Administration and Configuration Guide
For use with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7.2
Abstract
Part I. Introduction
Chapter 1. Setting up Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
1.1. Prerequisites
The only prerequisites to set up Red Hat JBoss Data Grid is a Java Virtual Machine and that the most recent supported version of the product is installed on your system.
1.2. Steps to Set up Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
The following steps outline the necessary (and optional, where stated) steps for a first time basic configuration of Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. It is recommended that the steps are followed in the order specified and not skipped unless they are identified as optional steps.
Set Up JBoss Data Grid
Set Up the Cache Manager
The foundation of a JBoss Data Grid configuration is a cache manager. Cache managers can retrieve cache instances and create cache instances quickly and easily using previously specified configuration templates. For details about setting up a cache manager, refer to the
Cache Managersection in the JBoss Data Grid Getting Started Guide .Set Up JVM Memory Management
An important step in configuring your JBoss Data Grid is to set up memory management for your Java Virtual Machine (JVM). JBoss Data Grid offers features such as eviction and expiration to help manage the JVM memory.
Set Up Eviction
Use eviction to specify the logic used to remove entries from the in-memory cache implementation based on how often they are used. JBoss Data Grid offers different eviction strategies for finer control over entry eviction in your data grid. Eviction strategies and instructions to configure them are available in Configuring Eviction.
Set Up Expiration
To set upper limits to an entry’s time in the cache, attach expiration information to each entry. Use expiration to set up the maximum period an entry is allowed to remain in the cache and how long the retrieved entry can remain idle before being removed from the cache. For details, see Configuring Expiration.
Monitor Your Cache
JBoss Data Grid uses logging via JBossLogging to help users monitor their caches.
Set Up Logging
It is not mandatory to set up logging for your JBoss Data Grid, but it is highly recommended. JBoss Data Grid uses JBossLogging, which allows the user to easily set up automated logging for operations in the data grid. Logs can subsequently be used to troubleshoot errors and identify the cause of an unexpected failure. For details, see Set Up Logging.
Set Up Cache Modes
Cache modes are used to specify whether a cache is local (simple, in-memory cache) or a clustered cache (replicates state changes over a small subset of nodes). Additionally, if a cache is clustered, either replication, distribution or invalidation mode must be applied to determine how the changes propagate across the subset of nodes. For details, see Set Up Cache Modes.
Set Up Locking for the Cache
When replication or distribution is in effect, copies of entries are accessible across multiple nodes. As a result, copies of the data can be accessed or modified concurrently by different threads. To maintain consistency for all copies across nodes, configure locking. For details, see Set Up Locking for the Cache and Set Up Isolation Levels.
Set Up and Configure a Cache Store
JBoss Data Grid offers the passivation feature (or cache writing strategies if passivation is turned off) to temporarily store entries removed from memory in a persistent, external cache store. To set up passivation or a cache writing strategy, you must first set up a cache store.
Set Up a Cache Store
The cache store serves as a connection to the persistent store. Cache stores are primarily used to fetch entries from the persistent store and to push changes back to the persistent store. For details, see Set Up and Configure a Cache Store.
Set Up Passivation
Passivation stores entries evicted from memory in a cache store. This feature allows entries to remain available despite not being present in memory and prevents potentially expensive write operations to the persistent cache. For details, see Set Up Passivation.
Set Up a Cache Writing Strategy
If passivation is disabled, every attempt to write to the cache results in writing to the cache store. This is the default Write-Through cache writing strategy. Set the cache writing strategy to determine whether these cache store writes occur synchronously or asynchronously. For details, see Set Up Cache Writing.
Monitor Caches and Cache Managers
JBoss Data Grid includes three primary tools to monitor the cache and cache managers once the data grid is up and running.
Set Up JMX
JMX is the standard statistics and management tool used for JBoss Data Grid. Depending on the use case, JMX can be configured at a cache level or a cache manager level or both. For details, see Set Up Java Management Extensions (JMX).
Access the Administration Console
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7.2.1 introduces an Administration Console, allowing for web-based monitoring and management of caches and cache managers. For usage details refer to Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console Getting Started.
Set Up Red Hat JBoss Operations Network (JON)
Red Hat JBoss Operations Network (JON) is the second monitoring solution available for JBoss Data Grid. JBoss Operations Network (JON) offers a graphical interface to monitor runtime parameters and statistics for caches and cache managers. For details, see Set Up Jboss Operations Network(JON).
NoteThe JON plugin has been deprecated in JBoss Data Grid 7.2 and is expected to be removed in a subsequent version.
Introduce Topology Information
Optionally, introduce topology information to your data grid to specify where specific types of information or objects in your data grid are located. Server hinting is one of the ways to introduce topology information in JBoss Data Grid.
Set Up Server Hinting
When set up, server hinting provides high availability by ensuring that the original and backup copies of data are not stored on the same physical server, rack or data center. This is optional in cases such as a replicated cache, where all data is backed up on all servers, racks and data centers. For details, see High Availability Using Server Hinting.
The subsequent chapters detail each of these steps towards setting up a standard JBoss Data Grid configuration.
Part II. Managing JVM Memory
Chapter 2. Eviction and Expiration
Eviction and expiration are strategies for preventing OutOfMemoryError exceptions in the Java heap space. In other words, eviction and expiration ensure that Red Hat JBoss Data Grid does not run out of memory.
2.1. Overview of Eviction and Expiration
- Eviction
- Removes unused entries from memory after the number of entries in the cache reaches a maximum limit.
- The operation is local to a single cache instance. It removes entries from memory only.
- Executes each time an entry is added or updated in the cache.
- Expiration
- Removes entries from memory after a certain amount of time.
- The operation is cluster-wide. It removes entries from memory across all cache instances and also removes entries from the cache store.
-
Expiration operations are processed by threads that you can configure with the
ExpirationManagerinterface.
2.2. Configuring Eviction
You configure Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to perform eviction with the <memory /> element in your cache configuration. Alternatively, you can use the MemoryConfigurationBuilder class to configure eviction programmatically.
2.2.1. Eviction Types
Eviction types define the maximum limit for entries in the cache.
COUNT- Measures the number of entries in the cache. When the count exceeds the maximum, JBoss Data Grid evicts unused entries.
MEMORY- Measures the amount of memory that all entries in the cache take up. When the total amount of memory exceeds the maximum, JBoss Data Grid evicts unused entries.
2.2.2. Storage Types
Storage types define how JBoss Data Grid stores entries in the cache.
| Storage Type | Description | Eviction Type | Policy |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| Stores entries as objects in the Java heap. This is the default storage type. |
| TinyLFU |
|
|
Stores entries as |
| TinyLFU |
|
|
Stores entries as |
| LRU |
The BINARY and OFF-HEAP storage types both violate object equality. This occurs because equality is determined by the equivalence of the resulting bytes[] that the storage types generate instead of the object instances.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes the Caffeine caching library that implements a variation of the Least Frequently Used (LFU) cache replacement algorithm known as TinyLFU. For OFFHEAP JBoss Data Grid uses a custom implementation of the Least Recently Used (LRU) algorithm.
2.2.3. Adding the Memory Element
The <memory> element controls how Red Hat JBoss Data Grid stores entries in memory.
For example, as a starting point to configure eviction for a standalone cache, add the <memory> element as follows:
<local-cache ...> <memory> </memory> </local-cache>
<local-cache ...>
<memory>
</memory>
</local-cache>2.2.4. Specifying the Storage Type
Define the storage type as a child element under <memory>, as follows:
OBJECT<memory> <object/> </memory>
<memory> <object/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow BINARY<memory> <binary/> </memory>
<memory> <binary/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OFFHEAP<memory> <offheap/> </memory>
<memory> <offheap/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.2.5. Specifying the Eviction Type
Include the eviction attribute with the value set to COUNT or MEMORY.
OBJECT<memory> <object/> </memory>
<memory> <object/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipThe
OBJECTstorage type supportsCOUNTonly so you do not need to explicitly set the eviction type.BINARY<memory> <binary eviction="COUNT"/> </memory>
<memory> <binary eviction="COUNT"/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OFFHEAP<memory> <offheap eviction="MEMORY"/> </memory>
<memory> <offheap eviction="MEMORY"/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.2.6. Setting the Cache Size
Include the size attribute with a value set to a number greater than zero.
-
For
COUNT, thesizeattribute sets the maximum number of entries the cache can hold before eviction starts. -
For
MEMORY, thesizeattribute sets the maximum number of bytes the cache can take from memory before eviction starts. For example, a value of10000000000is 10 GB.
Try different cache sizes to determine the optimal setting. A cache size that is too large can cause Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to run out of memory. At the same time, a cache size that is too small wastes available memory.
OBJECT<memory> <object size="100000"/> </memory>
<memory> <object size="100000"/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow BINARY<memory> <binary eviction="COUNT" size="100000"/> </memory>
<memory> <binary eviction="COUNT" size="100000"/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OFFHEAP<memory> <offheap eviction="MEMORY" size="10000000000"/> </memory>
<memory> <offheap eviction="MEMORY" size="10000000000"/> </memory>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.2.7. Tuning the Off Heap Configuration
Include the address-count attribute when using OFFHEAP storage to prevent collisions that might decrease performance. This attribute specifies the number of pointers that are available in the hash map.
Set the value of the address-count attribute to a number that is greater than the number of cache entries. By default address-count is 2^20, or 1048576. The parameter is always rounded up to a power of 2.
<memory> <offheap eviction="MEMORY" size="10000000000" address-count="1048576"/> </memory>
<memory>
<offheap eviction="MEMORY" size="10000000000" address-count="1048576"/>
</memory>2.2.8. Setting the Eviction Strategy
Eviction strategies control how Red Hat JBoss Data Grid performs eviction. You set eviction strategies with the strategy attribute.
The default strategy is NONE, which disables eviction unless you explicitly configure it. For example, here are two configurations that have the same effect:
<memory/>
<memory/><memory> <object strategy="NONE"/> </memory>
<memory>
<object strategy="NONE"/>
</memory>
When you configure eviction, you implicitly use the REMOVE strategy. For example, the following two configurations have the same effect:
<memory> <object/> </memory>
<memory>
<object/>
</memory><memory> <object strategy="REMOVE"/> </memory>
<memory>
<object strategy="REMOVE"/>
</memory>2.2.8.1. Eviction Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
|
| JBoss Data Grid does not evict entries. This is the default setting unless you configure eviction. |
|
| JBoss Data Grid removes entries from memory so that the cache does not exceed the configured size. This is the default setting when you configure eviction. |
|
|
JBoss Data Grid does not perform eviction. Eviction takes place manually by invoking the |
|
|
JBoss Data Grid does not write new entries to the cache if doing so would exceed the configured size. Instead of writing new entries to the cache, JBoss Data Grid throws a |
2.2.9. Configuring Passivation
Passivation configures Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to write entries to a persistent cache store when it removes those entries from memory. In this way, passivation ensures that only a single copy of an entry is maintained, either in-memory or in a cache store but not both.
For more information, see Setting Up Passivation.
2.3. Configuring Expiration
You configure Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to perform expiration at either the entry or cache level.
If you configure expiration for the cache, all entries in that cache inherit that configuration. However, configuring expiration for specific entries takes precedence over configuration for the cache.
You configure expiration for a cache with the <expiration /> element. Alternatively, you can use the ExpirationConfigurationBuilder class to programmatically configure expiration for a cache.
You configure expiration for specific entries with the Cache API.
2.3.1. Expiration Parameters
Expiration parameters configure the amount of time entries can remain in the cache.
lifespan-
Specifies how long entries can remain in the cache before they expire. The default value is
-1, which is unlimited time. max-idle-
Specifies how long entries can remain idle before they expire. An entry in the cache is idle when no operation is performed with the key. The default value is
-1, which is unlimited time. interval-
Specifies the amount of time between expiration operations. The default value is
60000.
While expiration parameters, lifespan and max-idle, are replicated across the cluster, only the value of the lifespan parameter is replicated along with cache entries. For this reason, you should not use the max-idle parameter with clustered caches. For more information on the limitations of using max-idle in clusters, see Red Hat knowledgebase workaround.
2.3.2. Configuring Expiration
Configure Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to perform expiration for a cache as follows:
Add the
<expiration />element<expiration />
<expiration />Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the
lifespanattribute.Specify the amount of time, in milliseconds, that an entry can remain in memory as the value, for example:
<expiration lifespan="1000" />
<expiration lifespan="1000" />Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the
max-idleattribute.Specify the amount of time, in milliseconds, that an entry can remain idle as the value, for example:
<expiration lifespan="1000" max-idle="1000" />
<expiration lifespan="1000" max-idle="1000" />Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the
intervalattribute.Specify the amount of time, in milliseconds, that Red Hat JBoss Data Grid waits between expiration operations, for example:
<expiration lifespan="1000" max-idle="1000" interval="120000" />
<expiration lifespan="1000" max-idle="1000" interval="120000" />Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow TipSet a value of
-1to disable periodic expiration.
2.3.3. Expiration Behavior
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cannot always expire entries immediately when they reach the time limit. Instead, JBoss Data Grid marks entries as expired and removes them when:
- Writing entries to the cache store.
- The maintenance thread that processes expiration identifies entries as expired.
This behavior might indicate that JBoss Data Grid is not performing expiration as expected. However it is the case that the entries are marked as expired but not yet removed from either the memory or the cache store.
To ensure that users cannot receive expired entries, JBoss Data Grid returns null values for entries that are marked as expired but not yet removed.
Part III. Monitoring Your Cache
Chapter 3. Set Up Logging
3.1. About Logging
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides highly configurable logging facilities for both its own internal use and for use by deployed applications. The logging subsystem is based on JBossLogManager and it supports several third party application logging frameworks in addition to JBossLogging.
The logging subsystem is configured using a system of log categories and log handlers. Log categories define what messages to capture, and log handlers define how to deal with those messages (write to disk, send to console, etc).
After a JBoss Data Grid cache is configured with operations such as eviction and expiration, logging tracks relevant activity (including errors or failures).
When set up correctly, logging provides a detailed account of what occurred in the environment and when. Logging also helps track activity that occurred just before a crash or problem in the environment. This information is useful when troubleshooting or when attempting to identify the source of a crash or error.
3.2. Supported Application Logging Frameworks
3.2.1. Supported Application Logging Frameworks
Red Hat JBoss LogManager supports the following logging frameworks:
- JBoss Logging, which is included with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7.
- Apache Commons Logging
- Simple Logging Facade for Java (SLF4J)
- Apache log4j
- Java SE Logging (java.util.logging)
3.2.2. About JBoss Logging
JBoss Logging is the application logging framework that is included in JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 7. As a result of this inclusion, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7 also uses JBoss Logging.
JBoss Logging provides an easy way to add logging to an application. Add code to the application that uses the framework to send log messages in a defined format. When the application is deployed to an application server, these messages can be captured by the server and displayed and/or written to file according to the server’s configuration.
3.2.3. JBoss Logging Features
JBossLogging includes the following features:
- Provides an innovative, easy to use typed logger.
- Full support for internationalization and localization. Translators work with message bundles in properties files while developers can work with interfaces and annotations.
- Build-time tooling to generate typed loggers for production, and runtime generation of typed loggers for development.
3.3. Boot Logging
3.3.1. Boot Logging
The boot log is the record of events that occur while the server is starting up (or booting). Red Hat JBoss Data Grid also includes a server log, which includes log entries generated after the server concludes the boot process.
3.3.2. Configure Boot Logging
Edit the logging.properties file to configure the boot log. This file is a standard Java properties file and can be edited in a text editor. Each line in the file has the format of property=value.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, the logging.properties file is available in the $JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration folder.
3.3.3. Default Log File Locations
The following table provides a list of log files in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid and their locations:
| Log File | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| boot.log | $JDG_HOME/standalone/log/ | The Server Boot Log. Contains log messages related to the start up of the server.
By default this file is prepended to the server.log . This file may be created independently of the server.log by defining the |
| server.log | $JDG_HOME/standalone/log/ | The Server Log. Contains all log messages once the server has launched. |
3.4. Logging Attributes
3.4.1. About Log Levels
Log levels are an ordered set of enumerated values that indicate the nature and severity of a log message. The level of a given log message is specified by the developer using the appropriate methods of their chosen logging framework to send the message.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid supports all the log levels used by the supported application logging frameworks. The six most commonly used log levels are (ordered by lowest to highest severity):
-
TRACE -
DEBUG -
INFO -
WARN -
ERROR -
FATAL
Log levels are used by log categories and handlers to limit the messages they are responsible for. Each log level has an assigned numeric value which indicates its order relative to other log levels. Log categories and handlers are assigned a log level and they only process log messages of that numeric value or higher. For example a log handler with the level of WARN will only record messages of the levels WARN, ERROR and FATAL.
3.4.2. Supported Log Levels
The following table lists log levels that are supported in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Each entry includes the log level, its value and description. The log level values indicate each log level’s relative value to other log levels. Additionally, log levels in different frameworks may be named differently, but have a log value consistent to the provided list.
| Log Level | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FINEST | 300 | - |
| FINER | 400 | - |
| TRACE | 400 |
Used for messages that provide detailed information about the running state of an application. |
| DEBUG | 500 |
Used for messages that indicate the progress of individual requests or activities of an application. |
| FINE | 500 | - |
| CONFIG | 700 | - |
| INFO | 800 | Used for messages that indicate the overall progress of the application. Used for application start up, shut down and other major lifecycle events. |
| WARN | 900 | Used to indicate a situation that is not in error but is not considered ideal. Indicates circumstances that can lead to errors in the future. |
| WARNING | 900 | - |
| ERROR | 1000 | Used to indicate an error that has occurred that could prevent the current activity or request from completing but will not prevent the application from running. |
| SEVERE | 1000 | - |
| FATAL | 1100 | Used to indicate events that could cause critical service failure and application shutdown and possibly cause JBoss Data Grid to shut down. |
3.4.3. About Log Categories
Log categories define a set of log messages to capture and one or more log handlers which will process the messages.
The log messages to capture are defined by their Java package of origin and log level. Messages from classes in that package and of that log level or higher (with greater or equal numeric value) are captured by the log category and sent to the specified log handlers. As an example, the WARNING log level results in log values of 900, 1000 and 1100 are captured.
Log categories can optionally use the log handlers of the root logger instead of their own handlers.
3.4.4. About the Root Logger
The root logger captures all log messages sent to the server (of a specified level) that are not captured by a log category. These messages are then sent to one or more log handlers.
By default the root logger is configured to use a console and a periodic log handler. The periodic log handler is configured to write to the file server.log . This file is sometimes referred to as the server log.
3.4.5. About Log Handlers
Log handlers define how captured log messages are recorded by Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. The six types of log handlers configurable in JBoss Data Grid are:
-
Console -
File -
Periodic -
Size -
Async -
Custom
Log handlers direct specified log objects to a variety of outputs (including the console or specified log files). Some log handlers used in JBoss Data Grid are wrapper log handlers, used to direct other log handlers' behavior.
Log handlers are used to direct log outputs to specific files for easier sorting or to write logs for specific intervals of time. They are primarily useful to specify the kind of logs required and where they are stored or displayed or the logging behavior in JBoss Data Grid.
3.4.6. Log Handler Types
The following table lists the different types of log handlers available in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid:
| Log Handler Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Console |
Console log handlers write log messages to either the host operating system’s standard out ( | The Console log handler is preferred when JBoss Data Grid is administered using the command line. In such a case, the messages from a Console log handler are not saved unless the operating system is configured to capture the standard out or standard error stream. |
| File | File log handlers are the simplest log handlers. Their primary use is to write log messages to a specified file. | File log handlers are most useful if the requirement is to store all log entries according to the time in one place. |
| Periodic | Periodic file handlers write log messages to a named file until a specified period of time has elapsed. Once the time period has elapsed, the specified time stamp is appended to the file name. The handler then continues to write into the newly created log file with the original name. | The Periodic file handler can be used to accumulate log messages on a weekly, daily, hourly or other basis depending on the requirements of the environment. |
| Size | Size log handlers write log messages to a named file until the file reaches a specified size. When the file reaches a specified size, it is renamed with a numeric prefix and the handler continues to write into a newly created log file with the original name. Each size log handler must specify the maximum number of files to be kept in this fashion. | The Size handler is best suited to an environment where the log file size must be consistent. |
| Async | Async log handlers are wrapper log handlers that provide asynchronous behavior for one or more other log handlers. These are useful for log handlers that have high latency or other performance problems such as writing a log file to a network file system. | The Async log handlers are best suited to an environment where high latency is a problem or when writing to a network file system. |
| Custom |
Custom log handlers enable to you to configure new types of log handlers that have been implemented. A custom handler must be implemented as a Java class that extends | Custom log handlers create customized log handler types and are recommended for advanced users. |
3.4.7. Selecting Log Handlers
The following are the most common uses for each of the log handler types available for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid:
-
The
Consolelog handler is preferred when JBoss Data Grid is administered using the command line. In such a case, errors and log messages appear on the console window and are not saved unless separately configured to do so. -
The
Filelog handler is used to direct log entries into a specified file. This simplicity is useful if the requirement is to store all log entries according to the time in one place. -
The
Periodiclog handler is similar to theFilehandler but creates files according to the specified period. As an example, this handler can be used to accumulate log messages on a weekly, daily, hourly or other basis depending on the requirements of the environment. -
The
Sizelog handler also writes log messages to a specified file, but only while the log file size is within a specified limit. Once the file size reaches the specified limit, log files are written to a new log file. This handler is best suited to an environment where the log file size must be consistent. -
The
Asynclog handler is a wrapper that forces other log handlers to operate asynchronously. This is best suited to an environment where high latency is a problem or when writing to a network file system. -
The
Customlog handler creates new, customized types of log handlers. This is an advanced log handler.
3.4.8. About Log Formatters
A log formatter is the configuration property of a log handler. The log formatter defines the appearance of log messages that originate from the relevant log handler. The log formatter is a string that uses the same syntax as the java.util.Formatter class.
See http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/util/Formatter.html for more information.
3.5. Logging Sample Configurations
3.5.1. Logging Sample Configuration Location
All of the sample configurations presented in this section should be placed inside the server’s configuration file, typically either standalone.xml or clustered.xml for standalone instances, or domain.xml for managed domain instances.
3.5.2. Sample XML Configuration for the Root Logger
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for the root logger.
Procedure: Configure the Root Logger
The
levelproperty sets the maximum level of log message that the root logger records.<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:logging:3.0"> <root-logger> <level name="INFO"/><subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:logging:3.0"> <root-logger> <level name="INFO"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow handlersis a list of log handlers that are used by the root logger.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.5.3. Sample XML Configuration for a Log Category
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for a log category.
Configure a Log Category
Use the
categoryproperty to specify the log category from which log messages will be captured.The
use-parent-handlersis set to"true"by default. When set to"true", this category will use the log handlers of the root logger in addition to any other assigned handlers.-
Use the
levelproperty to set the maximum level of log message that the log category records. -
The
handlerselement contains a list of log handlers.
3.5.4. Sample XML Configuration for a Console Log Handler
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for a console log handler.
Configure the Console Log Handler
Add the Log Handler Identifier Information
The
nameproperty sets the unique identifier for this log handler.When
autoflushis set to"true"the log messages will be sent to the handler’s target immediately upon request.Set the
levelPropertyThe
levelproperty sets the maximum level of log messages recorded.Set the
encodingOutputUse
encodingto set the character encoding scheme to be used for the output.Define the
targetValueThe
targetproperty defines the system output stream where the output of the log handler goes. This can beSystem.errfor the system error stream, orSystem.outfor the standard out stream.Define the
filter-specPropertyThe
filter-specproperty is an expression value that defines a filter. The example provided defines a filter that does not match a pattern:not(match("JBAS.*")).Specify the
formatterUse
formatterto list the log formatter used by the log handler.
3.5.5. Sample XML Configuration for a File Log Handler
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for a file log handler.
Configure the File Log Handler
Add the File Log Handler Identifier Information
The
nameproperty sets the unique identifier for this log handler.When
autoflushis set to"true"the log messages will be sent to the handler’s target immediately upon request.Set the
levelPropertyThe
levelproperty sets the maximum level of log message that the root logger records.Set the
encodingOutputUse
encodingto set the character encoding scheme to be used for the output.Set the
fileObjectThe
fileobject represents the file where the output of this log handler is written to. It has two configuration properties:relative-toandpath.The
relative-toproperty is the directory where the log file is written to. JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6 file path variables can be specified here. Thejboss.server.log.dirvariable points to the log/ directory of the server.The
pathproperty is the name of the file where the log messages will be written. It is a relative path name that is appended to the value of therelative-toproperty to determine the complete path.Specify the
formatterUse
formatterto list the log formatter used by the log handler.Set the
appendPropertyWhen the
appendproperty is set to"true", all messages written by this handler will be appended to an existing file. If set to"false"a new file will be created each time the application server launches. Changes toappendrequire a server reboot to take effect.
3.5.6. Sample XML Configuration for a Periodic Log Handler
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for a periodic log handler.
Configure the Periodic Log Handler
Add the Periodic Log Handler Identifier Information
The
nameproperty sets the unique identifier for this log handler.When
autoflushis set to"true"the log messages will be sent to the handler’s target immediately upon request.Set the
levelPropertyThe
levelproperty sets the maximum level of log message that the root logger records.Set the
encodingOutputUse
encodingto set the character encoding scheme to be used for the output.Specify the
formatterUse
formatterto list the log formatter used by the log handler.Set the
fileObjectThe
fileobject represents the file where the output of this log handler is written to. It has two configuration properties:relative-toandpath.The
relative-toproperty is the directory where the log file is written to. JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6 file path variables can be specified here. Thejboss.server.log.dirvariable points to the log/ directory of the server.The
pathproperty is the name of the file where the log messages will be written. It is a relative path name that is appended to the value of therelative-toproperty to determine the complete path.Set the
suffixValueThe
suffixis appended to the filename of the rotated logs and is used to determine the frequency of rotation. The format of thesuffixis a dot (.) followed by a date string, which is parsable by thejava.text.SimpleDateFormatclass. The log is rotated on the basis of the smallest time unit defined by thesuffix. For example,yyyy-MM-ddwill result in daily log rotation. See http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/api/index.html?java/text/SimpleDateFormat.htmlSet the
appendPropertyWhen the
appendproperty is set to"true", all messages written by this handler will be appended to an existing file. If set to"false"a new file will be created each time the application server launches. Changes toappendrequire a server reboot to take effect.
3.5.7. Sample XML Configuration for a Size Log Handler
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for a size log handler.
Configure the Size Log Handler
Add the Size Log Handler Identifier Information
The
nameproperty sets the unique identifier for this log handler.When
autoflushis set to"true"the log messages will be sent to the handler’s target immediately upon request.Set the
levelPropertyThe
levelproperty sets the maximum level of log message that the root logger records.Set the
encodingObjectUse
encodingto set the character encoding scheme to be used for the output.Set the
fileObjectThe
fileobject represents the file where the output of this log handler is written to. It has two configuration properties:relative-toandpath.The
relative-toproperty is the directory where the log file is written to. JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6 file path variables can be specified here. Thejboss.server.log.dirvariable points to the log/ directory of the server.The
pathproperty is the name of the file where the log messages will be written. It is a relative path name that is appended to the value of therelative-toproperty to determine the complete path.Specify the
rotate-sizeValueThe maximum size that the log file can reach before it is rotated. A single character appended to the number indicates the size units:
bfor bytes,kfor kilobytes,mfor megabytes,gfor gigabytes. For example:50mfor 50 megabytes.Set the
max-backup-indexNumberThe maximum number of rotated logs that are kept. When this number is reached, the oldest log is reused.
Specify the
formatterUse
formatterto list the log formatter used by the log handler.Set the
appendPropertyWhen the
appendproperty is set to"true", all messages written by this handler will be appended to an existing file. If set to"false"a new file will be created each time the application server launches. Changes toappendrequire a server reboot to take effect.
3.5.8. Sample XML Configuration for a Async Log Handler
The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration for an async log handler
Configure the Async Log Handler
-
The
nameproperty sets the unique identifier for this log handler. -
The
levelproperty sets the maximum level of log message that the root logger records. -
The
queue-lengthdefines the maximum number of log messages that will be held by this handler while waiting for sub-handlers to respond. -
The
overflow-actiondefines how this handler responds when its queue length is exceeded. This can be set toBLOCKorDISCARD.BLOCKmakes the logging application wait until there is available space in the queue. This is the same behavior as an non-async log handler.DISCARDallows the logging application to continue but the log message is deleted. -
The
subhandlerslist is the list of log handlers to which this async handler passes its log messages.
Part IV. Set Up Cache Modes
Chapter 4. Cache Modes
4.1. Cache Modes
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides two modes:
- Local mode is the only non-clustered cache mode offered in JBoss Data Grid. In local mode, JBoss Data Grid operates as a simple single-node in-memory data cache. Local mode is most effective when scalability and failover are not required and provides high performance in comparison with clustered modes.
- Clustered mode replicates state changes to a subset of nodes. The subset size should be sufficient for fault tolerance purposes, but not large enough to hinder scalability. Before attempting to use clustered mode, it is important to first configure JGroups for a clustered configuration. For details about configuring JGroups, see Configure JGroups (Library Mode)
4.2. About Cache Containers
Cache containers are used in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode as a starting point for a cache. The cache-container element acts as a parent of one or more (local or clustered) caches. To add clustered caches to the container, transport must be defined.
The following procedure demonstrates a sample cache container configuration:
How to Configure the Cache Container
Configure the Cache Container
The
cache-containerelement specifies information about the cache container using the following parameters:-
The
nameparameter defines the name of the cache container. -
The
default-cacheparameter defines the name of the default cache used with the cache container. -
The
statisticsattribute is optional and istrueby default. Statistics are useful in monitoring JBoss Data Grid via JMX or JBoss Operations Network, however they adversely affect performance. Disable this attribute by setting it tofalseif it is not required. -
The
startparameter indicates when the cache container starts, i.e. whether it will start lazily when requested or "eagerly" when the server starts up. Valid values for this parameter areEAGERandLAZY.
-
The
Configure Per-cache Statistics
If
statisticsare enabled at the container level, per-cache statistics can be selectively disabled for caches that do not require monitoring by setting thestatisticsattribute tofalse.
4.3. Local Mode
4.3.1. Local Mode
Using Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s local mode instead of a map provides a number of benefits.
Caches offer features that are unmatched by simple maps, such as:
- Write-through and write-behind caching to persist data.
- Entry eviction to prevent the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) running out of memory.
- Support for entries that expire after a defined period.
JBoss Data Grid is built around a high performance, read-based data container that uses techniques such as optimistic and pessimistic locking to manage lock acquisitions.
JBoss Data Grid also uses compare-and-swap and other lock-free algorithms, resulting in high throughput multi-CPU or multi-core environments. Additionally, JBoss Data Grid’s Cache API extends the JDK's ConcurrentMap, resulting in a simple migration process from a map to JBoss Data Grid.
4.3.2. Configure Local Mode
A local cache can be added to any cache container in both Library Mode and Remote Client-Server Mode. The following example demonstrates how to add the local-cache element.
The local-cache Element
The local-cache element specifies information about the local cache used with the cache container using the following parameters: . The name parameter specifies the name of the local cache to use. . If statistics are enabled at the container level, per-cache statistics can be selectively disabled for caches that do not require monitoring by setting the statistics attribute to false.
Local and clustered caches are able to coexist in the same cache container, however where the container is without a <transport/> it can only contain local caches. The container used in the example can only contain local caches as it does not have a <transport/>.
The cache interface extends the ConcurrentMap and is compatible with multiple cache systems.
4.4. Clustered Modes
4.4.1. Clustered Modes
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid offers the following clustered modes:
- Replication Mode replicates any entry that is added across all cache instances in the cluster.
- Invalidation Mode does not share any data, but signals remote caches to initiate the removal of invalid entries.
- Distribution Mode stores each entry on a subset of nodes instead of on all nodes in the cluster.
The clustered modes can be further configured to use synchronous or asynchronous transport for network communications.
4.4.2. Asynchronous and Synchronous Operations
When a clustered mode (such as invalidation, replication or distribution) is used, data is propagated to other nodes in either a synchronous or asynchronous manner.
If synchronous mode is used, the sender waits for responses from receivers before allowing the thread to continue, whereas asynchronous mode transmits data but does not wait for responses from other nodes in the cluster to continue operations.
JBoss Data Grid clusters are configured to use synchronous operations by default.
4.4.3. About Asynchronous Communications
Asynchronous mode prioritizes speed over consistency, which is ideal for use cases such as HTTP session replications with sticky sessions enabled. Such a session (or data for other use cases) is always accessed on the same cluster node, unless this node fails. If data consistency is required for your use case, you should use synchronous operations.
Additionally, it is not possible for JBoss Data Grid nodes to determine if asynchronous operations succeed because receiving nodes do not send status for operations back to the originating nodes.
In JBoss Data Grid, distributed and replicated caches are represented by the distributed-cache and replicated-cache elements.
Each of these elements contains a mode property, the value of which can be set to SYNC for synchronous, which is the default, or ASYNC for asynchronous communications.
Asynchronous Communications Example Configuration
<replicated-cache name="default"
statistics="true"
mode="ASYNC">
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</replicated-cache>
<replicated-cache name="default"
statistics="true"
mode="ASYNC">
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</replicated-cache>
The preceding configuration is valid for both JBoss Data Grid usage modes (Library mode and Remote Client-Server mode). However, this configuration does not apply to local caches local-cache because they are not clustered and do not communicate with other nodes.
4.4.4. Cache Mode Troubleshooting
4.4.4.1. Invalid Data in ReadExternal
If invalid data is passed to readExternal, it can be because when using Cache.putAsync(), starting serialization can cause your object to be modified, causing the datastream passed to readExternal to be corrupted. This can be resolved if access to the object is synchronized.
4.4.4.2. Cluster Physical Address Retrieval
How can the physical addresses of the cluster be retrieved?
The physical address can be retrieved using an instance method call. For example: AdvancedCache.getRpcManager().getTransport().getPhysicalAddresses() .
Chapter 5. Set Up Distribution Mode
5.1. About Distribution Mode
In distribution mode, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid stores cache entries across a subset of nodes in the cluster instead of replicating entries on each node. This improves JBoss Data Grid scalability.
5.2. Consistent Hashing in Distribution Mode
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid uses an algorithm based on consistent hashing to distribute cache entries on nodes across clusters. JBoss Data Grid splits keys in distributed caches into fixed numbers of hash space segments, using MurmurHash3 by default.
Segments are distributed across the cluster to nodes that act as primary and backup owners. Primary owners coordinate locking and write operations for the keys in each segment. Backup owners provide redundancy in the event the primary owner becomes unavailable.
You configure the number of owners with the owners attribute. This attribute defines how many copies of each entry are available across the cluster. The default value is 2, a primary owner and one backup owner.
You can configure the number of hash space segments with the segments attribute. This attribute defines the hash space segments for the named cache across the cluster. The cache always has the configured number of hash segments available across the JBoss Data Grid cluster, no matter how many nodes join or leave.
Additionally, the key-to-segment mapping is fixed. In other words, keys always map to the same segments, regardless of changes to the cluster topology.
The default number of segments is 256, which is suitable for JBoss Data Grid clusters of 25 nodes or less. The recommended value is 20 * the number of nodes for each cluster, which allows you to add nodes and still have capacity.
However, any value within the range of 10 * the number of nodes and 100 * the number of nodes per cluster is fine.
With a perfect segment-to-node mapping, nodes are:
-
primary owner for segments calculated as
number of segments / number of nodes -
any kind of owner for segments calculated as
number of owners * number of segments / number of nodes
However, JBoss Data Grid does not always distribute segments evenly and can map more segments to some nodes than others.
Consider a scenario where a cluster has 10 nodes and there are 20 segments per node. If segments are distributed evenly across the cluster, each node is the primary owner for 2 segments. If segments are not distributed evenly, some nodes are primary owners for 3 segments, which represents an increase of 50% for the planned capacity.
Likewise, if the number of owners is 2, each node should own 4 segments. However it could be the case that some nodes are owners for 5 segments, which represents a 25% increase for the planned capacity.
You must restart the JBoss Data Grid cluster for changes to the number of segments to take effect.
5.3. Locating Entries in Distribution Mode
The consistent hash algorithm used in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s distribution mode can locate entries deterministically, without multicasting a request or maintaining expensive metadata.
A PUT operation can result in as many remote calls as specified by the owners parameter, while a GET operation executed on any node in the cluster results in a single remote call. In the background, the GET operation results in the same number of remote calls as a PUT operation (specifically the value of the owners parameter), but these occur in parallel and the returned entry is passed to the caller as soon as one returns.
5.4. Return Values in Distribution Mode
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s distribution mode, a synchronous request is used to retrieve the previous return value if it cannot be found locally. A synchronous request is used for this task irrespective of whether distribution mode is using asynchronous or synchronous processes.
5.5. Configure Distribution Mode
Distribution mode is a clustered mode in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Distribution mode can be added to any cache container, in both Library Mode and Remote Client-Server Mode, using the following procedure:
The distributed-cache Element
The distributed-cache element configures settings for the distributed cache using the following parameters:
-
The
nameparameter provides a unique identifier for the cache. -
If
statisticsare enabled at the container level, per-cache statistics can be selectively disabled for caches that do not require monitoring by setting thestatisticsattribute tofalse.
JGroups must be appropriately configured for clustered mode before attempting to load this configuration.
5.6. Synchronous and Asynchronous Distribution
To elicit meaningful return values from certain public API methods, it is essential to use synchronized communication when using distribution mode.
Communication Mode example
For example, with three nodes in a cluster, node A, B and C, and a key K that maps nodes A and B. Perform an operation on node C that requires a return value, for example Cache.remove(K). To execute successfully, the operation must first synchronously forward the call to both node A and B, and then wait for a result returned from either node A or B. If asynchronous communication was used, the usefulness of the returned values cannot be guaranteed, despite the operation behaving as expected.
Chapter 6. Set Up Replication Mode
6.1. About Replication Mode
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s replication mode is a simple clustered mode. Cache instances automatically discover neighboring instances on other Java Virtual Machines (JVM) on the same network and subsequently form a cluster with the discovered instances. Any entry added to a cache instance is replicated across all cache instances in the cluster and can be retrieved locally from any cluster cache instance.
In JBoss Data Grid’s replication mode, return values are locally available before the replication occurs.
6.2. Optimized Replication Mode Usage
Replication mode is used for state sharing across a cluster; however, if you have a replicated cache and a large number of nodes are in use then there will be many writes to the replicated cache to keep all of the nodes synchronized. The amount of work performed will depend on many factors and on the specific use case, and for this reason it is recommended to ensure that each workload is tested thoroughly to determine if replication mode will be beneficial with the number of planned nodes. For many situations replication mode is not recommended once there are ten servers; however, in some workloads, such as if load read is important, this mode may be beneficial.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid can be configured to use UDP multicast, which improves performance to a limited degree for larger clusters.
6.3. Configure Replication Mode
Replication mode is a clustered cache mode in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Replication mode can be added to any cache container, in both Library Mode and Remote Client-Server Mode, using the following procedure.
The replicated-cache Element
JGroups must be appropriately configured for clustered mode before attempting to load this configuration.
The replicated-cache element configures settings for the distributed cache using the following parameters:
-
The
nameparameter provides a unique identifier for the cache. -
If
statisticsare enabled at the container level, per-cache statistics can be selectively disabled for caches that do not require monitoring by setting thestatisticsattribute tofalse.
For details about the cache-container and locking, see the appropriate chapter.
6.4. Synchronous and Asynchronous Replication
6.4.1. Synchronous and Asynchronous Replication
Replication mode can be synchronous or asynchronous depending on the problem being addressed.
-
Synchronous replication blocks a thread or caller (for example on a
put()operation) until the modifications are replicated across all nodes in the cluster. By waiting for acknowledgments, synchronous replication ensures that all replications are successfully applied before the operation is concluded. - Asynchronous replication operates significantly faster than synchronous replication because it does not need to wait for responses from nodes. Asynchronous replication performs the replication in the background and the call returns immediately. Errors that occur during asynchronous replication are written to a log. As a result, a transaction can be successfully completed despite the fact that replication of the transaction may not have succeeded on all the cache instances in the cluster.
6.4.2. Troubleshooting Asynchronous Replication Behavior
In some instances, a cache configured for asynchronous replication or distribution may wait for responses, which is synchronous behavior. This occurs because caches behave synchronously when both state transfers and asynchronous modes are configured. This synchronous behavior is a prerequisite for state transfer to operate as expected.
Use one of the following to remedy this problem:
-
Disable state transfer and use a
ClusteredCacheLoaderto lazily look up remote state as and when needed. -
Enable state transfer and
REPL_SYNC. Use the Asynchronous API (for example, thecache.putAsync(k, v)) to activate 'fire-and-forget' capabilities. -
Enable state transfer and
REPL_ASYNC. All RPCs end up becoming synchronous, but client threads will not be held up if a replication queue is enabled (which is recommended for asynchronous mode).
6.5. The Replication Queue
6.5.1. The Replication Queue
In replication mode, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid uses a replication queue to replicate changes across nodes based on the following:
- Previously set intervals.
- The queue size exceeding the number of elements.
- A combination of previously set intervals and the queue size exceeding the number of elements.
The replication queue ensures that during replication, cache operations are transmitted in batches instead of individually. As a result, a lower number of replication messages are transmitted and fewer envelopes are used, resulting in improved JBoss Data Grid performance.
A disadvantage of using the replication queue is that the queue is periodically flushed based on the time or the queue size. Such flushing operations delay the realization of replication, distribution, or invalidation operations across cluster nodes. When the replication queue is disabled, the data is directly transmitted and therefore the data arrives at the cluster nodes faster.
A replication queue is used in conjunction with asynchronous mode.
6.5.2. Replication Queue Usage
When using the replication queue, do one of the following:
- Disable asynchronous marshalling.
Set the
max-threadscount value to1for theexecutorattribute of thetransportelement. Theexecutoris only available in Library Mode, and is therefore defined in its configuration file as follows:<transport executor="infinispan-transport"/>
<transport executor="infinispan-transport"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To implement either of these solutions, the replication queue must be in use in asynchronous mode. Asynchronous mode can be set by defining mode="ASYNC", as seen in the following example:
Replication Queue in Asynchronous Mode
<replicated-cache name="asyncCache"
mode="ASYNC"
statistics="true"
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</replicated-cache>
<replicated-cache name="asyncCache"
mode="ASYNC"
statistics="true"
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</replicated-cache>The replication queue allows requests to return to the client faster, therefore using the replication queue together with asynchronous marshalling does not present any significant advantages.
6.6. About Replication Guarantees
In a clustered cache, the user can receive synchronous replication guarantees as well as the parallelism associated with asynchronous replication. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides an asynchronous API for this purpose.
The asynchronous methods used in the API return Futures, which can be queried. The queries block the thread until a confirmation is received about the success of any network calls used.
6.7. Replication Traffic on Internal Networks
Some cloud providers charge less for traffic over internal IP addresses than for traffic over public IP addresses, or do not charge at all for internal network traffic (for example, ). To take advantage of lower rates, you can configure Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to transfer replication traffic using the internal network. With such a configuration, it is difficult to know the internal IP address you are assigned. JBoss Data Grid uses JGroups interfaces to solve this problem.
Chapter 7. Set Up Invalidation Mode
7.1. About Invalidation Mode
Invalidation is a clustered mode that does not share any data, but instead removes potentially obsolete data from remote caches. Using this cache mode requires another, more permanent store for the data such as a database.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, in such a situation, is used as an optimization for a system that performs many read operations and prevents database usage each time a state is needed.
When invalidation mode is in use, data changes in a cache prompts other caches in the cluster to evict their outdated data from memory.
7.2. Configure Invalidation Mode
Invalidation mode is a clustered mode in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Invalidation mode can be added to any cache container, in both Library Mode and Remote Client-Server Mode, using the following procedure:
The invalidation-cache Element
The invalidation-cache element configures settings for the distributed cache using the following parameters:
-
The
nameparameter provides a unique identifier for the cache. -
If
statisticsare enabled at the container level, per-cache statistics can be selectively disabled for caches that do not require monitoring by setting thestatisticsattribute tofalse.
JGroups must be appropriately configured for clustered mode before attempting to load this configuration.
For details about the cache-container see the appropriate chapter.
7.3. Synchronous/Asynchronous Invalidation
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode, invalidation operates either asynchronously or synchronously.
- Synchronous invalidation blocks the thread until all caches in the cluster have received invalidation messages and evicted the obsolete data.
- Asynchronous invalidation operates in a fire-and-forget mode that allows invalidation messages to be broadcast without blocking a thread to wait for responses.
7.4. The L1 Cache and Invalidation
An invalidation message is generated each time a key is updated. This message is multicast to each node that contains data that corresponds to current L1 cache entries. The invalidation message ensures that each of these nodes marks the relevant entry as invalidated.
Chapter 8. State Transfer
8.1. State Transfer
State transfer is a basic data grid or clustered cache functionality. Without state transfer, data would be lost as nodes are added to or removed from the cluster.
State transfer adjusts the cache’s internal state in response to a change in a cache membership. The change can be when a node joins or leaves, when two or more cluster partitions merge, or a combination of joins, leaves, and merges. State transfer occurs automatically in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid whenever a node joins or leaves the cluster.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s replication mode, a new node joining the cache receives the entire cache state from the existing nodes. In distribution mode, the new node receives only a part of the state from the existing nodes, and the existing nodes remove some of their state in order to keep owners copies of each key in the cache (as determined through consistent hashing). In invalidation mode the initial state transfer is similar to replication mode, the only difference being that the nodes are not guaranteed to have the same state. When a node leaves, a replicated mode or invalidation mode cache does not perform any state transfer. A distributed cache needs to make additional copies of the keys that were stored on the leaving nodes, again to keep owners copies of each key.
A State Transfer transfers both in-memory and persistent state by default, but both can be disabled in the configuration. When State Transfer is disabled a ClusterLoader must be configured, otherwise a node will become the owner or backup owner of a key without the data being loaded into its cache. In addition, if State Transfer is disabled in distributed mode then a key will occasionally have less than owners owners.
8.2. Non-Blocking State Transfer
Non-Blocking State Transfer in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid minimizes the time in which a cluster or node is unable to respond due to a state transfer in progress. Non-blocking state transfer is a core architectural improvement with the following goals:
- Minimize the interval(s) where the entire cluster cannot respond to requests because of a state transfer in progress.
- Minimize the interval(s) where an existing member stops responding to requests because of a state transfer in progress.
- Allow state transfer to occur with a drop in the performance of the cluster. However, the drop in the performance during the state transfer does not throw any exception, and allows processes to continue.
-
Allows a
GEToperation to successfully retrieve a key from another node without returning a null value during a progressive state transfer.
For simplicity, the total order-based commit protocol uses a blocking version of the currently implemented state transfer mechanism. The main differences between the regular state transfer and the total order state transfer are:
- The blocking protocol queues the transaction delivery during the state transfer.
- State transfer control messages (such as CacheTopologyControlCommand) are sent according to the total order information.
The total order-based commit protocol works with the assumption that all the transactions are delivered in the same order and they see the same data set. So, no transactions are validated during the state transfer because all the nodes must have the most recent key or values in memory.
Using the state transfer and blocking protocol in this manner allows the state transfer and transaction delivery on all on the nodes to be synchronized. However, transactions that are already involved in a state transfer (sent before the state transfer began and delivered after it concludes) must be resent. When resent, these transactions are treated as new joiners and assigned a new total order value.
8.3. Suppress State Transfer via JMX
State transfer can be suppressed using JMX in order to bring down and relaunch a cluster for maintenance. This operation permits a more efficient cluster shutdown and startup, and removes the risk of Out Of Memory errors when bringing down a grid.
When a new node joins the cluster and rebalancing is suspended, the getCache() call will timeout after stateTransfer.timeout expires unless rebalancing is re-enabled or stateTransfer.awaitInitialTransferis set to false.
Disabling state transfer and rebalancing can be used for partial cluster shutdown or restart, however there is the possibility that data may be lost in a partial cluster shutdown due to state transfer being disabled.
8.4. The rebalancingEnabled Attribute
Suppressing rebalancing can only be triggered via the rebalancingEnabled JMX attribute, and requires no specific configuration.
The rebalancingEnabled attribute can be modified for the entire cluster from the LocalTopologyManager JMX Mbean on any node. This attribute is true by default, and is configurable programmatically.
Servers such as Hot Rod attempt to start all caches declared in the configuration during startup. If rebalancing is disabled, the cache will fail to start. Therefore, it is mandatory to use the following setting in a server environment:
<state-transfer enabled="true" await-initial-transfer="false"/>
<state-transfer enabled="true" await-initial-transfer="false"/>Part V. Enabling APIs
Chapter 9. Enabling APIs Declaratively
9.1. Enabling APIs Declaratively
The various APIs that JBoss Data Grid provides are fully documented in the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide ; however, Administrators can enable these declaratively by adding elements to the configuration file. The following sections discuss methods on implementing the various APIs.
9.2. Batching API
Batching allows atomicity and some characteristics of a transaction, but does not allow full-blown JTA or XA capabilities. Batching is typically lighter and cheaper than a full-blown transaction, and should be used whenever the only participant in the transaction is the JBoss Data Grid cluster. If the transaction involves multiple systems then JTA Transactions should be used. For example, consider a transaction which transfers money from one bank account to another. If both accounts are stored within the JBoss Data Grid cluster then batching could be used; however, if only one account is inside the cluster, with the second being in an external database, then distributed transactions are required.
Transaction batching is only available in JBoss Data Grid’s Library Mode.
Enabling the Batching API
Batching may be enabled on a per-cache basis by defining a transaction mode of BATCH. The following example demonstrates this:
<local-cache name="batchingCache"> <transaction mode="BATCH"/> </local-cache>
<local-cache name="batchingCache">
<transaction mode="BATCH"/>
</local-cache>By default invocation batching is disabled; in addition, a transaction manager is not required to use batching.
9.3. Grouping API
The grouping API allows a group of entries to be co-located on the same node, instead of the default behavior of having each entry being stored on a node corresponding to a calculated hash code of the entry. By default JBoss Data Grid will take a hash code of each key when it is stored and map that key to a hash segment; this allows an algorithm to be used to determine the node that contains the key, allowing each node in the cluster to know which node contains the key without distributing ownership information. This behavior reduces overhead and improves redundancy as the ownership information does not need to be replicated should a node fail.
By enabling the grouping API the hash of the key is ignored when deciding which node to store the entry on. Instead, a hash of the group is obtained and used in its place, while the hash of the key is used internally to prevent performance degradation. When the group API is in use every node can still determine the owners of the key, and due to this reason the group may not be manually specified. A group may either be intrinsic to the entry, generated by the key class, or extrinsic to the entry, generated by an external function.
Enabling the Grouping API
The grouping API may be enabled on a per-cache basis by adding the groups element as seen in the following example:
<distributed-cache name="groupingCache">
<groups enabled="true"/>
</distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache name="groupingCache">
<groups enabled="true"/>
</distributed-cache>Defining an Extrinsic Group
Assuming a custom Grouper exists it may be defined by passing in the classname as seen below:
<distributed-cache name="groupingCache">
<groups enabled="true">
<grouper class="com.acme.KXGrouper" />
</groups>
</distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache name="groupingCache">
<groups enabled="true">
<grouper class="com.acme.KXGrouper" />
</groups>
</distributed-cache>9.4. Externalizable API
9.4.1. The Externalizable API
An Externalizer is a class that can:
- Marshall a given object type to a byte array.
- Unmarshall the contents of a byte array into an instance of the object type.
Externalizers are used by Red Hat JBoss Data Grid and allow users to specify how their object types are serialized. The marshalling infrastructure used in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid builds upon JBoss Marshalling and provides efficient payload delivery and allows the stream to be cached. The stream caching allows data to be accessed multiple times, whereas normally a stream can only be read once.
The Externalizable interface uses and extends serialization. This interface is used to control serialization and deserialization in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
9.4.2. Register the Advanced Externalizer (Declaratively)
After the advanced externalizer is set up, register it for use with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. This registration is done declaratively (via XML) as follows:
Register the Advanced Externalizer
-
Add the
serializationelement to thecache-containerelement. -
Add the
advanced-externalizerelement, defining the custom Externalizer with theclassattribute. Replace theBook$BookExternalizervalues as required.
9.4.3. Configuring the Deserialization Whitelist
For security reasons, the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server does not deserialize objects of an arbitrary class. JBoss Data Grid allows deserialization only for strings and primitives. If you want JBoss Data Grid to deserialize objects for other Java class instances, you must configure a deserialization whitelist.
Add the following system properties to the JVM at start up:
-
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.classesSpecifies the fully qualified names of one or more Java classes. JBoss Data Grid deserializes objects that belong to those classes. -
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.regexpsSpecifies one or more regular expressions. JBoss Data Grid deserializes objects that belong to any class that matches those expressions.
Both system properties are optional. You can specify a combination of both properties or specify either property by itself.
For example, the following system properties enable deserialization for the com.foo.bar.spotprice.Price and com.foo.bar.spotprice.Currency classes as well as for any classes that match the .*SpotPrice.* expression:
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.classes=com.foo.bar.spotprice.Price,com.foo.bar.spotprice.Currency -Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.regexps=.*SpotPrice.*
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.classes=com.foo.bar.spotprice.Price,com.foo.bar.spotprice.Currency
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.regexps=.*SpotPrice.*If you want to configure the whitelist so that JBoss Data Grid allows deserialization for any Java class, specify the following:
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.regexps=.*
-Dinfinispan.deserialization.whitelist.regexps=.*For information on configuring clients to restrict deserialization to specific Java classes, see Restricting Deserialization to Specific Java Classes in the Developer Guide.
9.4.4. Custom Externalizer ID Values
9.4.4.1. Custom Externalizer ID Values
Advanced externalizers can be assigned custom IDs if desired. Some ID ranges are reserved for other modules or frameworks and must be avoided:
| ID Range | Reserved For |
|---|---|
| 1000-1099 | The Infinispan Tree Module |
| 1100-1199 | Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server modules |
| 1200-1299 | Hibernate Infinispan Second Level Cache |
| 1300-1399 | JBoss Data Grid Lucene Directory |
| 1400-1499 | Hibernate OGM |
| 1500-1599 | Hibernate Search |
| 1600-1699 | Infinispan Query Module |
| 1700-1799 | Infinispan Remote Query Module |
| 1800-1849 | JBoss Data Grid Scripting Module |
| 1850-1899 | JBoss Data Grid Server Event Logger Module |
| 1900-1999 | JBoss Data Grid Remote Store |
9.4.4.2. Customize the Externalizer ID (Declaratively)
Customize the advanced externalizer ID declaratively (via XML) as follows:
Customizing the Externalizer ID (Declaratively)
-
Add the
serializationelement to thecache-containerelement. -
Add the
advanced-externalizerelement to add information about the new advanced externalizer. -
Define the externalizer ID using the
idattribute. Ensure that the selected ID is not from the range of IDs reserved for other modules. -
Define the externalizer class using the
classattribute. Replace theBook$BookExternalizervalues as required.
Chapter 10. Set Up and Configure the Infinispan Query API
10.1. Set Up Infinispan Query
10.1.1. Infinispan Query Dependencies in Library Mode
To use the JBoss Data Grid Infinispan Query via Maven, add the following dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.infinispan</groupId>
<artifactId>infinispan-embedded-query</artifactId>
<version>${infinispan.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.infinispan</groupId>
<artifactId>infinispan-embedded-query</artifactId>
<version>${infinispan.version}</version>
</dependency>Non-Maven users must install all of the infinispan-embedded-query.jar and infinispan-embedded.jar files from the JBoss Data Grid distribution.
The Infinispan query API directly exposes the Hibernate Search and the Lucene APIs and cannot be embedded within the infinispan-embedded-query.jar file. Do not include other versions of Hibernate Search and Lucene in the same deployment as infinispan-embedded-query . This action will cause classpath conflicts and result in unexpected behavior.
10.2. Directory Providers
10.2.1. Directory Providers
The following directory providers are supported in Infinispan Query:
- RAM Directory Provider
- Filesystem Directory Provider
- Infinispan Directory Provider
10.2.2. RAM Directory Provider
Storing the global index locally in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Query Module allows each node to
- maintain its own index.
-
use
Lucene's in-memory or filesystem-based index directory.
The following example demonstrates an in-memory, RAM-based index store:
<local-cache name="indexesInMemory">
<indexing index="LOCAL">
<property name="default.directory_provider">ram</property>
</indexing>
</local-cache>
<local-cache name="indexesInMemory">
<indexing index="LOCAL">
<property name="default.directory_provider">ram</property>
</indexing>
</local-cache>10.2.3. Filesystem Directory Provider
To configure the storage of indexes, set the appropriate properties when enabling indexing in the JBoss Data Grid configuration.
This example shows a disk-based index store:
Disk-based Index Store
10.2.4. Infinispan Directory Provider
In addition to the Lucene directory implementations, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid also ships with an infinispan-directory module.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid only supports infinispan-directory in the context of the Querying feature, not as a standalone feature.
The infinispan-directory allows Lucene to store indexes within the distributed data grid. This allows the indexes to be distributed, stored in-memory, and optionally written to disk using the cache store for durability.
Sharing the same index instance using the Infinispan Directory Provider introduces a write contention point, as only one instance can write on the same index at the same time.
By default the exclusive_index_use is set to true, as this provides major performance increases; however, if external applications access the same index in use by Infinispan this property must be set to false. The default value is recommended for the majority of applications and use cases due to the performance increases, so only change this if absolutely necessary.
InfinispanIndexManager provides a default back end that sends all updates to master node which later applies the updates to the index. In case of master node failure, the update can be lost, therefore keeping the cache and index non-synchronized. Non-default back ends are not supported.
Enable Shared Indexes
When using an indexed, clustered cache ensure that the caches containing the index data are also clustered, as described in Tuning Infinispan Directory.
10.3. Configure Indexing
10.3.1. Configure the Index in Remote Client-Server Mode
In Remote Client-Server Mode, index configuration depends on the provider and its configuration. The indexing mode depends on the provider and whether or not it is local or distributed.
The following indexing modes are supported:
- NONE
- LOCAL = indexLocalOnly="true"
- ALL = indexLocalOnly="false"
Index configuration in Remote Client-Server Mode is as follows:
Configuration in Remote Client-Server Mode
<indexing index="LOCAL">
<property name="default.directory_provider">ram</property>
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</indexing>
<indexing index="LOCAL">
<property name="default.directory_provider">ram</property>
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</indexing>Configure Lucene Caches
By default the Lucene caches will be created as local caches; however, with this configuration the Lucene search results are not shared between nodes in the cluster. To prevent this define the caches required by Lucene in a clustered mode, as seen in the following configuration snippet:
Configuring the Lucene cache in Remote Client-Server Mode
These caches are discussed in further detail at in the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide .
10.3.2. Automatic Indexing
You can use the auto-config attribute to automatically configure indexing based on the cache type.
- Replicated and local caches: Indexing is persisted to disk and is not shared with other processes. Indexing is also configured so that there is minimum delay between the time an object is indexed and the time it becomes available for searches.
- Distributed caches: Indexing is handled internally to Red Hat JBoss Data Grid as a master-slave mechanism so that indexing operations are delegated to a single node that writes to the index.
The following XML snippet shows a local cache configuration with the auto-config attribute:
<local-cache name="default"> <indexing index="LOCAL" auto-config="true"> </indexing> </local-cache>
<local-cache name="default">
<indexing index="LOCAL" auto-config="true">
</indexing>
</local-cache>
The auto-config attribute adds properties to the cache. You can tune the indexing behavior by re-defining the properties or adding new properties.
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| filesystem | Use a filesystem to store the index. |
|
| true | Perform indexing operations in exclusive mode. This mode allows Hibernate Search to optimize writes. |
|
| near-real-time | Use Lucene’s Near-Real-Time (NRT) search feature. |
|
| shared | Reuse the index reader across several queries. |
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| infinispan | Store indexes interally to JBoss Data Grid. |
|
| true | Perform indexing operations in exclusive mode. This mode allows Hibernate Search to optimize writes. |
|
| org.infinispan.query.indexmanager.InfinispanIndexManager | Delegate index write operations to a single node in the cluster. |
|
| shared | Reuse the index reader across several queries. |
10.3.3. Rebuilding the Index
You can manually rebuild the Lucene index if required. However, you do not usually need to rebuild the index manually because JBoss Data Grid maintains the index during normal operation.
Rebuilding the index actually reconstructs the entire index from the data store, which requires JBoss Data Grid to process all data in the grid and can take a very long time to complete. You should only need to rebuild the Lucene index if:
- The definition of what is indexed in the types has changed.
-
A parameter affecting how the index is defined, such as the
Analyserchanges. - The index is destroyed or corrupted, possibly due to a system administration error.
Rebuilding the index may be performed by executing the Start operation on the MassIndexer MBean.
10.4. Tuning the Index
10.4.1. Near-Realtime Index Manager
By default, each update is immediately flushed into the index. In order to achieve better throughput, the updates can be batched. However, this can result in a lag between the update and query — the query can see outdated data. If this is acceptable, you can use the Near-Realtime Index Manager by setting the following.
<property name="default.indexmanager">near-real-time</property>
<property name="default.indexmanager">near-real-time</property>10.4.2. Tuning Infinispan Directory
Lucene directory uses three caches to store the index:
- Data cache
- Metadata cache
- Locking cache
Configuration for these caches can be set explicitly, specifying the cache names as in the example below, and configuring those caches as usual. All of these caches must be clustered unless Infinispan Directory is used in local mode.
Tuning the Infinispan Directory
10.4.3. Per-Index Configuration
The indexing properties in examples above apply for all indices - this is because we use the default. prefix for each property. To specify different configuration for each index, replace default with the index name. By default, this is the full class name of the indexed object, however you can override the index name in the @Indexed annotation.
Chapter 11. The Health Check API
11.1. The Health Check API
The Health Check API allows users to monitor the health of the cluster, and the caches contained within. This information is particularly important when working in a cloud environment, as it provides a method of querying to report the status of the cluster or cache.
This API exposes the following information:
- The name of the cluster.
- The number of machines in the cluster.
The overall status of the cluster or cache, represented in one of three values:
- Healthy - The entity is healthy.
- Unhealthy - The entity is unhealthy. This value indicates that one or more caches are in a degraded state.
- Rebalancing - The entity is operational, but a rebalance is in progress. Cluster nodes should not be adjusted when this value is reported.
- The status of each cache.
- A tail of the server log.
For information on using the Health Check API programmatically, refer to the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide.
11.2. Accessing the Health API using JMX
The Health Check API may be accessed through JMX, as seen in the following steps:
- Connect to the JBoss Data Grid node using JMX, such as by Connecting to JDG via JConsole.
-
Expand
jboss.datagrid-infinispan. -
Expand
CacheManager. -
Select the desired cache manager. By default the cache manager will be named
local, if the server was started in local mode, orclustered, if the server was started in a clustered mode. -
Expand the
CacheContainerHealthobject. - The Health Check API attributes are now available to be viewed.
An example of this using JConsole is seen below:
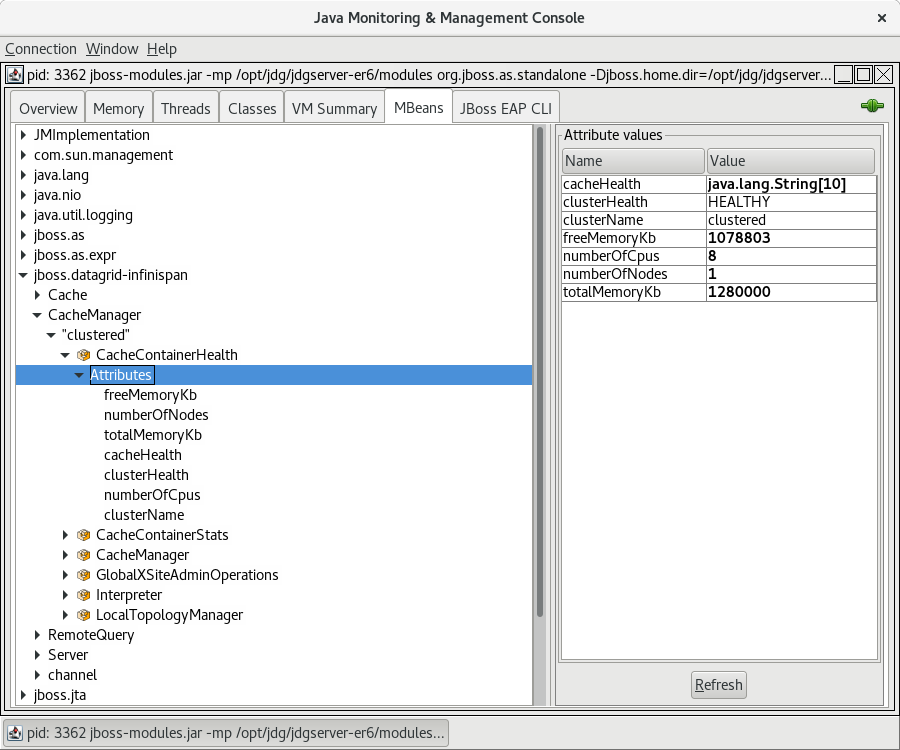
11.3. Accessing the Health Check API using the CLI
The Health Check API may be accessed using the included CLI. Once connected to the server use the following command, substituting the desired cache container for CONTAINERNAME:
/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=CONTAINERNAME/health=HEALTH:read-resource(include-runtime=true)
/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=CONTAINERNAME/health=HEALTH:read-resource(include-runtime=true)
The following demonstrates sample output from the above command, using the clustered cache-container:
11.4. Accessing the Health Check API using the Management REST Interface
The Health Check API is integrated into the Management REST interface as Metrics (read-only runtime resources).
Due to the metrics being exposed in runtime a HTTP POST method must be used instead of the typical HTTP GET.
To access these Metrics a HTTP POST method must be sent that contains valid user credentials. The following command demonstrates one such request:
curl --digest -L -D - "http://JDGADDRESS:_JDGPORT_/management/subsystem/datagrid-infinispan/cache-container/CONTAINERNAME/health/HEALTH?operation=resource&include-runtime=true&json.pretty=1" --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u username:password
curl --digest -L -D - "http://JDGADDRESS:_JDGPORT_/management/subsystem/datagrid-infinispan/cache-container/CONTAINERNAME/health/HEALTH?operation=resource&include-runtime=true&json.pretty=1" --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u username:passwordThe following properties should be substituted from the above command:
- JDGADDRESS - This should be the hostname or IP address where the JBoss Data Grid server is located.
- JDGPORT - This should be the port where the management interface is listening. By default this is 9990.
-
CONTAINERNAME - This should be the name of the cache container to query. By default the cache manager will be named
local, if the server was started in local mode, orclustered, if the server was started in a clustered mode. - username - The username for accessing the Administration Console.
- password - The associated password for accessing the Administration Console.
If successful, a 200 response should be received along with the health status, such as seen below:
Part VI. Remote Client-Server Mode Interfaces
Chapter 12. Remote Client-Server Mode Interfaces
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid offers the following APIs to interact with the data grid in Remote Client-Server mode:
- The Hot Rod Interface, including the RemoteCache API
- The Asynchronous API (can only be used in conjunction with the Hot Rod Client in Remote Client-Server Mode)
- The REST Interface
- The Memcached Interface
Chapter 13. The Hot Rod Interface
13.1. About Hot Rod
Hot Rod is a binary TCP client-server protocol used in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. It was created to overcome deficiencies in other client/server protocols, such as Memcached.
Hot Rod will failover on a server cluster that undergoes a topology change. Hot Rod achieves this by providing regular updates to clients about the cluster topology.
Hot Rod enables clients to do smart routing of requests in partitioned or distributed Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server clusters. To do this, Hot Rod allows clients to determine the partition that houses a key and then communicate directly with the server that has the key. This functionality relies on Hot Rod updating the cluster topology with clients, and that the clients use the same consistent hash algorithm as the servers.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid contains a server module that implements the Hot Rod protocol. The Hot Rod protocol facilitates faster client and server interactions in comparison to other text-based protocols and allows clients to make decisions about load balancing, failover and data location operations.
13.2. The Benefits of Using Hot Rod over Memcached
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid offers a choice of protocols for allowing clients to interact with the server in a Remote Client-Server environment. When deciding between using memcached or Hot Rod, the following should be considered.
- Memcached
The memcached protocol causes the server endpoint to use the
memcached text wire protocol. Thememcached wire protocolhas the benefit of being commonly used, and is available for almost any platform. All of JBoss Data Grid’s functions, including clustering, state sharing for scalability, and high availability, are available when using memcached.However the memcached protocol lacks dynamicity, resulting in the need to manually update the list of server nodes on your clients in the event one of the nodes in a cluster fails. Also, memcached clients are not aware of the location of the data in the cluster. This means that they will request data from a non-owner node, incurring the penalty of an additional request from that node to the actual owner, before being able to return the data to the client. This is where the Hot Rod protocol is able to provide greater performance than memcached.
- Hot Rod
JBoss Data Grid’s Hot Rod protocol is a binary wire protocol that offers all the capabilities of memcached, while also providing better scaling, durability, and elasticity.
The Hot Rod protocol does not need the hostnames and ports of each node in the remote cache, whereas memcached requires these parameters to be specified. Hot Rod clients automatically detect changes in the topology of clustered Hot Rod servers; when new nodes join or leave the cluster, clients update their Hot Rod server topology view. Consequently, Hot Rod provides ease of configuration and maintenance, with the advantage of dynamic load balancing and failover.
Additionally, the Hot Rod wire protocol uses smart routing when connecting to a distributed cache. This involves sharing a consistent hash algorithm between the server nodes and clients, resulting in faster read and writing capabilities than memcached.
When using JCache over Hot Rod it is not possible to create remote clustered caches, as the operation is executed on a single node as opposed to the entire cluster; however, once a cache has been created on the cluster it may be obtained using the cacheManager.getCache method.
It is recommended to create caches using either configuration files or the CLI.
13.3. Hot Rod Hash Functions
Hot Rod uses the same algorithm as on the server. The Hot Rod client always connects to the primary owner of the key, which is the first node in the list of owners. For more information about consistent hashing in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, see Distribution Mode’s Consistent Hash Algorithm.
13.4. The Hot Rod Interface Connector
13.4.1. The Hot Rod Interface Connector
The following enables a Hot Rod server using the hotrod socket binding.
<hotrod-connector socket-binding="hotrod" cache-container="local" />
<hotrod-connector socket-binding="hotrod"
cache-container="local" />
The connector creates a supporting topology cache with default settings. These settings can be tuned by adding the <topology-state-transfer /> child element to the connector as follows:
The Hot Rod connector can be tuned with additional settings. See Configure Hot Rod Connectors for more information on how to configure the Hot Rod connector.
The Hot Rod connector can provide security and authentication, using TLS/SSL and SASL, respectively. See the Securing Interfaces section of the Developer Guide for more information.
13.4.2. Configure Hot Rod Connectors
The following procedure describes the attributes used to configure the Hot Rod connector in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server Mode. Both the hotrod-connector and topology-state-transfer elements must be configured based on the following procedure.
Configuring Hot Rod Connectors for Remote Client-Server Mode
The
hotrod-connectorelement defines the configuration elements for use with Hot Rod.-
The
socket-bindingparameter specifies the socket binding port used by the Hot Rod connector. This is a mandatory parameter. -
The
cache-containerparameter names the cache container used by the Hot Rod connector. This is a mandatory parameter. -
The
worker-threadsparameter specifies the number of worker threads available for the Hot Rod connector. The default value for this parameter is160. This is an optional parameter. -
The
idle-timeoutparameter specifies the time, in seconds, that the connector can remain idle before the connection times out. The default value for this parameter is0, which means that no timeout period is set. This is an optional parameter. -
The
tcp-nodelayparameter specifies whether TCP packets will be delayed and sent out in batches. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. The default value for this parameter istrue. This is an optional parameter. -
The
send-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the send buffer for the Hot Rod connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter. -
The
receive-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the receive buffer for the Hot Rod connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter.
-
The
The
topology-state-transferelement specifies the topology state transfer configurations for the Hot Rod connector. This element can only occur once within ahotrod-connectorelement.-
The
lock-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) after which the operation attempting to obtain a lock times out. The default value for this parameter is10seconds. This is an optional parameter. -
The
replication-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) after which the replication operation times out. The default value for this parameter is10seconds. This is an optional parameter. -
The
external-hostparameter specifies the hostname sent by the Hot Rod server to clients listed in the topology information. The default value for this parameter is the host address. This is an optional parameter. -
The
external-portparameter specifies the port sent by the Hot Rod server to clients listed in the topology information. The default value for this parameter is the configured port. This is an optional parameter. -
The
lazy-retrievalparameter indicates whether the Hot Rod connector will carry out retrieval operations lazily. The default value for this parameter istrue. This is an optional parameter.
-
The
Chapter 14. The REST Interface
14.1. The REST Interface
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides a REST interface, allowing for loose coupling between the client and server. Its primary benefit is interoperability with existing HTTP clients, along with providing a connection for php clients. In addition, the need for specific versions of client libraries and bindings is eliminated.
The REST API introduces an overhead, and requires a REST client or custom code to understand and create REST calls. It is recommended to use the Hot Rod client where performance is a concern.
To interact with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s REST API only a HTTP client library is required. For Java, this may be the Apache HTTP Commons Client, or the java.net API.
The following examples assume that REST security is disabled on the REST connector. To disable REST security remove the authentication and encryption elements from the connector.
14.2. The REST Interface Connector
14.2.1. The REST Interface Connector
The REST connector differs from the Hot Rod and Memcached connectors because it requires a web subsystem. Therefore configurations such as socket-binding, worker threads, timeouts, etc, must be performed on the web subsystem.
Once the REST interface has been enabled on the server it may be used normally for adding, removing, and retrieving data. For information on these processes refer to the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide .
14.2.2. Configure REST Connectors
Use the following procedure to configure the rest-connector element in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode.
Configuring REST Connectors for Remote Client-Server Mode
<subsystem xmlns="urn:infinispan:server:endpoint:8.1">
<rest-connector cache-container="local"
context-path="${CONTEXT_PATH}"/>
</subsystem>
<subsystem xmlns="urn:infinispan:server:endpoint:8.1">
<rest-connector cache-container="local"
context-path="${CONTEXT_PATH}"/>
</subsystem>
The rest-connector element specifies the configuration information for the REST connector.
-
The
cache-containerparameter names the cache container used by the REST connector. This is a mandatory parameter. -
The
context-pathparameter specifies the context path for the REST connector. The default value for this parameter is an empty string (""). This is an optional parameter.
Chapter 15. The Memcached Interface
15.1. The Memcached Interface
Memcached is an in-memory caching system used to improve response and operation times for database-driven websites. The Memcached caching system defines a text based protocol called the Memcached protocol. The Memcached protocol uses in-memory objects or (as a last resort) passes to a persistent store such as a special memcached database.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid offers a server that uses the Memcached protocol, removing the necessity to use Memcached separately with JBoss Data Grid. Additionally, due to JBoss Data Grid’s clustering features, its data failover capabilities surpass those provided by Memcached.
15.2. About Memcached Servers
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid contains a server module that implements the memcached protocol. This allows memcached clients to interact with one or multiple JBoss Data Grid based memcached servers.
The servers can be either:
- Standalone, where each server acts independently without communication with any other memcached servers.
- Clustered, where servers replicate and distribute data to other memcached servers.
15.3. Memcached Statistics
The following table contains a list of valid statistics available using the memcached protocol in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
| Statistic | Data Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| uptime | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the time (in seconds) that the memcached instance has been available and running. |
| time | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the current time. |
| version | String | Contains the current version. |
| curr_items | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the number of items currently stored by the instance. |
| total_items | 32-bit unsigned integer. | Contains the total number of items stored by the instance during its lifetime. |
| cmd_get | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of get operation requests (requests to retrieve data). |
| cmd_set | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of set operation requests (requests to store data). |
| get_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys that are present from the keys requested. |
| get_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys that were not found from the keys requested. |
| delete_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be deleted that were located and successfully deleted. |
| delete_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be deleted that were not located and therefore could not be deleted. |
| incr_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be incremented that were located and successfully incremented |
| incr_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be incremented that were not located and therefore could not be incremented. |
| decr_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be decremented that were located and successfully decremented. |
| decr_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be decremented that were not located and therefore could not be decremented. |
| cas_hits | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be compared and swapped that were found and successfully compared and swapped. |
| cas_misses | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys to be compared and swapped that were not found and therefore not compared and swapped. |
| cas_badval | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of keys where a compare and swap occurred but the original value did not match the supplied value. |
| evictions | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the number of eviction calls performed. |
| bytes_read | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of bytes read by the server from the network. |
| bytes_written | 64-bit unsigned integer | Contains the total number of bytes written by the server to the network. |
15.4. The Memcached Interface Connector
15.4.1. The Memcached Interface Connector
The following enables a Memcached server using the memcached socket binding, and exposes the memcachedCache cache declared in the local container, using defaults for all other settings.
<memcached-connector socket-binding="memcached" cache-container="local"/>
<memcached-connector socket-binding="memcached"
cache-container="local"/>Due to the limitations in the Memcached protocol, only one cache can be exposed by a connector. To expose more than one cache, declare additional memcached-connectors on different socket-bindings. See Configure Memcached Connectors.
15.4.2. Configure Memcached Connectors
The following procedure describes the attributes used to configure the memcached connector within the connectors element in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server Mode.
Configuring the Memcached Connector in Remote Client-Server Mode
The memcached-connector element defines the configuration elements for use with memcached.
-
The
socket-bindingparameter specifies the socket binding port used by the memcached connector. This is a mandatory parameter. -
The
cache-containerparameter names the cache container used by the memcached connector. This is a mandatory parameter. -
The
worker-threadsparameter specifies the number of worker threads available for the memcached connector. The default value for this parameter is 160. This is an optional parameter. -
The
idle-timeoutparameter specifies the time, in seconds, that the connector can remain idle before the connection times out. The default value for this parameter is0, which means that no timeout period is set. This is an optional parameter. -
The
tcp-nodelayparameter specifies whether TCP packets will be delayed and sent out in batches. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. The default value for this parameter istrue. This is an optional parameter. -
The
send-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the send buffer for the memcached connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter. -
The
receive-buffer-sizeparameter indicates the size of the receive buffer for the memcached connector. The default value for this parameter is the size of the TCP stack buffer. This is an optional parameter.
Part VII. Set Up Locking for the Cache
Chapter 16. Locking
16.1. Locking
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides locking mechanisms to prevent dirty reads (where a transaction reads an outdated value before another transaction has applied changes to it) and non-repeatable reads.
16.2. Configure Locking (Remote Client-Server Mode)
In Remote Client-Server mode, locking is configured using the locking element within the cache tags (for example, invalidation-cache, distributed-cache, replicated-cache or local-cache).
The default isolation mode for the Remote Client-Server mode configuration is READ_COMMITTED. If the isolation attribute is included to explicitly specify an isolation mode, it is ignored, a warning is thrown, and the default value is used instead.
The following is a sample procedure of a basic locking configuration for a default cache in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode.
Configure Locking (Remote Client-Server Mode)
-
The
acquire-timeoutparameter specifies the number of milliseconds after which lock acquisition will time out. -
The
concurrency-levelparameter defines the number of lock stripes used by the LockManager. -
The
stripingparameter specifies whether lock striping will be used for the local cache.
16.3. Configure Locking (Library Mode)
For Library mode, the locking element and its parameters are set within the default element found within cache element. An example of this configuration on a local cache is below:
Configure Locking (Library Mode)
-
The
concurrency-levelparameter specifies the concurrency level for the lock container. Set this value according to the number of concurrent threads interacting with the data grid. -
The
isolationparameter specifies the cache’s isolation level. Valid isolation levels areREAD_COMMITTEDandREPEATABLE_READ. For details about isolation levels, see About Isolation Levels. -
The
acquire-timeoutparameter specifies time (in milliseconds) after which a lock acquisition attempt times out. -
The
stripingparameter specifies whether a pool of shared locks are maintained for all entries that require locks. If set toFALSE, locks are created for each entry in the cache. For details, see About Lock Striping. -
The
write-skewparameter is only valid if theisolationis set toREPEATABLE_READ. If this parameter is set toFALSE, a disparity between a working entry and the underlying entry at write time results in the working entry overwriting the underlying entry. If the parameter is set toTRUE, such conflicts (namely write skews) throw an exception. Thewrite-skewparameter can be only used withOPTIMISTICtransactions and it requires entry versioning to be enabled, withSIMPLEversioning scheme.
16.4. Locking Types
16.4.1. About Optimistic Locking
Optimistic locking allows multiple transactions to complete simultaneously by deferring lock acquisition to the transaction prepare time.
Optimistic mode assumes that multiple transactions can complete without conflict. It is ideal where there is little contention between multiple transactions running concurrently, as transactions can commit without waiting for other transaction locks to clear. With write-skew enabled, transactions in optimistic locking mode roll back if one or more conflicting modifications are made to the data before the transaction completes.
16.4.2. About Pessimistic Locking
Pessimistic locking is also known as eager locking.
Pessimistic locking prevents more than one transaction to modify a value of a key by enforcing cluster-wide locks on each write operation. Locks are only released once the transaction is completed either through committing or being rolled back.
Pessimistic mode is used where a high contention on keys is occurring, resulting in inefficiencies and unexpected roll back operations.
16.4.3. Pessimistic Locking Types
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes explicit pessimistic locking and implicit pessimistic locking:
- Explicit Pessimistic Locking, which uses the JBoss Data Grid Lock API to allow cache users to explicitly lock cache keys for the duration of a transaction. The Lock call attempts to obtain locks on specified cache keys across all nodes in a cluster. This attempt either fails or succeeds for all specified cache keys. All locks are released during the commit or rollback phase.
- Implicit Pessimistic Locking ensures that cache keys are locked in the background as they are accessed for modification operations. Using Implicit Pessimistic Locking causes JBoss Data Grid to check and ensure that cache keys are locked locally for each modification operation. Discovering unlocked cache keys causes JBoss Data Grid to request a cluster-wide lock to acquire a lock on the unlocked cache key.
16.4.4. Explicit Pessimistic Locking Example
The following is an example of explicit pessimistic locking that depicts a transaction that runs on one of the cache nodes:
Transaction with Explicit Pessimistic Locking
tx.begin() cache.lock(K) cache.put(K,V5) tx.commit()
tx.begin()
cache.lock(K)
cache.put(K,V5)
tx.commit()-
When the line
cache.lock(K)executes, a cluster-wide lock is acquired onK. -
When the line
cache.put(K,V5)executes, it guarantees success. -
When the line
tx.commit()executes, the locks held for this process are released.
16.4.5. Implicit Pessimistic Locking Example
An example of implicit pessimistic locking using a transaction that runs on one of the cache nodes is as follows:
Transaction with Implicit Pessimistic locking
tx.begin() cache.put(K,V) cache.put(K2,V2) cache.put(K,V5) tx.commit()
tx.begin()
cache.put(K,V)
cache.put(K2,V2)
cache.put(K,V5)
tx.commit()-
When the line
cache.put(K,V)executes, a cluster-wide lock is acquired onK. -
When the line
cache.put(K2,V2)executes, a cluster-wide lock is acquired onK2. -
When the line
cache.put(K,V5)executes, the lock acquisition is non operational because a cluster-wide lock forKhas been previously acquired. Theputoperation will still occur. -
When the line
tx.commit()executes, all locks held for this transaction are released.
16.4.6. Configure Locking Mode (Remote Client-Server Mode)
To configure a locking mode in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, use the transaction element as follows:
<transaction locking="{OPTIMISTIC/PESSIMISTIC}" />
<transaction locking="{OPTIMISTIC/PESSIMISTIC}" />16.4.7. Configure Locking Mode (Library Mode)
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode, the locking mode is set within the transaction element as follows:
<transaction transaction-manager-lookup="{TransactionManagerLookupClass}"
mode="{NONE, BATCH, NON_XA, NON_DURABLE_XA, FULL_XA}"
locking="{OPTIMISTIC,PESSIMISTIC}">
</transaction>
<transaction transaction-manager-lookup="{TransactionManagerLookupClass}"
mode="{NONE, BATCH, NON_XA, NON_DURABLE_XA, FULL_XA}"
locking="{OPTIMISTIC,PESSIMISTIC}">
</transaction>
Set the locking value to OPTIMISTIC or PESSIMISTIC to configure the locking mode used for the transactional cache.
16.5. Locking Operations
16.5.1. About the LockManager
The LockManager component is responsible for locking an entry before a write process initiates. The LockManager uses a LockContainer to locate, hold and create locks. There are two types of LockContainers JBoss Data Grid uses internally and their choice is dependent on the useLockStriping setting. The first type offers support for lock striping while the second type supports one lock per entry.
See Also: Set Up Lock Striping
16.5.2. About Lock Acquisition
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid acquires remote locks lazily by default. The node running a transaction locally acquires the lock while other cluster nodes attempt to lock cache keys that are involved in a two phase prepare/commit phase. JBoss Data Grid can lock cache keys in a pessimistic manner either explicitly or implicitly.
16.5.3. About Concurrency Levels
Concurrency refers to the number of threads simultaneously interacting with the data grid. In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, concurrency levels refer to the number of concurrent threads used within a lock container.
In JBoss Data Grid, concurrency levels determine the size of each striped lock container. Additionally, concurrency levels tune all related JDK ConcurrentHashMap based collections, such as those internal to DataContainers.
Chapter 17. Set Up Lock Striping
17.1. About Lock Striping
Lock Striping allocates locks from a shared collection of (fixed size) locks in the cache. Lock allocation is based on the hash code for each entry’s key. Lock Striping provides a highly scalable locking mechanism with fixed overhead. However, this comes at a cost of potentially unrelated entries being blocked by the same lock.
Lock Striping is disabled by default in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. If lock striping remains disabled, a new lock is created for each entry. This alternative approach can provide greater concurrent throughput, but also results in additional memory usage, garbage collection churn, and other disadvantages.
17.2. Configure Lock Striping (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Lock striping in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode is enabled by setting the striping element to true.
Lock Striping (Remote Client-Server Mode)
<locking acquire-timeout="20000" concurrency-level="500" striping="true" />
<locking acquire-timeout="20000"
concurrency-level="500"
striping="true" />
The default isolation mode for the Remote Client-Server mode configuration is READ_COMMITTED. If the isolation attribute is included to explicitly specify an isolation mode, it is ignored, a warning is thrown, and the default value is used instead.
The locking element uses the following attributes:
-
The
acquire-timeoutattribute specifies the maximum time to attempt a lock acquisition. The default value for this attribute is10000milliseconds. -
The
concurrency-levelattribute specifies the concurrency level for lock containers. Adjust this value according to the number of concurrent threads interacting with JBoss Data Grid. The default value for this attribute is32. -
The
stripingattribute specifies whether a shared pool of locks is maintained for all entries that require locking (true). If set tofalse, a lock is created for each entry. Lock striping controls the memory footprint but can reduce concurrency in the system. The default value for this attribute isfalse.
17.3. Configure Lock Striping (Library Mode)
Lock striping is disabled by default in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Configure lock striping in JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode using the striping parameter as demonstrated in the following procedure.
Configure Lock Striping (Library Mode)
-
The
concurrency-levelis used to specify the size of the shared lock collection use when lock striping is enabled. -
The
isolationparameter specifies the cache’s isolation level. Valid isolation levels areREAD_COMMITTEDandREPEATABLE_READ. -
The
acquire-timeoutparameter specifies time (in milliseconds) after which a lock acquisition attempt times out. -
The
stripingparameter specifies whether a pool of shared locks are maintained for all entries that require locks. If set toFALSE, locks are created for each entry in the cache. If set toTRUE, lock striping is enabled and shared locks are used as required from the pool. -
The
write-skewcheck determines if a modification to the entry from a different transaction should roll back the transaction. Write skew set to true requiresisolation_levelset toREPEATABLE_READ. The default value forwrite-skewandisolation_levelareFALSEandREAD_COMMITTEDrespectively. Thewrite-skewparameter can be only used withOPTIMISTICtransactions and it requires entry versioning to be enabled, withSIMPLEversioning scheme.
Chapter 18. Set Up Isolation Levels
18.1. About Isolation Levels
Isolation levels determine when readers can view a concurrent write. READ_COMMITTED and REPEATABLE_READ are the two isolation modes offered in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
-
READ_COMMITTED. This isolation level is applicable to a wide variety of requirements. This is the default value in Remote Client-Server and Library modes. REPEATABLE_READ.ImportantThe only valid value for locks in Remote Client-Server mode is the default
READ_COMMITTEDvalue. The value explicitly specified with theisolationvalue is ignored.If the
lockingelement is not present in the configuration, the default isolation value isREAD_COMMITTED.
For isolation mode configuration examples in JBoss Data Grid, see the lock striping configuration samples:
- See Configure Lock Striping (Remote Client-Server Mode) for a Remote Client-Server mode configuration sample.
- See Configure Lock Striping (Library Mode)for a Library mode configuration sample.
18.2. About READ_COMMITTED
READ_COMMITTED is one of two isolation modes available in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
In JBoss Data Grid’s READ_COMMITTED mode, write operations are made to copies of data rather than the data itself. A write operation blocks other data from being written, however writes do not block read operations. As a result, both READ_COMMITTED and REPEATABLE_READ modes permit read operations at any time, regardless of when write operations occur.
In READ_COMMITTED mode multiple reads of the same key within a transaction can return different results due to write operations in different transactions modifying data between reads. This phenomenon is known as non-repeatable reads and is avoided in REPEATABLE_READ mode.
18.3. About REPEATABLE_READ
REPEATABLE_READ is one of two isolation modes available in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
Traditionally, REPEATABLE_READ does not allow write operations while read operations are in progress, nor does it allow read operations when write operations occur. This prevents the "non-repeatable read" phenomenon, which occurs when a single transaction has two read operations on the same row but the retrieved values differ (possibly due to a write operation modifying the value between the two read operations).
JBoss Data Grid’s REPEATABLE_READ isolation mode preserves the value of an entry before a modification occurs. As a result, the "non-repeatable read" phenomenon is avoided because a second read operation on the same entry retrieves the preserved value rather than the new modified value. As a result, the two values retrieved by the two read operations in a single transaction will always match, even if a write operation occurs in a different transaction between the two reads.
Part VIII. Set Up and Configure a Cache Store
Chapter 19. Cache Stores
19.1. Cache Stores
The cache store connects Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to the persistent data store. Cache stores are associated with individual caches. Different caches attached to the same cache manager can have different cache store configurations.
If a clustered cache is configured with an unshared cache store (where shared is set to false), on node join, stale entries which might have been removed from the cluster might still be present in the stores and can reappear.
19.2. Cache Loaders and Cache Writers
Integration with the persistent store is done through the following SPIs located in org.infinispan.persistence.spi:
-
CacheLoader -
CacheWriter -
AdvancedCacheLoader -
AdvancedCacheWriter
CacheLoader and CacheWriter provide basic methods for reading and writing to a store. CacheLoader retrieves data from a data store when the required data is not present in the cache, and CacheWriter is used to enforce entry passivation and activation on eviction in a cache.
AdvancedCacheLoader and AdvancedCacheWriter provide operations to manipulate the underlying storage in bulk: parallel iteration and purging of expired entries, clear and size.
The org.infinispan.persistence.file.SingleFileStore is a good starting point to write your own store implementation.
Previously, JBoss Data Grid used the old API (CacheLoader, extended by CacheStore), which is also still available.
19.3. Cache Store Configuration
19.3.1. Configuring the Cache Store
Cache stores can be configured in a chain. Cache read operations checks each cache store in the order configured until a valid non-null element of data has been located. Write operations affect all cache stores unless the ignoreModifications element has been set to "true" for a specific cache store.
19.3.2. Configure the Cache Store using XML (Library Mode)
The following example demonstrates cache store configuration using XML in JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
19.3.3. About SKIP_CACHE_LOAD Flag
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, when the cache is preloaded from a cache store and eviction is disabled, read requests go to the memory. If the entry is not found in a memory during a read request, it accesses the cache store which may impact the read performance.
To avoid referring to the cache store when a key is not found in the memory, use the SKIP_CACHE_LOAD flag.
19.3.4. About the SKIP_CACHE_STORE Flag
When the SKIP_CACHE_STORE Flag is used then the cache store will not be considered for the specified cache operations. This flag can be useful to place an entry in the cache without having it included in the configured cache store, along with determining if an entry is found within a cache without retrieving it from the associated cache store.
19.5. Connection Factories
19.5.1. Connection Factories
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, all JDBC cache stores rely on a ConnectionFactory implementation to obtain a database connection. This process is also known as connection management or pooling.
A connection factory can be specified using the ConnectionFactoryClass configuration attribute. JBoss Data Grid includes the following ConnectionFactory implementations:
- ManagedConnectionFactory
- SimpleConnectionFactory.
- PooledConnectionFactory.
19.5.2. About ManagedConnectionFactory
ManagedConnectionFactory is a connection factory that is ideal for use within managed environments such as application servers. This connection factory can explore a configured location in the JNDI tree and delegate connection management to the DataSource.
19.5.3. About SimpleConnectionFactory
SimpleConnectionFactory is a connection factory that creates database connections on a per invocation basis. This connection factory is not designed for use in a production environment.
19.5.4. About PooledConnectionFactory
PooledConnectionFactory is a connection factory based on C3P0, and is typically recommended for standalone deployments as opposed to deployments utilizing a servlet container, such as JBoss EAP. This connection factory functions by allowing the user to define a set of parameters which may be used for all DataSource instances generated by the factory.
Chapter 20. Cache Store Implementations
20.1. Cache Stores
The cache store connects Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to the persistent data store. Cache stores are associated with individual caches. Different caches attached to the same cache manager can have different cache store configurations.
If a clustered cache is configured with an unshared cache store (where shared is set to false), on node join, stale entries which might have been removed from the cluster might still be present in the stores and can reappear.
20.2. Cache Store Comparison
Select a cache store based on your requirements. The following is a summary of high level differences between the cache stores available in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid:
- The Single File Cache Store is a local file cache store. It persists data locally for each node of the clustered cache. The Single File Cache Store provides superior read and write performance, but keeps keys in memory which limits its use when persisting large data sets at each node. See Single File Cache Store for details.
- The LevelDB file cache store is a local file cache store which provides high read and write performance. It does not have the limitation of Single File Cache Store of keeping keys in memory. See LevelDB Cache Store for details.
- The JDBC cache store is a cache store that may be shared, if required. When using it, all nodes of a clustered cache persist to a single database or a local JDBC database for every node in the cluster. The shared cache store lacks the scalability and performance of a local cache store such as the LevelDB cache store, but it provides a single location for persisted data. The JDBC cache store persists entries as binary blobs, which are not readable outside JBoss Data Grid. See JDBC Based Cache Stores for details.
- The JPA Cache Store (supported in Library mode only) is a shared cache store like JDBC cache store, but preserves schema information when persisting to the database. Therefore, the persisted entries can be read outside JBoss Data Grid. See JPA Cache Store for details.
20.3. Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode)
The following lists contain details about the configuration elements and parameters for cache store elements in JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode. The following list is meant to highlight certain parameters on each element, and a full list may be found in the schemas.
The persistence Element
-
The
passivationparameter affects the way in which Red Hat JBoss Data Grid interacts with stores. When an object is evicted from in-memory cache, passivation writes it to a secondary data store, such as a system or a database. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalsebutpassivationis set tofalseby default.
The file-store Element
-
The
sharedparameter indicates that the cache store is shared by different cache instances. For example, where all instances in a cluster use the same JDBC settings to talk to the same remote, shared database.sharedisfalseby default. When set totrue, it prevents duplicate data being written to the cache store by different cache instances. For the LevelDB cache stores, this parameter must be excluded from the configuration, or set tofalsebecause sharing this cache store is not supported. -
The
preloadparameter is set tofalseby default. When set totruethe data stored in the cache store is preloaded into the memory when the cache starts. This allows data in the cache store to be available immediately after startup and avoids cache operations delays as a result of loading data lazily. Preloaded data is only stored locally on the node, and there is no replication or distribution of the preloaded data. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid will only preload up to the maximum configured number of entries in eviction. -
The
fetch-stateparameter determines whether or not to fetch the persistent state of a cache and apply it to the local cache store when joining the cluster. If the cache store is shared the fetch persistent state is ignored, as caches access the same cache store. A configuration exception will be thrown when starting the cache service if more than one cache store has this property set totrue. Thefetch-stateproperty isfalseby default. -
In order to speed up lookups, the single file cache store keeps an index of keys and their corresponding position in the file. To avoid this index resulting in memory consumption problems, this cache store can be bounded by a maximum number of entries that it stores, defined by the
max-entriesparameter. If this limit is exceeded, entries are removed permanently using the LRU algorithm both from the in-memory index and the underlying file based cache store. The default value is-1, allowing unlimited entries. -
The
singletonparameter enables a singleton store cache store. SingletonStore is a delegating cache store used when only one instance in a cluster can interact with the underlying store; however,singletonparameter is not recommended forfile-store. The default value isfalse. -
The
purgeparameter controls whether cache store is purged when it starts up. -
The
locationconfiguration element sets a location on disk where the store can write.
The write-behind Element
The write-behind element contains parameters that configure various aspects of the cache store.
-
The
thread-pool-sizeparameter specifies the number of threads that concurrently apply modifications to the store. The default value for this parameter is1. -
The
flush-lock-timeoutparameter specifies the time to acquire the lock which guards the state to be flushed to the cache store periodically. The default value for this parameter is1. -
The
modification-queue-sizeparameter specifies the size of the modification queue for the asynchronous store. If updates are made at a rate that is faster than the underlying cache store can process this queue, then the asynchronous store behaves like a synchronous store for that period, blocking until the queue can accept more elements. The default value for this parameter is1024elements. -
The
shutdown-timeoutparameter specifies maximum amount of time that can be taken to stop the cache store. Default value for this parameter is25000milliseconds.
The remote-store Element
-
The
cacheattribute specifies the name of the remote cache to which it intends to connect in the remote Infinispan cluster. The default cache will be used if the remote cache name is unspecified. -
The
fetch-stateattribute, when set totrue, ensures that the persistent state is fetched when the remote cache joins the cluster. If multiple cache stores are chained, only one cache store can have this property set totrue. The default for this value isfalse. -
The
sharedattribute is set totruewhen multiple cache instances share a cache store, which prevents multiple cache instances writing the same modification individually. The default for this attribute isfalse. -
The
preloadattribute ensures that the cache store data is pre-loaded into memory and is immediately accessible after starting up. The disadvantage of setting this totrueis that the start up time increases. The default value for this attribute isfalse. -
The
singletonparameter enables the SingletonStore delegating cache store, used in situations when only one instance in a cluster should interact with the underlying store. The default value isfalse. -
The
purgeattribute ensures that the cache store is purged during the start up process. The default value for this attribute isfalse. -
The
tcp-no-delayattribute triggers the TCPNODELAYstack. The default value for this attribute istrue. -
The
ping-on-startattribute sends a ping request to a back end server to fetch the cluster topology. The default value for this attribute istrue. -
The
key-size-estimateattribute provides an estimation of the key size. The default value for this attribute is64. -
The
value-size-estimateattribute specifies the size of the byte buffers when serializing and deserializing values. The default value for this attribute is512. -
The
force-return-valuesattribute sets whetherFORCE_RETURN_VALUEis enabled for all calls. The default value for this attribute isfalse.
The remote-server Element
Create a remote-server element within the remote-store element to define the server information.
-
The
hostattribute configures the host address. -
The
portattribute configures the port used by the Remote Cache Store. This defaults to11222.
The connection-pool Element (Remote Store)
-
The
max-activeparameter indicates the maximum number of active connections for each server at a time. The default value for this attribute is-1which indicates an infinite number of active connections. -
The
max-idleparameter indicates the maximum number of idle connections for each server at a time. The default value for this attribute is-1which indicates an infinite number of idle connections. -
The
max-totalparameter indicates the maximum number of persistent connections within the combined set of servers. The default setting for this attribute is-1which indicates an infinite number of connections. -
The
min-idle-timeparameter sets a target value for the minimum number of idle connections (per server) that should always be available. If this parameter is set to a positive number andtimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis0, each time the idle connection eviction thread runs, it will try to create enough idle instances so that there will beminIdleidle instances available for each server. The default setting for this parameter is1. -
The
eviction-intervalparameter indicates how long the eviction thread should sleep before "runs" of examining idle connections. When non-positive, no eviction thread will be launched. The default setting for this parameter is120000milliseconds, or 2 minutes. -
The
min-evictable-idle-timeparameter specifies the minimum amount of time that an connection may sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction due to idle time. When non-positive, no connection will be dropped from the pool due to idle time alone. This setting has no effect unlesstimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis0. The default setting for this parameter is1800000, or (30 minutes). -
The
test-idleparameter indicates whether or not idle connections should be validated by sending an TCP packet to the server, during idle connection eviction runs. Connections that fail to validate will be dropped from the pool. This setting has no effect unlesstimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis0. The default setting for this parameter istrue.
The leveldb-store Element
-
The
relative-toparameter specifies the base directory in which to store the cache state. -
The
pathparameter specifies the location within therelative-toparameter to store the cache state. -
The
sharedparameter specifies whether the cache store is shared. The only supported value for this parameter in the LevelDB cache store isfalse. -
The
preloadparameter specifies whether the cache store will be pre-loaded. Valid values aretrueandfalse. -
The
block-sizeparameter defines the block size of the cache store. -
The
singletonparameter enables the SingletonStore delegating cache store, used in situations when only one instance in a cluster should interact with the underlying store. The default value isfalse. -
The
cache-sizeparameter defines the cache size of the cache store. -
The
clear-thresholdparameter defines the cache clear threshold of the cache store.
The jpa-store Element
-
The
persistence-unitattribute specifies the name of the JPA cache store. -
The
entity-classattribute specifies the fully qualified class name of the JPA entity used to store the cache entry value. -
The
batch-size(optional) attribute specifies the batch size for cache store streaming. The default value for this attribute is100. -
The
store-metadata(optional) attribute specifies whether the cache store keeps the metadata (for example expiration and versioning information) with the entries. The default value for this attribute istrue. -
The
singletonparameter enables the SingletonStore delegating cache store, used in situations when only one instance in a cluster should interact with the underlying store. The default value isfalse.
The binary-keyed-jdbc-store, string-keyed-jdbc-store, and mixed-keyed-jdbc-store Elements
-
The
fetch-stateparameter determines whether the persistent state is fetched when joining a cluster. Set this totrueif using a replication and invalidation in a clustered environment. Additionally, if multiple cache stores are chained, only one cache store can have this property enabled. If a shared cache store is used, the cache does not allow a persistent state transfer despite this property being set totrue. Thefetch-stateparameter isfalseby default. -
The
singletonparameter enables the SingletonStore delegating cache store, used in situations when only one instance in a cluster should interact with the underlying store. The default value isfalse. -
The
purgeparameter specifies whether the cache store is purged when initially started. -
The
key-to-string-mapperparameter specifies the class name used to map keys to strings for the database tables.
The connection-pool Element (JDBC Store)
-
The
connection-urlparameter specifies the JDBC driver-specific connection URL. -
The
usernameparameter contains the username used to connect via theconnection-url. -
The
passwordparameter contains the password to use when connecting via theconnection-url -
The
driverparameter specifies the class name of the driver used to connect to the database.
The binary-keyed-table and string-keyed-table Elements
-
The
prefixattribute defines the string prepended to name of the target cache when composing the name of the cache bucket table. -
The
drop-on-exitparameter specifies whether the database tables are dropped upon shutdown. -
The
create-on-startparameter specifies whether the database tables are created by the store on startup. -
The
fetch-sizeparameter specifies the size to use when querying from this table. Use this parameter to avoid heap memory exhaustion when the query is large. -
The
batch-sizeparameter specifies the batch size used when modifying this table.
The id-column, data-column, and timestamp-column Elements
-
The
nameparameter specifies the name of the column used. -
The
typeparameter specifies the type of the column used.
The custom-store Element
-
The
classparameter specifies the class name of the cache store implementation. -
The
preloadparameter specifies whether to load entries into the cache during start up. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. -
The
sharedparameter specifies whether the cache store is shared. This is used when multiple cache instances share a cache store. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse.
The property Element
A property may be defined inside of a cache store, with the entry between the property tags being the stored value. For instance, in the below example a value of 1 is defined for minOccurs.
<property name="minOccurs">1</property>
<property name="minOccurs">1</property>-
The
nameattribute specifies the name of the property.
20.4. Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following tables contain details about the configuration elements and parameters for cache store elements in JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode. The following list is meant to highlight certain parameters on each element, and a full list may be found in the schemas.
The local-cache Element
-
The
nameparameter of thelocal-cacheattribute is used to specify a name for the cache. -
The
statisticsparameter specifies whether statistics are enabled at the container level. Enable or disable statistics on a per-cache basis by setting thestatisticsattribute tofalse.
The file-store Element
-
The
nameparameter of thefile-storeelement is used to specify a name for the file store. -
The
passivationparameter determines whether entries in the cache are passivated (true) or if the cache store retains a copy of the contents in memory (false). -
The
purgeparameter specifies whether or not the cache store is purged when it is started. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. -
The
sharedparameter is used when multiple cache instances share a cache store. This parameter can be set to prevent multiple cache instances writing the same modification multiple times. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. However, thesharedparameter is not recommended for the LevelDB cache store because this cache store cannot be shared. -
The
relative-toproperty is the directory where thefile-storestores the data. It is used to define a named path. -
The
pathproperty is the name of the file where the data is stored. It is a relative path name that is appended to the value of therelative-toproperty to determine the complete path. -
The
max-entriesparameter provides maximum number of entries allowed. The default value is -1 for unlimited entries. -
The
fetch-stateparameter when set to true fetches the persistent state when joining a cluster. If multiple cache stores are chained, only one of them can have this property enabled. Persistent state transfer with a shared cache store does not make sense, as the same persistent store that provides the data will just end up receiving it. Therefore, if a shared cache store is used, the cache does not allow a persistent state transfer even if a cache store has this property set totrue. It is recommended to set this property to true only in a clustered environment. The default value for this parameter is false. -
The
preloadparameter when set to true, loads the data stored in the cache store into memory when the cache starts. However, setting this parameter to true affects the performance as the startup time is increased. The default value for this parameter is false. -
The
singletonparameter enables a singleton store cache store. SingletonStore is a delegating cache store used when only one instance in a cluster can interact with the underlying store; however,singletonparameter is not recommended forfile-store. The default value isfalse.
The store Element
-
The
classparameter specifies the class name of the cache store implementation.
The property Element
-
The
nameparameter specifies the name of the property. -
The
valueparameter specifies the value assigned to the property.
The remote-store Element
-
The
cacheparameter defines the name for the remote cache. If left undefined, the default cache is used instead. -
The
socket-timeoutparameter sets whether the value defined inSO_TIMEOUT(in milliseconds) applies to remote Hot Rod servers on the specified timeout. A timeout value of0indicates an infinite timeout. The default value is 60,000 ms, or one minute. -
The
tcp-no-delaysets whetherTCP_NODELAYapplies on socket connections to remote Hot Rod servers. -
The
hotrod-wrappingsets whether a wrapper is required for Hot Rod on the remote store. -
The
singletonparameter enables the SingletonStore delegating cache store, used in situations when only one instance in a cluster should interact with the underlying store. The default value isfalse.
The remote-server Element
-
The
outbound-socket-bindingparameter sets the outbound socket binding for the remote server.
The binary-keyed-jdbc-store, string-keyed-jdbc-store, and mixed-keyed-jdbc-store Elements
-
The
datasourceparameter defines the name of a JNDI for the datasource. -
The
passivationparameter determines whether entries in the cache are passivated (true) or if the cache store retains a copy of the contents in memory (false). -
The
preloadparameter specifies whether to load entries into the cache during start up. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. -
The
purgeparameter specifies whether or not the cache store is purged when it is started. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. -
The
sharedparameter is used when multiple cache instances share a cache store. This parameter can be set to prevent multiple cache instances writing the same modification multiple times. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse. -
The
singletonparameter enables a singleton store cache store. SingletonStore is a delegating cache store used when only one instance in a cluster can interact with the underlying store
The binary-keyed-table and string-keyed-table Elements
-
The
prefixparameter specifies a prefix string for the database table name.
The id-column, data-column, and timestamp-column Elements
-
The
nameparameter specifies the name of the database column. -
The
typeparameter specifies the type of the database column.
The leveldb-store Element
-
The
relative-toparameter specifies the base directory to store the cache state. This value defaults tojboss.server.data.dir. -
The
pathparameter defines where, within the directory specified in therelative-toparameter, the cache state is stored. If undefined, the path defaults to the cache container name. -
The
passivationparameter specifies whether passivation is enabled for the LevelDB cache store. Valid values aretrueandfalse. -
The
singletonparameter enables the SingletonStore delegating cache store, used in situations when only one instance in a cluster should interact with the underlying store. The default value isfalse. -
The
purgeparameter specifies whether the cache store is purged when it starts up. Valid values aretrueandfalse.
20.5. Single File Cache Store
20.5.1. Single File Cache Store
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes one file system based cache store: the SingleFileCacheStore.
The SingleFileCacheStore is a simple file system based implementation and a replacement to the older file system based cache store: the FileCacheStore.
SingleFileCacheStore stores all key/value pairs and their corresponding metadata information in a single file. To speed up data location, it also keeps all keys and the positions of their values and metadata in memory. Hence, using the single file cache store slightly increases the memory required, depending on the key size and the amount of keys stored. Hence SingleFileCacheStore is not recommended for use cases where the keys are too big.
To reduce memory consumption, the size of the cache store can be set to a fixed number of entries to store in the file; however, this works only when JBoss Data Grid is used as a cache. When JBoss Data Grid is used this way, data which is not present in the cache can be recomputed or re-retrieved from the authoritative data store and stored in the JBoss Data Grid cache. This limitation exists so that once the maximum number of entries is reached older data in the cache store is removed. If JBoss Data Grid were used as an authoritative data store in this scenario it would lead to potential data loss.
Due to its limitations, SingleFileCacheStore can be used in a limited capacity in production environments. It can not be used on shared file system (such as NFS and Windows shares) due to a lack of proper file locking, resulting in data corruption. Furthermore, file systems are not inherently transactional, resulting in file writing failures during the commit phase if the cache is used in a transactional context.
20.5.2. Single File Store Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is an example of a Single File Store configuration for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.5.3. Single File Store Configuration (Library Mode)
In Red Hat JBoss Grid’s Library mode, configure a Single File Cache Store as follows:.
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.5.4. Upgrade JBoss Data Grid Cache Stores
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7 stores data in a different format than previous versions of JBoss Data Grid. As a result, the newer version of JBoss Data Grid cannot read data stored by older versions. Use rolling upgrades to upgrade persisted data from the format used by the old JBoss Data Grid to the new format. Additionally, the newer version of JBoss Data Grid also stores persistence configuration information in a different location.
Rolling upgrades is the process by which a JBoss Data Grid installation is upgraded without a service shutdown. For JBoss Data Grid servers, this procedure refers to the server side components. The upgrade can be due to either hardware or software change, such as upgrading JBoss Data Grid.
Rolling upgrades are only available in JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode.
20.6. LevelDB Cache Store
20.6.1. LevelDB Cache Store
LevelDB is a key-value storage engine that provides an ordered mapping from string keys to string values.
The LevelDB Cache Store uses two filesystem directories. Each directory is configured for a LevelDB database. One directory stores the non-expired data and the second directory stores the keys pending to be purged permanently.
20.6.2. Configuring LevelDB Cache Store (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Procedure: To configure LevelDB Cache Store:
Add the following elements to a cache definition in standalone.xml to configure the database:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteDirectories will be automatically created if they do not exist.
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.6.3. LevelDB Cache Store Sample XML Configuration (Library Mode)
The following is a sample XML configuration of LevelDB Cache Store:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.6.4. Configure a LevelDB Cache Store Using JBoss Operations Network
Use the following procedure to set up a new LevelDB cache store using the JBoss Operations Network.
- Ensure that Red Hat JBoss Operations Network 3.2 or higher is installed and started.
- Install the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Plugin Pack for JBoss Operations Network 3.2.0.
- Ensure that JBoss Data Grid is installed and started.
- Import JBoss Data Grid server into the inventory.
- Configure the JBoss Data Grid connection settings.
Create a new LevelDB cache store as follows:
Figure 20.1. Create a new LevelDB Cache Store

-
Right-click the
defaultcache. - In the menu, mouse over the option.
- In the submenu, click menu:LevelDB Store[] .
-
Right-click the
Name the new LevelDB cache store as follows:
Figure 20.2. Name the new LevelDB Cache Store
- In the Resource Create Wizard that appears, add a name for the new LevelDB Cache Store.
- Click btn:[Next] to continue.
Configure the LevelDB Cache Store settings as follows:
Figure 20.3. Configure the LevelDB Cache Store Settings
- Use the options in the configuration window to configure a new LevelDB cache store.
- Click menu:Finish[] to complete the configuration.
Schedule a restart operation as follows:
Figure 20.4. Schedule a Restart Operation
- In the screen’s left panel, expand the JBoss AS7 Standalone Servers entry, if it is not currently expanded.
- Click JDG (0.0.0.0:9990) from the expanded menu items.
- In the screen’s right panel, details about the selected server display. Click the menu:Operations[] tab.
- In the Operation drop-down box, select the Restart operation.
- Select the radio button for the Now entry.
- Click menu:Schedule[] to restart the server immediately.
Discover the new LevelDB cache store as follows:
Figure 20.5. Discover the New LevelDB Cache Store
- In the screen’s left panel, select each of the following items in the specified order to expand them: menu:JBoss AS7 Standalong Servers[JDG (0.0.0.0:9990) > infinispan > Cache Containers > local > Caches > default > LevelDB Stores]
- Click the name of your new LevelDB Cache Store to view its configuration information in the right panel.
20.7. JDBC Based Cache Stores
20.7.1. JDBC Based Cache Stores
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid offers several cache stores for use with common data storage formats. JDBC based cache stores are used with any cache store that exposes a JDBC driver. JBoss Data Grid offers the following JDBC based cache stores depending on the key to be persisted:
-
JdbcBinaryStore. -
JdbcStringBasedStore. -
JdbcMixedStore.
Both Binary and Mixed JDBC stores are deprecated in JBoss Data Grid 7.2, and are not recommended for production use. It is recommended to utilize a String Based store instead.
20.7.2. JdbcBinaryStores
20.7.2.1. JdbcBinaryStores
The JdbcBinaryStore supports all key types. It stores all keys with the same hash value (hashCode method on the key) in the same table row/blob. The hash value common to the included keys is set as the primary key for the table row/blob. As a result of this hash value, JdbcBinaryStore offers excellent flexibility but at the cost of concurrency and throughput.
As an example, if three keys (k1, k2 and k3) have the same hash code, they are stored in the same table row. If three different threads attempt to concurrently update k1, k2 and k3, they must do it sequentially because all three keys share the same row and therefore cannot be simultaneously updated.
Binary JDBC stores are deprecated in JBoss Data Grid 7.2, and are not recommended for production use. It is recommended to utilize a String Based store instead.
20.7.2.2. JdbcBinaryStore Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is a configuration for JdbcBinaryStore using Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode with Passivation enabled:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.7.2.3. JdbcBinaryStore Configuration (Library Mode)
The following is a sample configuration for the JdbcBinaryStore:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.7.3. JdbcStringBasedStores
20.7.3.1. JdbcStringBasedStores
The JdbcStringBasedStore stores each entry in its own row in the table, instead of grouping multiple entries into each row, resulting in increased throughput under a concurrent load. It also uses a (pluggable) bijection that maps each key to a String object. The key-to-string-mapper interface defines the bijection.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes a default implementation called DefaultTwoWayKey2StringMapper that handles primitive types.
20.7.3.2. JdbcStringBasedStore Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is a sample JdbcStringBasedStore for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.7.3.3. JdbcStringBasedStore Configuration (Library Mode)
The following is a sample configuration for the JdbcStringBasedStore:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.7.3.4. JdbcStringBasedStore Multiple Node Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is a configuration for the JdbcStringBasedStore in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode. This configuration is used when multiple nodes must be used.
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.7.4. JdbcMixedStores
20.7.4.1. JdbcMixedStores
The JdbcMixedStore is a hybrid implementation that delegates keys based on their type to either the JdbcBinaryStore or JdbcStringBasedStore.
Mixed JDBC stores are deprecated in JBoss Data Grid 7.2, and are not recommended for production use. It is recommended to utilize a String Based store instead.
20.7.4.2. JdbcMixedStore Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is a configuration for a JdbcMixedStore for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.7.4.3. JdbcMixedStore Configuration (Library Mode)
The following is a sample configuration for the JdbcMixedStore:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.7.5. Cache Store Troubleshooting
20.7.5.1. IOExceptions with JdbcStringBasedStore
An IOException Unsupported protocol version 48 error when using JdbcStringBasedStore indicates that your data column type is set to VARCHAR, CLOB or something similar instead of the correct type, BLOB or VARBINARY. Despite its name, JdbcStringBasedStore only requires that the keys are strings while the values can be any data type, so that they can be stored in a binary column.
20.8. The Remote Cache Store
20.8.1. Remote Cache Stores
The RemoteCacheStore is an implementation of the cache loader that stores data in a remote Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cluster. The RemoteCacheStore uses the Hot Rod client-server architecture to communicate with the remote cluster.
For remote cache stores, Hot Rod provides load balancing, fault tolerance and the ability to fine tune the connection between the RemoteCacheStore and the cluster.
20.8.2. Remote Cache Store Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is a sample remote cache store configuration for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Remote Client-Server Mode).
20.8.3. Remote Cache Store Configuration (Library Mode)
The following is a sample remote cache store configuration for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.8.4. Define the Outbound Socket for the Remote Cache Store
The Hot Rod server used by the remote cache store is defined using the outbound-socket-binding element in a standalone.xml file.
An example of this configuration in the standalone.xml file is as follows:
Define the Outbound Socket
20.9. JPA Cache Store
20.9.1. JPA Cache Stores
The JPA (Java Persistence API) Cache Store stores cache entries in the database using a formal schema, which allows other applications to read the persisted data and load data provided by other applications into Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. The database should not be used by the other applications concurrently with JBoss Data Grid.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, JPA cache stores are only supported in Library mode.
20.9.2. JPA Cache Store Sample XML Configuration (Library Mode)
To configure JPA Cache Stores using XML in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, add the following configuration to the infinispan.xml file:
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
20.9.3. Storing Metadata in the Database
When storeMetadata is set to true (default value), meta information about the entries such as expiration, creation and modification timestamps, and versioning is stored in the database. JBoss Data Grid stores the metadata in an additional table named _ispn_metadata_ because the entity table has a fixed layout that cannot accommodate the metadata.
The structure of this table depends on the database in use. Enable the automatic creation of this table using the same database as the test environment and then transfer the structure to the production database.
Configure persistence.xml for Metadata Entities
Using Hibernate as the JPA implementation allows automatic creation of these tables using the property
hibernate.hbm2ddl.autoin persistence.xml as follows:<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="update"/>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="update"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Declare the metadata entity class to the JPA provider by adding the following to persistence.xml :
<class>org.infinispan.persistence.jpa.impl.MetadataEntity</class>
<class>org.infinispan.persistence.jpa.impl.MetadataEntity</class>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
As outlined, metadata is always stored in a new table. If metadata information collection and storage is not required, set the storeMetadata attribute to false in the JPA Store configuration.
20.9.4. Deploying JPA Cache Stores in Various Containers
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid JPA Cache Store implementations are deployed normally for all supported containers, except Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform. The JBoss Data Grid JBoss EAP modules contain the JPA cache store and related libraries such as Hibernate. As a result, the relevant libraries are not packaged inside the application, but instead the application refers to the libraries in the JBoss EAP modules that have them installed.
These modules are not required for containers other than JBoss EAP. As a result, all the relevant libraries are packaged in the application’s WAR/EAR file, such as with the following Maven dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.infinispan</groupId>
<artifactId>infinispan-cachestore-jpa</artifactId>
<version>{FullInfinispanVersion}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.infinispan</groupId>
<artifactId>infinispan-cachestore-jpa</artifactId>
<version>{FullInfinispanVersion}</version>
</dependency>Deploy JPA Cache Stores in JBoss EAP 6.3.x and earlier
To add dependencies from the JBoss Data Grid modules to the application’s classpath, provide the JBoss EAP deployer a list of dependencies in one of the following ways:
Add a dependency configuration to the MANIFEST.MF file:
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Dependencies: org.infinispan:jdg-7.2 services, org.infinispan.persistence.jpa:jdg-7.2 services
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Dependencies: org.infinispan:jdg-7.2 services, org.infinispan.persistence.jpa:jdg-7.2 servicesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a dependency configuration to the jboss-deployment-structure.xml file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Deploy JPA Cache Stores in JBoss EAP 6.4 and later
Add the following property in persistence.xml :
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the following dependencies to the jboss-deployment-structure.xml :
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Add any additional dependencies, such as additional JDG modules, are in use add these to the
dependenciessection in jboss-deployment-structure.xml .
JPA Cache Store is not supported in Apache Karaf in JBoss Data Grid 7.2.
20.10. Cassandra Cache Store
20.10.1. Cassandra Cache Store
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid allows Apache Cassandra to function as a Cache Store, leveraging their distributed database architecture to provide a virtually unlimited, horizontally scalable persistent store for cache entries.
In order to use the Cassandra Cache Store an appropriate keyspace must first be created on the Cassandra database. This may either be performed automatically or by enabling the auto-create-keyspace parameter in the cache store configuration. A sample keyspace creation is demonstrated below:
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS Infinispan WITH replication = {'class':'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor':1};
CREATE TABLE Infinispan.InfinispanEntries (key blob PRIMARY KEY, value blob, metadata blob);
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS Infinispan WITH replication = {'class':'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor':1};
CREATE TABLE Infinispan.InfinispanEntries (key blob PRIMARY KEY, value blob, metadata blob);20.10.2. Enabling the Cassandra Cache Store
The Cassandra Cache Store is included based on the downloaded distribution. The following indicates where this is located, and steps to enable it if required:
-
Library Mode- The infinispan-cachestore-cassandra-8.5.0.Final-redhat-9-deployable.jar is included in the jboss-datagrid-${jdg-version}-library/ directory, and may be added to any projects that are using the Cassandra Cache Store. -
Remote Client-Server Mode- The Cassandra Cache Store is prepackaged in the modules/ directory of the server, and may be used by default with no additional configuration necessary. -
JBoss Data Grid modules for JBoss EAP- The Cassandra Cache Store is included in the modules distributed, and may be added by using theorg.infinispan.persistence.cassandraas the module name.
20.10.3. Cassandra Cache Store Sample XML Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
In Remote Client-Server mode the Cassandra Cache Store is defined by using the class org.infinispan.persistence.cassandra.CassandraStore and defining the properties individually within the store.
The following configuration snippet provides an example on how to define a Cassandra Cache Store inside of an xml file:
20.10.4. Cassandra Cache Store Sample XML Configuration (Library Mode)
In Library Mode the Cassandra Cache Store may be configured using two different methods:
- Option 1: Using the same method discussed for Remote Client-Server Mode, found in Cassandra Cache Store Sample XML Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode).
Option 2: Using the
cassandra-storeschema. The following snippet shows an example configuration defining a Cassandra Cache Store:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.10.5. Cassandra Configuration Parameters
When defining a backing Cassandra instance in Library Mode one or more cassandra-server elements may be specified in the configuration. Each of the elements has the following properties:
| Parameter Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
| The hostname or ip address of a Cassandra server. | 127.0.0.1 |
|
| The port on which the server is listening. | 9042 |
The following properties may be configured on the Cassandra Cache Store:
| Parameter Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
| Determines whether the keyspace and entry table should be automatically created on startup. | true |
|
| Name of the keyspace to use. | Infinispan |
|
| Name of the table storing entries. | InfinispanEntries |
|
| Consistency level to use for the queries. | LOCAL_ONE |
|
| Serial consistency level to use for the queries. | SERIAL |
A connection-pool may also be defined with the following elements:
| Parameter Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
| Time that the driver blocks when no connection from hosts pool is available. After this timeout, the driver will try the next host. | 5 |
|
| Application-side heartbeat to avoid the connections being dropped when no activity is happening. Set to 0 to disable. | 30 |
|
| Timeout before an idle connection is removed. | 120 |
20.11. Custom Cache Stores
20.11.1. Custom Cache Stores
Custom cache stores are a customized implementation of Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cache stores.
In order to create a custom cache store (or loader), implement all or a subset of the following interfaces based on the need:
-
CacheLoader -
CacheWriter -
AdvancedCacheLoader -
AdvancedCacheWriter -
ExternalStore -
AdvancedLoadWriteStore
See Cache Loaders and Cache Writers for individual functions of the interfaces.
If the AdvancedCacheWriter is not implemented, the expired entries cannot be purged or cleared using the given writer.
If the AdvancedCacheLoader is not implemented, the entries stored in the given loader will not be used for preloading.
To migrate the existing cache store to the new API or to write a new store implementation, use SingleFileStore as an example. To view the SingleFileStore example code, download the JBoss Data Grid source code.
Use the following procedure to download SingleFileStore example code from the Customer Portal:
Download JBoss Data Grid Source Code
- To access the Red Hat Customer Portal, navigate to https://access.redhat.com/home in a browser.
- Click menu:Downloads[] .
- In the section labeled JBoss Development and Management , click menu:Red Hat JBoss Data Grid[] .
- Enter the relevant credentials in the Red Hat Login and Password fields and click menu:Log In[] .
- From the list of downloadable files, locate Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7 Source Code and click menu:Download[] . Save and unpack it in a desired location.
-
Locate the
SingleFileStoresource code by navigating through jboss-datagrid-7.2.3-sources/infinispan-8.5.3.Final-redhat-00002/core/src/main/java/org/infinispan/persistence/file/SingleFileStore.java .
20.11.2. Custom Cache Store Maven Archetype
An easy way to get started with developing a Custom Cache Store is to use the Maven archetype; creating an archetype will generate a new Maven project with the correct directory layout and sample code.
Generate a Maven Archetype
- Ensure the JBoss Data Grid Maven repository has been installed by following the instructions in the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Getting Started Guide .
Open a command prompt and execute the following command to generate an archetype in the current directory:
mvn -Dmaven.repo.local="path/to/unzipped/jboss-datagrid-7.2.x-maven-repository/" archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=org.infinispan -DarchetypeArtifactId=custom-cache-store-archetype -DarchetypeVersion=8.5.0.Final-redhat-9
mvn -Dmaven.repo.local="path/to/unzipped/jboss-datagrid-7.2.x-maven-repository/" archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=org.infinispan -DarchetypeArtifactId=custom-cache-store-archetype -DarchetypeVersion=8.5.0.Final-redhat-9Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe above command has been broken into multiple lines for readability; however, when executed this command and all arguments must be on a single line.
20.11.3. Custom Cache Store Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
20.11.3.1. Custom Cache Store Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following is a sample configuration for a custom cache store in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode:
Custom Cache Store Configuration
<distributed-cache name="cacheStore" mode="SYNC" segments="256" owners="2" remote-timeout="30000">
<store class="my.package.CustomCacheStore">
<property name="customStoreProperty">10</property>
</store>
</distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache name="cacheStore" mode="SYNC" segments="256" owners="2" remote-timeout="30000">
<store class="my.package.CustomCacheStore">
<property name="customStoreProperty">10</property>
</store>
</distributed-cache>See the reference information for the elements and parameters in the preceding configuration example:
20.11.3.2. Option 1: Add Custom Cache Store using deployments (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Deploy Custom Cache Store .jar file to JDG server using deployments
Add the following Java service loader file
META-INF/services/org.infinispan.persistence.spi.AdvancedLoadWriteStoreto the module and add a reference to the Custom Cache Store Class, such as seen below:my.package.CustomCacheStore
my.package.CustomCacheStoreCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Copy the jar to the
$JDG_HOME/standalone/deployments/directory. If the .jar file is available the server the following message will be displayed in the logs:
JBAS010287: Registering Deployed Cache Store service for store 'my.package.CustomCacheStore'
JBAS010287: Registering Deployed Cache Store service for store 'my.package.CustomCacheStore'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the
infinispan-coresubsystem add an entry for the cache inside acache-container, specifying the class that overrides one of the interfaces from Custom Cache Stores:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.11.3.3. Option 2: Add Custom Cache Store using the CLI (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Deploying Custom Cache Store .jar file to JDG server using the CLI
Connect to the JDG server by running the below command:
[$JDG_HOME] $ bin/cli.sh --connect --controller=$IP:$PORT
[$JDG_HOME] $ bin/cli.sh --connect --controller=$IP:$PORTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the .jar file by executing the following command:
deploy /path/to/artifact.jar
deploy /path/to/artifact.jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.11.3.4. Option 3: Add Custom Cache Store using JON (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Deploying Custom Cache Store .jar file to JDG server using JBoss Operation Network
- Log into JON.
-
Navigate to
Bundlesalong the upper bar. -
Click the
Newbutton and choose theReciperadio button. Insert a deployment bundle file content that references the store, similar to the following example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Proceed with
Nextbutton toBundle Groupsconfiguration wizard page and proceed withNextbutton once again. -
Locate custom cache store
.jarfile using file uploader andUploadthe file. -
Proceed with
Nextbutton toSummaryconfiguration wizard page. Proceed withFinishbutton in order to finish bundle configuration. -
Navigate back to the
Bundlestab along the upper bar. -
Select the newly created bundle and click
Deploybutton. -
Enter
Destination Nameand choose the proper Resource Group; this group should only consist of JDG servers. -
Choose
Install DirectoryfromBase Location's radio box group. -
Enter
/standalone/deploymentsinDeployment Directorytext field below. - Proceed with the wizard using the default options.
Validate the deployment using the following command on the server’s host:
find $JDG_HOME -name "custom-store.jar"
find $JDG_HOME -name "custom-store.jar"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Confirm the bundle has been installed in
$JDG_HOME/standalone/deployments.
Once the above steps are completed the .jar file will be successfully uploaded and registered by the JDG server.
The JON plugin has been deprecated in JBoss Data Grid 7.2 and is expected to be removed in a subsequent version.
20.11.4. Custom Cache Store Configuration (Library Mode)
Custom Cache Store classes must be in the JBoss Data Grid classpath. Either package the Custom Cache Store with JBoss Data Grid or define it as an EAP module that you list as a dependency.
The following is a sample configuration for a custom cache store in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode:
Custom Cache Store Configuration
For details about the elements and parameters used in this sample configuration, see Cache Store Configuration Details (Library Mode).
Part IX. Set Up Passivation
Chapter 21. Activation and Passivation Modes
21.1. Activation and Passivation Modes
Activation is the process of restoring an entry from the data store into the in-memory cache. Activation occurs when a thread attempts to access an entry that is in the store but not the memory (namely a passivated entry).
Passivation mode allows entries to be stored in the cache store after they are evicted from memory. Passivation prevents unnecessary and potentially expensive writes to the cache store. It is used for entries that are frequently used or referenced and therefore not evicted from memory.
While passivation is enabled, the cache store is used as an overflow tank, similar to virtual memory implementation in operating systems that swap memory pages to disk.
The passivation flag is used to toggle passivation mode, a mode that stores entries in the cache store only after they are evicted from memory.
21.2. Passivation Mode Benefits
The primary benefit of passivation mode is that it prevents unnecessary and potentially expensive writes to the cache store. This is particularly useful if an entry is frequently used or referenced and therefore is not evicted from memory.
21.3. Configure Passivation
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, add the passivation parameter to the cache store element to toggle passivation for it:
Toggle Passivation in Remote Client-Server Mode
<local-cache name="customCache"/> <!-- Additional configuration elements for local-cache here --> <file-store passivation="true" <!-- Additional configuration elements for file-store here --> </local-cache>
<local-cache name="customCache"/>
<!-- Additional configuration elements for local-cache here -->
<file-store passivation="true"
<!-- Additional configuration elements for file-store here -->
</local-cache>
In Library mode, add the passivation parameter to the persistence element to toggle passivation:
Toggle Passivation in Library Mode
<persistence passivation="true"> <!-- Additional configuration elements here --> </persistence>
<persistence passivation="true">
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
</persistence>21.4. Evication and Passivation
21.4.1. Eviction and Passivation
To ensure that a single copy of an entry remains, either in memory or in a cache store, use passivation in conjunction with eviction.
The primary reason to use passivation instead of a normal cache store is that updating entries require less resources when passivation is in use. This is because passivation does not require an update to the cache store.
21.4.2. Eviction and Passivation Usage
If the eviction policy caused the eviction of an entry from the cache while passivation is enabled, the following occur as a result:
- A notification regarding the passivated entry is emitted to the cache listeners.
- The evicted entry is stored.
When an attempt to retrieve an evicted entry is made, the entry is lazily loaded into memory from the cache loader. After the entry and its children are loaded a notification regarding the entry’s activation is sent to the cache listeners.
Entries which have been activated, will continue to exist in the cache store if it has been configured as shared. This happens because backup owners might still need to access it.
21.4.3. Cache Loader Behavior with Passivation Disabled vs Enabled
With passivation disabled, when an element is modified, added, or removed, the modification is persisted in the backend store via the cache loader. There is no direct relationship between eviction and cache loading. When eviction is not in use, the persistent store is effectively a copy of what’s in memory. If eviction is in use, the persistent store is effectively a superset of what’s in memory (i.e. it includes entries that have been evicted from memory).
When passivation is enabled and the cache store is unshared, there is a direct relationship between eviction and the cache loader. Writes to the persistent store via the cache loader only occur as part of the eviction process. Data is deleted from the persistent store when the application reads it back into memory. In this case, the data in memory and data in the persistent store are two subsets of the total information set, with no intersection between the subsets. With a shared store, entries which have been passivated in the past will continue to exist in the store, although they may have a stale value if this has been overwritten in memory.
21.4.4. Eviction Examples
The following example indicates the state of the memory and the persistent store during eviction operations in three different configurations: passivation off, passivation on with a cache store with shared off, and passivation on with a cache store with shared on.
| Operation | Passivation Off | Passivation On, Shared Off | Passivation On, Shared On |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
| Insert keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne, keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne, keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne, keyTwo |
| Eviction thread runs, evicts keyOne |
Memory: keyTwo |
Memory: keyTwo |
Memory: keyTwo |
| Read keyOne |
Memory: keyOne, keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne, keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne, keyTwo |
| Eviction thread runs, evicts keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
| Remove keyTwo |
Memory: keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
Memory: keyOne |
Part X. Set Up Cache Writing
Chapter 22. Cache Writing Modes
22.1. Cache Writing Modes
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid presents configuration options with a single or multiple cache stores. This allows it to store data in a persistent location, for example a shared JDBC database or a local file system. JBoss Data Grid supports two caching modes:
- Write-Through (Synchronous)
- Write-Behind (Asynchronous)
22.2. Write-Through Caching
22.2.1. Write-Through Caching
The Write-Through (or Synchronous) mode in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid ensures that when clients update a cache entry (usually via a Cache.put() invocation), the call does not return until JBoss Data Grid has located and updated the underlying cache store. This feature allows updates to the cache store to be concluded within the client thread boundaries.
22.2.2. Write-Through Caching Benefits and Disadvantages
Write-Through Caching Benefits
The primary advantage of the Write-Through mode is that the cache and cache store are updated simultaneously, which ensures that the cache store remains consistent with the cache contents.
Write-Through Caching Disadvantages
Due to the cache store being updated simultaneously with the cache entry, there is a possibility of reduced performance for cache operations that occur concurrently with the cache store accesses and updates.
22.2.3. Write-Through Caching Configuration (Library Mode)
No specific configuration operations are required to configure a Write-Through or synchronous cache store. All cache stores are Write-Through or synchronous unless explicitly marked as Write-Behind or asynchronous. The following procedure demonstrates a sample configuration file of a Write-Through unshared local file cache store.
Configure a Write-Through Local File Cache Store
-
The
nameparameter specifies the name of thelocal-cacheto use. -
The
fetch-stateparameter determines whether the persistent state is fetched when joining a cluster. Set this totrueif using a replication and invalidation in a clustered environment. Additionally, if multiple cache stores are chained, only one cache store can have this property enabled. If a shared cache store is used, the cache does not allow a persistent state transfer despite this property being set totrue. Thefetch-stateparameter isfalseby default. -
The
purgeparameter specifies whether the cache is purged when initially started. -
The
sharedparameter is used when multiple cache instances share a cache store and is now defined at the cache store level. This parameter can be set to prevent multiple cache instances writing the same modification multiple times. Valid values for this parameter aretrueandfalse.
22.3. Write-Behind Caching
22.3.1. Write-Behind Caching
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Write-Behind (Asynchronous) mode, cache updates are asynchronously written to the cache store. Asynchronous updates ensure that cache store updates are carried out by a thread different from the client thread interacting with the cache.
One of the foremost advantages of the Write-Behind mode is that the cache operation performance is not affected by the underlying store update. However, because of the asynchronous updates, for a brief period the cache store contains stale data compared to the cache.
22.3.2. About Unscheduled Write-Behind Strategy
In the Unscheduled Write-Behind Strategy mode, Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Data Grid attempts to store changes as quickly as possible by applying pending changes in parallel. This results in multiple threads waiting for modifications to conclude. Once these modifications are concluded, the threads become available and the modifications are applied to the underlying cache store.
This strategy is ideal for cache stores with low latency and low operational costs. An example of this is a local unshared file based cache store in which the cache store is local to the cache itself. Using this strategy the period of time where an inconsistency exists between the contents of the cache and the contents of the cache store is reduced to the shortest possible interval.
22.3.3. Unscheduled Write-Behind Strategy Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
To set the write-behind strategy in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, add the write-behind element to the target cache store configuration as follows:
The write-behind Element
The write-behind element uses the following configuration parameters:
-
The
modification-queue-sizeparameter sets the modification queue size for the asynchronous store. If updates occur faster than the cache store can process the queue, the asynchronous store behaves like a synchronous store. The store behavior remains synchronous and blocks elements until the queue is able to accept them, after which the store behavior becomes asynchronous again. -
The
shutdown-timeoutparameter specifies the time in milliseconds after which the cache store is shut down. When the store is stopped some modifications may still need to be applied. Setting a large timeout value will reduce the chance of data loss. The default value for this parameter is25000. -
The
flush-lock-timeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) to acquire the lock that guards the state to be periodically flushed. The default value for this parameter is15000. -
The
thread-pool-sizeparameter specifies the size of the thread pool. The threads in this thread pool apply modifications to the cache store. The default value for this parameter is5.
22.3.4. Unscheduled Write-Behind Strategy Configuration (Library Mode)
To enable the write-behind strategy of the cache entries to a store, add the async element to the store configuration as follows:
The async Element
-
The
asyncelement uses the following configuration parameters: . ThemodificationQueueSizeparameter sets the modification queue size for the asynchronous store. If updates occur faster than the cache store can process the queue, the asynchronous store behaves like a synchronous store. The store behavior remains synchronous and blocks elements until the queue is able to accept them, after which the store behavior becomes asynchronous again. -
The
shutdownTimeoutparameter specifies the time in milliseconds after which the cache store is shut down. This provides time for the asynchronous writer to flush data to the store when a cache is shut down. The default value for this parameter is25000. -
The
flushLockTimeoutparameter specifies the time (in milliseconds) to acquire the lock that guards the state to be periodically flushed. The default value for this parameter is15000. -
The
threadPoolSizeparameter specifies the number of threads that concurrently apply modifications to the store. The default value for this parameter is5.
Part XI. Monitor Caches and Cache Managers
Chapter 23. Set Up Java Management Extensions (JMX)
23.1. About Java Management Extensions (JMX)
Java Management Extension (JMX) is a Java based technology that provides tools to manage and monitor applications, devices, system objects, and service oriented networks. Each of these objects is managed, and monitored by MBeans.
JMX is the de facto standard for middleware management and administration. As a result, JMX is used in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to expose management and statistical information.
23.2. Using JMX with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
Management in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instances aims to expose as much relevant statistical information as possible. This information allows administrators to view the state of each instance. While a single installation can comprise of tens or hundreds of such instances, it is essential to expose and present the statistical information for each of them in a clear and concise manner.
In JBoss Data Grid, JMX is used in conjunction with JBoss Operations Network (JON) to expose this information and present it in an orderly and relevant manner to the administrator.
23.3. JMX Statistic Levels
JMX statistics can be enabled at two levels:
- At the cache level, where management information is generated by individual cache instances.
- At the CacheManager level, where the CacheManager is the entity that governs all cache instances created from it. As a result, the management information is generated for all these cache instances instead of individual caches.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, statistics are enabled by default in Remote Client-Server mode and disabled by default for Library mode. While statistics are useful in assessing the status of JBoss Data Grid, they adversely affect performance and must be disabled if they are not required.
23.4. Enabling JMX for Cache Instances
You can enable JMX statistics at the Cache level either declaratively or programmatically.
Declaratively Enabling JMX at the Cache Level
Add the statistics attribute to the target <*-cache> element as follows:
<*-cache statistics="true">
<*-cache statistics="true">Programmatically Enabling JMX at the Cache Level
Programmatically enable JMX at the cache level as follows:
Configuration configuration = new ConfigurationBuilder().jmxStatistics().enable().build();
Configuration configuration = new
ConfigurationBuilder().jmxStatistics().enable().build();23.5. Enabling JMX for CacheManagers
You can enable JMX statistics at the CacheManager level either declaratively or programmatically.
Declaratively Enabling JMX at the CacheManager Level
Add the statistics attribute to the <cache-container> element as follows:
<cache-container statistics="true">
<cache-container statistics="true">Programmatically Enabling JMX at the CacheManager Level
Programmatically enable JMX at the CacheManager level as follows:
GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration = new GlobalConfigurationBuilder().globalJmxStatistics().enable().build();
GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration = new
GlobalConfigurationBuilder().globalJmxStatistics().enable().build();23.6. Disabling the CacheStore via JMX When Using Rolling Upgrades
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid allows the CacheStore to be disabled via JMX by invoking the disconnectSource operation on the RollingUpgradeManager MBean.
See Also: RollingUpgradeManager
23.7. Multiple JMX Domains
Multiple JMX domains are used when multiple CacheManager instances exist on a single virtual machine, or if the names of cache instances in different CacheManagers clash.
To resolve this issue, name each CacheManager in manner that allows it to be easily identified and used by monitoring tools such as JMX and JBoss Operations Network.
Set a CacheManager Name Declaratively
Add the following snippet to the relevant CacheManager configuration:
<globalJmxStatistics enabled="true" cacheManagerName="Hibernate2LC"/>
<globalJmxStatistics enabled="true" cacheManagerName="Hibernate2LC"/>23.8. MBeans
23.8.1. MBeans
An MBean represents a manageable resource such as a service, component, device or an application.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides MBeans that monitor and manage multiple aspects. For example, MBeans that provide statistics on the transport layer are provided. If a JBoss Data Grid server is configured with JMX statistics, an MBean that provides information such as the hostname, port, bytes read, bytes written and the number of worker threads exists at the following location:
jboss.infinispan:type=Server,name=<Memcached|Hotrod>,component=Transport
jboss.infinispan:type=Server,name=<Memcached|Hotrod>,component=Transport
MBeans are available under two JMX domains:
-
jboss.as - these
MBeansare created by the server subsystem. -
jboss.infinispan - these
MBeansare symmetric to those created by embedded mode.
Only the MBeans under jboss.infinispan should be used for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, as the ones under jboss.as are for Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform.
A full list of available MBeans, their supported operations and attributes, is available in the Appendix
23.8.2. Understanding MBeans
When JMX reporting is enabled at either the Cache Manager or Cache level, use a standard JMX GUI such as JConsole or VisualVM to connect to a Java Virtual Machine running Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. When connected, the following MBeans are available:
-
If Cache Manager-level
JMXstatistics are enabled, anMBeannamedjboss.infinispan:type=CacheManager,name="DefaultCacheManager"exists, with properties specified by the Cache ManagerMBean. If the cache-level
JMXstatistics are enabled, multipleMBeansdisplay depending on the configuration in use. For example, if a write behind cache store is configured, anMBeanthat exposes properties that belong to the cache store component is displayed. All cache-levelMBeansuse the same format:jboss.infinispan:type=Cache,name="<name-of-cache>(<cache-mode>)",manager="<name-of-cache-manager>",component=<component-name>
jboss.infinispan:type=Cache,name="<name-of-cache>(<cache-mode>)",manager="<name-of-cache-manager>",component=<component-name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this format:
-
Specify the default name for the cache using the
cache-containerelement’sdefault-cacheattribute. -
The
cache-modeis replaced by the cache mode of the cache. The lower case version of the possible enumeration values represents the cache mode. -
The
component-nameis replaced by one of theJMXcomponent names from theJMXreference documentation.
-
Specify the default name for the cache using the
As an example, the cache store JMX component MBean for a default cache configured for synchronous distribution would be named as follows:
jboss.infinispan:type=Cache,name="default(dist_sync)", manager="default",component=CacheStore
jboss.infinispan:type=Cache,name="default(dist_sync)", manager="default",component=CacheStoreEach cache and cache manager name is within quotation marks to prevent the use of unsupported characters in these user-defined names.
23.8.3. Registering MBeans in Non-Default MBean Servers
The default location where all the MBeans used are registered is the standard JVM MBeanServer platform. Users can set up an alternative MBeanServer instance as well. Implement the MBeanServerLookup interface to ensure that the getMBeanServer() method returns the desired (non default) MBeanServer.
To set up a non default location to register your MBeans, create the implementation and then configure Red Hat JBoss Data Grid with the fully qualified name of the class. An example is as follows:
To Add the Fully Qualified Domain Name Declaratively
Add the following snippet:
<globalJmxStatistics enabled="true" mBeanServerLookup="com.acme.MyMBeanServerLookup"/>
<globalJmxStatistics enabled="true" mBeanServerLookup="com.acme.MyMBeanServerLookup"/>Chapter 24. Set Up JBoss Operations Network (JON)
24.1. About JBoss Operations Network (JON)
The JBoss Operations Network (JON) is JBoss' administration and management platform used to develop, test, deploy and monitor the application life cycle. JBoss Operations Network is JBoss' enterprise management solution and is recommended for the management of multiple Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instances across servers. JBoss Operations Network’s agent and auto discovery features facilitate monitoring the Cache Manager and Cache instances in JBoss Data Grid. JBoss Operations Network presents graphical views of key runtime parameters and statistics and allows administrators to set thresholds and be notified if usage exceeds or falls under the set thresholds.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Remote Client-Server mode, statistics are enabled by default. While statistics are useful in assessing the status of JBoss Data Grid, they adversely affect performance and must be disabled if they are not required. In JBoss Data Grid Library mode, statistics are disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled when required.
To achieve full functionality of JBoss Operations Network library plugin for JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode, upgrade to JBoss Operations Network 3.3.0 with patch Update 04 or higher. For information on upgrading the JBoss Operations Network, see the Upgrading JBoss ON section in the JBoss Operations Network Installation Guide .
JBoss Data Grid will support the JON plugin until its end of life in June 2019.
24.2. Download JBoss Operations Network (JON)
24.2.1. Prerequisites for Installing JBoss Operations Network (JON)
In order to install JBoss Operations Network in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, the following is required:
- A Linux, Windows, or Mac OSX operating system, and an x86_64, i686, or ia64 processor.
- Java 6 or higher is required to run both the JBoss Operations Network Server and the JBoss Operations Network Agent.
- Synchronized clocks on JBoss Operations Network Servers and Agents.
- An external database must be installed.
24.2.2. Download JBoss Operations Network
Use the following procedure to download Red Hat JBoss Operations Network (JON) from the Customer Portal:
Download JBoss Operations Network
- To access the Red Hat Customer Portal, navigate to https://access.redhat.com/home in a browser.
- Click Downloads.
- In the section labeled JBoss Development and Management , click Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
- Enter the relevant credentials in the Red Hat Login and Password fields and click Log In.
- Select the appropriate version in the Version drop down menu list.
- Click the Download button next to the desired download file.
24.2.3. Remote JMX Port Values
A port value must be provided to allow Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instances to be located. The value itself can be any available port.
Provide unique (and available) remote JMX ports to run multiple JBoss Data Grid instances on a single machine. A locally running JBoss Operations Network agent can discover each instance using the remote port values.
24.2.4. Download JBoss Operations Network (JON) Plugin
Download Installation Files
- Open http://access.redhat.com in a web browser.
- Click Downloads in the menu across the top of the page.
-
Click Red Hat JBoss Operations Network in the list under
JBoss Development and Management. Enter your login information.
You are taken to the Software Downloads page.
Download the JBoss Operations Network Plugin
If you intend to use the JBoss Operations Network plugin for JBoss Data Grid, select
JBoss ON for Data Gridfrom either the Product drop-down box, or the menu on the left.If you intend to use the JBoss Operations Network plugin for JBoss Enterprise Web Server, select
JBoss ON for Web Serverfrom either the Product drop-down box, or the menu on the left.- Click the Red Hat JBoss Operations Network VERSION Base Distribution Download button.
- Repeat the steps to download the Data Grid Management Plugin Pack for JBoss ON VERSION
24.3. JBoss Operations Network Server Installation
The core of JBoss Operations Network is the server, which communicates with agents, maintains the inventory, manages resource settings, interacts with content providers, and provides a central management UI.
For more detailed information about configuring JBoss Operations Network, see the JBoss Operations Network Installation Guide .
24.4. JBoss Operations Network Agent
The JBoss Operations Network Agent is a standalone Java application. Only one agent is required per machine, regardless of how many resources you require the agent to manage.
The JBoss Operations Network Agent does not ship fully configured. Once the agent has been installed and configured it can be run as a Windows service from a console, or run as a daemon or init.d script in a UNIX environment.
A JBoss Operations Network Agent must be installed on each of the machines being monitored in order to collect data.
The JBoss Operations Network Agent is typically installed on the same machine on which Red Hat JBoss Data Grid is running, however where there are multiple machines an agent must be installed on each machine.
For more detailed information about configuring JBoss Operations Network agents, see the JBoss Operations Network Installation Guide .
24.5. JBoss Operations Network for Remote Client-Server Mode
24.5.1. JBoss Operations Network for Remote Client-Server Mode
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, the JBoss Operations Network plug-in is used to
- initiate and perform installation and configuration operations.
- monitor resources and their metrics.
In Remote Client-Server mode, the JBoss Operations Network plug-in uses JBoss Enterprise Application Platform’s management protocol to obtain metrics and perform operations on the JBoss Data Grid server.
24.5.2. Installing the JBoss Operations Network Plug-in (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following procedure details how to install the JBoss Operations Network plug-ins for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode.
Install the plug-ins
- Copy the JBoss Data Grid server rhq plug-in to $JON_SERVER_HOME/plugins .
- Copy the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform plug-in to $JON_SERVER_HOME/plugins .
The server will automatically discover plug-ins here and deploy them. The plug-ins will be removed from the plug-ins directory after successful deployment.
Obtain plug-ins
Obtain all available plug-ins from the JBoss Operations Network server. To do this, type the following into the agent’s console:
plugins update
plugins updateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow List installed plug-ins
Ensure the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform plug-in and the JBoss Data Grid server rhq plug-in are installed correctly using the following:
plugins info
plugins infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
JBoss Operation Network can now discover running JBoss Data Grid servers.
24.6. JBoss Operations Network Remote-Client Server Plugin
24.6.1. JBoss Operations Network Plugin Metrics
| Trait Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cache-manager-status | Cache Container Status | The current runtime status of a cache container. |
| cluster-name | Cluster Name | The name of the cluster. |
| members | Cluster Members | The names of the members of the cluster. |
| coordinator-address | Coordinator Address | The coordinator node’s address. |
| local-address | Local Address | The local node’s address. |
| version | Version | The cache manager version. |
| defined-cache-names | Defined Cache Names | The caches that have been defined for this manager. |
| Metric Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cluster-size | Cluster Size | How many members are in the cluster. |
| defined-cache-count | Defined Cache Count | How many caches that have been defined for this manager. |
| running-cache-count | Running Cache Count | How many caches are running under this manager. |
| created-cache-count | Created Cache Count | How many caches have actually been created under this manager. |
| Trait Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cache-status | Cache Status | The current runtime status of a cache. |
| cache-name | Cache Name | The current name of the cache. |
| version | Version | The cache version. |
| Metric Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cache-status | Cache Status | The current runtime status of a cache. |
| number-of-locks-available | [LockManager] Number of locks available | The number of exclusive locks that are currently available. |
| concurrency-level | [LockManager] Concurrency level | The LockManager’s configured concurrency level. |
| average-read-time | [Statistics] Average read time | Average number of milliseconds required for a read operation on the cache to complete. |
| hit-ratio | [Statistics] Hit ratio | The result (in percentage) when the number of hits (successful attempts) is divided by the total number of attempts. |
| elapsed-time | [Statistics] Seconds since cache started | The number of seconds since the cache started. |
| read-write-ratio | [Statistics] Read/write ratio | The read/write ratio (in percentage) for the cache. |
| average-write-time | [Statistics] Average write time | Average number of milliseconds a write operation on a cache requires to complete. |
| hits | [Statistics] Number of cache hits | Number of cache hits. |
| evictions | [Statistics] Number of cache evictions | Number of cache eviction operations. |
| remove-misses | [Statistics] Number of cache removal misses | Number of cache removals where the key was not found. |
| time-since-reset | [Statistics] Seconds since cache statistics were reset | Number of seconds since the last cache statistics reset. |
| number-of-entries | [Statistics] Number of current cache entries | Number of entries currently in the cache. |
| stores | [Statistics] Number of cache puts | Number of cache put operations |
| remove-hits | [Statistics] Number of cache removal hits | Number of cache removal operation hits. |
| misses | [Statistics] Number of cache misses | Number of cache misses. |
| success-ratio | [RpcManager] Successful replication ratio | Successful replications as a ratio of total replications in numeric double format. |
| replication-count | [RpcManager] Number of successful replications | Number of successful replications |
| replication-failures | [RpcManager] Number of failed replications | Number of failed replications |
| average-replication-time | [RpcManager] Average time spent in the transport layer | The average time (in milliseconds) spent in the transport layer. |
| commits | [Transactions] Commits | Number of transaction commits performed since the last reset. |
| prepares | [Transactions] Prepares | Number of transaction prepares performed since the last reset. |
| rollbacks | [Transactions] Rollbacks | Number of transaction rollbacks performed since the last reset. |
| invalidations | [Invalidation] Number of invalidations | Number of invalidations. |
| passivations | [Passivation] Number of cache passivations | Number of passivation events. |
| activations | [Activations] Number of cache entries activated | Number of activation events. |
| cache-loader-loads | [Activation] Number of cache store loads | Number of entries loaded from the cache store. |
| cache-loader-misses | [Activation] Number of cache store misses | Number of entries that did not exist in the cache store. |
| cache-loader-stores | [CacheStore] Number of cache store stores | Number of entries stored in the cache stores. |
Gathering of some of these statistics is disabled by default.
JBoss Operations Network Metrics for Connectors
The metrics provided by the JBoss Operations Network (JON) plugin for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid are for REST and Hot Rod endpoints only. For the REST protocol, the data must be taken from the Web subsystem metrics. For details about each of these endpoints, see the Getting Started Guide.
| Metric Name | Display Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bytesRead | Bytes Read | Number of bytes read. |
| bytesWritten | Bytes Written | Number of bytes written. |
Gathering of these statistics is disabled by default.
24.6.2. JBoss Operations Network Plugin Operations
| Operation Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Start Cache | Starts the cache. |
| Stop Cache | Stops the cache. |
| Clear Cache | Clears the cache contents. |
| Reset Statistics | Resets statistics gathered by the cache. |
| Reset Activation Statistics | Resets activation statistics gathered by the cache. |
| Reset Invalidation Statistics | Resets invalidations statistics gathered by the cache. |
| Reset Passivation Statistics | Resets passivation statistics gathered by the cache. |
| Reset Rpc Statistics | Resets replication statistics gathered by the cache. |
| Remove Cache | Removes the given cache from the cache-container. |
| Record Known Global Keyset | Records the global known keyset to a well-known key for retrieval by the upgrade process. |
| Synchronize Data | Synchronizes data from the old cluster to this using the specified migrator. |
| Disconnect Source | Disconnects the target cluster from the source cluster according to the specified migrator. |
JBoss Operations Network Plugin Operations for the Cache Backups
The cache backups used for these operations are configured using cross-datacenter replication. In the JBoss Operations Network (JON) User Interface, each cache backup is the child of a cache. For more information about cross-datacenter replication, see Set Up Cross-Datacenter Replication.
| Operation Name | Description |
|---|---|
| status | Display the site status. |
| bring-site-online | Brings the site online. |
| take-site-offline | Takes the site offline. |
Cache (Transactions)
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid does not support using Transactions in Remote Client-Server mode. As a result, none of the endpoints can use transactions.
24.6.3. JBoss Operations Network Plugin Attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cluster | string | The name of the group communication cluster. |
| executor | string | The executor used for the transport. |
| lock-timeout | long |
The timeout period for locks on the transport. The default value is |
| machine | string | A machine identifier for the transport. |
| rack | string | A rack identifier for the transport. |
| site | string | A site identifier for the transport. |
| stack | string | The JGroups stack used for the transport. |
24.6.4. Create a New Cache Using JBoss Operations Network (JON)
Use the following steps to create a new cache using JBoss Operations Network (JON) for Remote Client-Server mode.
Creating a new cache in Remote Client-Server mode
Log into the JBoss Operations Network Console.
- From the JBoss Operations Network console, click Inventory.
- Select Servers from the Resources list on the left of the console.
Select the specific Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server from the servers list.
- Below the server name, click infinispan and then Cache Containers.
Select the desired cache container that will be parent for the newly created cache.
- Right-click the selected cache container. For example, clustered.
- In the context menu, navigate to Create Child and select Cache.
Create a new cache in the resource create wizard.
- Enter the new cache name and click Next.
- Set the cache attributes in the Deployment Options and click Finish.
Refresh the view of caches in order to see newly added resource. It may take several minutes for the Resource to show up in the Inventory.
24.7. JBoss Operations Network for Library Mode
24.7.1. JBoss Operations Network for Library Mode
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode, the JBoss Operations Network plug-in is used to
- initiate and perform installation and configuration operations.
- monitor resources and their metrics.
In Library mode, the JBoss Operations Network plug-in uses JMX to obtain metrics and perform operations on an application using the JBoss Data Grid library.
24.7.2. Installing the JBoss Operations Network Plug-in (Library Mode)
Use the following procedure to install the JBoss Operations Network plug-in for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode.
Install JBoss Operations Network Library Mode Plug-in
Open the JBoss Operations Network Console
- From the JBoss Operations Network console, select Administration.
- Select Agent Plugins from the Configuration options on the left side of the console.
Figure 24.1. JBoss Operations Network Console for JBoss Data Grid
Upload the Library Mode Plug-in
- Click Browse, locate the InfinispanPlugin on your local file system.
- Click Upload to add the plug-in to the JBoss Operations Network Server.
Figure 24.2. Upload the InfinispanPlugin.
Scan for Updates
- Once the file has successfully uploaded, click Scan For Updates at the bottom of the screen.
- The InfinispanPlugin will now appear in the list of installed plug-ins.
Figure 24.3. Scan for Updated Plug-ins.
24.7.3. Monitoring of JBoss Data Grid Instances in Library Mode
24.7.3.1. Prerequisites
The following is a list of common prerequisites for Monitor an Application Deployed in Standalone Mode, Monitor an Application Deployed in Domain Mode, and Manually Adding JBoss Data Grid Instances in Library Mode.
- A correctly configured instance of JBoss Operations Network (JON) 3.2.0 with patch Update 02 or higher version.
- A running instance of JON Agent on the server where the application will run. For more information, see JBoss Operations Network Agent.
-
An operational instance of the RHQ agent with a full JDK. Ensure that the agent has access to the tools.jar file from the JDK in particular. In the JON agent’s environment file (bin/rhq-env.sh ), set the value of the
RHQ_AGENT_JAVA_HOMEproperty to point to a full JDK home. - The RHQ agent must have been initiated using the same user as the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform instance. As an example, running the JON agent as a user with root privileges and the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform process under a different user does not work as expected and must be avoided.
- An installed JON plugin for JBoss Data GridLibrary Mode. For more information, see Installing the JBoss Operations Network Plug-in (Library Mode)
- Generic JMX plugin from JBoss Operation Networks 3.2.0 with patch Update 02 or better version in use.
- A custom application using Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library mode with enabled JMX statistics for library mode caches in order to make statistics and monitoring working. For details how to enable JMX statistics for cache instances, see Enable JMX for Cache Instances and to enable JMX for cache managers see Enable JMX for CacheManagers.
- The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) must be configured to expose the JMX MBean Server. For the Oracle/Sun JDK, see http://docs.oracle.com/javase/1.5.0/docs/guide/management/agent.html
- A correctly added and configured management user for JBoss Enterprise Application Platform.
24.7.3.2. Manually Adding JBoss Data Grid Instances in Library Mode
To add Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instances to JBoss Operations Network manually, use the following procedure in the JBoss Operations Network interface.
Add JBoss Data Grid Instances in Library Mode
Import the Platform
- Navigate to the Inventory and select Discovery Queue from the Resources list on the left of the console.
- Select the platform on which the application is running and click Import at the bottom of the screen.
Figure 24.4. Import the Platform from the menu:Discovery Queue[].
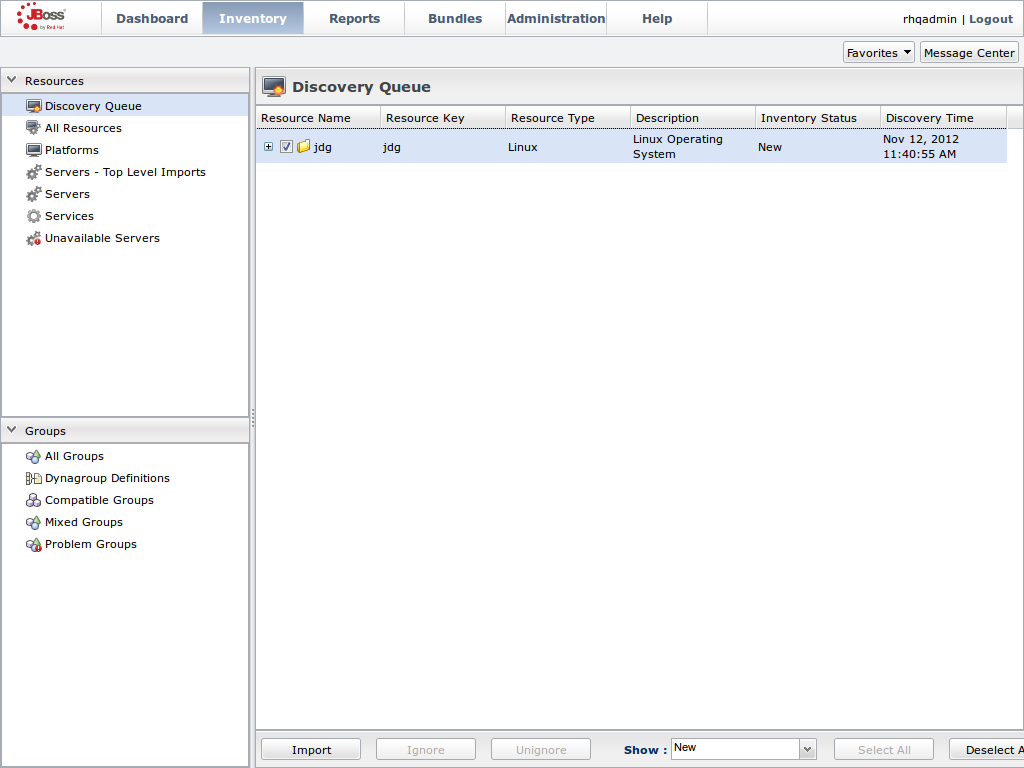
Access the Servers on the Platform
-
The
jdgPlatform now appears in the Platforms list. - Click on the Platform to access the servers that are running on it.
Figure 24.5. Open the
jdgPlatform to view the list of servers.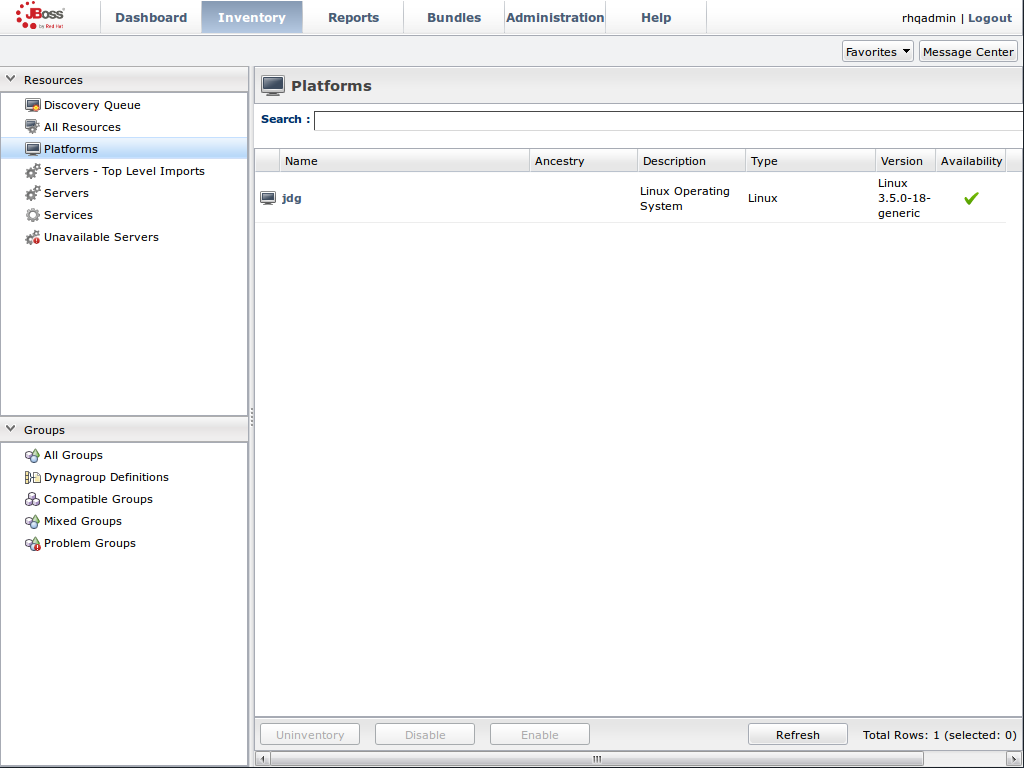
-
The
Import the JMX Server
- From the Inventory tab, select Child Resources.
- Click the Import button at the bottom of the screen and select the JMX Server** option from the list.
Figure 24.6. Import the JMX Server
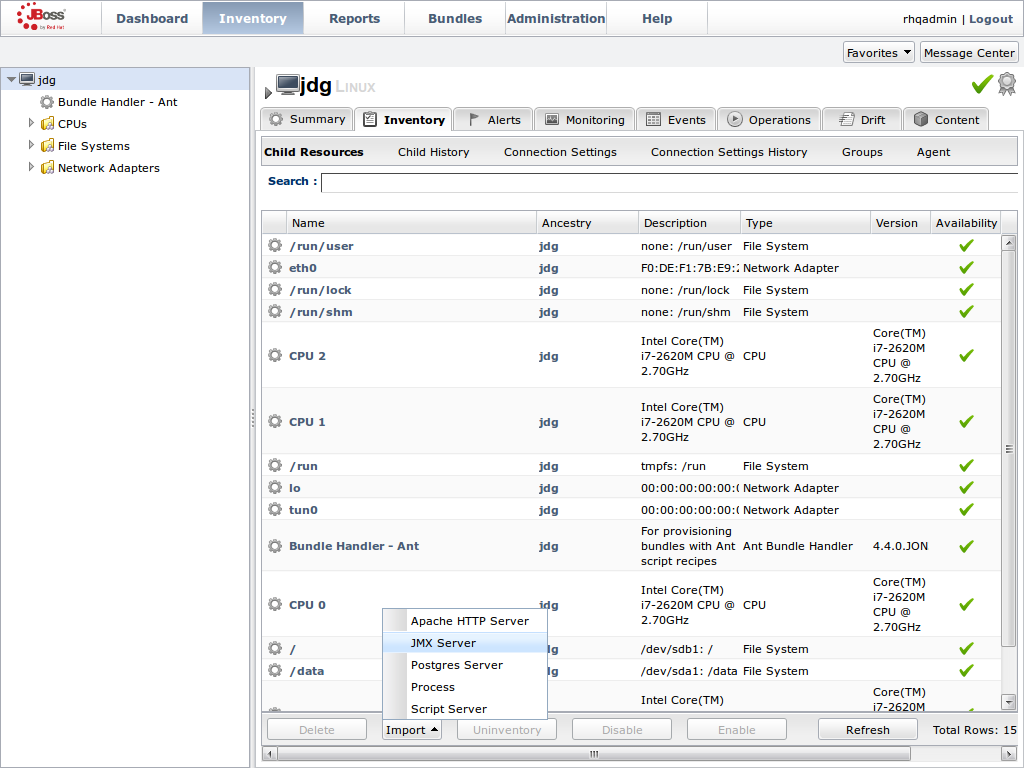
Enable JDK Connection Settings
- In the Resource Import Wizard window, specify JDK 8 from the list of Connection Settings Template options.
Figure 24.7. Select the JDK 5 Template.
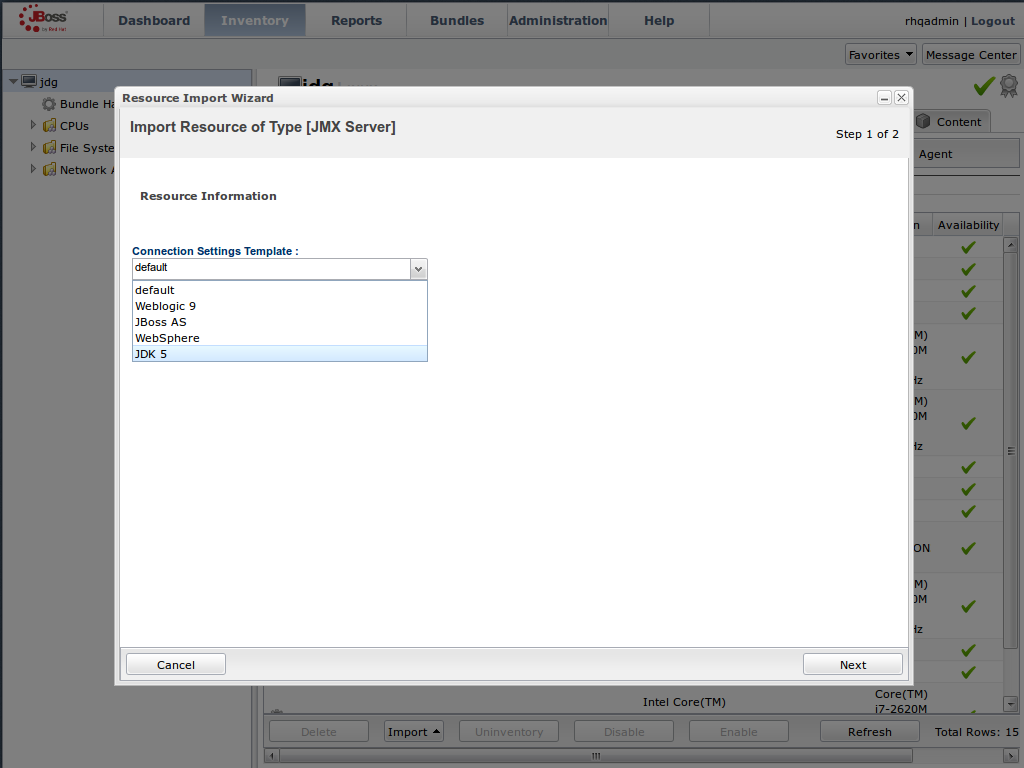
Modify the Connector Address
- In the Deployment Options menu, modify the supplied Connector Address with the hostname and JMX port of the process containing the Infinispan Library.
Enter the JMX connector address of the new JBoss Data Grid instance you want to monitor. For example:
Connector Address:
service:jmx:rmi://127.0.0.1/jndi/rmi://127.0.0.1:7997/jmxrmi
service:jmx:rmi://127.0.0.1/jndi/rmi://127.0.0.1:7997/jmxrmiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe connector address varies depending on the host and the JMX port assigned to the new instance. In this case, instances require the following system properties at start up:
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=7997 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=7997 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Specify the Principal and Credentials information if required.
- Click Finish.
Figure 24.8. Modify the values in the Deployment Options screen.
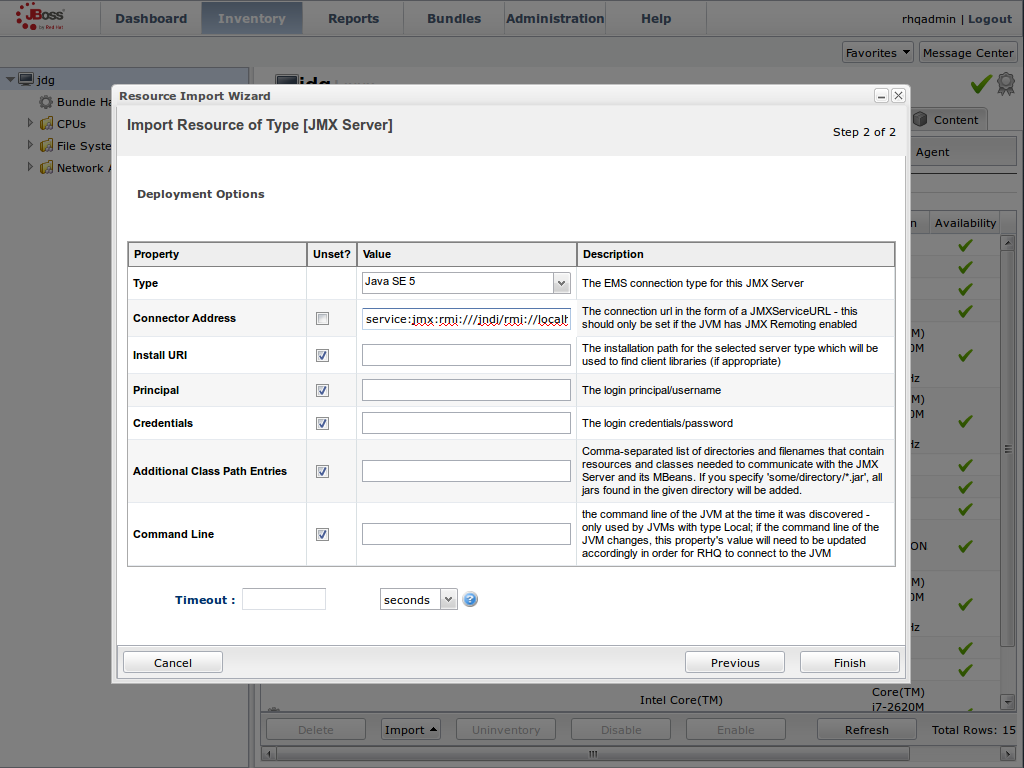
View Cache Statistics and Operations
- Click Refresh to refresh the list of servers.
- The JMX Servers tree in the panel on the left side of the screen contains the Infinispan Cache Managers node, which contains the available cache managers. The available cache managers contain the available caches.
- Select a cache from the available caches to view metrics.
- Select the Monitoring tab.
- The Tables view shows statistics and metrics.
- The Operations tab provides access to the various operations that can be performed on the services.
Figure 24.9. Metrics and operational data relayed through JMX is now available in the JBoss Operations Network console.
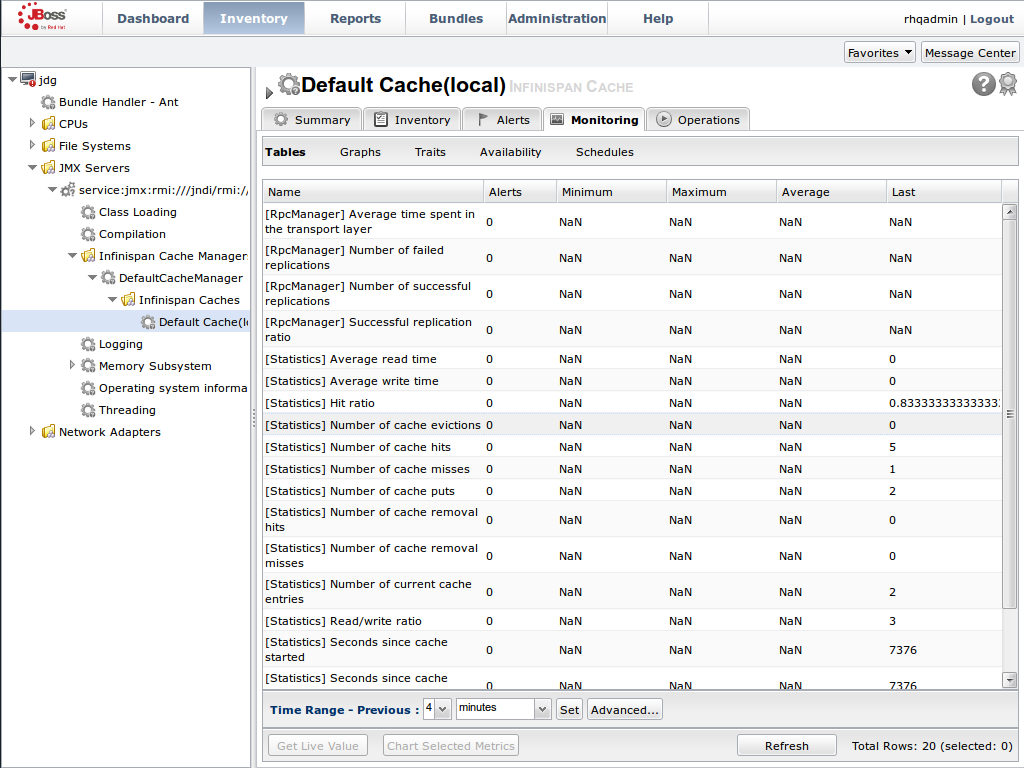
24.7.3.3. Monitor Custom Applications Using Library Mode Deployed On JBoss Enterprise Application Platform
24.7.3.3.1. Monitor an Application Deployed in Standalone Mode
Use the following instructions to monitor an application deployed in JBoss Enterprise Application Platform using its standalone mode:
Monitor an Application Deployed in Standalone Mode
Start the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform Instance
Start the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform instance as follows:
Enter the following command at the command line or change standalone configuration file (/bin/standalone.conf ) respectively:
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.rhq.resourceKey=MyEAP"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.rhq.resourceKey=MyEAP"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform instance in standalone mode as follows:
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/standalone.sh
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/standalone.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Deploy the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Application
Deploy the
WARfile that contains the JBoss Data Grid Library mode application withglobalJmxStatisticsandjmxStatisticsenabled.Run JBoss Operations Network (JON) Discovery
Run the
discovery --fullcommand in the JBoss Operations Network (JON) agent.Locate Application Server Process
In the JBoss Operations Network (JON) web interface, the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform process is listed as a JMX server.
Import the Process Into Inventory
Import the process into the JBoss Operations Network (JON) inventory.
Optional: Run Discovery Again
If required, run the
discovery --fullcommand again to discover the new resources.
24.7.3.3.2. Monitor an Application Deployed in Domain Mode
Use the following instructions to monitor an application deployed in JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6 using its domain mode:
Monitor an Application Deployed in Domain Mode
Edit the Host Configuration
Edit the domain/configuration/host.xml file to replace the
serverelement with the following configuration:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6
Start JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6 in domain mode:
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/domain.sh
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/domain.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Application
Deploy the
WARfile that contains the JBoss Data Grid Library mode application withglobalJmxStatisticsandjmxStatisticsenabled.Run Discovery in JBoss Operations Network (JON)
If required, run the
discovery --fullcommand for the JBoss Operations Network (JON) agent to discover the new resources.
24.8. JBoss Operations Network Plug-in Quickstart
For testing or demonstrative purposes with a single JBoss Operations Network agent, upload the plug-in to the server then type "plugins update" at the agent command line to force a retrieval of the latest plugins from the server.
24.9. Other Management Tools and Operations
24.9.1. Other Management Tools and Operations
Managing Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instances requires exposing significant amounts of relevant statistical information. This information allows administrators to get a clear view of each JBoss Data Grid node’s state. A single installation can comprise of tens or hundreds of JBoss Data Grid nodes and it is important to provide this information in a clear and concise manner. JBoss Operations Network is one example of a tool that provides runtime visibility. Other tools, such as JConsole can be used where JMX is enabled.
24.9.2. Accessing Data via URLs
Caches that have been configured with a REST interface have access to Red Hat JBoss Data Grid using RESTful HTTP access.
The RESTful service only requires a HTTP client library, eliminating the need for tightly coupled client libraries and bindings. For more information about how to retrieve data using the REST interface, refer to the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide .
HTTP put() and post() methods place data in the cache, and the URL used determines the cache name and key(s) used. The data is the value placed into the cache, and is placed in the body of the request.
A Content-Type header must be set for these methods. GET and HEAD methods are used for data retrieval while other headers control cache settings and behavior.
It is not possible to have conflicting server modules interact with the data grid. Caches must be configured with a compatible interface in order to have access to JBoss Data Grid.
24.9.3. Limitations of Map Methods
Specific Map methods, such as size(), values(), keySet() and entrySet(), can be used with certain limitations with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid as they are unreliable. These methods do not acquire locks (global or local) and concurrent modification, additions and removals are excluded from consideration in these calls.
The listed methods have a significant impact on performance. As a result, it is recommended that these methods are used for informational and debugging purposes only.
Performance Concerns
In JBoss Data Grid 7.2 the map methods size(), values(), keySet(), and entrySet() include entries in the cache loader by default. The cache loader in use will determine the performance of these commands; for instance, when using a database these methods will run a complete scan of the table where data is stored, which may result in slower processing. To not load entries from the cache loader, and avoid any potential performance hit, use Cache.getAdvancedCache().withFlags(Flag.SKIP_CACHE_LOAD) before executing the desired method.
Understanding the size() Method (Embedded Caches)
In JBoss Data Grid 7.2 the Cache.size() method provides a count of all elements in both this cache and cache loader across the entire cluster. When using a loader or remote entries, only a subset of entries is held in memory at any given time to prevent possible memory issues, and the loading of all entries may be slow.
In this mode of operation, the result returned by the size() method is affected by the flags org.infinispan.context.Flag#CACHE_MODE_LOCAL, to force it to return the number of entries present on the local node, and org.infinispan.context.Flag#SKIP_CACHE_LOAD, to ignore any passivated entries. Either of these flags may be used to increase performance of this method, at the cost of not returning a count of all elements across the entire cluster.
Understanding the size() Method (Remote Caches)
In JBoss Data Grid 7.2 the Hot Rod protocol contain a dedicated SIZE operation, and the clients use this operation to calculate the size of all entries.
Part XII. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Web Administration
Chapter 25. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console
25.1. About JBoss Data Grid Administration Console
The Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to monitor caches and JBoss Data Grid clusters, while providing a web interface for making dynamic changes to caches, cache-containers, and cluster nodes.
25.2. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console Prerequisites
The Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console is only available in Remote Client-Server Mode.
25.3. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administation Console Getting Started
25.3.1. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console Getting Started
The Administration Console is started automatically when JBoss Data Grid is running in Remote Client-Server Mode. A management user must be added to the server instance, which will then be used to access the web console.
25.3.2. Adding Management User
In order to use the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console, a new management user must be created. To add a new user, execute the add-user.sh utility script within the bin folder of your JBoss Data Grid Server installation and enter the requested information.
The following procedure outlines the steps to add a new management user:
Adding a Management User
Run the add-user script within the bin folder as follows:
./add-user.sh
./add-user.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Select the option for the type of user to be added. For management user, select option
a. - Set the Username and password as per the listed recommendations.
Enter the name of the group or groups in which the user has to be added. Leave blank for no group.
NoteSee the Download and Install JBoss Data Grid section in the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Getting Started Guide for download and installation details.
Confirm if you need the user to be used for Application Server process connection.
NoteBefore proceeding, make sure $JBOSS_HOME is not set to a different installation. Otherwise, you may get unpredictable results.
25.3.3. Logging in the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console
Once the JBoss Data Grid server is running, in either domain or standalone mode, the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console may be accessed at the following login page:
http://${jboss.bind.address.management}:9990/console/index.html
http://${jboss.bind.address.management}:9990/console/index.htmlFigure 25.1. JBoss Data Grid Administration Console Login Screen
Enter the user credentials to log in. After logging in, the cache container view is displayed.
25.4. Dashboard View
25.4.1. Dashboard View
The Dashboard view is split into 3 tabs namely:
- Caches
- Clusters
- Status Events
The Clusters and Status Events tabs are not available when running JBoss Data Grid in standalone non-clustered mode.
25.4.2. Cache Containers View
The first default view after logging in is the Cache Container list. A Cache Container is the primary mechanism for treating a cache instance and is used as a starting point for using a cache itself.
Cache centric view presents the list of configured caches. It is used for viewing and adding caches to clusters, adding and adjusting new cache configurations, adding and configuring endpoints and other cache related administrative tasks.
Figure 25.2. Cache Containers View
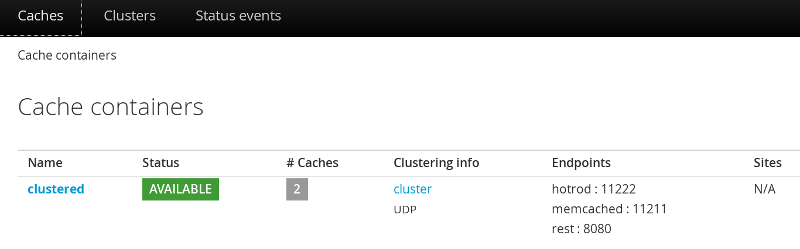
In this instance, there is one cache container with the name clustered with two caches deployed on the cluster group with UDP transport and three Endpoints attached to it. There are no remote sites configured for this cache container.
25.4.3. Clusters View
The Cluster tab presents the summary of the clusters along with the current status, number of hosts and number of nodes.
Figure 25.3. Clusters View
The Cluster view will not appear when the server is running in standalone non-clustered mode.
25.4.4. Status Events View
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console displays the cluster wide events such as local rebalancing, cluster start and stop, cluster-split and cluster-merge events in a consolidated section. To view the detailed status events, navigate to the Status Events tab from the Dashboard.
Figure 25.4. Status Events View
The status events are displayed with the associated timestamp and the event description.
The Status Events view will not appear when the server is running in standalone non-clustered mode.
25.5. Cache Administration
25.5.1. Adding a New Cache
To add a new cache, follow these steps:
Adding a New Cache
In the Cache Containers view, click on the name of the cache container.
Figure 25.5. Cache Containers View
The Caches view is displayed listing all the configured caches. Click Add Cache to add and configure a new cache. The new cache creation window is opened.
Figure 25.6. Add Cache
Enter the new cache name, select the base configuration template from the drop-down menu, check the Edit button, and click Next. If the Edit button is not selected then the cache will be immediately created using the selected template.
Figure 25.7. Cache Properties
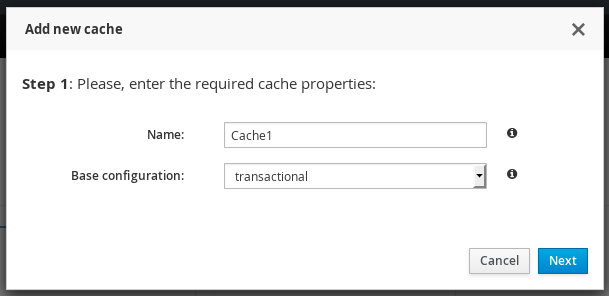
The cache configuration screen is displayed. Enter the cache parameters and click Create.
Figure 25.8. Cache Configuration
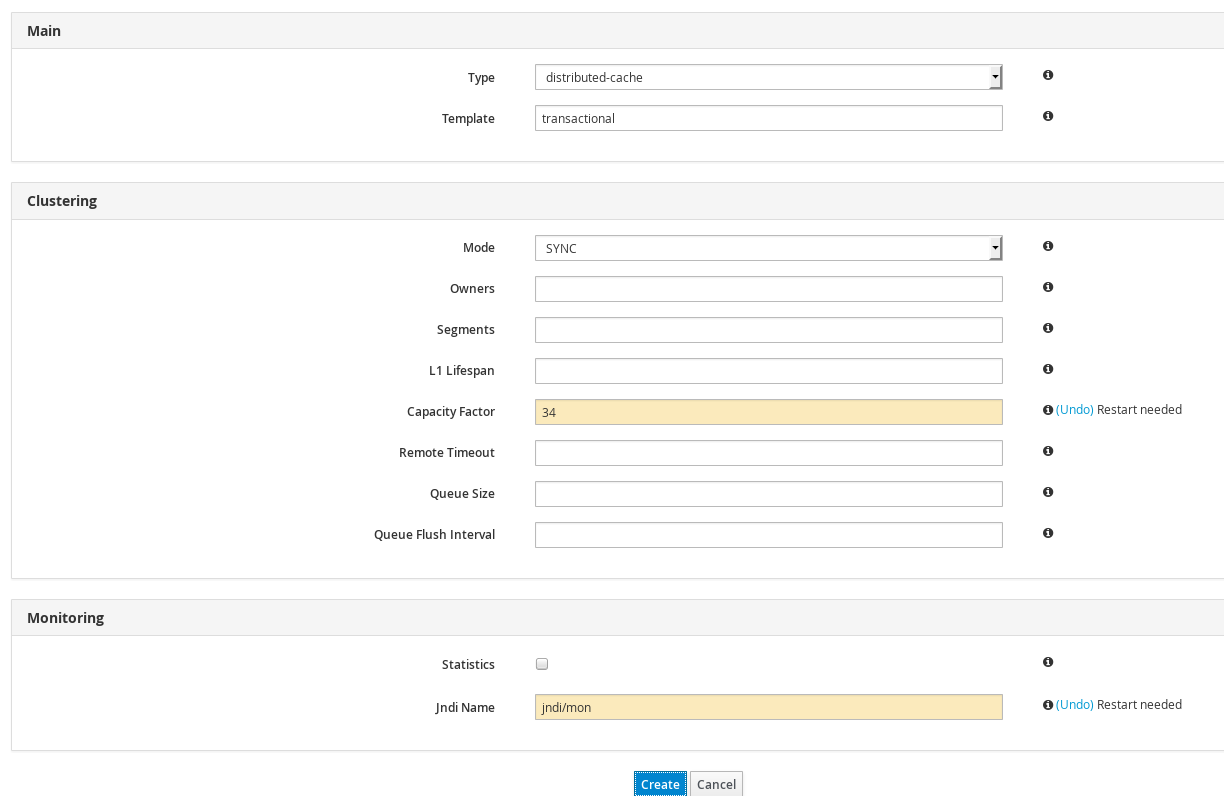
A confirmation screen is displayed. Click Create to create the cache.
Figure 25.9. Cache Confirmation
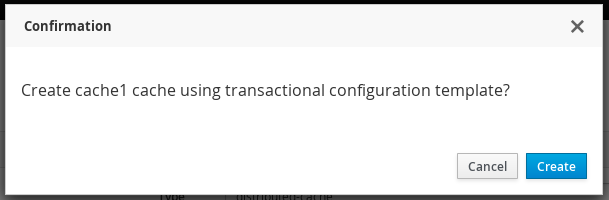
25.5.2. Editing Cache Configuration
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to edit the configuration of an existing cache.
The following procedure outlines the steps to edit a cache configuration:
Editing Cache Configuration
Log into the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console and click on the cache container name.
Figure 25.10. Cache Containers
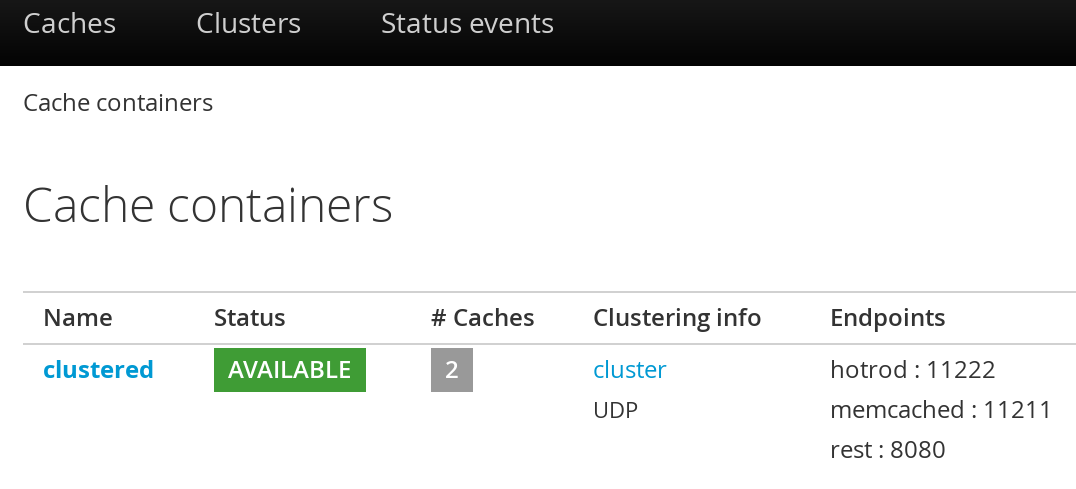
In the Caches view, click on the cache name.
Figure 25.11. Caches View
The cache statistics and properties page is displayed. On the right hand side, click the Configuration tab.
Figure 25.12. Cache Configuration Button
The edit cache configuration interface is opened. The editable cache properties are found in the cache properties menu at the left hand side.
Figure 25.13. Editing Cache Configuration Interface
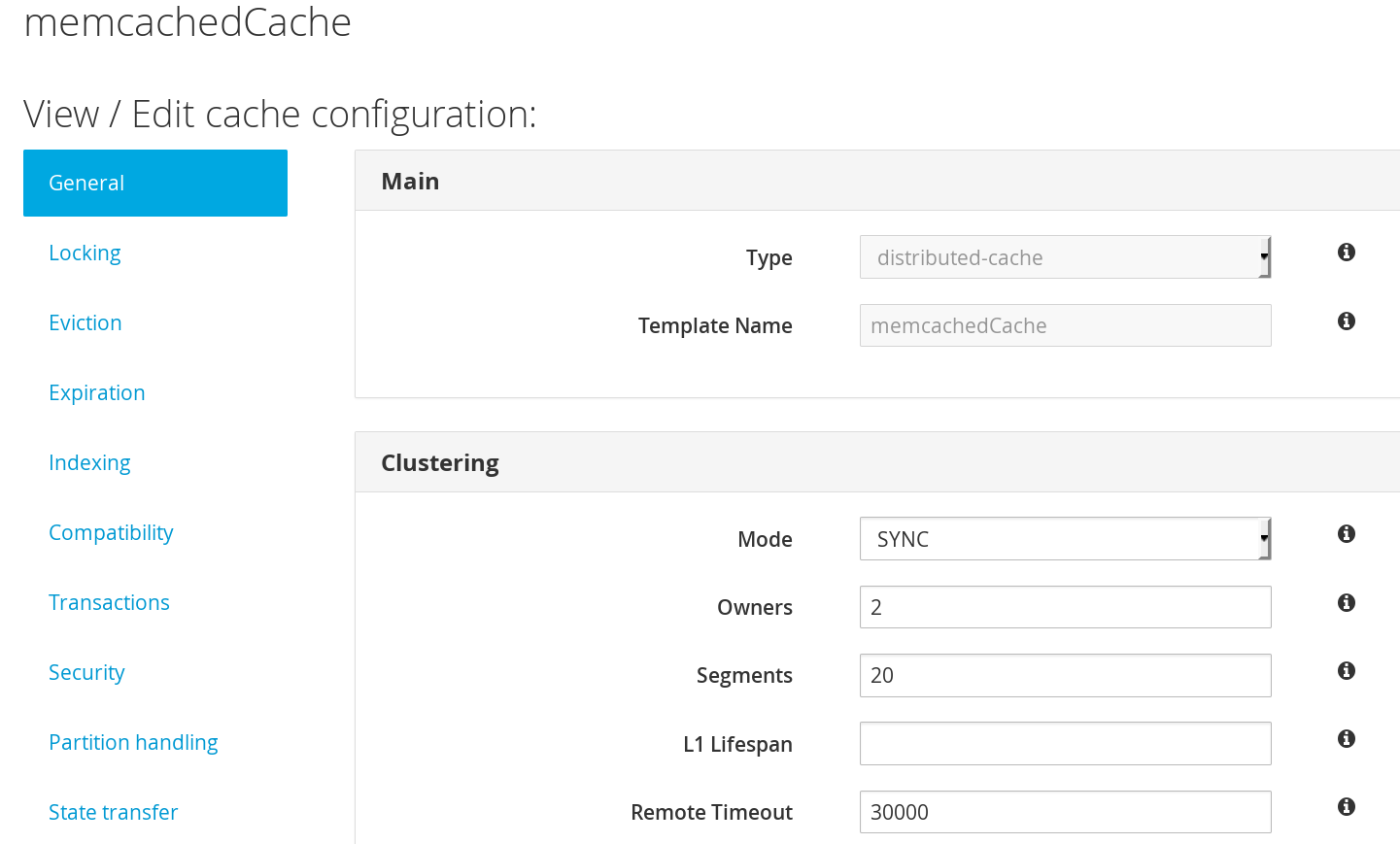
Select the cache configuration property to be edited from the cache properties menu along the left-hand side. To get a description on the cache configuration parameters, hover the cursor over the information icon to the right of each field. The parameter description is presented in form of a tooltip.
Figure 25.14. Cache configuration paramaters
- The General property is selected by default. Edit the required values in the given parameter input fields and click Apply changes below
The restart dialogue box appears. Click Restart Now to apply the changes, or Restart Later to continue editing the cache properties.
Figure 25.15. Restart Dialogue Box
 Note
NoteIn standalone mode the dialog instead contains the following text:
Config changes will only be made available after you manually restart the server!
25.5.3. Cache Statistics and Properties View
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to view all the cache statistics including the average time for reads, average times for writes, total number of entries, total number of reads, total number of failed reads and total number of writes.
To view the cache statistics, follow these steps:
Viewing Cache Statistics
- Navigate to the list of caches by clicking on the name of the cache container in the Cache Container view.
Click on the name of the cache from the list of caches. Optionally you can use the cache filter on the left side to filter caches. The caches can be filtered by a keyword, substring or by selecting the type, the trait, and the status.
Figure 25.16. Caches View
The next page displays the comprehensive cache statistics under the headings:
Cache content,Operations performanceandCaching Activity.Figure 25.17. Cache Statistics
Additional cache statistics are displayed under the headings:
Entries Lifecycle,Cache LoaderandLockingFigure 25.18. Cache Statistics
To view cache properties, click on Configuration at the right hand side.
Figure 25.19. Configuration Button
The cache properties menu is displayed at the left hand side.
Figure 25.20. Cache Properties Menu

To view on which node a cache resides, click on the Nodes tab next to the General Status tab on the cache statistics page.
Figure 25.21. General Status Tab
The name of the Node(s) is displayed along with the read-write statistics.
Figure 25.22. Cache Node Labels
25.5.4. Enable and Disable Caches
The following procedure outlines the steps to disable a cache:
Disabling a Cache
Navigate to the caches view by clicking on the name of the cache container in the Cache Container view. Click on the name of the cache to be disabled.
Figure 25.23. Caches View
The cache statistics will be displayed. On the right hand side of the interface, click on the Actions tab and then click Disable.
Figure 25.24. Cache Disable
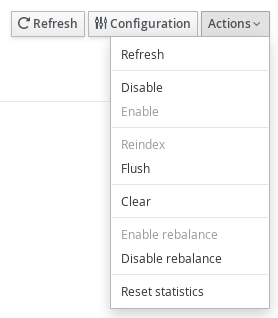
A confirmation dialogue box will appear. Click Disable to disable the cache.
Figure 25.25. Cache Disable Confirmation
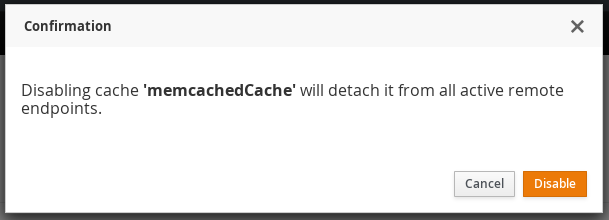
A subsequent dialogue box appears. Click Ok.
Figure 25.26. Confirmation Box
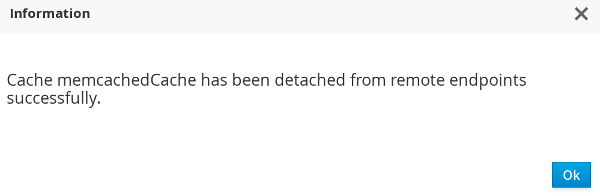
The selected cache is disabled successfully with a visual indicator Disabled next to the cache name label.
Figure 25.27. Disabled Cache

The following procedure outlines the steps to enable a cache:
Enabling a Cache
To enable a cache, click on the specific disabled cache from the Cache view.
Figure 25.28. Caches View

On the right hand side of the interface, click on the Actions tab.

From the Actions tab, click Enable
Figure 25.29. Actions Menu
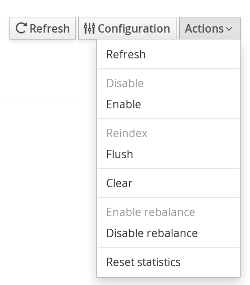
A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Enable.
Figure 25.30. Confirmation Box
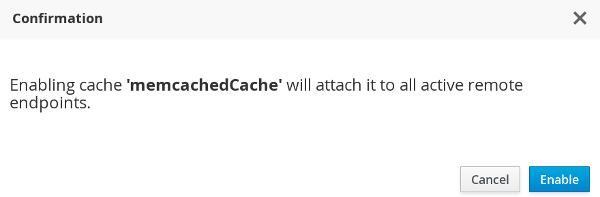
A subsequent dialogue box appears. Click Ok
Figure 25.31. Information Box
The selected cache is enabled successfully with a visual indicator Enabled next to the cache name label.
Figure 25.32. Cache Enabled

25.5.5. Cache Flush and Clear
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to remove all the entries from a cache and the cache stores through the cache Clear operation. The console also provides the Flush operation to store the entries from the cache memory to the cache store. These entries are not removed from the cache memory, as during a Clear operation.
Flushing a Cache
To flush a cache, follow these steps:
Flushing a Cache
- In the Cache Containers view, click on the name of the cache container.
The Caches view is displayed. Click on the cache to be flushed.
Figure 25.33. Caches View
The cache statistics page is displayed. At the right hand side, click Actions.
Figure 25.34. Actions Button

From the Actions menu, click Flush.
Figure 25.35. Actions Menu
A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Flush.
Figure 25.36. Cache Flush Confirmation Box
The cache is successfully flushed. Click Ok.
Figure 25.37. Cache Flush Information Box
Clearing a Cache
To clear a cache, follow these steps:
Clearing a Cache
- In the Cache Containers view, click on the name of the cache container.
The Caches view is displayed. Click on the cache to be cleared.
Figure 25.38. Caches View

On the cache statistics page, at the right hand side, click Actions.

From the Actions menu, click Clear.
Figure 25.39. Clear Button

A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Clear.
Figure 25.40. Confirmation Box
The cache is successfully cleared. Click Ok.
Figure 25.41. Information Box
25.5.6. Server Tasks Execution
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to start a server script job on the JBoss Data Grid cluster.
25.5.7. Server Tasks
25.5.7.1. New Server Task
The following procedure outlines the steps to launch a new server task:
Launching a new task is not supported if the server is running in standalone non-clustered mode.
Launching a New Server Task
- In the Cache Containers view of the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console, click on the name of the Cache container.
On the cache view page, click the Task Execution tab.
Figure 25.42. Task Execution

In the Tasks execution tab, click Launch new task.
Figure 25.43. Launch New Task
Enter the new task properties and click Launch task.
Figure 25.44. Task Properties
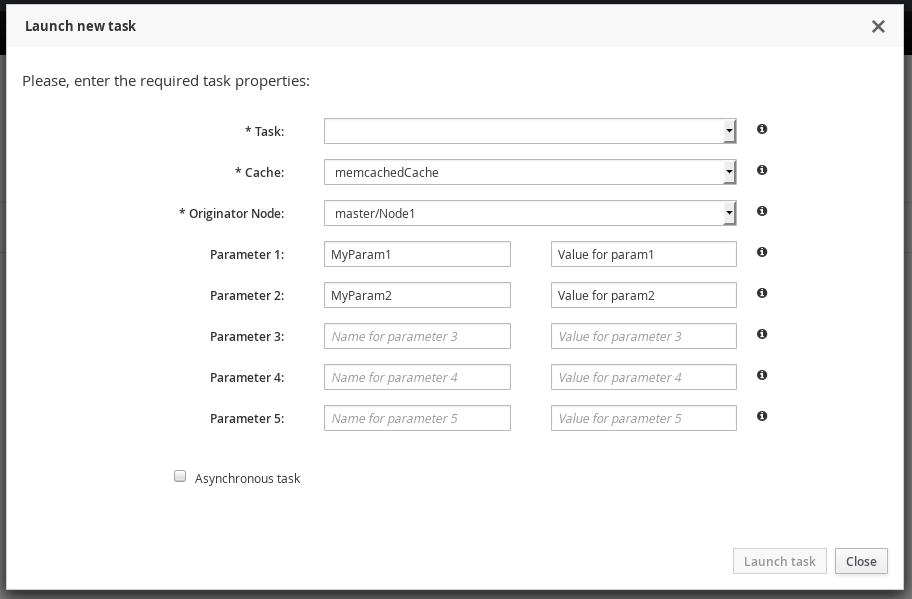
25.5.7.2. Server Tasks View
After the server task is launched, it can be viewed in the Task execution tab along with the other running tasks. The set of completed server script jobs with the start time and end time can be viewed. Additionally, number of successful executions and number of failed executions can also be viewed.
Figure 25.45. Server Tasks View
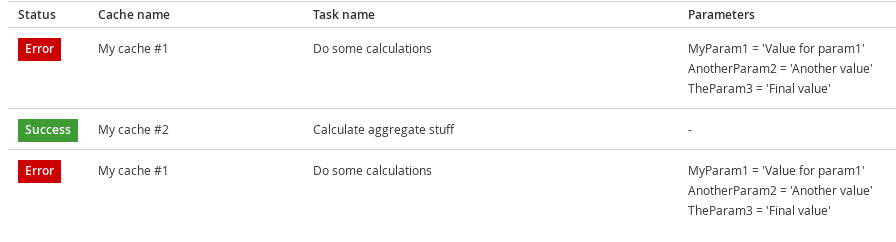
Figure 25.46. Task Start/End Time
25.6. Cache Container Configuration
25.6.1. Cache Container Configuration
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows users to view and set Cache Container level settings such as transport, thread pools, security, cache templates, deployment of remote Executables/Scripts. Each cache container is associated with a cluster.
The following procedure outlines the steps to aceess the Cache Container Configuration settings:
Accessing Cache Container Configuration Settings
In the Cache Container View, click on the name of the cache container.
Figure 25.47. Cache Container View
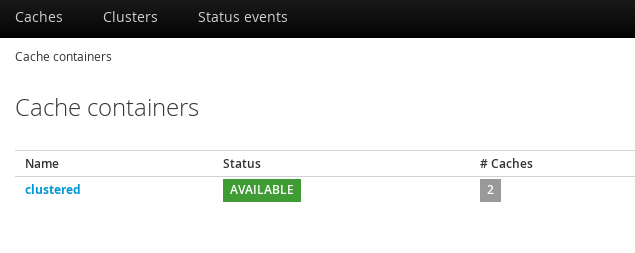
Click Configuration setting button at the top right hand side of the interface.
Figure 25.48. Configuration
The Cache Container Configuration interface is displayed.
Figure 25.49. Cache Container Configuration
25.6.2. Defining Protocol Buffer Schema
A Protocol Buffer Schema is defined in the Cache Container Configuration interface.
The following procedure outlines the steps to define a protobuf schema:
Defining a Protobuf Schema
- Click Add at the right hand side of the Schema tab to launch the create schema window.
Enter the schema name and the schema in the respective fields and click Create Schema.
Figure 25.50. New Schema
The protocol buffer schema is added.
Figure 25.51. Protocol Buffer
25.6.3. Transport Setting
To access the Transport setting, click on the Transport tab in the Cache Container Configuration interface. Enter the Transport settings and click Save .
Figure 25.52. Transport Setting
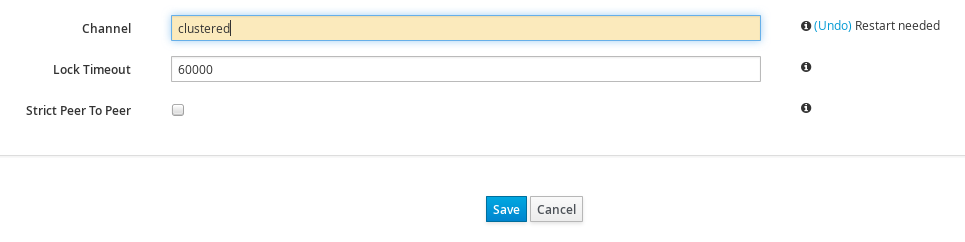
A dialog box will prompt to restart the server due to configuration changes. Restart to apply the changes.
Figure 25.53. Restart Confirmation
25.6.4. Defining Thread Pools
To define thread pools for different cache related operations, click on the Thread Pools tab in the Cache Container Configuration interface.
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to set Thread Pool values for the following cache level operations:
Async Operations
Figure 25.54. Async Operations

The currently set value for each parameter is set by the console. Hover the cursor over the information icon to view the parameter description in form of a tooltip. To change a thread pool value, enter the new value in the parameter field and click Save . A server restart is needed after every change of values.
Expiration
For Expiration settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.55. Expiration Values

Listener
For Listener settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.56. Listener Values

Persistence
For Persistence settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.57. Persistence Values

Remote Commands
For Remote Commands settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.58. Remote Commands
Replication Queue
For Replication Queue settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.59. Replication Queue Values

State Transfer
For Listener settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.60. State Transfer Values
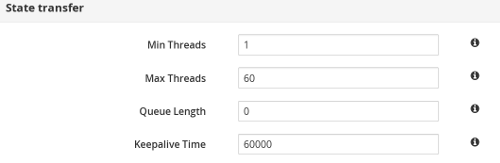
Transport
For Transport settings, the user can set values for the following parameters:
Figure 25.61. Transport Values
25.6.5. Adding New Security Role
The following procedure outlines the steps to add a new security role:
Adding a Security Role
Click on the Security tab. If authorization is not defined for a cache container, click Yes to define.
Figure 25.62. Define Authorization
Select the Role Mapper from the drop-down menu. Click Add to launch the permissions window.
Figure 25.63. Role Mapper Selection
In the Permissions window, enter the name of the new role and assign the permissions by checking the required check-boxes. Click Save changes to save the role.
Figure 25.64. Role Permissions
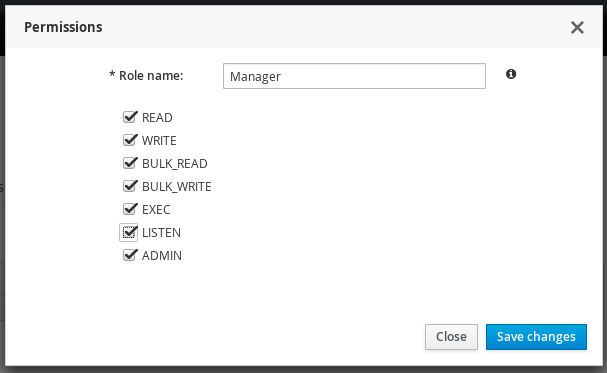
The new security role is added.
Figure 25.65. New Security Role
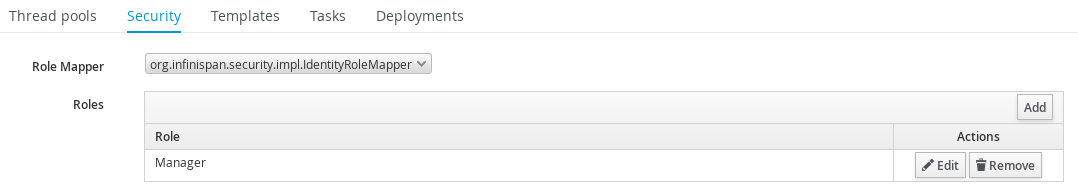
25.6.6. Creating Cache Configuration Template
The Templates tab in the Cache Container Configuration interface lists all the configured and available cache templates.
Figure 25.66. Cache Templates View
The following procedure outlines the steps to create a new Cache configuration template :
Creating New Cache Configuration Template
- Click Create new Template on the right hand side of the templates list.
Enter the cache configuration template name and select the base configuration from the drop-down and click Next.
Figure 25.67. Cache Configuration Template
Set the cache template attributes for the various cache operations such as Locking, Expiration, Indexing and others.
Figure 25.68. Cache Configuration Template
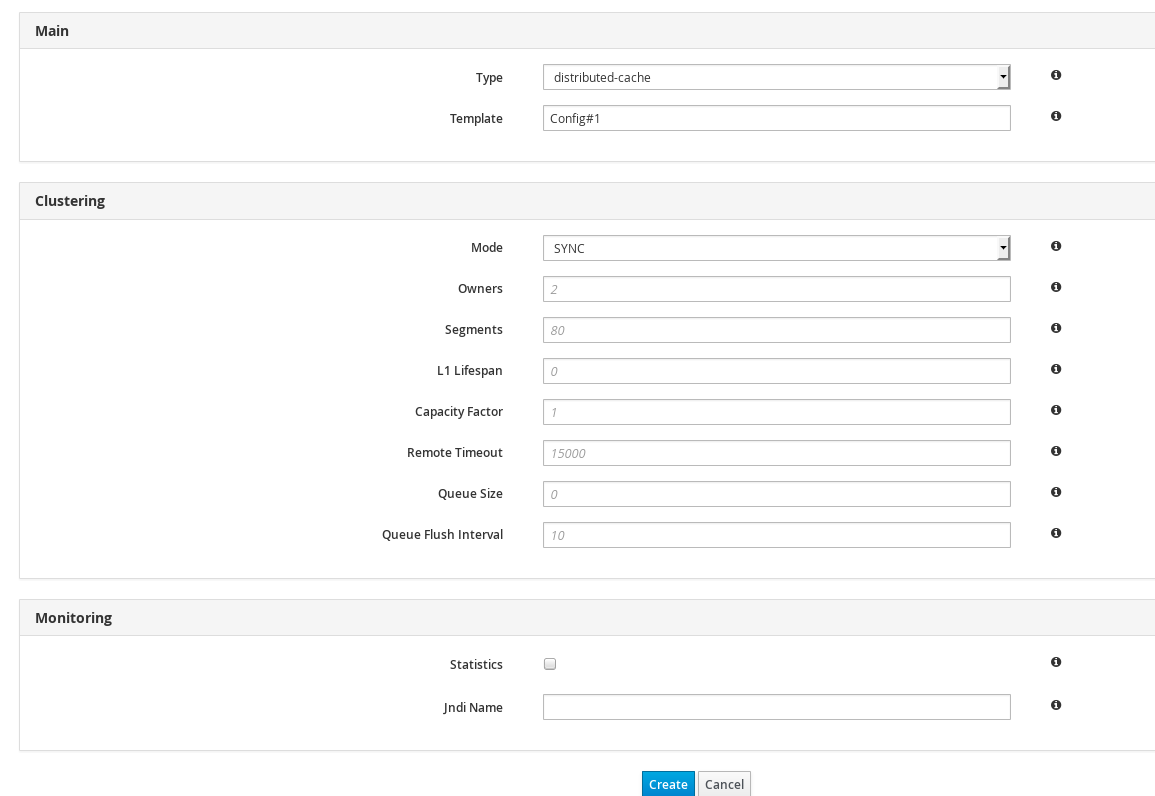
- After entering the values, click Create to create the Cache Template.
25.7. Cluster Administration
25.7.1. Cluster Nodes View
Clusters centric view allows to view the nodes created for each server group and the list of deployed servers can be viewed. In Clusters view, you can add new nodes to the cluster group and view performance metrics of the particular nodes.
The Cluster view will not appear when the server is running in standalone non-clustered mode. When running in standalone clustered mode the Cluster view will be displayed, but no operations on cluster nodes may be performed.
To access the Clusters view, navigate to the Clusters tab from the Dashboard and click on the name of the cluster.
Figure 25.69. Nodes View
25.7.2. Cluster Nodes Mismatch
The total number of server nodes on the JBoss Data Grid cluster should ideally match the number of nodes shown in the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console. If in case, due to some reason, the expected nodes in the console do not match with the exact number of nodes on the JBoss Data Grid physical cluster, the console issues a mismatch warning by displaying the number of nodes detected and the number of expected nodes. Knowing the expected number of server nodes helps in handling Network Partitions.
If nodes mismatch occurs, it can be viewed in the clusters view, above the list of nodes as a warning. To access the Clusters view, navigate to the Clusters tab from the Dashboard and click on the name of the cluster.
In the following screen, the Console alerts the user in the form of a warning. The expected number of server nodes are 5 but only 3 are detected by the console.
Figure 25.70. Cluster Nodes Mismatch
25.7.3. Cluster Rebalancing
The Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows the user to enable and disable cluster rebalancing at the cache container and cache levels.
Cluster rebalancing is enabled by default.
The following procedure outlines the steps to enable and disable cluster rebalancing at a cache container level :
Enable and Disable Rebalancing
- From the cache container view, click on the name of the cache container.
In the caches view, at the right hand side, click on Actions.

A callout menu is opened. Click Disable Rebalancing.
A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Accept.
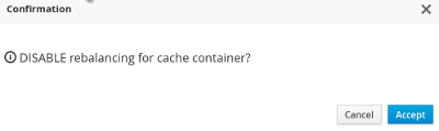
Cluster rebalancing is successfully disabled.
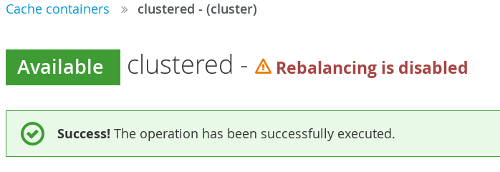
To enable rebalancing, click Actions Enable Rebalancing.
A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Accept.
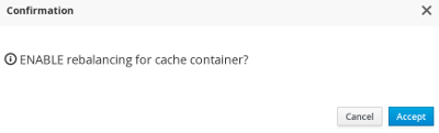
Rebalancing is successfully enabled.
The following procedure outlines the steps to enable and disable cluster rebalancing at a cache level :
Enable and Disable Rebalancing
- From the cache container view, click on the name of the cache container.
- In the caches view, click on a specific cache.
The cache statistics page is displayed. At the right hand side, click Actions.

From the callout menu, click Disable Rebalance.
A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Disable Rebalance.
The rebalancing for the cache is successfully disabled.
To enable cache level rebalancing, click Enable rebalance from the Actions menu.
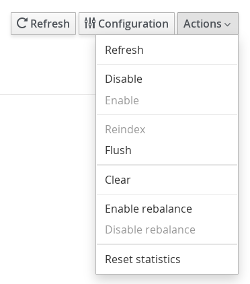
A confirmation dialogue box appears. Click Enable rebalance.
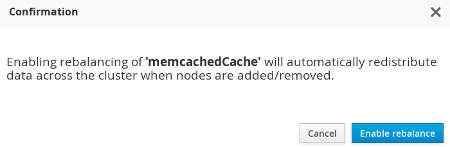
The rebalancing for the cache is successfully enabled.
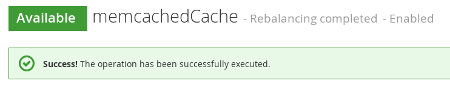
25.7.4. Cluster Partition Handling
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console alerts the user with a visual warning when the cluster changes state to DEGRADED.
The assumed causes for a DEGRADED cluster are occurrence of a network partition, unreachable node(s) or unexpected extra nodes.
The visual warning is displayed in the Clusters view.
To access the Clusters view, navigate to the Clusters tab from the Dashboard and click on the name of the cluster.
In the following screen, the visual warning DEGRADED is displayed next to the cluster name JDG Cluster #1.
Figure 25.71. Network Partition Warning

This visual warning for a DEGRADED cluster is shown at Cluster, Cache Container, and Cache levels of the console.
Partitions can enter Degraded mode only if the DENY_READ_WRITES partition handling strategy is configured. Otherwise all partitions are AVAILABLE in the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console.
25.7.5. Cluster Events
The JBoss Data Grid Console displays the cluster wide events such as cluster-split and cluster-merge events in a consolidated section.
Cluster Events are not available when the server is running in standalone non-clustered mode.
Along with the cluster events, the console displays the timestamp of the associated event. Cluster events can be viewed in the Cache containers page, the Clusters view page and also in the Status Events tab of the Dashboard.
To view cluster events on the cache containers page, navigate to the default cache containers view which is the default landing interface after logging into the console. The Cluster events are displayed at the right hand side in a consolidated section under the title Latest Grid Events
To view the cluster events on the Clusters view page, navigate to the Clusters view by clicking on the Clusters tab. The Cluster events are displayed at the right hand side in a consolidated section under the title Latest status Events
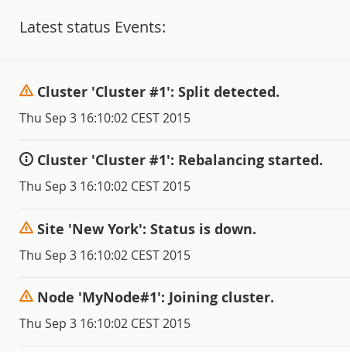
25.7.6. Adding Nodes
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to configure new nodes.
The following procedure outlines the steps to add a new Node:
Adding a New Node
In the Dashboard view, click Cluster tab.
Figure 25.72. Clusters Tab
Click on the name of the cluster where the new node has to be added.
Figure 25.73. Cluster Selection
Click Add Node.
Figure 25.74. Add Node Created
The node configuration window is opened. Enter the node properties in the respective fields and click Create
Figure 25.75. Node Properties
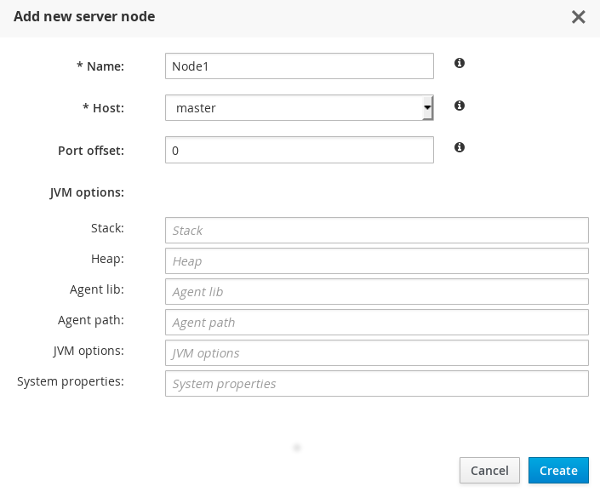
The system boots up.
Figure 25.76. System Boot
The new node is successfully created.
Figure 25.77. New Node
25.7.7. Node Statistics and Properties View
JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows users to view the average time for reads, average times for writes, total number of entries, total number of reads, total number of failed reads, total number of writes and other data.
To view the Node statistics, click on the name of the Node in the Clusters tab on the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console.
Figure 25.78. Nodes Statistics
25.7.8. Node Performance Metrics View
To view the Node performance metrics, click on the name of the node in the Clusters tab of the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console
Figure 25.79. Node Performance Metrics
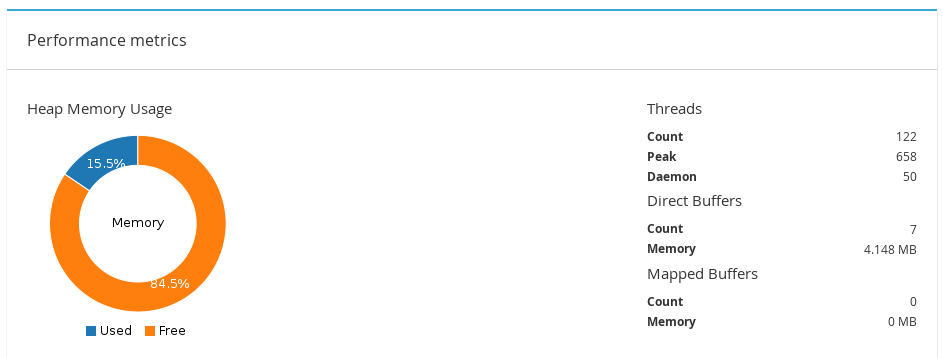
25.7.9. Disabling a Node
The JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows administrators to disable nodes.
To disable a node of a cluster, follow these steps:
Adding a New Node
- Click on the name of the cluster in the Cluster View of the JBoss Data Grid Administration Console.
In the Nodes view, click on the node to be disabled.
Figure 25.80. Nodes View
The Node statistics view is opened. Click on the Actions tab located at the right hand side of the page and then click Stop.
Figure 25.81. Nodes Stop
A confirmation box appears. Click Stop to shut down the node.
Figure 25.82. Confirmation Box
25.7.10. Cluster Shutdown and Restart
25.7.10.1. Cluster Shutdown
JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows convenient and controlled shutdown of JBoss Data Grid clusters for maintenance purposes. For caches with a configured cache store, the data will be persisted without any data loss.For caches without a configured cache store, data will be lost after cluster shutdown.
To shut down or stop a cluster, follow these steps:
Shutting Down Cluster
Navigate to the Clusters view in the JBoss Data Grid Administration console and click on the name of the cluster.
Figure 25.83. Clusters View
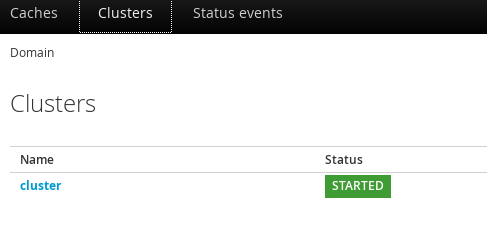
On the Nodes view page, locate the Actions tab to the top right hand side of the interface. Click on Actions tab and then click Stop.
Figure 25.84. Cluster Stop
A confirmation box will appear. To confirm, click Stop.
Figure 25.85. Confirmation Box
25.7.10.2. Cluster Start
JBoss Data Grid Administration Console allows restarting a stopped cluster. The cache data is preloaded without any data loss for caches with configured cache-store. Caches without a configured cache store, will initially contain no data.
Preloading will only happen if preload is enabled on the cache store. If the local cache state on one of the nodes is corrupt, the cache will not start and manual intervention will be required.
To a cluster, follow these steps:
Starting Cluster
- Navigate to the Clusters view in the JBoss Data Grid Administration console and click on the name of the cluster.
On the Nodes view page, locate the Actions tab to the top right hand side of the interface. Click on Actions tab and then click Start.
Figure 25.86. Cluster Start
- A confirmation box will appear. Click Start to start the cluster.
Part XIII. Securing Data in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
Chapter 26. Introduction
26.1. Securing Data in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, data security can be implemented in the following ways:
Role-based Access Control
JBoss Data Grid features role-based access control for operations on designated secured caches. Roles can be assigned to users who access your application, with roles mapped to permissions for cache and cache-manager operations. Only authenticated users are able to perform the operations that are authorized for their role.
In Library mode, data is secured via role-based access control for CacheManagers and Caches, with authentication delegated to the container or application. In Remote Client-Server mode, JBoss Data Grid is secured by passing identity tokens from the Hot Rod client to the server, and role-based access control of Caches and CacheManagers.
Node Authentication and Authorization
Node-level security requires new nodes or merging partitions to authenticate before joining a cluster. Only authenticated nodes that are authorized to join the cluster are permitted to do so. This provides data protection by preventing unauthorized servers from storing your data.
Encrypted Communications Within the Cluster
JBoss Data Grid increases data security by supporting encrypted communications between the nodes in a cluster by using a user-specified cryptography algorithm, as supported by Java Cryptography Architecture (JCA).
JBoss Data Grid also provides audit logging for operations, and the ability to encrypt communication between the Hot Rod Client and Server using Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL).
Chapter 27. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Security: Authorization and Authentication
27.1. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Security: Authorization and Authentication
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid is able to perform authorization on CacheManagers and Caches. JBoss Data Grid authorization is built on standard security features available in a JDK, such as JAAS and the SecurityManager.
If an application attempts to interact with a secured CacheManager and Cache, it must provide an identity which JBoss Data Grid’s security layer can validate against a set of required roles and permissions. Once validated, the client is issued a token for subsequent operations. Where access is denied, an exception indicating a security violation is thrown.
When a cache has been configured for with authorization, retrieving it returns an instance of SecureCache. SecureCache is a simple wrapper around a cache, which checks whether the "current user" has the permissions required to perform an operation. The "current user" is a Subject associated with the AccessControlContext.
JBoss Data Grid maps Principals names to roles, which in turn, represent one or more permissions. The following diagram represents these relationships:
Figure 27.1. Roles and Permissions Mapping
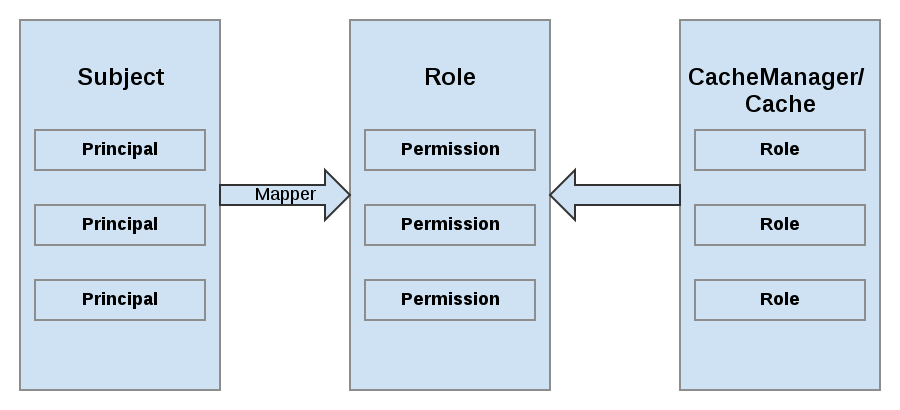
27.2. Permissions
Access to a CacheManager or a Cache is controlled using a set of required permissions. Permissions control the type of action that is performed on the CacheManager or Cache, rather than the type of data being manipulated. Some of these permissions can apply to specifically name entities, such as a named cache. Different types of permissions are available depending on the entity.
| Permission | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONFIGURATION | defineConfiguration | Whether a new cache configuration can be defined. |
| LISTEN | addListener | Whether listeners can be registered against a cache manager. |
| LIFECYCLE | stop, start | Whether the cache manager can be stopped or started respectively. |
| ALL | A convenience permission which includes all of the above. |
| Permission | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| READ | get, contains | Whether entries can be retrieved from the cache. |
| WRITE | put, putIfAbsent, replace, remove, evict | Whether data can be written/replaced/removed/evicted from the cache. |
| EXEC | distexec, mapreduce | Whether code execution can be run against the cache. |
| LISTEN | addListener | Whether listeners can be registered against a cache. |
| BULK_READ | keySet, values, entrySet,query | Whether bulk retrieve operations can be executed. |
| BULK_WRITE | clear, putAll | Whether bulk write operations can be executed. |
| LIFECYCLE | start, stop | Whether a cache can be started / stopped. |
| ADMIN | getVersion, addInterceptor*, removeInterceptor, getInterceptorChain, getEvictionManager, getComponentRegistry, getDistributionManager, getAuthorizationManager, evict, getRpcManager, getCacheConfiguration, getCacheManager, getInvocationContextContainer, setAvailability, getDataContainer, getStats, getXAResource | Whether access to the underlying components/internal structures is allowed. |
| ALL | A convenience permission which includes all of the above. | |
| ALL_READ | Combines READ and BULK_READ. | |
| ALL_WRITE | Combines WRITE and BULK_WRITE. |
Some permissions may need to be combined with others in order to be useful. For example, EXEC with READ or with WRITE.
27.3. Role Mapping
In order to convert the Principals in a Subject into a set of roles used for authorization, a PrincipalRoleMapper must be specified in the global configuration. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid ships with three mappers, and also allows you to provide a custom mapper.
| Mapper Name | Java | XML | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| IdentityRoleMapper | org.infinispan.security.impl.IdentityRoleMapper | <identity-role-mapper /> | Uses the Principal name as the role name. |
| CommonNameRoleMapper | org.infinispan.security.impl.CommonRoleMapper | <common-name-role-mapper /> |
If the Principal name is a Distinguished Name (DN), this mapper extracts the Common Name (CN) and uses it as a role name. For example the DN |
| ClusterRoleMapper | org.infinispan.security.impl.ClusterRoleMapper | <cluster-role-mapper /> |
Uses the |
| Custom Role Mapper | <custom-role-mapper class="a.b.c" /> |
Supply the fully-qualified class name of an implementation of |
27.4. Configuring Authentication and Role Mapping using Login Modules
When using the authentication login-module for querying roles from LDAP, you must implement your own mapping of Principals to Roles, as custom classes are in use. An example implementation of this conversion is found in the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide , while a declarative configuration example is below:
Example of LDAP Login Module Configuration
Example of Login Module Configuration
When using GSSAPI authentication, this would typically involve using LDAP for role mapping, with the JBoss Data Grid server authenticating itself to the LDAP server via GSSAPI. For an example on configuring this authentication to an Active Directory server refer to Active Directory Authentication Using Kerberos (GSSAPI).
For information on configuring an LDAP server, or specifying users and roles in an LDAP server, refer to the Red Hat Directory Server Administration Guide .
27.5. Configuring Red Hat JBoss Data Grid for Authorization
Authorization is configured at two levels: the cache container (CacheManager), and at the single cache.
CacheManager
The following is an example configuration for authorization at the CacheManager level:
CacheManager Authorization (Declarative Configuration)
Each cache container determines:
- whether to use authorization.
- a class which will map principals to a set of roles.
- a set of named roles and the permissions they represent.
You can choose to use only a subset of the roles defined at the container level.
Roles
Roles may be applied on a cache-per-cache basis, using the roles defined at the cache-container level, as follows:
Defining Roles
<local-cache name="secured">
<security>
<authorization roles="admin reader writer supervisor"/>
</security>
</local-cache>
<local-cache name="secured">
<security>
<authorization roles="admin reader writer supervisor"/>
</security>
</local-cache>Any cache that is intended to require authentication must have a listing of roles defined; otherwise authentication is not enforced as the no-anonymous policy is defined by the cache’s authorization.
The REST protocol is not supported for use with authorization, and any attempts to access a cache with authorization enabled will result in a SecurityException.
27.6. Authorization Using a SecurityManager
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, authorization is able to work without a SecurityManager for basic cache operations. In Library mode, a SecurityManager may also be used to perform some of the more complex tasks, such as distexec and query among others.
In order to enforce access restrictions, enable the SecurityManager in your JVM using one of the following methods:
Command Line
java -Djava.security.manager ...
java -Djava.security.manager ...Programmaticaly
System.setSecurityManager(new SecurityManager());
System.setSecurityManager(new SecurityManager());
Using the JDK’s default implementation is not required; however, an appropriate policy file must be supplied. The policy file defines a set of permissions, which the SecurityManager examines when an application performs an action. If the action is allowed by the policy file, then the SecurityManager will permit the action to take place; however, if the action is not allowed by the policy then the SecurityManager denies that action.
Example policy files are below:
Library Mode Security Policy File Example
Remote Client-Server Security Policy File Example
27.7. SecurityManager in Java
27.7.1. About the Java Security Manager
Java Security Manager
The Java Security Manager is a class that manages the external boundary of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) sandbox, controlling how code executing within the JVM can interact with resources outside the JVM. When the Java Security Manager is activated, the Java API checks with the security manager for approval before executing a wide range of potentially unsafe operations.
The Java Security Manager uses a security policy to determine whether a given action will be permitted or denied.
27.7.2. About Java Security Manager Policies
Security Policy
A set of defined permissions for different classes of code. The Java Security Manager compares actions requested by applications against the security policy. If an action is allowed by the policy, the Security Manager will permit that action to take place. If the action is not allowed by the policy, the Security Manager will deny that action. The security policy can define permissions based on the location of code, on the code’s signature, or based on the subject’s principals.
The Java Security Manager and the security policy used are configured using the Java Virtual Machine options java.security.manager and java.security.policy.
Basic Information
A security policy’s entry consists of the following configuration elements, which are connected to the policytool:
- CodeBase
- The URL location (excluding the host and domain information) where the code originates from. This parameter is optional.
- SignedBy
- The alias used in the keystore to reference the signer whose private key was used to sign the code. This can be a single value or a comma-separated list of values. This parameter is optional. If omitted, presence or lack of a signature has no impact on the Java Security Manager.
- Principals
-
A list of
principal_type/principal_namepairs, which must be present within the executing thread’s principal set. The Principals entry is optional. If it is omitted, it signifies that the principals of the executing thread will have no impact on the Java Security Manager. - Permissions
- A permission is the access which is granted to the code. Many permissions are provided as part of the Java Enterprise Edition 6 (Java EE 6) specification. This document only covers additional permissions which are provided by JBoss EAP 6.
Refer to your container documentation on how to configure the security policy, as it may differ depending on the implementation.
27.7.3. Write a Java Security Manager Policy
Introduction
An application called policytool is included with most JDK and JRE distributions, for the purpose of creating and editing Java Security Manager security policies. Detailed information about policytool is linked from http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/tools/.
Setup a new Java Security Manager Policy
Start policytool
Start the
policytooltool in one of the following ways.Red Hat Enterprise Linux
From your GUI or a command prompt, run
/usr/bin/policytool.Microsoft Windows Server
Run
policytool.exefrom your Start menu or from the bin\ of your Java installation. The location can vary.
Create a policy.
To create a policy, select Add Policy Entry. Add the parameters you need, then click Done. .
Edit an existing policy.
Select the policy from the list of existing policies, and select the Edit Policy Entry button. Edit the parameters as needed.
Delete an existing policy.
Select the policy from the list of existing policies, and select the Remove Policy Entry button.
27.7.4. Run Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server Within the Java Security Manager
To specify a Java Security Manager policy, you need to edit the Java options passed to the server instance during the bootstrap process. For this reason, you cannot pass the parameters as options to the standalone.sh script. The following procedure guides you through the steps of configuring your instance to run within a Java Security Manager policy.
Prerequisites
Before you following this procedure, you need to write a security policy, using the policytool command which is included with your Java Development Kit (JDK). This procedure assumes that your policy is located at JDG_HOME/bin/server.policy . As an alternative, write the security policy using any text editor and manually save it as JDG_HOME/bin/server.policy * The JBoss Data Grid server must be completely stopped before you edit any configuration files.
Perform the following procedure for each physical host or instance in your environment.
Configure the Security Manager for JBoss Data Grid Server
Open the configuration file.
Open the configuration file for editing. This location of this file is listed below by OS. Note that this is not the executable file used to start the server, but a configuration file that contains runtime parameters. For Linux: JDG_HOME/bin/standalone.conf For Windows: JDG_HOME\bin\standalone.conf.bat
Add the Java options to the file.
To ensure the Java options are used, add them to the code block that begins with:
if [ "x$JAVA_OPTS" = "x" ]; then
if [ "x$JAVA_OPTS" = "x" ]; thenCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can modify the
-Djava.security.policyvalue to specify the exact location of your security policy. It should go onto one line only, with no line break. Using==when setting the-Djava.security.policyproperty specifies that the security manager will use only the specified policy file. Using=specifies that the security manager will use the specified policy combined with the policy set in thepolicy.urlsection of JAVA_HOME/lib/security/java.security .ImportantJBoss Enterprise Application Platform releases from 6.2.2 onwards require that the system property
jboss.modules.policy-permissionsis set to true.standalone.conf
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy==$PWD/server.policy -Djboss.home.dir=$JBOSS_HOME -Djboss.modules.policy-permissions=true"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy==$PWD/server.policy -Djboss.home.dir=$JBOSS_HOME -Djboss.modules.policy-permissions=true"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow standalone.conf.bat
set "JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy==\path\to\server.policy -Djboss.home.dir=%JBOSS_HOME% -Djboss.modules.policy-permissions=true"
set "JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Djava.security.manager -Djava.security.policy==\path\to\server.policy -Djboss.home.dir=%JBOSS_HOME% -Djboss.modules.policy-permissions=true"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the server.
Start the server as normal.
27.8. Data Security for Remote Client Server Mode
27.8.1. About Security Realms
A security realm is a series of mappings between users and passwords, and users and roles. Security realms are a mechanism for adding authentication and authorization to your EJB and Web applications. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server provides two security realms by default:
-
ManagementRealmstores authentication information for the Management API, which provides the functionality for the Management CLI and web-based Management Console. It provides an authentication system for managing JBoss Data Grid Server itself. You could also use theManagementRealmif your application needed to authenticate with the same business rules you use for the Management API. -
ApplicationRealmstores user, password, and role information for Web Applications and EJBs.
Each realm is stored in two files on the filesystem:
- REALM-users.properties stores usernames and hashed passwords.
- REALM-roles.properties stores user-to-role mappings.
-
mgmt-groups.properties stores user-to-role mapping file for
ManagementRealm.
The properties files are stored in the standalone/configuration/ directories. The files are written simultaneously by the add-user.sh or add-user.bat command. When you run the command, the first decision you make is which realm to add your new user to.
27.8.2. Add a New Security Realm
Run the Management CLI
Start the cli.sh or cli.bat command and connect to the server.
Create the new security realm itself
Run the following command to create a new security realm named
MyDomainRealmon a domain controller or a standalone server./host=master/core-service=management/security-realm=MyDomainRealm:add()
/host=master/core-service=management/security-realm=MyDomainRealm:add()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the reference to the properties file which will store information about the new realm’s users
Run the below command to define the location of the new security realm’s properties file; this file contains information regarding the users of this security realm. The following command references a file named myfile.properties in the
jboss.server.config.dir.NoteThe newly-created properties file is not managed by the included add-user.sh and add-user.bat scripts. It must be managed externally.
/host=master/core-service=management/security-realm=MyDomainRealm/authentication=properties:add(path="myfile.properties",relative-to="jboss.server.config.dir")
/host=master/core-service=management/security-realm=MyDomainRealm/authentication=properties:add(path="myfile.properties",relative-to="jboss.server.config.dir")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server
Reload the server so the changes will take effect.
:reload
:reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Result
The new security realm is created. When you add users and roles to this new realm, the information will be stored in a separate file from the default security realms. You can manage this new file using your own applications or procedures.
27.8.3. Add a User to a Security Realm
Run the add-user.sh or add-user.bat command
Open a terminal and change directories to the JDG_HOME/bin/ directory. If you run Red Hat Enterprise Linux or another UNIX-like operating system, run add-user.sh. If you run Microsoft Windows Server, run add-user.bat.
Choose whether to add a Management User or Application User
For this procedure, type
bto add an Application User.Choose the realm this user will be added to
By default, the only available realms are the
ManagementRealmandApplicationRealm; however, if a custom realm has been added, then its name may be entered instead.Type the username, password, and roles, when prompted
Type the desired username, password, and optional roles when prompted. Verify your choice by typing
yes, or typenoto cancel the changes. The changes are written to each of the properties files for the security realm.
27.8.4. Configuring Security Realms Declaratively
In Remote Client-Server mode, a Hot Rod endpoint must specify a security realm.
The security realm declares an authentication and an authorization section.
Configuring Security Realms Declaratively
The server-identities parameter can also be used to specify certificates.
27.8.5. Loading Roles from LDAP for Authorization (Remote Client-Server Mode)
An LDAP directory contains entries for user accounts and groups, cross referenced by attributes. Depending on the LDAP server configuration, a user entity may map the groups the user belongs to through memberOf attributes; a group entity may map which users belong to it through uniqueMember attributes; or both mappings may be maintained by the LDAP server.
Users generally authenticate against the server using a simple user name. When searching for group membership information, depending on the directory server in use, searches could be performed using this simple name or using the distinguished name of the user’s entry in the directory.
The authentication step of a user connecting to the server always happens first. Once the user is successfully authenticated the server loads the user’s groups. The authentication step and the authorization step each require a connection to the LDAP server. The realm optimizes this process by reusing the authentication connection for the group loading step. As will be shown within the configuration steps below it is possible to define rules within the authorization section to convert a user’s simple user name to their distinguished name. The result of a "user name to distinguished name mapping" search during authentication is cached and reused during the authorization query when the force attribute is set to "false". When force is true, the search is performed again during authorization (while loading groups). This is typically done when different servers perform authentication and authorization.
These examples specify some attributes with their default values. This is done for demonstration. Attributes that specify their default values are removed from the configuration when it is persisted by the server. The exception is the force attribute. It is required, even when set to the default value of false.
username-to-dn
The username-to-dn element specifies how to map the user name to the distinguished name of their entry in the LDAP directory. This element is only required when both of the following are true:
- The authentication and authorization steps are against different LDAP servers.
The group search uses the distinguished name.
- 1:1 username-to-dn
- This specifies that the user name entered by the remote user is the user’s distinguished name.
<username-to-dn force="false"> <username-is-dn /> </username-to-dn>
<username-to-dn force="false">
<username-is-dn />
</username-to-dn>+ This defines a 1:1 mapping and there is no additional configuration.
- username-filter
- The next option is very similar to the simple option described above for the authentication step. A specified attribute is searched for a match against the supplied user name.
<username-to-dn force="true">
<username-filter base-dn="dc=people,dc=harold,dc=example,dc=com" recursive="false" attribute="sn" user-dn-attribute="dn" />
</username-to-dn>
<username-to-dn force="true">
<username-filter base-dn="dc=people,dc=harold,dc=example,dc=com" recursive="false" attribute="sn" user-dn-attribute="dn" />
</username-to-dn>+ The attributes that can be set here are:
-
base-dn: The distinguished name of the context to begin the search. -
recursive: Whether the search will extend to sub contexts. Defaults tofalse. -
attribute: The attribute of the users entry to try and match against the supplied user name. Defaults touid. user-dn-attribute: The attribute to read to obtain the users distinguished name. Defaults todn.- advanced-filter
- The final option is to specify an advanced filter, as in the authentication section this is an opportunity to use a custom filter to locate the users distinguished name.
<username-to-dn force="true">
<advanced-filter base-dn="dc=people,dc=harold,dc=example,dc=com" recursive="false" filter="sAMAccountName={0}" user-dn-attribute="dn" />
</username-to-dn>
<username-to-dn force="true">
<advanced-filter base-dn="dc=people,dc=harold,dc=example,dc=com" recursive="false" filter="sAMAccountName={0}" user-dn-attribute="dn" />
</username-to-dn>+ For the attributes that match those in the username-filter example, the meaning and default values are the same. There is one new attribute:
filter: Custom filter used to search for a user’s entry where the user name will be substituted in the{0}place holder.ImportantThe XML must remain valid after the filter is defined so if any special characters are used such as
&ensure the proper form is used. For example&for the&character.The Group Search
There are two different styles that can be used when searching for group membership information. The first style is where the user’s entry contains an attribute that references the groups the user is a member of. The second style is where the group contains an attribute referencing the users entry.
When there is a choice of which style to use Red Hat recommends that the configuration for a user’s entry referencing the group is used. This is because with this method group information can be loaded by reading attributes of known distinguished names without having to perform any searches. The other approach requires extensive searches to identify the groups that reference the user.
Before describing the configuration here are some LDIF examples to illustrate this.
Principal to Group - LDIF example.
This example illustrates where we have a user TestUserOne who is a member of GroupOne, GroupOne is in turn a member of GroupFive. The group membership is shown by the use of a memberOf attribute which is set to the distinguished name of the group of which the user (or group) is a member.
It is not shown here but a user could potentially have multiple memberOf attributes set, one for each group of which the user is directly a member.
Group to Principal - LDIF Example
This example shows the same user TestUserOne who is a member of GroupOne which is in turn a member of GroupFive - however in this case it is an attribute uniqueMember from the group to the user being used for the cross reference.
Again the attribute used for the group membership cross reference can be repeated, if you look at GroupFive there is also a reference to another user TestUserFive which is not shown here.
General Group Searching
Before looking at the examples for the two approaches shown above we first need to define the attributes common to both of these.
<group-search group-name="..." iterative="..." group-dn-attribute="..." group-name-attribute="..." >
...
</group-search>
<group-search group-name="..." iterative="..." group-dn-attribute="..." group-name-attribute="..." >
...
</group-search>-
group-name: This attribute is used to specify the form that should be used for the group name returned as the list of groups of which the user is a member. This can either be the simple form of the group name or the group’s distinguished name. If the distinguished name is required this attribute can be set toDISTINGUISHED_NAME. Defaults toSIMPLE. -
iterative: This attribute is used to indicate if, after identifying the groups a user is a member of, we should also iteratively search based on the groups to identify which groups the groups are a member of. If iterative searching is enabled we keep going until either we reach a group that is not a member if any other groups or a cycle is detected. Defaults tofalse.
Cyclic group membership is not a problem. A record of each search is kept to prevent groups that have already been searched from being searched again.
For iterative searching to work the group entries need to look the same as user entries. The same approach used to identify the groups a user is a member of is then used to identify the groups of which the group is a member. This would not be possible if for group to group membership the name of the attribute used for the cross reference changes or if the direction of the reference changes.
-
group-dn-attribute: On an entry for a group which attribute is its distinguished name. Defaults todn. -
group-name-attribute: On an entry for a group which attribute is its simple name. Defaults touid.
Principal to Group Example Configuration
Based on the example LDIF from above here is an example configuration iteratively loading a user’s groups where the attribute used to cross reference is the memberOf attribute on the user.
The most important aspect of this configuration is that the principal-to-group element has been added with a single attribute.
-
group-attribute: The name of the attribute on the user entry that matches the distinguished name of the group the user is a member of. Defaults tomemberOf.
Group to Principal Example Configuration
This example shows an iterative search for the group to principal LDIF example shown above.
Here an element group-to-principal is added. This element is used to define how searches for groups that reference the user entry will be performed. The following attributes are set:
-
base-dn: The distinguished name of the context to use to begin the search. -
recursive: Whether sub-contexts also be searched. Defaults tofalse. -
search-by: The form of the role name used in searches. Valid values areSIMPLEandDISTINGUISHED_NAME. Defaults toDISTINGUISHED_NAME.
Within the group-to-principal element there is a membership-filter element to define the cross reference.
-
principal-attribute: The name of the attribute on the group entry that references the user entry. Defaults tomember.
27.9. Securing Interfaces
27.9.1. Hot Rod Interface Security
27.9.1.1. Publish Hot Rod Endpoints as a Public Interface
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Hot Rod server operates as a management interface as a default. To extend its operations to a public interface, alter the value of the interface parameter in the socket-binding element from management to public as follows:
<socket-binding name="hotrod" interface="public" port="11222" />
<socket-binding name="hotrod" interface="public" port="11222" />27.9.1.2. Encryption of communication between Hot Rod Server and Hot Rod client
Hot Rod can be encrypted using TLS/SSL, and has the option to require certificate-based client authentication.
Use the following procedure to secure the Hot Rod connector using SSL.
Secure Hot Rod Using SSL/TLS
Generate a Keystore
Create a Java Keystore using the keytool application distributed with the JDK and add your certificate to it. The certificate can be either self signed, or obtained from a trusted CA depending on your security policy.
Place the Keystore in the Configuration Directory
Put the keystore in the ~/JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration directory with the standalone-hotrod-ssl.xml file from the ~/JDG_HOME/docs/examples/configs directory.
Declare an SSL Server Identify
Declare an SSL server identity within a security realm in the management section of the configuration file. The SSL server identity must specify the path to a keystore and its secret key.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See Configure Hot Rod Authentication (X.509) for details about these parameters.
Add the Security Element
Add the security element to the Hot Rod connector as follows:
<hotrod-connector socket-binding="hotrod" cache-container="local"> <encryption security-realm="ApplicationRealm" require-ssl-client-auth="false" /> </hotrod-connector><hotrod-connector socket-binding="hotrod" cache-container="local"> <encryption security-realm="ApplicationRealm" require-ssl-client-auth="false" /> </hotrod-connector>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optionally Configure Client Certificate Authentication
If you require the server to authenticate the client certificate, create a truststore that contains the valid client certificates and set the
require-ssl-client-authattribute totrue.Start the Server
Start the server using the following:
bin/standalone.sh -c standalone-hotrod-ssl.xml
bin/standalone.sh -c standalone-hotrod-ssl.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This will start a server with a Hot Rod endpoint on port 11222. This endpoint will only accept SSL connections.
This will start a server with a Hot Rod endpoint on port 11222. This endpoint will only accept SSL connections.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
To prevent plain text passwords from appearing in configurations or source codes, plain text passwords should be changed to Vault passwords. For more information about how to set up Vault passwords, see the Password Vault section of the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform security documentation. .
27.9.1.3. Securing Hot Rod to LDAP Server using SSL
When connecting to an LDAP server with SSL enabled it may be necessary to specify a trust store or key store containing the appropriate certificates.
Encryption of communication between Hot Rod Server and Hot Rod client describes how to set up SSL for Hot Rod client-server communication. This can be used, for example, for secure Hot Rod client authentication with PLAIN username/password. When the username/password is checked against credentials in LDAP, a secure connection from the Hot Rod server to the LDAP server is also required. To enable connection from the Hot Rod server to LDAP via SSL, a security realm must be defined as follows:
Hot Rod Client Authentication to LDAP Server
To prevent plain text passwords from appearing in configurations or source codes, plain text passwords should be changed to Vault passwords. For more information about how to set up Vault passwords, see the Red Hat Enterprise Application Platform Security Guide .
27.9.1.4. User Authentication over Hot Rod Using SASL
27.9.1.4.1. User Authentication over Hot Rod Using SASL
User authentication over Hot Rod can be implemented using the following Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) mechanisms:
-
PLAINis the least secure mechanism because credentials are transported in plain text format. However, it is also the simplest mechanism to implement. This mechanism can be used in conjunction with encryption (SSL) for additional security. -
DIGEST-MD5is a mechanism than hashes the credentials before transporting them. As a result, it is more secure than thePLAINmechanism. -
GSSAPIis a mechanism that uses Kerberos tickets. As a result, it requires a correctly configured Kerberos Domain Controller (for example, Microsoft Active Directory). -
EXTERNALis a mechanism that obtains the required credentials from the underlying transport (for example, from aX.509client certificate) and therefore requires client certificate encryption to work correctly.
27.9.1.4.2. Configure Hot Rod Authentication (GSSAPI/Kerberos)
Use the following steps to set up Hot Rod Authentication using the SASL GSSAPI/Kerberos mechanism:
Configure SASL GSSAPI/Kerberos Authentication - Server-side Configuration
Define a Kerberos security login module using the security domain subsystem:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that the cache-container has authorization roles defined, and these roles are applied in the cache’s authorization block as seen in Configuring Red Hat JBoss Data Grid for Authorization.
Configure a Hot Rod connector as follows:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
server-nameattribute specifies the name that the server declares to incoming clients. The client configuration must also contain the same server name value. -
The
server-context-nameattribute specifies the name of the login context used to retrieve a server subject for certain SASL mechanisms (for example, GSSAPI). -
The
mechanismsattribute specifies the authentication mechanism in use. See User Authentication over Hot Rod Using SASL for a list of supported mechanisms. -
The
qopattribute specifies the SASL quality of protection value for the configuration. Supported values for this attribute areauth(authentication),auth-int(authentication and integrity, meaning that messages are verified against checksums to detect tampering), andauth-conf(authentication, integrity, and confidentiality, meaning that messages are also encrypted). Multiple values can be specified, for example,auth-int auth-conf. The ordering implies preference, so the first value which matches both the client and server’s preference is chosen. -
The
strengthattribute specifies the SASL cipher strength. Valid values arelow,medium, andhigh. -
The
no-anonymouselement within thepolicyelement specifies whether mechanisms that accept anonymous login are permitted. Set this value tofalseto permit andtrueto deny.
-
The
- Perform the Client-Side configuration on each client. As the Hot Rod client is configured programmatically information on this configuration is found in the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide .
27.9.1.4.3. Configure Hot Rod Authentication (MD5)
Use the following steps to set up Hot Rod Authentication using the SASL MD5 mechanism:
Configure Hot Rod Authentication (MD5)
Set up the Hot Rod Connector configuration by adding the
saslelement to theauthenticationelement (for details on theauthenticationelement, see Configuring Security Realms Declaratively) as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
server-nameattribute specifies the name that the server declares to incoming clients. The client configuration must also contain the same server name value. -
The
mechanismsattribute specifies the authentication mechanism in use. See User Authentication over Hot Rod Using SASL for a list of supported mechanisms. -
The
qopattribute specifies the SASL quality of production value for the configuration. Supported values for this attribute areauth,auth-int, andauth-conf.
-
The
- Configure each client to be connected to the Hot Rod connector. As this step is performed programmatically instructions are found in JBoss Data Grid’s Developer Guide .
27.9.1.4.4. Configure Hot Rod Using LDAP/Active Directory
Use the following to configure authentication over Hot Rod using LDAP or Microsoft Active Directory:
The following are some details about the elements and parameters used in this configuration:
-
The
security-realmelement’snameparameter specifies the security realm to reference to use when establishing the connection. -
The
authenticationelement contains the authentication details. The
ldapelement specifies how LDAP searches are used to authenticate a user. First, a connection to LDAP is established and a search is conducted using the supplied user name to identify the distinguished name of the user. A subsequent connection to the server is established using the password supplied by the user. If the second connection succeeds, the authentication is a success.-
The
connectionparameter specifies the name of the connection to use to connect to LDAP. -
The (optional)
recursiveparameter specifies whether the filter is executed recursively. The default value for this parameter isfalse. -
The
base-dnparameter specifies the distinguished name of the context to use to begin the search from. -
The (optional)
user-dnparameter specifies which attribute to read for the user’s distinguished name after the user is located. The default value for this parameter isdn.
-
The
-
The
outbound-connectionselement specifies the name of the connection used to connect to the LDAP directory. The
ldapelement specifies the properties of the outgoing LDAP connection.-
The
nameparameter specifies the unique name used to reference this connection. -
The
urlparameter specifies the URL used to establish the LDAP connection. -
The
search-dnparameter specifies the distinguished name of the user to authenticate and to perform the searches. -
The
search-credentialparameter specifies the password required to connect to LDAP as thesearch-dn. -
The (optional)
initial-context-factoryparameter allows the overriding of the initial context factory. the default value of this parameter iscom.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory.
-
The
27.9.1.4.5. Configure Hot Rod Authentication (X.509)
The X.509 certificate can be installed at the node, and be made available to other nodes for authentication purposes for inbound and outbound SSL connections. This is enabled using the <server-identities/> element of a security realm definition, which defines how a server appears to external applications. This element can be used to configure a password to be used when establishing a remote connection, as well as the loading of an X.509 key.
The following example shows how to install an X.509 certificate on the node.
In the provided example, the SSL element contains the <keystore/> element, which is used to define how to load the key from the file-based keystore. The following parameters ave available for this element.
| Parameter | Mandatory/Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Mandatory | This is the path to the keystore, this can be an absolute path or relative to the next attribute. |
|
| Optional | The name of a service representing a path the keystore is relative to. |
|
| Mandatory | The password required to open the keystore. |
|
| Optional | The alias of the entry to use from the keystore - for a keystore with multiple entries in practice the first usable entry is used but this should not be relied on and the alias should be set to guarantee which entry is used. |
|
| Optional | The password to load the key entry, if omitted the keystore-password will be used instead. |
If the following error occurs, specify a key-password as well as an alias to ensure only one key is loaded.
UnrecoverableKeyException: Cannot recover key
UnrecoverableKeyException: Cannot recover key27.9.2. REST Interface Security
27.9.2.1. Publish REST Endpoints as a Public Interface
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s REST server operates as a management interface by default. To extend its operations to a public interface, alter the value of the interface parameter in the socket-binding element from management to public as follows:
<socket-binding name="http" interface="public" port="8080"/>
<socket-binding name="http"
interface="public"
port="8080"/>27.9.2.2. Enable Security for the REST Endpoint
Use the following procedure to enable security for the REST endpoint in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
The REST endpoint supports any of the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform security subsystem providers.
Enable Security for the REST Endpoint
To enable security for JBoss Data Grid when using the REST interface, make the following changes to standalone.xml:
Ensure that the rest endpoint defines a valid configuration for the
authenticationattribute. An example configuration is below:<subsystem xmlns="urn:infinispan:server:endpoint:8.1"> <rest-connector socket-binding="rest" cache-container="security"> <authentication security-realm="ApplicationRealm" auth-method="BASIC"/> </rest-connector> </subsystem><subsystem xmlns="urn:infinispan:server:endpoint:8.1"> <rest-connector socket-binding="rest" cache-container="security"> <authentication security-realm="ApplicationRealm" auth-method="BASIC"/> </rest-connector> </subsystem>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check Security Domain Declaration
Ensure that the security subsystem contains the corresponding security-domain declaration. For details about setting up security-domain declarations, see the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 7 documentation.
Add an Application User
Run the relevant script and enter the configuration settings to add an application user.
Run the adduser.sh script (located in $JDG_HOME/bin ).
- On a Windows system, run the adduser.bat file (located in $JDG_HOME/bin ) instead.
-
When prompted about the type of user to add, select
Application User (application-users.properties)by enteringb. -
Accept the default value for realm (
ApplicationRealm) by pressing the return key. - Specify a username and password.
-
When prompted for a group, enter
REST. - Ensure the username and application realm information is correct when prompted and enter "yes" to continue.
Verify the Created Application User
Ensure that the created application user is correctly configured.
Check the configuration listed in the application-users.properties file (located in $JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration/ ). The following is an example of what the correct configuration looks like in this file:
user1=2dc3eacfed8cf95a4a31159167b936fc
user1=2dc3eacfed8cf95a4a31159167b936fcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the configuration listed in the application-roles.properties file (located in $JDG_HOME/standalone/configuration/ ). The following is an example of what the correct configuration looks like in this file:
user1=REST
user1=RESTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Test the Server
Start the server and enter the following link in a browser window to access the REST endpoint:
http://localhost:8080/rest/namedCache
http://localhost:8080/rest/namedCacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf testing using a GET request, a
405response code is expected and indicates that the server was successfully authenticated.
27.9.3. Memcached Interface Security
27.9.3.1. Publish Memcached Endpoints as a Public Interface
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s memcached server operates as a management interface by default. It is possible to extend the memcached operations to a public interface, but there is no additional security available for this interface. If security is a concern then it is recommended to keep this interface on an isolated, internal network, or to use either the REST or Hot Rod interfaces.
To configure the memcached interface as a public interface, alter the value of the interface parameter in the socket-binding element from management to public as follows:
<socket-binding name="memcached" interface="public" port="11211" />
<socket-binding name="memcached"
interface="public"
port="11211" />27.10. Active Directory Authentication (Non-Kerberos)
See Example of LDAP Login Module Configuration for a non-Kerberos Active Directory Authentication configuration example.
27.11. Active Directory Authentication Using Kerberos (GSSAPI)
When using Red Hat JBoss Data Grid with Microsoft Active Directory, data security can be enabled via Kerberos authentication. To configure Kerberos authentication for Microsoft Active Directory, use the following procedure.
Configure Kerberos Authentication for Active Directory (Library Mode)
Configure JBoss EAP server to authenticate itself to Kerberos. This can be done by configuring a dedicated security domain, for example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The security domain for authentication must be configured correctly for JBoss EAP, an application must have a valid Kerberos ticket. To initiate the Kerberos ticket, you must reference another security domain using
<module-option name="usernamePasswordDomain" value="krb-admin"/>
<module-option name="usernamePasswordDomain" value="krb-admin"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This points to the standard Kerberos login module described in Step 3.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The security domain authentication configuration described in the previous step points to the following standard Kerberos login module:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
27.12. The Security Audit Logger
27.12.1. The Security Audit Logger
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes a logger to audit security logs for the cache, specifically whether a cache or a cache manager operation was allowed or denied for various operations.
The default audit logger is org.infinispan.security.impl.DefaultAuditLogger. This logger outputs audit logs using the available logging framework (for example, JBoss Logging) and provides results at the TRACE level and the AUDIT category.
To send the AUDIT category to either a log file, a JMS queue, or a database, use the appropriate log appender.
27.12.2. Configure the Security Audit Logger (Library Mode)
Use the following to configure the audit logger in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid:
27.12.3. Configure the Security Audit Logger (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Use the following code to configure the audit logger in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Remote Client-Server Mode.
To use a different audit logger, specify it in the authorization element. The authorization element must be within the cache-container element in the Infinispan subsystem (in the standalone.xml configuration file).
The default audit logger for server mode is org.jboss.as.clustering.infinispan.subsystem.ServerAuditLogger which sends the log messages to the server audit log. See the Management Interface Audit Logging chapter in the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform Administration and Configuration Guide for more information.
27.12.4. Custom Audit Loggers
Users can implement custom audit loggers in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Library and Remote Client-Server Mode. The custom logger must implement the org.infinispan.security.AuditLogger interface. If no custom logger is provided, the default logger (DefaultAuditLogger) is used.
Chapter 28. Security for Cluster Traffic
28.1. Node Authentication and Authorization (Remote Client-Server Mode)
28.1.1. Node Authentication and Authorization (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Security can be enabled at node level via SASL protocol, which enables node authentication against a security realm. This requires nodes to authenticate each other when joining or merging with a cluster. For detailed information about security realms, see About Security Realms.
The following example depicts the <sasl /> element, which leverages the SASL protocol. Both DIGEST-MD5 or GSSAPI mechanisms are currently supported.
Configure SASL Authentication
In the provided example, the nodes use the DIGEST-MD5 mechanism to authenticate against the ClusterRealm. In order to join, nodes must have the cluster role.
The cluster-role attribute determines the role all nodes must belong to in the security realm in order to JOIN or MERGE with the cluster. Unless it has been specified, the cluster-role attribute is the name of the clustered <cache-container> by default. Each node identifies itself using the client-name property. If none is specified, the hostname on which the server is running will be used.
This name can also be overridden by specifying the jboss.node.name system property that can be overridden on the command line. For example:
standalone.sh -Djboss.node.name=node001
$ standalone.sh -Djboss.node.name=node001JGroups AUTH protocol is not integrated with security realms, and its use is not advocated for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
28.1.2. Configure Node Authentication for Cluster Security (DIGEST-MD5)
The following example demonstrates how to use DIGEST-MD5 with a properties-based security realm, with a dedicated realm for cluster node.
Using the DIGEST-MD5 Mechanism
In the provided example, supposing the hostnames of the various nodes are node001, node002, node003, the cluster-users.properties will contain:
-
node001=/<node001passwordhash>/ -
node002=/<node002passwordhash>/ -
node003=/<node003passwordhash>/
The cluster-roles.properties will contain:
- node001=clustered
- node002=clustered
- node003=clustered
To generate these values, the following add-users.sh script can be used:
add-user.sh -up cluster-users.properties -gp cluster-roles.properties -r ClusterRealm -u node001 -g clustered -p <password>
$ add-user.sh -up cluster-users.properties -gp cluster-roles.properties -r ClusterRealm -u node001 -g clustered -p <password>
The MD5 password hash of the node must also be placed in the "client_password" property of the <sasl/> element.
<property name="client_password>...</property>
<property name="client_password>...</property>To increase security, it is recommended that this password be stored using a Vault. For more information about vault expressions, see the Red Hat Enterprise Application Platform Security Guide
Once node security has been set up as discussed here, the cluster coordinator will validate each JOINing and MERGEing node’s credentials against the realm before letting the node become part of the cluster view.
28.1.3. Configure Node Authentication for Cluster Security (GSSAPI/Kerberos)
When using the GSSAPI mechanism, the client_name is used as the name of a Kerberos-enabled login module defined within the security domain subsystem. For a full procedure on how to do this, see Configure Hot Rod Authentication (GSSAPI/Kerberos).
Using the Kerberos Login Module
The following property must be set in the <sasl/> element to reference it:
<sasl <!-- Additional configuration information here --> >
<property name="login_module_name">
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</property>
</sasl>
<sasl <!-- Additional configuration information here --> >
<property name="login_module_name">
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</property>
</sasl>
As a result, the authentication section of the security realm is ignored, as the nodes will be validated against the Kerberos Domain Controller. The authorization configuration is still required, as the node principal must belong to the required cluster-role.
In all cases, it is recommended that a shared authorization database, such as LDAP, be used to validate node membership in order to simplify administration.
By default, the principal of the joining node must be in the following format:
jgroups/$NODE_NAME/$CACHE_CONTAINER_NAME@REALM
jgroups/$NODE_NAME/$CACHE_CONTAINER_NAME@REALM28.2. Configure Node Security in Library Mode
28.2.1. Configure Node Security in Library Mode
In Library mode, node authentication is configured directly in the JGroups configuration. JGroups can be configured so that nodes must authenticate each other when joining or merging with a cluster. The authentication uses SASL and is enabled by adding the SASL protocol to your JGroups XML configuration.
SASL relies on JAAS notions, such as CallbackHandlers, to obtain certain information necessary for the authentication handshake. Users must supply their own CallbackHandlers on both client and server sides.
The JAAS API is only available when configuring user authentication and authorization, and is not available for node security.
In the provided example, CallbackHandler classes are examples only, and not contained in the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid release. Users must provide the appropriate CallbackHandler classes for their specific LDAP implementation.
Setting Up SASL Authentication in JGroups
The above example uses the DIGEST-MD5 mechanism. Each node must declare the user and password it will use when joining the cluster.
The SASL protocol must be placed before the GMS protocol in order for authentication to take effect.
28.2.2. Simple Authorizing Callback Handler
For instances where a more complex Kerberos or LDAP approach is not needed the SimpleAuthorizingCallbackHandler class may be used. To enable this set both the server_callback_handler and the client_callback_handler to org.jgroups.auth.sasl.SimpleAuthorizingCallbackHandler , as seen in the below example:
The SimpleAuthorizingCallbackHandler may be configured either programmatically, by passing the constructor an instance of of java.util.Properties , or via standard Java system properties, set on the command line using the -DpropertyName=propertyValue notation. The following properties are available:
-
sasl.credentials.properties- the path to a property file which contains principal/credential mappings represented as principal=password . -
sasl.local.principal- the name of the principal that is used to identify the local node. It must exist in the sasl.credentials.properties file. -
sasl.roles.properties- (optional) the path to a property file which contains principal/roles mappings represented as principal=role1,role2,role3 . -
sasl.role- (optional) if present, authorizes joining nodes only if their principal is. -
sasl.realm- (optional) the name of the realm to use for the SASL mechanisms that require it
28.2.3. Configure Node Authentication for Library Mode (DIGEST-MD5)
The behavior of a node differs depending on whether it is the coordinator node or any other node. The coordinator acts as the SASL server, with the joining or merging nodes behaving as SASL clients. When using the DIGEST-MD5 mechanism in Library mode, the server and client callback must be specified so that the server and client are aware of how to obtain the credentials. Therefore, two CallbackHandlers are required:
-
The
server_callback_handler_classis used by the coordinator. -
The
client_callback_handler_classis used by other nodes.
The following example demonstrates these CallbackHandlers.
Callback Handlers
JGroups is designed so that all nodes are able to act as coordinator or client depending on cluster behavior, so if the current coordinator node goes down, the next node in the succession chain will become the coordinator. Given this behavior, both server and client callback handlers must be identified within SASL for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid implementations.
28.2.4. Configure Node Authentication for Library Mode (GSSAPI)
When performing node authentication in Library mode using the GSSAPI mechanism, the login_module_name parameter must be specified instead of callback.
This login module is used to obtain a valid Kerberos ticket, which is used to authenticate a client to the server. The server_name must also be specified, as the client principal is constructed as jgroups/$server_name@REALM .
Specifying the login module and server on the coordinator node
<SASL mech="GSSAPI"
server_name="node0/clustered"
login_module_name="krb-node0"
server_callback_handler_class="org.infinispan.test.integration.security.utils.SaslPropCallbackHandler" />
<SASL mech="GSSAPI"
server_name="node0/clustered"
login_module_name="krb-node0"
server_callback_handler_class="org.infinispan.test.integration.security.utils.SaslPropCallbackHandler" />
On the coordinator node, the server_callback_handler_class must be specified for node authorization. This will determine if the authenticated joining node has permission to join the cluster.
The server principal is always constructed as jgroups/server_name, therefore the server principal in Kerberos must also be jgroups/server_name. For example, if the server name in Kerberos is jgroups/node1/mycache, then the server name must be node1/mycache.
28.3. JGroups Encryption
28.3.1. JGroups Encryption
JGroups includes the SYM_ENCRYPT and ASYM_ENCRYPT protocols to provide encryption for cluster traffic.
The ENCRYPT protocol has been deprecated and should not be used in production environments. It is recommended to use either SYM_ENCRYPT or ASYM_ENCRYPT
By default, both of these protocols only encrypt the message body; they do not encrypt message headers. To encrypt the entire message, including all headers, as well as destination and source addresses, the property encrypt_entire_message must be true. When defining these protocols they should be placed directly under NAKACK2.
Both protocols may be used to encrypt and decrypt communication in JGroups, and are used in the following ways:
-
SYM_ENCRYPT: Configured with a secret key in a keystore using theJCEKSstore type. -
ASYM_ENCRYPT: Configured with algorithms and key sizes. In this scenario the secret key is not retrieved from the keystore, but instead generated by the coordinator and distributed to new members. Once a member joins the cluster they send a request for the secret key to the coordinator; the coordinator responds with the secret key back to the new member encrypted with the member’s public key.
Each message is identified as encrypted with a specific encryption header identifying the encrypt header and an MD5 digest identifying the version of the key being used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
28.3.2. Configuring JGroups Encryption Protocols
JGroups encryption protocols are placed in the JGroups configuration file, and there are three methods of including this file depending on how JBoss Data Grid is in use:
-
Standard Java properties can also be used in the configuration, and it is possible to pass the path to JGroups configuration via the
-Doption during start up. - The default, pre-configured JGroups files are packaged in infinispan-embedded.jar , alternatively, you can create your own configuration file. See Configure JGroups (Library Mode) for instructions on how to set up JBoss Data Grid to use custom JGroups configurations in library mode.
- In Remote Client-Server mode, the JGroups configuration is part of the main server configuration file.
When defining both the SYM_ENCRYPT and ASYM_ENCRYPT protocols, place them directly above NAKACK2 in the configuration file.
28.3.3. SYM_ENCRYPT: Using a Key Store
SYM_ENCRYPT uses store type JCEKS. To generate a keystore compatible with JCEKS, use the following command line options to keytool:
keytool -genseckey -alias myKey -keypass changeit -storepass changeit -keyalg Blowfish -keysize 56 -keystore defaultStore.keystore -storetype JCEKS
$ keytool -genseckey -alias myKey -keypass changeit -storepass changeit -keyalg Blowfish -keysize 56 -keystore defaultStore.keystore -storetype JCEKS
SYM_ENCRYPT can then be configured by adding the following information to the JGroups file used by the application.
<SYM_ENCRYPT sym_algorithm="AES"
encrypt_entire_message="true"
keystore_name="defaultStore.keystore"
store_password="changeit"
alias="myKey"/>
<SYM_ENCRYPT sym_algorithm="AES"
encrypt_entire_message="true"
keystore_name="defaultStore.keystore"
store_password="changeit"
alias="myKey"/>
The defaultStore.keystore must be found in the classpath.
28.3.4. ASYM_ENCRYPT: Configured with Algorithms and Key Sizes
In this encryption mode, the coordinator selects the secretKey and distributes it to all peers. There is no keystore, and keys are distributed using a public/private key exchange. Instead, encryption occurs as follows:
- The secret key is generated and distributed by the coordinator.
- When a view change occurs, a peer requests the secret key by sending a key request with its own public key.
- The coordinator encrypts the secret key with the public key, and sends it back to the peer.
- The peer then decrypts and installs the key as its own secret key.
- Any further communications are encrypted and decrypted using the secret key.
ASYM_ENCRYPT Example
In the provided example, ASYM_ENCRYPT has been placed immediately before NAKACK2, and encrypt_entire_message has been enabled, indicating that the message headers will be encrypted along with the message body. This means that the NAKACK2 and UNICAST3 protocols are also encrypted. In addition, AUTH has been included as part of the configuration, so that only authenticated nodes may request the secret key from the coordinator.
View changes that identify a new controller result in a new secret key being generated and distributed to all peers. This is a substantial overhead in an application with high peer churn. A new secret key may optionally be generated when a cluster member leaves by setting change_key_on_leave to true.
When encrypting an entire message, the message must be marshalled into a byte buffer before being encrypted, resulting in decreased performance.
28.3.5. JGroups Encryption Configuration Parameters
The following table provides configuration parameters for the ENCRYPT JGroups protocol, which both SYM_ENCRYPT and ASYM_ENCRYPT extend:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| asym_algorithm | Cipher engine transformation for asymmetric algorithm. Default is RSA. |
| asym_keylength | Initial public/private key length. Default is 512. |
| asym_provider | Cryptographic Service Provider. Default is Bouncy Castle Provider. |
| encrypt_entire_message |
By default only the message body is encrypted. Enabling |
| sym_algorithm | Cipher engine transformation for symmetric algorithm. Default is AES. |
| sym_keylength | Initial key length for matching symmetric algorithm. Default is 128. |
| sym_provider | Cryptographic Service Provider. Default is Bouncy Castle Provider. |
The following table provides a list of the SYM_ENCRYPT protocol parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| alias | Alias used for recovering the key. Change the default. |
| key_password | Password for recovering the key. Change the default. |
| keystore_name | File on classpath that contains keystore repository. |
| store_password | Password used to check the integrity/unlock the keystore. Change the default. |
The following table provides a list of the ASYM_ENCRYPT protocol parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| change_key_on_leave | When a member leaves the view, change the secret key, preventing old members from eavesdropping. |
Part XIV. Command Line Tools
Chapter 29. Introduction
29.1. Command Line Tools
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes two command line tools for interacting with the caches in the data grid:
- The JBoss Data Grid Library CLI. For more information, see Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Library Mode CLI.
- The JBoss Data Grid Server CLI. For more information, see Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server CLI.
Chapter 30. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid CLIs
30.1. JBoss Data Grid CLIs
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes two Command Line Interfaces: a Library Mode CLI (see Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Library Mode CLI for details) and a Server Mode CLI (see Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server CLI for details).
30.2. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Library Mode CLI
30.2.1. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Library Mode CLI
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Library Mode Command Line Interface (CLI) that is used to inspect and modify data within caches and internal components (such as transactions, cross-datacenter replication sites, and rolling upgrades). The JBoss Data Grid Library Mode CLI can also be used for more advanced operations such as transactions.
30.2.2. Start the Library Mode CLI (Server)
Start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid CLI’s server-side module with the standalone and domain files. For Linux, use the standalone.sh or domain.sh script and for Windows, use the standalone.bat or domain.bat file.
30.2.3. Start the Library Mode CLI (Client)
Start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid CLI client using the cli files in the bin directory. For Linux, run bin/cli.sh and for Windows, run bin\cli.bat .
When starting up the CLI client, specific command line switches can be used to customize the start up.
30.2.4. CLI Client Switches for the Command Line
The listed command line switches are appended to the command line when starting the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid CLI command:
| Short Option | Long Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -c | --connect=${URL} |
Connects to a running Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instance. For example, for JMX over RMI use |
| -f | --file=${FILE} |
Read the input from the specified file rather than using interactive mode. If the value is set to |
| -h | --help | Displays the help information. |
| -v | --version | Displays the CLI version information. |
30.2.5. Connect to the Application
Use the following command to connect to the application using the CLI:
[disconnected//]> connect 127.0.0.1:9990 [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/>
[disconnected//]> connect 127.0.0.1:9990
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/>
The port value 9990 depends on the value the JVM is started with. This port may be changed by starting the JVM with the -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=$PORT_NUMBER command line parameter. When the remoting protocol (remoting://localhost:9990) is used, the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server administration port is used (the default is port 9990).
The command line prompt displays the active connection information, along with the current directory.
Use the container command to select a cache manager, and then select a cache with the cache command. A cache must be selected before performing cache operations. The CLI supports tab completion, therefore using the cache and pressing the tab button displays a list of active caches. The following example assumes a cache manager, MyCacheManager, defined in the configuration.
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/> container MyCacheManager [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/> cache default namedCache [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/]> cache default [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/default]>
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/> container MyCacheManager
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/> cache
default namedCache
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/]> cache default
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/default]>Additionally, pressing tab displays a list of valid commands for the CLI.
30.3. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server CLI
30.3.1. Red Hat Data Grid Server Mode CLI
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes a new Remote Client-Server mode CLI. This CLI can only be used for specific use cases, such as manipulating the server subsystem for the following:
- configuration
- management
- obtaining metrics
30.3.2. Start the Server Mode CLI
Use the following commands to run the JBoss Data Grid Server CLI from the command line:
For Linux:
JDG_HOME/bin/cli.sh
$ JDG_HOME/bin/cli.shFor Windows:
C:\>JDG_HOME\bin\cli.bat
C:\>JDG_HOME\bin\cli.bat30.4. CLI Commands
30.4.1. CLI Commands
Unless specified otherwise, all listed commands for the JBoss Data Grid CLIs can be used with both the Library Mode and Server Mode CLIs. Specifically, the deny (see The deny Command), grant (see The grant Command), and roles (see The roles command) commands are only available on the Server Mode CLI.
30.4.2. The abort Command
The abort command aborts a running batch initiated using the start command. Batching must be enabled for the specified cache. The following is a usage example:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> start [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> abort [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a null
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> start
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> abort
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a
null30.4.3. The begin Command
The begin command starts a transaction. This command requires transactions enabled for the cache it targets. An example of this command’s usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> begin [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> commit
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> begin
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> commit30.4.4. The cache Command
The cache command specifies the default cache used for all subsequent operations. If invoked without any parameters, it shows the currently selected cache. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> cache default [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/default]> cache default [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/default]>
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> cache default
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/default]> cache
default
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/default]>30.4.5. The clearcache Command
The clearcache command clears all content from the cache. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> clearcache [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a null
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> clearcache
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a
null30.4.6. The commit Command
The commit command commits changes to an ongoing transaction. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> begin [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> commit
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> begin
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> commit30.4.7. The container Command
The container command selects the default cache container (cache manager). When invoked without any parameters, it lists all available containers. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> container MyCacheManager OtherCacheManager [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> container OtherCacheManager [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/OtherCacheManager/]>
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> container
MyCacheManager OtherCacheManager
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> container OtherCacheManager
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/OtherCacheManager/]>30.4.8. The create Command
The create command creates a new cache based on the configuration of an existing cache definition. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> create newCache like namedCache [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> cache newCache [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/newCache]>
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> create newCache like namedCache
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> cache newCache
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/newCache]>30.4.9. The deny Command
When authorization is enabled and the role mapper has been configured to be the ClusterRoleMapper, principal to role mappings are stored within the cluster registry (a replicated cache available to all nodes). The deny command can be used to deny roles previously assigned to a principal:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990]> deny supervisor to user1
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990]> deny supervisor to user1
The deny command is only available to the JBoss Data Grid Server Mode CLI.
30.4.10. The disconnect Command
The disconnect command disconnects the currently active connection, which allows the CLI to connect to another instance. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> disconnect [disconnected//]
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> disconnect
[disconnected//]30.4.11. The encoding Command
The encoding command sets a default codec to use when reading and writing entries to and from a cache. If invoked with no arguments, the currently selected codec is displayed. An example of its usage is as follows:
30.4.12. The end Command
The end command ends a running batch initiated using the start command. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> start [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> end [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> start
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> end
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a
a30.4.13. The evict Command
The evict command evicts an entry associated with a specific key from the cache. An example of it usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> evict a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> evict a30.4.14. The get Command
The get command shows the value associated with a specified key. For primitive types and Strings, the get command prints the default representation. For other objects, a JSON representation of the object is printed. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> get a
a30.4.15. The grant Command
When authorization is enabled and the role mapper has been configured to be the ClusterRoleMapper, the principal to role mappings are stored within the cluster registry (a replicated cache available to all nodes). The grant command can be used to grant new roles to a principal as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990]> grant supervisor to user1
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990]> grant supervisor to user1
The grant command is only available to the JBoss Data Grid Server Mode CLI.
30.4.16. The info Command
The info command displays the configuration of a selected cache or container. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> info
GlobalConfiguration{asyncListenerExecutor=ExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultExecutorFactory@98add58}, asyncTransportExecutor=ExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultExecutorFactory@7bc9c14c}, evictionScheduledExecutor=ScheduledExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultScheduledExecutorFactory@7ab1a411}, replicationQueueScheduledExecutor=ScheduledExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultScheduledExecutorFactory@248a9705}, globalJmxStatistics=GlobalJmxStatisticsConfiguration{allowDuplicateDomains=true, enabled=true, jmxDomain='jboss.infinispan', mBeanServerLookup=org.jboss.as.clustering.infinispan.MBeanServerProvider@6c0dc01, cacheManagerName='local', properties={}}, transport=TransportConfiguration{clusterName='ISPN', machineId='null', rackId='null', siteId='null', strictPeerToPeer=false, distributedSyncTimeout=240000, transport=null, nodeName='null', properties={}}, serialization=SerializationConfiguration{advancedExternalizers={1100=org.infinispan.server.core.CacheValue$Externalizer@5fabc91d, 1101=org.infinispan.server.memcached.MemcachedValue$Externalizer@720bffd, 1104=org.infinispan.server.hotrod.ServerAddress$Externalizer@771c7eb2}, marshaller=org.infinispan.marshall.VersionAwareMarshaller@6fc21535, version=52, classResolver=org.jboss.marshalling.ModularClassResolver@2efe83e5}, shutdown=ShutdownConfiguration{hookBehavior=DONT_REGISTER}, modules={}, site=SiteConfiguration{localSite='null'}}
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> info
GlobalConfiguration{asyncListenerExecutor=ExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultExecutorFactory@98add58}, asyncTransportExecutor=ExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultExecutorFactory@7bc9c14c}, evictionScheduledExecutor=ScheduledExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultScheduledExecutorFactory@7ab1a411}, replicationQueueScheduledExecutor=ScheduledExecutorFactoryConfiguration{factory=org.infinispan.executors.DefaultScheduledExecutorFactory@248a9705}, globalJmxStatistics=GlobalJmxStatisticsConfiguration{allowDuplicateDomains=true, enabled=true, jmxDomain='jboss.infinispan', mBeanServerLookup=org.jboss.as.clustering.infinispan.MBeanServerProvider@6c0dc01, cacheManagerName='local', properties={}}, transport=TransportConfiguration{clusterName='ISPN', machineId='null', rackId='null', siteId='null', strictPeerToPeer=false, distributedSyncTimeout=240000, transport=null, nodeName='null', properties={}}, serialization=SerializationConfiguration{advancedExternalizers={1100=org.infinispan.server.core.CacheValue$Externalizer@5fabc91d, 1101=org.infinispan.server.memcached.MemcachedValue$Externalizer@720bffd, 1104=org.infinispan.server.hotrod.ServerAddress$Externalizer@771c7eb2}, marshaller=org.infinispan.marshall.VersionAwareMarshaller@6fc21535, version=52, classResolver=org.jboss.marshalling.ModularClassResolver@2efe83e5}, shutdown=ShutdownConfiguration{hookBehavior=DONT_REGISTER}, modules={}, site=SiteConfiguration{localSite='null'}}30.4.17. The locate Command
The locate command displays the physical location of a specified entry in a distributed cluster. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> locate a [host/node1,host/node2]
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> locate a
[host/node1,host/node2]30.4.18. The put Command
The put command inserts an entry into the cache. If a mapping exists for a key, the put command overwrites the old value. The CLI allows control over the type of data used to store the key and value. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b 100
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put c 4139l
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put d true
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put e { "package.MyClass": {"i": 5, "x": null, "b": true } }
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b 100
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put c 4139l
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put d true
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put e { "package.MyClass": {"i": 5, "x": null, "b": true } }
Optionally, the put can specify a life span and maximum idle time value as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a expires 10s [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a expires 10m maxidle 1m
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a expires 10s
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a expires 10m maxidle 1m30.4.19. The replace Command
The replace command replaces an existing entry in the cache with a specified new value. An example of its usage is as follows:
30.4.20. The roles command
When authorization is enabled and the role mapper has been configured to be the ClusterRoleMapper, the principal to role mappings are stored within the cluster registry (a replicated cache available to all nodes). The roles command can be used to list the roles associated to a specific user, or to all users if one is not given:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990]> roles user1 [supervisor, reader]
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990]> roles user1
[supervisor, reader]
The roles command is only available to the JBoss Data Grid Server Mode CLI.
30.4.21. The rollback Command
The rollback command rolls back any changes made by an ongoing transaction. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> begin [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> rollback
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> begin
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> rollback30.4.22. The site Command
The site command performs administration tasks related to cross-datacenter replication. This command also retrieves information about the status of a site and toggles the status of a site. An example of its usage is as follows:
30.4.23. The start Command
The start command initiates a batch of operations. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> start [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> end
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> start
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put a a
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> put b b
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> end30.4.24. The stats Command
The stats command displays statistics for the cache. An example of its usage is as follows:
30.4.25. The upgrade Command
The upgrade command implements the rolling upgrade procedure. For details about rolling upgrades, refer to Rolling Upgrades.
An example of the upgrade command’s use is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> upgrade --synchronize=hotrod --all [standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> upgrade --disconnectsource=hotrod --all
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> upgrade --synchronize=hotrod --all
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> upgrade --disconnectsource=hotrod --all30.4.26. The version Command
The version command displays version information for the CLI client and server. An example of its usage is as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> version Client Version 5.2.1.Final Server Version 5.2.1.Final
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache]> version
Client Version 5.2.1.Final
Server Version 5.2.1.FinalPart XV. Other Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Functions
Chapter 31. Set Up the L1 Cache
31.1. About the L1 Cache
The Level 1 (or L1) cache stores remote cache entries after they are initially accessed, preventing unnecessary remote fetch operations for each subsequent use of the same entries. The L1 cache is only available when Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s cache mode is set to distribution. In other cache modes any configuration related to the L1 cache is ignored.
When caches are configured with distributed mode, the entries are evenly distributed between all clustered caches. Each entry is copied to a desired number of owners, which can be less than the total number of caches. As a result, the system’s scalability is improved but also means that some entries are not available on all nodes and must be fetched from their owner node. In this situation, configure the Cache component to use the L1 Cache to temporarily store entries that it does not own to prevent repeated fetching for subsequent uses.
Each time a key is updated an invalidation message is generated. This message is multicast to each node that contains data that corresponds to current L1 cache entries. The invalidation message ensures that each of these nodes marks the relevant entry as invalidated. Also, when the location of an entry changes in the cluster, the corresponding L1 cache entry is invalidated to prevent outdated cache entries.
31.2. L1 Cache Configuration
31.2.1. L1 Cache Configuration (Library Mode)
The following sample configuration shows the L1 cache default values in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library Mode.
L1 Cache Configuration in Library Mode
<distributed-cache name="distributed_cache"
l1-lifespan="0"
l1-cleanup-interval="60000"/>
<distributed-cache name="distributed_cache"
l1-lifespan="0"
l1-cleanup-interval="60000"/>The following attributes control the L1 cache behavior:
-
The
l1-lifespanattribute indicates the maximum lifespan in milliseconds of entries placed in the L1 cache, and is not allowed in non-distributed caches. By default L1 this value is 0, indicating that L1 caching is disabled, and is only enabled if a positive value is defined. -
The
l1-cleanup-intervalparameter controls how often a cleanup task to prune L1 tracking data is run, in milliseconds, and by default is defined to 10 minutes.
31.2.2. L1 Cache Configuration (Remote Client-Server Mode)
The following sample configuration shows the L1 cache default value of 0, indicating it is disabled, in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode:
L1 Cache Configuration for Remote Client-Server Mode
<distributed-cache l1-lifespan="0"> <!-- Additional configuration information here --> </distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache l1-lifespan="0">
<!-- Additional configuration information here -->
</distributed-cache>
The l1-lifespan element is added to a distributed-cache element to enable L1 caching and to set the life span of the L1 cache entries for the cache. This element is only valid for distributed caches.
If l1-lifespan is set to 0 or a negative number (-1), L1 caching is disabled. L1 caching is enabled when the l1-lifespan value is greater than 0.
When the cache is accessed remotely via the Hot Rod protocol, the client accesses the owner node directly. Therefore, using L1 Cache via the Hot Rod protocol is not recommended; instead, refer to the Near Caching section in the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide . Other remote clients (Memcached, REST) cannot target the owner, therefore, using L1 Cache may increase the performance (at the cost of higher memory consumption).
In Remote Client-Server mode, the L1 cache was enabled by default when distributed cache was used, even if the l1-lifespan attribute is not set. The default lifespan value was 10 minutes. Since JBoss Data Grid 6.3, the default lifespan is 0 which disables the L1 cache. Set a non-zero value for the l1-lifespan parameter to enable the L1 cache.
Chapter 32. Set Up Transactions
32.1. About Transactions
32.1.1. About Transactions
A transaction consists of a collection of interdependent or related operations or tasks. All operations within a single transaction must succeed for the overall success of the transaction. If any operations within a transaction fail, the transaction as a whole fails and rolls back any changes. Transactions are particularly useful when dealing with a series of changes as part of a larger operation.
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, transactions are only available in Library mode.
32.1.2. About the Transaction Manager
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, the Transaction Manager coordinates transactions across a single or multiple resources. The responsibilities of a Transaction Manager include:
- initiating and concluding transactions
- managing information about each transaction
- coordinating transactions as they operate over multiple resources
- recovering from a failed transaction by rolling back changes
32.1.3. XA Resources and Synchronizations
XA Resources are fully fledged transaction participants. In the prepare phase (see About Two Phase Commit (2PC) for details), the XA Resource returns a vote with either the value OK or ABORT. If the Transaction Manager receives OK votes from all XA Resources, the transaction is committed, otherwise it is rolled back.
Synchronizations are a type of listener that receive notifications about events leading to the transaction life cycle. Synchronizations receive an event before and after the operation completes.
Unless recovery is required, it is not necessary to register as a full XA resource. An advantage of synchronizations is that they allow the Transaction Manager to optimize 2PC (Two Phase Commit) with a 1PC (One Phase Commit) where only one other resource is enlisted with that transaction (last resource commit optimization). This makes registering a synchronization more efficient.
However, if the operation fails in the prepare phase within Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, the transaction is not rolled back and if there are more participants in the transaction, they can ignore this failure and commit. Additionally, errors encountered in the commit phase are not propagated to the application code that commits the transaction.
By default JBoss Data Grid registers to the transaction as a synchronization.
32.1.4. Optimistic and Pessimistic Transactions
Pessimistic transactions acquire the locks when the first write operation on the key executes. After the key is locked, no other transaction can modify the key until this transaction is committed or rolled back. It is up to the application code to acquire the locks in correct order to prevent deadlocks.
With optimistic transactions locks are acquired at transaction prepare time and are held until the transaction commits (or rolls back). Also, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid sorts keys for all entries modified within a transaction automatically, preventing any deadlocks occurring due to the incorrect order of keys being locked. This results in:
- less messages being sent during the transaction execution
- locks held for shorter periods
- improved throughput
Read operations never acquire any locks. Acquiring the lock for a read operation on demand is possible only with pessimistic transactions, using the FORCE_WRITE_LOCK flag with the operation.
32.1.5. Write Skew Checks
A common use case for entries is that they are read and subsequently written in a transaction. However, a third transaction can modify the entry between these two operations. In order to detect such a situation and roll back a transaction Red Hat JBoss Data Grid offers entry versioning and write skew checks. If the modified version is not the same as when it was last read during the transaction, the write skew checks throws an exception and the transaction is rolled back.
Enabling write skew check requires the REPEATABLE_READ isolation level. Also, in clustered mode (distributed or replicated modes), set up entry versioning. For local mode, entry versioning is not required.
With optimistic transactions, write skew checks are required for (atomic) conditional operations.
32.1.6. Transactions Spanning Multiple Cache Instances
Each cache operates as a separate, standalone Java Transaction API (JTA) resource. However, components can be internally shared by Red Hat JBoss Data Grid for optimization, but this sharing does not affect how caches interact with a Java Transaction API (JTA) Manager.
32.2. Configure Transactions
32.2.1. Configure Transactions (Library Mode)
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, transactions in Library mode can be configured with synchronization and transaction recovery. Transactions in their entirety (which includes synchronization and transaction recovery) are not available in Remote Client-Server mode.
In order to execute a cache operation, the cache requires a reference to the environment’s Transaction Manager. Configure the cache with the class name that belongs to an implementation of the TransactionManagerLookup interface. When initialized, the cache creates an instance of the specified class and invokes its getTransactionManager() method to locate and return a reference to the Transaction Manager.
In Library mode, transactions are configured as follows:
Configure Transactions in Library Mode (XML Configuration)
-
Enable
transactionsby defining amode. By default the mode isNONE, therefore disabling transactions. Valid transaction modes areBATCH,NON_XA,NON_DURABLE_XA,FULL_XA. -
Define a
stop-timeout, so that if there are any ongoing transactions when a cache is stopped the instance will wait for ongoing transactions to finish. Defaults to30000milliseconds. -
Enable
auto-commit, so that single operation transactions do not need to be manually initiated. Defaults totrue. -
Define the commit
protocolin use. Valid commit protocols areDEFAULTandTOTAL_ORDER. -
Define the name of the
recovery-cache, where recovery related information is kept. Defaults to_recoveryInfoCacheName_. -
Enable
versioningof entries by defining theschemeattribute asSIMPLE. Defaults toNONE, indicating that versioning is disabled.
32.2.2. Configure Transactions (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid does not offer transactions in Remote Client-Server mode. The default configuration is non-transactional, which is set as follows:
Default Transaction Configuration in Remote Client-Server Mode
<cache> <!-- Additional configuration elements here --> <transaction mode="NONE" /> <!-- Additional configuration elements here --> </cache>
<cache>
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
<transaction mode="NONE" />
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
</cache>
JBoss Data Grid in Remote Client-Server mode does not support transactions directly. However, if you use conditional operators such as replaceWithVersion, putIfAbsent, or removeWithVersion you should enable transactions.
To enable transactions for the use of conditional operators use the following configuration:
Transaction Configuration for Conditional Operators in Remote Client-Server Mode
<cache>
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
<transaction mode="NON_XA" />
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
</cache>
<cache>
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
<transaction mode="NON_XA" />
<!-- Additional configuration elements here -->
</cache>32.3. Transaction Recovery
32.3.1. Transaction Recovery
The Transaction Manager coordinates the recovery process and works with Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to determine which transactions require manual intervention to complete operations. This process is known as transaction recovery.
JBoss Data Grid uses JMX for operations that explicitly force transactions to commit or roll back. These methods receive byte arrays that describe the XID instead of the number associated with the relevant transactions.
The System Administrator can use such JMX operations to facilitate automatic job completion for transactions that require manual intervention. This process uses the Transaction Manager’s transaction recovery process and has access to the Transaction Manager’s XID objects.
32.3.2. Transaction Recovery Process
The following process outlines the transaction recovery process in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
The Transaction Recovery Process
- The Transaction Manager creates a list of transactions that require intervention.
-
The system administrator, connected to JBoss Data Grid using JMX, is presented with the list of transactions (including transaction IDs) using email or logs. The status of each transaction is either
COMMITTEDorPREPARED. If some transactions are in bothCOMMITTEDandPREPAREDstates, it indicates that the transaction was committed on some nodes while in the preparation state on others. - The System Administrator visually maps the XID received from the Transaction Manager to a JBoss Data Grid internal ID. This step is necessary because the XID (a byte array) cannot be conveniently passed to the JMX tool and then reassembled by JBoss Data Grid without this mapping.
- The system administrator forces the commit or rollback process for a transaction based on the mapped internal ID.
32.3.3. Transaction Recovery Example
The following example describes how transactions are used in a situation where money is transferred from an account stored in a database to an account stored in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
Money Transfer from an Account Stored in a Database to an Account in JBoss Data Grid
-
The
TransactionManager.commit()method is invoked to run the two phase commit protocol between the source (the database) and the destination (JBoss Data Grid) resources. -
The
TransactionManagertells the database and JBoss Data Grid to initiate the prepare phase (the first phase of a Two Phase Commit).
During the commit phase, the database applies the changes but JBoss Data Grid fails before receiving the Transaction Manager’s commit request. As a result, the system is in an inconsistent state due to an incomplete transaction. Specifically, the amount to be transferred has been subtracted from the database but is not yet visible in JBoss Data Grid because the prepared changes could not be applied.
Transaction recovery is used here to reconcile the inconsistency between the database and JBoss Data Grid entries.
To use JMX to manage transaction recoveries, JMX support must be explicitly enabled.
32.4. Deadlock Detection
32.4.1. Deadlock Detection
A deadlock occurs when multiple processes or tasks wait for the other to release a mutually required resource. Deadlocks can significantly reduce the throughput of a system, particularly when multiple transactions operate against one key set.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid provides deadlock detection to identify such deadlocks. Deadlock detection is enabled by default.
32.4.2. Enable Deadlock Detection
Deadlock detection in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid is enabled by default, and may be configured by adjusting the deadlock-detection-spin attribute of the cache configuration element, as seen below:
<local-cache [...] deadlock-detection-spin="1000"/>
<local-cache [...] deadlock-detection-spin="1000"/>
The deadlock-detection-spin attribute defines how often lock acquisition is attempted within the maximum time allowed to acquire a particular lock (in milliseconds). This value defaults to 100 milliseconds, and negative values disable deadlock detection.
Deadlock detection can only be applied to individual caches. Deadlocks that are applied on more than one cache cannot be detected by JBoss Data Grid.
Chapter 33. Configure JGroups
33.1. About JGroups
JGroups is the underlying group communication library used to connect Red Hat JBoss Data Grid instances. For a full list of JGroups protocols supported in JBoss Data Grid, see Supported JGroups Protocols.
33.2. Configure Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Interface Binding (Remote Client-Server Mode)
33.2.1. Interfaces
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid allows users to specify an interface type rather than a specific (unknown) IP address.
If you use JBoss Data Grid as a containerized image with OpenShift, you must set environment variables to change the XML configuration during pod creation. See the Data Grid for OpenShift Guide.
link-local: Uses a169.orx.x.x254.address. This suits the traffic within one box.x.x.xCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow site-local: Uses a private IP address, for example192.168.[replaceable]x.[replaceable]x````. This prevents extra bandwidth charged from GoGrid, and similar providers.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow global: Picks a public IP address. This should be avoided for replication traffic.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow non-loopback: Uses the first address found on an active interface that is not a127.address.x.x.xCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
33.2.2. Binding Sockets
33.2.2.1. Binding Sockets
Socket bindings provide a method of associating a name with networking details, such as an interface, a port, a multicast-address, or other details. Sockets may be bound to the interface either individually or using a socket binding group.
33.2.2.2. Binding a Single Socket Example
The following is an example depicting the use of JGroups interface socket binding to bind an individual socket using the socket-binding element.
Socket Binding
<socket-binding name="jgroups-udp" <!-- Additional configuration elements here --> interface="site-local"/>
<socket-binding name="jgroups-udp" <!-- Additional configuration elements here --> interface="site-local"/>33.2.2.3. Binding a Group of Sockets Example
The following is an example depicting the use of Groups interface socket bindings to bind a group, using the socket-binding-group element:
Bind a Group
The two sample socket bindings in the example are bound to the same default-interface (global), therefore the interface attribute does not need to be specified.
33.2.3. Configure JGroups Socket Binding
Each JGroups stack, configured in the JGroups subsystem, uses a specific socket binding. Set up the socket binding as follows:
JGroups UDP Socket Binding Configuration
The following example utilizes UDP automatically form the cluster. In this example the jgroups-udp socket binding is defined for the transport:
JGroups TCP Socket Binding Configuration
The following example uses TCP to establish direct communication between two clusters nodes. In the example below node1 is located at 192.168.1.2:7600, and node2 is located at 192.168.1.3:7600. The port in use will be defined by the jgroups-tcp property in the socket-binding section.
The decision of UDP vs TCP must be made in each environment. By default JGroups uses UDP, as it allows for dynamic detection of clustered members and scales better in larger clusters due to a smaller network footprint. In addition, when using UDP only one packet per cluster is required, as multicast packets are received by all subscribers to the multicast address; however, in environments where multicast traffic is prohibited, or if UDP traffic can not reach the remote cluster nodes, such as when cluster members are on separate VLANs, TCP traffic can be used to create a cluster.
When using UDP as the JGroups transport, the socket binding has to specify the regular (unicast) port, multicast address, and multicast port.
33.3. Configure JGroups (Library Mode)
33.3.1. Configure JGroups for Clustered Modes
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid must have an appropriate JGroups configuration in order to operate in clustered mode.
JGroups XML Configuration
JBoss Data Grid will first search for jgroups.xml in the classpath; if no instances are found in the classpath it will then search for an absolute path name.
33.3.2. JGroups Transport Protocols
33.3.2.1. JGroups Transport Protocols
A transport protocol is the protocol at the bottom of a protocol stack. Transport Protocols are responsible for sending and receiving messages from the network.
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid ships with both UDP and TCP transport protocols.
33.3.2.2. The UDP Transport Protocol
UDP is a transport protocol that uses:
- IP multicasting to send messages to all members of a cluster.
- UDP datagrams for unicast messages, which are sent to a single member.
When the UDP transport is started, it opens a unicast socket and a multicast socket. The unicast socket is used to send and receive unicast messages, the multicast socket sends and receives multicast sockets. The physical address of the channel will be the same as the address and port number of the unicast socket.
UDP is the default transport protocol used in JBoss Data Grid as it allows for dynamic discovery of additional cluster nodes, and scales well with cluster sizes.
33.3.2.3. The TCP Transport Protocol
TCP/IP is a replacement transport for UDP in situations where IP multicast cannot be used, such as operations over a WAN where routers may discard IP multicast packets.
TCP is a transport protocol used to send unicast and multicast messages.
- When sending multicast messages, TCP sends multiple unicast messages.
As IP multicasting cannot be used to discover initial members, another mechanism must be used to find initial membership.
33.3.2.4. Using the TCPPing Protocol
Some networks only allow TCP to be used. The pre-configured default-configs/default-jgroups-tcp.xml includes the MPING protocol, which uses UDP multicast for discovery. When UDP multicast is not available, the MPING protocol, has to be replaced by a different mechanism. The recommended alternative is the TCPPING protocol. The TCPPING configuration contains a static list of IP addresses which are contacted for node discovery.
Configure the JGroups Subsystem to Use TCPPING
<TCP bind_port="7800" />
<TCPPING initial_hosts="${jgroups.tcpping.initial_hosts:HostA[7800],HostB[7801]}"
port_range="1" />
<TCP bind_port="7800" />
<TCPPING initial_hosts="${jgroups.tcpping.initial_hosts:HostA[7800],HostB[7801]}"
port_range="1" />33.3.3. Pre-Configured JGroups Files
33.3.3.1. Pre-Configured JGroups Files
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid ships with pre-configured JGroups files in infinispan-embedded.jar, available on the classpath by default.
These JGroups configuration files contain default settings that you should adjust and tune to achieve optimal network performance.
To use a JGroups configuration file, replace jgroups.xml with one of the following:
- default-configs/default-jgroups-udp.xml
- default-configs/default-jgroups-tcp.xml
- default-configs/default-jgroups-ec2.xml
- default-configs/default-jgroups-google.xml
- default-configs/default-jgroups-kubernetes.xml
33.3.3.2. default-jgroups-udp.xml
-
uses
UDPfor transport andUDPmulticast for discovery, allowing for dynamic discovery of nodes. -
is suitable for larger clusters because it requires less resources than
TCP. - is recommended for clusters that send the same information to all nodes, such as when using Invalidation or Replication modes.
Add the following system properties to the JVM at start up to configure these settings:
| System Property | Description | Default | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| jgroups.udp.mcast_addr | IP address to use for multicast (both for communications and discovery). Must be a valid Class D IP address, suitable for IP multicast | 228.6.7.8 | No |
| jgroups.udp.mcast_port | Port to use for multicast socket | 46655 | No |
| jgroups.ip_ttl | Specifies the time-to-live (TTL) for IP multicast packets. The value here refers to the number of network hops a packet is allowed to make before it is dropped | 2 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.min_threads | Minimum thread pool size for the thread pool | 0 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.max_threads | Maximum thread pool size for the thread pool | 200 | No |
| jgroups.join_timeout | The maximum number of milliseconds to wait for a new node JOIN request to succeed | 5000 | No |
33.3.3.3. default-jgroups-tcp.xml
-
uses
TCPfor transport andUDPmulticast for discovery. -
is typically used where multicast
UDPis not an option. - is recommended for point-to-point (unicast) communication, such as when using Distribution mode because it has a more refined method of flow control.
Add the following system properties to the JVM at start up to configure these settings:
| System Property | Description | Default | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| jgroups.tcp.address | IP address to use for the TCP transport. | 127.0.0.1 | Not required, but should be changed for clustering servers located on different systems |
| jgroups.tcp.port | Port to use for TCP socket | 7800 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.min_threads | Minimum thread pool size for the thread pool | 0 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.max_threads | Maximum thread pool size for the thread pool | 200 | No |
| jgroups.mping.mcast_addr | IP address to use for multicast (for discovery). Must be a valid Class D IP address, suitable for IP multicast. | 228.2.4.6 | No |
| jgroups.mping.mcast_port | Port to use for multicast socket | 43366 | No |
| jgroups.udp.ip_ttl | Specifies the time-to-live (TTL) for IP multicast packets. The value here refers to the number of network hops a packet is allowed to make before it is dropped | 2 | No |
| jgroups.join_timeout | The maximum number of milliseconds to wait for a new node JOIN request to succeed | 5000 | No |
33.3.3.4. default-jgroups-ec2.xml
-
uses
TCPfor transport andS3_PINGfor discovery. - is suitable on EC2 nodes where UDP multicast is not available.
Add the following system properties to the JVM at start up to configure these settings:
| System Property | Description | Default | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| jgroups.tcp.address | IP address to use for the TCP transport. | 127.0.0.1 | Not required, but should be changed for clustering servers located on different EC2 nodes |
| jgroups.tcp.port | Port to use for TCP socket | 7800 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.min_threads | Minimum thread pool size for the thread pool | 0 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.max_threads | Maximum thread pool size for the thread pool | 200 | No |
| jgroups.s3.access_key | The Amazon S3 access key used to access an S3 bucket | Yes | |
| jgroups.s3.secret_access_key | The Amazon S3 secret key used to access an S3 bucket | Yes | |
| jgroups.s3.bucket | Name of the Amazon S3 bucket to use. Must be unique and must already exist | Yes | |
| jgroups.s3.pre_signed_delete_url | The pre-signed URL to be used for the DELETE operation. | Yes | |
| jgroups.s3.pre_signed_put_url | The pre-signed URL to be used for the PUT operation. | Yes | |
| jgroups.s3.prefix | If set, S3_PING searches for a bucket with a name that starts with the prefix value. | No | |
| jgroups.join_timeout | The maximum number of milliseconds to wait for a new node JOIN request to succeed | 5000 | No |
33.3.3.5. default-jgroups-google.xml
-
uses
TCPfor transport andGOOGLE_PINGfor discovery. - is suitable on Google Compute Engine nodes where UDP multicast is not available.
Add the following system properties to the JVM at start up to configure these settings:
| System Property | Description | Default | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| jgroups.tcp.address | IP address to use for the TCP transport. | 127.0.0.1 | Not required, but should be changed for clustering systems located on different nodes |
| jgroups.tcp.port | Port to use for TCP socket | 7800 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.min_threads | Minimum thread pool size for the thread pool | 0 | No |
| jgroups.thread_pool.max_threads | Maximum thread pool size for the thread pool | 200 | No |
| jgroups.google.access_key | The Google Compute Engine User’s access key used to access the bucket | Yes | |
| jgroups.google.secret_access_key | The Google Compute Engine User’s secret access key used to access the bucket | Yes | |
| jgroups.google.bucket | Name of the Google Compute Engine bucket to use. Must be unique and already exist | Yes | |
| jgroups.join_timeout | The maximum number of milliseconds to wait for a new node JOIN request to succeed | 5000 | No |
33.3.3.6. default-jgroups-kubernetes.xml
-
uses
TCPfor transport andKUBE_PINGfor discovery. - is suitable for Kubernetes and OpenShift nodes where UDP multicast is not available.
Add the following system properties to the JVM at start up to configure these settings:
| System Property | Description | Default | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| jgroups.tcp.address | IP address to use for the TCP transport. | eth0 | Not required, but should be changed for clustering systems located on different nodes |
| jgroups.tcp.port | Port to use for TCP socket | 7800 | No |
33.4. Test Multicast Using JGroups
33.4.1. Test Multicast Using JGroups
Learn how to ensure that the system has correctly configured multicasting within the cluster.
33.4.2. Testing With Different Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Versions
The following table details which Red Hat JBoss Data Grid versions are compatible with this multicast test:
${infinispan.version} corresponds to the version of Infinispan included in the specific release of JBoss Data Grid. This will appear in a x.y.z format, with the major version, minor version, and revision being included.
| Version | Test Case | Details |
|---|---|---|
| JBoss Data Grid 7.2.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 7.1.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 7.0.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.6.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.5.1 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.5.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.4.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.3.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.2.1 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.2.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.1.0 | Available | The location of the test classes depends on the distribution:
|
| JBoss Data Grid 6.0.1 | Not Available | This version of JBoss Data Grid is based on JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6.0, which does not include the test classes used for this test. |
| JBoss Data Grid 6.0.0 | Not Available | This version of JBoss Data Grid is based on JBoss Enterprise Application Server 6.0, which does not include the test classes used for this test. |
33.4.3. Testing Multicast Using JGroups
The following procedure details the steps to test multicast using JGroups if you are using Red Hat JBoss Data Grid:
Prerequisites
Ensure that the following prerequisites are met before starting the testing procedure.
-
Set the
bind_addrvalue to the appropriate IP address for the instance. -
For added accuracy, set
mcast_addrandportvalues that are the same as the cluster communication values. - Start two command line terminal windows. Navigate to the location of the JGroups JAR file for one of the two nodes in the first terminal and the same location for the second node in the second terminal.
Test Multicast Using JGroups
Run the Multicast Server on Node One
Run the following command on the command line terminal for the first node (replace jgroups.jar with the infinispan-embedded.jar for Library mode):
java -cp jgroups.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastReceiverTest -mcast_addr 230.1.2.3 -port 5555 -bind_addr $YOUR_BIND_ADDRESS
java -cp jgroups.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastReceiverTest -mcast_addr 230.1.2.3 -port 5555 -bind_addr $YOUR_BIND_ADDRESSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the Multicast Server on Node Two
Run the following command on the command line terminal for the second node (replace jgroups.jar with the infinispan-embedded.jar for Library mode):
java -cp jgroups.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastSenderTest -mcast_addr 230.1.2.3 -port 5555 -bind_addr $YOUR_BIND_ADDRESS
java -cp jgroups.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastSenderTest -mcast_addr 230.1.2.3 -port 5555 -bind_addr $YOUR_BIND_ADDRESSCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Transmit Information Packets
Enter information on instance for node two (the node sending packets) and press enter to send the information.
View Receives Information Packets
View the information received on the node one instance. The information entered in the previous step should appear here.
Confirm Information Transfer
Repeat steps 3 and 4 to confirm all transmitted information is received without dropped packets.
Repeat Test for Other Instances
Repeat steps 1 to 4 for each combination of sender and receiver. Repeating the test identifies other instances that are incorrectly configured.
Result
All information packets transmitted from the sender node must appear on the receiver node. If the sent information does not appear as expected, multicast is incorrectly configured in the operating system or the network.
Chapter 34. Use Red Hat JBoss Data Grid with Amazon Web Services
34.1. The S3_PING JGroups Discovery Protocol
S3_PING is a discovery protocol that is ideal for use with Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) because EC2 does not allow multicast and therefore MPING is not allowed.
Each EC2 instance adds a small file to an S3 data container, known as a bucket. Each instance then reads the files in the bucket to discover the other members of the cluster.
34.2. S3_PING Configuration Options
34.2.1. S3_PING Configuration Options
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid works with Amazon Web Services in two ways:
- In Library mode, use JGroups' default-configs/default-jgroups-ec2.xml file (see default-jgroups-ec2.xml for details) or use the S3_PING protocol.
- In Remote Client-Server mode, use JGroups' S3_PING protocol.
In Library and Remote Client-Server mode, there are three ways to configure the S3_PING protocol for clustering to work in Amazon AWS:
- Use Private S3 Buckets. These buckets use Amazon AWS credentials.
- Use Pre-Signed URLs. These pre-assigned URLs are assigned to buckets with private write and public read rights.
- Use Public S3 Buckets. These buckets do not have any credentials.
34.2.2. Using Private S3 Buckets
This configuration requires access to a private bucket that can only be accessed with the appropriate AWS credentials. To confirm that the appropriate permissions are available, confirm that the user has the following permissions for the bucket:
- List
- Upload/Delete
- View Permissions
- Edit Permissions
Ensure that the S3_PING configuration includes the following properties:
-
the
locationwhere the bucket is found. -
the
access_keyandsecret_access_keyproperties for the AWS user.
If a 403 error displays when using this configuration, verify that the properties have the correct values. If the problem persists, confirm that the system time in the EC2 node is correct. Amazon S3 rejects requests with a time stamp that is more than 15 minutes old compared to their server’s times for security purposes.
Start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server with a Private Bucket
Run the following command from the top level of the server directory to start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server using a private S3 bucket:
-
Replace
{node_name}with the server’s desired node name. -
Replace
{port_offset}with the port offset. To use the default ports specify this as0. -
Replace
{s3_bucket_name}with the appropriate bucket name. -
Replace
{access_key}with the user’s access key. -
Replace
{secret_access_key}with the user’s secret access key.
34.2.3. Using Pre-Signed URLs
34.2.3.1. Using Pre-Signed URLs
For this configuration, create a publically readable bucket in S3 by setting the List permissions to Everyone to allow public read access. Each node in the cluster may share a pre-signed URL that points to a single file, allowing a single file to be shared across every node in the cluster. This URL points to a unique file and can include a folder path within the bucket.
Longer paths will cause errors in S3_PING . For example, a path such as my_bucket/DemoCluster/jgroups.list works while a longer path such as my_bucket/Demo/Cluster/jgroups.list will not.
34.2.3.2. Generating Pre-Signed URLs
JGroup’s S3_PING class includes a utility method to generate pre-signed URLs. The last argument for this method is the time when the URL expires expressed in the number of seconds since the Unix epoch (January 1, 1970).
The syntax to generate a pre-signed URL is as follows:
String Url = S3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl("{access_key}", "{secret_access_key}", "{operation}", "{bucket_name}", "{path}", {seconds});
String Url = S3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl("{access_key}", "{secret_access_key}", "{operation}", "{bucket_name}", "{path}", {seconds});-
Replace
{operation}with eitherPUTorDELETE. -
Replace
{access_key}with the user’s access key. -
Replace
{secret_access_key}with the user’s secret access key. -
Replace
{bucket_name}with the name of the bucket. -
Replace
{path}with the desired path to the file within the bucket. -
Replace
{seconds}with the number of seconds since the Unix epoch (January 1, 1970) that the path remains valid.
Generate a Pre-Signed URL
String putUrl = S3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl("access_key", "secret_access_key", "put", "my_bucket", "DemoCluster/jgroups.list", 1234567890);
String putUrl = S3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl("access_key", "secret_access_key", "put", "my_bucket", "DemoCluster/jgroups.list", 1234567890);
Ensure that the S3_PING configuration includes the pre_signed_put_url and pre_signed_delete_url properties generated by the call to S3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl(). This configuration is more secure than one using private S3 buckets, because the AWS credentials are not stored on each node in the cluster
If a pre-signed URL is entered into an XML file, then the & characters in the URL must be replaced with its XML entity (&).
34.2.3.3. Set Pre-Signed URLs Using the Command Line
To set the pre-signed URLs using the command line, use the following guidelines:
-
Enclose the URL in double quotation marks (
" "). -
In the URL, each occurrence of the ampersand (
&) character must be escaped with a backslash (\)
Start a JBoss Data Grid Server with a Pre-Signed URL
-
Replace
{node_name}with the server’s desired node name. -
Replace
{port_offset}with the port offset. To use the default ports specify this as0. -
Replace
{s3_bucket_name}with the appropriate bucket name. -
Replace
{access_key}with the user’s access key. -
Replace
{expiration_time}with the values for the URL that are passed into theS3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl()method. -
Replace
{signature}with the values generated by theS3_PING.generatePreSignedUrl()method.
34.2.4. Using Public S3 Buckets
This configuration involves an S3 bucket that has public read and write permissions, which means that Everyone has permissions to List , Upload/Delete , View Permissions , and Edit Permissions for the bucket.
The location property must be specified with the bucket name for this configuration. This configuration method is the least secure because any user who knows the name of the bucket can upload and store data in the bucket and the bucket creator’s account is charged for this data.
To start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server, use the following command:
-
Replace
{node_name}with the server’s desired node name. -
Replace
{port_offset}with the port offset. To use the default ports specify this as0. -
Replace
{s3_bucket_name}with the appropriate bucket name.
34.3. Utilizing an Elastic IP Address
While each node in the cluster is able to discover other nodes in the cluster using the S3_PING protocol, all network traffic is over the internal private network. It is recommended to configure an Elastic IP, or static IP, for a single node, so that a consistent address is available for configuring the cluster, such as through the Administration Console, across restarts. If no Elastic IP is configured each instance will contain a randomized IP address on its public network whenever it is started.
Full instructions for configuring an Elastic IP address may be found in Amazon’s Getting Started Guide.
Chapter 35. Use Red Hat JBoss Data Grid with Google Compute Engine
35.1. The GOOGLE_PING Protocol
GOOGLE_PING is a discovery protocol used by JGroups during cluster formation. It is ideal to use with Google Compute Engine (GCE) and uses Google Cloud Storage to store information about individual cluster members.
35.2. GOOGLE_PING Configuration
35.2.1. GOOGLE_PING Configuration
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid works with Google Compute Engine in the following way:
- In Library mode, use the JGroups' configuration file default-configs/default-jgroups-google.xml or use the GOOGLE_PING protocol in an existing configuration file.
- In Remote Client-Server mode, define the properties on the command line when you start the server to use the JGroups Google stack ( see example in Starting the Server in Google Compute Engine).
To configure the GOOGLE_PING protocol to work in Google Compute Engine in Library and Remote Client-Server mode:
- Use JGroups bucket. These buckets use Google Compute Engine credentials.
- Use the access key.
- Use the secret access key.
Only the TCP protocol is supported in Google Compute Engine since multicasts are not allowed.
35.2.2. Starting the Server in Google Compute Engine
This configuration requires access to a bucket that can only be accessed with the appropriate Google Compute Engine credentials.
Ensure that the GOOGLE_PING configuration includes the following properties:
-
the
access_keyand thesecret_access_keyproperties for the Google Compute Engine user.
Start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Server with a Bucket
Run the following command from the top level of the server directory to start the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server using a bucket:
-
Replace
{node_name}with the server’s desired node name. -
Replace
{port_offset}with the port offset. To use the default ports specify this as0. -
Replace
{google_bucket_name}with the appropriate bucket name. -
Replace
{access_key}with the user’s access key. -
Replace
{secret_access_key}with the user’s secret access key.
35.3. Utilizing a Static IP Address
While each node in the cluster is able to discover other nodes in the cluster using the GOOGLE_PING protocol, all network traffic is over the internal private network. It is recommended to configure an external static IP address for a single node, so that a consistent address is available for configuring the cluster, such as through the Administration Console, across restarts. If no static address is configured each instance will contain a randomized IP address on its public network whenever it is started.
Full instructions for configuring an external static IP address may be found in Google’s Configuring an Instance’s IP Address documentation.
Chapter 36. High Availability Using Server Hinting
36.1. Server Hinting
Server Hinting helps you achieve high availability with your Red Hat JBoss Data Grid deployment.
To use Server Hinting, you provide information about the physical topology with attributes that identify servers, racks, or data centers to achieve more resilience with your data in the event that all the nodes in a given physical location become unavailable.
When you configure Server Hinting, JBoss Data Grid uses the location information you provided to distribute data across the cluster so that backup copies of data are stored on as many servers, racks, and data centers as possible.
In some cases JBoss Data Grid stores copies of data on nodes that share the same physical location. For example, if the number of owners for segments is greater than the number of distinct sites, then JBoss Data Grid assigns more than one owner for a given segment in the same site.
Server Hinting does not apply to total replication, which requires complete copies of data on every node.
Consistent Hashing controls how data is distributed across nodes. JBoss Data Grid uses TopologyAwareSyncConsistentHashFactory if you enable Server Hinting. For policy configuration details, see ConsistentHashFactories in the Developer Guide.
36.2. Establishing Server Hinting with JGroups
When setting up a clustered environment in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, Server Hinting is configured when establishing JGroups configuration.
JBoss Data Grid ships with several JGroups files pre-configured for clustered mode. These files can be used as a starting point when configuring Server Hinting in JBoss Data Grid.
See Also: Pre-Configured JGroups Files
36.3. Configuring Server Hinting
You configure Server Hinting with the following attributes:
-
clusteridentifies the cluster where the node runs. Note that nodes with different cluster names are not visible to each other. As a result, multiple clusters can use the same multicast address if the cluster names are different. -
machineidentifies the physical host where the node runs. -
rackidentifies the rack that contains the physical host where the node runs. -
siteidentifies the data center where the node runs. -
node-nameis the name of the JBoss Data Grid instance, or node. Having unique names for each node helps identify them for diagnostics, but is not required. In Remote Client-Server mode, the default value is a combination of the host name and a random number. In Library mode, the default value is the host name appended with a random number, which is added even when the node name is set in the configuration.
In Remote Client-Server mode, you configure Server Hinting in the JGroups subsystem on the transport element for the default stack, as in the following example:
In Library mode, you configure Server Hinting at the transport level, as in the following example:
<transport cluster = "MyCluster"
machine = "LinuxServer01"
rack = "Rack01"
site = "US-WestCoast"
node-name = "Node01" />
<transport cluster = "MyCluster"
machine = "LinuxServer01"
rack = "Rack01"
site = "US-WestCoast"
node-name = "Node01" />Chapter 37. Set Up Cross-Datacenter Replication
37.1. Cross-Datacenter Replication
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, Cross-Datacenter Replication allows the administrator to create data backups in multiple clusters. These clusters can be at the same physical location or different ones. JBoss Data Grid’s Cross-Site Replication implementation is based on JGroups' RELAY2 protocol.
Cross-Datacenter Replication ensures data redundancy across clusters. In addition to creating backups for data restoration, these datasets may also be used in an active-active mode. When configured in this manner systems in separate environments are able to handle sessions should one cluster fail. Ideally, each of these clusters should be in a different physical location than the others.
37.2. Cross-Datacenter Replication Operations
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Cross-Datacenter Replication operation is explained through the use of an example, as follows:
Figure 37.1. Cross-Datacenter Replication Example
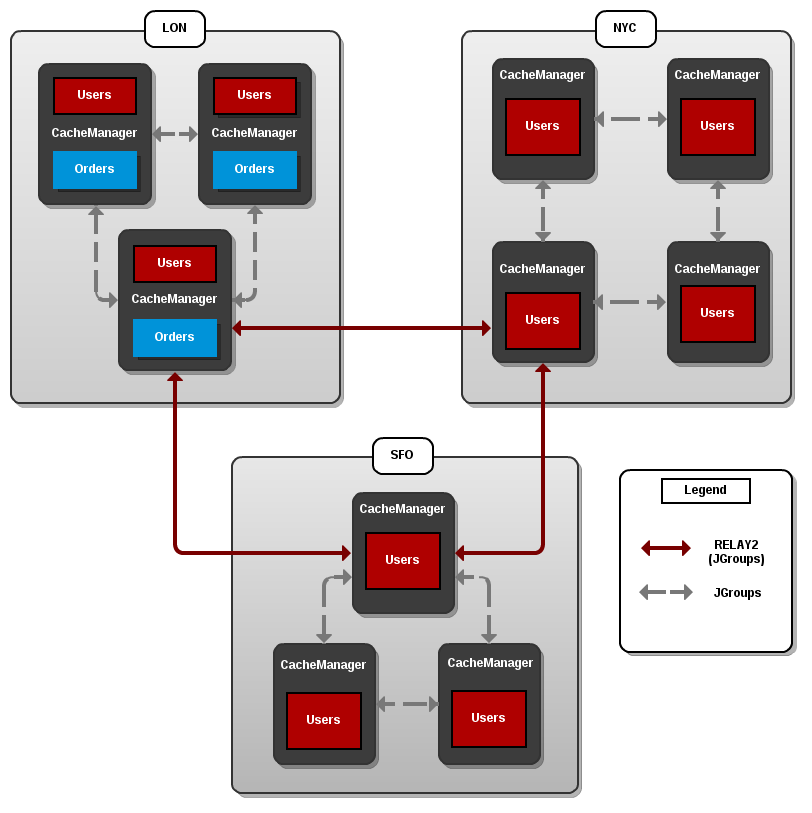
Three sites are configured in this example: LON, NYC and SFO. Each site hosts a running JBoss Data Grid cluster made up of three to four physical nodes.
The Users cache is active in all three sites - LON, NYC and SFO. Changes to the Users cache at the any one of these sites will be replicated to the other two as long as the cache defines the other two sites as its backups through configuration. The Orders cache, however, is only available locally at the LON site because it is not replicated to the other sites.
The Users cache can use different replication mechanisms each site. For example, it can back up data synchronously to SFO and asynchronously to NYC and LON.
The Users cache can also have a different configuration from one site to another. For example, it can be configured as a distributed cache with owners set to 2 in the LON site, as a replicated cache in the NYC site and as a distributed cache with owners set to 1 in the SFO site.
JGroups is used for communication within each site as well as inter-site communication. Specifically, a JGroups protocol called RELAY2 facilitates communication between sites. For more information, see About RELAY2.
37.3. Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication
37.3.1. Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication (Remote Client-Server Mode)
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode, cross-datacenter replication is set up as follows:
Set Up Cross-Datacenter Replication
Set Up RELAY
Add the following configuration to the standalone.xml file to set up RELAY :
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The RELAY protocol creates an additional stack (running parallel to the existing UDP stack) to communicate with the remote site. In the above example the
xsitechannel references the currenttcpstack. If a TCP based stack is used for the local cluster, two TCP based stack configurations are required: one for local communication and one to connect to the remote site. For an illustration, see Cross-Datacenter Replication Operations.Set Up Sites
Use the following configuration in the standalone.xml file to set up sites for each distributed cache in the cluster:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the Transport
In our first step we indicated the remote datacenters would be connecting over TCP, via the
xsitechannel. Now the TCP stack is configured to point to the remote sites:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the Backup Sites
Repeat steps 1-3 for each site in this configuration, adjusting the site names in the RELAY configuration as appropriate.
A cross-datacenter example configuration file may be found at $JDG_SERVER/docs/examples/configs/clustered-xsite.xml .
37.3.2. Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication (Library Mode)
37.3.2.1. Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication Declaratively
When configuring Cross-Datacenter Replication, the relay.RELAY2 protocol creates an additional stack (running parallel to the existing TCP stack) to communicate with the remote site. If a TCP -based stack is used for the local cluster, two TCP based stack configurations are required: one for local communication and one to connect to the remote site.
In JBoss Data Grid Library mode, cross-datacenter replication is set up as follows:
Setting Up Cross-Datacenter Replication
Configure the Local Site
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Add the
siteattribute to thetransportelement to define the local site (in this example, the local site is namedLON). -
Cross-site replication requires a non-default JGroups configuration. Define the
jgroupselement and define a customstack-file, passing in the name of the file to be referenced and the location to this custom configuration. In this example, the JGroups configuration file is named jgroups-with-relay.xml . -
Configure the cache in site
LONto back up to the sitesNYCandSFO. Configure the back up caches:
Configure the cache in site
NYCto receive back up data fromLON:<local-cache name="backupNYC"> <backups/> <backup-for remote-cache="default" remote-site="LON"/> </local-cache><local-cache name="backupNYC"> <backups/> <backup-for remote-cache="default" remote-site="LON"/> </local-cache>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the cache in site
SFOto receive back up data fromLON:<local-cache name="backupSFO"> <backups/> <backup-for remote-cache="default" remote-site="LON"/> </local-cache><local-cache name="backupSFO"> <backups/> <backup-for remote-cache="default" remote-site="LON"/> </local-cache>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Add the
Add the Contents of the Configuration File
As a default, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid includes JGroups configuration files such as default-configs/default-jgroups-tcp.xml and default-configs/default-jgroups-udp.xml in the infinispan-embedded-{VERSION}.jar package.
Copy the JGroups configuration to a new file (in this example, it is named jgroups-with-relay.xml ) and add the provided configuration information to this file. Note that the relay.RELAY2 protocol configuration must be the last protocol in the configuration stack.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the relay.xml File
Set up the relay.RELAY2 configuration in the relay.xml file. This file describes the global cluster configuration.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the Global Cluster
The file jgroups-global.xml referenced in relay.xml contains another JGroups configuration which is used for the global cluster: communication between sites.
The global cluster configuration is usually TCP -based and uses the TCPPING protocol (instead of PING or MPING ) to discover members. Copy the contents of default-configs/default-jgroups-tcp.xml into jgroups-global.xml and add the following configuration in order to configure TCPPING :
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace the hostnames (or IP addresses) in
TCPPING.initial_hostswith those used for your site masters. The ports (7800in this example) must match theTCP.bind_port.For more information about the TCPPING protocol, see Using the TCPPing Protocol.
37.4. Taking a Site Offline
37.4.1. Taking a Site Offline
In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Cross-datacenter replication configuration, if backing up to one site fails a certain number of times during a time interval, that site can be marked as offline automatically. This feature removes the need for manual intervention by an administrator to mark the site as offline.
It is possible to configure JBoss Data Grid to take down a site automatically when specified conditions are met, or for an administrator to manually take down a site:
Configure automatically taking a site offline:
- Declaratively in Remote Client-Server mode.
- Declaratively in Library mode.
- Using the programmatic method.
Manually taking a site offline:
- Using JBoss Operations Network (JON).
- Using the JBoss Data Grid Command Line Interface (CLI).
37.4.2. Taking a Site Offline
To take a site offline in either mode of JBoss Data Grid, add the take-offline element to the backup element. This will configure when a site is automatically taken offline.
You can take sites offline automatically with the SYNC backup strategy only. If the backup strategy is ASYNC then you must take sites offline manually.
Taking a Site Offline in Remote Client-Server Mode
<backup site="${sitename}" strategy="SYNC" failure-policy="FAIL">
<take-offline after-failures="${NUMBER}"
min-wait="${PERIOD}" />
</backup>
<backup site="${sitename}" strategy="SYNC" failure-policy="FAIL">
<take-offline after-failures="${NUMBER}"
min-wait="${PERIOD}" />
</backup>
The take-offline element use the following parameters to configure when to take a site offline:
-
The
after-failuresparameter specifies the number of times attempts to contact a site can fail before the site is taken offline. -
The
min-waitparameter specifies the number (in milliseconds) to wait to mark an unresponsive site as offline. The site is offline when themin-waitperiod elapses after the first attempt, and the number of failed attempts specified in theafter-failuresparameter occur.
37.4.3. Taking a Site Offline via JBoss Operations Network (JON)
A site can be taken offline in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid using the JBoss Operations Network operations. For a list of the metrics, see JBoss Operations Network Plugin Operations.
37.4.4. Taking a Site Offline via the CLI
Use Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Command Line Interface (CLI) to manually take a site from a cross-datacenter replication configuration down if it is unresponsive using the site command.
The site command can be used to check the status of a site as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache] site --status ${SITENAME}
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache] site --status ${SITENAME}
The result of this command would either be online or offline according to the current status of the named site.
The command can be used to bring a site online or offline by name as follows:
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache] site --offline ${SITENAME}
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache] site --offline ${SITENAME}[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache] site --online ${SITENAME}
[standalone@127.0.0.1:9990/MyCacheManager/namedCache] site --online ${SITENAME}
If the command is successful, the output ok displays after the command. As an alternate, the site can also be brought online using JMX (see Bring a Site Back Online for details).
For more information about the JBoss Data Grid CLI and its commands, see the Developer Guide 's chapter on the JBoss Data Grid Command Line Interface (CLI)
37.4.5. Bring a Site Back Online
After a site is taken offline, the site can be brought back online either using the JMX console to invoke the bringSiteOnline([replaceable]siteName) operation on the XSiteAdmin MBean (See XSiteAdmin for details) or using the CLI (see Taking a Site Offline via the CLI for details).
37.5. State Transfer Between Sites
37.5.1. State Transfer Between Sites
When an offline master site is back online, it is necessary to synchronize its state with the latest data from the backup site. State transfer allows state to be transferred from one site to another, meaning the master site is synchronized and made consistent with the backup site. Similarly, when a backup site becomes available, state transfer can be utilized to make it consistent with the master site.
Consider a scenario of two sites - Master site A and Backup site B. Clients can originally access only Master site A whereas Backup Site B acts as an invisible backup. Cross Site State Transfer can be pushed bidirectionally. When the new backup site B goes online, in order to synchronize its state with the master site A, a State Transfer can be initiated to push the state from the Master site A to the Backup site B.
Similarly, when the Master site A is brought back online, in order to synchronize it with the Backup site B, a State Transfer can be initiated to push the state from Backup site B to Master Site A.
The use cases applies for both Active-Passive and Active-Active State Transfer. The difference is that during Active-Active State Transfer we assume that cache operations can be performed in the site, which consumes state.
A system administrator or an authorized entity initiates the state transfer manually using JMX. The system administrator invokes the pushState(SiteName String) operation available in the XSiteAdminOperations MBean.
The following interface shows the pushState(SiteName String) operation in JConsole:
Figure 37.2. PushState Operation
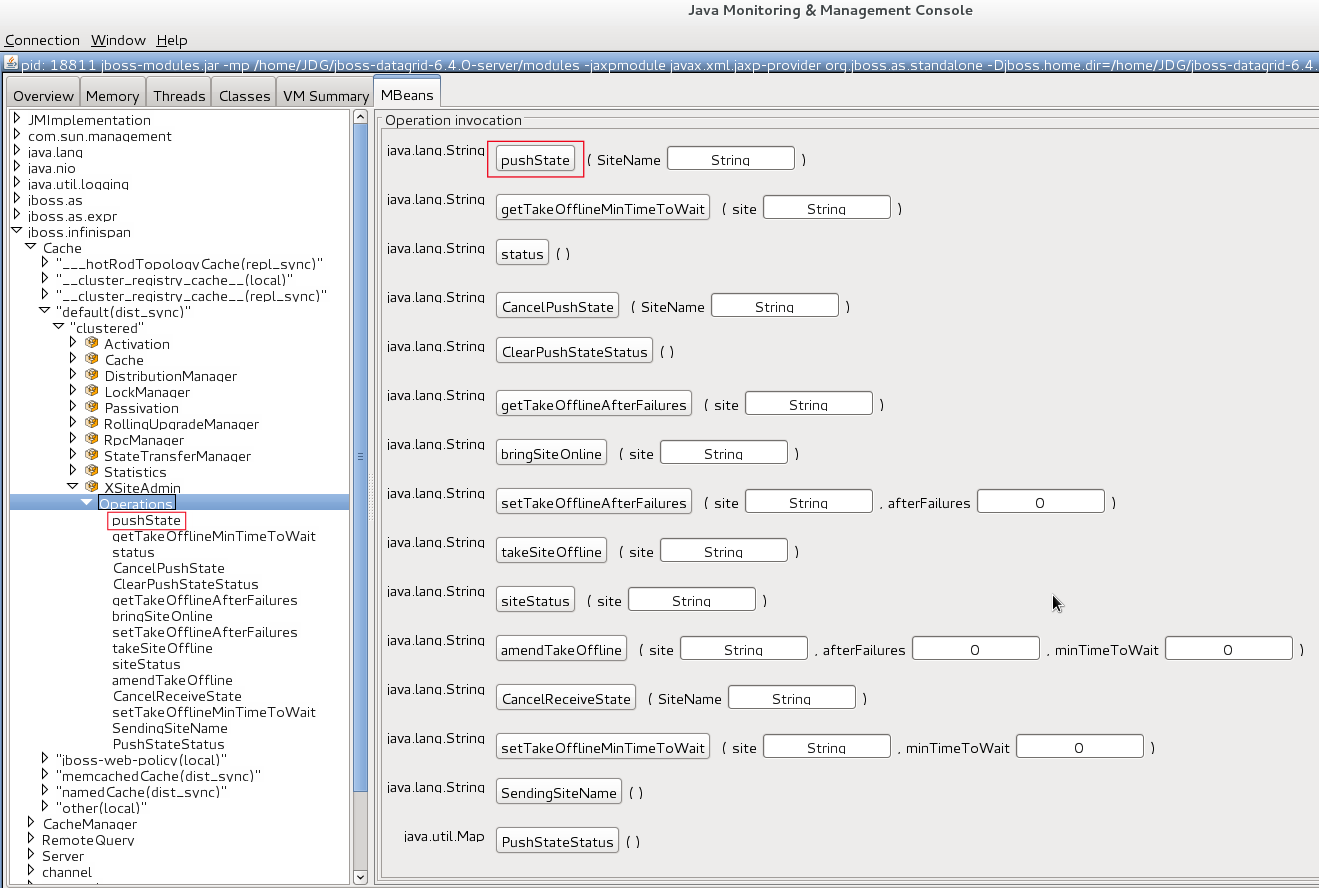
State transfer is also invoked using the Command Line Interface (CLI) by the site push sitename command. For example, when the master site is brought back online, the system administrator invokes the state transfer operation in the backup site, specifying the master site name that is to receive the state.
The master site can be offline at the time of the push operation. On successful state transfer, the state data common to both the sites is overwritten on the master site. For example, if key A exists on the master site but not on the backup site, key A will not be deleted from the master site. Whereas, if key B exists on the backup as well as the master site, key B is overwritten on the master site.
Updates on keys performed after initiating state transfer are not overwritten by incoming state transfer.
Cross-site state transfer can be transactional and supports 1PC and 2PC transaction options. 1PC and 2PC options define whether data modified inside a transaction is backed up to a remote site in one or two phases. 2PC includes a prepare phase in which backup sites acknowledges that transaction has been successfully prepared. Both options are supported.
37.5.2. Active-Passive State Transfer
The active-passive state transfer is used when cross-site replication is used to back up the master site. The master site processes all the requests but if it goes offline, the backup site starts to handle them. When the master site is back online, it receives the state from the backup site and starts to handle the client requests. In Active-Passive state transfer mode, transactional writes happen concurrently with state transfer on the site which sends the state.
In active-passive state transfer mode, the client read-write requests occurs only on the backup site. The master site acts as an invisible backup until the client requests are switched to it when the state transfer is completed. The active-passive state transfer mode is fully supported in cross-datacenter replication.
When an Active-Passive State Transfer is interrupted by a network failure, the System Administrator invokes the JMX operation manually to resume the state transfer. To transfer the state, for example from Master site A to Backup site B, invoke the JMX operation on Master site A. Similarly, to transfer state from Backup site B to Master site A, invoke the JMX operation on the Backup site B.
The JMX operation is invoked on the site from which the state is transferred to the other site that is online to synchronize the states.
For example, there is a running backup site and the system administrator wants to bring back the master site online. To use active-passive state transfer, the system administrator will perform the following steps.
- Boot the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cluster in the master site.
- Command the backup site to push state to the master site.
- Wait until the state transfer is complete.
- Make the clients aware that the master site is available to process the requests.
37.5.3. Active-Active State Transfer
In active-active state transfer mode, the client requests occur concurrently in both the sites while the state transfer is in progress. The current implementation supports handling requests in the new site while the state transfer is in progress, which may break the data consistency.
Active-active state transfer mode is not fully supported, as it may lead to data inconsistencies.
In active-active state transfer mode, both the sites, the master and the backup sites share the same role. There is no clear distinction between the master and backup sites in the active-active state transfer mode
For example, there is a running site and the system administrator wants to bring a new site online. To use active-active state transfer, the system administrator must perform the following steps.
- Boot the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cluster in the new site.
- Command the running site to push state to the new site.
- Make the clients aware that the new site is available to process the requests.
37.5.4. State Transfer Configuration
State transfer between sites is not enabled or disabled but it allows to tune some parameters. The only configuration is done by the system administrator while configuring the load balancer to switch the request to the master site during or after the state transfer. The implementation handles a case in which a key is updated by a client before it receives the state, ignoring when it is delivered.
The following are default parameter values:
37.6. Configure Multiple Site Masters
37.6.1. Configure Multiple Site Masters
A standard Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cross-datacenter replication configuration includes one master node for each site. The master node is a gateway for other nodes to communicate with the master nodes at other sites.
This standard configuration works for a simple cross-datacenter replication configuration. However, with a larger volume of traffic between the sites, passing traffic through a single master node can create a bottleneck, which slows communication across nodes.
In JBoss Data Grid, configure multiple master nodes for each site to optimize traffic across multiple sites.
37.6.2. Multiple Site Master Operations
When multiple site masters are enabled and configured, the master nodes in each site joins the local cluster (i.e. the local site) as well as the global cluster (which includes nodes that are members of multiple sites).
Each node that acts as a site master and maintains a routing table that consists of a list of target sites and site masters. When a message arrives, a random master node for the destination site is selected. The message is then forwarded to the random master node, where it is sent to the destination node (unless the randomly selected node was the destination).
37.6.3. Configure Multiple Site Masters (Remote Client-Server Mode)
Prerequisites
Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server Mode.
Set Multiple Site Masters in Remote Client-Server Mode
Locate the Target Configuration
Locate the target site’s configuration in the clustered-xsite.xml example configuration file. The sample configuration looks like example provided above.
Configure Maximum Sites
Use the
max_site_mastersproperty to determine the maximum number of master nodes within the site. Set this value to the number of nodes in the site to make every node a master.Configure Site Master
Use the
can_become_site_masterproperty to allow the node to become the site master. This flag is set totrueas a default. Setting this flag tofalseprevents the node from becoming a site master. This is required in situations where the node does not have a network interface connected to the external network.
37.6.4. Configure Multiple Site Masters (Library Mode)
To configure multiple site masters in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Library Mode:
Configure Multiple Site Masters (Library Mode)
Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication
Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication in JBoss Data Grid. Use the instructions in Configure Cross-Datacenter Replication Declaratively for an XML configuration. For instructions on a programmatic configuration refer to the JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide.
Add the Contents of the Configuration File
Add the
can_become_site_masterandmax_site_mastersparameters to the configuration as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
max_site_mastersvalue to the number of nodes in the cluster to make all nodes masters.
37.7. Cross-Datacenter Replication Concerns
When using Cross-Datacenter Replication in active-active mode, where each site is using the other as an active backup, there may be issues if the same key is written to both locations simultaneously.
Consider the following image:
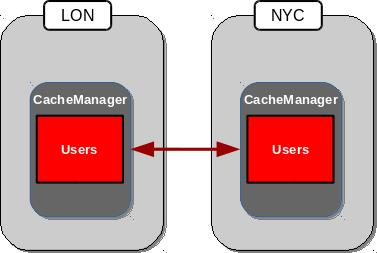
In this scenario both LON and NYC are backing up the Users cache to the other location. If the same entry were edited in both locations simultaneously, each site would update their local copy and then replicate this copy to the other site. This replication would overwrite the local copy’s value with the newly received, replicated, copy, resulting in LON and NYC swapping the expected value. The following example demonstrates this:
- Both LON and NYC have an entry in the Users cache with a key of 1 and a value of Smith.
- LON updates the value to Johnson.
- NYC updates the value to Williams.
- The cache is replicated to its backups, resulting in LON containing a value of Williams, and NYC containing a value of Johnson.
Chapter 38. Rolling Upgrades
38.1. Performing Rolling Upgrades
Upgrade Red Hat JBoss Data Grid clusters without downtime or data loss.
You can perform rolling upgrades only:
- in Remote Client-Server mode.
- using the Hot Rod protocol.
See the following Red Hat KCS solutions for additional detail:
38.1.1. Setting Up the Target Cluster
The target cluster is the desired version of JBoss Data Grid to which you migrate data.
Rolling upgrades are supported from JBoss Data Grid version 6.6.2.
- Start the target cluster with unique network properties or a different JGroups cluster name to keep it separate from the source cluster.
Configure a
RemoteCacheStoreon each node in the target cluster for each cache you want to migrate from the source cluster.NoteThe
RemoteCacheStoreon the target cluster is in addition to any other persistent store.RemoteCacheStoresettings-
remote-servermust point to the source cluster via theoutbound-socket-bindingproperty. -
remoteCacheNamemust match the cache name on the source cluster. -
hotrod-wrappingmust betrue(enabled). -
sharedmust betrue(enabled). -
purgemust befalse(disabled). -
passivationmust befalse(disabled). protocol-versionmatches the Hot Rod protocol version of the source cluster.Expand JBoss Data Grid Version
Hot Rod Protocol Version
7.2
2.6
7.1
2.6
7.0
2.5
6.6.2
2.4 (Requires 2.5.)
If you plan to perform a rolling upgrade from JBoss Data Grid version 6.6.2, contact your Red Hat support team to upgrade to Hot Rod version 2.5.
-
Example RemoteCacheStore Configuration
38.1.2. Migrating Data to the Target Cluster
Configure the target cluster to handle all client requests instead of the source cluster:
- Configure all clients to point to the target cluster instead of the source cluster.
Restart each client node.
The target cluster lazily loads data from the source cluster on demand via
RemoteCacheStore.
Fetch data from the source cluster.
NoteYou synchronize data on the target cluster to fetch data from the source cluster. If you are migrating from JBoss Data Grid 6.6.2, you must synchronize data on each node in the target cluster.
Do one of the following on the target cluster for each cache that you want to migrate:
- JMX
-
Invoke the
synchronizeDataoperation and specify thehotrodparameter on theRollingUpgradeManagerMBean. See RollingUpgradeManager. - CLI
JDG_HOME/bin/cli.sh --connect controller=127.0.0.1:9990 -c "/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=clustered/distributed-cache=MyCache:synchronize-data(migrator-name=hotrod)"
$ JDG_HOME/bin/cli.sh --connect controller=127.0.0.1:9990 -c "/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=clustered/distributed-cache=MyCache:synchronize-data(migrator-name=hotrod)"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Data migrates to all nodes in the target cluster in parallel, with each node receiving a subset of the data.
Use the following parameters to tune the operation:
-
read-batchconfigures the number of entries to read from the source cluster at a time. The default value is10000. write-threadsconfigures the number of threads used to write data. The default value is the number of processors available.For example:
synchronize-data(migrator-name=hotrod, read-batch=100000, write-threads=3)
-
The synchronizeData method call is blocking so no other operations are performed until the data migration is complete.
38.1.3. Finalizing Rolling Upgrades
After the target cluster fetches all data from the source cluster, do the following:
Disable the
RemoteCacheStoreon the target cluster.NoteYou must complete this step on each node in the target cluster.
Do one of the following:
- JMX
-
Invoke the
disconnectSourceoperation and specify thehotrodparameter on theRollingUpgradeManagerMBean. See RollingUpgradeManager. - CLI
JDG_HOME/bin/cli.sh --connect controller=127.0.0.1:9990 -c "/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=clustered/distributed-cache=MyCache:disconnect-source(migrator-name=hotrod)"
$ JDG_HOME/bin/cli.sh --connect controller=127.0.0.1:9990 -c "/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=clustered/distributed-cache=MyCache:disconnect-source(migrator-name=hotrod)"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Decommission the source cluster.
Chapter 39. Externalize Sessions
39.1. Externalize Sessions
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid can be used as an external cache for containers, such as JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (EAP). This allows JBoss Data Grid to store HTTP Sessions, among other data, independent of the application layer, which provides the following benefits:
Application Elasticity
By making the application stateless additional nodes may be added to the EAP cluster without expensive data rebalancing operations. The EAP cluster may also be replaced without downtime by keeping the state in the JBoss Data Grid layer, as upgraded nodes may be brought online and retrieve the sessions.
Failover Across Data Centers
Should a data center become unavailable the session data persists, as it is stored safely within the JBoss Data Grid cluster. This allows a load balancer to redirect incoming requests to a second cluster to retrieve the session information.
Reduced Memory Footprint
There is reduced memory pressure, resulting in shorter garbage collection time and frequency of collections, as the HTTP Sessions have been moved out of the application layer and into the backing caches.
39.2. Externalize HTTP Session from JBoss EAP to JBoss Data Grid
The following procedure applies for both standalone and domain mode of EAP; however, in domain mode each server group requires a unique remote cache configured.
While multiple server groups can utilize the same Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cluster the respective remote caches will be unique to the EAP server group.
The following procedures have been tested and validated on JBoss EAP 7.0 and JBoss Data Grid 7.0.
Externalize HTTP Sessions
Ensure the remote cache containers are defined in EAP’s
infinispansubsystem; in the example below thecacheattribute in theremote-storeelement defines the cache name on the remote JBoss Data Grid server:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define the location of the remote Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server by adding the networking information to the
socket-binding-group:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Repeat the above steps for each cache-container and each Red Hat JBoss Data Grid server. Each server defined must have a separate
<outbound-socket-binding>element defined. Add passivation and cache information into the application’s
jboss-web.xml. In the following examplewebis the name of the cache container, andjdgis the name of the default cache located in this container. An example file is shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The passivation timeouts above are provided assuming that a typical session is abandoned within 15 minutes and uses the default HTTP session timeout in JBoss EAP of 30 minutes. These values may need to be adjusted based on each application’s workload.
39.3. Externalize HTTP Sessions from JBoss Web Server (JWS) to JBoss Data Grid
39.3.1. Externalize HTTP Session from JBoss Web Server (JWS) to JBoss Data Grid
A session manager has been provided as part of the JBoss Data Grid distribution, allowing JWS users to externalize sessions to JBoss Data Grid by integrating with an extension of Tomcat’s Manager. This allows the Tomcat layer to remain stateless while providing session management persistence.
39.3.2. Prerequisites
This manager requires the following versions, or later, be installed:
- JBoss Web Server 3.0
- JBoss Data Grid 7.1
39.3.3. Installation
Complete the following steps to install this manager for either Tomcat 7 or Tomcat 8:
Download one of the following from the JBoss Data Grid product page:
- jboss-datagrid-7.2.0-tomcat7-session-client.zip
- jboss-datagrid-7.2.0-tomcat8-session-client.zip
- Extract the archive.
-
Copy the
lib/directory from the extracted archive into$CATALINA_HOME. Define the implementation of the Session Manager in
context.xml, as seen below:<Manager className="org.wildfly.clustering.tomcat.hotrod.HotRodManager" server_list="www.server1.com:7600;www.server2.com:7600" <!-- Additional Configuration Elements --> /><Manager className="org.wildfly.clustering.tomcat.hotrod.HotRodManager" server_list="www.server1.com:7600;www.server2.com:7600" <!-- Additional Configuration Elements --> />Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
39.3.4. Session Management Details
When using the HotRodManager all sessions are placed into the default cache located on the Remote JBoss Data Grid server. Cache names are not configurable.
Sessions stored in JBoss Web Server are all mutable by default. If an object changes during the course of the request then it will be replicated after the request ends. To define immutable objects, use one of the following annotations:
-
The Wildfly specific annotation -
org.wildfly.clustering.web.annotation.Immutable. - Any generic immutable annotation.
- Any known immutable type from the JDK implementation.
Objects may have custom marshalling by defining an Externalizer. By default the Wildfly Externalizer is recognized; however, any implementation of this Externalizer may be used. Additionally, non-serializable objects may be stored without issue as long as they have an Externalizer defined.
39.3.5. Configure the JBoss Web Server Session Manager
The HotRodManager is configured by defining properties on the Manager element inside of context.xml. These are pulled from two separate lists:
-
org.apache.catalina.Manager- As the session manager implements this class many of theCommon Attributesare configurable. -
ConfigurationParameters- This session manager also uses the HotRod Configuration Properties.
The following table displays all of the configurable elements
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| name |
The name of this cluster manager. The name is used to identify a session manager on a node. The name might get modified by the |
| sessionIdLength |
The length of session ids created by this Manager, measured in bytes, excluding subsequent conversion to a hexadecimal string and excluding any JVM route information used for load balancing. This attribute is deprecated. Set the length on a nested |
| secureRandomClass |
Name of the Java class that extends |
| secureRandomProvider |
Name of the provider to use to create the |
| secureRandomAlgorithm |
Name of the algorithm to use to create the |
| recordAllActions | Flag whether send all actions for session across Tomcat cluster nodes. If set to false, if already done something to the same attribute, make sure don’t send multiple actions across Tomcat cluster nodes. In that case, sends only the actions that have been added at last. Default is false. |
There is also a property specific to the JWS HotRodManager, shown below:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| persistenceStrategy |
Determines whether or not all attributes that compose a session should be serialized together ( |
In addition to the attributes inherited from Tomcat, the HotRodManager may use any of the properties typically available to a RemoteCacheManager. These are outlined in HotRod Properties.
When using HotRod properties only the property name itself is required. For instance, to configure TCP KEEPALIVE and TCP NODELAY on the manager the following xml snippet would be used:
<Manager className="org.wildfly.clustering.tomcat.hotrod.HotRodManager"
tcp_no_delay="true"
tcp_keep_alive="true"/>
<Manager className="org.wildfly.clustering.tomcat.hotrod.HotRodManager"
tcp_no_delay="true"
tcp_keep_alive="true"/>Chapter 40. Handling Network Partitions (Split Brain)
40.1. Network Partition Recovery
Network Partitions occur when a cluster breaks into two or more partitions. As a result, the nodes in each partition are unable to locate or communicate with nodes in the other partitions. This results in an unintentionally partitioned network.
In the event of a network partition in a distributed system like Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, the CAP (Brewer’s) theorem becomes relevant. The CAP theorem states that in the event of a Network Partition [P], a distributed system can provide either Consistency [C] or Availability [A] for the data, but not both.
By default, reads and writes are enabled on all nodes in JBoss Data Grid. During a network partition, the partitions continue to remain Available [A], at the cost of Consistency [C].
In JBoss Data Grid, a cache consists of data stored on a number of nodes. To prevent data loss if a node fails, JBoss Data Grid replicates a data item over multiple nodes. In distribution mode, this redundancy is configured using the owners configuration attribute, which specifies the number of replicas for each cache entry in the cache. As a result, as long as the number of nodes that have failed are less than the value of owners, JBoss Data Grid retains a copy of the lost data and can recover.
In JBoss Data Grid’s replication mode, however, owners is always equal to the number of nodes in the cache, because each node contains a copy of every data item in the cache in this mode.
In certain cases, a number of nodes greater than the value of owners can disappear from the cache. Two common reasons for this are:
- Split-Brain: Usually, as the result of a router crash, the cache is divided into two or more partitions. Each of the partitions operates independently of the other and each may contain different versions of the same data.
-
Sucessive Crashed Nodes: A number of nodes greater than the value of
ownerscrashes in succession for any reason. JBoss Data Grid is unable to properly balance the state between crashes, and the result is partial data loss.
The partition handling functionality described in this section determines what operations can be performed on a cache in the event of a split-brain scenario. JBoss Data Grid provides multiple partition handling strategies, which, in terms of the CAP theorem, determine whether availability or consistency is ensured. The provided strategies are listed in the table below:
| Strategy Name | Description | CAP |
|---|---|---|
|
| Allows entries on each partition to diverge, with conflicts resolved during merge. This is the default partition handling strategy in JBoss Data Grid. | Availability |
|
| If the partition does not have all owners for a given segment, both reads and writes are denied for all keys in that segment. | Consistency |
|
| Allows reads for a given key if it exists in this partition, but only allows writes if this partition contains all owners of a segment. | Availability |
40.2. Detecting and Recovering from a Split-Brain Problem
When a Split-Brain occurs in the data grid, each network partition installs its own JGroups view with nodes from other partitions removed. The partitions remain unaware of each other, therefore there is no way to determine how many partitions the network has split into. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid assumes the cache has unexpectedly split if one or more nodes disappear from the JGroups cache without sending an explicit leaving message, while in reality the cause can be physical (crashed switches, cable failure, etc.) to virtual (stop-the-world garbage collection).
This state is dangerous because each of the newly split partitions operates independently and can store conflicting updates for the same data entries.
A possible limitation is that if two partitions start as isolated partitions and do not merge, they can read and write inconsistent data. JBoss Data Grid does not identify such partitions as split partitions.
40.3. Partition Handling Strategies
JBoss Data Grid provides multiple partition handling strategies that can provide either data consistency or data availability. Application requirements should determine which strategy to use. For example, when data read from the system must be accurate, DENY_READ_WRITES may be the best choice, as it ensures data consistency.
40.3.1. ALLOW_READ_WRITES
When JBoss Data Grid is configured to use ALLOW_READ_WRITES, each partition continues to function as an independent cluster, with all partitions remaining in AVAILABLE mode. This means each partition may only see part of the data, and each partition could write conflicting updates to the cache. During a partition merge these conflicts are automatically resolved by utilising the ConflictManager and the configured EntryMergePolicy. The default partition handling strategy for JBoss Data Grid is ALLOW_READ_WRITES and the default merge policy is PREFERRED_ALWAYS. That is, if conflicts arise due to a split-brain scenario, upon merge, the preferredEntry cache entry will be used to resolve the conflict.
40.3.2. DENY_READ_WRITES
When DENY_READ_WRITES is configured, and JBoss Data Grid suspects one or more nodes are no longer accessible, each partition does not start a rebalance immediately, but first it checks whether it should enter degraded mode instead. To enter Degraded Mode, one of the following conditions must be true:
-
At least one segment has lost all its owners, which means that a number of nodes equal to or greater than the value of
ownershave left the JGroups view. - The partition does not contain a majority of nodes (greater than half) of the nodes from the latest stable topology. The stable topology is updated each time a rebalance operation successfully concludes and the coordinator determines that additional rebalancing is not required.
If neither of the conditions are met, the partition continues normal operations and JBoss Data Grid attempts to rebalance its nodes. If at least one of these conditions is met, at most one partition can remain in Available mode. Other partitions will enter Degraded Mode.
When a partition enters into Degraded Mode, it only allows read/write access to those entries for which all owners (copies) of the entry exist on nodes within the same partition. Read and write requests for an entry for which one or more of its owners (copies) exist on nodes that have disappeared from the partition are rejected with an AvailabilityException.
This guarantees partitions cannot write different values for the same key (cache is consistent), and also that one partition can not read keys that have been updated in the other partitions (no stale data).
40.3.2.1. Partition Recovery Example with DENY_READ_WRITE
In this example, a distributed cache is configured on a four node cluster with four data entries (k1, k2, k3 and k4). The parameter owners is set to 2, so the four data entries each have two copies in the cache.
Figure 40.1. Cache Before and After a Network Partition
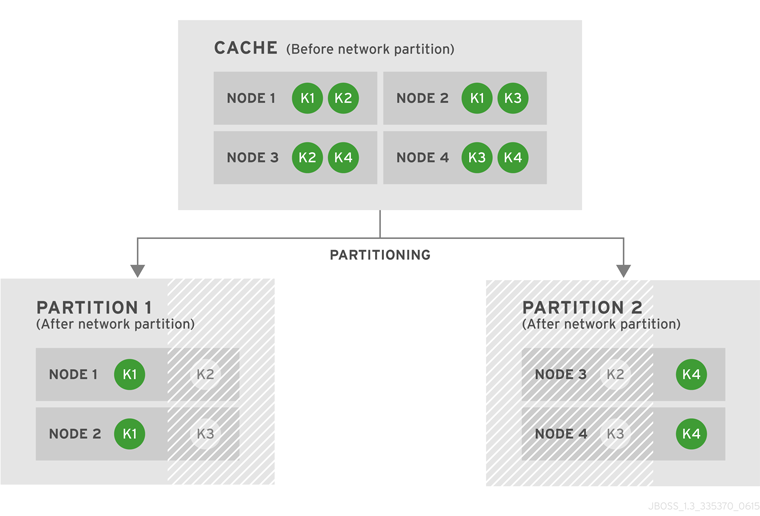
After the network partition occurs, Partitions 1 and 2 enter Degraded Mode (depicted in the diagram as grayed-out nodes). Within each partition, an entry will only be available for read or write operations if both its copies are in the same partition. In Partition 1, the data entry k1 is available for reads and writes because owners equals 2 and both copies of the entry remain in Partition 1. In Partition 2, k4 is available for reads and writes for the same reason. The entries k2 and k3 become unavailable in both partitions, as neither partition contains all copies of these entries. A new entry k5 can be written to a partition only if that partition were to own both copies of k5.
Figure 40.2. Cache After Partitions Are Merged
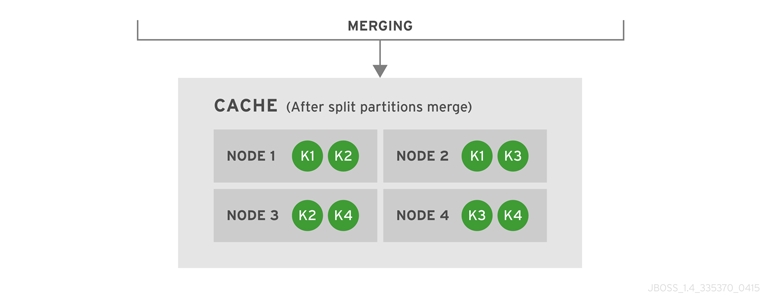
JBoss Data Grid subsequently merges the two split partitions into a single cache. No state transfer is required and the cache returns to Available Mode with four nodes and four data entries (k1, k2, k3 and k4).
Data consistency can be at risk from the time (t1) when the cache physically split to the time (t2) when JBoss Data Grid detects the connectivity change and changes the state of the partitions:
- Transactional writes that were in progress at t1 when the split physically occurred may be rolled back on some of the owners. This can result in inconsistency between the copies (after the partitions rejoin) of an entry that is affected by such a write. However, transactional writes that started after t1 will fail as expected.
- If the write is non-transactional, then during this time window, a value written only in a minor partition (due to physical split and because the partition has not yet been Degraded) can be lost when partitions rejoin, if this minor partition receives state from a primary (Available) partition upon rejoin. If the partition does not receive state upon rejoin (i.e. all partitions are degraded), then the value is not lost, but an inconsistency can remain.
- There is also a possibility of a stale read in a minor partition during this transition period, as an entry is still Available until the minor partition enters Degraded state.
When partitions merge after a network partition has occurred:
- If one of the partitions was Available during the network partition, then the joining partition(s) are wiped out and state transfer occurs from the Available (primary) partition to the joining nodes.
- If all joining partitions were Degraded during the Split Brain, then no state transfer occurs during the merge. The combined cache is then Available only if the merging partitions contain a simple majority of the members in the latest stable topology (one with the highest topology ID) and has at least an owner for each segment (i.e. keys are not lost).
Between the time (t1) when partitions begin merging to the time (t2) when the merge is complete, nodes reconnect through a series of merge events. During this time window, it is possible that a node can be reported as having temporarily left the cluster. For a Transactional cache, if during this window between t1 and t2, such a node is executing a transaction that spans other nodes, then this transaction may not execute on the remote node, but still succeed on the originating node. The result is a potential stale value for affected entries on a node that did not commit this transaction.
After t2, once the merge has completed on all nodes, this situation will not occur for subsequent transactions. However, an inconsistency introduced on entries that were affected by a transaction in progress during the time window between t1 and t2 is not resolved until these entries are subsequently updated or deleted. Until then, a read on such impacted entries can potentially return the stale value.
40.3.3. ALLOW_READS
Partitions are handled in the same manner as DENY_READ_WRITES, except that when a partition is in DEGRADED mode read operations on a partially owned key will not throw an AvailabilityException.
40.4. Detecting and Recovering from Successive Node Failures
Nodes can leave a cluster for reasons other than network failures. For example, a process might stop running or the JVM pauses due to Garbage Collection (GC). However, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cannot detect these different causes. When a node leaves the JGroups cluster abruptly, JBoss Data Grid handles it as a network failure.
If only one node leaves a cluster and there are backup owners (numOwners) then:
- The cluster remains available.
- JBoss Data Grid attempts to create new replicas of the lost data.
If multiple nodes leave a cluster, it is possible that unrecoverable data loss can occur. For example, additional nodes crash while JBoss Data Grid is attempting to create replicas of data that were lost during a previous node crash. In this case, all copies of data for some entries might no longer be available on any node in the cluster.
Either the DENY_READ_WRITES or ALLOW_READS partition handling strategy causes JBoss Data Grid to enter DEGRADED mode when it detects one or more nodes are no longer available. These strategies help prevent unrecoverable data loss even if a Split-Brain has not occurred.
Data loss can also occur when nodes are shut down in rapid succession, or not gracefully, if those nodes are all owners for data that was stored on those nodes only.
When you shut down nodes gracefully, JBoss Data Grid knows that the nodes cannot come back. However, the cluster does not track how each node leaves the cluster. As a result, the cache still enters DEGRADED mode as if those nodes had crashed.
When nodes crash or are shut down in rapid succession, it is not possible for the cluster to recover its state unless you stop it and then repopulate the data from an external source when you restart the cluster. For this reason, you should configure the numOwners parameter so that there is an adequate number of data copies to prevent data loss from successive node failures.
Alternatively, if you can tolerate some data loss, you can force JBoss Data Grid into AVAILABLE mode from DEGRADED mode using the Cache JMX MBean. See Cache JMX MBean.
Likewise, the AdvancedCache interface lets you read and change the cache availability. See The AdvancedCache Interface in the Developer Guide.
40.5. Conflict Manager
The most basic function of the conflict manager is to allow the retrieval of all stored replica values for a given key. This provides the opportunity to process a stream of cache entries whose stored replicas have conflicting values. By using implementations of the EntryMergePolicy interface it is possible for conflicts to be resolved automatically.
40.5.1. Detecting Conflicts
The conflict manager detects conflicts by comparing each of the stored values for a given key. The result of the .equals method on the stored values is used to determine whether all values are equal. If all values are equal then no conflicts exist for the key, otherwise a conflict has occurred. Note that null values are returned if no entry exists on a given node. JBoss Data Grid indicates a conflict has occurred if both a null and non-null value exist for a given key.
40.5.2. Merge Policies
If a conflict between one or more replicas of a given CacheEntry exists, a conflict resolution algorithm can be used to resolve it. JBoss Data Grid provides the EntryMergePolicy interface for this purpose. This interface consists of a single method, merge, whose returned CacheEntry is used as the resolved entry for a given key. When a non-null CacheEntry is returned, this entry’s value is put to all replicas in the cache. However, when the merge implementation returns a null value, all replicas associated with the conflicting key are removed from the cache.
The merge method takes two parameters, preferredEntry, and otherEntries. In the context of a partition merge, the preferredEntry is the CacheEntry associated with the partition whose coordinator is conducting the merge (or if multiple entries exist in this partition, it is the primary replica). However, in all other contexts, the preferredEntry is the primary replica. The second parameter, otherEntries, is a list of all other entries associated with the key for which a conflict was detected.
EntryMergePolicy::merge is only called when a conflict has been detected, it is not called if all CacheEntrys are the same.
The following table describes the merge policies that JBoss Data Grid provides:
| Policy | Description | Possible Risks |
|---|---|---|
|
| Do not attempt to resolve conflicts on merge. This is the default merge policy. | Nodes drop segments if they no longer own the segments. This can lead to the loss of segments. |
|
|
Always use the |
Even the |
|
|
Use the | This policy could restore deleted entries. |
|
| Always remove the key and value from the cache when a conflict is detected. | This policy results in the loss of all entries that are modified concurrently and have different values. |
Along with the implementations of the EntryMergePolicy interface that JBoss Data Grid provides, you can also create custom implementations. See Creating Custom Merge Policies.
40.6. Split Brain Timing: Detecting a Split
When using the FD_ALL protocol a given node becomes suspected after the following amount of milliseconds have passed:
FD_ALL.timeout + FD_ALL.interval + VERIFY_SUSPECT.timeout + GMS.view_ack_collection_timeout
FD_ALL.timeout + FD_ALL.interval + VERIFY_SUSPECT.timeout + GMS.view_ack_collection_timeout40.7. Split Brain Timing: Recovering From a Split
After a split occurs JBoss Data Grid will merge the partitions back, and the maximum time to detect a merge after the network partition is healed is:
3.1 * MERGE3.max_interval
3.1 * MERGE3.max_intervalIn some cases multiple merges will occur after a split so that the cluster may contain all available partitions. In this case, where multiple merges occur, time should be allowed for all of these to complete, and as there may be as many as three merges occurring sequentially the total delay should be no more than the following:
10 * MERGE3.max_interval
10 * MERGE3.max_interval40.7.1. Considerations with Garbage Collection
A Java Virtual Machine (JVM) provides the runtime environment for Red Hat JBoss Data Grid. Garbage Collection (GC) in the JVM can cause splits and impact the behavior of the conflict manager.
It is important to monitor GC when you deploy JBoss Data Grid so that "stop-the-world" suspension of the JVM does not negatively impact performance of your cluster.
Long GC times can increase the amount of time it takes JBoss Data Grid to detect and recover from splits. In some cases, GC can cause JBoss Data Grid to exceed the maximum time to detect a split.
Additionally, when merging partitions after a split, JBoss Data Grid attempts to confirm all nodes are present in the cluster. Because no timeout or upper bound applies to the response time from nodes, the operation to merge the cluster view can be delayed. This can result from network issues as well as long GC times.
Another scenario in which GC can impact performance through partition handling is when GC suspends the JVM, causing one or more nodes to leave the cluster. When this occurs, and suspended nodes resume after GC completes, the nodes can have out of date or conflicting cluster topologies.
If the merge policy is configured to detect conflicts, JBoss Data Grid attempts to resolve conflicts before merging the nodes. However the merge policy is enforced only if more than one node in the cluster is suspended due to GC. In cases where JBoss Data Grid detects a single suspended node, it clears the out of date topology without attempting to resolve conflicts. JBoss Data Grid then rebalances the nodes after the merge completes.
40.8. Configuring Partition Handling
Unless the cache is distributed or replicated, partition handling configuration is ignored. The default partition handling strategy is ALLOW_READ_WRITES and the default EntryMergePolicy is MergePolicies::NONE.
40.8.1. Example Configurations
Declarative Configuration (Library Mode)
Enable partition handling declaratively as follows:
<distributed-cache name="distributed_cache"
l1-lifespan="20000">
<partition-handling when-split="DENY_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="REMOVE_ALL"/>
</distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache name="distributed_cache"
l1-lifespan="20000">
<partition-handling when-split="DENY_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="REMOVE_ALL"/>
</distributed-cache>Declarative Configuration (Remote Client-server Mode)
Enable partition handling declaratively in remote client-server mode by using the following configuration:
A programmatic configuration example of partition handling is included in the Developer Guide.
40.8.2. Configuration of Partition Handling Between Releases
If you migrate the configuration from a previous release, there are specific changes that apply to partition handling.
In JBoss Data Grid 7.1 and earlier, you could disable or enable partition handling. Either option provides specific functionality that is limited to a subset of what you can now configure in JBoss Data Grid.
40.8.2.1. No Partition Handling Configuration or Partition Handling Disabled
If the partition-handling element is not specified in the configuration or if the configuration is as follows:
<partition-handling enabled="false">
<partition-handling enabled="false">Then it is equivalent to the following configuration:
<partition-handling when-split="ALLOW_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="NONE"/>
<partition-handling when-split="ALLOW_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="NONE"/>
This configuration enables the conflict manager. If you do not want to enable the conflict manager, set the merge policy to PREFERRED_ALWAYS.
40.8.2.2. Partition Handling Enabled
<partition-handling enabled="true">
<partition-handling enabled="true">The preceding configuration from JBoss Data Grid 7.1 and earlier is equivalent to the following configuration:
<partition-handling when-split="DENY_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="NONE"/>
<partition-handling when-split="DENY_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="NONE"/>
This configuration enables partition handling with similar behavior to JBoss Data Grid 7.1 and earlier. No merge policy is necessary because different data cannot be written to copies of the entry on different nodes given that the DENY_READ_WRITES strategy is configured.
To find out more about merge policies in JBoss Data Grid 7.2, see Merge Policies.
40.9. Creating Custom Merge Policies
A custom merge policy is an implementation of the EntryMergePolicy interface such as the following:
To use custom merge policies in Remote Client-Server Mode, you must package the implementation class files to JBoss Data Grid in a JAR file that contains the following file:
META-INF/services/org.infinispan.conflict.EntryMergePolicy
This file must provide the fully qualified class name of the EntryMergePolicy implementation.
In Library Mode, you should ensure that the custom merge policy is on the classpath.
Data Interoperability with Custom Merge Policies
When using JBoss Data Grid in Remote Client-Server Mode, custom merge policies that exchange data with the cache must be able to handle data interoperability. JBoss Data Grid stores cache entries in a marshalled format and returns key/value pairs to custom merge policies as byte arrays.
To handle cache entries in a marshalled format, custom merge policies must be able to perform marshalling. Alternatively you can configure the media type for data in the cache so that JBoss Data Grid converts between storage formats.
In cases where your custom merge policy depends on metadata associated with cache entries only, you do not need to configure your merge policy to handle marshalling.
For more information, see the following sections in the Developer Guide:
40.9.1. Specifying Custom Merge Policies
You can declaratively configure custom merge policies as follows:
<distributed-cache name="the-default-cache"> <partition-handling when-split="DENY_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="org.example.CustomMergePolicy"/> </distributed-cache>
<distributed-cache name="the-default-cache">
<partition-handling when-split="DENY_READ_WRITES" merge-policy="org.example.CustomMergePolicy"/>
</distributed-cache>Alternatively, you can programmatically configure custom merge policies as follows:
ConfigurationBuilder dcc = new ConfigurationBuilder();
dcc.clustering().partitionHandling()
.whenSplit(PartitionHandling.DENY_READ_WRITES)
.mergePolicy(new CustomMergePolicy());
ConfigurationBuilder dcc = new ConfigurationBuilder();
dcc.clustering().partitionHandling()
.whenSplit(PartitionHandling.DENY_READ_WRITES)
.mergePolicy(new CustomMergePolicy());Appendix A. Recommended JGroups Values for JBoss Data Grid
A.1. Supported JGroups Protocols
The table contains a list of the JGroups protocols supported in JBoss Data Grid.
| Protocol | Details |
|---|---|
| TCP | TCP/IP is a replacement transport for UDP in situations where IP multicast cannot be used, such as operations over a WAN where routers may discard IP multicast packets. TCP is a transport protocol used to send unicast and multicast messages.
As IP multicasting cannot be used to discover initial members, another mechanism must be used to find initial membership. Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Hot Rod is a custom TCP client/server protocol. |
| UDP | UDP is a transport protocol that uses:
When the UDP transport is started, it opens a unicast socket and a multicast socket. The unicast socket is used to send and receive unicast messages, the multicast socket sends and receives multicast sockets. The physical address of the channel with be the same as the address and port number of the unicast socket. |
| PING | The PING protocol is used for the initial discovery of members. It is used to detect the coordinator, which is the oldest member, by multicasting PING requests to an IP multicast address. Each member responds to the ping with a packet containing the coordinator’s and their own address. After a specified number of milliseconds (N) or replies (M), the joiner determines the coordinator from the responses and sends it a JOIN request (handled by GMS). If there is no response, the joiner is considered the first member of the group. PING differs from TCPPING because it used dynamic discovery, which means that a member does not need to know in advance where the other cluster members are. PING uses the transport’s IP multicasting abilities to send a discovery request to the cluster. As a result, PING requires UDP as transport. |
| TCPPING | The TCCPING protocol uses a set of known members and pings them for discovery. This protocol has a static configuration. |
| MPING | The MPING (Multicast PING) protocol uses IP multicast to discover the initial membership. It can be used with all transports, but is usually used in combination with TCP. |
| S3_PING | S3_PING is a discovery protocol that is ideal for use with Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) because EC2 does not allow multicast and therefore MPING is not allowed. Each EC2 instance adds a small file to an S3 data container, known as a bucket. Each instance then reads the files in the bucket to discover the other members of the cluster. |
| JDBC_PING | JDBC_PING is a discovery protocol that utilizes a shared database to store information regarding nodes in the cluster. |
| TCPGOSSIP | TCPGOSSIP is a discovery protocol that uses one or more configured GossipRouter processes to store information about the nodes in the cluster. |
| MERGE3 | The MERGE3 protocol is available in JGroups 3.1 onwards. Unlike MERGE2, in MERGE3, all members periodically send an INFO message with their address (UUID), logical name, physical address and View ID. Periodically, each coordinator reviews the INFO details to ensure that there are no inconsistencies. |
| FD_ALL | Used for failure detection, FD_ALL uses a simple heartbeat protocol. Each member maintains a table of all other members (except itself) and periodically multicasts a heartbeat. For example, when data or a heartbeat from P is received, the timestamp for P is set to the current time. Periodically, expired members are identified using the timestamp values. |
| FD_SOCK | FD_SOCK is a failure detection protocol based on a ring of TCP sockets created between cluster members. Each cluster member connects to its neighbor (the last member connects to the first member), which forms a ring. Member B is suspected when its neighbor A detects an abnormal closing of its TCP socket (usually due to node B crashing). However, if member B is leaving gracefully, it informs member A and does not become suspected when it does exit. |
| FD_HOST | FD_HOST is a failure detection protocol that detects the crashing or hanging of entire hosts and suspects all cluster members of that host through ICMP ping messages or custom commands. FD_HOST does not detect the crashing or hanging of single members on the local hosts, but only checks whether all the other hosts in the cluster are live and available. It is therefore used in conjunction with other failure detection protocols such as FD_ALL and FD_SOCK. This protocol is typically used when multiple cluster members are running on the same physical box.
The FD_HOST protocol is supported on Windows for JBoss Data Grid. The |
| VERIFY_SUSPECT | The VERIFY_SUSPECT protocol verifies whether a suspected member is dead by pinging the member before excluding it. If the member responds, the suspect message is discarded. |
| NAKACK2 | The NAKACK2 protocol is a successor to the NAKACK protocol and was introduced in JGroups 3.1. The NACKACK2 protocol is used for multicast messages and uses NAK. Each message is tagged with a sequence number. The receiver tracks the sequence numbers and delivers the messages in order. When a gap in the sequence numbers is detected, the receiver asks the sender to retransmit the missing message. |
| UNICAST3 | The UNICAST3 protocol provides reliable delivery (no message sent by a sender is lost because they are sent in a numbered sequence) and uses the FIFO (First In First Out) properties for point to point messages between a sender and a receiver. UNICAST3 uses positive acks for retransmission. For example, sender A keeps sending message M until receiver B receives message M and returns an ack to indicate a successful delivery. Sender A keeps resending message M until it receives an ack from B, until B leaves the cluster, or A crashes. |
| STABLE | The STABLE protocol is a garbage collector for messages that have been viewed by all members in a cluster. Each member stores all messages because retransmission may be required. A message can only be removed from the retransmission buffers when all members have seen the message. The STABLE protocol periodically gossips its highest and lowest messages seen. The lowest value is used to compute the min (all lowest sequence numbers for all members) and messages with a sequence number below the min value can be discarded |
| GMS | The GMS protocol is the group membership protocol. This protocol handles joins/leaves/crashes (suspicions) and emits new views accordingly. |
| MFC | MFC is the Multicast version of the flow control protocol. |
| UFC | UFC is the Unicast version of the flow control protocol. |
| FRAG3 | The FRAG3 protocol fragments large messages into smaller ones and then sends the smaller messages. At the receiver side, the smaller fragments are reassembled into larger, complete messages and delivered to the application. FRAG3 is used for both multicast and unicast messages. |
| SYM_ENCRYPT |
JGroups includes the SYM_ENCRYPT protocol to provide encryption for cluster traffic. By default, encryption only encrypts the message body; it does not encrypt message headers. To encrypt the entire message, including all headers, as well as destination and source addresses, the property The SYM_ENCRYPT layer is used to encrypt and decrypt communication in JGroups by defining a secret key in a keystore. Each message is identified as encrypted with a specific encryption header identifying the encrypt header and an MD5 digest identifying the version of the key being used to encrypt and decrypt messages. |
| ASYM_ENCRYPT |
JGroups includes the ASYM_ENCRYPT protocol to provide encryption for cluster traffic. By default, encryption only encrypts the message body; it does not encrypt message headers. To encrypt the entire message, including all headers, as well as destination and source addresses, the property The ASYM_ENCRYPT layer is used to encrypt and decrypt communication in JGroups by having a coordinator generate a secret key using defined algorithms and key sizes. Each message is identified as encrypted with a specific encryption header identifying the encrypt header and an MD5 digest identifying the version of the key being used to encrypt and decrypt messages. |
| SASL | The SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) protocol is a framework that provides authentication and data security services in connection-oriented protocols using replaceable mechanisms. Additionally, SASL provides a structured interface between protocols and mechanisms. |
| RELAY2 | The RELAY protocol bridges two remote clusters by creating a connection between one node in each site. This allows multicast messages sent out in one site to be relayed to the other and vice versa. JGroups includes the RELAY2 protocol, which is used for communication between sites in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Cross-Site Replication. The RELAY2 protocol works similarly to RELAY but with slight differences. Unlike RELAY, the RELAY2 protocol:
|
A.2. TCP Default and Recommended Values
To learn more about JGroups and using TCP and UDP, see Configure JGroups (Library Mode).
-
Values in
JGroups Default Valueindicate values that are configured internally to JGroups, but may be overridden by a custom configuration file or by a JGroups configuration file shipped with JBoss Data Grid. -
Values in
JBoss Data Grid Configured Valuesindicate values that are in use by default when using one of the configuration files for JGroups as shipped with JBoss Data Grid. It is recommended to use these values when custom configuration files for JGroups are in use with JBoss Data Grid. For more information on the configuration files included with JBoss Data Grid refer to JBoss Data Grid JGroups Configuration Files.
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| bind_addr | Any non-loopback | Set address on specific interface |
| bind_port | Any free port | Set specific port |
| loopback | true | Same as default |
| port_range | 50 | Set based on desired range of ports |
| recv_buf_size | 150,000 | Same as default |
| send_buf_size | 150,000 | 640,000 |
| sock_conn_timeout | 2,000 | 300 |
| bundler_type | transfer-queue | no-bundler |
| max_bundle_size | 64,000 | 64,000 |
| enable_diagnostics | true | false |
| thread_pool.enabled | true | Same as default |
| thread_pool.min_threads | 2 | This should equal the number of nodes |
| thread_pool.max_threads | 30 |
This should be higher than |
| thread_pool.keep_alive_time | 30,000 | 60,000 |
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7.2 uses JGroups 4.0.4.Final, in which the TCPPING timeout value no longer exists. Use the pbcast.GMS join_timeout value to indicate the timeout period instead.
Recommended Values for S3_PING
See S3_PING Configuration Options for details about configuring S3_PING for JBoss Data Grid.
Recommended Values for TCPGOSSIP
See TCPGOSSIP Configuration Options for details about configuring TCPGOSSIP for JBoss Data Grid.
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| bind_addr | Any non-loopback | Set address on specific interface |
| break_on_coord_rsp | true | Same as default |
| mcast_addr | 230.5.6.7 | 228.2.4.6 |
| mcast_port | 7555 | 43366 |
| ip_ttl | 8 | 2 |
In JGroups 3.6.1, the MPING timeout value was removed and the pbcast.GMS join_timeout value indicates the timeout period instead.
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| min_interval | 1,000 | 10,000 |
| max_interval | 10,000 | 30,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| client_bind_por | 0 (randomly selects a port and uses it) | Same as default |
| get_cache_timeout | 1000 milliseconds | Same as default |
| keep_alive | true | Same as default |
| num_tries | 3 | Same as default |
| start_port | 0 (randomly selects a port and uses it) | Same as default |
| suspect_msg_interval | 5000 milliseconds. | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | 40,000 | 60,000. The FD_ALL timeout value is set to two times the longest possible stop the world garbage collection pause in the CMS garbage collector. In a well-tuned JVM, the longest pause is proportional to heap size and should not exceed 1 second per GB of heap. For example, an 8GB heap should not have a pause longer than 8 seconds, so the FD_ALL timeout value must be set to 16 seconds. If longer garbage collection pauses are used, then this timeout value should be increased to avoid false failure detection on a node. |
| interval | 8,000 |
15,000. The FD_ALL |
| timeout_check_interval | 2,000 | 5,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| check_timeout | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| cmd | InetAddress.isReachable() (ICMP ping) | - |
| interval | 20,000 |
15,000. The |
| timeout | 60,000 | 60,000. |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | 2,000 | 5,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| use_mcast_xmit | true | false |
| xmit_interval | 1,000 | 100 |
| xmit_table_num_rows | 50 | Same as default |
| xmit_table_msgs_per_row | 10,000 | 1,024 |
| xmit_table_max_compaction_time | 10,000 | 30,000 |
| max_msg_batch_size | 100 | Same as default |
| resend_last_seqno | false | true |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| xmit_interval | 500 | 100 |
| xmit_table_num_rows | 100 | 50 |
| xmit_table_msgs_per_row | 1,0000 | 1,024 |
| xmit_table_max_compaction_time | 600,000 | 30,000 |
| max_msg_batch_size | 500 | 100 |
| conn_close_timeout | 60,000 | No recommended value. |
| conn_expiry_timeout | 120,000 | 0 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| stability_delay | 6,000 | 500 |
| desired_avg_gossip | 20,000 | 5,000 |
| max_bytes | 2,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| print_local_addr | true | false |
| join_timeout | 5,000 | Same as default |
| view_bundling | true | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| max_credits | 500,000 | 2,000,000 |
| min_threshold | 0.40 | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| frag_size | 60,000 | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| sym_algorithm | AES | - |
| sym_keylength | 128 | - |
| provider | Bouncy Castle Provider | - |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| asym_algorithm | RSA | - |
| asym_keylength | 512 | - |
| sym_provider | Bouncy Castle Provider | - |
| change_key_on_leave | false | - |
Recommended Values for SASL
See the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide 's User Authentication over Hot Rod Using SASL section for details.
Recommended Values for RELAY2
See Set Up Cross-Datacenter Replication for details.
A.3. UDP Default and Recommended Values
To learn more about JGroups and using TCP and UDP, see Configure JGroups (Library Mode).
-
Values in
JGroups Default Valueindicate values that are configured internally to JGroups, but may be overridden by a custom configuration file or by a JGroups configuration file shipped with JBoss Data Grid. -
Values in
JBoss Data Grid Configured Valuesindicate values that are in use by default when using one of the configuration files for JGroups as shipped with JBoss Data Grid. It is recommended to use these values when custom configuration files for JGroups are in use with JBoss Data Grid. For more information on the configuration files included with JBoss Data Grid refer to JBoss Data Grid JGroups Configuration Files.
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| bind_addr | Any non-loopback | Set address on specific interface |
| bind_port | Any free port | Set specific port |
| loopback | true | true |
| port_range | 50 | Set based on desired range of ports |
| mcast_addr | 228.8.8.8 | 228.6.7.8 |
| mcast_port | 7600 | 46655 |
| tos | 8 | Same as default |
| ucast_recv_buf_size | 64,000 | 5,000,000 |
| ucast_send_buf_size | 100,000 | 2,000,000 |
| mcast_recv_buf_size | 500,000 | 5,000,000 |
| mcast_send_buf_size | 100,000 | 1,000,000 |
| ip_ttl | 8 | 2 |
| thread_naming_pattern | cl | pl |
| bundler_type | transfer-queue | no-bundler |
| max_bundle_size | 64,000 | 8700 |
| enable_diagnostics | true | false |
| thread_pool.enabled | true | Same as default |
| thread_pool.min_threads | 2 | This should equal the number of nodes. |
| thread_pool.max_threads | 30 | This should be higher than thread_pool.min_threads. For example, for a smaller grid (2-10 nodes), set this value to twice the number of nodes, but for a larger grid (20 or more nodes), the ratio should be lower. As an example, if a grid contains 20 nodes, set this value to 25 and if the grid contains 100 nodes, set the value to 110. |
| thread_pool.keep_alive_time | 30,000 | 60,000 |
In JGroups 3.5, the PING timeout value is removed and the pbcast.GMS join_timeout value indicates the timeout period instead.
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| min_interval | 1,000 | 10,000 |
| max_interval | 10,000 | 30,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| client_bind_por | 0 (randomly selects a port and uses it) | Same as default |
| get_cache_timeout | 1000 milliseconds | Same as default |
| keep_alive | true | Same as default |
| num_tries | 3 | Same as default |
| start_port | 0 (randomly selects a port and uses it) | Same as default |
| suspect_msg_interval | 5000 milliseconds. | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | 40,000 | 60,000. The FD_ALL timeout value is set to two times the longest possible stop the world garbage collection pause in the CMS garbage collector. In a well-tuned JVM, the longest pause is proportional to heap size and should not exceed 1 second per GB of heap. For example, an 8GB heap should not have a pause longer than 8 seconds, so the FD_ALL timeout value must be set to 16 seconds. If longer garbage collection pauses are used, then this timeout value should be increased to avoid false failure detection on a node. |
| interval | 8,000 |
15,000. The FD_ALL |
| timeout_check_interval | 2,000 | 5,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| check_timeout | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| cmd | InetAddress.isReachable() (ICMP ping) | - |
| interval | 20,000 |
15,000. The |
| timeout | - | 60,000. |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | 2,000 | 5,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| use_mcast_xmit | true | Same as default |
| xmit_interval | 1,000 | 100 |
| xmit_table_num_rows | 50 | Same as default |
| xmit_table_msgs_per_row | 10,000 | 1,024 |
| xmit_table_max_compaction_time | 10,000 | 30,000 |
| max_msg_batch_size | 100 | Same as default |
| resend_last_seqno | false | true |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| xmit_interval | 500 | 100 |
| xmit_table_num_rows | 100 | 50 |
| xmit_table_msgs_per_row | 1,0000 | 1,024 |
| xmit_table_max_compaction_time | 600,000 | 30,000 |
| max_msg_batch_size | 500 | 100 |
| conn_close_timeout | 60,000 | No recommended value |
| conn_expiry_timeout | 120,000 | 0 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| stability_delay | 6,000 | 500 |
| desired_avg_gossip | 20,000 | 5,000 |
| max_bytes | 2,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| print_local_addr | true | false |
| join_timeout | 5,000 | Same as default |
| view_bundling | true | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| max_credits | 500,000 | 2,000,000 |
| min_threshold | 0.40 | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| max_credits | 500,000 | 2,000,000 |
| min_threshold | 0.40 | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| frag_size | 60,000 | Same as default |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| sym_algorithm | AES | - |
| sym_keylength | 128 | - |
| provider | Bouncy Castle Provider | - |
| Parameter | JGroups Default Value | JBoss Data Grid Configured Values |
|---|---|---|
| asym_algorithm | RSA | - |
| asym_keylength | 512 | - |
| provider | Bouncy Castle Provider | - |
| change_key_on_leave | false | - |
Recommended Values for SASL
See the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide 's User Authentication over Hot Rod Using SASL section for details.
Recommended Values for RELAY2
See Set Up Cross-Datacenter Replication for details.
A.4. The TCPGOSSIP JGroups Protocol
The TCPGOSSIP discovery protocol uses one or more configured GossipRouter processes to store information about the nodes in the cluster.
It is vital that the GossipRouter process consistently be available to all nodes in the cluster, as without this process it will not be possible to add additional nodes. For this reason it is strongly recommended to deploy this process in a highly available method; for example, an Availability Set with multiple virtual machines may be used.
Running the GossipRouter
The GossipRouter is included in the JGroups jar file, and must be running before any nodes are started. This process may be started by pointing to the GossipRouter class in the JGroups jar file included with JBoss Data Grid:
java -classpath jgroups-${jgroups.version}.jar org.jgroups.stack.GossipRouter -bindaddress IP_ADDRESS -port PORT
java -classpath jgroups-${jgroups.version}.jar org.jgroups.stack.GossipRouter -bindaddress IP_ADDRESS -port PORTIn the event that multiple GossipRouters are available, and specified, a node will always register with all specified GossipRouters; however, it will only retrieve information from the first available GossipRouter. If a GossipRouter is unavailable it will be marked as failed and removed from the list, with a background thread started to periodically attempt reconnecting to the failed GossipRouter. Once the thread successfully reconnects the GossipRouter will be reinserted into the list.
Configuring JBoss Data Grid to use TCPGOSSIP (Library Mode)
In Library Mode the JGroups xml file should be used to configure TCPGOSSIP; however, there is no TCPGOSSIP configuration included by default. It is recommended to use one of the preexisting files specified in Pre-Configured JGroups Files and then adjust the configuration to include TCPGOSSIP. For instance, default-configs/default-jgroups-ec2.xml could be selected and the S3_PING protocol removed, and then the following block added in its place:
<TCPGOSSIP initial_hosts="IP_ADDRESS_0[PORT_0],IP_ADDRESS_1[PORT_1]" />
<TCPGOSSIP initial_hosts="IP_ADDRESS_0[PORT_0],IP_ADDRESS_1[PORT_1]" />Configuring JBoss Data Grid to use TCPGOSSIP (Remote Client-Server Mode)
In Remote Client-Server Mode a stack may be defined for TCPGOSSIP in the jgroups subsystem of the server’s configuration file.
The following snippet shows an example of this configuration:
A.5. TCPGOSSIP Configuration Options
The following TCPGOSSIP specific properties may be configured:
-
initial_hosts- Comma delimited list of hosts to be contacted for initial membership. -
reconnect_interval- Interval (in milliseconds) by which a disconnected node attempts to reconnect to the Gossip Router. -
sock_conn_timeout- Max time (in milliseconds) allowed for socket creation. Defaults to1000.
A.6. JBoss Data Grid JGroups Configuration Files
The following configuration files are included with JBoss Data Grid and contain the recommended values for JGroups. All of the following files are included in infinispan-embedded-${infinispan.version}.jar found with the Library mode distribution.
-
default-configs/default-jgroups-ec2.xml -
default-configs/default-jgroups-google.xml -
default-configs/default-jgroups-tcp.xml -
default-configs/default-jgroups-udp.xml
Appendix B. Hotrod.Properties
B.1. Hotrod.Properties
The following is a list of parameters that may be used to configure the behavior of a RemoteCacheManager. These elements are placed into the hotrod-client.properties file which is read when starting the application.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| infinispan.client.hotrod.request_balancing_strategy |
For replicated (vs. distributed) Hot Rod server clusters, the client balances requests to the servers according to this strategy. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.server_list |
This is the initial list of Hot Rod servers to connect to, specified in the following format: host1:port1;host2:port2… At least one host:port must be specified. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.force_return_values |
Whether or not to implicitly force return values for all calls. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.tcp_no_delay |
Affects TCP NODELAY on the TCP stack. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.tcp_keep_alive |
Affects TCP KEEPALIVE on the TCP stack. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.ping_on_startup |
If true, a ping request is sent to a back end server in order to fetch cluster’s topology. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.transport_factory |
Controls which tansport to use. Currently only the |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.marshaller |
Allows you to specify a custom |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.async_executor_factory |
Allows you to specify a custom asynchronous executor for async calls. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.default_executor_factory.pool_size |
If the default executor is used, this configures the number of threads to initialize the executor with. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.default_executor_factory.queue_size |
If the default executor is used, this configures the queue size to initialize the executor with. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.hash_function_impl.1 |
This specifies the version of the hash function and consistent hash algorithm in use, and is closely tied with the HotRod server version used. By default it uses the hash function specified by the server in the responses as indicated in |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.key_size_estimate |
This hint allows sizing of byte buffers when serializing and deserializing keys, to minimize array resizing. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.value_size_estimate |
This hint allows sizing of byte buffers when serializing and deserializing values, to minimize array resizing. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.socket_timeout |
This property defines the maximum socket read timeout before giving up waiting for bytes from the server. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.protocol_version |
This property defines the protocol version that this client should use. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.connect_timeout |
This property defines the maximum socket connect timeout before giving up connecting to the server. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.max_retries |
This property defines the maximum number of retries in case of a recoverable error. A valid value should be greater or equals to 0 (zero). Zero mean no retry. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.use_ssl |
This property defines if SSL is enabled. Defaults to |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.key_store_file_name |
Specifies the filename of a keystore to use to create the |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.key_store_password |
Specifies the password needed to open the keystore. A |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.trust_store_file_name |
Specifies the filename of a truststore to use to create the |
| infinispan.client.hotrod.trust_store_password |
Specified the password needed to open the truststore. A |
Appendix C. Connecting with JConsole
C.1. Connect to JDG via JConsole
JConsole is a JMX GUI that allows a user to connect to a JVM, either local or remote, to monitor the JVM, its MBeans, and execute operations.
Add Management User to JBoss Data Grid
Before being able to connect to a remote JBoss Data Grid instance a user will need to be created; to add a user execute the following steps on the remote instance.
Navigate to the
bindirectorycd $JDG_HOME/bin
cd $JDG_HOME/binCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the
add-user.shscript../add-user.sh
./add-user.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Accept the default option of
ManagementUserby pressing return. -
Accept the default option of
ManagementRealmby pressing return. -
Enter the desired username. In this example
jmxadminwill be used. - Enter and confirm the password.
- Accept the default option of no groups by pressing return.
-
Confirm that the desired user will be added to the
ManagementRealmby enteringyes. -
Enter
noas this user will not be used for connections between processes. The following image shows an example execution run.
Figure C.1. Execution of add-user.sh
Binding the Management Interface
By default JBoss Data Grid will start with the management interface binding to 127.0.0.1. In order to connect remotely this interface must be bound to an IP address that is visible by the network. Either of the following options will correct this:
Option 1: Runtime - By adjusting the
jboss.bind.address.managementproperty on startup a new IP address can be specified. In the following example JBoss Data Grid is starting with this bound to 192.168.122.5:./standalone.sh ... -Djboss.bind.address.management=192.168.122.5
./standalone.sh ... -Djboss.bind.address.management=192.168.122.5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Option 2: Configuration - Adjust the
jboss.bind.address.managementin the configuration file. This is found in theinterfacessubsystem. A snippet of the configuration file, with the IP adjusted to 192.168.122.5, is provided below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Running JConsole
A jconsole.sh script is provided in the $JDG_HOME/bin directory. Executing this script will launch JConsole.
Connecting to a remote JBoss Data Grid instance using JConsole.
Execute the
$JDG_HOME/bin/jconsole.shscript. This will result in the following window appearing:Figure C.2. JConsole
-
Select
Remote Process. -
Enter
service:jmx:remote://$IP:9990in the text area. -
Enter the username and password, created from the
add-user.shscript. -
Click
Connectto initiate the connection. Once connected ensure that the cache-related nodes may be viewed. The following screenshot shows such a node.
Figure C.3. JConsole: Showing a Cache
Appendix D. JMX MBeans in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
D.1. Activation
org.infinispan.eviction.ActivationManagerImpl
Activates entries that have been passivated to the CacheStore by loading the entries into memory.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| activations | Number of activation events. | String | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.2. Cache
org.infinispan.CacheImpl
The Cache component represents an individual cache instance.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheName | Returns the cache name. | String | No |
| cacheStatus | Returns the cache status. | String | No |
| configurationAsProperties | Returns the cache configuration in form of properties. | Properties | No |
| version | Returns the version of Infinispan | String | No |
| cacheAvailability | Returns the cache availability | String | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| start | Starts the cache. | void start() |
| stop | Stops the cache. | void stop() |
| clear | Clears the cache. | void clear() |
D.3. CacheContainerStats
org.infinispan.stats.impl.CacheContainerStatsImpl
The CacheContainerStats component contains statistics such as timings, hit/miss ratio, and operation information.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| averageReadTime | Cache container total average number of milliseconds for all read operations in this cache container. | long | No |
| averageReadTimeNanos | Cache container total average number of nanoseconds for all read operations in this cache container. | long | No |
| averageRemoveTime | Cache container total average number of milliseconds for all remove operations in this cache container. | long | No |
| averageRemoveTimeNanos | Cache container total average number of nanoseconds for all remove operations in this cache container. | long | No |
| averageWriteTime | Cache container total average number of milliseconds for all write operations in this cache container. | long | No |
| averageWriteTimeNanos | Cache container total average number of nanoseconds for all write operations in this cache container. | long | No |
| currentNumberOfEntriesInMemory | Total number of entries that are currently in memory for all caches in this cache container. | int | No |
| dataMemoryUsed | Amount of memory, in bytes, allocated for a cache container for entries when eviction is enabled. | long | No |
| evictions | Cache container total number of cache eviction operations. | long | No |
| hitRatio | Cache container total percentage hit/(hit+miss) ratio for this cache. | double | No |
| hits | Cache container total number of cache attribute hits. | long | No |
| misses | Cache container total number of cache attribute misses. | long | No |
| numberOfEntries | Cache container total number of entries currently in all caches from this cache container. | int | No |
| offHeapMemoryUsed | Amount of off-heap memory, in bytes, that this cache container uses. | long | No |
| readWriteRatio | Cache container read/writes ratio in all caches from this cache container. | double | No |
| removeHits | Cache container total number of removal hits. | double | No |
| removeMisses | Cache container total number of cache removals where keys were not found. | long | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| stores | Cache container total number of cache attribute put operations. | long | No |
| timeSinceReset | Number of seconds since the statistics were reset for the cache container. | long | No |
D.4. CacheLoader
org.infinispan.interceptors.CacheLoaderInterceptor
This component loads entries from a CacheStore into memory.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheLoaderLoads | Number of entries loaded from the cache store. | long | No |
| cacheLoaderMisses | Number of entries that did not exist in cache store. | long | No |
| stores | Returns a collection of cache loader types which are configured and enabled. | Collection | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| disableStore | Disable all cache loaders of a given type, where type is a fully qualified class name of the cache loader to disable. | void disableStore(String storeType) |
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.5. CacheManager
org.infinispan.manager.DefaultCacheManager
The CacheManager component acts as a manager, factory, and container for caches in the system.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheManagerStatus | The status of the cache manager instance. | String | No |
| clusterMembers | Lists members in the cluster. | String | No |
| clusterName | Cluster name. | String | No |
| clusterSize | Size of the cluster in the number of nodes. | int | No |
| createdCacheCount | The total number of created caches, including the default cache. | String | No |
| definedCacheCount | The total number of defined caches, excluding the default cache. | String | No |
| definedCacheNames | The defined cache names and their statuses. The default cache is not included in this representation. | String | No |
| name | The name of this cache manager. | String | No |
| nodeAddress | The network address associated with this instance. | String | No |
| physicalAddresses | The physical network addresses associated with this instance. | String | No |
| runningCacheCount | The total number of running caches, including the default cache. | String | No |
| version | Infinispan version. | String | No |
| globalConfigurationAsProperties | Global configuration properties | Properties | No |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| startCache | Starts the default cache associated with this cache manager. | void startCache() |
| startCache | Starts a named cache from this cache manager. | void startCache (String p0) |
D.6. CacheStore
org.infinispan.interceptors.CacheWriterInterceptor
The CacheStore component stores entries to a CacheStore from memory.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| writesToTheStores | Number of writes to the store. | long | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.7. ClusterCacheStats
org.infinispan.stats.impl.ClusterCacheStatsImpl
The ClusterCacheStats component contains statistics such as timings, hit/miss ratio, and operation information for the whole cluster.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| activations | The total number of activations in the cluster. | long | No |
| averageReadTime | Cluster-wide total average number of milliseconds for a read operation on the cache. | long | No |
| averageReadTimeNanos | Cluster-wide total average number of nanoseconds for a read operation on the cache. | long | No |
| averageRemoveTime | Cluster-wide total average number of milliseconds for a remove operation in the cache. | long | No |
| averageRemoveTimeNanos | Cluster-wide total average number of nanoseconds for a remove operation in the cache. | long | No |
| averageWriteTime | Cluster-wide average number of milliseconds for a write operation in the cache. | long | No |
| averageWriteTimeNanos | Cluster-wide average number of nanoseconds for a write operation in the cache. | long | No |
| cacheLoaderLoads | The total number of cacheloader load operations in the cluster. | long | No |
| cacheLoaderMisses | The total number of cacheloader load misses in the cluster. | long | No |
| currentNumberOfEntriesInMemory | Cluster-wide total number of entries currently stored in memory. | int | No |
| dataMemoryUsed | Amount of memory, in bytes, allocated across the cluster for entries in the cache when eviction is enabled. | long | No |
| evictions | Cluster-wide total number of cache eviction operations. | long | No |
| hitRatio | Cluster-wide total percentage hit/(hit+miss) ratio for this cache. | double | No |
| hits | Cluster-wide total number of cache hits. | long | No |
| invalidations | The total number of invalidations in the cluster. | long | No |
| misses | Cluster-wide total number of cache attribute misses. | long | No |
| numberOfEntries | Cluster-wide total number of entries currently in the cache. | int | No |
| numberOfLocksAvailable | Total number of exclusive locks available in the cluster. | int | No |
| numberOfLocksHeld | The total number of locks held in the cluster. | int | No |
| offHeapMemoryUsed | Cluster-wide amount of off-heap memory, in bytes, that this cache uses. | long | No |
| passivations | The total number of passivations in the cluster. | long | No |
| readWriteRatio | Cluster-wide read/writes ratio for the cache. | double | No |
| removeHits | Cluster-wide total number of cache removal hits. | double | No |
| removeMisses | Cluster-wide total number of cache removals where keys were not found. | long | No |
| staleStatsThreshold | Returns the threshold for refreshing cluster-wide stats in milliseconds. | long | Yes |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| storeWrites | The total number of cachestore store operations in the cluster. | long | No |
| stores | Cluster-wide total number of cache attribute put operations. | long | No |
| timeSinceReset | Number of seconds since the cluster-wide statistics were last reset. | long | No |
| timeSinceStart | Number of seconds since the first cache node started. | long | No |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. |
|
D.8. ClusterContainerStats
org.infinispan.stats.impl.ClusterContainerStatsImpl
The ClusterContainerStats component contains statistics on Java Virtual Machines (JVM) memory for the whole cluster.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| timeSinceReset | Number of seconds since the cluster-wide statistics were last reset. | long | No |
| memoryAvailable | Amount of free memory, in bytes, for JVMs across the cluster. | long | No |
| memoryMax | Maximum amount of memory, in bytes, that JVMs across the cluster will attempt to use. | long | No |
| memoryTotal | Total amount of memory, in bytes, in JVMs across the cluster. | long | No |
| memoryUsed | Amount of memory, in bytes, used by JVMs across the cluster. | long | No |
| staleStatsThreshold | Returns the threshold for refreshing cluster-wide stats in milliseconds. | long | Yes |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. |
|
D.9. DeadlockDetectingLockManager
org.infinispan.util.concurrent.locks.DeadlockDetectingLockManager
This component provides information about the number of deadlocks that were detected.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| detectedLocalDeadlocks | Number of local transactions that were rolled back due to deadlocks. | long | No |
| detectedRemoteDeadlocks | Number of remote transactions that were rolled back due to deadlocks. | long | No |
| overlapWithNotDeadlockAwareLockOwners | Number of situations when we try to determine a deadlock and the other lock owner is NOT a transaction. In this scenario we cannot run the deadlock detection mechanism. | long | No |
| totalNumberOfDetectedDeadlocks | Total number of local detected deadlocks. | long | No |
| concurrencyLevel | The concurrency level that the MVCC Lock Manager has been configured with. | int | No |
| numberOfLocksAvailable | The number of exclusive locks that are available. | int | No |
| numberOfLocksHeld | The number of exclusive locks that are held. | int | No |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.10. DistributionManager
org.infinispan.distribution.DistributionManagerImpl
The DistributionManager component handles the distribution of content across a cluster.
The DistrubutionManager component is only available in clustered mode.
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| isAffectedByRehash | Determines whether a given key is affected by an ongoing rehash. | boolean isAffectedByRehash(Object p0) |
| isLocatedLocally | Indicates whether a given key is local to this instance of the cache. Only works with String keys. | boolean isLocatedLocally(String p0) |
| locateKey | Locates an object in a cluster. Only works with String keys. | List locateKey(String p0) |
D.11. Interpreter
org.infinispan.cli.interpreter.Interpreter
The Interpreter component executes command line interface (CLI operations).
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheNames | Retrieves a list of caches for the cache manager. | String[] | No |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| createSessionId | Creates a new interpreter session. | String createSessionId(String cacheName) |
| execute | Parses and executes IspnCliQL statements. | String execute(String p0, String p1) |
D.12. Invalidation
org.infinispan.interceptors.InvalidationInterceptor
The Invalidation component invalidates entries on remote caches when entries are written locally.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| invalidations | Number of invalidations. | long | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.13. LockManager
org.infinispan.util.concurrent.locks.LockManagerImpl
The LockManager component handles MVCC locks for entries.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| concurrencyLevel | The concurrency level that the MVCC Lock Manager has been configured with. | int | No |
| numberOfLocksAvailable | The number of exclusive locks that are available. | int | No |
| numberOfLocksHeld | The number of exclusive locks that are held. | int | No |
D.14. LocalTopologyManager
org.infinispan.topology.LocalTopologyManagerImpl
The LocalTopologyManager component controls the cache membership and state transfer in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
The LocalTopologyManager component is only available in clustered mode.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| rebalancingEnabled |
If false, newly started nodes will not join the existing cluster nor will the state be transferred to them. If any of the current cluster members are stopped when rebalancing is disabled, the nodes will leave the cluster but the state will not be rebalanced among the remaining nodes. This will result in fewer copies than specified by the | boolean | Yes |
| clusterAvailability |
If | String | No |
D.15. MassIndexer
org.infinispan.query.MassIndexer
The MassIndexer component rebuilds the index using cached data.
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| start | Starts rebuilding the index. | void start() |
This operation is available only for caches with indexing enabled. For more information, see the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid Developer Guide
D.16. Passivation
org.infinispan.eviction.PassivationManager
The Passivation component handles the passivation of entries to a CacheStore on eviction.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| passivations | Number of passivation events. | String | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.17. RecoveryAdmin
org.infinispan.transaction.xa.recovery.RecoveryAdminOperations
The RecoveryAdmin component exposes tooling for handling transaction recovery.
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| forceCommit | Forces the commit of an in-doubt transaction. | String forceCommit(long p0) |
| forceCommit | Forces the commit of an in-doubt transaction | String forceCommit(int p0, byte[] p1, byte[] p2) |
| forceRollback | Forces the rollback of an in-doubt transaction. | String forceRollback(long p0) |
| forceRollback | Forces the rollback of an in-doubt transaction | String forceRollback(int p0, byte[] p1, byte[] p2) |
| forget | Removes recovery info for the given transaction. | String forget(long p0) |
| forget | Removes recovery info for the given transaction. | String forget(int p0, byte[] p1, byte[] p2) |
| showInDoubtTransactions | Shows all the prepared transactions for which the originating node crashed. | String showInDoubtTransactions() |
D.18. RollingUpgradeManager
org.infinispan.upgrade.RollingUpgradeManager
The RollingUpgradeManager component handles the control hooks in order to migrate data from one version of Red Hat JBoss Data Grid to another.
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| disconnectSource | Disconnects the target cluster from the source cluster according to the specified migrator. | void disconnectSource(String p0) |
| recordKnownGlobalKeyset | Dumps the global known keyset to a well-known key for retrieval by the upgrade process. | void recordKnownGlobalKeyset() |
| synchronizeData | Synchronizes data from the old cluster to this using the specified migrator. | long synchronizeData(String p0) |
D.19. RpcManager
org.infinispan.remoting.rpc.RpcManagerImpl
The RpcManager component manages all remote calls to remote cache instances in the cluster.
The RpcManager component is only available in clustered mode.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| averageReplicationTime | The average time spent in the transport layer, in milliseconds. | long | No |
| committedViewAsString | Retrieves the committed view. | String | No |
| pendingViewAsString | Retrieves the pending view. | String | No |
| replicationCount | Number of successful replications. | long | No |
| replicationFailures | Number of failed replications. | long | No |
| successRatio | Successful replications as a ratio of total replications. | String | No |
| successRatioFloatingPoint | Successful replications as a ratio of total replications in numeric double format. | double | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
| setStatisticsEnabled | Whether statistics should be enabled or disabled (true/false) | void setStatisticsEnabled(boolean enabled) |
D.20. StateTransferManager
org.infinispan.statetransfer.StateTransferManager
The StateTransferManager component handles state transfer in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
The StateTransferManager component is only available in clustered mode.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| If true, the cluster topology is updated to include the node. If false, the node is not yet joined to the cluster. | boolean | No |
|
| Checks whether there is a pending inbound state transfer on this node. | boolean | No |
|
| Checks if there is a state transfer in progress for the cache. | String | No |
D.21. Statistics
org.infinispan.interceptors.CacheMgmtInterceptor
The CacheMgmtInterceptor component handles general statistics such as timings, hit/miss ratio, etc.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| averageReadTime | Average number of milliseconds for a read operation on the cache. | long | No |
| averageReadTimeNanos | Average number of nanoseconds for a read operation on the cache. | long | No |
| averageRemoveTime | Average number of milliseconds for a remove operation in the cache | long | No |
| averageRemoveTimeNanos | Average number of nanoseconds for a remove operation in the cache | long | No |
| averageWriteTime | Average number of milliseconds for a write operation in the cache. | long | No |
| averageWriteTimeNanos | Average number of nanoseconds for a write operation in the cache. | long | No |
| dataMemoryUsed | Amount of memory, in bytes, allocated for the cache entries when eviction is enabled. | long | No |
| elapsedTime | Number of seconds since cache started. | long | No |
| evictions | Number of cache eviction operations. | long | No |
| hitRatio | Percentage hit/(hit+miss) ratio for the cache. | double | No |
| hits | Number of cache attribute hits. | long | No |
| misses | Number of cache attribute misses. | long | No |
| numberOfEntries | Number of entries currently in the cache. | int | No |
| numberOfEntriesInMemory | Total number of entries that are currently in memory excluding expired entries. | int | No |
| offHeapMemoryUsed | Amount of off-heap memory, in bytes, that is allocated. | long | No |
| readWriteRatio | Read/writes ratio for the cache. | double | No |
| removeHits | Number of cache removal hits. | long | No |
| removeMisses | Number of cache removals where keys were not found. | long | No |
| requiredMinimumNumberOfNodes | Number of nodes that are required to guarantee data consistency. | int | No |
| stores | Number of cache attribute PUT operations. | long | No |
| timeSinceReset | Number of seconds since the cache statistics were last reset. | long | No |
| timeSinceStart | Number of seconds since the cache started. | long | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.22. Transactions
org.infinispan.interceptors.TxInterceptor
The Transactions component manages the cache’s participation in JTA transactions.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| commits | Number of transaction commits performed since last reset. | long | No |
| prepares | Number of transaction prepares performed since last reset. | long | No |
| rollbacks | Number of transaction rollbacks performed since last reset. | long | No |
| statisticsEnabled | Enables or disables the gathering of statistics by this component. | boolean | Yes |
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| resetStatistics | Resets statistics gathered by this component. | void resetStatistics() |
D.23. Transport
org.infinispan.server.core.transport.NettyTransport
The Transport component manages read and write operations to and from the server.
| Name | Description | Type | Writable |
|---|---|---|---|
| hostName | Returns the host to which the transport binds. | String | No |
| idleTimeout | Returns the idle timeout. | String | No |
| numberOfGlobalConnections | Returns a count of active connections in the cluster. This operation will make remote calls to aggregate results, so latency may have an impact on the speed of calculation for this attribute. | Integer | false |
| numberOfLocalConnections | Returns a count of active connections this server. | Integer | No |
| numberWorkerThreads | Returns the number of worker threads. | String | No |
| port | Returns the port to which the transport binds. | String | receiveBufferSize |
| Returns the receive buffer size. | String | No | sendBufferSize |
| Returns the send buffer size. | String | No | totalBytesRead |
| Returns the total number of bytes read by the server from clients, including both protocol and user information. | String | No | totalBytesWritten |
| Returns the total number of bytes written by the server back to clients, including both protocol and user information. | String | No | tcpNoDelay |
D.24. XSiteAdmin
org.infinispan.xsite.XSiteAdminOperations
The XSiteAdmin component exposes tooling for backing up data to remote sites.
| Name | Description | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| bringSiteOnline | Brings the given site back online on all the cluster. | String bringSiteOnline(String p0) |
| amendTakeOffline | Amends the values for 'TakeOffline' functionality on all the nodes in the cluster. | String amendTakeOffline(String p0, int p1, long p2) |
| getTakeOfflineAfterFailures | Returns the value of the 'afterFailures' for the 'TakeOffline' functionality. | String getTakeOfflineAfterFailures(String p0) |
| getTakeOfflineMinTimeToWait | Returns the value of the 'minTimeToWait' for the 'TakeOffline' functionality. | String getTakeOfflineMinTimeToWait(String p0) |
| setTakeOfflineAfterFailures | Amends the values for 'afterFailures' for the 'TakeOffline' functionality on all the nodes in the cluster. | String setTakeOfflineAfterFailures(String p0, int p1) |
| setTakeOfflineMinTimeToWait | Amends the values for 'minTimeToWait' for the 'TakeOffline' functionality on all the nodes in the cluster. | String setTakeOfflineMinTimeToWait(String p0, long p1) |
| siteStatus | Check whether the given backup site is offline or not. | String siteStatus(String p0) |
| status | Returns the status(offline/online) of all the configured backup sites. | String status() |
| takeSiteOffline | Takes this site offline in all nodes in the cluster. | String takeSiteOffline(String p0) |
| pushState | Starts the cross-site state transfer to the site name specified. | String pushState(String p0) |
| cancelPushState | Cancels the cross-site state transfer to the site name specified. | String cancelPushState(String p0) |
| getSendingSiteName | Returns the site name that is pushing state to this site. | String getSendingSiteName() |
| cancelReceiveState | Restores the site to the normal state. It is used when the link between the sites is broken during the state transfer. | String cancelReceiveState(String p0) |
| getPushStateStatus | Returns the status of completed and running cross-site state transfer. | String getPushStateStatus() |
| clearPushStateStatus | Clears the status of completed cross-site state transfer. | String clearPushStateStatus() |
Appendix E. Configuration Recommendations
E.1. Timeout Values
| Timeout Value | Parent Element | Default Value | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| distributedSyncTimeout | transport | 240,000 (4 minutes) | Same as default |
| lockAcquisitionTimeout | locking | 10,000 (10 seconds) | Same as default |
| cacheStopTimeout | transaction | 30,000 (30 seconds) | Same as default |
| completedTxTimeout | transaction | 60,000 (60 seconds) | Same as default |
| replTimeout | sync | 15,000 (15 seconds) | Same as default |
| timeout | stateTransfer | 240,000 (4 minutes) | Same as default |
| timeout | backup | 10,000 (10 seconds) | Same as default |
| flushLockTimeout | async | 1 (1 millisecond) | Same as default. Note that this value applies to asynchronous cache stores, but not asynchronous caches. |
| shutdownTimeout | async | 25,000 (25 seconds) | Same as default. Note that this value applies to asynchronous cache stores, but not asynchronous caches. |
| pushStateTimeout | singletonStore | 10,000 (10 seconds) | Same as default. |
| backup | replicationTimeout | 10,000 (10 seconds) | remoteCallTimeout |
Appendix F. Performance Recommendations
F.1. Concurrent Startup for Large Clusters
When starting a large number of instances, each managing a large number of caches, in parallel this may take a while as rebalancing attempts to distribute the data evenly as each node joins the cluster. To limit the number of rebalancing attempts made during the initial startup of the cluster disable rebalancing temporarily by following the below steps:
- Start the first node in the cluster.
-
Set JMX attribute
jboss.infinispan/CacheManager/"clustered"/LocalTopologyManager/rebalancingEnabledtofalse, as seen in LocalTopologyManager. - Start the remaining nodes in the cluster.
-
Re-enable the JMX attribute
jboss.infinispan/CacheManager/"clustered"/LocalTopologyManager/rebalancingEnabledby setting this value back totrue, as seen in LocalTopologyManager.
Appendix G. References
G.1. About Consistency
Consistency is the policy that states whether it is possible for a data record on one node to vary from the same data record on another node.
For example, due to network speeds, it is possible that a write operation performed on the master node has not yet been performed on another node in the store, a strong consistency guarantee will ensure that data which is not yet fully replicated is not returned to the application.
G.2. About Consistency Guarantee
Despite the locking of a single owner instead of all owners, Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s consistency guarantee remains intact. Consider the following situation:
-
If Key
Kis hashed to nodes{A,B}and transactionTX1acquires a lock forKon, for example, nodeAand -
If another cache access occurs on node
B, or any other node, andTX2attempts to lockK, this access attempt fails with a timeout because the transactionTX1already holds a lock onK.
This lock acquisition attempt always fails because the lock for key K is always deterministically acquired on the same node of the cluster, irrespective of the transaction’s origin.
G.3. About JBoss Cache
Red Hat JBoss Cache is a tree-structured, clustered, transactional cache that can also be used in a standalone, non-clustered environment. It caches frequently accessed data in-memory to prevent data retrieval or calculation bottlenecks that occur while enterprise features such as Java Transactional API (JTA) compatibility, eviction and persistence are provided.
JBoss Cache is the predecessor to Infinispan and Red Hat JBoss Data Grid.
G.4. About RELAY2
The RELAY protocol bridges two remote clusters by creating a connection between one node in each site. This allows multicast messages sent out in one site to be relayed to the other and vice versa.
JGroups includes the RELAY2 protocol, which is used for communication between sites in Red Hat JBoss Data Grid’s Cross-Site Replication.
The RELAY2 protocol works similarly to RELAY but with slight differences. Unlike RELAY , the RELAY2 protocol:
- connects more than two sites.
- connects sites that operate autonomously and are unaware of each other.
- offers both unicasts and multicast routing between sites.
G.5. About Return Values
Values returned by cache operations are referred to as return values. In Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, these return values remain reliable irrespective of which cache mode is employed and whether synchronous or asynchronous communication is used.
G.6. About Runnable Interfaces
A Runnable Interface (also known as a Runnable) declares a single run() method, which executes the active part of the class' code. The Runnable object can be executed in its own thread after it is passed to a thread constructor.
G.7. About Two Phase Commit (2PC)
A Two Phase Commit protocol (2PC) is a consensus protocol used to atomically commit or roll back distributed transactions. It is successful when faced with cases of temporary system failures, including network node and communication failures, and is therefore widely utilized.
G.8. About Key-Value Pairs
A key-value pair (KVP) is a set of data consisting of a key and a value.
- A key is unique to a particular data entry. It consists of entry data attributes from the related entry.
- A value is the data assigned to and identified by the key.
G.9. Requesting a Full Byte Array
How can I request the Red Hat JBoss Data Grid return a full byte array instead of partial byte array contents?
As a default, JBoss Data Grid only partially prints byte arrays to logs to avoid unnecessarily printing large byte arrays. This occurs when either:
- JBoss Data Grid caches are configured for lazy deserialization. Lazy deserialization is not available in JBoss Data Grid’s Remote Client-Server mode.
- A Memcached or Hot Rod server is run.
In such cases, only the first ten positions of the byte array display in the logs. To display the complete contents of the byte array in the logs, pass the -Dinfinispan.arrays.debug=true system property at start up.
Partial Byte Array Log