6.0 Release Notes
Release Notes for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
Abstract
1. Introduction
- i386
- AMD64/Intel64
- System z
- IBM Power (64-bit)
Note
2. Installer
anaconda) assists in the installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. This section of the release notes provides an overview of the new features implemented in the installer for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
Note
2.1. Installation Methods
2.1.1. Graphical Installer
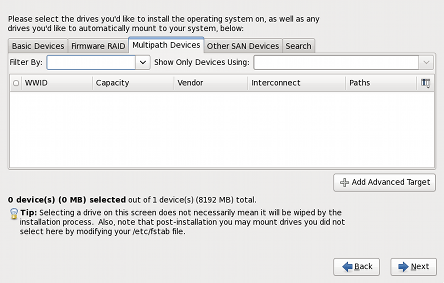
Figure 1. Specialized Storage Devices Configuration
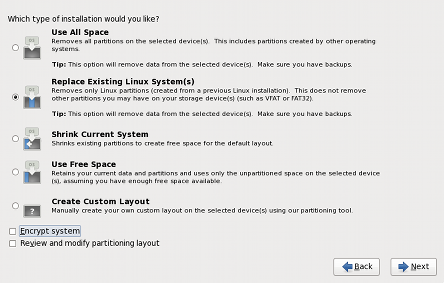
Figure 2. Partitioning layout choices
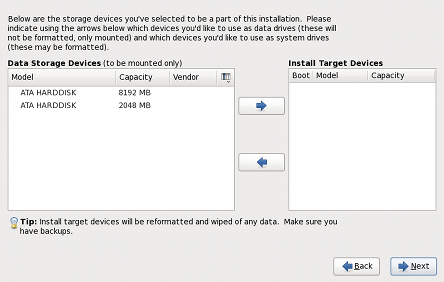
Figure 3. Specifying Storage Devices
2.1.2. Kickstart
2.1.3. Text-based Installer
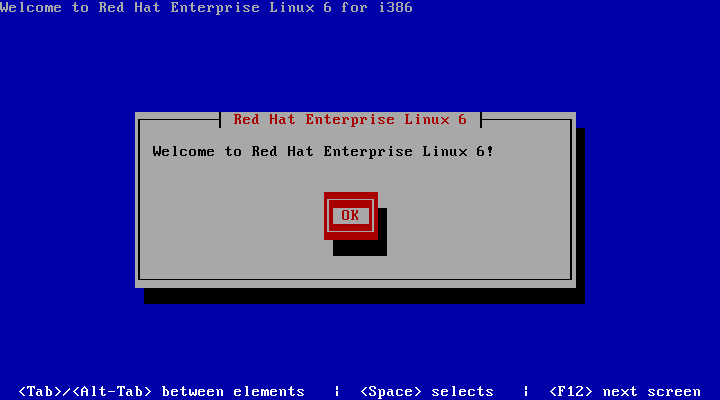
Figure 4. text-based installer
Note
2.2. Creating Backup Passphrases During Installation
Note
2.3. DVD Media Boot Catalog Entries
Important
Note
2.4. Installation Crash Reporting
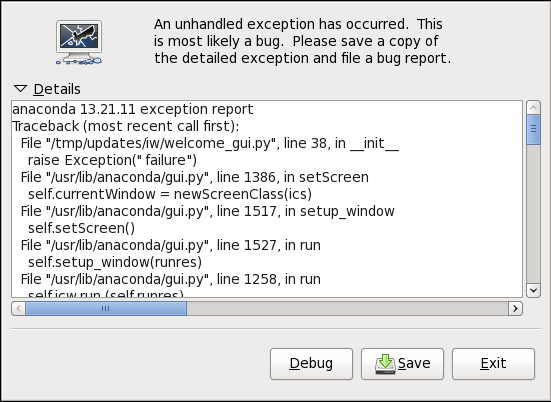
Figure 5. installation error reporting
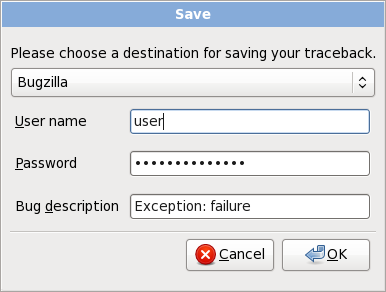
Figure 6. Sending to Bugzilla
2.5. Installation Logs
3. File Systems
Note
3.1. Fourth Extended Filesystem (ext4) Support
3.2. XFS
3.3. Block Discard — enhanced support for thinly provisioned LUNs and SSD devices
3.4. Network File System (NFS)
4. Storage
4.1. Storage Input/Output Alignment and Size
Note
4.2. Dynamic Load Balancing with DM-Multipath
Note
4.3. Logical Volume Manager (LVM)
Important
system-config-lvm is a graphical user interface provided in Red Hat Enterprise Linux to manage logical volumes. The functionality provided by system-config-lvm is in the process of transitioning to a more maintainable tool named gnome-disk-utility (also referred to as palimpsest). As a result, Red Hat will be very selective in updating system-config-lvm. As gnome-disk-utility reaches feature parity with system-config-lvm, Red Hat reserves the right to remove system-config-lvm during the life of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
Note
4.3.1. LVM Mirror Improvements
4.3.1.1. Snapshots of Mirrors
4.3.1.2. Merging Snapshots
lvconvert manpage.
4.3.1.3. Four-Volume Mirrors
4.3.1.4. Mirroring mirror logs
4.3.2. LVM Application Library
5. Power Management
Note
5.1. powertop
5.2. tuned
6. Package Management
6.1. Strong package checksums
6.2. The PackageKit Package Manager
6.3. Yum
7. Clustering
Note
7.1. Corosync Cluster Engine
7.2. Unified Logging Configuration
7.3. High Availability Administration
7.4. General High Availability Improvements
- Enhanced support for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
- SCSI persistent reservation fencing support is improved.
- Virtualized KVM guests can now be run as managed services.
8. Security
Note
8.1. System Security Services Daemon (SSSD)
Note
8.2. Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux)
8.2.1. Confined Users
8.2.2. Sandbox
8.2.3. X Access Control Extension (XACE)
8.3. Backup Passphrases for Encrypted Storage Devices

Figure 7. Decrypting Data
8.4. sVirt
8.5. Enterprise Security Client
9. Networking
9.1. Multiqueue Networking
9.2. Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
9.2.1. Optimistic Duplicate Address Detection
9.2.2. Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol
9.3. Netlabel
9.4. Generic Receive Offload
9.5. Wireless Support
10. Desktop
10.1. Graphical Startup

Figure 8. Graphical Boot Screen
Note
10.2. Suspend and Resume
10.3. Multiple Display Support
Note
10.3.1. Display Preferences
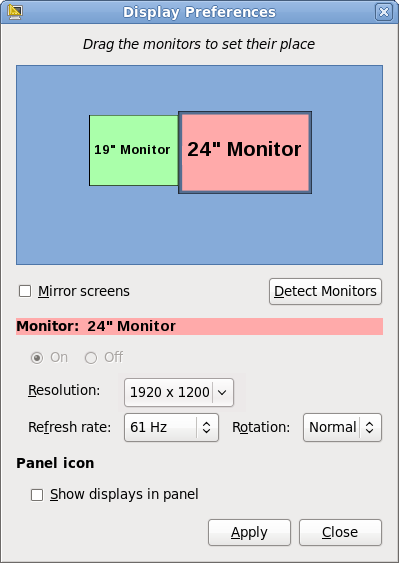
Figure 9. Display Preferences dialog
10.4. nouveau Driver for NVIDIA Graphics Devices
Note
10.5. Internationalization
10.5.1. IBus
10.5.2. Choosing and Configuring Input Methods
im-chooser, a graphical user interface to enable and configure input methods. im-chooser (located under System > Preferences > Input Method in the main menu) allows the user to easily enable and configure the input methods available on the system.
10.5.3. Indic Onscreen Keyboard
10.5.4. Indic Collation Support
10.5.5. Fonts
10.6. Applications
10.6.1. Firefox
10.6.2. Thunderbird 3
10.6.3. OpenOffice.org 3.1
Figure 10. OpenOffice.org 3.1
10.7. NetworkManager
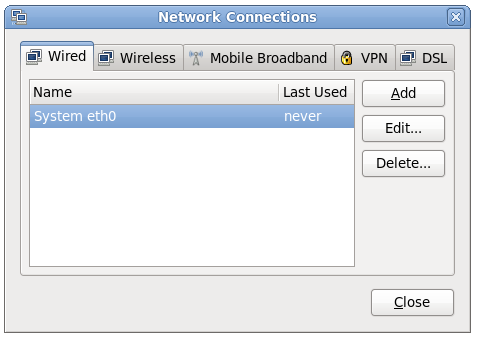
Figure 11. NetworkManager
10.8. KDE 4.3
- The new Plasma Desktop Workspace, including Plasma Widgets for a more customizable desktop.
- Oxygen, with enhanced icon and sound themes.
- Enhancements to the KDE Window Manager (kwin)
dolphin file browser has replaced konqueror as the KDE default.
11. Documentation
- Release Documentation
- Installation and Deployment
- Security
- Tools and Performance
- Clustering
- Virtualization
11.1. Release Documentation
The Release Notes document the major new features in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux Technical Notes contains detailed information specific to this release, including: Technology Previews, package change details and known issues.
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux Migration Guide documents migration from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
11.2. Installation and Deployment
The Installation Guide documents relevant information regarding the installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
The Deployment Guide documents relevant information regarding the deployment, configuration and administration of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
The Storage Administration Guide provides instructions on how to effectively manage storage devices and file systems on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. It is intended for use by system administrators with intermediate experience in either Red Hat Enterprise Linux or Fedora distributions of Linux.
The Global File System 2 book provides information about configuring and maintaining Red Hat GFS2 (Red Hat Global File System 2) for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
The Logical Volume Manager Administration book describes the LVM logical volume manager, including information on running LVM in a clustered environment.
11.3. Security
The Security Guide is designed to assist users and administrators in learning the processes and practices of securing workstations and servers against local and remote intrusion, exploitation and malicious activity.
The SELinux User Guide covers the management and use of Security-Enhanced Linux for those with minimal or no experience with the framework. It serves as an introduction to SELinux and explains the terms and concepts in use.
The Managing Confined Services guide is designed to assist advanced users and administrators when using and configuring Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux). It is focused on Red Hat Enterprise Linux and describes the components of SELinux as they pertain to services an advanced user or administrator might need to configure. Also included are real-world examples of configuring these services and demonstrations of how SELinux complements their operation.
11.4. Tools & Performance
The Resource Management Guide documents tools and techniques for managing system resources on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
The Power Management Guide explains how to manage power consumption on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 systems effectively. This document discusses different techniques that lower power consumption (for both server and laptop), and how each technique affects the overall performance of a system.
The Developer Guide describes the different features and utilities that make Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 an ideal enterprise platform for application development.
The SystemTap Beginners Guide provides basic instructions on how to use SystemTap to monitor different subsystems of Red Hat Enterprise Linux in finer detail.
The SystemTap Tapset Reference guide describes the most common tapset definitions users can apply to SystemTap scripts.
11.5. High Availability
The Cluster Suite Overview document provides an overview of High Availability for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
The High Availability Administration document describes the configuration and management of Red Hat High Availability systems for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
The Virtual Server Administration book discusses the configuration of high-performance systems and services with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and the Linux Virtual Server (LVS) system.
The DM Multipath book provides information on using the Device-Mapper Multipath feature of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
11.6. Virtualization
The Virtualization Guide details the process to install, configure and manage the virtualization technologies in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
12. Kernel
12.1. Resource Control
12.1.1. Control Groups
libcgroup, enabling system administrators to create new control groups, start new processes in a specific control group and set control group parameters.
Note
12.2. Scalability
12.2.1. Completely Fair Scheduler (CFS)
O(1) scheduler with the new Completely Fair Scheduler (CFS). The CFS implements the fair queuing scheduling algorithm.
12.2.2. Virtual Memory Pageout Scalability
12.3. Error Reporting
12.3.1. Advanced Error Reporting (AER)
12.3.2. Kdump Auto Enablement
- systems with more than 4GB of memory on architectures with a 4KB page size (i.e. x86 or x86_64), or
- systems with more than 8GB of memory on architectures with larger than a 4KB page size (i.e PPC64).
12.4. Power Management
12.4.1. Aggressive Link Power Management (ALPM)
12.4.2. Tickless Kernel
12.5. Analyzing Kernel Performance
12.5.1. Performance Counter for Linux (PCL)
12.5.2. Ftrace and perf
12.6. General Kernel Updates
12.6.1. Physical Address Extension (PAE)
12.6.2. Loadable Firmware Files
13. Compiler and Tools
13.1. SystemTap
- Improved support for user-space probing.
- Support for probing C++ programs with native C++ syntax.
- A more secure script-compile server.
- The new unprivileged mode, allowing non-root users to use SystemTap.
Important
13.2. OProfile
13.3. GNU Compiler Collection (GCC)
- Conformance to version 3.0 of the Open Multi-Processing (OpenMP) application programming interface (API).
- Additional C++ libraries to utilize OpenMP threads
- Futher implementations of the next ISO C++ standard draft (C++0x)
- Introduction of variable tracking assignments to improve debugging using the GNU Project Debugger (GDB) and SystemTap.
13.4. GNU C Library (glibc)
- An enhanced dynamic memory allocation (malloc) behaviour enabling higher scalability across many sockets and cores. This is achieved by assigning threads their own memory pools and by avoiding locking in some situations. The amount of additional memory used for the memory pools (if any) can be controlled using the environment variables MALLOC_ARENA_TEST and MALLOC_ARENA_MAX. MALLOC_ARENA_TEST specifies that a test for the number of cores is performed once the number of memory pools reaches this value. MALLOC_ARENA_MAX sets the maximum number of memory pools used, regardless of the number of cores.
- Improved efficiency when using condition variables (condvars) with priority inheritance (PI) mutual exclusion (mutex) operations by utilizing support in the kernel for PI fast userspace mutexes.
- Optimized string operations on the x86_64 architecture.
- The
getaddrinfo()function now has support for the Datagram Congestion Control Protocol (DCCP) and the UDP-Lite protocol. Additionally,getaddrinfo()now has the ability to look up IPv4 and IPv6 addresses simultaneously.
13.5. GNU Project debugger (GDB)
This updated version of GDB introduces the new Python API, allowing GDB to be automated using scripts written in the Python Programming Language.
Support for the C++ programming language in GDB has been improved. Notable improvements include:
- Many improvements to expression parsing.
- Better handling of type names.
- The need for extraneous quoting has nearly been eliminated
- "next" and other stepping commands work properly even when the inferior throws an exception.
- GDB has a new "catch syscall" command. This can be used to stop the inferior whenever it makes a system call.
Thread execution now permits debugging threads individually and independently of each other; enabled by new settings "set target-async" and "set non-stop".
14. Interoperability
14.1. Samba
- Internet Protocol version 6 support (IPv6)
- Support for Windows 2008 (R2) trust relationships.
- Support for Windows 7 domain members.
- Support for Active Directory LDAP signing/sealing policy.
- Improvements for libsmbclient
- Better support for Windows management tools (mmc and User Manager)
- Automatic machine password changes as domain member
- New registry based configuration layer
- Encrypted SMB transport between Samba client and server
- Full support for Windows cross-forest, transitive trusts and one-way domain trusts
- New NetApi remote management and winbind client C libraries
- A new graphical user interface for joining Windows Domains
Note
15. Virtualization
15.1. Kernel-based Virtual Machine
15.1.1. Memory enhancements
- Transparent Hugepages increase the memory page size from 4 kilobytes to 2 megabytes. Transparent Hugepages provide significant performance advantages on systems with highly contended resources and large memory workloads. Additionally, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 provides support for utilizing Transparent Hugepages with KSM.
- Extended Page Table age bits enables a host to make smarter choices for swapping memory under memory pressure and allows swapping of Transparent Hugepages by breaking the extended pages into smaller pages.
15.1.2. Virtualized CPU features
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 supports up to 64 virtualized CPUs for a single virtualized guest.
- CPU extensions present on the host processor can now be utilized by virtualized guests. Support for these instruction sets allow virtualized guests to take advantage of modern processor instruction sets and hardware features.
- The new
x2apicvirtual Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) improves virtualizedx86_64guest performance by allowing direct guest APIC access and removing the overhead of emulated access. - New user space notifiers allow the caching of CPU registers, avoiding the computationally expensive actions of preserving register states of unused components during context switches.
- Read copy update (RCU) kernel locking is now uses enhanced symmetric multiprocessing support. RCU kernel locking provides greater performance for networking functions and multi-processing systems.
15.1.3. Storage
- The QEMU emulated block driver features support for fully asynchronous I/O,
preadvandpwritevfunctions. These functions increase performance for storage devices using the QEMU emulated block driver. - The QEMU Monitor Protocol (QMP) allows applications to communicate with the QEMU Monitor correctly. QEMU provides a text-based format that can be easily parsed and support for asynchronous messages and capabilities negotiation.
- Indirect ring entries (spin locks) for the para-virtualized (virtio) driver improve block I/O performance and allows more concurrent I/O operations.
- Virtualized storage devices can now be added and removed (hot plugged) from guests during runtime.
- Support for block alignment storage topology awareness. Underlying storage hardware features and physical storage sector sizes (for example, 4KB sectors) are presented to guests. This feature requires compatible storage device information and commands. Guest topology awareness allows virtualized guests to optimize file system layouts and improved performance of applications using I/O optimizations.
- Performance enhancements for the qcow2 virtualized image format.
15.1.4. Networking
- The vhost-net feature moves various network functions from the QEMU user space into the kernel. vhost-net uses fewer context switches and vmexit calls. These enhancements improve performance of SR-IOV devices, directly assigned network device and other network devices.
- MSI-X support which increases the number of interrupts available to network devices. MSI-X support increases the performance of compatible hardware.
- Virtualized network devices can now be hot plugged and hot removed from running guests. Network boot using gpxe fora more advanced PXE network booting.
15.1.5. Kernel SamePage Merging
15.1.6. PCI passthrough
15.1.7. SR-IOV
15.1.8. virtio-serial
15.1.9. sVirt
15.1.10. Migration
- Guest ABI stability provides enhanced migration support. Guests PCI device numbers are preserved during migration and identical PCI device positions are presented after migrating the guest.
- Migration now accounts for CPU models. CPU models allow guests to take advantage of new processor instruction sets. Guests can be migrated to hosts with a compatible CPU model.
- The vhost-net feature allows guests using SR-IOV to migrate to non-identical host configurations that also use SR-IOV devices.
- Enhancements to the migration protocol.
15.1.11. Guest device ABI stability
Note
15.2. Xen
Note
15.3. virt-v2v
virt-v2v tool, enabling system administrators to convert and import virtual machines created on other systems such as Xen and VMware ESX. virt-v2v provides a migration path for Xen guests running on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 hypervisor.
16. Supportability and Maintenance
16.1. firstaidkit System Recovery Tool
firstaidkit system recovery tool. By automating common recovery processes, firstaidkit provides an interactive environment to assists in the troubleshooting and recovery of a system that boots incorrectly. Additionally, system administrators are able to create custom automated recovery processes using the firstaidkit plugin infrastructure.
Important
firstaidkit is considered a Technology Preview in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
16.2. Bug Reporting
16.2.1. Installation Crash Reporting
16.3. Automated Bug Reporting Tool
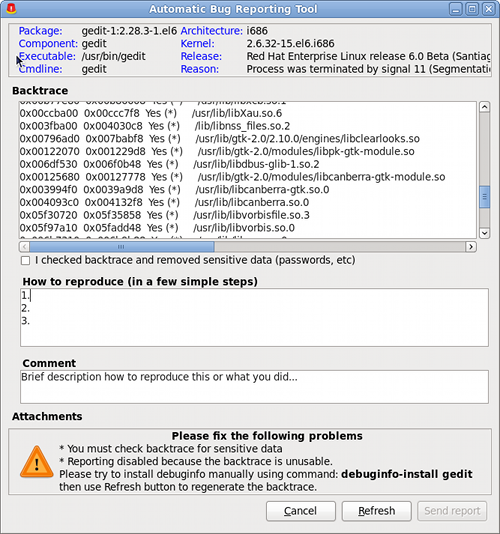
Figure 12. Automated Bug Reporting Tool
17. Web Servers and Services
17.1. Apache HTTP Web Server
17.2. PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP)
17.3. memcached
18. Databases
18.1. PostgreSQL
18.2. MySQL
19. Architecture Specific Notes
A. Revision History
| Revision History | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Revision 1-1 | Wed Feb 25 2015 | ||
| |||
| Revision 1-0 | Wed Aug 12 2010 | ||
| |||