Designing APIs
Designing REST APIs for Fuse applications on OpenShift
Abstract
Chapter 1. Overview of the API Designer
Red Hat Fuse on OpenShift provides API Designer, a web-based API editor, that you can use to design REST APIs that comply with the OpenAPI specification (versions 3 or 2), a vendor-neutral and portable open description format for API services. API Designer is a “light” version of the Apicurio Studio open source project (https://www.apicur.io/). This means that your API Designer sessions are stateless and you must save your API definition as a JSON file at the end of each session.
You can also use API Designer to generate a preliminary Fuse project based on a REST API definition. In your Fuse development environment, you can then complete the project’s Camel routes and build the project. Finally, you can deploy the resulting REST service on Fuse on OpenShift.
Here is an overview of how you can use API Designer to incorporate REST APIs in your Fuse on OpenShift application solution:
- Add API Designer as a service to your OpenShift project.
In API Designer:
- Create an API definition with API Designer. Save the REST API definition as a JSON file to your local file system. You can save your API definition at any point during your editing session, even if the API definition is not complete.
- Upload an API definition to API Designer.
- Generate a Fuse Camel project based on the current REST API definition. API Designer provides a downloadable zip file that contains a complete Maven project.
- In your Fuse development environment, complete the skeleton implementation provided by the generated Fuse project.
- Build and deploy the Fuse application to OpenShift.
- (Optional) Integrate the Fuse application with Red Hat 3scale API Management, using the 3scale service discovery capability to find and configure your Fuse application.
Chapter 2. Adding API Designer as a service to your OpenShift Cluster
2.1. Adding API Designer as a service to an OpenShift 4 project
For OpenShift 4.x, you need to verify that your OpenShift administrator has installed and subscribed to the API Designer operator in your project as described in the Fuse on OpenShift Guide.
Optionally, the OpenShift administrator might have also added the API Designer as a service to the project. If not, you must do that task.
A previous name for API Designer, Apicurito, is still visible in the API Designer operator’s interface.
Prerequisite
- You have administrator access to the OpenShift cluster.
- You have configured authentication to the Red Hat Container Registry.
Procedure
- Start the OpenShift 4.x Server.
- In a web browser, navigate to the OpenShift console in your browser. Log in to the console with your credentials.
- Click Operators and then click OperatorHub.
- In the search field, type API Designer.
- Click API Designer card. The API Designer operator install page opens.
Click Install. The Install Operator page opens.
- For Installation mode, select a namespace (project) from the list of namespaces on the cluster,
For the Approval Strategy, select Automatic or Manual to configure how OpenShift handles updates to the API Designer Operator.
- If you select Automatic updates, when a new version of the API Designer operator is available, the OpenShift Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) automatically upgrades the running instance of the API Designer without human intervention.
- If you select Manual updates, when a newer version of an Operator is available, the OLM creates an update request. As a cluster administrator, you must then manually approve that update request to have the API Designer operator updated to the new version.
- Click Install to make the API Designer Operator available to the specified namespace (project).
- To verify that the API Designer is installed in the project, click Operators and then click Installed Operators to see the API Designer in the list.
2.2. Adding API Designer as a service to an OpenShift 3.11 project
You can add API Designer as a service to your OpenShift 3.11 project by deploying the API Designer template from the command line.
Prerequisites
- Obtain the hostname that will allow you to access API Designer by following the guidelines recommended by your OpenShift system administrator.
Verify that the Fuse on OpenShift images and templates, including
apidesigner-uiandfuse-apidesigner-generator, are installed on your OpenShift cluster, by running the following command in a command window:oc get is -n openshift
If the images and templates are not pre-installed, or if the provided versions are out of date, install (or update) the Fuse on OpenShift images and templates as described in the Fuse on OpenShift Guide.
Procedure
To add the API Designer service from the command line:
In a command window, log in to the OpenShift server:
oc login -u developer -p developer
Create a new project namespace. For example, the following command creates a new project named myproject:
oc new-project myproject
Create a new application based on the API Designer template by running the following command (where myproject is the name of your project):
oc new-app -n myproject -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jboss-fuse/application-templates/application-templates-2.1.0.fuse-sb2-7_10_0-00015-redhat-00001/fuse-apicurito.yml -p ROUTE_HOSTNAME=myhost
Note: Optionally, you can specify other template parameters by appending additional
-poptions to theoc new-appcommand. For example, if you installed the Fuse on OpenShift images and templates in a namespace other than the default openshift namespace, you can set theIMAGE_STREAM_NAMESPACEto specify the namespace in which the Fuse image streams are installed:oc new-app -n myproject -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jboss-fuse/application-templates/application-templates-2.1.0.fuse-sb2-7_10_0-00015-redhat-00001/fuse-apicurito.yml -p ROUTE_HOSTNAME=myhost -p IMAGE_STREAM_NAMESPACE=othernamespace
Obtain the status and the URL of your API Designer deployment by running this command:
oc status
If the API Designer is not deployed, run the following command to verify that you installed the correct versions of the
apicurito-uiandfuse-apicurito-generatorimages:oc get is -n openshift | grep "apicurito"
- To access the API Designer from a browser, use the provided URL (for example, https://apicurito.192.168.64.12.nip.io).
Chapter 3. Designing and developing an API definition with API Designer
You can use API Designer to design and develop a REST API definition that complies with the OpenAPI 3 (or 2) specification.
Prerequisites
- You created an OpenShift project.
- You added the API Designer service to your OpenShift project.
3.1. Creating a REST API definition in API Designer
The following steps describe how to create a REST API definition.
- You can access the API Designer user interface from Fuse Online or Fuse on OpenShift.
- For Fuse on OpenShift only, API Designer is stateless which means that it does not save your work between OpenShift sessions. You need to save the API to your local file system between sessions.
About the example
The Task Management API example simulates a simple API that sales consultants might use to track the tasks that they need to do when interacting with customer contacts. Example "to-do" tasks might be "create an account for a new contact" or "place an order for an existing contact". To implement the Task Management API example, you create two paths - one for tasks and one for a specific task. You then define operations to create a task, retrieve all tasks or a specific task, update a task, and delete a task.
Prerequisites
-
You know the endpoints for the API that you want to create. For the Task Management API example, there are two endpoints:
/todoand/todo/{id}. - For Fuse on OpenShift only, you created an OpenShift project and you added the API Designer service to your OpenShift project.
Procedure
If you are using Fuse Online, skip to step 2.
If you are using Fuse on OpenShift:
- Log in to your OpenShift web console and then open the project that contains API Designer.
For OpenShift 4.x, select Topology and then click the URL link for the apicurito-service icon.
For OpenShift 3.11, from the list of applications, click the URL for API Designer, for example
https://apidesigner-myproject.192.168.64.43.nip.ioA new browser window or tab opens for API Designer.
NoteBecause API Designer is a “light” version of the Apicurio Studio open source project, "Apicurio" shows in the API Designer interface.
Click New API. A new API page opens.
By default, API Designer uses the OpenAPI 3 specification. If you want to use the OpenAPI 2 specification, click the arrow next to the New API button and then select OpenAPI 2.
NoteIf you open an API based on the OpenAPI 2 specification, you can use the API Designer’s Convert to OpenAPI 3 option to convert the API to comply with the OpenAPI 3 specification.
To change the API name:
-
Hover the cursor over the name and then click the edit icon (
 ) that appears.
) that appears.
- Edit the name. For example, type Task API.
- Click the checkmark icon to confirm the name change.
-
Hover the cursor over the name and then click the edit icon (
Optionally:
- Provide a version number and a description.
- Add your contact information (name, email address, and URL).
- Select a license.
- Define tags.
- Define one or more servers.
- Configure a security scheme.
- Specify security requirements.
Define a relative path to each individual endpoint of the API. The field name must begin with a slash (/).
For the Task Management API example, create two paths:
-
A path for tasks:
/todo A path for a specific task by ID:
/todo/{id}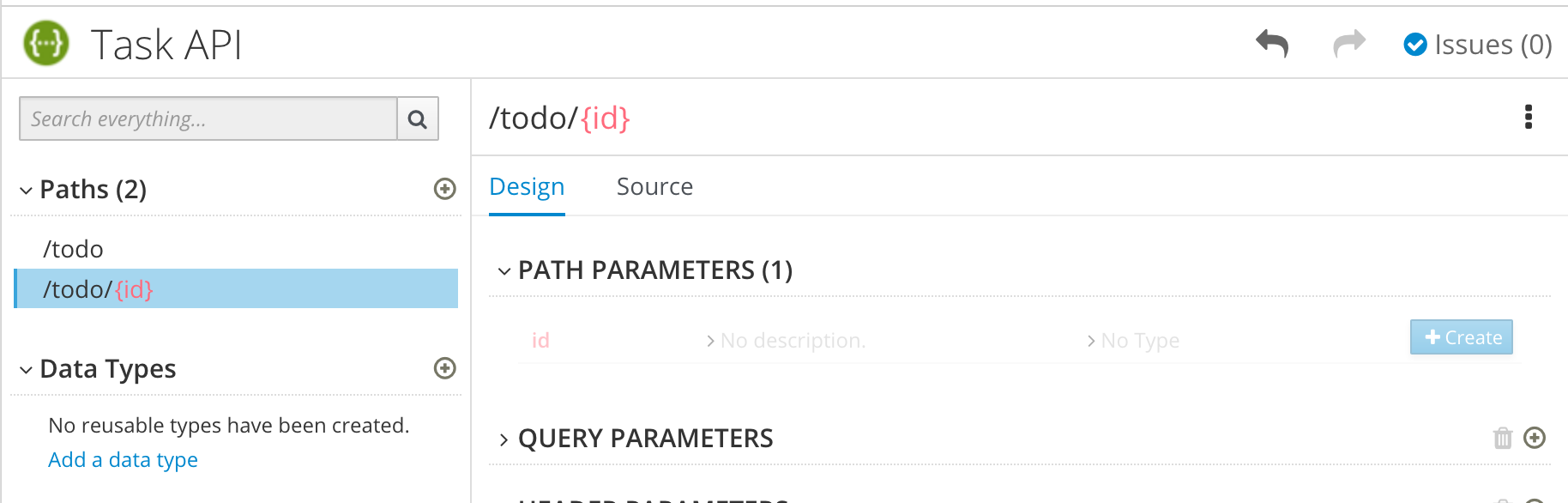
-
A path for tasks:
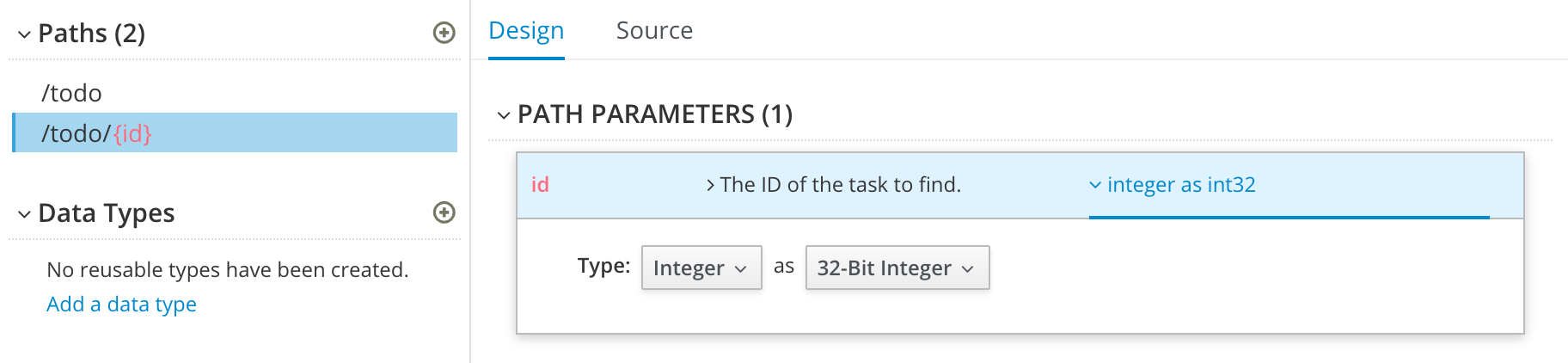
Specify the type of any path parameters.
For the example
idparameter:In the Paths list, click
/todo/{id}.The id parameter appears in the PATH PARAMETERS section.
- Click Create.
- For the description, type: The ID of the task to find.
For the type, select integer as 32-Bit integer.
In the Data Types section, define reusable types for the API.
- Click Add a data type.
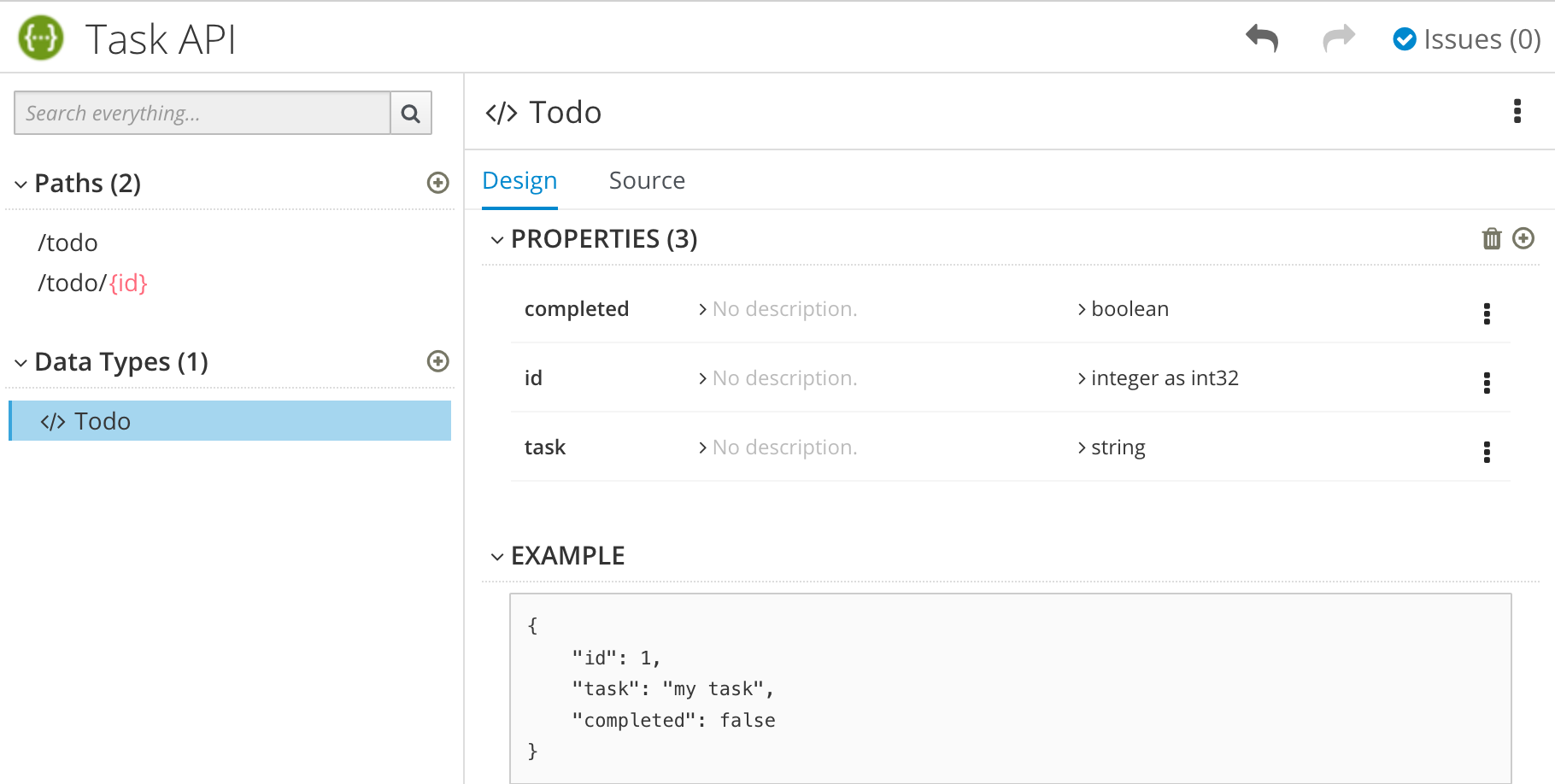
- In the Add Data Type dialog, type a name. For the Task Management API example, type Todo.
Optionally, you can provide an example from which API Designer creates the data type’s schema. You can then edit the generated schema.
For the Task Management API example, start with the following JSON example:
{ "id": 1, "task": "my task", "completed": false }- Optionally, you can choose to create a REST Resource with the data type.
Click Save. If you provided an example, API Designer generates a schema from the example:
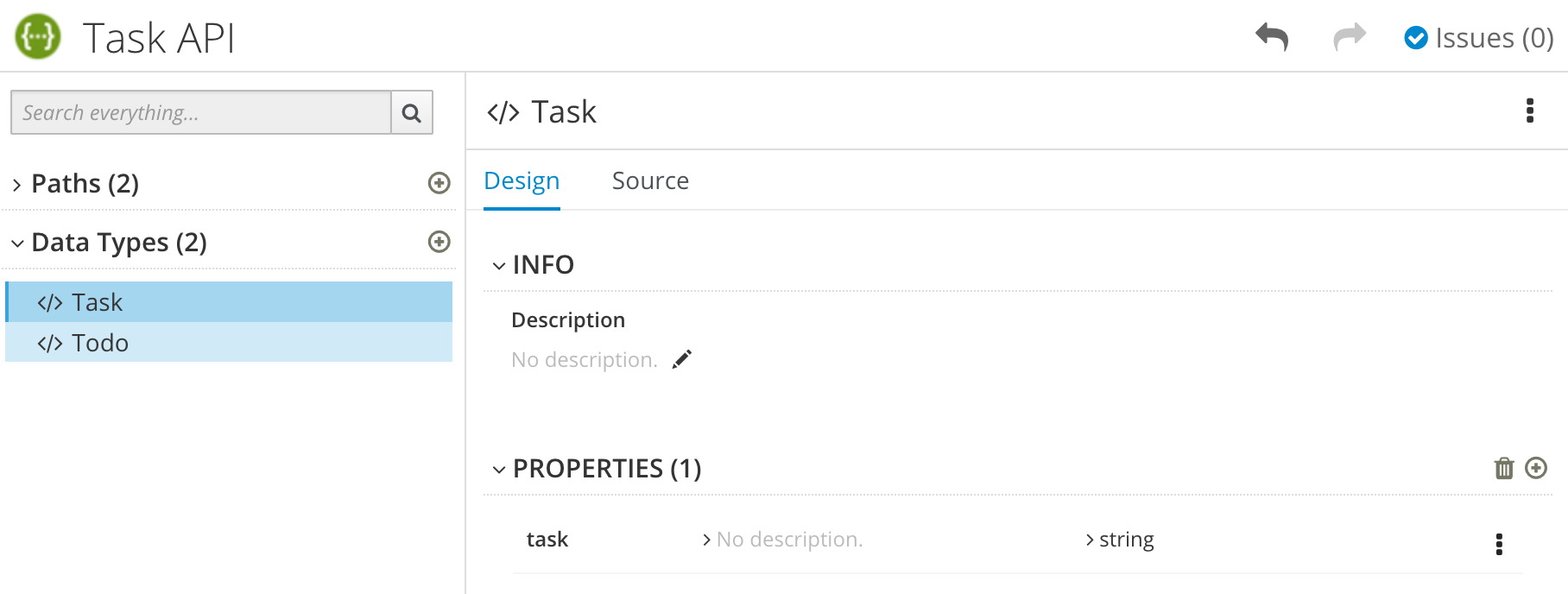
- Optionally, you can add edit the schema properties and add new ones.
For the Task Management API example, create another data type named Task with one property named task of type string.
For each path, define operations (GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, OPTIONS, HEAD, or PATCH).
For the Task Management API example, define the operations as described in the following table:
Table 3.1. Task Management API operations Path Operation Description Request Body Response /todoPOST
Create a new task.
Media Type:
application/jsonData Type: TaskStatus Code: 201 Description: Task created
Response Body: Media Type:
application/jsonData Type: Todo
/todoGET
Get all tasks.
Not applicable
- Status Code: 200 Description: List of Tasks
/todo/{id}GET
Get a task by ID.
Not applicable
-
Status Code: 200 Description: Task found for ID Response Body: Media Type:
application/jsonData type: Task - Status Code: 404 Description: No task with provided identifier found.
/todo/{id}PUT
Update a task by ID.
Request Body type: Task
- Status Code: 200 Description: Completed
- Status Code: 400 Description: Task not updated
/todo/{id}DELETE
Delete a task by ID.
Not applicable
- Status Code: 200 Description: Task deleted
- Status Code: 400 Description: Task not deleted
- Resolve any issues, as described in Resolving validation issues in API Designer.
For Fuse on OpenShift only, save your API specification by clicking Save As and then select JSON or YAML format.
The JSON or YAML file is downloaded to your local download folder. The default filename is
openapi-specwith the appropriate file extension.
Additional resources
- For information about the OpenAPI Specification, go to: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification
3.2. Resolving validation issues in API Designer
When you create and edit an API, API Designer identifies issues that you must resolve with an exclamation (!) icon and also with a list of issues in the API Designer title bar.
Prerequisites
- Open an API in API Designer.
Procedure
Find an issue indicated by an exclamation (!) icon. For example:

Click the exclamation icon to view a description of the issue. For example:
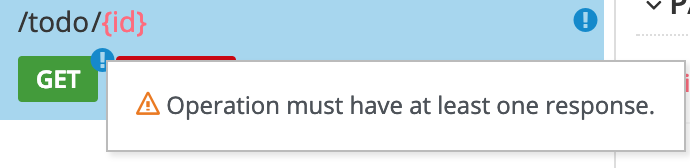
Based on the information provided by the issue description, navigate to the location of the issue and fix it.
For example, to fix the "Operation must have at least one response" issue, click the GET operation to open it and then click Add a response.
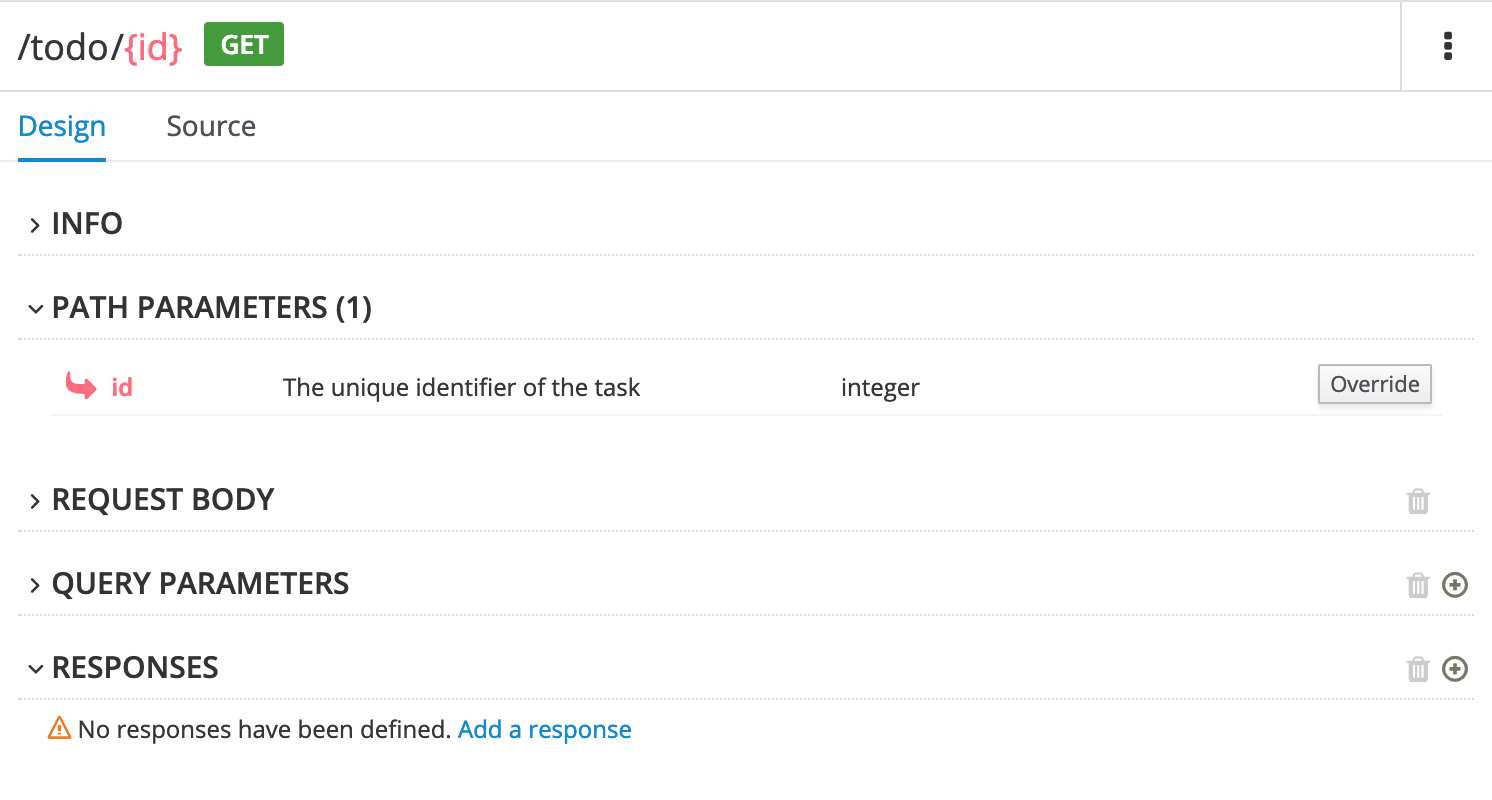
After you type a description for the response, the issue is resolved and the exclamation icon disappears:
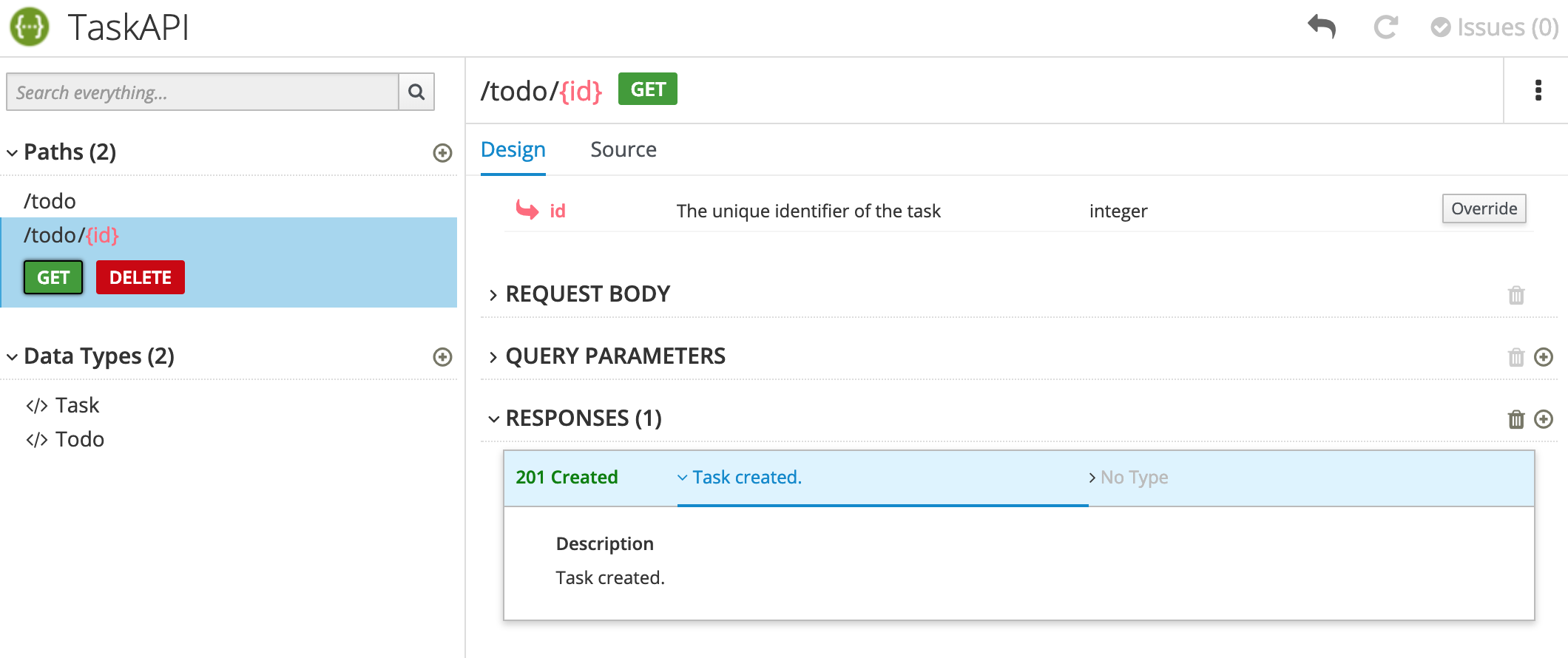
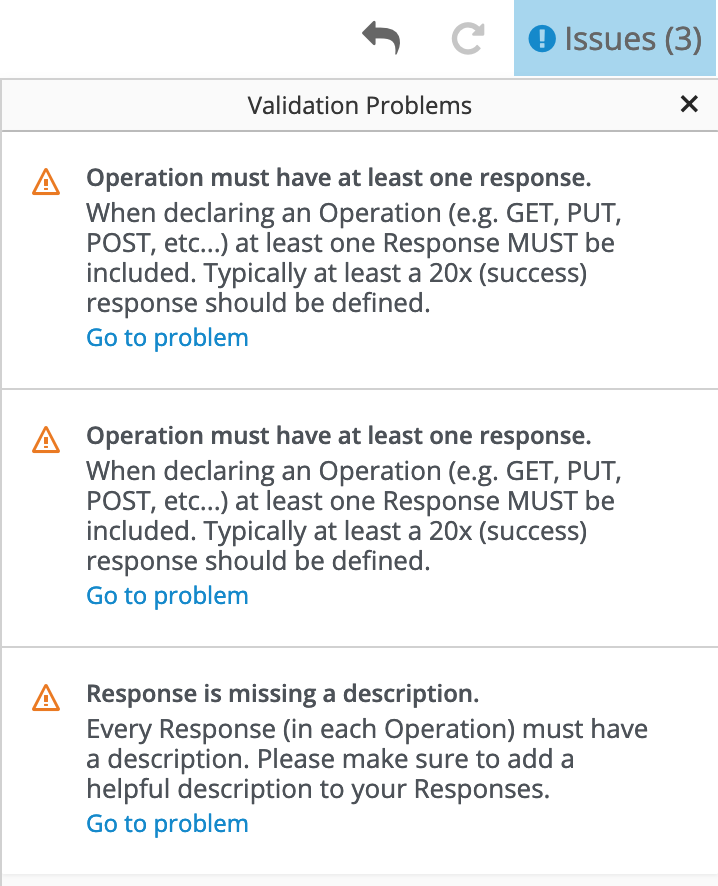
For a summary of all issues:
Click the Issues link in the upper right corner.

Click Go to a problem for a specific issue to go to the location of the issue so that you can resolve it.
Chapter 4. Implementing, building, and deploying a Fuse application based on a REST API
You can use Red Hat Fuse API Designer to generate a Camel Fuse project based on a REST API definition. In your Fuse development environment, you can complete the Camel routes and Rest DSL API. Finally, you can build the project and deploy the resulting application to Fuse on OpenShift.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing API definition, which complies with the OpenAPI 3 (or 2) specification. For example, an
openapi-spec.jsonfile that you created with API Designer. - API Designer is installed and running on your local OpenShift cluster.
- You have an existing OpenShift project with API Designer added as a service.
- You have installed Maven and Red Hat Fuse.
The following topics describe how to implement, build, and deploy a Fuse application based on a REST API:
4.1. Uploading an API definition to API Designer
You can upload an existing API definition to API Designer.
Prerequisites
-
You have an existing API definition, which complies with the OpenAPI 3 (or 2) specification. For example, an
openapi.jsonfile that you created with API Designer. - API Designer is installed and running on your local OpenShift cluster.
- You have an existing OpenShift project with API Designer added as an application.
Procedure
- In your OpenShift web console, open the project that contains API Designer.
Open the API Designer console. In the list of applications for the project, click the URL under apidesigner. For example:
https://apidesigner-myproject.192.168.64.38.nip.ioThe API Designer console opens in a separate web browser tab or window.
Click Open API.
A file manager window opens.
In the file manager window:
-
Navigate to the folder that contains the existing OpenAPI definition file, for example,
openapi.json. Select the OpenAPI definition file and then click Open.
The OpenAPI definition opens in the API Designer console.
-
Navigate to the folder that contains the existing OpenAPI definition file, for example,
4.2. Generating a Fuse Camel project from API Designer
You can use API Designer to generate a Fuse Camel project based on an API definition.
Prerequisites
- API Designer is installed and running on your local OpenShift cluster.
- You have an existing OpenShift project with API Designer added as an application.
- You have created or opened an API definition file in the API Designer console.
Procedure
In the API Designer console:
- Click Generate.
- Select Fuse Camel Project from the drop-down list.
API Designer generates a camel-project.zip file and downloads it to your local default download folder.
The zip file contains a Fuse Camel project that provides a default skeleton implementation of the API definition using Camel’s Rest DSL and includes all resource operations. The project also includes the original OpenAPI definition file that you used to generate the project.
4.3. Completing the API Designer-generated Camel project
API Designer generates a Fuse project that provides a default skeleton implementation of the API definition using Camel’s Rest DSL and covering all resource operations. In your Fuse development environment, you complete the project.
Prerequisites
-
You have a
camel-project.zipfile generated by API Designer. - (Optional) You have installed Red Hat Developer Studio with Fuse Tooling.
Procedure
-
Unzip the API Designer-generated
camel-project.zipfile to a temporary folder. - Open Red Hat Developer Studio.
- In Developer Studio, select File → Import.
- In the Import dialog, select Maven → Existing Maven Projects.
-
Open the project’s
camel-context.xmlfile in the editor view. Click the REST tab to edit the Rest DSL components.
For information on defining REST services, see the "Defining REST services" section of the Apache Camel Development Guide.
For information on extending JAX-RS endpoints with Swagger support, see the Apache CXF Development Guide.
For information on using the Fuse Tooling REST editor, see the "Viewing and editing Rest DSL components" section of the Tooling User Guide.
In the Design tab, edit the Camel routes.
For information on editing Camel routes, see the "Editing a routing context in the route editor" section of the Tooling User Guide.
4.4. Building and deploying a REST service
After you complete the Fuse project, you can build and deploy the project in OpenShift.
Prerequisites
- You have a complete, error-free Fuse project that defines a REST service.
- You have installed Java 8 JDK (or later) and Maven 3.3.x (or later).
Procedure
If you have a single-node OpenShift cluster, such as Minishift or the Red Hat Container Development Kit, installed and running, you can deploy your project there.
To deploy this project to a running single-node OpenShift cluster:
Log in to your OpenShift cluster:
$ oc login -u developer -p developer
Create a new OpenShift project for the project. For example, the following command creates a new project named test-deploy.
$ oc new-project test-deploy
Change the directory to the folder that contains your Fuse Camel project (for example,
myworkspace/camel-project) :$ cd myworkspace/camel-project
Build and deploy the project to the OpenShift cluster:
$ mvn clean fabric8:deploy -Popenshift
-
In your browser, open the OpenShift console and navigate to the project (for example, test-deploy). Wait until you can see that the pod for the
camel-projectapplication has started. -
On the project’s Overview page, locate the URL for the
camel-projectapplication. The URL uses this form:http://camel-project-MY_PROJECT_NAME.OPENSHIFT_IP_ADDR.nip.io. - Click the URL to access the service.
Chapter 5. Preparing an API service for 3scale discovery
Red Hat 3scale API Management is an offering from Red Hat that enables you to regulate access to API services on the public Internet. The functionality of 3scale includes the ability to enforce service-level agreements (SLAs), manage API versions, provide security and authentication services and more. Fuse supports a service discovery feature for 3scale, which makes it easy to discover Fuse services from the 3scale Admin Portal UI. Using service discovery, you can scan for Fuse applications running in the same OpenShift cluster and automatically import the associated API definitions into 3scale.
Prerequisites
- A Fuse application that provides an API service is deployed and running in OpenShift.
The Fuse application is annotated with the requisite annotations to make it discoverable by 3scale.
NoteFuse projects that are generated by API Designer are pre-configured to automatically provide the requisite annotations.
For Fuse projects that are not generated by API Designer, you must configure your project as described in Adding annotations for Fuse projects that are not generated by API Designer .
- The 3scale API Management system is deployed on the same OpenShift cluster as the API service that is to be discovered.
For details of the procedure to discover an API service in 3scale, see the service discovery section of the Red Hat 3scale API Management Admin Portal Guide.
Additional resources
5.1. Adding annotations for Fuse projects that are not generated by API Designer
In order for 3scale to discover an API service, the Fuse application that provides the API service must include Kubernetes Service Annotations that make it discoverable. These annotations are provided by the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher which is part of the Fabric8 Maven Plugin.
For Apache Camel Rest DSL projects, the Fabric8 Maven Plugin runs the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher by default.
Fuse projects that are generated by API Designer are pre-configured to automatically provide the required annotations.
Procedure
For a Fuse Rest DSL project that is not generated by API Designer, configure the project as follows:
Edit the Fuse project’s
pom.xmlfile to include thefabric8-maven-plugindependency, as shown in this example:<plugin> <groupId>org.jboss.redhat-fuse</groupId> <artifactId>fabric8-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${fuse.version}</version> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>resource</goal> <goal>build</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin>The Fabric8 Maven Plugin runs the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher if certain project-level conditions are met (for example, the project must be a Camel Rest DSL project). You do not need to specify the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher as a dependency in the
pom.xmlfile, unless you want to customize the enricher’s behavior (as described in Customizing the API service annotation values.)In the Fuse Rest DSL project’s
camel-context.xmlfile, specify the following attributes in therestConfigurationelement:-
scheme: The scheme part of the URL where the service is hosted. You can specify “http” or “https”. -
contextPath: The path part of the URL where the API service is hosted. apiContextPath: The path to the location where the API service description document is hosted. You can specify either a relative path if the document is self-hosted or a full URL if the document is hosted externally.The following excerpt from an example
camel-context.xmlfile shows annotation attribute values in therestConfigurationelement:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd"> <camelContext xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"> <restConfiguration component="servlet" scheme="https" contextPath="myapi" apiContextPath="myapi/openapi.json"/> ...
-
The enricher uses the information provided by these restConfiguration element attribute values to create values for the discovery.3scale.net/scheme, discovery.3scale.net/path, and the discovery.3scale.net/description-path annotations, thereby making the project’s deployed OpenShift service discoverable by 3scale as described in the see the service discovery section of the Red Hat 3scale API Management Admin Portal Guide.
The enricher adds the following label and annotations to make the service discoverable by 3scale:
-
The
discovery.3scale.netlabel: By default, the enricher sets this value to “true”. 3scale uses this label when it executes the selector definition to find all services that need discovery. The following annotations:
-
discovery.3scale.net/discovery-version: (optional) The version of the 3scale discovery process. The enricher sets this value to "v1" by default. -
discovery.3scale.net/scheme: The scheme part of the URL where the service is hosted. The enricher uses the default "http" unless you override it in therestConfigurationelement’sschemeattribute. The other possible value is "https". -
discovery.3scale.net/path: The path part of the URL where the service is hosted. This annotation is omitted when the path is at root, "/". The enricher gets this value from therestConfigurationelement’spathattribute. -
discovery.3scale.net/port: The port of the service. The enricher obtains this value from the Kubernetes service definition, which contains the the port numbers of the services it exposes. If the Kubernetes service definition exposes more than one service, the enricher uses the first port listed. -
discovery.3scale.net/description-path: (optional) The path to the OpenAPI service description document. The enricher gets this value from therestConfigurationelement’scontextPathattribute.
-
You can customize the behavior of the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher, as described in Customizing the API service annotation values.
5.2. Customizing the API service annotation values
The Maven Fabric8 Plugin runs the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher by default. The enricher adds annotations to the Fuse Rest DSL project’s API service so that the API service is discoverable by 3scale, as described in Using Service Discovery in the Red Hat 3scale API Management Admin Portal Guide guide.
The enricher uses default values for some annotations and obtains values for other annotations from the project’s camel-context.xml file.
You can override the default values and the values defined in the camel-context.xml file by defining values in the Fuse project pom.xml file or in a service.yml file. (If you define values in both files, the enricher uses the values from the service.yml file.) See Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher elements for a description of the elements that you can specify for the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher.
Procedure
To specify annotation values in the Fuse project pom.xml file:
-
Open your Fuse project’s
pom.xmlfile in an editor of your choice. Locate the
fabric8-maven-plugindependency, as shown in this example:<plugin> <groupId>org.jboss.redhat-fuse</groupId> <artifactId>fabric8-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${fuse.version}</version> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>resource</goal> <goal>build</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin>Add the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher as a dependency to the Fabric8-Maven plugin as shown in the following example.
<plugin> <groupId>org.jboss.redhat-fuse</groupId> <artifactId>fabric8-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${fuse.version}</version> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>resource</goal> <goal>build</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.acme</groupId> <artifactId>myenricher</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <configuration> <enricher> <config> <f8-service-discovery> <scheme>https</scheme> <path>/api</path> <descriptionPath>/api/openapi.json</descriptionPath> </f8-service-discovery> </config> </enricher> </configuration> </dependency> </dependencies> </plugin>- Save your changes.
Alternatively, you can use a src/main/fabric8/service.yml fragment to override the annotation values, as shown in the following example:
kind: Service
name:
metadata:
labels:
discovery.3scale.net/discoverable : "true"
annotations:
discovery.3scale.net/discovery-version : "v1"
discovery.3scale.net/scheme : "https"
discovery.3scale.net/path : "/api"
discovery.3scale.net/port : "443"
discovery.3scale.net/description-path : "/api/openapi.json"
spec:
type: LoadBalancer5.3. Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher elements
The following table describes the elements that you can specify for the Fabric8 Service Discovery Enricher, if you want to override the default values and the values defined in the camel-context.xml file.
You can define these values in the Fuse Rest DSL project’s pom.xml file or in a src/main/fabric8/service.yml file. (If you define values in both files, the enricher uses the values from the service.yml file.) See Customizing the API service annotation values for examples.
| Element | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The path to the spring configuration directory that contains the |
The |
|
| The scheme part of the URL where the service is hosted. You can specify “http” or “https”. | http |
|
| The path part of the URL where the API service is hosted. | |
|
| The port part of the URL where the API service is hosted. | 80 |
|
| The path to a location where the API service description document is hosted. You can specify either a relative path if the document is self-hosted or a full URL if the document is hosted externally. | |
|
| The version of the 3scale discovery implementation. | v1 |
|
|
The element that sets the If set to true, 3scale will try to discover this service. If set to false, 3scale will not try to discover this service. You can use this element as a switch, to temporary turn off 3scale discovery integration by setting it to "false". | If you do not specify a value, the enricher tries to auto-detect whether it can make the service discoverable. If the enricher determines that it cannot make the service discoverable, 3scale will not try to discover this service. |