devfile:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Additional resources
6.5. Using NuGet artifact repositories
To configure NuGet in a restricted environment, modify the nuget.config file and use the SSL_CERT_FILE environment variable in the devfile to add self-signed certificates.
6.5.1. Configuring NuGet to use a non-standard artifact repository
NuGet searches for configuration files anywhere between the solution directory and the driver root directory. If you put the nuget.config file in the /projects directory, the nuget.config file defines NuGet behavior for all projects in /projects.
Procedure
Create and place the
nuget.configfile in the/projectsdirectory.Example
nuget.configwith a Nexus repository hosted atnexus.example.org:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.5.2. Using self-signed certificates in NuGet projects
Internal artifact repositories often do not have a self-signed TLS certificate signed by an authority that is trusted by default. They are usually signed by an internal company authority or are self-signed. Configure your tools to accept these certificates.
Procedure
-
Obtain the certificate file of a non-standard repository and place it in the
/projects/tls/rootCA.crtfile to make it accessible from all your containers. Specify the location of the certificate file in the
SSL_CERT_FILEenvironment variable in your devfile for the OmniSharp plug-in and for the .NET container.Example of the devfile:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.6. Using npm artifact repositories
npm is usually configured using the npm config command, writing values to the .npmrc files. However, configuration values can also be set using the environment variables beginning with NPM_CONFIG_.
The Javascript/Typescript plug-in used in Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces does not download any artifacts. It is enough to configure npm in the dev-machine component.
Use the following environment variables for configuration:
-
The URL for the artifact repository:
NPM_CONFIG_REGISTRY -
For using a certificate from a file:
NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS
To be able to reference the certificate in a devfile, get a copy of the certificate of the npm repository server and put it inside the /project folder.
An example configuration for the use of an internal repository with a self-signed certificate:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 7. Troubleshooting CodeReady Workspaces
This section provides troubleshooting procedures for most frequent issues an user can came in conflict with.
Additional resources
7.1. Troubleshooting slow workspaces
Sometimes, workspaces can take a long time to start. Tuning can reduce this start time. Depending on the options, administrators or users can do the tuning.
This section includes several tuning options for starting workspaces faster or improving workspace runtime performance.
7.1.1. Improving workspace start time
- Caching images with Image Puller
Role: Administrator
When starting a workspace, OpenShift pulls the images from the registry. A workspace can include many containers meaning that OpenShift pulls Pod’s images (one per container). Depending on the size of the image and the bandwidth, it can take a long time.
Image Puller is a tool that can cache images on each of OpenShift nodes. As such, pre-pulling images can improve start times. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/administration_guide/index#caching-images-for-faster-workspace-start_crw.
- Choosing better storage type
Role: Administrator and user
Every workspace has a shared volume attached. This volume stores the project files, so that when restarting a workspace, changes are still available. Depending on the storage, attach time can take up to a few minutes, and I/O can be slow.
To avoid this problem, use ephemeral or asynchronous storage. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#configuring-storage-types_crw.
- Installing offline
Role: Administrator
Components of CodeReady Workspaces are OCI images. Setup Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces in offline mode (air-gap scenario) to allow for reducing any extra download at runtime as everything needs to be present from the beginning. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-che-in-a-restricted-environment.adoc.
- Optimizing workspace plug-ins
Role: User
When selecting various plug-ins, each plug-in can bring its own sidecar container, which is an OCI image. OpenShift pulls the images of these sidecar containers.
Reduce the number of plug-ins, or disable them to see if start time is faster. See also https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/administration_guide/index#caching-images-for-faster-workspace-start_crw.
- Reducing the number of public endpoints
Role: Administrator
For each endpoint, OpenShift is creating OpenShift Route objects. Depending on the underlying configuration, this creation can be slow.
To avoid this problem, reduce the exposure. For example, to automatically detect a new port listening inside containers and redirect traffic for the processes using a local IP address (
127.0.0.1), the Che-Theia IDE plug-in has three optional routes.By reducing the number of endpoints and checking endpoints of all plug-ins, workspace start can be faster.
- CDN configuration
The IDE editor uses a CDN (Content Delivery Network) to serve content. Check that the content uses a CDN to the client (or a local route for offline setup).
To check that, open Developer Tools in the browser and check for
vendorsin the Network tab.vendors.<random-id>.jsoreditor.main.*should come from CDN URLs.
7.1.2. Improving workspace runtime performance
- Providing enough CPU resources
Plug-ins consume CPU resources. For example, when a plug-in provides IntelliSense features, adding more CPU resources may lead to better performance.
Ensure the CPU settings in the devfile definition (
devfile.yaml) are correct:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Providing enough memory
Plug-ins consume CPU and memory resources. For example, when a plug-in provides IntelliSense features, collecting data can consume all the memory allocated to the container.
Providing more memory to the plug-in can increase performance. Ensure the memory settings in the plug-in definition (
meta.yaml) are correct:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Specifies the memory limit for the plug-in.
In the devfile definition (
devfile.yaml):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Choosing better storage type
- Use ephemeral or asynchronous storage for faster I/O. See https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#configuring-storage-types_crw.
7.2. Troubleshooting network problems
Most often, connection problems occur because a firewall, proxy server, corporate network, or other network is configured in a way that blocks CodeReady Workspaces.
This section describes how to prevent or resolve issues related to corporate network policies. The network administrator may be required to enable ports or the WebSockets protocol, which CodeReady Workspaces requires for proper functionality.
Common scenarios:
- Open additional ports for a specific web site.
- Enable WebSockets on the proxy server.
7.2.1. Enabling the WebSocket protocol
Enabling the WebSocket protocol is critical for the proper functionality of CodeReady Workspaces IDE.
While the WebSocket protocol itself is unaware of proxy servers and firewalls, HTTP servers can share their default HTTP and HTTPS ports with a WebSocket server.
- HTTP: port 80
- HTTPS: port 433
Some proxy servers operate with WebSockets by default, but others prevent WebSockets from working correctly, which causes the connection to fail.
In some cases, the proxy server requires the additional configuration, and the specific proxy servers need an upgrade, which allows WebSockets support.
7.2.2. Troubleshooting WebSocket Secure connections
Secure WebSocket connections improve confidentiality and also reliability because they reduce the risk of interference by bad proxies. CodeReady Workspaces operates under WebSocket Secure connections by default and usually no action is required. Some customer’s security policy blocks some aspects of the WebSocket protocol that causes problems with proper CodeReady Workspaces functionality. Those problems are however out of scope for CodeReady Workspaces support and have to be solved by a network administrator.
To troubleshoot a failing WebSocket Secure (WSS) connection, use the instructions in this section.
Prerequisites
Using a supported web browser:
- Chrome
- Firefox
NoteUsing an unsupported web browser causes a connection interruption, followed by a warning message.
Procedure
Check browser support:
Check that the WebSocket protocol is enabled using a realtime web test in one of the supported browsers.
If the problem is not resolved, follow with the next step.
Check proxy servers and firewalls settings:
Ask the system administrator to check if there is a proxy server or firewall that blocks WebSocket Secure (WSS) connections on port 443.
Possible required actions:
- Add an exception to the firewall.
- Have the proxy intercept WebSocket connection.
Verification
Check that the WebSocket protocol is enabled using a realtime web test in one of the supported browsers.
7.3. Starting a CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode
This section describes how to start the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. See Section 3.3, “Creating and configuring a new CodeReady Workspaces 2.4 workspace”.
Procedure
Find the target workspace from the recent workspaces. Right-click the workspace name to open a context menu. Select the Run in debug mode item:
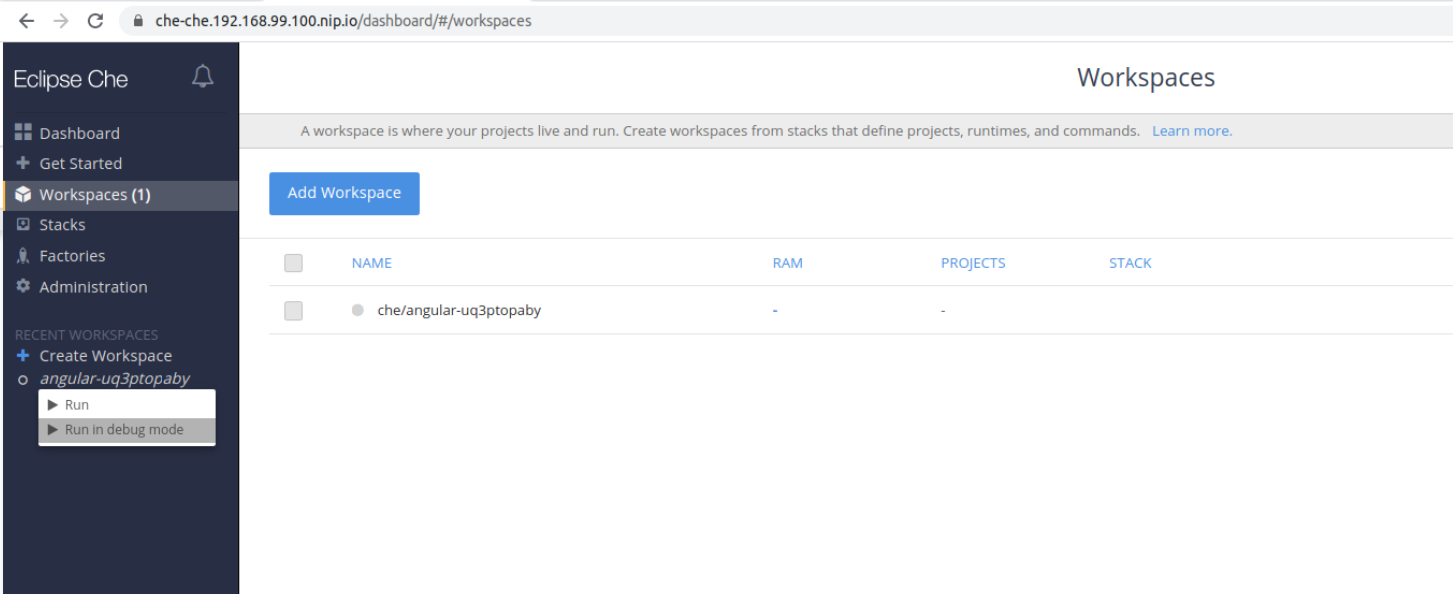
- Click the target workspace to see the logs.
The workspace logs are displayed:
7.4. Restarting a CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode after start failure
This section describes how to restart the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces workspace in debug mode after a failure during workspace start.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
- An existing workspace that failed to start.
Procedure
Find the target workspace from the recent workspaces. Click on the target workspace to see the logs:
- Click the link for restarting in debug mode.
Download full logs after start fail with the Download logs link:
Chapter 8. OpenShift Connector overview
OpenShift Connector, also referred to as Visual Studio Code OpenShift Connector for Red Hat OpenShift, is a plug-in for CodeReady Workspaces that provides a method for interacting with Red Hat OpenShift 3 or 4 clusters.
OpenShift Connector makes it possible to create, build, and debug applications in the CodeReady Workspaces IDE and then deploy the applications directly to a running OpenShift cluster.
OpenShift Connector is a GUI for the OpenShift Do (odo) utility, which aggregates OpenShift CLI (oc) commands into compact units. As such, OpenShift Connector helps new developers who do not have OpenShift background with creating applications and running them on the cloud. Instead of using several oc commands, the user creates a new component or service by selecting a preconfigured template, such as a Project, an Application, or a Service, and then deploys it as an OpenShift Component to their cluster.
This section provides information about installing, enabling, and basic use of the OpenShift Connector plug-in.
- Section 8.1, “Features of OpenShift Connector”
- Section 8.2, “Installing OpenShift Connector in CodeReady Workspaces”
- Section 8.3, “Authenticating with OpenShift Connector from CodeReady Workspaces”
- Section 8.4, “Creating Components with OpenShift Connector in CodeReady Workspaces”
- Section 8.5, “Connecting source code from GitHub to an OpenShift Component using OpenShift Connector”
8.1. Features of OpenShift Connector
The OpenShift Connector plug-in enables the user create, deploy, and push OpenShift Components to an OpenShift Cluster in a GUI.
When used in CodeReady Workspaces, the OpenShift Connector GUI provides the following benefits to its users:
Cluster management
- Logging in to clusters using tokens and username and password combinations.
-
Switching contexts between different
.kube/configentries directly from the extension view. - Viewing and managing OpenShift resources as build and deployment. configurations from the Explorer view.
Development
- Connecting to a local or hosted OpenShift cluster directly from CodeReady Workspaces.
- Quickly updating the cluster with your changes.
- Creating Components, Services, and Routes on the connected cluster.
- Adding storage directly to a component from the extension itself.
Deployment
- Deploying to OpenShift clusters with a single click directly from CodeReady Workspaces.
- Navigating to the multiple Routes, created to access the deployed application.
- Deploying multiple interlinked Components and Services directly on the cluster.
- Pushing and watching component changes from the CodeReady Workspaces IDE.
- Streaming logs directly on the integrated terminal view of CodeReady Workspaces.
Monitoring
- Working with OpenShift resources directly from the CodeReady Workspaces IDE.
- Starting and resuming build and deployment configurations.
- Viewing and following logs for deployments, pods, and containers.
8.2. Installing OpenShift Connector in CodeReady Workspaces
OpenShift Connector is a plug-in designed to create basic OpenShift Components, using CodeReady Workspaces as the editor, and to deploy the Component to an OpenShift cluster. To visually verify that the plug-in is available in your instance, see whether the OpenShift icon is displayed in the CodeReady Workspaces left menu.
To install and enable OpenShift Connector in a CodeReady Workspaces instance, use instructions in this section.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
Procedure
Install OpenShift Connector in CodeReady Workspaces by adding it as an extension in the CodeReady Workspaces Plugins panel.
- Open the CodeReady Workspaces Plugins panel by pressing Ctrl+Shift+J or by navigating to View → Plugins.
- Search for vscode-openshift-connector, and click the button.
- Restart the workspace for the changes to take effect.
- The dedicated OpenShift Application Explorer icon is added to the left panel.
8.3. Authenticating with OpenShift Connector from CodeReady Workspaces
Before the user can develop and push Components from CodeReady Workspaces, they need to authenticate with an OpenShift cluster.
OpenShift Connector offers the following methods for logging in to the OpenShift Cluster from the CodeReady Workspaces instance:
- Using the notification that asks to log in to the OpenShift cluster where CodeReady Workspaces is deployed to.
- Using the button.
- Using the Command Palette.
In CodeReady Workspaces 2.4, Openshift Connector plug-in requires manual connecting to the target cluster
By default, the Openshift Connector plug-in logs into the cluster as inClusterUser, which may not have the manage project permission. This causes an error message to be displayed when a new project is being created using Openshift Application Explorer:
Failed to create Project with error 'Error: Command failed: "/tmp/vscode-unpacked/redhat.vscode-openshift -connector.latest.qvkozqtkba.openshift-connector-0.1.4-523.vsix/extension/out/tools/linux/odo" project create test-project ✗ projectrequests.project.openshift.io is forbidden
Failed to create Project with error 'Error: Command failed: "/tmp/vscode-unpacked/redhat.vscode-openshift -connector.latest.qvkozqtkba.openshift-connector-0.1.4-523.vsix/extension/out/tools/linux/odo" project create test-project ✗ projectrequests.project.openshift.io is forbiddenTo work around this temporary issue, log out from the local cluster and relog in to OpenShift cluster using the OpenShift user’s credentials.
When using a local instance of OpenShift (such as CodeReady Containers or Minishift), the user’s credentials are stored in the workspace ~/.kube/config file, and may be used for automatic authentication in subsequent logins. In the context of CodeReady Workspaces, the ~/.kube/config is stored as a part of the plug-in sidecar container.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- A CodeReady Workspaces workspace has been created.
- The OpenShift Connector plug-in is available.
- The OpenShift OAuth provider is configured (only for the auto-login to the OpenShift cluster where CodeReady Workspaces is deployed. See Section 5.2, “Configuring OpenShift OAuth”).
Procedure
In the left panel, select the OpenShift Application Explorer icon.
The OpenShift Connector panel is displayed.
Log in using the OpenShift Application Explorer. Use one of the following methods:
- Click the button in the top left corner of the pane.
Press F1 to open the Command Palette, or navigate to View → Find Command in the top menu.
Search for OpenShift: Log in to cluster and press Enter.
If a You are already logged in a cluster. message appears, click Yes.
A selection whether to log in using Credentials or Token is displayed at the top of the screen.
Select the method to log in to the cluster and follow the login instructions.
NoteFor authenticating with a token, the required token information is in the top right corner of the main OpenShift Container Platform screen, under <User name> → Copy Login Command.
8.4. Creating Components with OpenShift Connector in CodeReady Workspaces
In the context of OpenShift, Components and Services are basic structures that need to be stored in Application, which is a part of the OpenShift project that organizes deployables into virtual folders for better readability.
This chapter describes how to create OpenShift Components in the CodeReady Workspaces using the OpenShift Connector plug-in and push them to an OpenShift cluster.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of CodeReady Workspaces, see https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_codeready_workspaces/2.4/html-single/installation_guide/index#installing-codeready-workspaces_crw.
- The user is logged in to an OpenShift cluster using the OpenShift Connector plug-in.
Procedure
- In the OpenShift Connector panel, right-click the row with the red OpenShift icon and select New Project.
- Enter a name for your project.
- Right-click the created project and select New Component.
When prompted, enter the name for a new OpenShift Application in which the component can be stored.
The following options of source for your component are displayed:
Git Repository
This prompts you to specify a Git repository URL and select the intended revision of the runtime.
Binary File
This prompts you to select a file from the file explorer.
Workspace Directory
This prompts you to select a folder from the file explorer.
- Enter the name for the component.
- Select the component type.
- Select the component type version.
- The component is created. Right-click the component, select New URL, and enter a name of your choice.
The component is ready to be pushed to the OpenShift cluster. To do so, right-click the component and select Push.
The component is now deployed to the cluster. Right-click for selecting additional actions, such as debugging and opening in a browser (requires port
8080to be exposed).
8.5. Connecting source code from GitHub to an OpenShift Component using OpenShift Connector
When the user has a Git-stored source code that is wanted for further development, it is more efficient to deploy it directly from the Git repository into the OpenShift Connector Component.
This chapter describes how to obtain the content from the Git repository and connect it with a CodeReady Workspaces-developed OpenShift Component.
Prerequisites
- Have a running CodeReady Workspaces workspace.
- Be logged in to the OpenShift cluster using the OpenShift Connector.
Procedure
To make changes to your GitHub component, clone the repository into CodeReady Workspaces to obtain this source code:
- In the CodeReady Workspaces main screen, open the Command Palette by pressing F1.
-
Type the
Git Clonecommand in the Command Palette and press Enter. - Provide the GitHub URL and select the destination for the deployment.
- Add source-code files to your Project by clicking the button.
For additional information about cloning Git repository, see: Accessing a Git repository via HTTPS.