Administration Guide
Configuring and Managing Red Hat Gluster Storage
Abstract
Part I. Preface
Chapter 1. Preface
1.1. About Red Hat Gluster Storage
1.2. About glusterFS
1.3. About On-premises Installation
Part II. Overview
Chapter 2. Architecture and Concepts
2.1. Architecture
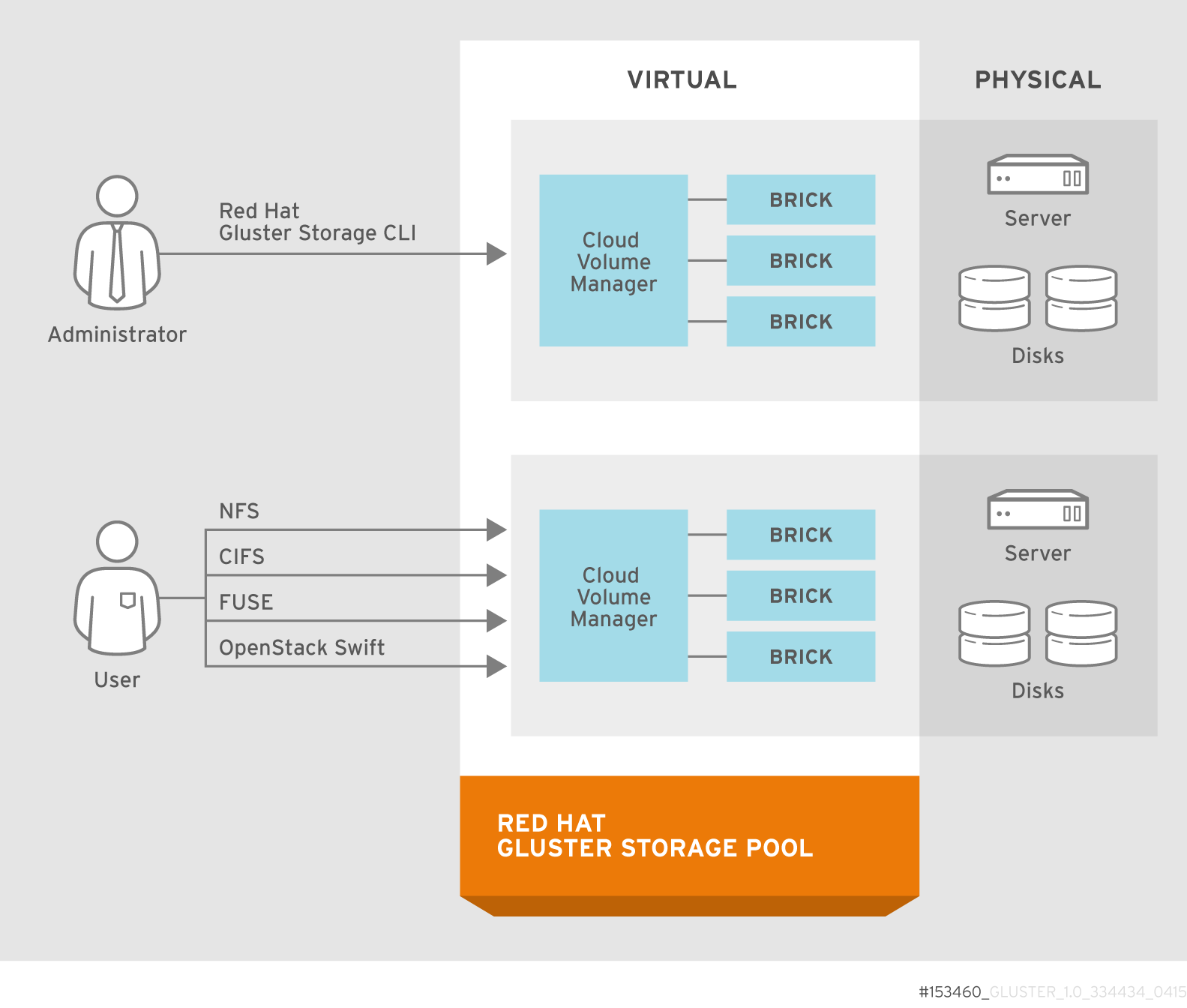
Figure 2.1. Red Hat Gluster Storage Architecture
2.2. On-premises Architecture

Figure 2.2. Red Hat Gluster Storage for On-premises Architecture
2.3. Storage Concepts
- Brick
- The glusterFS basic unit of storage, represented by an export directory on a server in the trusted storage pool. A brick is expressed by combining a server with an export directory in the following format:
SERVER:EXPORTFor example:myhostname:/exports/myexportdir/ - Volume
- A volume is a logical collection of bricks. Most of the Red Hat Gluster Storage management operations happen on the volume.
- Translator
- A translator connects to one or more subvolumes, does something with them, and offers a subvolume connection.
- Subvolume
- A brick after being processed by at least one translator.
- Volfile
- Volume (vol) files are configuration files that determine the behavior of your Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool. At a high level, GlusterFS has three entities, that is, Server, Client and Management daemon. Each of these entities have their own volume files. Volume files for servers and clients are generated by the management daemon upon creation of a volume.Server and Client Vol files are located in
/var/lib/glusterd/vols/VOLNAMEdirectory. The management daemon vol file is named asglusterd.voland is located in/etc/glusterfs/directory.Warning
You must not modify any vol file in/var/lib/glusterdmanually as Red Hat does not support vol files that are not generated by the management daemon. - glusterd
- glusterd is the glusterFS Management Service that must run on all servers in the trusted storage pool.
- Cluster
- A trusted pool of linked computers working together, resembling a single computing resource. In Red Hat Gluster Storage, a cluster is also referred to as a trusted storage pool.
- Client
- The machine that mounts a volume (this may also be a server).
- File System
- A method of storing and organizing computer files. A file system organizes files into a database for the storage, manipulation, and retrieval by the computer's operating system.Source: Wikipedia
- Distributed File System
- A file system that allows multiple clients to concurrently access data which is spread across servers/bricks in a trusted storage pool. Data sharing among multiple locations is fundamental to all distributed file systems.
- Virtual File System (VFS)
- VFS is a kernel software layer that handles all system calls related to the standard Linux file system. It provides a common interface to several kinds of file systems.
- POSIX
- Portable Operating System Interface (for Unix) (POSIX) is the name of a family of related standards specified by the IEEE to define the application programming interface (API), as well as shell and utilities interfaces, for software that is compatible with variants of the UNIX operating system. Red Hat Gluster Storage exports a fully POSIX compatible file system.
- Metadata
- Metadata is data providing information about other pieces of data.
- FUSE
- Filesystem in User space (FUSE) is a loadable kernel module for Unix-like operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a "bridge" to the kernel interfaces.Source: Wikipedia
- Geo-Replication
- Geo-replication provides a continuous, asynchronous, and incremental replication service from one site to another over Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN), and the Internet.
- N-way Replication
- Local synchronous data replication that is typically deployed across campus or Amazon Web Services Availability Zones.
- Petabyte
- A petabyte is a unit of information equal to one quadrillion bytes, or 1000 terabytes. The unit symbol for the petabyte is PB. The prefix peta- (P) indicates a power of 1000:1 PB = 1,000,000,000,000,000 B = 1000^5 B = 10^15 B.The term "pebibyte" (PiB), using a binary prefix, is used for the corresponding power of 1024.Source: Wikipedia
- RAID
- Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a technology that provides increased storage reliability through redundancy. It combines multiple low-cost, less-reliable disk drives components into a logical unit where all drives in the array are interdependent.
- RRDNS
- Round Robin Domain Name Service (RRDNS) is a method to distribute load across application servers. RRDNS is implemented by creating multiple records with the same name and different IP addresses in the zone file of a DNS server.
- Server
- The machine (virtual or bare metal) that hosts the file system in which data is stored.
- Block Storage
- Block special files, or block devices, correspond to devices through which the system moves data in the form of blocks. These device nodes often represent addressable devices such as hard disks, CD-ROM drives, or memory regions. As of Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4, block storage supports only Container-Native Storage (CNS) and Container-Ready Storage (CRS) use cases. Block storage can be created and configured for this use case by using the
gluster-blockcommand line tool. For more information, see Container-Native Storage for OpenShift Container Platform. - Scale-Up Storage
- Increases the capacity of the storage device in a single dimension. For example, adding additional disk capacity in a trusted storage pool.
- Scale-Out Storage
- Increases the capability of a storage device in single dimension. For example, adding more systems of the same size, or adding servers to a trusted storage pool that increases CPU, disk capacity, and throughput for the trusted storage pool.
- Trusted Storage Pool
- A storage pool is a trusted network of storage servers. When you start the first server, the storage pool consists of only that server.
- Namespace
- An abstract container or environment that is created to hold a logical grouping of unique identifiers or symbols. Each Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool exposes a single namespace as a POSIX mount point which contains every file in the trusted storage pool.
- User Space
- Applications running in user space do not directly interact with hardware, instead using the kernel to moderate access. User space applications are generally more portable than applications in kernel space. glusterFS is a user space application.
- Hashed subvolume
- A Distributed Hash Table Translator subvolume to which the file or directory name is hashed to.
- Cached subvolume
- A Distributed Hash Table Translator subvolume where the file content is actually present. For directories, the concept of cached-subvolume is not relevant. It is loosely used to mean subvolumes which are not hashed-subvolume.
- Linkto-file
- For a newly created file, the hashed and cached subvolumes are the same. When directory entry operations like rename (which can change the name and hence hashed subvolume of the file) are performed on the file, instead of moving the entire data in the file to a new hashed subvolume, a file is created with the same name on the newly hashed subvolume. The purpose of this file is only to act as a pointer to the node where the data is present. In the extended attributes of this file, the name of the cached subvolume is stored. This file on the newly hashed-subvolume is called a linkto-file. The linkto file is relevant only for non-directory entities.
- Directory Layout
- The directory layout helps determine where files in a gluster volume are stored.When a client creates or requests a file, the DHT translator hashes the file's path to create an integer. Each directory in a gluster subvolume holds files that have integers in a specific range, so the hash of any given file maps to a specific subvolume in the gluster volume. The directory layout determines which integer ranges are assigned to a given directory across all subvolumes.Directory layouts are assigned when a directory is first created, and can be reassigned by running a rebalance operation on the volume. If a brick or subvolume is offline when a directory is created, it will not be part of the layout until after a rebalance is run.You should rebalance a volume to recalculate its directory layout after bricks are added to the volume. See Section 11.11, “Rebalancing Volumes” for more information.
- Fix Layout
- A command that is executed during the rebalance process.The rebalance process itself comprises of two stages:
- Fixes the layouts of directories to accommodate any subvolumes that are added or removed. It also heals the directories, checks whether the layout is non-contiguous, and persists the layout in extended attributes, if needed. It also ensures that the directories have the same attributes across all the subvolumes.
- Migrates the data from the cached-subvolume to the hashed-subvolume.
Part III. Configure and Verify
Chapter 3. Considerations for Red Hat Gluster Storage
3.1. Firewall and Port Access
3.1.1. Configuring the Firewall
iptables command to open a port:
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5667 -j ACCEPT # service iptables save
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5667 -j ACCEPT
# service iptables savefirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs --permanentfirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/protocol # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/protocol --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/protocol
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/protocol --permanentfirewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5667/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5667/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5667/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5667/tcp --permanent3.1.2. Port Access Requirements
| Connection source | TCP Ports | UDP Ports | Recommended for | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any authorized network entity with a valid SSH key | 22 | - | All configurations | Remote backup using geo-replication |
| Any authorized network entity; be cautious not to clash with other RPC services. | 111 | 111 | All configurations | RPC port mapper and RPC bind |
| Any authorized SMB/CIFS client | 139 and 445 | 137 and 138 | Sharing storage using SMB/CIFS | SMB/CIFS protocol |
| Any authorized NFS clients | 2049 | 2049 | Sharing storage using Gluster NFS or NFS-Ganesha | Exports using NFS protocol |
| All servers in the Samba-CTDB cluster | 4379 | - | Sharing storage using SMB and Gluster NFS | CTDB |
| Any authorized network entity | 24007 | - | All configurations | Management processes using glusterd |
| Any authorized network entity | 24009 | - | All configurations | Gluster events daemon |
| Any network entity monitored by Nagios | 5666 | - | Monitoring using Red Hat Gluster Storage Console and Nagios | NRPE service |
| NFSv3 clients | 662 | 662 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha and Gluster NFS | statd |
| NFSv3 clients | 32803 | 32803 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha and Gluster NFS | NLM protocol |
| NFSv3 clients sending mount requests | - | 32769 | Sharing storage using Gluster NFS | Gluster NFS MOUNT protocol |
| NFSv3 clients sending mount requests | 20048 | 20048 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha | NFS-Ganesha MOUNT protocol |
| NFS clients | 875 | 875 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha | NFS-Ganesha RQUOTA protocol (fetching quota information) |
| Servers in pacemaker/corosync cluster | 2224 | - | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha | pcsd |
| Servers in pacemaker/corosync cluster | 3121 | - | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha | pacemaker_remote |
| Servers in pacemaker/corosync cluster | - | 5404 and 5405 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha | corosync |
| Servers in pacemaker/corosync cluster | 21064 | - | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha | dlm |
| Any authorized network entity to access gluster-swift proxy server via SSL/TLS mode; SSL/TLS cert is required. | 443 | - | Object storage configurations | HTTPS requests |
| Any authorized network entity with valid object server gluster-swift credentials | 6010 | - | Object storage configurations | Object server |
| Any authorized network entity with valid container server gluster-swift credentials | 6011 | - | Object storage configurations | Container server |
| Any authorized network entity with valid gluster-swift account credentials | 6012 | - | Object storage configurations | Account server |
| Any authorized network entity with valid gluster-swift proxy credentials | 8080 | - | Object storage configurations | Proxy server |
| Any authorized network entity | 49152 - 49664 | - | All configurations | Brick communication ports. The total number of ports required depends on the number of bricks on the node. One port is required for each brick on the machine. |
| Connection source | TCP Ports | UDP Ports | Recommended for | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFSv3 servers | 662 | 662 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha and Gluster NFS | statd |
| NFSv3 servers | 32803 | 32803 | Sharing storage using NFS-Ganesha and Gluster NFS | NLM protocol |
| Connection source | TCP Ports | UDP Ports | Recommended for | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Console clients | 80 | - | Monitoring using Red Hat Gluster Storage Console and Nagios | HTTP protocol when Nagios server runs on a Red Hat Gluster Storage server |
| Console clients | 443 | - | Monitoring using Red Hat Gluster Storage Console and Nagios | HTTPS protocol when Nagios server runs on a Red Hat Gluster Storage server |
| Servers monitored by Nagios | 5667 | - | Monitoring using Red Hat Gluster Storage Console and Nagios | NSCA service when Nagios server runs on a Red Hat Gluster Storage server |
3.2. Feature Compatibility Support
Note
| Feature | Version |
|---|---|
| Arbiter bricks | 3.2 |
| Bitrot detection | 3.1 |
| Erasure coding | 3.1 |
| Google Compute Engine | 3.1.3 |
| Metadata caching | 3.2 |
| Microsoft Azure | 3.1.3 |
| NFS version 4 | 3.1 |
| SELinux | 3.1 |
| Sharding | 3.2.0 |
| Snapshots | 3.0 |
| Snapshots, cloning | 3.1.3 |
| Snapshots, user-serviceable | 3.0.3 |
| Tiering | 3.1.2 |
| Volume Shadow Copy (VSS) | 3.1.3 |
| Volume Type | Sharding | Tiering | Quota | Snapshots | Geo-Rep | Bitrot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arbitrated-Replicated | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Distributed | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Distributed-Dispersed | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Distributed-Replicated | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Replicated | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sharded | N/A | No | No | No | Yes | No |
| Tiered | No | N/A | Limited[a] | Limited[a] | Limited[a] | Limited[a] |
[a]
See Section 17.3. Tiering Limitations in the Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 Administration Guide for details.
| ||||||
| Feature | FUSE | Gluster-NFS | NFS-Ganesha | SMB | Swift/S3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arbiter | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Bitrot detection | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| dm-cache | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Encryption (TLS-SSL) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Erasure coding | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Export subdirectory | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| Geo-replication | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Quota | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| RDMA | Yes | No | No | No | N/A |
| Snapshots | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Snapshot cloning | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Tiering | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Chapter 4. Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool
Important
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesfirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=glusterfs --permanentNote
gluster volume status VOLNAME command is executed from two of the nodes simultaneously.
4.1. Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool
gluster peer probe [server] command is used to add servers to the trusted server pool.
Note
Adding Three Servers to a Trusted Storage Pool
Prerequisites
- The
glusterdservice must be running on all storage servers requiring addition to the trusted storage pool. See Chapter 24, Starting and Stopping the glusterd service for service start and stop commands. Server1, the trusted storage server, is started.- The host names of the target servers must be resolvable by DNS.
- Run
gluster peer probe [server]from Server 1 to add additional servers to the trusted storage pool.Note
- Self-probing
Server1will result in an error because it is part of the trusted storage pool by default. - All the servers in the Trusted Storage Pool must have RDMA devices if either
RDMAorRDMA,TCPvolumes are created in the storage pool. The peer probe must be performed using IP/hostname assigned to the RDMA device.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the peer status from all servers using the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Important
Note
for peer in `gluster peer status | grep Hostname | awk -F':' '{print $2}' | awk '{print $1}'`; do clockdiff $peer; done
# for peer in `gluster peer status | grep Hostname | awk -F':' '{print $2}' | awk '{print $1}'`; do clockdiff $peer; done4.2. Removing Servers from the Trusted Storage Pool
Warning
gluster peer detach server to remove a server from the storage pool.
Removing One Server from the Trusted Storage Pool
Prerequisites
- The
glusterdservice must be running on the server targeted for removal from the storage pool. See Chapter 24, Starting and Stopping the glusterd service for service start and stop commands. - The host names of the target servers must be resolvable by DNS.
- Run
gluster peer detach [server]to remove the server from the trusted storage pool.gluster peer detach server4 Detach successful
# gluster peer detach server4 Detach successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the peer status from all servers using the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 5. Setting Up Storage Volumes
Warning
Note
yum groupinstall "Infiniband Support" to install Infiniband packages.
Volume Types
- Distributed
- Distributes files across bricks in the volume.Use this volume type where scaling and redundancy requirements are not important, or provided by other hardware or software layers.See Section 5.5, “Creating Distributed Volumes” for additional information about this volume type.
- Replicated
- Replicates files across bricks in the volume.Use this volume type in environments where high-availability and high-reliability are critical.See Section 5.6, “Creating Replicated Volumes” for additional information about this volume type.
- Distributed Replicated
- Distributes files across replicated bricks in the volume.Use this volume type in environments where high-reliability and scalability are critical. This volume type offers improved read performance in most environments.See Section 5.7, “Creating Distributed Replicated Volumes” for additional information about this volume type.
- Arbitrated Replicated
- Replicates files across two bricks in a replica set, and replicates only metadata to the third brick.Use this volume type in environments where consistency is critical, but underlying storage space is at a premium.See Section 5.8, “Creating Arbitrated Replicated Volumes” for additional information about this volume type.
- Dispersed
- Disperses the file's data across the bricks in the volume.Use this volume type where you need a configurable level of reliability with a minimum space waste.See Section 5.9, “Creating Dispersed Volumes” for additional information about this volume type.
- Distributed Dispersed
- Distributes file's data across the dispersed sub-volume.Use this volume type where you need a configurable level of reliability with a minimum space waste.See Section 5.10, “Creating Distributed Dispersed Volumes” for additional information about this volume type.
5.1. Setting up Gluster Storage Volumes using gdeploy
- Setting-up the backend on several machines can be done from one's laptop/desktop. This saves time and scales up well when the number of nodes in the trusted storage pool increase.
- Flexibility in choosing the drives to configure. (sd, vd, ...).
- Flexibility in naming the logical volumes (LV) and volume groups (VG).
5.1.1. Getting Started
- Generate the passphrase-less SSH keys for the nodes which are going to be part of the trusted storage pool by running the following command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -N ''
# ssh-keygen -t rsa -N ''Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Set up key-based SSH authentication access between the gdeploy controller and servers by running the following command:
ssh-copy-id -i root@server
# ssh-copy-id -i root@serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
If you are using a Red Hat Gluster Storage node as the deployment node and not an external node, then the key-based SSH authentication must be set up for the Red Hat Gluster Storage node from where the installation is performed. - Enable the repository required to install Ansible by running the following command:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-ansible-2-rpms
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-ansible-2-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Install
ansibleby executing the following command:yum install ansible
# yum install ansibleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You must also ensure the following:
- Devices should be raw and unused
- Default system locale must be set to
en_USFor information on system locale, refer to the Setting the System Locale of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 System Administrator's Guide. - For multiple devices, use multiple volume groups, thinpool, and thinvol in the
gdeployconfiguration file
- Using a node in a trusted storage pool
- Using a machine outside the trusted storage pool
The gdeploy package is bundled as part of the initial installation of Red Hat Gluster Storage.
You must ensure that the Red Hat Gluster Storage is subscribed to the required channels. For more information see, Subscribing to the Red Hat Gluster Storage Server Channels in the Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 Installation Guide.
yum install gdeploy
# yum install gdeploygdeploy see, Installing Ansible to Support Gdeploy section in the Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 Installation Guide.
5.1.2. Setting up a Trusted Storage Pool
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sample
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sampleNote
gdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txtNote
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sample. To invoke the new configuration file, run gdeploy -c /path_to_file/config.txt command.
only setup the backend see, Section 5.1.3, “Setting up the Backend ”
only create a volume see, Section 5.1.4, “Creating Volumes”
only mount clients see, Section 5.1.5, “Mounting Clients”
5.1.3. Setting up the Backend
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sample
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sample- Using the [backend-setup] module
- Creating Physical Volume (PV), Volume Group (VG), and Logical Volume (LV) individually
Note
xfsprogs package must be installed before setting up the backend bricks using gdeploy.
5.1.3.1. Using the [backend-setup] Module
- Generic
- Specific
If the disk names are uniform across the machines then backend setup can be written as below. The backend is setup for all the hosts in the `hosts’ section.
If the disks names vary across the machines in the cluster then backend setup can be written for specific machines with specific disk names. gdeploy is quite flexible in allowing to do host specific setup in a single configuration file.
5.1.3.2. Creating Backend by Setting up PV, VG, and LV
5.1.4. Creating Volumes
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sample
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.samplegdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txt
Note
5.1.5. Mounting Clients
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sample
/usr/share/doc/gdeploy/examples/gluster.conf.sampleNote
fstype is NFS, then mention it as nfs-version. By default it is 3.
gdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txt5.1.6. Configuring a Volume
5.1.6.1. Adding and Removing a Brick
Modify the [volume] section in the configuration file to add a brick. For example:
[volume] action=add-brick volname=10.0.0.1:glustervol bricks=10.0.0.1:/rhgs/new_brick
[volume]
action=add-brick
volname=10.0.0.1:glustervol
bricks=10.0.0.1:/rhgs/new_brickgdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txtModify the [volume] section in the configuration file to remove a brick. For example:
[volume] action=remove-brick volname=10.0.0.1:glustervol bricks=10.0.0.2:/rhgs/brick state=commit
[volume]
action=remove-brick
volname=10.0.0.1:glustervol
bricks=10.0.0.2:/rhgs/brick
state=commitstate are stop, start, and force.
gdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txt5.1.6.2. Rebalancing a Volume
[volume] action=rebalance volname=10.70.46.13:glustervol state=start
[volume]
action=rebalance
volname=10.70.46.13:glustervol
state=startstate are stop, and fix-layout.
gdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txt5.1.6.3. Starting, Stopping, or Deleting a Volume
Modify the [volume] section in the configuration file to start a volume. For example:
[volume] action=start volname=10.0.0.1:glustervol
[volume]
action=start
volname=10.0.0.1:glustervolgdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txtModify the [volume] section in the configuration file to start a volume. For example:
[volume] action=stop volname=10.0.0.1:glustervol
[volume]
action=stop
volname=10.0.0.1:glustervolgdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txtModify the [volume] section in the configuration file to start a volume. For example:
[volume] action=delete volname=10.70.46.13:glustervol
[volume]
action=delete
volname=10.70.46.13:glustervolgdeploy -c conf.txt
# gdeploy -c conf.txt5.1.7. Configuration File
- [hosts]
- [devices]
- [disktype]
- [diskcount]
- [stripesize]
- [vgs]
- [pools]
- [lvs]
- [mountpoints]
- [peer]
- [clients]
- [volume]
- [backend-setup]
- [pv]
- [vg]
- [lv]
- [RH-subscription]
- [yum]
- [shell]
- [update-file]
- [service]
- [script]
- [firewalld]
- hosts
This is a mandatory section which contains the IP address or hostname of the machines in the trusted storage pool. Each hostname or IP address should be listed in a separate line.
For example:[hosts] 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2
[hosts] 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - devices
This is a generic section and is applicable to all the hosts listed in the [hosts] section. However, if sections of hosts such as the [hostname] or [IP-address] is present, then the data in the generic sections like [devices] is ignored. Host specific data take precedence. This is an optional section.
For example:[devices] /dev/sda /dev/sdb
[devices] /dev/sda /dev/sdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
When configuring the backend setup, the devices should be either listed in this section or in the host specific section. - disktype
This section specifies the disk configuration that is used while setting up the backend. gdeploy supports RAID 10, RAID 6, RAID 5, and JBOD configurations. This is an optional section and if the field is left empty, JBOD is taken as the default configuration. Valid values for this field are
raid10,raid6,raid5, andjbod.For example:[disktype] raid6
[disktype] raid6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - diskcount
This section specifies the number of data disks in the setup. This is a mandatory field if a RAID disk type is specified under
[disktype]. If the [disktype] is JBOD the [diskcount] value is ignored. This parameter is host specific.For example:[diskcount] 10
[diskcount] 10Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - stripesize
This section specifies the stripe_unit size in KB.
Case 1: This field is not necessary if the [disktype] is JBOD, and any given value will be ignored.Case 2: This is a mandatory field if [disktype] is specified as RAID 5 or RAID 6.For [disktype] RAID 10, the default value is taken as 256KB. Red Hat does not recommend changing this value. If you specify any other value the following warning is displayed:"Warning: We recommend a stripe unit size of 256KB for RAID 10"
"Warning: We recommend a stripe unit size of 256KB for RAID 10"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Do not add any suffixes like K, KB, M, etc. This parameter is host specific and can be added in the hosts section.For example:[stripesize] 128
[stripesize] 128Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - vgs
This section is deprecated in gdeploy 2.0. Please see [backend-setup] for more details for gdeploy 2.0. This section specifies the volume group names for the devices listed in [devices]. The number of volume groups in the [vgs] section should match the one in [devices]. If the volume group names are missing, the volume groups will be named as GLUSTER_vg{1, 2, 3, ...} as default.
For example:[vgs] CUSTOM_vg1 CUSTOM_vg2
[vgs] CUSTOM_vg1 CUSTOM_vg2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - pools
This section is deprecated in gdeploy 2.0. Please see [backend-setup] for more details for gdeploy 2.0. This section specifies the pool names for the volume groups specified in the [vgs] section. The number of pools listed in the [pools] section should match the number of volume groups in the [vgs] section. If the pool names are missing, the pools will be named as GLUSTER_pool{1, 2, 3, ...}.
For example:[pools] CUSTOM_pool1 CUSTOM_pool2
[pools] CUSTOM_pool1 CUSTOM_pool2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - lvs
This section is deprecated in gdeploy 2.0. Please see [backend-setup] for more details for gdeploy 2.0. This section provides the logical volume names for the volume groups specified in [vgs]. The number of logical volumes listed in the [lvs] section should match the number of volume groups listed in [vgs]. If the logical volume names are missing, it is named as GLUSTER_lv{1, 2, 3, ...}.
For example:[lvs] CUSTOM_lv1 CUSTOM_lv2
[lvs] CUSTOM_lv1 CUSTOM_lv2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - mountpoints
This section is deprecated in gdeploy 2.0. Please see [backend-setup] for more details for gdeploy 2.0. This section specifies the brick mount points for the logical volumes. The number of mount points should match the number of logical volumes specified in [lvs] If the mount points are missing, the mount points will be names as /gluster/brick{1, 2, 3…}.
For example:[mountpoints] /rhgs/brick1 /rhgs/brick2
[mountpoints] /rhgs/brick1 /rhgs/brick2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - peer
This section specifies the configurations for the Trusted Storage Pool management (TSP). This section helps in making all the hosts specified in the [hosts] section to either probe each other to create the trusted storage pool or detach all of them from the trusted storage pool. The only option in this section is the option names 'action' which can have it's values to be either probe or detach.
For example:[peer] action=probe
[peer] action=probeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - clients
This section specifies the client hosts and client_mount_points to mount the gluster storage volume created. The 'action' option is to be specified for the framework to determine the action that has to be performed. The options are 'mount' and 'unmount'. The Client hosts field is mandatory. If the mount points are not specified, default will be taken as /mnt/gluster for all the hosts.
The option fstype specifies how the gluster volume is to be mounted. Default is glusterfs (FUSE mount). The volume can also be mounted as NFS. Each client can have different types of volume mount, which has to be specified with a comma separated. The following fields are included:* action * hosts * fstype * client_mount_points
* action * hosts * fstype * client_mount_pointsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - volume
The section specifies the configuration options for the volume. The following fields are included in this section:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - action
This option specifies what action must be performed in the volume. The choices can be [create, delete, add-brick, remove-brick].
create: This choice is used to create a volume.delete: If the delete choice is used, all the options other than 'volname' will be ignored.add-brick or remove-brick: If the add-brick or remove-brick is chosen, extra option bricks with a comma separated list of brick names(in the format <hostname>:<brick path> should be provided. In case of remove-brick, state option should also be provided specifying the state of the volume after brick removal. - volname
This option specifies the volume name. Default name is glustervol
Note
- In case of a volume operation, the 'hosts' section can be omitted, provided volname is in the format <hostname>:<volname>, where hostname is the hostname / IP of one of the nodes in the cluster
- Only single volume creation/deletion/configuration is supported.
- transport
This option specifies the transport type. Default is tcp. Options are tcp or rdma or tcp,rdma.
- replica
This option will specify if the volume should be of type replica. options are yes and no. Default is no. If 'replica' is provided as yes, the 'replica_count' should be provided.
- disperse
This option specifies if the volume should be of type disperse. Options are yes and no. Default is no.
- disperse_count
This field is optional even if 'disperse' is yes. If not specified, the number of bricks specified in the command line is taken as the disperse_count value.
- redundancy_count
If this value is not specified, and if 'disperse' is yes, it's default value is computed so that it generates an optimal configuration.
- force
This is an optional field and can be used during volume creation to forcefully create the volume.
For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - backend-setup
Available in gdeploy 2.0. This section sets up the backend for using with GlusterFS volume. If more than one backend-setup has to be done, they can be done by numbering the section like [backend-setup1], [backend-setup2], ...
backend-setup section supports the following variables:- devices: This replaces the [pvs] section in gdeploy 1.x. devices variable lists the raw disks which should be used for backend setup. For example:
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This is a mandatory field. - dalign:The Logical Volume Manager can use a portion of the physical volume for storing its metadata while the rest is used as the data portion. Align the I/O at the Logical Volume Manager (LVM) layer using the dalign option while creating the physical volume. For example:
[backend-setup] devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=256k
[backend-setup] devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=256kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For JBOD, use an alignment value of 256K. For hardware RAID, the alignment value should be obtained by multiplying the RAID stripe unit size with the number of data disks. If 12 disks are used in a RAID 6 configuration, the number of data disks is 10; on the other hand, if 12 disks are used in a RAID 10 configuration, the number of data disks is 6.The following example is appropriate for 12 disks in a RAID 6 configuration with a stripe unit size of 128 KiB:[backend-setup] devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1280k
[backend-setup] devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1280kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example is appropriate for 12 disks in a RAID 10 configuration with a stripe unit size of 256 KiB:[backend-setup] devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1536k
[backend-setup] devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1536kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the previously configured physical volume settings for the dalign option, run thepvs -o +pe_start devicecommand. For example:pvs -o +pe_start disk PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree 1st PE /dev/sdb lvm2 a-- 9.09t 9.09t 1.25m
# pvs -o +pe_start disk PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree 1st PE /dev/sdb lvm2 a-- 9.09t 9.09t 1.25mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also set the dalign option in the PV section. - vgs: This is an optional variable. This variable replaces the [vgs] section in gdeploy 1.x. vgs variable lists the names to be used while creating volume groups. The number of VG names should match the number of devices or should be left blank. gdeploy will generate names for the VGs. For example:
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg1,custom_vg2,custom_vg3
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg1,custom_vg2,custom_vg3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A pattern can be provided for the vgs like custom_vg{1..3}, this will create three vgs.[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg{1..3}[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg{1..3}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - pools: This is an optional variable. The variable replaces the [pools] section in gdeploy 1.x. pools lists the thin pool names for the volume.
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg1,custom_vg2,custom_vg3 pools=custom_pool1,custom_pool2,custom_pool3
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg1,custom_vg2,custom_vg3 pools=custom_pool1,custom_pool2,custom_pool3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Similar to vg, pattern can be provided for thin pool names. For example custom_pool{1..3} - lvs: This is an optional variable. This variable replaces the [lvs] section in gdeploy 1.x. lvs lists the logical volume name for the volume.
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg1,custom_vg2,custom_vg3 pools=custom_pool1,custom_pool2,custom_pool3 lvs=custom_lv1,custom_lv2,custom_lv3
[backend-setup] devices=sda,sdb,sdc vgs=custom_vg1,custom_vg2,custom_vg3 pools=custom_pool1,custom_pool2,custom_pool3 lvs=custom_lv1,custom_lv2,custom_lv3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Patterns for LV can be provided similar to vg. For example custom_lv{1..3}. - mountpoints: This variable deprecates the [mountpoints] section in gdeploy 1.x. Mountpoints lists the mount points where the logical volumes should be mounted. Number of mount points should be equal to the number of logical volumes. For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - ssd - This variable is set if caching has to be added. For example, the backed setup with ssd for caching should be:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Specifying the name of the data LV is necessary while adding SSD. Make sure the datalv is created already. Otherwise ensure to create it in one of the earlier `backend-setup’ sections.
- PV
Available in gdeploy 2.0. If the user needs to have more control over setting up the backend, and does not want to use backend-setup section, then pv, vg, and lv modules are to be used. The pv module supports the following variables.
- action: Mandatory. Supports two values, 'create' and 'resize'Example: Creating physical volumes
[pv] action=create devices=vdb,vdc,vdd
[pv] action=create devices=vdb,vdc,vddCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example: Creating physical volumes on a specific host[pv:10.0.5.2] action=create devices=vdb,vdc,vdd
[pv:10.0.5.2] action=create devices=vdb,vdc,vddCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - devices: Mandatory. The list of devices to use for pv creation.
- expand: Used when
action=resize.Example: Expanding an already created pv[pv] action=resize devices=vdb expand=yes
[pv] action=resize devices=vdb expand=yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - shrink: Used when
action=resize.Example: Shrinking an already created pv[pv] action=resize devices=vdb shrink=100G
[pv] action=resize devices=vdb shrink=100GCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - dalign:The Logical Volume Manager can use a portion of the physical volume for storing its metadata while the rest is used as the data portion. Align the I/O at the Logical Volume Manager (LVM) layer using the dalign option while creating the physical volume. For example:
[pv] action=create devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=256k
[pv] action=create devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=256kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For JBOD, use an alignment value of 256K. For hardware RAID, the alignment value should be obtained by multiplying the RAID stripe unit size with the number of data disks. If 12 disks are used in a RAID 6 configuration, the number of data disks is 10; on the other hand, if 12 disks are used in a RAID 10 configuration, the number of data disks is 6.The following example is appropriate for 12 disks in a RAID 6 configuration with a stripe unit size of 128 KiB:[pv] action=create devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1280k
[pv] action=create devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1280kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example is appropriate for 12 disks in a RAID 10 configuration with a stripe unit size of 256 KiB:[pv] action=create devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1536k
[pv] action=create devices=sdb,sdc,sdd,sde dalign=1536kCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the previously configured physical volume settings for the dalign option, run thepvs -o +pe_start devicecommand. For example:pvs -o +pe_start disk PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree 1st PE /dev/sdb lvm2 a-- 9.09t 9.09t 1.25m
# pvs -o +pe_start disk PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree 1st PE /dev/sdb lvm2 a-- 9.09t 9.09t 1.25mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also set the dalign option in the backend-setup section.
- VG
Available in gdeploy 2.0. This module is used to create and extend volume groups. The vg module supports the following variables.
- action - Action can be one of create or extend.
- pvname - PVs to use to create the volume. For more than one PV use comma separated values.
- vgname - The name of the vg. If no name is provided GLUSTER_vg will be used as default name.
- one-to-one - If set to yes, one-to-one mapping will be done between pv and vg.
If action is set to extend, the vg will be extended to include pv provided.Example1: Create a vg named images_vg with two PVs[vg] action=create vgname=images_vg pvname=sdb,sdc
[vg] action=create vgname=images_vg pvname=sdb,sdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example2: Create two vgs named rhgs_vg1 and rhgs_vg2 with two PVs[vg] action=create vgname=rhgs_vg pvname=sdb,sdc one-to-one=yes
[vg] action=create vgname=rhgs_vg pvname=sdb,sdc one-to-one=yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example3: Extend an existing vg with the given disk.[vg] action=extend vgname=rhgs_images pvname=sdc
[vg] action=extend vgname=rhgs_images pvname=sdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - LV
Available in gdeploy 2.0. This module is used to create, setup-cache, and convert logical volumes. The lv module supports the following variables:
action - The action variable allows three values `create’, `setup-cache’, `convert’, and `change’. If the action is 'create', the following options are supported:- lvname: The name of the logical volume, this is an optional field. Default is GLUSTER_lv
- poolname - Name of the thinpool volume name, this is an optional field. Default is GLUSTER_pool
- lvtype - Type of the logical volume to be created, allowed values are `thin’ and `thick’. This is an optional field, default is thick.
- size - Size of the logical volume volume. Default is to take all available space on the vg.
- extent - Extent size, default is 100%FREE
- force - Force lv create, do not ask any questions. Allowed values `yes’, `no’. This is an optional field, default is yes.
- vgname - Name of the volume group to use.
- pvname - Name of the physical volume to use.
- chunksize - The size of the chunk unit used for snapshots, cache pools, and thin pools. By default this is specified in kilobytes. For RAID 5 and 6 volumes, gdeploy calculates the default chunksize by multiplying the stripe size and the disk count. For RAID 10, the default chunksize is 256 KB. See Section 20.2, “Brick Configuration” for details.
Warning
Red Hat recommends using at least the default chunksize. If the chunksize is too small and your volume runs out of space for metadata, the volume is unable to create data. This includes the data required to increase the size of the metadata pool or to migrate data away from a volume that has run out of metadata space. Red Hat recommends monitoring your logical volumes to ensure that they are expanded or more storage created before metadata volumes become completely full. - poolmetadatasize - Sets the size of pool's metadata logical volume. Allocate the maximum chunk size (16 GiB) if possible. If you allocate less than the maximum, allocate at least 0.5% of the pool size to ensure that you do not run out of metadata space.
Warning
If your metadata pool runs out of space, you cannot create data. This includes the data required to increase the size of the metadata pool or to migrate data away from a volume that has run out of metadata space. Monitor your metadata pool using thelvs -o+metadata_percentcommand and ensure that it does not run out of space. - virtualsize - Creates a thinly provisioned device or a sparse device of the given size
- mkfs - Creates a filesystem of the given type. Default is to use xfs.
- mkfs-opts - mkfs options.
- mount - Mount the logical volume.
If the action is setup-cache, the below options are supported:- ssd - Name of the ssd device. For example sda/vda/ … to setup cache.
- vgname - Name of the volume group.
- poolname - Name of the pool.
- cache_meta_lv - Due to requirements from dm-cache (the kernel driver), LVM further splits the cache pool LV into two devices - the cache data LV and cache metadata LV. Provide the cache_meta_lv name here.
- cache_meta_lvsize - Size of the cache meta lv.
- cache_lv - Name of the cache data lv.
- cache_lvsize - Size of the cache data.
- force - Force
If the action is convert, the below options are supported:- lvtype - type of the lv, available options are thin and thick
- force - Force the lvconvert, default is yes.
- vgname - Name of the volume group.
- poolmetadata - Specifies cache or thin pool metadata logical volume.
- cachemode - Allowed values writeback, writethrough. Default is writethrough.
- cachepool - This argument is necessary when converting a logical volume to a cache LV. Name of the cachepool.
- lvname - Name of the logical volume.
- chunksize - The size of the chunk unit used for snapshots, cache pools, and thin pools. By default this is specified in kilobytes. For RAID 5 and 6 volumes, gdeploy calculates the default chunksize by multiplying the stripe size and the disk count. For RAID 10, the default chunksize is 256 KB. See Section 20.2, “Brick Configuration” for details.
Warning
Red Hat recommends using at least the default chunksize. If the chunksize is too small and your volume runs out of space for metadata, the volume is unable to create data. Red Hat recommends monitoring your logical volumes to ensure that they are expanded or more storage created before metadata volumes become completely full. - poolmetadataspare - Controls creation and maintanence of pool metadata spare logical volume that will be used for automated pool recovery.
- thinpool - Specifies or converts logical volume into a thin pool's data volume. Volume’s name or path has to be given.
If the action is change, the below options are supported:- lvname - Name of the logical volume.
- vgname - Name of the volume group.
- zero - Set zeroing mode for thin pool.
Example 1: Create a thin LVCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 2: Create a thick LVCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If there are more than one LVs, then the LVs can be created by numbering the LV sections, like [lv1], [lv2] … - RH-subscription
Available in gdeploy 2.0. This module is used to subscribe, unsubscribe, attach, enable repos etc. The RH-subscription module allows the following variables:
This module is used to subscribe, unsubscribe, attach, enable repos etc. The RH-subscription module allows the following variables:If the action is register, the following options are supported:- username/activationkey: Username or activationkey.
- password/activationkey: Password or activation key
- auto-attach: true/false
- pool: Name of the pool.
- repos: Repos to subscribe to.
- disable-repos: Repo names to disable. Leaving this option blank will disable all the repos.
- ignore_register_errors: If set to no, gdeploy will exit if system registration fails.
- If the action is attach-pool the following options are supported:pool - Pool name to be attached.ignore_attach_pool_errors - If set to no, gdeploy fails if attach-pool fails.
- If the action is enable-repos the following options are supported:repos - List of comma separated repos that are to be subscribed to.ignore_enable_errors - If set to no, gdeploy fails if enable-repos fail.
- If the action is disable-repos the following options are supported:repos - List of comma separated repos that are to be subscribed to.ignore_disable_errors - If set to no, gdeploy fails if disable-repos fail
- If the action is unregister the systems will be unregistered.ignore_unregister_errors - If set to no, gdeploy fails if unregistering fails.
Example 1: Subscribe to Red Hat Subscription network:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 2: Disable all the repos:[RH-subscription2] action=disable-repos repos=
[RH-subscription2] action=disable-repos repos=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 3: Enable a few repos[RH-subscription3] action=enable-repos repos=rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-7-server-rhev-mgmt-agent-rpms ignore_enable_errors=no
[RH-subscription3] action=enable-repos repos=rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-7-server-rhev-mgmt-agent-rpms ignore_enable_errors=noCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - yum
Available in gdeploy 2.0. This module is used to install or remove rpm packages, with the yum module we can add repos as well during the install time.
The action variable allows two values `install’ and `remove’.If the action is install the following options are supported:- packages - Comma separated list of packages that are to be installed.
- repos - The repositories to be added.
- gpgcheck - yes/no values have to be provided.
- update - Whether yum update has to be initiated.
If the action is remove then only one option has to be provided:- remove - The comma separated list of packages to be removed.
For exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Install a package on a particular host.[yum2:host1] action=install gpgcheck=no packages=rhevm-appliance
[yum2:host1] action=install gpgcheck=no packages=rhevm-applianceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - shell
Available in gdeploy 2.0. This module allows user to run shell commands on the remote nodes.
Currently shell provides a single action variable with value execute. And a command variable with any valid shell command as value.The below command will execute vdsm-tool on all the nodes.[shell] action=execute command=vdsm-tool configure --force
[shell] action=execute command=vdsm-tool configure --forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - update-file
Available in gdeploy 2.0. update-file module allows users to copy a file, edit a line in a file, or add new lines to a file. action variable can be any of copy, edit, or add.
When the action variable is set to copy, the following variables are supported.- src - The source path of the file to be copied from.
- dest - The destination path on the remote machine to where the file is to be copied to.
When the action variable is set to edit, the following variables are supported.- dest - The destination file name which has to be edited.
- replace - A regular expression, which will match a line that will be replaced.
- line - Text that has to be replaced.
When the action variable is set to add, the following variables are supported.- dest - File on the remote machine to which a line has to be added.
- line - Line which has to be added to the file. Line will be added towards the end of the file.
Example 1: Copy a file to a remote machine.[update-file] action=copy src=/tmp/foo.cfg dest=/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
[update-file] action=copy src=/tmp/foo.cfg dest=/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 2: Edit a line in the remote machine, in the below example lines that have allowed_hosts will be replaced with allowed_hosts=host.redhat.com[update-file] action=edit dest=/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg replace=allowed_hosts line=allowed_hosts=host.redhat.com
[update-file] action=edit dest=/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg replace=allowed_hosts line=allowed_hosts=host.redhat.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 3: Add a line to the end of a file[update-file] action=add dest=/etc/ntp.conf line=server clock.redhat.com iburst
[update-file] action=add dest=/etc/ntp.conf line=server clock.redhat.com iburstCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - service
Available in gdeploy 2.0. The service module allows user to start, stop, restart, reload, enable, or disable a service. The action variable specifies these values.
When action variable is set to any of start, stop, restart, reload, enable, disable the variable servicename specifies which service to start, stop etc.- service - Name of the service to start, stop etc.
Example: enable and start ntp daemon.[service1] action=enable service=ntpd
[service1] action=enable service=ntpdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow [service2] action=restart service=ntpd
[service2] action=restart service=ntpdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - script
Available in gdeploy 2.0. script module enables user to execute a script/binary on the remote machine. action variable is set to execute. Allows user to specify two variables file and args.
- file - An executable on the local machine.
- args - Arguments to the above program.
Example: Execute script disable-multipath.sh on all the remote nodes listed in `hosts’ section.[script] action=execute file=/usr/share/ansible/gdeploy/scripts/disable-multipath.sh
[script] action=execute file=/usr/share/ansible/gdeploy/scripts/disable-multipath.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - firewalld
Available in gdeploy 2.0. firewalld module allows the user to manipulate firewall rules. action variable supports two values `add’ and `delete’. Both add and delete support the following variables:
- ports/services - The ports or services to add to firewall.
- permanent - Whether to make the entry permanent. Allowed values are true/false
- zone - Default zone is public
For example:[firewalld] action=add ports=111/tcp,2049/tcp,54321/tcp,5900/tcp,5900-6923/tcp,5666/tcp,16514/tcp services=glusterfs
[firewalld] action=add ports=111/tcp,2049/tcp,54321/tcp,5900/tcp,5900-6923/tcp,5666/tcp,16514/tcp services=glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.1.8. Deploying NFS Ganesha using gdeploy
5.1.8.1. Prerequisites
You must subscribe to subscription manager and obtain the NFS Ganesha packages before continuing further.
[RH-subscription1] action=register username=<user>@redhat.com password=<password> pool=<pool-id>
[RH-subscription1]
action=register
username=<user>@redhat.com
password=<password>
pool=<pool-id>gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>To enable the required repos, add the following details in the configuration file:
[RH-subscription2] action=enable-repos repos=rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-nfs-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-ha-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-7-server-ansible-2-rpms
[RH-subscription2]
action=enable-repos
repos=rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-nfs-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-ha-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-7-server-ansible-2-rpmsgdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>To enable the firewall ports, add the following details in the configuration file:
[firewalld] action=add ports=111/tcp,2049/tcp,54321/tcp,5900/tcp,5900-6923/tcp,5666/tcp,16514/tcp services=glusterfs,nlm,nfs,rpc-bind,high-availability,mountd,rquota
[firewalld]
action=add
ports=111/tcp,2049/tcp,54321/tcp,5900/tcp,5900-6923/tcp,5666/tcp,16514/tcp
services=glusterfs,nlm,nfs,rpc-bind,high-availability,mountd,rquotaNote
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>To install the required package, add the following details in the configuration file
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>5.1.8.2. Supported Actions
- Creating a Cluster
- Destroying a Cluster
- Adding a Node
- Deleting a Node
- Exporting a Volume
- Unexporting a Volume
- Refreshing NFS Ganesha Configuration
This action creates a fresh NFS-Ganesha setup on a given volume. For this action the nfs-ganesha in the configuration file section supports the following variables:
- ha-name: This is an optional variable. By default it is ganesha-ha-360.
- cluster-nodes: This is a required argument. This variable expects comma separated values of cluster node names, which is used to form the cluster.
- vip: This is a required argument. This variable expects comma separated list of ip addresses. These will be the virtual ip addresses.
- volname: This is an optional variable if the configuration contains the [volume] section
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
The action, destroy-cluster cluster disables NFS Ganesha. It allows one variable, cluster-nodes.
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>The add-node action allows three variables:
nodes: Accepts a list of comma separated hostnames that have to be added to the clustervip: Accepts a list of comma separated ip addresses.cluster_nodes: Accepts a list of comma separated nodes of the NFS Ganesha cluster.
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
The delete-node action takes one variable, nodes, which specifies the node or nodes to delete from the NFS Ganesha cluster in a comma delimited list.
This action exports a volume. export-volume action supports one variable, volname.
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
This action unexports a volume. unexport-volume action supports one variable, volname.
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
This action will add/delete or add a config block to the configuration file and runs refresh-config on the cluster.
refresh-config supports the following variables:
- del-config-lines
- block-name
- volname
- ha-conf-dir
- update_config_lines
Note
refresh-config with client block has few limitations:
- Works for only one client
- User cannot delete a line from a config block
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>5.1.9. Deploying Samba / CTDB using gdeploy
5.1.9.1. Prerequisites
You must subscribe to subscription manager and obtain the Samba packages before continuing further.
[RH-subscription1] action=register username=<user>@redhat.com password=<password> pool=<pool-id>
[RH-subscription1]
action=register
username=<user>@redhat.com
password=<password>
pool=<pool-id>gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>To enable the required repos, add the following details in the configuration file:
[RH-subscription2] action=enable-repos repos=rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-samba-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-7-server-ansible-2-rpms
[RH-subscription2]
action=enable-repos
repos=rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-samba-for-rhel-7-server-rpms,rhel-7-server-ansible-2-rpmsgdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>To enable the firewall ports, add the following details in the configuration file:
[firewalld] action=add ports=54321/tcp,5900/tcp,5900-6923/tcp,5666/tcp,4379/tcp services=glusterfs,samba,high-availability
[firewalld]
action=add
ports=54321/tcp,5900/tcp,5900-6923/tcp,5666/tcp,4379/tcp
services=glusterfs,samba,high-availabilitygdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>To install the required package, add the following details in the configuration file
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>5.1.9.2. Setting up Samba
- Enabling Samba on an existing volume
- Enabling Samba while creating a volume
If a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume is already present, then the user has to mention the action as smb-setup in the volume section. It is necessary to mention all the hosts that are in the cluster, as gdeploy updates the glusterd configuration files on each of the hosts.
Note
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
If Samba has be set up while creating a volume, the a variable smb has to be set to yes in the configuration file.
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>Note
smb_username and smb_mountpoint are necessary if samba has to be setup with the acls set correctly.
5.1.9.3. Setting up CTDB
ctdb_nodes parameter, as shown in the following example.
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>5.1.10. Enabling SSL on a Volume
5.1.10.1. Creating a Volume and Enabling SSL
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>5.1.10.2. Enabling SSL on an Existing Volume:
gdeploy -c <config_file_name>
# gdeploy -c <config_file_name>5.1.11. Limiting Gluster Resources
slice_setup=yes when you start the glusterd service. This applies a set of resource limitations for the glusterd service and all of its child processes.
systemctl.
5.1.12. Gdeploy log files
/home/username/.gdeploy/logs/gdeploy.log instead of the /var/log directory.
GDEPLOY_LOGFILE environment variable. For example, to set the gdeploy log location to /var/log/gdeploy/gdeploy.log for this session, run the following command:
export GDEPLOY_LOGFILE=/var/log/gdeploy/gdeploy.log
$ export GDEPLOY_LOGFILE=/var/log/gdeploy/gdeploy.log/home/username/.bash_profile file for that user.
5.2. Managing Volumes using Heketi
Note

Figure 5.1. Heketi volume creation
5.2.1. Prerequisites
- Configure SSH access
- Configure key-based SSH authentication without a password for the Heketi user. For a non-root user:
- Ensure the user and server specified when copying SSH keys matches the user provided to Heketi in the Heketi configuration file.
- Ensure the user can use
sudoby disablingrequirettyin the/etc/sudoersfile and addingsudo: trueto the sshexec configuration section in the Heketi configuration file.
- Configure the firewall
- Ensure that Heketi can accept TCP requests over the port specified in the
heketi.jsonfile. For example, on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations, run the following commands:firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=port/tcp --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations, run the following commands:iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport port -j ACCEPT service iptables save
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport port -j ACCEPT # service iptables saveCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start glusterd
- After Red Hat Gluster Storage is installed, ensure that the
glusterdservice is started. - Ensure disks are raw format
- Disks to be registered with Heketi must be in the raw format.
5.2.2. Installing Heketi
Note
yum install heketi-client
# yum install heketi-clientyum install heketi
# yum install heketi5.2.3. Starting the Heketi Server
- Generate the passphrase-less SSH keys for the nodes which are going to be part of the trusted storage pool by running the following command:
ssh-keygen -f /etc/heketi/heketi_key -t rsa -N ''
# ssh-keygen -f /etc/heketi/heketi_key -t rsa -N ''Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change the owner and the group permissions for the heketi keys using the following command:
chown heketi:heketi /etc/heketi/heketi_key*
# chown heketi:heketi /etc/heketi/heketi_key*Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Set up key-based SSH authentication access between Heketi and the Red Hat Gluster Storage servers by running the following command:
ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/heketi_key.pub root@server
# ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/heketi_key.pub root@serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - As a non root user, set up password-less SSH access between Heketi and the Red Hat Gluster Storage servers by running the following command:
ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/heketi_key.pub user@server
$ ssh-copy-id -i /etc/heketi/heketi_key.pub user@serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
To run SSH as a non-root, the username mentioned inusername>@serverfor ssh-copy-id must match with the user name provided to Heketi in the Heketi configuration file below.- Setup the heketi.json configuration file. The file is located in /etc/heketi/heketi.json. The configuration file has the information required to run the Heketi server. The config file must be in JSON format with the following settings:
- port: string, Heketi REST service port number
- use_auth: bool, Enable JWT Authentication
- jwt: map, JWT Authentication settings
- admin: map, Settings for the Heketi administrator
- key: string,
- user: map, Settings for the Heketi volume requests access user
- key: string, t
- glusterfs: map, Red Hat Gluster Storage settings
- executor: string, Determines the type of command executor to use. Possible values are:
- mock: Does not send any commands out to servers. Can be used for development and tests
- ssh: Sends commands to real systems over ssh
- db: string, Location of Heketi database
- sshexec: map, SSH configuration
- keyfile: string, File with private ssh key
- user: string, SSH user
Following is an example of the JSON file:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The location for the private SSH key that is created must be set in thekeyfilesetting of the configuration file, and the key should be readable by the heketi user.
5.2.3.1. Starting the Server
- Enable heketi by executing the following command:
systemctl enable heketi
# systemctl enable heketiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the Heketi server, by executing the following command:
systemctl start heketi
# systemctl start heketiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To check the status of the Heketi server, execute the following command:
systemctl status heketi
# systemctl status heketiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To check the logs, execute the following command:
journalctl -u heketi
# journalctl -u heketiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
5.2.3.2. Verifying the Configuration
curl http://<server:port>/hello
# curl http://<server:port>/helloheketi-cli --server http://<server:port> --user <user> --secret <secret> cluster list
# heketi-cli --server http://<server:port> --user <user> --secret <secret> cluster list5.2.4. Setting up the Topology
5.2.4.1. Prerequisites
Note
5.2.4.2. Topology Setup
Note
topology-sample.json) is installed with the ‘heketi-client’ package in the /usr/share/heketi/ directory.
export HEKETI_CLI_SERVER=http://<heketi_server:port> heketi-cli topology load --json=<topology_file>
# export HEKETI_CLI_SERVER=http://<heketi_server:port>
# heketi-cli topology load --json=<topology_file>topology_file is a file in JSON format describing the clusters, nodes, and disks to add to Heketi. The format of the file is as follows:
- Each element on the array is a map which describes the cluster as follows
- nodes: Array of nodes in a clusterEach element on the array is a map which describes the node as follows
- node: Same as Node Add, except there is no need to supply the cluster ID.
- devices: Name of each disk to be added
- zone: The value represents failure domain on which the node exists.
- Topology file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Load the Heketi JSON file:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to check the details of a particular node:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to check the details of the cluster:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To check the details of the device, execute the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.5. Creating a Volume
- Execute the following command to check the various option for creating a volume:
heketi-cli volume create --size=<size in Gb> [options]
# heketi-cli volume create --size=<size in Gb> [options]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For example: After setting up the topology file with two nodes on one failure domain, and two nodes in another failure domain, create a 100Gb volume using the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To check the details of the device, execute the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.6. Expanding a Volume
- Find the volume id using the volume list command.
heketi-cli volume list Id:9d219903604cabed5ba234f4f04b2270 Cluster:dab7237f6d6d4825fca8b83a0fac24ac Name:vol_9d219903604cabed5ba234f4f04b2270 Id:a8770efe13a2269a051712905449f1c1 Cluster:dab7237f6d6d4825fca8b83a0fac24ac Name:user1vol1
# heketi-cli volume list Id:9d219903604cabed5ba234f4f04b2270 Cluster:dab7237f6d6d4825fca8b83a0fac24ac Name:vol_9d219903604cabed5ba234f4f04b2270 Id:a8770efe13a2269a051712905449f1c1 Cluster:dab7237f6d6d4825fca8b83a0fac24ac Name:user1vol1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - This volume id can be used as input to heketi-cli for expanding the volume.
heketi-cli volume expand --volume <volume_id> --expand-size <size>
# heketi-cli volume expand --volume <volume_id> --expand-size <size>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2.7. Deleting a Volume
heketi-cli volume delete <vol_id>
# heketi-cli volume delete <vol_id>heketi-cli volume delete 0729fe8ce9cee6eac9ccf01f84dc88cc Volume 0729fe8ce9cee6eac9ccf01f84dc88cc deleted
$ heketi-cli volume delete 0729fe8ce9cee6eac9ccf01f84dc88cc
Volume 0729fe8ce9cee6eac9ccf01f84dc88cc deleted5.3. About Encrypted Disk
- For RHEL 6, see Disk Encryption Appendix of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Installation Guide.
- For RHEL 7, see Encryption of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Security Guide.
5.4. Formatting and Mounting Bricks
5.4.1. Creating Bricks Manually
Important
- Red Hat supports formatting a Logical Volume using the XFS file system on the bricks.
5.4.1.1. Creating a Thinly Provisioned Logical Volume
- Create a physical volume(PV) by using the
pvcreatecommand.pvcreate --dataalignment alignment_value device
# pvcreate --dataalignment alignment_value deviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:pvcreate --dataalignment 1280K /dev/sdb
# pvcreate --dataalignment 1280K /dev/sdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Here,/dev/sdbis a storage device.Use the correctdataalignmentoption based on your device. For more information, see Section 20.2, “Brick Configuration”Note
The device name and the alignment value will vary based on the device you are using. - Create a Volume Group (VG) from the PV using the
vgcreatecommand:vgcreate --physicalextentsize alignment_value volgroup device
# vgcreate --physicalextentsize alignment_value volgroup deviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:vgcreate --physicalextentsize 1280K rhs_vg /dev/sdb
# vgcreate --physicalextentsize 1280K rhs_vg /dev/sdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a thin-pool using the following commands:
lvcreate --thin volgroup/poolname --size pool_sz --chunksize chunk_sz --poolmetadatasize metadev_sz --zero n
# lvcreate --thin volgroup/poolname --size pool_sz --chunksize chunk_sz --poolmetadatasize metadev_sz --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:lvcreate --thin rhs_vg/rhs_pool --size 2T --chunksize 1280K --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin rhs_vg/rhs_pool --size 2T --chunksize 1280K --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure you read Chapter 20, Tuning for Performance to select appropriate values forchunksizeandpoolmetadatasize. - Create a thinly provisioned volume that uses the previously created pool by running the
lvcreatecommand with the--virtualsizeand--thinoptions:lvcreate --virtualsize size --thin volgroup/poolname --name volname
# lvcreate --virtualsize size --thin volgroup/poolname --name volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:lvcreate --virtualsize 1G --thin rhs_vg/rhs_pool --name rhs_lv
# lvcreate --virtualsize 1G --thin rhs_vg/rhs_pool --name rhs_lvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow It is recommended that only one LV should be created in a thin pool. - Format bricks using the supported XFS configuration, mount the bricks, and verify the bricks are mounted correctly. To enhance the performance of Red Hat Gluster Storage, ensure you read Chapter 20, Tuning for Performance before formatting the bricks.
Important
Snapshots are not supported on bricks formatted with external log devices. Do not use-l logdev=deviceoption withmkfs.xfscommand for formatting the Red Hat Gluster Storage bricks.mkfs.xfs -f -i size=512 -n size=8192 -d su=128k,sw=10 device
# mkfs.xfs -f -i size=512 -n size=8192 -d su=128k,sw=10 deviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow DEVICE is the created thin LV. The inode size is set to 512 bytes to accommodate for the extended attributes used by Red Hat Gluster Storage. - Run
# mkdir /mountpointto create a directory to link the brick to.mkdir /rhgs
# mkdir /rhgsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add an entry in
/etc/fstab:/dev/volgroup/volname /mountpoint xfs rw,inode64,noatime,nouuid,x-systemd.device-timeout=10min 1 2
/dev/volgroup/volname /mountpoint xfs rw,inode64,noatime,nouuid,x-systemd.device-timeout=10min 1 2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:/dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv /rhgs xfs rw,inode64,noatime,nouuid,x-systemd.device-timeout=10min 1 2
/dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv /rhgs xfs rw,inode64,noatime,nouuid,x-systemd.device-timeout=10min 1 2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
mount /mountpointto mount the brick. - Run the
df -hcommand to verify the brick is successfully mounted:df -h /dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv 16G 1.2G 15G 7% /rhgs
# df -h /dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv 16G 1.2G 15G 7% /rhgsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If SElinux is enabled, then the SELinux labels that has to be set manually for the bricks created using the following commands:
semanage fcontext -a -t glusterd_brick_t /rhgs/brick1 restorecon -Rv /rhgs/brick1
# semanage fcontext -a -t glusterd_brick_t /rhgs/brick1 # restorecon -Rv /rhgs/brick1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.4.2. Using Subdirectory as the Brick for Volume
/rhgs directory is the mounted file system and is used as the brick for volume creation. However, for some reason, if the mount point is unavailable, any write continues to happen in the /rhgs directory, but now this is under root file system.
/bricks. After the file system is available, create a directory called /rhgs/brick1 and use it for volume creation. Ensure that no more than one brick is created from a single mount. This approach has the following advantages:
- When the
/rhgsfile system is unavailable, there is no longer/rhgs/brick1directory available in the system. Hence, there will be no data loss by writing to a different location. - This does not require any additional file system for nesting.
- Create the
brick1subdirectory in the mounted file system.mkdir /rhgs/brick1
# mkdir /rhgs/brick1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Repeat the above steps on all nodes. - Create the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume using the subdirectories as bricks.
gluster volume create distdata01 ad-rhs-srv1:/rhgs/brick1 ad-rhs-srv2:/rhgs/brick2
# gluster volume create distdata01 ad-rhs-srv1:/rhgs/brick1 ad-rhs-srv2:/rhgs/brick2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
gluster volume start distdata01
# gluster volume start distdata01Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of the volume.
gluster volume status distdata01
# gluster volume status distdata01Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
df -h /dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv1 16G 1.2G 15G 7% /rhgs1 /dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv2 16G 1.2G 15G 7% /rhgs2
# df -h
/dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv1 16G 1.2G 15G 7% /rhgs1
/dev/rhs_vg/rhs_lv2 16G 1.2G 15G 7% /rhgs2gluster volume create test-volume server1:/rhgs1/brick1 server2:/rhgs1/brick1 server1:/rhgs2/brick2 server2:/rhgs2/brick2
# gluster volume create test-volume server1:/rhgs1/brick1 server2:/rhgs1/brick1 server1:/rhgs2/brick2 server2:/rhgs2/brick25.4.3. Reusing a Brick from a Deleted Volume
# mkfs.xfs -f -i size=512 device to reformat the brick to supported requirements, and make it available for immediate reuse in a new volume.
Note
5.4.4. Cleaning An Unusable Brick
- Delete all previously existing data in the brick, including the
.glusterfssubdirectory. - Run
# setfattr -x trusted.glusterfs.volume-id brickand# setfattr -x trusted.gfid brickto remove the attributes from the root of the brick. - Run
# getfattr -d -m . brickto examine the attributes set on the volume. Take note of the attributes. - Run
# setfattr -x attribute brickto remove the attributes relating to the glusterFS file system.Thetrusted.glusterfs.dhtattribute for a distributed volume is one such example of attributes that need to be removed.
5.5. Creating Distributed Volumes
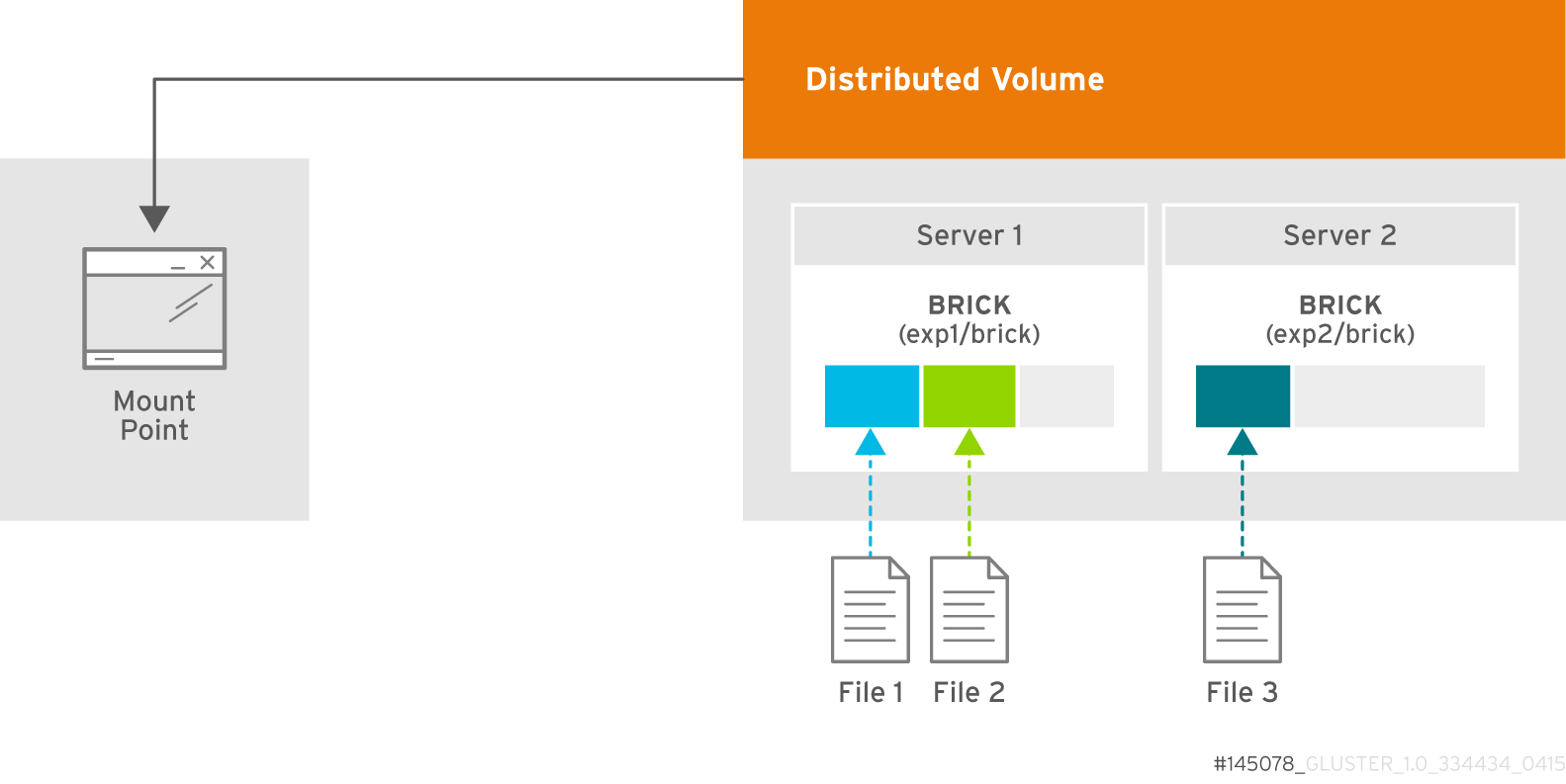
Figure 5.2. Illustration of a Distributed Volume
Warning
Create a Distributed Volume
gluster volume create command to create different types of volumes, and gluster volume info command to verify successful volume creation.
Prerequisites
- A trusted storage pool has been created, as described in Section 4.1, “Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool”.
- Understand how to start and stop volumes, as described in Section 5.11, “Starting Volumes”.
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the distributed volume.The syntax isgluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” for a full list of parameters.Red Hat recommends disabling theperformance.client-io-threadsoption on distributed volumes, as this option tends to worsen performance. Run the following command to disableperformance.client-io-threads:gluster volume set VOLNAME performance.client-io-threads off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME performance.client-io-threads offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 5.1. Distributed Volume with Two Storage Servers
gluster volume create test-volume server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 5.2. Distributed Volume over InfiniBand with Four Servers
gluster volume create test-volume transport rdma server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume transport rdma server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.The following output is the result of Example 5.1, “Distributed Volume with Two Storage Servers”.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.6. Creating Replicated Volumes
gluster volume create to create different types of volumes, and gluster volume info to verify successful volume creation.
- A trusted storage pool has been created, as described in Section 4.1, “Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool”.
- Understand how to start and stop volumes, as described in Section 5.11, “Starting Volumes”.
5.6.1. Creating Two-way Replicated Volumes (Deprecated)
Warning
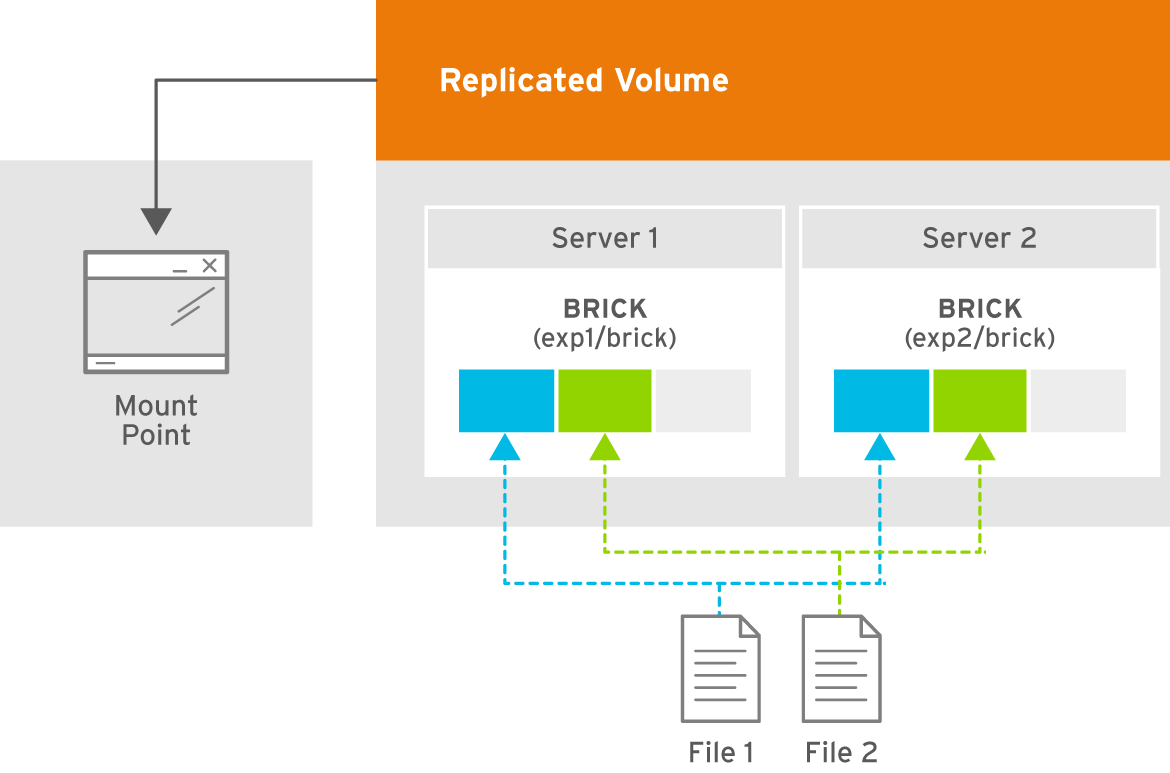
Figure 5.3. Illustration of a Two-way Replicated Volume
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the replicated volume.The syntax is# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME [replica COUNT] [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” for a full list of parameters.Example 5.3. Replicated Volume with Two Storage Servers
The order in which bricks are specified determines how they are replicated with each other. For example, every2bricks, where2is the replica count, forms a replica set. This is illustrated in Figure 5.3, “Illustration of a Two-way Replicated Volume” .gluster volume create test-volume replica 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick2 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume replica 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick2 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.
Important
5.6.2. Creating Three-way Replicated Volumes
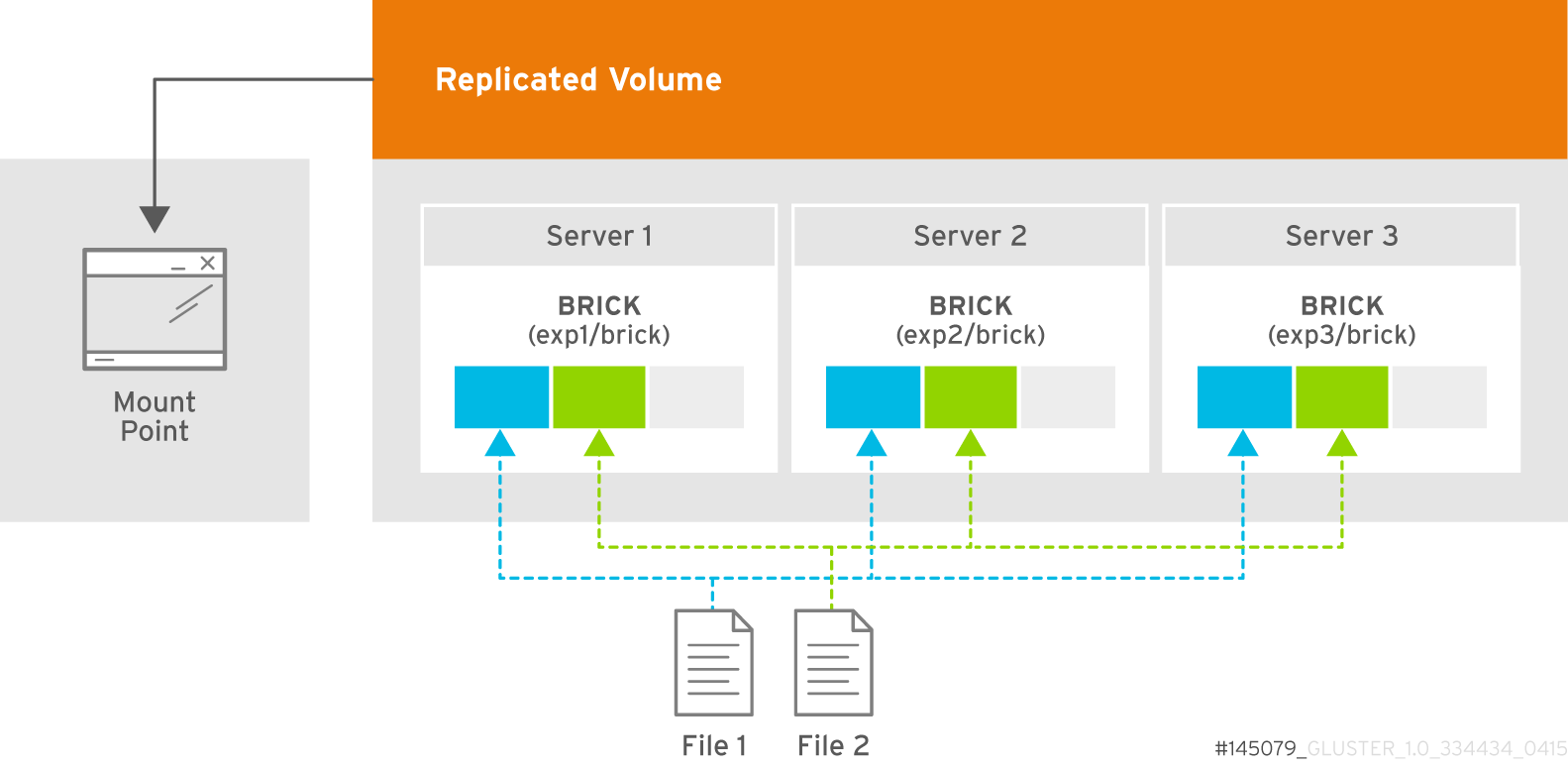
Figure 5.4. Illustration of a Three-way Replicated Volume
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the replicated volume.The syntax is# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME [replica COUNT] [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” for a full list of parameters.Example 5.4. Replicated Volume with Three Storage Servers
The order in which bricks are specified determines how bricks are replicated with each other. For example, everynbricks, where3is the replica count forms a replica set. This is illustrated in Figure 5.4, “Illustration of a Three-way Replicated Volume”.gluster volume create test-volume replica 3 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick2 server3:/rhgs/brick3 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume replica 3 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick2 server3:/rhgs/brick3 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.
Important
5.6.3. Creating Sharded Replicated Volumes
.shard directory, and are named with the GFID and a number indicating the order of the pieces. For example, if a file is split into four pieces, the first piece is named GFID and stored normally. The other three pieces are named GFID.1, GFID.2, and GFID.3 respectively. They are placed in the .shard directory and distributed evenly between the various bricks in the volume.
5.6.3.1. Supported use cases
Important
Important
Example 5.5. Example: Three-way replicated sharded volume
- Set up a three-way replicated volume, as described in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Administration Guide: https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/red_hat_gluster_storage/3.4/html/Administration_Guide/sect-Creating_Replicated_Volumes.html#Creating_Three-way_Replicated_Volumes.
- Before you start your volume, enable sharding on the volume.
gluster volume set test-volume features.shard enable
# gluster volume set test-volume features.shard enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the volume and ensure it is working as expected.
gluster volume test-volume start gluster volume info test-volume
# gluster volume test-volume start # gluster volume info test-volumeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.6.3.2. Configuration Options
-
features.shard - Enables or disables sharding on a specified volume. Valid values are
enableanddisable. The default value isdisable.gluster volume set volname features.shard enable
# gluster volume set volname features.shard enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that this only affects files created after this command is run; files created before this command is run retain their old behaviour. -
features.shard-block-size - Specifies the maximum size of the file pieces when sharding is enabled. The supported value for this parameter is 512MB.
gluster volume set volname features.shard-block-size 32MB
# gluster volume set volname features.shard-block-size 32MBCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that this only affects files created after this command is run; files created before this command is run retain their old behaviour.
5.6.3.3. Finding the pieces of a sharded file
getfattr -d -m. -e hex path_to_file
# getfattr -d -m. -e hex path_to_filels /rhgs/*/.shard -lh | grep GFID
# ls /rhgs/*/.shard -lh | grep GFID5.7. Creating Distributed Replicated Volumes
Note
- A trusted storage pool has been created, as described in Section 4.1, “Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool”.
- Understand how to start and stop volumes, as described in Section 5.11, “Starting Volumes”.
5.7.1. Creating Two-way Distributed Replicated Volumes
Warning
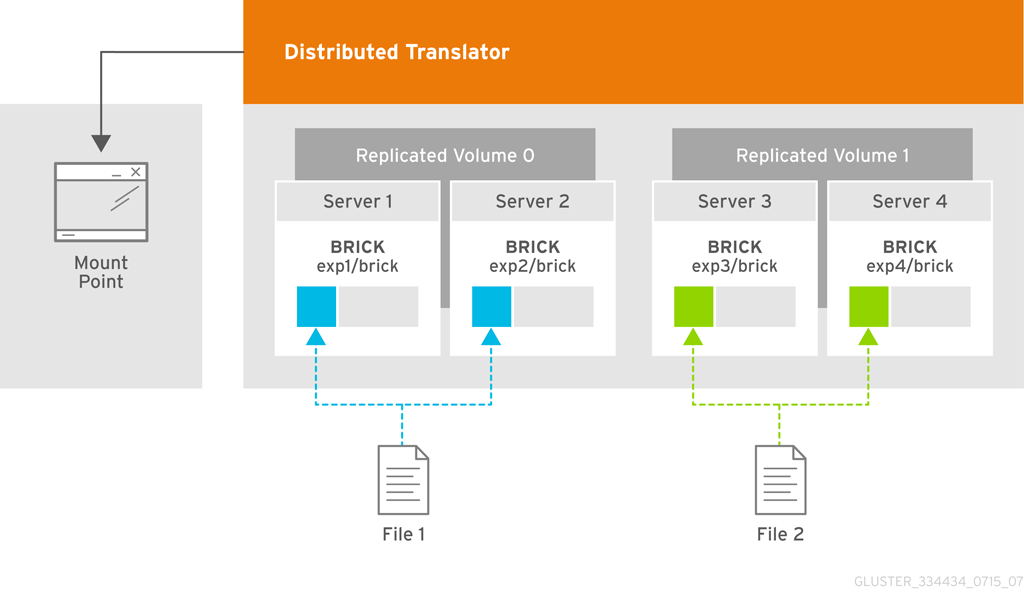
Figure 5.5. Illustration of a Two-way Distributed Replicated Volume
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the distributed replicated volume.The syntax is# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME [replica COUNT] [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” for a full list of parameters.Example 5.6. Four Node Distributed Replicated Volume with a Two-way Replication
The order in which bricks are specified determines how they are replicated with each other. For example, the first two bricks specified replicate each other where 2 is the replica count.gluster volume create test-volume replica 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume replica 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 5.7. Six Node Distributed Replicated Volume with a Two-way Replication
gluster volume create test-volume replica 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 server6:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume replica 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 server6:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.
Important
5.7.2. Creating Three-way Distributed Replicated Volumes
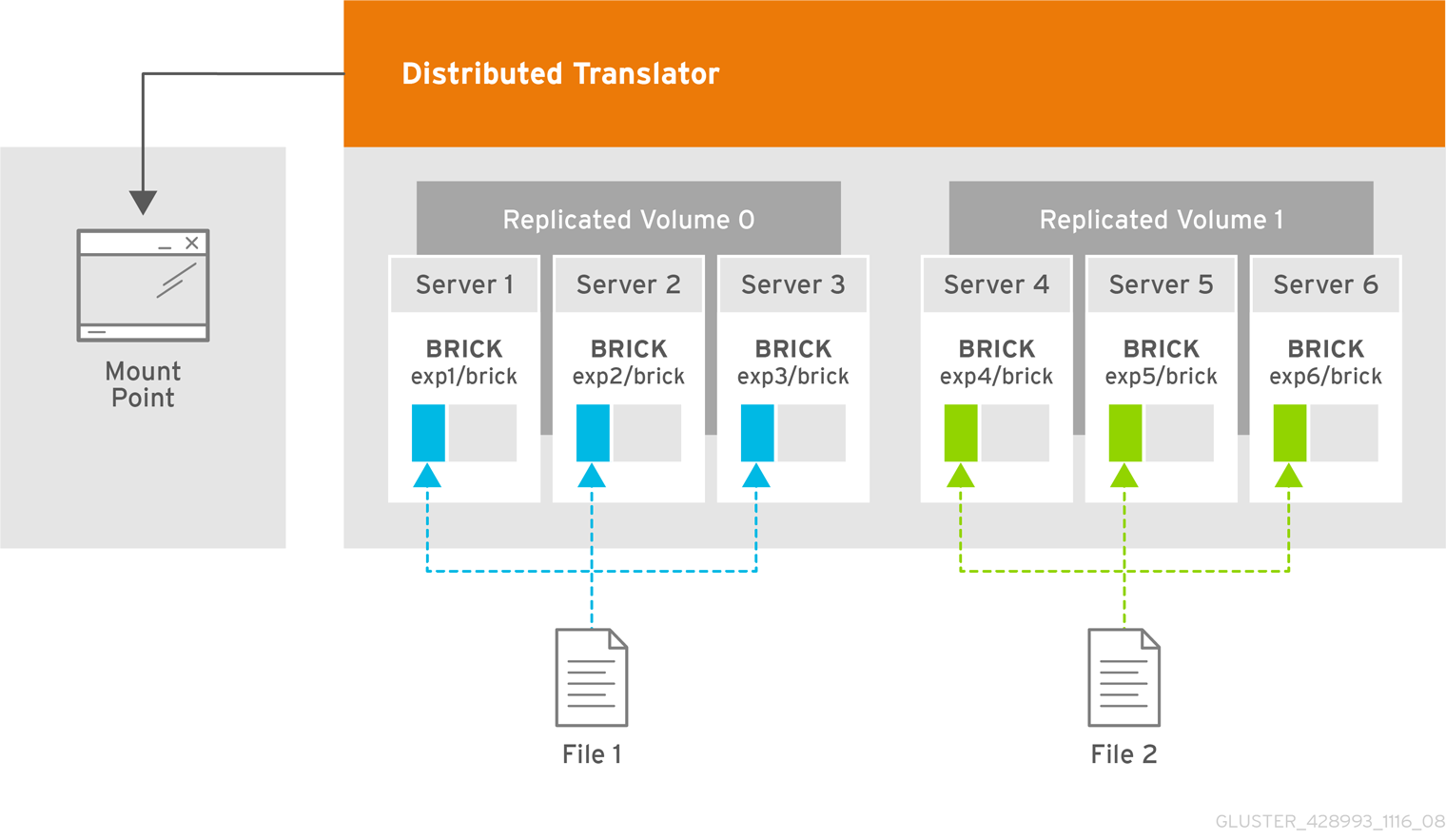
Figure 5.6. Illustration of a Three-way Distributed Replicated Volume
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the distributed replicated volume.The syntax is# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME [replica COUNT] [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” for a full list of parameters.Example 5.8. Six Node Distributed Replicated Volume with a Three-way Replication
The order in which bricks are specified determines how bricks are replicated with each other. For example, first 3 bricks, where 3 is the replica count forms a replicate set.gluster volume create test-volume replica 3 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 server6:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume replica 3 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 server6:/rhgs/brick1 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.
Important
5.8. Creating Arbitrated Replicated Volumes
Advantages of arbitrated replicated volumes
- Better consistency
- When an arbiter is configured, arbitration logic uses client-side quorum in auto mode to prevent file operations that would lead to split-brain conditions.
- Less disk space required
- Because an arbiter brick only stores file names and metadata, an arbiter brick can be much smaller than the other bricks in the volume.
- Fewer nodes required
- The node that contains the arbiter brick of one volume can be configured with the data brick of another volume. This "chaining" configuration allows you to use fewer nodes to fulfill your overall storage requirements.
- Easy migration from deprecated two-way replicated volumes
- Red Hat Gluster Storage can convert a two-way replicated volume without arbiter bricks into an arbitrated replicated volume. See Section 5.8.5, “Converting to an arbitrated volume” for details.
Limitations of arbitrated replicated volumes
- Arbitrated replicated volumes provide better data consistency than a two-way replicated volume that does not have arbiter bricks. However, because arbitrated replicated volumes store only metadata, they provide the same level of availability as a two-way replicated volume that does not have arbiter bricks. To achieve high-availability, you need to use a three-way replicated volume instead of an arbitrated replicated volume.
- Tiering is not compatible with arbitrated replicated volumes.
- Arbitrated volumes can only be configured in sets of three bricks at a time. Red Hat Gluster Storage can convert an existing two-way replicated volume without arbiter bricks into an arbitrated replicated volume by adding an arbiter brick to that volume. See Section 5.8.5, “Converting to an arbitrated volume” for details.
5.8.1. Arbitrated volume requirements
5.8.1.1. System requirements for nodes hosting arbiter bricks
| Configuration type | Min CPU | Min RAM | NIC | Arbiter Brick Size | Max Latency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dedicated arbiter | 64-bit quad-core processor with 2 sockets | 8 GB[a] | Match to other nodes in the storage pool | 1 TB to 4 TB[b] | 5 ms[c] |
| Chained arbiter | Match to other nodes in the storage pool | 1 TB to 4 TB[d] | 5 ms[e] | ||
[a]
More RAM may be necessary depending on the combined capacity of the number of arbiter bricks on the node.
[b]
Arbiter and data bricks can be configured on the same device provided that the data and arbiter bricks belong to different replica sets. See Section 5.8.1.2, “Arbiter capacity requirements” for further details on sizing arbiter volumes.
[c]
This is the maximum round trip latency requirement between all nodes irrespective of Aribiter node. See KCS#413623 to know how to determine latency between nodes.
[d]
Multiple bricks can be created on a single RAIDed physical device. Please refer the following product documentation: Section 20.2, “Brick Configuration”
[e]
This is the maximum round trip latency requirement between all nodes irrespective of Aribiter node. See KCS#413623 to know how to determine latency between nodes.
| |||||
- minimum 4 vCPUs
- minimum 16 GB RAM
- 1 TB to 4 TB of virtual disk space
- maximum 5 ms latency
5.8.1.2. Arbiter capacity requirements
minimum arbiter brick size = 4 KB * ( size in KB of largest data brick in volume or replica set / average file size in KB)
minimum arbiter brick size = 4 KB * ( size in KB of largest data brick in volume or replica set / average file size in KB)minimum arbiter brick size = 4 KB * ( 1 TB / 2 GB )
= 4 KB * ( 1000000000 KB / 2000000 KB )
= 4 KB * 500 KB
= 2000 KB
= 2 MB
minimum arbiter brick size = 4 KB * ( 1 TB / 2 GB )
= 4 KB * ( 1000000000 KB / 2000000 KB )
= 4 KB * 500 KB
= 2000 KB
= 2 MBminimum arbiter brick size = 4 KB * ( size in KB of largest data brick in volume or replica set / shard block size in KB )
minimum arbiter brick size = 4 KB * ( size in KB of largest data brick in volume or replica set / shard block size in KB )5.8.2. Arbitration logic
| Volume state | Arbitration behavior |
|---|---|
| All bricks available | All file operations permitted. |
| Arbiter and 1 data brick available |
If the arbiter does not agree with the available data node, write operations fail with ENOTCONN (since the brick that is correct is not available). Other file operations are permitted.
If the arbiter's metadata agrees with the available data node, all file operations are permitted.
|
| Arbiter down, data bricks available | All file operations are permitted. The arbiter's records are healed when it becomes available. |
| Only one brick available |
If the available brick is a data brick, client quorum is not met, and the volume enters an EROFS state.
If the available brick is the arbiter, all file operations fail with ENOTCONN.
|
5.8.3. Creating an arbitrated replicated volume
gluster volume create VOLNAME replica 3 arbiter 1 HOST1:DATA_BRICK1 HOST2:DATA_BRICK2 HOST3:ARBITER_BRICK3
# gluster volume create VOLNAME replica 3 arbiter 1 HOST1:DATA_BRICK1 HOST2:DATA_BRICK2 HOST3:ARBITER_BRICK3Note
gluster volume create testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 \ server1:/bricks/brick server2:/bricks/brick server3:/bricks/arbiter_brick \ server4:/bricks/brick server5:/bricks/brick server6:/bricks/arbiter_brick
# gluster volume create testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 \
server1:/bricks/brick server2:/bricks/brick server3:/bricks/arbiter_brick \
server4:/bricks/brick server5:/bricks/brick server6:/bricks/arbiter_brick5.8.4. Creating multiple arbitrated replicated volumes across fewer total nodes
- Chain multiple arbitrated replicated volumes together, by placing the arbiter brick for one volume on the same node as a data brick for another volume. Chaining is useful for write-heavy workloads when file size is closer to metadata file size (that is, from 32–128 KiB). This avoids all metadata I/O going through a single disk.In arbitrated distributed-replicated volumes, you can also place an arbiter brick on the same node as another replica sub-volume's data brick, since these do not share the same data.
- Place the arbiter bricks from multiple volumes on a single dedicated node. A dedicated arbiter node is suited to write-heavy workloads with larger files, and read-heavy workloads.
Example 5.9. Example of a dedicated configuration
gluster volume create firstvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/brick server2:/bricks/brick server3:/bricks/arbiter_brick gluster volume create secondvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server4:/bricks/data_brick server5:/bricks/brick server3:/bricks/brick
# gluster volume create firstvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/brick server2:/bricks/brick server3:/bricks/arbiter_brick
# gluster volume create secondvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server4:/bricks/data_brick server5:/bricks/brick server3:/bricks/brick
Example 5.10. Example of a chained configuration
gluster volume create arbrepvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/brick1 server2:/bricks/brick1 server3:/bricks/arbiter_brick1 server2:/bricks/brick2 server3:/bricks/brick2 server4:/bricks/arbiter_brick2 server3:/bricks/brick3 server4:/bricks/brick3 server5:/bricks/arbiter_brick3 server4:/bricks/brick4 server5:/bricks/brick4 server6:/bricks/arbiter_brick4 server5:/bricks/brick5 server6:/bricks/brick5 server1:/bricks/arbiter_brick5 server6:/bricks/brick6 server1:/bricks/brick6 server2:/bricks/arbiter_brick6
# gluster volume create arbrepvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/brick1 server2:/bricks/brick1 server3:/bricks/arbiter_brick1 server2:/bricks/brick2 server3:/bricks/brick2 server4:/bricks/arbiter_brick2 server3:/bricks/brick3 server4:/bricks/brick3 server5:/bricks/arbiter_brick3 server4:/bricks/brick4 server5:/bricks/brick4 server6:/bricks/arbiter_brick4 server5:/bricks/brick5 server6:/bricks/brick5 server1:/bricks/arbiter_brick5 server6:/bricks/brick6 server1:/bricks/brick6 server2:/bricks/arbiter_brick6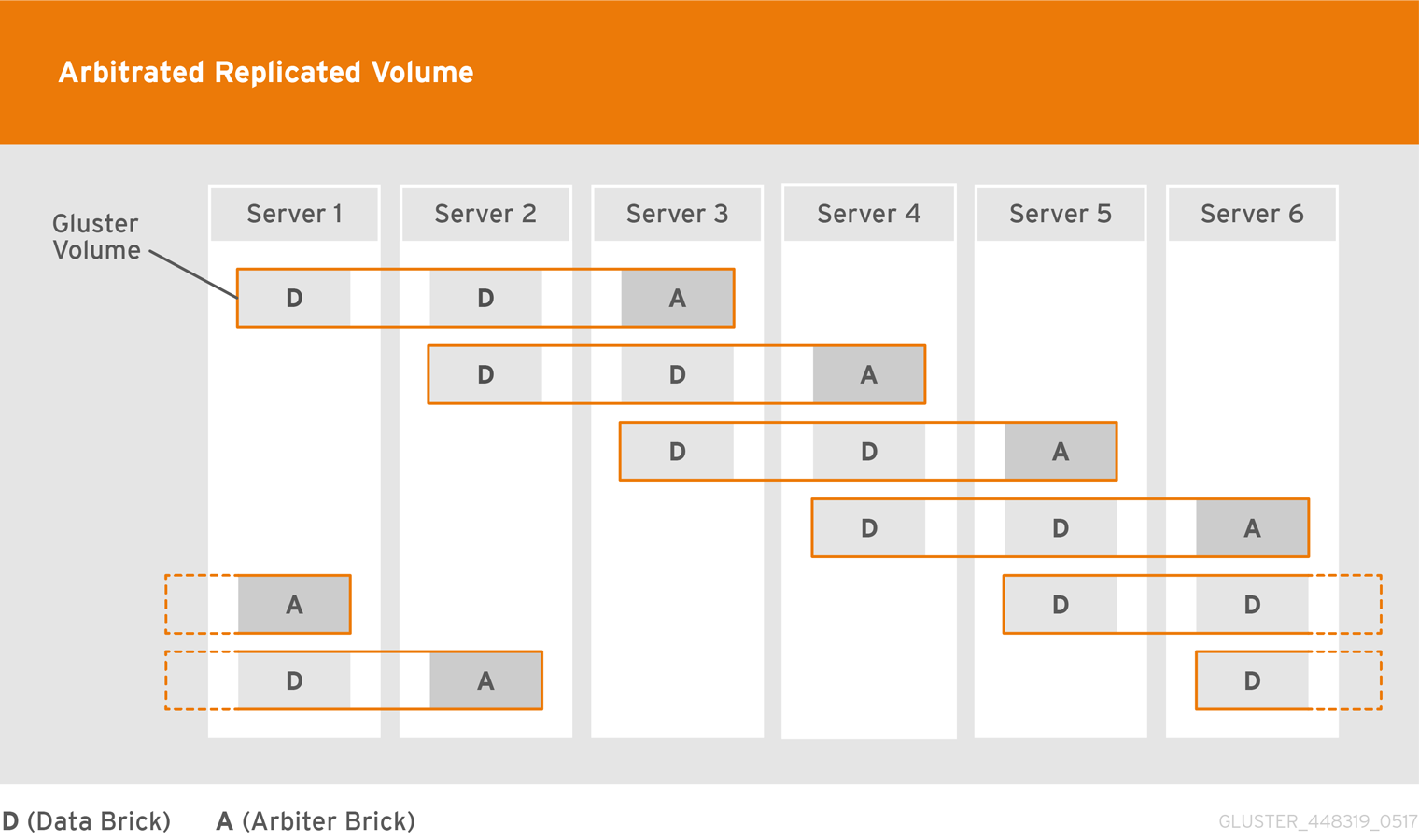
5.8.5. Converting to an arbitrated volume
Procedure 5.1. Converting a replica 2 volume to an arbitrated volume
Warning
Verify that healing is not in progress
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until pending heal entries is0before proceeding.Disable and stop self-healing
Run the following commands to disable data, metadata, and entry self-heal, and the self-heal daemon.gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add arbiter bricks to the volume
Convert the volume by adding an arbiter brick for each replicated sub-volume.gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME replica 3 arbiter 1 HOST:arbiter-brick-path
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME replica 3 arbiter 1 HOST:arbiter-brick-pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, if you have an existing two-way replicated volume called testvol, and a new brick for the arbiter to use, you can add a brick as an arbiter with the following command:gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server:/bricks/arbiter_brick
# gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server:/bricks/arbiter_brickCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you have an existing two-way distributed-replicated volume, you need a new brick for each sub-volume in order to convert it to an arbitrated distributed-replicated volume, for example:gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/arbiter_brick1 server2:/bricks/arbiter_brick2
# gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/arbiter_brick1 server2:/bricks/arbiter_brick2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait for client volfiles to update
This takes about 5 minutes.Verify that bricks added successfully
gluster volume info VOLNAME gluster volume status VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAME # gluster volume status VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Re-enable self-healing
Run the following commands to re-enable self-healing on the servers.gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all entries are healed
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until pending heal entries is0to ensure that all heals completed successfully.
Procedure 5.2. Converting a replica 3 volume to an arbitrated volume
Warning
Verify that healing is not in progress
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until pending heal entries is0before proceeding.Reduce the replica count of the volume to 2
Remove one brick from every sub-volume in the volume so that the replica count is reduced to 2. For example, in a replica 3 volume that distributes data across 2 sub-volumes, run the following command:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME replica 2 HOST:subvol1-brick-path HOST:subvol2-brick-path force
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME replica 2 HOST:subvol1-brick-path HOST:subvol2-brick-path forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
In a distributed replicated volume, data is distributed across sub-volumes, and replicated across bricks in a sub-volume. This means that to reduce the replica count of a volume, you need to remove a brick from every sub-volume.Bricks are grouped by sub-volume in thegluster volume infooutput. If the replica count is 3, the first 3 bricks form the first sub-volume, the next 3 bricks form the second sub-volume, and so on.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this volume, data is distributed across two sub-volumes, which each consist of three bricks. The first sub-volume consists of bricks 1, 2, and 3. The second sub-volume consists of bricks 4, 5, and 6. Removing any one brick from each subvolume using the following command reduces the replica count to 2 as required.gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME replica 2 HOST:subvol1-brick-path HOST:subvol2-brick-path force
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME replica 2 HOST:subvol1-brick-path HOST:subvol2-brick-path forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable and stop self-healing
Run the following commands to disable data, metadata, and entry self-heal, and the self-heal daemon.gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add arbiter bricks to the volume
Convert the volume by adding an arbiter brick for each replicated sub-volume.gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME replica 3 arbiter 1 HOST:arbiter-brick-path
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME replica 3 arbiter 1 HOST:arbiter-brick-pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, if you have an existing replicated volume:gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server:/bricks/brick
# gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server:/bricks/brickCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you have an existing distributed-replicated volume:gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/arbiter_brick1 server2:/bricks/arbiter_brick2
# gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 arbiter 1 server1:/bricks/arbiter_brick1 server2:/bricks/arbiter_brick2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait for client volfiles to update
This takes about 5 minutes. Verify that this is complete by running the following command on each client.grep -ir connected mount-path/.meta/graphs/active/volname-client-*/private
# grep -ir connected mount-path/.meta/graphs/active/volname-client-*/privateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The number of timesconnected=1appears in the output is the number of bricks connected to the client.Verify that bricks added successfully
gluster volume info VOLNAME gluster volume status VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAME # gluster volume status VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Re-enable self-healing
Run the following commands to re-enable self-healing on the servers.gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all entries are healed
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until pending heal entries is0to ensure that all heals completed successfully.
5.8.6. Converting an arbitrated volume to a three-way replicated volume
Warning
Procedure 5.3. Converting an arbitrated volume to a replica 3 volume
Verify that healing is not in progress
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until pending heal entries is0before proceeding.Remove arbiter bricks from the volume
Check which bricks are listed as(arbiter), and then remove those bricks from the volume.gluster volume info VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME replica 2 HOST:arbiter-brick-path force
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME replica 2 HOST:arbiter-brick-path forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable and stop self-healing
Run the following commands to disable data, metadata, and entry self-heal, and the self-heal daemon.gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal off gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal off # gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add full bricks to the volume
Convert the volume by adding a brick for each replicated sub-volume.gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME replica 3 HOST:brick-path
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME replica 3 HOST:brick-pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, if you have an existing arbitrated replicated volume:gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 server:/bricks/brick
# gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 server:/bricks/brickCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you have an existing arbitrated distributed-replicated volume:gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 server1:/bricks/brick1 server2:/bricks/brick2
# gluster volume add-brick testvol replica 3 server1:/bricks/brick1 server2:/bricks/brick2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait for client volfiles to update
This takes about 5 minutes.Verify that bricks added successfully
gluster volume info VOLNAME gluster volume status VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAME # gluster volume status VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Re-enable self-healing
Run the following commands to re-enable self-healing on the servers.gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal on gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.data-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.metadata-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.entry-self-heal on # gluster volume set VOLNAME self-heal-daemon onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify all entries are healed
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Wait until pending heal entries is0to ensure that all heals completed successfully.
5.8.7. Tuning recommendations for arbitrated volumes
- For dedicated arbiter nodes, use JBOD for arbiter bricks, and RAID6 for data bricks.
- For chained arbiter volumes, use the same RAID6 drive for both data and arbiter bricks.
5.9. Creating Dispersed Volumes
Important
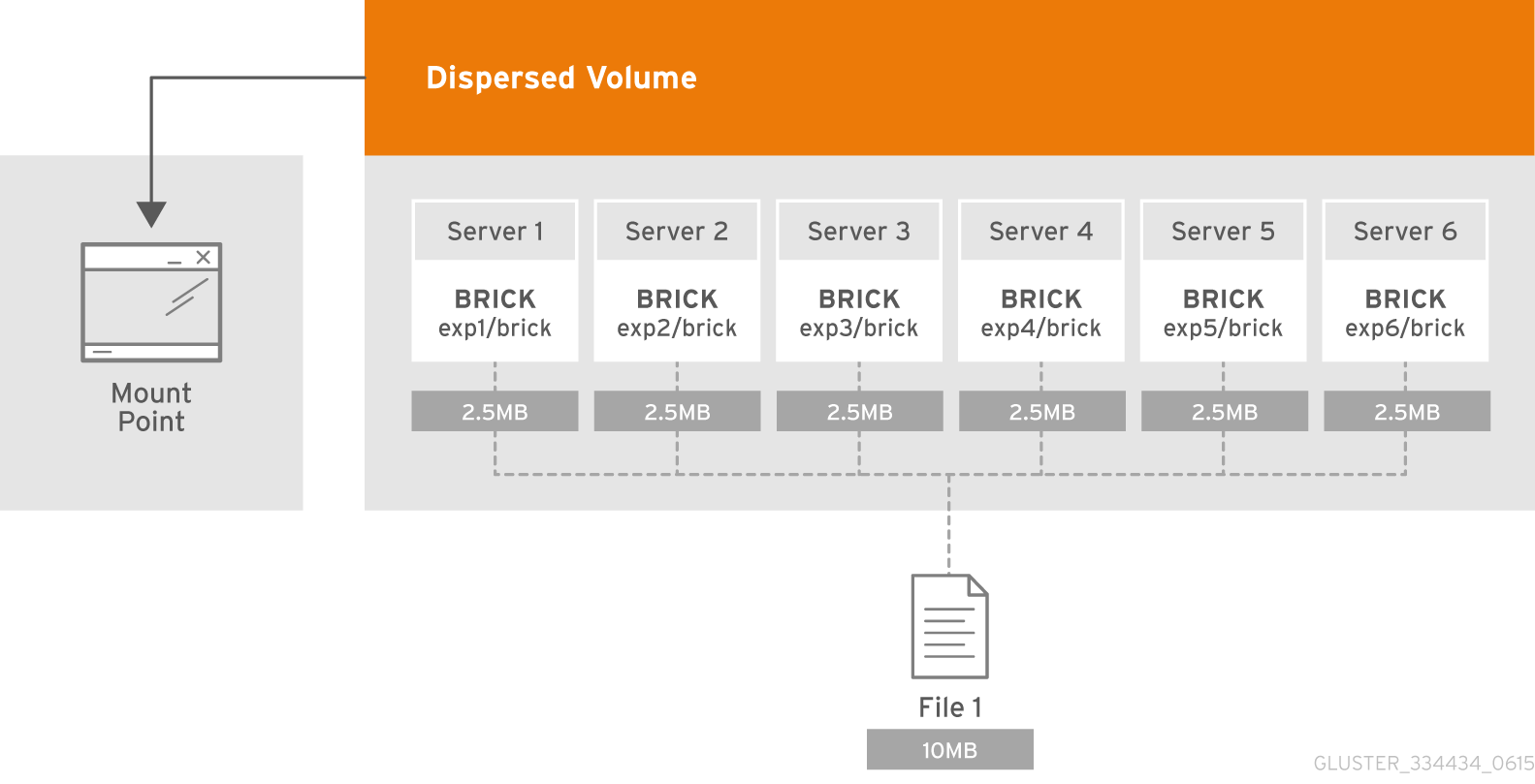
Figure 5.7. Illustration of a Dispersed Volume
n = k + m. Here n is the total number of bricks, we would require any k bricks out of n bricks for recovery. In other words, we can tolerate failure up to any m bricks. With this release, the following configurations are supported:
- 6 bricks with redundancy level 2 (4 + 2)
- 10 bricks with redundancy level 2 (8 + 2)
- 11 bricks with redundancy level 3 (8 + 3)
- 12 bricks with redundancy level 4 (8 + 4)
- 20 bricks with redundancy level 4 (16 + 4)
gluster volume create to create different types of volumes, and gluster volume info to verify successful volume creation.
- Create a trusted storage pool as described in Section 4.1, “Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool”.
- Understand how to start and stop volumes, as described in Section 5.11, “Starting Volumes”.
Important
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the dispersed volume.The syntax is# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME [disperse-data COUNT] [redundancy COUNT] [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The number of bricks required to create a disperse volume is the sum ofdisperse-data countandredundancy count.Thedisperse-datacountoption specifies the number of bricks that is part of the dispersed volume, excluding the count of the redundant bricks. For example, if the total number of bricks is 6 andredundancy-countis specified as 2, then the disperse-data count is 4 (6 - 2 = 4). If thedisperse-data countoption is not specified, and only theredundancy countoption is specified, then thedisperse-data countis computed automatically by deducting the redundancy count from the specified total number of bricks.Redundancy determines how many bricks can be lost without interrupting the operation of the volume. Ifredundancy countis not specified, based on the configuration it is computed automatically to the optimal value and a warning message is displayed.The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 5.3, “About Encrypted Disk” for a full list of parameters.Example 5.11. Dispersed Volume with Six Storage Servers
gluster volume create test-volume disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs1/brick1 server2:/rhgs2/brick2 server3:/rhgs3/brick3 server4:/rhgs4/brick4 server5:/rhgs5/brick5 server6:/rhgs6/brick6 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs1/brick1 server2:/rhgs2/brick2 server3:/rhgs3/brick3 server4:/rhgs4/brick4 server5:/rhgs5/brick5 server6:/rhgs6/brick6 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Theopen-behindvolume option is enabled by default. If you are accessing the dispersed volume using the SMB protocol, you must disable theopen-behindvolume option to avoid performance bottleneck on large file workload. Run the following command to disableopen-behindvolume option:gluster volume set VOLNAME open-behind off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME open-behind offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For information onopen-behindvolume option, see Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.
5.10. Creating Distributed Dispersed Volumes
- Multiple disperse sets containing 6 bricks with redundancy level 2
- Multiple disperse sets containing 10 bricks with redundancy level 2
- Multiple disperse sets containing 11 bricks with redundancy level 3
- Multiple disperse sets containing 12 bricks with redundancy level 4
- Multiple disperse sets containing 20 bricks with redundancy level 4
Important
gluster volume create to create different types of volumes, and gluster volume info to verify successful volume creation.
- A trusted storage pool has been created, as described in Section 4.1, “Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool”.
- Understand how to start and stop volumes, as described in Section 5.11, “Starting Volumes”.
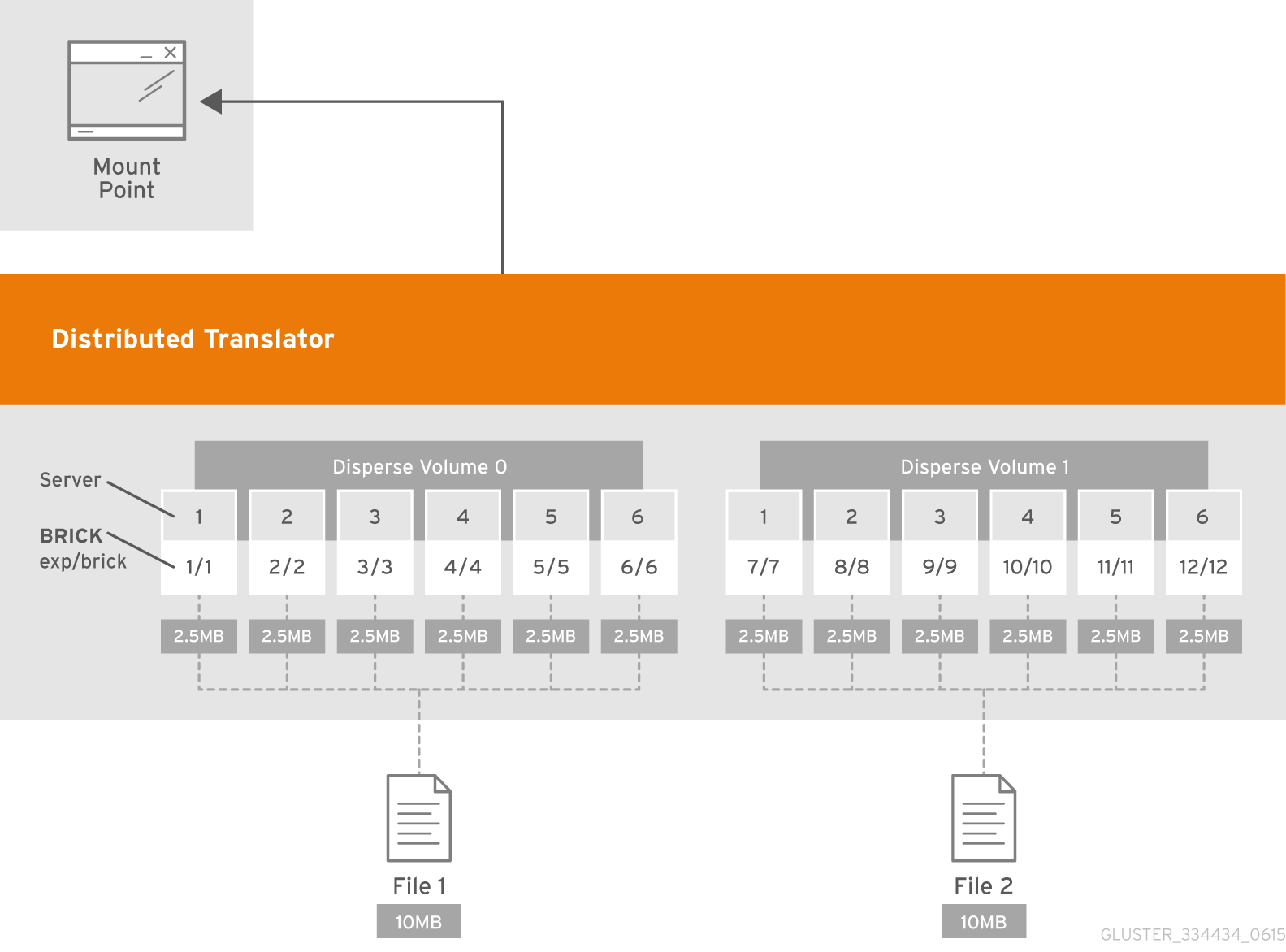
Figure 5.8. Illustration of a Distributed Dispersed Volume
Important
- Run the
gluster volume createcommand to create the dispersed volume.The syntax is# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME disperse-data COUNT [redundancy COUNT] [transport tcp | rdma | tcp,rdma] NEW-BRICK...The default value for transport istcp. Other options can be passed such asauth.alloworauth.reject. See Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” for a full list of parameters.Example 5.12. Distributed Dispersed Volume with Six Storage Servers
gluster volume create test-volume disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs1/brick1 server2:/rhgs2/brick2 server3:/rhgs3/brick3 server4:/rhgs4/brick4 server5:/rhgs5/brick5 server6:/rhgs6/brick6 server1:/rhgs7/brick7 server2:/rhgs8/brick8 server3:/rhgs9/brick9 server4:/rhgs10/brick10 server5:/rhgs11/brick11 server6:/rhgs12/brick12 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.
# gluster volume create test-volume disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs1/brick1 server2:/rhgs2/brick2 server3:/rhgs3/brick3 server4:/rhgs4/brick4 server5:/rhgs5/brick5 server6:/rhgs6/brick6 server1:/rhgs7/brick7 server2:/rhgs8/brick8 server3:/rhgs9/brick9 server4:/rhgs10/brick10 server5:/rhgs11/brick11 server6:/rhgs12/brick12 Creation of test-volume has been successful Please start the volume to access data.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The above example is illustrated in Figure 5.7, “Illustration of a Dispersed Volume” . In the illustration and example, you are creating 12 bricks from 6 servers. - Run
# gluster volume start VOLNAMEto start the volume.gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Theopen-behindvolume option is enabled by default. If you are accessing the distributed dispersed volume using the SMB protocol, you must disable theopen-behindvolume option to avoid performance bottleneck on large file workload. Run the following command to disableopen-behindvolume option:gluster volume set VOLNAME open-behind off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME open-behind offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For information onopen-behindvolume option, see Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options” - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.
5.11. Starting Volumes
# gluster volume start VOLNAME
Note
gluster volume start test-volume Starting test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume start test-volume
Starting test-volume has been successfulChapter 6. Creating Access to Volumes
- Native Client (see Section 6.1, “Native Client”)
- Network File System (NFS) v3 (see Section 6.2, “NFS”)
- Server Message Block (SMB) (see Section 6.3, “SMB”)
Because of differences in locking semantics, a single Red Hat Gluster Storage volume cannot be concurrently accessed by multiple protocols. Current support for concurrent access is defined in the following table.
| SMB | Gluster NFS | NFS-Ganesha | Native FUSE | Object | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMB | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Gluster NFS | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| NFS-Ganesha | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Native FUSE | No | No | No | Yes | Yes [a] |
| Object | No | No | No | Yes [a] | Yes |
[a]
For more information, refer Section 6.5, “Managing Object Store”.
| |||||
The following table provides the support matrix for the supported access protocols with TCP/RDMA.
| Access Protocols | TCP | RDMA |
|---|---|---|
| FUSE | Yes | Yes |
| SMB | Yes | No |
| NFS | Yes | Yes |
Important
6.1. Native Client
- Install Native Client packages
- Mount Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes (manually and automatically)
- Verify that the Gluster Storage volume has mounted successfully
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux version | Red Hat Gluster Storage version | Native client version |
|---|---|---|
| 6.5 | 3.0 | 3.0, 2.1* |
| 6.6 | 3.0.2, 3.0.3, 3.0.4 | 3.0, 2.1* |
| 6.7 | 3.1, 3.1.1, 3.1.2 | 3.1, 3.0, 2.1* |
| 6.8 | 3.1.3 | 3.1.3 |
| 6.9 | 3.2 | 3.2, 3.1.3* |
| 6.9 | 3.3 | 3.3, 3.2 |
| 6.9 | 3.3.1 | 3.3.1, 3.3, 3.2 |
| 6.10 | 3.4 | 3.4, 3.3.z |
| 7.1 | 3.1, 3.1.1 | 3.1.1, 3.1, 3.0 |
| 7.2 | 3.1.2 | 3.1.2, 3.1, 3.0 |
| 7.2 | 3.1.3 | 3.1.3 |
| 7.3 | 3.2 | 3.2, 3.1.3 |
| 7.4 | 3.2 | 3.2, 3.1.3 |
| 7.4 | 3.3 | 3.3, 3.2 |
| 7.4 | 3.3.1 | 3.3.1, 3.3, 3.2 |
| 7.5 | 3.3.1, 3.4 | 3.3.z, 3.4.z |
| 7.6 | 3.3.1, 3.4 | 3.3.z, 3.4.z |
Warning
Warning
gluster volume heal VOLNAME infois unresponsive for some volumes. (BZ#1500542)- Gluster brick process crashes frequently. (BZ#1510725)
- Multiple disconnects on NFS mounts. (BZ#1425740)
Warning
- For Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4, Red Hat supports Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.3 and 3.4 clients only.
- For Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.2, you need to have Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.2 clients. This version is not compatible with backward versions of the client.
6.1.1. Installing Native Client
Important
Use the Command Line to Register and Subscribe a System to Red Hat Subscription Management
Prerequisites
- Know the user name and password of the Red Hat Subscription Manager account with Red Hat Gluster Storage entitlements.
- Run the
subscription-manager registercommand to list the available pools. Select the appropriate pool and enter your Red Hat Subscription Manager user name and password to register the system with Red Hat Subscription Manager.subscription-manager register
# subscription-manager registerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Depending on your client, run one of the following commands to subscribe to the correct repositories.
- For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.x clients:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms --enable=rh-gluster-3-client-for-rhel-7-server-rpms
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rpms --enable=rh-gluster-3-client-for-rhel-7-server-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The following command can also be used, but Red Hat Gluster Storage may deprecate support for this repository in future releases.subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rh-common-rpms
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-rh-common-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.1 and later clients:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-6-server-rpms --enable=rhel-6-server-rhs-client-1-rpms
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-6-server-rpms --enable=rhel-6-server-rhs-client-1-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.7 and later clients:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-5-server-rpms --enable=rhel-5-server-rhs-client-1-rpms
# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-5-server-rpms --enable=rhel-5-server-rhs-client-1-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For more information, see Section 3.2 Registering from the Command Line in Using and Configuring Red Hat Subscription Management. - Verify that the system is subscribed to the required repositories.
yum repolist
# yum repolistCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Use the Web Interface to Register and Subscribe a System
Prerequisites
- Know the user name and password of the Red Hat Subsrciption Management (RHSM) account with Red Hat Gluster Storage entitlements.
- Log on to Red Hat Subscription Management (https://access.redhat.com/management).
- Click the Systems link at the top of the screen.
- Click the name of the system to which the Red Hat Gluster Storage Native Client channel must be appended.
- Click in the Subscribed Channels section of the screen.
- Expand the node for Additional Services Channels for
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 for x86_64orRed Hat Enterprise Linux 6 for x86_64or forRed Hat Enterprise Linux 5 for x86_64depending on the client platform. - Click the button to finalize the changes.When the page refreshes, select the Details tab to verify the system is subscribed to the appropriate channels.
Install Native Client Packages
Prerequisites
- Run the
yum installcommand to install the native client RPM packages.yum install glusterfs glusterfs-fuse
# yum install glusterfs glusterfs-fuseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For Red Hat Enterprise 5.x client systems, run the
modprobecommand to load FUSE modules before mounting Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes.modprobe fuse
# modprobe fuseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on loading modules at boot time, see https://access.redhat.com/knowledge/solutions/47028 .
6.1.2. Upgrading Native Client
Warning
Unmount gluster volumes
Unmount any gluster volumes prior to upgrading the native client.umount /mnt/glusterfs
# umount /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Upgrade the client
Run theyum updatecommand to upgrade the native client:yum update glusterfs glusterfs-fuse
# yum update glusterfs glusterfs-fuseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remount gluster volumes
Remount volumes as discussed in Section 6.1.3, “Mounting Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes”.
6.1.3. Mounting Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes
Note
- Clients should be on the same version as the server, and at least on the version immediately previous to the server version. For Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4, the recommended native client version should either be 3.4 or 3.3.z. For other versions, see Section 6.1, “Native Client”.
- Server names selected during volume creation should be resolvable in the client machine. Use appropriate
/etc/hostsentries, or a DNS server to resolve server names to IP addresses. - Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) support is available only for Red Hat Hyperconverged Infrastructure for Virtualization environments and not for Red Hat Gluster Storage standalone environments.
6.1.3.1. Mount Commands and Options
mount -t glusterfs command. All options must be separated with commas.
mount -t glusterfs -o backup-volfile-servers=volfile_server2:volfile_server3:.... ..:volfile_serverN,transport-type tcp,log-level=WARNING,reader-thread-count=2,log-file=/var/log/gluster.log server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs -o backup-volfile-servers=volfile_server2:volfile_server3:.... ..:volfile_serverN,transport-type tcp,log-level=WARNING,reader-thread-count=2,log-file=/var/log/gluster.log server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs- backup-volfile-servers=<volfile_server2>:<volfile_server3>:...:<volfile_serverN>
- List of the backup volfile servers to mount the client. If this option is specified while mounting the fuse client, when the first volfile server fails, the servers specified in
backup-volfile-serversoption are used as volfile servers to mount the client until the mount is successful.Note
This option was earlier specified asbackupvolfile-serverwhich is no longer valid. - log-level
- Logs only specified level or higher severity messages in the
log-file. - log-file
- Logs the messages in the specified file.
- transport-type
- Specifies the transport type that FUSE client must use to communicate with bricks. If the volume was created with only one transport type, then that becomes the default when no value is specified. In case of
tcp,rdmavolume, tcp is the default. - dump-fuse
- This mount option creates dump of fuse traffic between the glusterfs client (fuse userspace server) and the kernel. The interface to mount a glusterfs volume is the standard mount(8) command from the CLI. This feature enables the same in the mount option.
# mount -t glusterfs -odump-fuse=filename hostname:/volname mount-pathFor example,mount -t glusterfs -odump-fuse=/dumpfile 10.70.43.18:/arbiter /mnt/arbiter
# mount -t glusterfs -odump-fuse=/dumpfile 10.70.43.18:/arbiter /mnt/arbiterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The above command generates a binary file with the namedumpfile.Note
The fusedump grows large with time and notably if the client gets a heavy load. So this is not an intended use case to do fusedump during normal usage. It is advised to use this to get a dump from a particular scenario, for diagnostic purposes.You need to unmount and remount the volume without the fusedump option to stop dumping. - ro
- Mounts the file system with read-only permissions.
- acl
- Enables POSIX Access Control List on mount. See Section 6.4.4, “Checking ACL enablement on a mounted volume” for further information.
- background-qlen=n
- Enables FUSE to handle n number of requests to be queued before subsequent requests are denied. Default value of n is 64.
- enable-ino32
- Enables file system to present 32-bit inodes instead of 64-bit inodes.
- reader-thread-count=n
- Enables FUSE to add n number of reader threads that can give better I/O performance. Default value of n is
1. - lru-limit
- This
mountcommand option clears the inodes from the least recently used (lru) list (which keeps non-referenced inodes) after the inode limit has reached.For example,mount -olru-limit=NNNN -t glusterfs hostname:/volname /mnt/mountdir
# mount -olru-limit=NNNN -t glusterfs hostname:/volname /mnt/mountdirCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where NNNN is a positive integer. The default value of NNNN is 128k (131072) and the recommended value is 20000 and above. If0is specified as thelru-limitthen it means that no invalidation of inodes from the lru-list.
6.1.3.2. Mounting Volumes Manually
Manually Mount a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume or Subdirectory
- For a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume
mount -t glusterfs HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR- For a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume's Subdirectory
mount -t glusterfs HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME/SUBDIRECTORY /MOUNTDIR
Note
- If a mount point has not yet been created for the volume, run the
mkdircommand to create a mount point.mkdir /mnt/glusterfs
# mkdir /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the
mount -t glusterfscommand, using the key in the task summary as a guide.- For a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume:
mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume's Subdirectory
mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-volume/sub-dir /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-volume/sub-dir /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.3.3. Mounting Volumes Automatically
- Open the
/etc/fstabfile in a text editor. - Append the following configuration to the
fstabfile:- For a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume
HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume's Subdirectory
HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME/SUBDIRECTORY /MOUNTDIR glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME/SUBDIRECTORY /MOUNTDIR glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Using the example server names, the entry contains the following replaced values.server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ORserver1:/test-volume/subdir /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
server1:/test-volume/subdir /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you want to specify the transport type then check the following example:server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev,transport=tcp 0 0
server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev,transport=tcp 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ORserver1:/test-volume/sub-dir /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev,transport=tcp 0 0
server1:/test-volume/sub-dir /mnt/glusterfs glusterfs defaults,_netdev,transport=tcp 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.3.4. Manually Mounting Sub-directories Using Native Client
- Provides namespace isolation so that multiple users can access the storage without risking namespace collision with other users.
- Prevents the root file system from becoming full in the event of a mount failure.
mount -t glusterfs hostname:/volname/subdir /mount-point
# mount -t glusterfs hostname:/volname/subdir /mount-pointmount -t glusterfs hostname:/volname -osubdir-mount=subdir /mount-point
# mount -t glusterfs hostname:/volname -osubdir-mount=subdir /mount-pointgluster volume set test-vol auth.allow "/(192.168.10.*|192.168.11.*),/subdir1(192.168.1.*),/subdir2(192.168.8.*)”
# gluster volume set test-vol auth.allow "/(192.168.10.*|192.168.11.*),/subdir1(192.168.1.*),/subdir2(192.168.8.*)”- The
auth.allowoption allows only the directories specified as the value of theauth.allowoption to be mounted. - Each group of auth-allow is separated by a comma (
,). - Each group has a directory separated by parentheses,
(), which contains the valid IP addresses. - All subdirectories start with
/, that is, no relative path to a volume, but everything is an absolute path, taking/as the root directory of the volume.
Note
*, where any given subdirectory in a volume can be mounted by all clients.
6.1.3.5. Testing Mounted Volumes
Testing Mounted Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes
Prerequisites
- Run the
mountcommand to check whether the volume was successfully mounted.mount server1:/test-volume on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072
# mount server1:/test-volume on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ORmount server1:/test-volume/sub-dir on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072
# mount server1:/test-volume/sub-dir on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If transport option is used while mounting a volume, mount status will have the transport type appended to the volume name. For example, for transport=tcp:mount server1:/test-volume.tcp on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072
# mount server1:/test-volume.tcp on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ORmount server1:/test-volume/sub-dir.tcp on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072
# mount server1:/test-volume/sub-dir.tcp on /mnt/glusterfs type fuse.glusterfs(rw,allow_other,default_permissions,max_read=131072Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the
dfcommand to display the aggregated storage space from all the bricks in a volume.df -h /mnt/glusterfs Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on server1:/test-volume 28T 22T 5.4T 82% /mnt/glusterfs
# df -h /mnt/glusterfs Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on server1:/test-volume 28T 22T 5.4T 82% /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Move to the mount directory using the
cdcommand, and list the contents.cd /mnt/glusterfs ls
# cd /mnt/glusterfs # lsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2. NFS
6.2.1. Support Matrix
| Features | glusterFS NFS (NFSv3) | NFS-Ganesha (NFSv3) | NFS-Ganesha (NFSv4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root-squash | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| All-squash | No | Yes | Yes |
| Sub-directory exports | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Locking | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Client based export permissions | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Netgroups | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mount protocols | UDP, TCP | UDP, TCP | Only TCP |
| NFS transport protocols | TCP | UDP, TCP | TCP |
| AUTH_UNIX | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| AUTH_NONE | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| AUTH_KRB | No | Yes | Yes |
| ACLs | Yes | No | Yes |
| Delegations | N/A | N/A | No |
| High availability | Yes (but with certain limitations. For more information see, "Setting up CTDB for NFS") | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-head | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Gluster RDMA volumes | Yes | Not supported | Not supported |
| DRC | Not supported | Yes | Yes |
| Dynamic exports | No | Yes | Yes |
| pseudofs | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| NFSv4.1 | N/A | N/A | Not Supported |
Note
- Red Hat does not recommend running NFS-Ganesha with any other NFS servers, such as, kernel-NFS and Gluster NFS servers.
- Only one of NFS-Ganesha, gluster-NFS or kernel-NFS servers can be enabled on a given machine/host as all NFS implementations use the port 2049 and only one can be active at a given time. Hence you must disable kernel-NFS before NFS-Ganesha is started.
6.2.2. Gluster NFS
Note
mount -t nfs” command on the client as below:
gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.disable off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.disable off- To set nfs.acl ON, run the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.acl on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.acl onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To set nfs.acl OFF, run the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.acl off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.acl offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
Important
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesfirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=nfs --add-service=rpc-bind firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=nfs --add-service=rpc-bind --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=nfs --add-service=rpc-bind
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=nfs --add-service=rpc-bind --permanent6.2.2.1. Setting up CTDB for Gluster NFS
Important
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesfirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp --permanentNote
6.2.2.1.1. Prerequisites
- If you already have an older version of CTDB (version <= ctdb1.x), then remove CTDB by executing the following command:
yum remove ctdb
# yum remove ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After removing the older version, proceed with installing the latest CTDB.Note
Ensure that the system is subscribed to the samba channel to get the latest CTDB packages. - Install CTDB on all the nodes that are used as NFS servers to the latest version using the following command:
yum install ctdb
# yum install ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - CTDB uses TCP port 4379 by default. Ensure that this port is accessible between the Red Hat Gluster Storage servers.
6.2.2.1.2. Port and Firewall Information for Gluster NFS
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \
--add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp \ --add-port=111/tcp --add-port=111/udp
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \
--add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp \ --add-port=111/tcp --add-port=111/udpfirewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \
--add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp \ --add-port=111/tcp --add-port=111/udp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \
--add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp \ --add-port=111/tcp --add-port=111/udp --permanent- Edit
/etc/sysconfig/nfsfile as mentioned below:sed -i '/STATD_PORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs
# sed -i '/STATD_PORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the services:
- For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6:
service nfslock restart # service nfs restart# service nfslock restart # service nfs restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl restart nfs-config # systemctl restart rpc-statd # systemctl restart nfs-mountd # systemctl restart nfslock# systemctl restart nfs-config # systemctl restart rpc-statd # systemctl restart nfs-mountd # systemctl restart nfslockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.2.1.3. Configuring CTDB on Red Hat Gluster Storage Server
- Create a replicate volume. This volume will host only a zero byte lock file, hence choose minimal sized bricks. To create a replicate volume run the following command:
gluster volume create volname replica n ipaddress:/brick path.......N times
# gluster volume create volname replica n ipaddress:/brick path.......N timesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,N: The number of nodes that are used as Gluster NFS servers. Each node must host one brick.For example:gluster volume create ctdb replica 3 10.16.157.75:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b1 10.16.157.78:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b2 10.16.157.81:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b3
# gluster volume create ctdb replica 3 10.16.157.75:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b1 10.16.157.78:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b2 10.16.157.81:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the following files, replace "all" in the statement META="all" to the newly created volume name
/var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/start/post/S29CTDBsetup.sh /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/stop/pre/S29CTDB-teardown.sh
/var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/start/post/S29CTDBsetup.sh /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/stop/pre/S29CTDB-teardown.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:META="all" to META="ctdb"
META="all" to META="ctdb"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the volume.
gluster volume start ctdb
# gluster volume start ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow As part of the start process, theS29CTDBsetup.shscript runs on all Red Hat Gluster Storage servers, adds an entry in/etc/fstabfor the mount, and mounts the volume at/gluster/lockon all the nodes with Gluster NFS server. It also enables automatic start of CTDB service on reboot.Note
When you stop the special CTDB volume, the S29CTDB-teardown.sh script runs on all Red Hat Gluster Storage servers and removes an entry in /etc/fstab for the mount and unmounts the volume at /gluster/lock. - Verify if the file /etc/sysconfig/ctdb exists on all the nodes that is used as Gluster NFS server. This file contains Red Hat Gluster Storage recommended CTDB configurations.
- Create /etc/ctdb/nodes file on all the nodes that is used as Gluster NFS servers and add the IPs of these nodes to the file.
10.16.157.0 10.16.157.3 10.16.157.6
10.16.157.0 10.16.157.3 10.16.157.6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The IPs listed here are the private IPs of NFS servers. - On all the nodes that are used as Gluster NFS server which require IP failover, create /etc/ctdb/public_addresses file and add the virtual IPs that CTDB should create to this file. Add these IP address in the following format:
<Virtual IP>/<routing prefix><node interface>
<Virtual IP>/<routing prefix><node interface>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:192.168.1.20/24 eth0 192.168.1.21/24 eth0
192.168.1.20/24 eth0 192.168.1.21/24 eth0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the CTDB service on all the nodes by executing the following command:
service ctdb start
# service ctdb startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
6.2.2.2. Using Gluster NFS to Mount Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes
Note
nfsmount.conf file at /etc/nfsmount.conf by adding the following text in the file:
Defaultvers=3
vers=3 manually in all the mount commands.
# mount nfsserver:export -o vers=3 /MOUNTPOINT
tcp,rdma volume it could be changed using the volume set option nfs.transport-type.
6.2.2.2.1. Manually Mounting Volumes Using Gluster NFS
mount command to manually mount a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume using Gluster NFS.
- If a mount point has not yet been created for the volume, run the
mkdircommand to create a mount point.mkdir /mnt/glusterfs
# mkdir /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the correct
mountcommand for the system.- For Linux
mount -t nfs -o vers=3 server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t nfs -o vers=3 server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For Solaris
mount -o vers=3 nfs://server1:38467/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -o vers=3 nfs://server1:38467/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
mount command to manually mount a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume using Gluster NFS over TCP.
Note
requested NFS version or transport protocol is not supported
nfs.mount-udp is supported for mounting a volume, by default it is disabled. The following are the limitations:
- If
nfs.mount-udpis enabled, the MOUNT protocol needed for NFSv3 can handle requests from NFS-clients that require MOUNT over UDP. This is useful for at least some versions of Solaris, IBM AIX and HP-UX. - Currently, MOUNT over UDP does not have support for mounting subdirectories on a volume. Mounting
server:/volume/subdirexports is only functional when MOUNT over TCP is used. - MOUNT over UDP does not currently have support for different authentication options that MOUNT over TCP honors. Enabling
nfs.mount-udpmay give more permissions to NFS clients than intended via various authentication options likenfs.rpc-auth-allow,nfs.rpc-auth-rejectandnfs.export-dir.
- If a mount point has not yet been created for the volume, run the
mkdircommand to create a mount point.mkdir /mnt/glusterfs
# mkdir /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the correct
mountcommand for the system, specifying the TCP protocol option for the system.- For Linux
mount -t nfs -o vers=3,mountproto=tcp server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t nfs -o vers=3,mountproto=tcp server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For Solaris
mount -o proto=tcp, nfs://server1:38467/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -o proto=tcp, nfs://server1:38467/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.2.2.2. Automatically Mounting Volumes Using Gluster NFS
Note
/etc/auto.master and /etc/auto.misc files, and restart the autofs service. Whenever a user or process attempts to access the directory it will be mounted in the background on-demand.
- Open the
/etc/fstabfile in a text editor. - Append the following configuration to the
fstabfile.HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR nfs defaults,_netdev, 0 0
HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR nfs defaults,_netdev, 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Using the example server names, the entry contains the following replaced values.server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs nfs defaults,_netdev, 0 0
server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs nfs defaults,_netdev, 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Open the
/etc/fstabfile in a text editor. - Append the following configuration to the
fstabfile.HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR nfs defaults,_netdev,mountproto=tcp 0 0
HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME /MOUNTDIR nfs defaults,_netdev,mountproto=tcp 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Using the example server names, the entry contains the following replaced values.server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs nfs defaults,_netdev,mountproto=tcp 0 0
server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs nfs defaults,_netdev,mountproto=tcp 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.2.2.3. Automatically Mounting Subdirectories Using NFS
nfs.export-dir and nfs.export-dirs options provide granular control to restrict or allow specific clients to mount a sub-directory. These clients can be authenticated during sub-directory mount with either an IP, host name or a Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) range.
- nfs.export-dirs
- This option is enabled by default. It allows the sub-directories of exported volumes to be mounted by clients without needing to export individual sub-directories. When enabled, all sub-directories of all volumes are exported. When disabled, sub-directories must be exported individually in order to mount them on clients.To disable this option for all volumes, run the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.export-dirs off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.export-dirs offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - nfs.export-dir
- When
nfs.export-dirsis set toon, thenfs.export-diroption allows you to specify one or more sub-directories to export, rather than exporting all subdirectories (nfs.export-dirs on), or only exporting individually exported subdirectories (nfs.export-dirs off).To export certain subdirectories, run the following command:gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.export-dir subdirectory
# gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.export-dir subdirectoryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The subdirectory path should be the path from the root of the volume. For example, in a volume with six subdirectories, to export the first three subdirectories, the command would be the following:gluster volume set myvolume nfs.export-dir /dir1,/dir2,/dir3
# gluster volume set myvolume nfs.export-dir /dir1,/dir2,/dir3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Subdirectories can also be exported based on the IP address, hostname, or a Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) range by adding these details in parentheses after the directory path:gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.export-dir subdirectory(IPADDRESS),subdirectory(HOSTNAME),subdirectory(CIDR)
# gluster volume set VOLNAME nfs.export-dir subdirectory(IPADDRESS),subdirectory(HOSTNAME),subdirectory(CIDR)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow gluster volume set myvolume nfs.export-dir /dir1(192.168.10.101),/dir2(storage.example.com),/dir3(192.168.98.0/24)
# gluster volume set myvolume nfs.export-dir /dir1(192.168.10.101),/dir2(storage.example.com),/dir3(192.168.98.0/24)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.2.2.4. Testing Volumes Mounted Using Gluster NFS
Testing Mounted Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes
Prerequisites
- Run the
mountcommand to check whether the volume was successfully mounted.mount server1:/test-volume on /mnt/glusterfs type nfs (rw,addr=server1)
# mount server1:/test-volume on /mnt/glusterfs type nfs (rw,addr=server1)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the
dfcommand to display the aggregated storage space from all the bricks in a volume.df -h /mnt/glusterfs Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on server1:/test-volume 28T 22T 5.4T 82% /mnt/glusterfs
# df -h /mnt/glusterfs Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on server1:/test-volume 28T 22T 5.4T 82% /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Move to the mount directory using the
cdcommand, and list the contents.cd /mnt/glusterfs ls
# cd /mnt/glusterfs # lsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.2.3. Troubleshooting Gluster NFS
- Q: The mount command on the NFS client fails with RPC Error: Program not registered. This error is encountered due to one of the following reasons:
- Q: The rpcbind service is not running on the NFS client. This could be due to the following reasons:
- Q: The NFS server glusterfsd starts but the initialization fails with nfsrpc- service: portmap registration of program failed error message in the log.
- Q: The NFS server start-up fails with the message Port is already in use in the log file.
- Q: The mount command fails with NFS server failed error:
- Q: The showmount command fails with clnt_create: RPC: Unable to receive error. This error is encountered due to the following reasons:
- Q: The application fails with Invalid argument or Value too large for defined data type
- Q: After the machine that is running NFS server is restarted the client fails to reclaim the locks held earlier.
- Q: The rpc actor failed to complete successfully error is displayed in the nfs.log, even after the volume is mounted successfully.
- Q: The mount command fails with No such file or directory.
RPC Error: Program not registered. This error is encountered due to one of the following reasons:
- The NFS server is not running. You can check the status using the following command:
gluster volume status
# gluster volume statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The volume is not started. You can check the status using the following command:
gluster volume info
# gluster volume infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - rpcbind is restarted. To check if rpcbind is running, execute the following command:
# ps ax| grep rpcbind
- If the NFS server is not running, then restart the NFS server using the following command:
gluster volume start VOLNAME
# gluster volume start VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the volume is not started, then start the volume using the following command:
gluster volume start VOLNAME
# gluster volume start VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If both rpcbind and NFS server is running then restart the NFS server using the following commands:
# gluster volume stop VOLNAME# gluster volume start VOLNAME
rpcbind service is not running on the NFS client. This could be due to the following reasons:
- The portmap is not running.
- Another instance of kernel NFS server or glusterNFS server is running.
rpcbind service by running the following command:
service rpcbind start
# service rpcbind start- Start the rpcbind service on the NFS server by running the following command:
service rpcbind start
# service rpcbind startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After starting rpcbind service, glusterFS NFS server needs to be restarted. - Stop another NFS server running on the same machine.Such an error is also seen when there is another NFS server running on the same machine but it is not the glusterFS NFS server. On Linux systems, this could be the kernel NFS server. Resolution involves stopping the other NFS server or not running the glusterFS NFS server on the machine. Before stopping the kernel NFS server, ensure that no critical service depends on access to that NFS server's exports.On Linux, kernel NFS servers can be stopped by using either of the following commands depending on the distribution in use:
service nfs-kernel-server stop service nfs stop
# service nfs-kernel-server stop # service nfs stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart glusterFS NFS server.
mount command fails with NFS server failed error:
mount: mount to NFS server '10.1.10.11' failed: timed out (retrying).
mount: mount to NFS server '10.1.10.11' failed: timed out (retrying).- Disable name lookup requests from NFS server to a DNS server.The NFS server attempts to authenticate NFS clients by performing a reverse DNS lookup to match host names in the volume file with the client IP addresses. There can be a situation where the NFS server either is not able to connect to the DNS server or the DNS server is taking too long to respond to DNS request. These delays can result in delayed replies from the NFS server to the NFS client resulting in the timeout error.NFS server provides a work-around that disables DNS requests, instead relying only on the client IP addresses for authentication. The following option can be added for successful mounting in such situations:
option nfs.addr.namelookup off
option nfs.addr.namelookup offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Remember that disabling the NFS server forces authentication of clients to use only IP addresses. If the authentication rules in the volume file use host names, those authentication rules will fail and client mounting will fail. - NFS version used by the NFS client is other than version 3 by default.glusterFS NFS server supports version 3 of NFS protocol by default. In recent Linux kernels, the default NFS version has been changed from 3 to 4. It is possible that the client machine is unable to connect to the glusterFS NFS server because it is using version 4 messages which are not understood by glusterFS NFS server. The timeout can be resolved by forcing the NFS client to use version 3. The vers option to mount command is used for this purpose:
# mount nfsserver:export -o vers=3 /MOUNTPOINT
- The firewall might have blocked the port.
- rpcbind might not be running.
NFS.enable-ino32 <on | off>
NFS.enable-ino32 <on | off>off by default, which permits NFS to return 64-bit inode numbers by default.
- built and run on 32-bit machines, which do not support large files by default,
- built to 32-bit standards on 64-bit systems.
-D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64
-D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64chkconfig --list nfslock to check if NSM is configured during OS boot.
on,run chkconfig nfslock off to disable NSM clients during boot, which resolves the issue.
rpc actor failed to complete successfully error is displayed in the nfs.log, even after the volume is mounted successfully.
nfs.log file.
[2013-06-25 00:03:38.160547] W [rpcsvc.c:180:rpcsvc_program_actor] 0-rpc-service: RPC program version not available (req 100003 4) [2013-06-25 00:03:38.160669] E [rpcsvc.c:448:rpcsvc_check_and_reply_error] 0-rpcsvc: rpc actor failed to complete successfully
[2013-06-25 00:03:38.160547] W [rpcsvc.c:180:rpcsvc_program_actor] 0-rpc-service: RPC program version not available (req 100003 4)
[2013-06-25 00:03:38.160669] E [rpcsvc.c:448:rpcsvc_check_and_reply_error] 0-rpcsvc: rpc actor failed to complete successfullynoacl option in the mount command as follows:
mount -t nfs -o vers=3,noacl server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t nfs -o vers=3,noacl server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsNo such file or directory.
6.2.3. NFS Ganesha
Note
6.2.3.1. Supported Features of NFS-Ganesha
In a highly available active-active environment, if a NFS-Ganesha server that is connected to a NFS client running a particular application goes down, the application/NFS client is seamlessly connected to another NFS-Ganesha server without any administrative intervention.
NFS-Ganesha supports addition and removal of exports dynamically. Dynamic exports is managed by the DBus interface. DBus is a system local IPC mechanism for system management and peer-to-peer application communication.
In NFS-Ganesha, multiple Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes or sub-directories can be exported simultaneously.
NFS-Ganesha creates and maintains a NFSv4 pseudo-file system, which provides clients with seamless access to all exported objects on the server.
NFS-Ganesha NFSv4 protocol includes integrated support for Access Control List (ACL)s, which are similar to those used by Windows. These ACLs can be used to identify a trustee and specify the access rights allowed, or denied for that trustee.This feature is disabled by default.
Note
6.2.3.2. Setting up NFS Ganesha
Note
6.2.3.2.1. Port and Firewall Information for NFS-Ganesha
| Service | Port Number | Protocol |
| sshd | 22 | TCP |
| rpcbind/portmapper | 111 | TCP/UDP |
| NFS | 2049 | TCP/UDP |
| mountd | 20048 | TCP/UDP |
| NLM | 32803 | TCP/UDP |
| RQuota | 875 | TCP/UDP |
| statd | 662 | TCP/UDP |
| pcsd | 2224 | TCP |
| pacemaker_remote | 3121 | TCP |
| corosync | 5404 and 5405 | UDP |
| dlm | 21064 | TCP |
Note
Ensure the statd service is configured to use the ports mentioned above by executing the following commands on every node in the nfs-ganesha cluster:
- Edit /etc/sysconfig/nfs file as mentioned below:
sed -i '/STATD_PORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs
# sed -i '/STATD_PORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the statd service:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl restart nfs-config systemctl restart rpc-statd
# systemctl restart nfs-config # systemctl restart rpc-statdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
- Edit '/etc/sysconfig/nfs' using following commands:
sed -i '/STATD_PORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs sed -i '/LOCKD_TCPPORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs sed -i '/LOCKD_UDPPORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs
# sed -i '/STATD_PORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs # sed -i '/LOCKD_TCPPORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfs # sed -i '/LOCKD_UDPPORT/s/^#//' /etc/sysconfig/nfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the services:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl restart nfs-config systemctl restart rpc-statd systemctl restart nfslock
# systemctl restart nfs-config # systemctl restart rpc-statd # systemctl restart nfslockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Open the ports that are configured in the first step using the following commnad:
firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \ --add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \ --add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \ --add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=662/tcp --add-port=662/udp \ --add-port=32803/tcp --add-port=32769/udp --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To ensure NFS client UDP mount does not fail, ensure to open port 2049 by executing the following command:
firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=2049/udp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=2049/udp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=2049/udp # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=2049/udp --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Firewall SettingsOn Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, enable the firewall services mentioned below.
- Get a list of active zones using the following command:
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Allow the firewall service in the active zones, run the following commands:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.3.2.2. Prerequisites to run NFS-Ganesha
- A Red Hat Gluster Storage volume must be available for export and NFS-Ganesha rpms are installed.
- Ensure that the fencing agents are configured. For more information on configuring fencing agents, refer to the following documenation:
- Fencing Configuration section in the High Availability Add-On Administration guide: https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/high_availability_add-on_administration/s1-fenceconfig-haaa
- Fence Devices section in the High Availability Add-On Reference guide: https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/high_availability_add-on_reference/s1-guiclustcomponents-haar#s2-guifencedevices-HAAR
- Only one of NFS-Ganesha, gluster-NFS or kernel-NFS servers can be enabled on a given machine/host as all NFS implementations use the port 2049 and only one can be active at a given time. Hence you must disable kernel-NFS before NFS-Ganesha is started.Disable the kernel-nfs using the following command:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
systemctl stop nfs-server systemctl disable nfs-server
# systemctl stop nfs-server # systemctl disable nfs-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify if kernel-nfs is disabled, execute the following command:systemctl status nfs-server
# systemctl status nfs-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The service should be in stopped state.Note
Gluster NFS will be stopped automatically when NFS-Ganesha is enabled.Ensure that none of the volumes have the variablenfs.disableset to 'off'. - Ensure to configure the ports as mentioned in Port/Firewall Information for NFS-Ganesha.
- Edit the ganesha-ha.conf file based on your environment.
- Reserve virtual IPs on the network for each of the servers configured in the ganesha.conf file. Ensure that these IPs are different than the hosts' static IPs and are not used anywhere else in the trusted storage pool or in the subnet.
- Ensure that all the nodes in the cluster are DNS resolvable. For example, you can populate the /etc/hosts with the details of all the nodes in the cluster.
- Make sure the SELinux is in Enforcing mode.
- Start network service on all machines using the following command:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl start network
# systemctl start networkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create and mount a gluster shared volume by executing the following command:
gluster volume set all cluster.enable-shared-storage enable volume set: success
# gluster volume set all cluster.enable-shared-storage enable volume set: successCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information, see Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume” - Create a directory named
nfs-ganeshaunder/var/run/gluster/shared_storage - Copy the
ganesha.confandganesha-ha.conffiles from/etc/ganeshato/var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha. - Enable the glusterfssharedstorage.service service using the following command:
systemctl enable glusterfssharedstorage.service
systemctl enable glusterfssharedstorage.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Enable the nfs-ganesha service using the following command:
systemctl enable nfs-ganesha
systemctl enable nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.3.2.3. Configuring the Cluster Services
Note
- Enable the pacemaker service using the following command:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl enable pacemaker.service
# systemctl enable pacemaker.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the pcsd service using the following command.For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl start pcsd
# systemctl start pcsdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- To start pcsd by default after the system is rebooted, execute the following command:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
systemctl enable pcsd
# systemctl enable pcsdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Set a password for the user ‘hacluster’ on all the nodes using the following command. Use the same password for all the nodes:
echo <password> | passwd --stdin hacluster
# echo <password> | passwd --stdin haclusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Perform cluster authentication between the nodes, where, username is ‘hacluster’, and password is the one you used in the previous step. Ensure to execute the following command on every node:
pcs cluster auth <hostname1> <hostname2> ...
# pcs cluster auth <hostname1> <hostname2> ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The hostname of all the nodes in the Ganesha-HA cluster must be included in the command when executing it on every node.For example, in a four node cluster; nfs1, nfs2, nfs3, and nfs4, execute the following command on every node:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Key-based SSH authentication without password for the root user has to be enabled on all the HA nodes. Follow these steps:
- On one of the nodes (node1) in the cluster, run:
ssh-keygen -f /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem -t rsa -N ''
# ssh-keygen -f /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem -t rsa -N ''Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Deploy the generated public key from node1 to all the nodes (including node1) by executing the following command for every node:
ssh-copy-id -i /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem.pub root@<node-ip/hostname>
# ssh-copy-id -i /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem.pub root@<node-ip/hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Copy the ssh keypair from node1 to all the nodes in the Ganesha-HA cluster by executing the following command for every node:
scp -i /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.* root@<node-ip/hostname>:/var/lib/glusterd/nfs/
# scp -i /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.* root@<node-ip/hostname>:/var/lib/glusterd/nfs/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- As part of cluster setup, port 875 is used to bind to the Rquota service. If this port is already in use, assign a different port to this service by modifying following line in ‘/etc/ganesha/ganesha.conf’ file on all the nodes.
# Use a non-privileged port for RQuota Rquota_Port = 875;
# Use a non-privileged port for RQuota Rquota_Port = 875;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.3.2.4. Creating the ganesha-ha.conf file
- Create a directory named nfs-ganesha under /var/run/gluster/shared_storage
- Copy the ganesha.conf and ganesha-ha.conf files from /etc/ganesha to /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha.
Note
- Pacemaker handles the creation of the VIP and assigning an interface.
- Ensure that the VIP is in the same network range.
- Ensure that the HA_CLUSTER_NODES are specified as hostnames. Using IP addresses will cause clustering to fail.
6.2.3.2.5. Configuring NFS-Ganesha using Gluster CLI
To setup the HA cluster, enable NFS-Ganesha by executing the following command:
- Enable NFS-Ganesha by executing the following command
gluster nfs-ganesha enable
# gluster nfs-ganesha enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Before enabling or disabling NFS-Ganesha, ensure that all the nodes that are part of the NFS-Ganesha cluster are up.For example,gluster nfs-ganesha enable Enabling NFS-Ganesha requires Gluster-NFS to be disabled across the trusted pool. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y This will take a few minutes to complete. Please wait .. nfs-ganesha : success
# gluster nfs-ganesha enable Enabling NFS-Ganesha requires Gluster-NFS to be disabled across the trusted pool. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y This will take a few minutes to complete. Please wait .. nfs-ganesha : successCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
After enabling NFS-Ganesha, ifrpcinfo -pshows the statd port different from 662, then, restart the statd service:For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:systemctl restart rpc-statd
# systemctl restart rpc-statdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Tearing down the HA clusterTo tear down the HA cluster, execute the following command:
gluster nfs-ganesha disable
# gluster nfs-ganesha disableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster nfs-ganesha disable Disabling NFS-Ganesha will tear down entire ganesha cluster across the trusted pool. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y This will take a few minutes to complete. Please wait .. nfs-ganesha : success
# gluster nfs-ganesha disable Disabling NFS-Ganesha will tear down entire ganesha cluster across the trusted pool. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y This will take a few minutes to complete. Please wait .. nfs-ganesha : successCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verifying the status of the HA clusterTo verify the status of the HA cluster, execute the following script:
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --status /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --status /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --status /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --status /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- It is recommended to manually restart the
ganesha.nfsdservice after the node is rebooted, to fail back the VIPs. - Disabling NFS Ganesha does not enable Gluster NFS by default. If required, Gluster NFS must be enabled manually.
6.2.3.2.6. Exporting and Unexporting Volumes through NFS-Ganesha
To export a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume, execute the following command:
gluster volume set <volname> ganesha.enable on
# gluster volume set <volname> ganesha.enable ongluster vol set testvol ganesha.enable on volume set: success
# gluster vol set testvol ganesha.enable on
volume set: successTo unexport a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume, execute the following command:
gluster volume set <volname> ganesha.enable off
# gluster volume set <volname> ganesha.enable offgluster vol set testvol ganesha.enable off volume set: success
# gluster vol set testvol ganesha.enable off
volume set: success6.2.3.2.7. Verifying the NFS-Ganesha Status
- Check if NFS-Ganesha is started by executing the following commands:On Red Hat Enterprise Linux-7
systemctl status nfs-ganesha
# systemctl status nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check if the volume is exported.
showmount -e localhost
# showmount -e localhostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:showmount -e localhost Export list for localhost: /volname (everyone)
# showmount -e localhost Export list for localhost: /volname (everyone)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The logs of ganesha.nfsd daemon are written to /var/log/ganesha/ganesha.log. Check the log file on noticing any unexpected behavior.
6.2.3.3. Accessing NFS-Ganesha Exports
- Execute the following commands to set the tunable:
sysctl -w sunrpc.tcp_slot_table_entries=128 echo 128 > /proc/sys/sunrpc/tcp_slot_table_entries echo 128 > /proc/sys/sunrpc/tcp_max_slot_table_entries
# sysctl -w sunrpc.tcp_slot_table_entries=128 # echo 128 > /proc/sys/sunrpc/tcp_slot_table_entries # echo 128 > /proc/sys/sunrpc/tcp_max_slot_table_entriesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To make the tunable persistent on reboot, execute the following commands:
echo "options sunrpc tcp_slot_table_entries=128" >> /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.conf echo "options sunrpc tcp_max_slot_table_entries=128" >> /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.conf
# echo "options sunrpc tcp_slot_table_entries=128" >> /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.conf # echo "options sunrpc tcp_max_slot_table_entries=128" >> /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
6.2.3.3.1. Mounting exports in NFSv3 Mode
mount -t nfs -o vers=3 virtual_ip:/volname /mountpoint
# mount -t nfs -o vers=3 virtual_ip:/volname /mountpointmount -t nfs -o vers=3 10.70.0.0:/testvol /mnt
mount -t nfs -o vers=3 10.70.0.0:/testvol /mnt6.2.3.3.2. Mounting exports in NFSv4 Mode
mount -t nfs -o vers=4.0 virtual_ip:/volname /mountpoint
# mount -t nfs -o vers=4.0 virtual_ip:/volname /mountpointmount -t nfs -o vers=4.0 10.70.0.0:/testvol /mnt
# mount -t nfs -o vers=4.0 10.70.0.0:/testvol /mnt6.2.3.3.3. Finding clients of an NFS server using dbus
dbus-send --type=method_call --print-reply --system --dest=org.ganesha.nfsd /org/ganesha/nfsd/ClientMgr org.ganesha.nfsd.clientmgr.ShowClients
# dbus-send --type=method_call --print-reply --system --dest=org.ganesha.nfsd /org/ganesha/nfsd/ClientMgr org.ganesha.nfsd.clientmgr.ShowClientsNote
6.2.3.4. Modifying the NFS-Ganesha HA Setup
6.2.3.4.1. Adding a Node to the Cluster
Note
/var/lib/glusterd/nfs/secret.pem SSH key are already generated, those steps should not be repeated.
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --add <HA_CONF_DIR> <HOSTNAME> <NODE-VIP>
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --add <HA_CONF_DIR> <HOSTNAME> <NODE-VIP>/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha.
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --add /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha server16 10.00.00.01
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --add /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha server16 10.00.00.01
6.2.3.4.2. Deleting a Node in the Cluster
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --delete <HA_CONF_DIR> <HOSTNAME>
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --delete <HA_CONF_DIR> <HOSTNAME>/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha.
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --delete /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha server16
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --delete /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha server166.2.3.5. Modifying the Default Export Configurations
ganesha-export-config 8 man page.
- Edit/add the required fields in the corresponding export file located at
/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha/exports/. - Execute the following command
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --refresh-config <HA_CONF_DIR> <volname>
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --refresh-config <HA_CONF_DIR> <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- HA_CONF_DIR: The directory path containing the ganesha-ha.conf file. By default it is located at
/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha. - volname: The name of the volume whose export configuration has to be changed.
- Providing Permissions for Specific Clients
- Enabling and Disabling NFSv4 ACLs
- Providing Pseudo Path for NFSv4 Mount
- Exporting Subdirectories
6.2.3.5.1. Providing Permissions for Specific Clients
EXPORT block applies to any client that mounts the exported volume. To provide specific permissions to specific clients , introduce a client block inside the EXPORT block.
EXPORT block.
export.conf file to see the expected behavior.
client block.
6.2.3.5.2. Enabling and Disabling NFSv4 ACLs
Disable_ACL = FALSE;
Disable_ACL = FALSE;Note
6.2.3.5.3. Providing Pseudo Path for NFSv4 Mount
Pseudo = "pseudo_path"; # NFSv4 pseudo path for this export. Eg: "/test_volume_pseudo"
Pseudo = "pseudo_path"; # NFSv4 pseudo path for this export. Eg: "/test_volume_pseudo"6.2.3.5.4. Exporting Subdirectories
- Stop the volume by executing the following command:
gluster volume stop <volname>
# gluster volume stop <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To export subdirectories within a volume, edit the following parameters in the
export.conffile.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change
Export_IDto an unused value. I should preferably be a larger value so that it cannot be re-used for other volumes. - Restart the volume to export the subdirectory.
gluster volume start <volname>
# gluster volume start <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
6.2.3.5.5. Configuring Upcall Poll Interval
up_poll_usec option. You can set an optimal value depending on the workload. The default value of up_poll_usec option is set to 10 miscroseconds and can be increased upto 60000000 microseconds (60s).
export.<volume name>.conf file.
up_poll_usec in the FSAL Gluster block in export.<volume name>.conf file.
6.2.3.5.6. Enabling all_squash option
all_squash, edit the following parameter:
Squash = all_squash ; # To enable/disable root squashing
Squash = all_squash ; # To enable/disable root squashing6.2.3.6. Configuring Kerberized NFS-Ganesha
- Install the krb5-workstation and the ntpdate packages on all the machines:
yum install krb5-workstation yum install ntpdate
# yum install krb5-workstation # yum install ntpdateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- The krb5-libs package will be updated as a dependent package.
- Configure the ntpdate based on the valid time server according to the environment:
echo <valid_time_server> >> /etc/ntp/step-tickers systemctl enable ntpdate systemctl start ntpdate
# echo <valid_time_server> >> /etc/ntp/step-tickers # systemctl enable ntpdate # systemctl start ntpdateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that all systems can resolve each other by FQDN in DNS.
- Configure the
/etc/krb5.conffile and add relevant changes accordingly. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
For further details regarding the file configuration, refer toman krb5.conf. - On the NFS-server and client, update the /etc/idmapd.conf file by making the required change. For example:
Domain = example.com
Domain = example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.3.6.1. Setting up the NFS-Ganesha Server:
Note
- Install the following packages:
yum install nfs-utils yum install rpcbind
# yum install nfs-utils # yum install rpcbindCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Install the relevant gluster and NFS-Ganesha rpms. For more information see, Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 Installation Guide.
- Create a Kerberos principle and add it to krb5.keytab on the NFS-Ganesha server
kadmin kadmin: addprinc -randkey nfs/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COM kadmin: ktadd nfs/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COM
$ kadmin $ kadmin: addprinc -randkey nfs/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COM $ kadmin: ktadd nfs/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COMCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Update
/etc/ganesha/ganesha.conffile as mentioned below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Based on the different kerberos security flavours (krb5, krb5i and krb5p) supported by nfs-ganesha, configure the 'SecType' parameter in the volume export file (/var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha/exports) with appropriate security flavour
- Create an unprivileged user and ensure that the users that are created are resolvable to the UIDs through the central user database. For example:
useradd guest
# useradd guestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The username of this user has to be the same as the one on the NFS-client.
6.2.3.6.2. Setting up the NFS Client
Note
- Install the following packages:
yum install nfs-utils yum install rpcbind
# yum install nfs-utils # yum install rpcbindCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a kerberos principle and add it to krb5.keytab on the client side. For example:
kadmin kadmin: addprinc -randkey host/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COM kadmin: ktadd host/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COM
# kadmin # kadmin: addprinc -randkey host/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COM # kadmin: ktadd host/<host_name>@EXAMPLE.COMCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check the status of nfs-client.target service and start it, if not already started:
systemctl status nfs-client.target systemctl start nfs-client.target systemctl enable nfs-client.target
# systemctl status nfs-client.target # systemctl start nfs-client.target # systemctl enable nfs-client.targetCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create an unprivileged user and ensure that the users that are created are resolvable to the UIDs through the central user database. For example:
useradd guest
# useradd guestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The username of this user has to be the same as the one on the NFS-server. - Mount the volume specifying kerberos security type:
mount -t nfs -o sec=krb5 <host_name>:/testvolume /mnt
# mount -t nfs -o sec=krb5 <host_name>:/testvolume /mntCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow As root, all access should be granted.For example:Creation of a directory on the mount point and all other operations as root should be successful.mkdir <directory name>
# mkdir <directory name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Login as a guest user:
su - guest
# su - guestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Without a kerberos ticket, all access to /mnt should be denied. For example:su guest ls ls: cannot open directory .: Permission denied
# su guest # ls ls: cannot open directory .: Permission deniedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Get the kerberos ticket for the guest and access /mnt:
kinit Password for guest@EXAMPLE.COM: ls <directory created>
# kinit Password for guest@EXAMPLE.COM: # ls <directory created>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
With this ticket, some access must be allowed to /mnt. If there are directories on the NFS-server where "guest" does not have access to, it should work correctly.
6.2.3.7. NFS-Ganesha Service Downtime
- If the ganesha.nfsd dies (crashes, oomkill, admin kill), the maximum time to detect it and put the ganesha cluster into grace is 20sec, plus whatever time pacemaker needs to effect the fail-over.
Note
This time taken to detect if the service is down, can be edited using the following command on all the nodes:pcs resource op remove nfs-mon monitor pcs resource op add nfs-mon monitor interval=<interval_period_value>
# pcs resource op remove nfs-mon monitor # pcs resource op add nfs-mon monitor interval=<interval_period_value>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the whole node dies (including network failure) then this down time is the total of whatever time pacemaker needs to detect that the node is gone, the time to put the cluster into grace, and the time to effect the fail-over. This is ~20 seconds.
- So the max-fail-over time is approximately 20-22 seconds, and the average time is typically less. In other words, the time taken for NFS clients to detect server reboot or resume I/O is 20 - 22 seconds.
6.2.3.7.1. Modifying the Fail-over Time
| Protocols | FOPs |
| NFSV3 |
|
| NLM |
|
| NFSV4 |
|
Note
/etc/ganesha/ganesha.conf file.
NFSv4 {
Grace_Period=<grace_period_value_in_sec>;
}
NFSv4 {
Grace_Period=<grace_period_value_in_sec>;
}/etc/ganesha/ganesha.conf file, restart the NFS-Ganesha service using the following command on all the nodes :
systemctl restart nfs-ganesha
# systemctl restart nfs-ganesha6.2.3.8. Manually Configuring NFS-Ganesha Exports
- Edit/add the required fields in the corresponding export configuration file in the
/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha/exportsdirectory. - Execute the following command
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --refresh-config <HA_CONF_DIR> <volname>
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --refresh-config <HA_CONF_DIR> <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- HA_CONF_DIR: The directory path containing the ganesha-ha.conf file. By default it is located at
/etc/ganesha. - volname: The name of the volume whose export configuration has to be changed.
export.conf file to see the expected behavior.
- Exporting Subdirectories
- Providing Permissions for Specific Clients
- Enabling and Disabling NFSv4 ACLs
- Providing Pseudo Path for NFSv4 Mount
To export subdirectories within a volume, edit the following parameters in the export.conf file.
The parameter values and permission values given in the EXPORT block applies to any client that mounts the exported volume. To provide specific permissions to specific clients , introduce a client block inside the EXPORT block.
EXPORT block.
client block.
To enable NFSv4 ACLs , edit the following parameter:
Disable_ACL = FALSE;
Disable_ACL = FALSE;To set NFSv4 pseudo path , edit the below parameter:
Pseudo = "pseudo_path"; # NFSv4 pseudo path for this export. Eg: "/test_volume_pseudo"
Pseudo = "pseudo_path"; # NFSv4 pseudo path for this export. Eg: "/test_volume_pseudo"6.2.3.9. Troubleshooting
Ensure you execute the following commands for all the issues/failures that is encountered:
- Make sure all the prerequisites are met.
- Execute the following commands to check the status of the services:
service nfs-ganesha status service pcsd status service pacemaker status pcs status
# service nfs-ganesha status # service pcsd status # service pacemaker status # pcs statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Review the followings logs to understand the cause of failure.
/var/log/ganesha/ganesha.log /var/log/ganesha/ganesha-gfapi.log /var/log/messages /var/log/pcsd.log
/var/log/ganesha/ganesha.log /var/log/ganesha/ganesha-gfapi.log /var/log/messages /var/log/pcsd.logCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Situation
NFS-Ganesha fails to start.
SolutionEnsure you execute all the mandatory checks to understand the root cause before proceeding with the following steps. Follow the listed steps to fix the issue:
- Ensure the kernel and gluster nfs services are inactive.
- Ensure that the port 875 is free to connect to the RQUOTA service.
- Ensure that the shared storage volume mount exists on the server after node reboot/shutdown. If it does not, then mount the shared storage volume manually using the following command:
mount -t glusterfs <local_node's_hostname>:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage
# mount -t glusterfs <local_node's_hostname>:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For more information see, section Manually Configuring NFS-Ganesha Exports. - Situation
NFS-Ganesha port 875 is unavailable.
SolutionEnsure you execute all the mandatory checks to understand the root cause before proceeding with the following steps. Follow the listed steps to fix the issue:
- Run the following command to extract the PID of the process using port 875:
netstat -anlp | grep 875
netstat -anlp | grep 875Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Determine if the process using port 875 is an important system or user process.
- Perform one of the following depending upon the importance of the process:
- If the process using port 875 is an important system or user process:
- Assign a different port to this service by modifying following line in ‘/etc/ganesha/ganesha.conf’ file on all the nodes:
# Use a non-privileged port for RQuota Rquota_Port = port_number;
# Use a non-privileged port for RQuota Rquota_Port = port_number;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the following commands after modifying the port number:
semanage port -a -t mountd_port_t -p tcp port_number semanage port -a -t mountd_port_t -p udp port_number
# semanage port -a -t mountd_port_t -p tcp port_number # semanage port -a -t mountd_port_t -p udp port_numberCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the following command to restart NFS-Ganesha:
systemctl restart nfs-ganesha
systemctl restart nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- If the process using port 875 is not an important system or user process:
- Run the following command to kill the process using port 875:
kill pid;
# kill pid;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the process ID extracted from the previous step. - Run the following command to ensure that the process is killed and port 875 is free to use:
ps aux | grep pid;
# ps aux | grep pid;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the following command to restart NFS-Ganesha:
systemctl restart nfs-ganesha
systemctl restart nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If required, restart the killed process.
- Situation
NFS-Ganesha Cluster setup fails.
SolutionEnsure you execute all the mandatory checks to understand the root cause before proceeding with the following steps.
- Ensure the kernel and gluster nfs services are inactive.
- Ensure that
pcs cluster authcommand is executed on all the nodes with same password for the userhacluster - Ensure that shared volume storage is mounted on all the nodes.
- Ensure that the name of the HA Cluster does not exceed 15 characters.
- Ensure UDP multicast packets are pingable using
OMPING. - Ensure that Virtual IPs are not assigned to any NIC.
- Situation
NFS-Ganesha has started and fails to export a volume.
SolutionEnsure you execute all the mandatory checks to understand the root cause before proceeding with the following steps. Follow the listed steps to fix the issue:
- Ensure that volume is in
Startedstate using the following command:gluster volume status <volname>
# gluster volume status <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following commands to check the status of the services:
service nfs-ganesha status showmount -e localhost
# service nfs-ganesha status # showmount -e localhostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Review the followings logs to understand the cause of failure.
/var/log/ganesha/ganesha.log /var/log/ganesha/ganesha-gfapi.log /var/log/messages
/var/log/ganesha/ganesha.log /var/log/ganesha/ganesha-gfapi.log /var/log/messagesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that dbus service is running using the following command
service messagebus status
# service messagebus statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the volume is not in a started state, run the following command to start the volume.
gluster volume start <volname>
# gluster volume start <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the volume is not exported as part of volume start, run the following command to re-export the volume:/usr/libexec/ganesha/dbus-send.sh /var/run/gluster/shared_storage on <volname>
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/dbus-send.sh /var/run/gluster/shared_storage on <volname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Situation
Adding a new node to the HA cluster fails.
SolutionEnsure you execute all the mandatory checks to understand the root cause before proceeding with the following steps. Follow the listed steps to fix the issue:
- Ensure to run the following command from one of the nodes that is already part of the cluster:
ganesha-ha.sh --add <HA_CONF_DIR> <NODE-HOSTNAME> <NODE-VIP>
# ganesha-ha.sh --add <HA_CONF_DIR> <NODE-HOSTNAME> <NODE-VIP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that gluster_shared_storage volume is mounted on the node that needs to be added.
- Make sure that all the nodes of the cluster is DNS resolvable from the node that needs to be added.
- Execute the following command for each of the hosts in the HA cluster on the node that needs to be added:
pcs cluster auth <hostname>
# pcs cluster auth <hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Situation
Cleanup required when nfs-ganesha HA cluster setup fails.
SolutionTo restore back the machines to the original state, execute the following commands on each node forming the cluster:
/usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --teardown /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --cleanup /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha systemctl stop nfs-ganesha
# /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --teardown /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha # /usr/libexec/ganesha/ganesha-ha.sh --cleanup /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha # systemctl stop nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Situation
Permission issues.
SolutionBy default, the
root squashoption is disabled when you start NFS-Ganesha using the CLI. In case, you encounter any permission issues, check the unix permissions of the exported entry.
6.3. SMB
Important
Overview of configuring SMB shares
- Verify that your system fulfils the requirements outlined in Section 6.3.1, “Requirements for using SMB with Red Hat Gluster Storage”.
- Configure CTDB to export Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes with Samba: Section 6.3.2, “Setting up CTDB for Samba”.
- Configure your volumes to be shared using SMB: Section 6.3.3, “Sharing Volumes over SMB”.
- If you want to mount volumes on macOS clients: Section 6.3.4.1, “Configuring the Apple Create Context for macOS users”.
- Set up permissions for user access: Section 6.3.4.2, “Configuring read/write access for a non-privileged user”.
- Mount the shared volume on a client:
- Verify that your shared volume is working properly: Section 6.3.6, “Starting and Verifying your Configuration”
6.3.1. Requirements for using SMB with Red Hat Gluster Storage
- Samba is the server software used to export Linux filesystems with the SMB protocol. For exporting Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes with Samba, it is mandatory to have CTDB configured, which is a component of Samba. For information on subscribing to the correct channels for SMB support, see Subscribing to the Red Hat Gluster Storage server channels in the Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 Installation Guide.
- Enable the Samba firewall service in the active zones for runtime and permanent mode. The following commands are for systems based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.To get a list of active zones, run the following command:
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To allow the firewall services in the active zones, run the following commandsfirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=samba firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=samba --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=samba # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-service=samba --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.2. Setting up CTDB for Samba
Important
Prerequisites
- If you already have an older version of CTDB (version <= ctdb1.x), then remove CTDB by executing the following command:
yum remove ctdb
# yum remove ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After removing the older version, proceed with installing the latest CTDB.Note
Ensure that the system is subscribed to the samba channel to get the latest CTDB packages. - Install CTDB on all the nodes that are used as Samba servers to the latest version using the following command:
yum install ctdb
# yum install ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In a CTDB based high availability environment of Samba , the locks will not be migrated on failover.
- Enable the CTDB firewall service in the active zones for runtime and permanent mode. The following commands are for systems based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.To get a list of active zones, run the following command:
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To add ports to the active zones, run the following commands:firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=4379/tcp --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configuring CTDB on Red Hat Gluster Storage Server
- Create a new replicated volume to house the CTDB lock file. The lock file has a size of zero bytes, so use small bricks.To create a replicated volume run the following command, replacing N with the number of nodes to replicate across:
gluster volume create volname replica N ip_address_1:brick_path ... ip_address_N:brick_path
# gluster volume create volname replica N ip_address_1:brick_path ... ip_address_N:brick_pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume create ctdb replica 3 10.16.157.75:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b1 10.16.157.78:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b2 10.16.157.81:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b3
# gluster volume create ctdb replica 3 10.16.157.75:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b1 10.16.157.78:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b2 10.16.157.81:/rhgs/brick1/ctdb/b3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the following files, replace
allin the statementMETA="all"with the newly created volume name, for example,META="ctdb"./var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/start/post/S29CTDBsetup.sh /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/stop/pre/S29CTDB-teardown.sh
/var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/start/post/S29CTDBsetup.sh /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/stop/pre/S29CTDB-teardown.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the
/etc/samba/smb.conffile, add the following line in the global section on all the nodes:clustering=yes
clustering=yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the volume.The S29CTDBsetup.sh script runs on all Red Hat Gluster Storage servers, adds an entry in
/etc/fstabfor the mount, and mounts the volume at/gluster/lockon all the nodes with Samba server. It also enables automatic start of CTDB service on reboot.Note
When you stop the special CTDB volume, the S29CTDB-teardown.sh script runs on all Red Hat Gluster Storage servers and removes an entry in/etc/fstabfor the mount and unmounts the volume at/gluster/lock. - Verify that the
/etc/sysconfig/ctdbfile exists on all nodes that are used as a Samba server. This file contains CTDB configuration details recommended for Red Hat Gluster Storage. - Create the
/etc/ctdb/nodesfile on all the nodes that are used as Samba servers and add the IP addresses of these nodes to the file.10.16.157.0 10.16.157.3 10.16.157.6
10.16.157.0 10.16.157.3 10.16.157.6Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The IP addresses listed here are the private IP addresses of Samba servers. - On nodes that are used as Samba servers and require IP failover, create the
/etc/ctdb/public_addressesfile. Add any virtual IP addresses that CTDB should create to the file in the following format:VIP/routing_prefix network_interface
VIP/routing_prefix network_interfaceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:192.168.1.20/24 eth0 192.168.1.21/24 eth0
192.168.1.20/24 eth0 192.168.1.21/24 eth0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the CTDB service on all the nodes.
service ctdb start
# service ctdb startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.3. Sharing Volumes over SMB
If you are using an older version of Samba:
- Enable SMB specific caching:
gluster volume set VOLNAME performance.cache-samba-metadata on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME performance.cache-samba-metadata onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also enable generic metadata caching to improve performance. See Section 20.7, “Directory Operations” for details. - Restart the
glusterdservice on each Red Hat Gluster Storage node. - Verify proper lock and I/O coherence:
gluster volume set VOLNAME storage.batch-fsync-delay-usec 0
# gluster volume set VOLNAME storage.batch-fsync-delay-usec 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you are using Samba-4.8.5-104 or later:
- To export gluster volume as SMB share via Samba, one of the following volume options,
user.cifsoruser.smbis required.To enable user.cifs volume option, run:gluster volume set VOLNAME user.cifs enable
# gluster volume set VOLNAME user.cifs enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow And to enable user.smb, run:gluster volume set VOLNAME user.smb enable
# gluster volume set VOLNAME user.smb enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 introduces a group commandsambafor configuring the necessary volume options for Samba-CTDB setup. - Execute the following command to configure the volume options for the Samba-CTDB:
gluster volume set VOLNAME group samba
# gluster volume set VOLNAME group sambaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command will enable the following option for Samba-CTDB setup:- performance.readdir-ahead: on
- performance.parallel-readdir: on
- performance.nl-cache-timeout: 600
- performance.nl-cache: on
- performance.cache-samba-metadata: on
- network.inode-lru-limit: 200000
- performance.md-cache-timeout: 600
- performance.cache-invalidation: on
- features.cache-invalidation-timeout: 600
- features.cache-invalidation: on
- performance.stat-prefetch: on
Then, for all Samba versions:
- Verify that the volume can be accessed from the SMB/CIFS share:
smbclient -L <hostname> -U%
# smbclient -L <hostname> -U%Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify that the SMB/CIFS share can be accessed by the user, run the following command:
smbclient //VIP/gluster-volname -U username%password
# smbclient //VIP/gluster-volname -U username%passwordCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Configure this share so that a client can mount it using the address of any server in the trusted storage pool that provides this volume.
- Open the
/etc/samba/smb.conffile in a text editor and add the following lines for a simple configuration:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The configuration options are described in the following table:Expand Table 6.7. Configuration Options Configuration Options Required? Default Value Description Path Yes n/a It represents the path that is relative to the root of the gluster volume that is being shared. Hence /represents the root of the gluster volume. Exporting a subdirectory of a volume is supported and /subdir in path exports only that subdirectory of the volume.glusterfs:volumeYes n/a The volume name that is shared. glusterfs:logfileNo NULL Path to the log file that will be used by the gluster modules that are loaded by the vfs plugin. Standard Samba variable substitutions as mentioned in smb.confare supported.glusterfs:loglevelNo 7 This option is equivalent to the client-log-leveloption of gluster. 7 is the default value and corresponds to the INFO level.glusterfs:volfile_serverNo localhost The gluster server to be contacted to fetch the volfilefor the volume. It takes the value, which is a list of white space separated elements, where each element isunix+/path/to/socket/fileor[tcp+]IP|hostname|\[IPv6\][:port] - Run
service smb [re]startto start or restart thesmbservice. - Run
smbpasswdto set the SMB password.smbpasswd -a username
# smbpasswd -a usernameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the SMB password. This password is used during the SMB mount.
6.3.4. Configuring User Access to Shared Volumes
6.3.4.1. Configuring the Apple Create Context for macOS users
- Add the following lines to the
[global]section of thesmb.conffile. Note that the indentation level shown is required.fruit:aapl = yes ea support = yesfruit:aapl = yes ea support = yesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Load the
vfs_fruitmodule and its dependencies by adding the following line to your volume's export configuration block in thesmb.conffile.vfs objects = fruit streams_xattr glusterfs
vfs objects = fruit streams_xattr glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.4.2. Configuring read/write access for a non-privileged user
- Add the user on all the Samba servers based on your configuration:
adduser username
# adduser usernameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the user to the list of Samba users on all Samba servers and assign password by executing the following command:
smbpasswd -a username
# smbpasswd -a usernameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - From any other Samba server, mount the volume using the FUSE protocol.
mount -t glusterfs -o acl ip-address:/volname /mountpoint
# mount -t glusterfs -o acl ip-address:/volname /mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:mount -t glusterfs -o acl rhs-a:/repvol /mnt
# mount -t glusterfs -o acl rhs-a:/repvol /mntCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Use the
setfaclcommand to provide the required permissions for directory access to the user.setfacl -m user:username:rwx mountpoint
# setfacl -m user:username:rwx mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:setfacl -m user:cifsuser:rwx /mnt
# setfacl -m user:cifsuser:rwx /mntCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.5. Mounting Volumes using SMB
6.3.5.1. Manually mounting volumes exported with SMB on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Install the
cifs-utilspackage on the client.yum install cifs-utils
# yum install cifs-utilsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
mount -t cifsto mount the exported SMB share, using the syntax example as guidance.mount -t cifs -o user=username,pass=password //hostname/gluster-volname /mountpoint
# mount -t cifs -o user=username,pass=password //hostname/gluster-volname /mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Thesec=ntlmsspparameter is also required when mounting a volume on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.mount -t cifs -o user=username,pass=password,sec=ntlmssp //hostname/gluster-volname /mountpoint
# mount -t cifs -o user=username,pass=password,sec=ntlmssp //hostname/gluster-volname /mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:mount -t cifs -o user=cifsuser,pass=redhat,sec=ntlmssp //server1/gluster-repvol /cifs
# mount -t cifs -o user=cifsuser,pass=redhat,sec=ntlmssp //server1/gluster-repvol /cifsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
# smbstatus -Son the server to display the status of the volume:Service pid machine Connected at ------------------------------------------------------------------- gluster-VOLNAME 11967 __ffff_192.168.1.60 Mon Aug 6 02:23:25 2012
Service pid machine Connected at ------------------------------------------------------------------- gluster-VOLNAME 11967 __ffff_192.168.1.60 Mon Aug 6 02:23:25 2012Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.5.2. Manually mounting volumes exported with SMB on Microsoft Windows
6.3.5.2.1. Using Microsoft Windows Explorer to manually mount a volume
- In Windows Explorer, click → . to open the Map Network Drive screen.
- Choose the drive letter using the drop-down list.
- In the Folder text box, specify the path of the server and the shared resource in the following format: \\SERVER_NAME\VOLNAME.
- Click to complete the process, and display the network drive in Windows Explorer.
- Navigate to the network drive to verify it has mounted correctly.
6.3.5.2.2. Using Microsoft Windows command line interface to manually mount a volume
- Click → , and then type
cmd. - Enter
net use z: \\SERVER_NAME\VOLNAME, where z: is the drive letter to assign to the shared volume.For example,net use y: \\server1\test-volume - Navigate to the network drive to verify it has mounted correctly.
6.3.5.3. Manually mounting volumes exported with SMB on macOS
Prerequisites
- Ensure that your Samba configuration allows the use the SMB Apple Create Context.
- Ensure that the username you're using is on the list of allowed users for the volume.
Manual mounting process
- In the Finder, click Go > Connect to Server.
- In the Server Address field, type the IP address or hostname of a Red Hat Gluster Storage server that hosts the volume you want to mount.
- Click .
- When prompted, select Registered User to connect to the volume using a valid username and password.If required, enter your user name and password, then select the server volumes or shared folders that you want to mount.To make it easier to connect to the computer in the future, select Remember this password in my keychain to add your user name and password for the computer to your keychain.
6.3.5.4. Configuring automatic mounting for volumes exported with SMB on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Open the
/etc/fstabfile in a text editor and add a line containing the following details:\\HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS\SHARE_NAME MOUNTDIR cifs OPTIONS DUMP FSCK
\\HOSTNAME|IPADDRESS\SHARE_NAME MOUNTDIR cifs OPTIONS DUMP FSCKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the OPTIONS column, ensure that you specify thecredentialsoption, with a value of the path to the file that contains the username and/or password.Using the example server names, the entry contains the following replaced values.\\server1\test-volume /mnt/glusterfs cifs credentials=/etc/samba/passwd,_netdev 0 0
\\server1\test-volume /mnt/glusterfs cifs credentials=/etc/samba/passwd,_netdev 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Thesec=ntlmsspparameter is also required when mounting a volume on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6, for example:\\server1\test-volume /mnt/glusterfs cifs credentials=/etc/samba/passwd,_netdev,sec=ntlmssp 0 0
\\server1\test-volume /mnt/glusterfs cifs credentials=/etc/samba/passwd,_netdev,sec=ntlmssp 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See themount.cifsman page for more information about these options. - Run
# smbstatus -Son the client to display the status of the volume:Service pid machine Connected at ------------------------------------------------------------------- gluster-VOLNAME 11967 __ffff_192.168.1.60 Mon Aug 6 02:23:25 2012
Service pid machine Connected at ------------------------------------------------------------------- gluster-VOLNAME 11967 __ffff_192.168.1.60 Mon Aug 6 02:23:25 2012Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.5.5. Configuring automatic mounting for volumes exported with SMB on Microsoft Windows
- In Windows Explorer, click → . to open the Map Network Drive screen.
- Choose the drive letter using the drop-down list.
- In the Folder text box, specify the path of the server and the shared resource in the following format: \\SERVER_NAME\VOLNAME.
- Click the Reconnect at logon check box.
- Click to complete the process, and display the network drive in Windows Explorer.
- If the Windows Security screen pops up, enter the username and password and click OK.
- Navigate to the network drive to verify it has mounted correctly.
6.3.5.6. Configuring automatic mounting for volumes exported with SMB on macOS
- Manually mount the volume using the process outlined in Section 6.3.5.3, “Manually mounting volumes exported with SMB on macOS”.
- In the Finder, click System Preferences > Users & Groups > Username > Login Items.
- Drag and drop the mounted volume into the login items list.Check Hide if you want to prevent the drive's window from opening every time you boot or log in.
6.3.6. Starting and Verifying your Configuration
Verify the Configuration
- Verify that CTDB is running using the following commands:
ctdb status ctdb ip ctdb ping -n all
# ctdb status # ctdb ip # ctdb ping -n allCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Mount a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume using any one of the VIPs.
- Run
# ctdb ipto locate the physical server serving the VIP. - Shut down the CTDB VIP server to verify successful configuration.When the Red Hat Gluster Storage server serving the VIP is shut down there will be a pause for a few seconds, then I/O will resume.
6.3.8. Accessing Snapshots in Windows
Note
6.3.8.1. Configuring Shadow Copy
Note
vfs objects = shadow_copy2 glusterfs
vfs objects = shadow_copy2 glusterfs| Configuration Options | Required? | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| shadow:snapdir | Yes | n/a | Path to the directory where snapshots are kept. The snapdir name should be .snaps. |
| shadow:basedir | Yes | n/a | Path to the base directory that snapshots are from. The basedir value should be /. |
| shadow:sort | Optional | unsorted | The supported values are asc/desc. By this parameter one can specify that the shadow copy directories should be sorted before they are sent to the client. This can be beneficial as unix filesystems are usually not listed alphabetically sorted. If enabled, it is specified in descending order. |
| shadow:localtime | Optional | UTC | This is an optional parameter that indicates whether the snapshot names are in UTC/GMT or in local time. |
| shadow:format | Yes | n/a | This parameter specifies the format specification for the naming of snapshots. The format must be compatible with the conversion specifications recognized by str[fp]time. The default value is _GMT-%Y.%m.%d-%H.%M.%S. |
| shadow:fixinodes | Optional | No | If you enable shadow:fixinodes then this module will modify the apparent inode number of files in the snapshot directories using a hash of the files path. This is needed for snapshot systems where the snapshots have the same device:inode number as the original files (such as happens with GPFS snapshots). If you don't set this option then the 'restore' button in the shadow copy UI will fail with a sharing violation. |
| shadow:snapprefix | Optional | n/a | Regular expression to match prefix of snapshot name. Red Hat Gluster Storage only supports Basic Regular Expression (BRE) |
| shadow:delimiter | Optional | _GMT | delimiter is used to separate shadow:snapprefix and shadow:format. |
Snap_GMT-2016.06.06-06.06.06 Sl123p_GMT-2016.07.07-07.07.07 xyz_GMT-2016.08.08-08.08.08
Snap_GMT-2016.06.06-06.06.06
Sl123p_GMT-2016.07.07-07.07.07
xyz_GMT-2016.08.08-08.08.08- Run
service smb [re]startto start or restart thesmbservice. - Enable User Serviceable Snapshot (USS) for Samba. For more information see Section 8.13, “User Serviceable Snapshots”
6.3.8.2. Accessing Snapshot
- Right Click on the file or directory for which the previous version is required.
- Click on .
- In the dialog box, select the Date/Time of the previous version of the file, and select either , , or .where,Open: Lets you open the required version of the file in read-only mode.Restore: Restores the file back to the selected version.Copy: Lets you copy the file to a different location.
Figure 6.1. Accessing Snapshot
6.3.9. Tuning Performance
- Enabling Metadata Caching to improve the performance of SMB access of Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes.
- Enhancing Directory Listing Performance
- Enhancing File/Directory Create Performance
6.3.9.1. Enabling Metadata Caching
Note
- Execute the following command to enable metadata caching and cache invalidation:
gluster volume set <volname> group metadata-cache
# gluster volume set <volname> group metadata-cacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This is group set option which sets multiple volume options in a single command. - To increase the number of files that can be cached, execute the following command:
gluster volume set <VOLNAME> network.inode-lru-limit <n>
# gluster volume set <VOLNAME> network.inode-lru-limit <n>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow n, is set to 50000. It can be increased if the number of active files in the volume is very high. Increasing this number increases the memory footprint of the brick processes.
6.3.9.2. Enhancing Directory Listing Performance
Note
- Verify if the
performance.readdir-aheadoption is enabled by executing the following command:gluster volume get <VOLNAME> performance.readdir-ahead
# gluster volume get <VOLNAME> performance.readdir-aheadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If theperformance.readdir-aheadis not enabled then execute the following command:gluster volume set <VOLNAME> performance.readdir-ahead on
# gluster volume set <VOLNAME> performance.readdir-ahead onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to enable
parallel-readdiroption:gluster volume set <VOLNAME> performance.parallel-readdir on
# gluster volume set <VOLNAME> performance.parallel-readdir onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
If there are more than 50 bricks in the volume it is recommended to increase the cache size to be more than 10Mb (default value):gluster volume set <VOLNAME> performance.rda-cache-limit <CACHE SIZE>
# gluster volume set <VOLNAME> performance.rda-cache-limit <CACHE SIZE>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.3.9.3. Enhancing File/Directory Create Performance
- Execute the following command to enable negative-lookup cache:
gluster volume set <volname> group nl-cache volume set success
# gluster volume set <volname> group nl-cache volume set successCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The above command also enables cache-invalidation and increases the timeout to 10 minutes.
6.4. POSIX Access Control Lists
6.4.1. Setting ACLs with setfacl
setfacl command lets you modify the ACLs of a specified file or directory. You can add access rules for a file with the -m subcommand, or remove access rules for a file with the -x subcommand. The basic syntax is as follows:
setfacl subcommand access_rule file_path
# setfacl subcommand access_rule file_path- Rules for users start with
u: setfacl -m u:user:perms file_path
# setfacl -m u:user:perms file_pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,setfacl -m u:fred:rw /mnt/datagives the userfredread and write access to the/mnt/datadirectory.setfacl -x u::w /works_in_progress/my_presentation.txtprevents all users from writing to the/works_in_progress/my_presentation.txtfile (except the owning user and members of the owning group, as these are controlled by POSIX).- Rules for groups start with
g: setfacl -m g:group:perms file_path
# setfacl -m g:group:perms file_pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,setfacl -m g:admins:rwx /etc/fstabgives users in theadminsgroup read, write, and execute permissions to the/etc/fstabfile.setfacl -x g:newbies:x /mnt/harmful_script.shprevents users in thenewbiesgroup from executing/mnt/harmful_script.sh.- Rules for other users start with
o: setfacl -m o:perms file_path
# setfacl -m o:perms file_pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,setfacl -m o:r /mnt/data/publicgives users without any specific rules about their username or group permission to read files in the/mnt/data/public directory.- Rules for setting a maximum access level using an effective rights mask start with
m: setfacl -m m:mask file_path
# setfacl -m m:mask file_pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,setfacl -m m:r-x /mount/harmless_script.shgives all users a maximum of read and execute access to the/mount/harmless_script.shfile.
d: to the beginning of any rule, or make a rule recursive with the -R option. For example, setfacl -Rm d:g:admins:rwx /etc gives all members of the admins group read, write, and execute access to any file created under the /etc directory after the point when setfacl is run.
6.4.2. Checking current ACLs with getfacl
getfacl command lets you check the current ACLs of a file or directory. The syntax for this command is as follows:
getfacl file_path
# getfacl file_pathdefault:, like so:
6.4.3. Mounting volumes with ACLs enabled
acl mount option. For further information, see Section 6.1.3, “Mounting Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes”.
6.4.4. Checking ACL enablement on a mounted volume
| Client type | How to check | Further info |
|---|---|---|
| Native FUSE |
Check the output of the
mount command for the default_permissions option:
mount | grep mountpoint
If
default_permissions appears in the output for a mounted volume, ACLs are not enabled on that volume.
Check the output of the
ps aux command for the gluster FUSE mount process (glusterfs):
ps aux | grep gluster root 30548 0.0 0.7 548408 13868 ? Ssl 12:39 0:00 /usr/local/sbin/glusterfs --acl --volfile-server=127.0.0.2 --volfile-id=testvol /mnt/fuse_mnt
If
--acl appears in the output for a mounted volume, ACLs are enabled on that volume.
| See Section 6.1, “Native Client” for more information. |
| Gluster Native NFS |
On the server side, check the output of the
gluster volume info volname command. If nfs.acl appears in the output, that volume has ACLs disabled. If nfs.acl does not appear, ACLs are enabled (the default state).
On the client side, check the output of the
mount command for the volume. If noacl appears in the output, ACLs are disabled on the mount point. If this does not appear in the output, the client checks that the server uses ACLs, and uses ACLs if server support is enabled.
|
Refer to the output of
gluster volume set help pertaining to NFS, or see the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Storage Administration Guide for more information: https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/Storage_Administration_Guide/ch-nfs.html
|
| NFS Ganesha |
On the server side, check the volume's export configuration file,
/run/gluster/shared_storage/nfs-ganesha/exports/export.volname.conf. If the Disable_ACL option is set to true, ACLs are disabled. Otherwise, ACLs are enabled for that volume.
Note
NFS-Ganesha supports NFSv4 protocol standardized ACLs but not NFSACL protocol used for NFSv3 mounts. Only NFSv4 mounts can set ACLs.
There is no option to disable NFSv4 ACLs on the client side, so as long as the server supports ACLs, clients can set ACLs on the mount point.
|
See Section 6.2.3, “NFS Ganesha” for more information. For client side settings, refer to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Storage Administration Guide: https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/Storage_Administration_Guide/ch-nfs.html
|
| samba |
POSIX ACLs are enabled by default when using Samba to access a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
| See Section 6.3, “SMB” for more information. |
6.5. Managing Object Store
6.5.1. Architecture Overview
- OpenStack Object Storage environment.For detailed information on Object Storage, see OpenStack Object Storage Administration Guide available at: http://docs.openstack.org/admin-guide-cloud/content/ch_admin-openstack-object-storage.html.
- Red Hat Gluster Storage environment.Red Hat Gluster Storage environment consists of bricks that are used to build volumes. For more information on bricks and volumes, see Section 5.4, “Formatting and Mounting Bricks”.

Figure 6.2. Object Store Architecture
Important
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zonesfirewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=6010/tcp --add-port=6011/tcp --add-port=6012/tcp --add-port=8080/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=6010/tcp --add-port=6011/tcp --add-port=6012/tcp --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=6010/tcp --add-port=6011/tcp --add-port=6012/tcp --add-port=8080/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=6010/tcp --add-port=6011/tcp --add-port=6012/tcp --add-port=8080/tcp --permanentonly if your swift proxy server is configured with SSL. To add the port number, run the following commands:
firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=443/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=443/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=443/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=443/tcp --permanent6.5.2. Components of Object Store
- Authenticate Object Store against an external OpenStack Keystone server.Each Red Hat Gluster Storage volume is mapped to a single account. Each account can have multiple users with different privileges based on the group and role they are assigned to. After authenticating using accountname:username and password, user is issued a token which will be used for all subsequent REST requests.Integration with Keystone
When you integrate Red Hat Gluster Storage Object Store with Keystone authentication, you must ensure that the Swift account name and Red Hat Gluster Storage volume name are the same. It is common that Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes are created before exposing them through the Red Hat Gluster Storage Object Store.
When working with Keystone, account names are defined by Keystone as thetenant id. You must create the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume using the Keystonetenant idas the name of the volume. This means, you must create the Keystone tenant before creating a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume.Important
Red Hat Gluster Storage does not contain any Keystone server components. It only acts as a Keystone client. After you create a volume for Keystone, ensure to export this volume for accessing it using the object storage interface. For more information on exporting volume, see Section 6.5.7.8, “Exporting the Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes”.Integration with GSwauthGSwauth is a Web Server Gateway Interface (WGSI) middleware that uses a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume itself as its backing store to maintain its metadata. The benefit in this authentication service is to have the metadata available to all proxy servers and saving the data to a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
To protect the metadata, the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume should only be able to be mounted by the systems running the proxy servers. For more information on mounting volumes, see Chapter 6, Creating Access to Volumes.Integration with TempAuthYou can also use the
TempAuthauthentication service to test Red Hat Gluster Storage Object Store in the data center.
6.5.3. Advantages of using Object Store
- Default object size limit of 1 TiB
- Unified view of data across NAS and Object Storage technologies
- High availability
- Scalability
- Replication
- Elastic Volume Management
6.5.4. Limitations
- Object NameObject Store imposes the following constraints on the object name to maintain the compatibility with network file access:
- Object names must not be prefixed or suffixed by a '/' character. For example,
a/b/ - Object names must not have contiguous multiple '/' characters. For example,
a//b
- Account Management
- Object Store does not allow account management even though OpenStack Swift allows the management of accounts. This limitation is because Object Store treats
accountsequivalent to the Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes. - Object Store does not support account names (i.e. Red Hat Gluster Storage volume names) having an underscore.
- In Object Store, every account must map to a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
- Subdirectory ListingHeaders
X-Content-Type: application/directoryandX-Content-Length: 0can be used to create subdirectory objects under a container, but GET request on a subdirectory would not list all the objects under it.
6.5.5. Swift API Support Matrix
| Feature | Status |
|---|---|
| Authentication | Supported |
| Get Account Metadata | Supported |
| Swift ACLs | Supported |
| List Containers | Supported |
| Delete Container | Supported |
| Create Container | Supported |
| Get Container Metadata | Supported |
| Update Container Metadata | Supported |
| Delete Container Metadata | Supported |
| List Objects | Supported |
| Static Website | Supported |
| Create/Update an Object | Supported |
| Create Large Object | Supported |
| Delete Object | Supported |
| Get Object | Supported |
| Copy Object | Supported |
| Get Object Metadata | Supported |
| Add/Update Object Metadata | Supported |
| Temp URL Operations | Supported |
| Expiring Objects | Supported |
| Object Versioning | Supported |
| Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) | Supported |
| Bulk Upload | Supported |
| Account Quota | Unsupported |
| Container Quota | Unsupported |
6.5.6. Prerequisites
- Ensure that the openstack-swift-* and swiftonfile packages have matching version numbers.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that the gluster-swift services are owned by and run as the
rootuser, not theswiftuser as in a typical OpenStack installation.cd /usr/lib/systemd/system sed -i s/User=swift/User=root/ openstack-swift-proxy.service openstack-swift-account.service openstack-swift-container.service openstack-swift-object.service openstack-swift-object-expirer.service
# cd /usr/lib/systemd/system # sed -i s/User=swift/User=root/ openstack-swift-proxy.service openstack-swift-account.service openstack-swift-container.service openstack-swift-object.service openstack-swift-object-expirer.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the
memcachedservice:service memcached start
# service memcached startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that the ports for the Object, Container, Account, and Proxy servers are open. Note that the ports used for these servers are configurable. The ports listed in Table 6.11, “Ports required for Red Hat Gluster Storage Object Store” are the default values.
Expand Table 6.11. Ports required for Red Hat Gluster Storage Object Store Server Port Object Server 6010 Container Server 6011 Account Server 6012 Proxy Server (HTTPS) 443 Proxy Server (HTTP) 8080 - Create and mount a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume for use as a Swift Account. For information on creating Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes, see Chapter 5, Setting Up Storage Volumes . For information on mounting Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes, see Chapter 6, Creating Access to Volumes .
6.5.7. Configuring the Object Store
Warning
/etc/swift directory would contain both *.conf extension and *.conf-gluster files. You must delete the *.conf files and create new configuration files based on *.conf-gluster template. Otherwise, inappropriate python packages will be loaded and the component may not work as expected.
.rpmnew extension. You must ensure to delete .conf files and folders (account-server, container-server, and object-server) for better understanding of the loaded configuration.
6.5.7.1. Configuring a Proxy Server
etc/swift/proxy-server.conf by referencing the template file available at /etc/swift/proxy-server.conf-gluster.
6.5.7.1.1. Configuring a Proxy Server for HTTPS
- Create self-signed cert for SSL using the following commands:
cd /etc/swift openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -out cert.crt -keyout cert.key
# cd /etc/swift # openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -out cert.crt -keyout cert.keyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the following lines to
/etc/swift/proxy-server.confunder [DEFAULT]bind_port = 443 cert_file = /etc/swift/cert.crt key_file = /etc/swift/cert.key
bind_port = 443 cert_file = /etc/swift/cert.crt key_file = /etc/swift/cert.keyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Important
memcache_servers configuration option in the proxy-server.conf and list all memcached servers.
proxy-server.conf file.
[filter:cache] use = egg:swift#memcache memcache_servers = 192.168.1.20:11211,192.168.1.21:11211,192.168.1.22:11211
[filter:cache]
use = egg:swift#memcache
memcache_servers = 192.168.1.20:11211,192.168.1.21:11211,192.168.1.22:112116.5.7.2. Configuring the Authentication Service
Keystone, GSwauth, and TempAuth authentication services.
6.5.7.2.1. Integrating with the Keystone Authentication Service
- To configure Keystone, add
authtokenandkeystoneauthto/etc/swift/proxy-server.confpipeline as shown below:[pipeline:main] pipeline = catch_errors healthcheck proxy-logging cache authtoken keystoneauth proxy-logging proxy-server
[pipeline:main] pipeline = catch_errors healthcheck proxy-logging cache authtoken keystoneauth proxy-logging proxy-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the following sections to
/etc/swift/proxy-server.conffile by referencing the example below as a guideline. You must substitute the values according to your setup:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verify that the Red Hat Gluster Storage Object Store has been configured successfully by running the following command:
swift -V 2 -A http://keystone.server.com:5000/v2.0 -U tenant_name:user -K password stat
$ swift -V 2 -A http://keystone.server.com:5000/v2.0 -U tenant_name:user -K password stat6.5.7.2.2. Integrating with the GSwauth Authentication Service
Perform the following steps to integrate GSwauth:
- Create and start a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume to store metadata.
gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME NEW-BRICK gluster volume start NEW-VOLNAME
# gluster volume create NEW-VOLNAME NEW-BRICK # gluster volume start NEW-VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume create gsmetadata server1:/rhgs/brick1 gluster volume start gsmetadata
# gluster volume create gsmetadata server1:/rhgs/brick1 # gluster volume start gsmetadataCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster-swift-gen-builderstool with all the volumes to be accessed using the Swift client includinggsmetadatavolume:gluster-swift-gen-builders gsmetadata other volumes
# gluster-swift-gen-builders gsmetadata other volumesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Edit the
/etc/swift/proxy-server.confpipeline as shown below:[pipeline:main] pipeline = catch_errors cache gswauth proxy-server
[pipeline:main] pipeline = catch_errors cache gswauth proxy-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the following section to
/etc/swift/proxy-server.conffile by referencing the example below as a guideline. You must substitute the values according to your setup.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
You must ensure to secure theproxy-server.conffile and thesuper_admin_keyoption to prevent unprivileged access. - Restart the proxy server by running the following command:
swift-init proxy restart
# swift-init proxy restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can set the following advanced options for GSwauth WSGI filter:
- default-swift-cluster: The default storage-URL for the newly created accounts. When you attempt to authenticate for the first time, the access token and the storage-URL where data for the given account is stored will be returned.
- token_life: The set default token life. The default value is 86400 (24 hours).
- max_token_life: The maximum token life. You can set a token lifetime when requesting a new token with header
x-auth-token-lifetime. If the passed in value is greater than themax_token_life, then themax_token_lifevalue will be used.
GSwauth provides CLI tools to facilitate managing accounts and users. All tools have some options in common:
- -A, --admin-url: The URL to the auth. The default URL is
http://127.0.0.1:8080/auth/. - -U, --admin-user: The user with administrator rights to perform action. The default user role is
.super_admin. - -K, --admin-key: The key for the user with administrator rights to perform the action. There is no default value.
Prepare the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume for gswauth to save its metadata by running the following command:
gswauth-prep [option]
# gswauth-prep [option]gswauth-prep -A http://10.20.30.40:8080/auth/ -K gswauthkey
# gswauth-prep -A http://10.20.30.40:8080/auth/ -K gswauthkey6.5.7.2.2.1. Managing Account Services in GSwauth
Create an account for GSwauth. This account is mapped to a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
gswauth-add-account [option] <account_name>
# gswauth-add-account [option] <account_name>gswauth-add-account -K gswauthkey <account_name>
# gswauth-add-account -K gswauthkey <account_name>You must ensure that all users pertaining to this account must be deleted before deleting the account. To delete an account:
gswauth-delete-account [option] <account_name>
# gswauth-delete-account [option] <account_name>gswauth-delete-account -K gswauthkey test
# gswauth-delete-account -K gswauthkey test
Sets a service URL for an account. User with reseller admin role only can set the service URL. This command can be used to change the default storage URL for a given account. All accounts will have the same storage-URL as default value, which is set using default-swift-cluster option.
gswauth-set-account-service [options] <account> <service> <name> <value>
# gswauth-set-account-service [options] <account> <service> <name> <value>gswauth-set-account-service -K gswauthkey test storage local http://newhost:8080/v1/AUTH_test
# gswauth-set-account-service -K gswauthkey test storage local http://newhost:8080/v1/AUTH_test6.5.7.2.2.2. Managing User Services in GSwauth
The following user roles are supported in GSwauth:
- A regular user has no rights. Users must be given both read and write privileges using Swift ACLs.
- The
adminuser is a super-user at the account level. This user can create and delete users for that account. These members will have both write and read privileges to all stored objects in that account. - The
reseller adminuser is a super-user at the cluster level. This user can create and delete accounts and users and has read and write privileges to all accounts under that cluster. - GSwauth maintains its own swift account to store all of its metadata on accounts and users. The
.super_adminrole provides access to GSwauth own swift account and has all privileges to act on any other account or user.
| Role/Group | Allowed Actions |
|---|---|
| .super_admin (username) |
|
| .reseller_admin (group) |
|
| .admin (group) |
|
| regular user (type) | No administrative actions. |
You can create an user for an account that does not exist. The account will be created before creating the user.
-r flag to create a reseller admin user and -a flag to create an admin user. To change the password or role of the user, you can run the same command with the new option.
gswauth-add-user [option] <account_name> <user> <password>
# gswauth-add-user [option] <account_name> <user> <password>gswauth-add-user -K gswauthkey -a test ana anapwd
# gswauth-add-user -K gswauthkey -a test ana anapwdDelete a user by running the following command:
gswauth-delete-user [option] <account_name> <user>
# gswauth-delete-user [option] <account_name> <user>gwauth-delete-user -K gswauthkey test ana
# gwauth-delete-user -K gswauthkey test anaThere are two methods to access data using the Swift client. The first and simple method is by providing the user name and password everytime. The swift client will acquire the token from gswauth.
swift -A http://127.0.0.1:8080/auth/v1.0 -U test:ana -K anapwd upload container1 README.md
$ swift -A http://127.0.0.1:8080/auth/v1.0 -U test:ana -K anapwd upload container1 README.mdcurl -v -H 'X-Storage-User: test:ana' -H 'X-Storage-Pass: anapwd' -k http://localhost:8080/auth/v1.0 ... < X-Auth-Token: AUTH_tk7e68ef4698f14c7f95af07ab7b298610 < X-Storage-Url: http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test ...
# curl -v -H 'X-Storage-User: test:ana' -H 'X-Storage-Pass: anapwd' -k http://localhost:8080/auth/v1.0
...
< X-Auth-Token: AUTH_tk7e68ef4698f14c7f95af07ab7b298610
< X-Storage-Url: http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test
...swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk7e68ef4698f14c7f95af07ab7b298610 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test upload container1 README.md README.md bash-4.2$ bash-4.2$ swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk7e68ef4698f14c7f95af07ab7b298610 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test list container1 README.md
$ swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk7e68ef4698f14c7f95af07ab7b298610 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test upload container1 README.md
README.md
bash-4.2$
bash-4.2$ swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk7e68ef4698f14c7f95af07ab7b298610 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test list container1
README.mdImportant
Reseller admins must always use the second method to acquire a token to get access to other accounts other than his own. The first method of using the username and password will give them access only to their own accounts.
6.5.7.2.2.3. Managing Accounts and Users Information
You can obtain the accounts and users information including stored password.
gswauth-list [options] [account] [user]
# gswauth-list [options] [account] [user]- If [account] and [user] are omitted, all the accounts will be listed.
- If [account] is included but not [user], a list of users within that account will be listed.
- If [account] and [user] are included, a list of groups that the user belongs to will be listed.
- If the [user] is .groups, the active groups for that account will be listed.
-p option provides the output in plain text format, -j provides the output in JSON format.
You can change the password of the user, account administrator, and reseller_admin roles.
- Change the password of a regular user by running the following command:
gswauth-add-user -U account1:user1 -K old_passwd account1 user1 new_passwd
# gswauth-add-user -U account1:user1 -K old_passwd account1 user1 new_passwdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change the password of an
account administratorby running the following command:gswauth-add-user -U account1:admin -K old_passwd -a account1 admin new_passwd
# gswauth-add-user -U account1:admin -K old_passwd -a account1 admin new_passwdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change the password of the
reseller_adminby running the following command:gswauth-add-user -U account1:radmin -K old_passwd -r account1 radmin new_passwd
# gswauth-add-user -U account1:radmin -K old_passwd -r account1 radmin new_passwdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Users with .super_admin role can delete the expired tokens.
gswauth-cleanup-tokens [options]
# gswauth-cleanup-tokens [options]gswauth-cleanup-tokens -K gswauthkey --purge test
# gswauth-cleanup-tokens -K gswauthkey --purge test- -t, --token-life: The expected life of tokens. The token objects modified before the give number of seconds will be checked for expiration (default: 86400).
- --purge: Purges all the tokens for a given account whether the tokens have expired or not.
- --purge-all: Purges all the tokens for all the accounts and users whether the tokens have expired or not.
6.5.7.2.3. Integrating with the TempAuth Authentication Service
Warning
cleartext in a single proxy-server.conf file. In your /etc/swift/proxy-server.conf file, enable TempAuth in pipeline and add user information in TempAuth section by referencing the below example.
user_accountname_username = password [.admin]
user_accountname_username = password [.admin]accountname is the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume used to store objects.
6.5.7.3. Configuring Object Servers
etc/swift/object.server.conf by referencing the template file available at /etc/swift/object-server.conf-gluster.
6.5.7.4. Configuring Container Servers
etc/swift/container-server.conf by referencing the template file available at /etc/swift/container-server.conf-gluster.
6.5.7.5. Configuring Account Servers
etc/swift/account-server.conf by referencing the template file available at /etc/swift/account-server.conf-gluster.
6.5.7.6. Configuring Swift Object and Container Constraints
/etc/swift/swift.conf by referencing the template file available at /etc/swift/swift.conf-gluster.
6.5.7.7. Configuring Object Expiration
Note
object-expirer daemon. This is an expected behavior.
6.5.7.7.1. Setting Up Object Expiration
gsexpiring for managing object expiration. Hence, you must create a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume and name it as gsexpiring.
/etc/swift/object.expirer.conf by referencing the template file available at /etc/swift/object-expirer.conf-gluster.
6.5.7.7.2. Using Object Expiration
The X-Delete-At header requires a UNIX epoch timestamp, in integer form. For example, 1418884120 represents Thu, 18 Dec 2014 06:27:31 GMT. By setting the header to a specific epoch time, you indicate when you want the object to expire, not be served, and be deleted completely from the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume. The current time in Epoch notation can be found by running this command:
date +%s
$ date +%s- Set the object expiry time during an object PUT with X-Delete-At header using cURL:
curl -v -X PUT -H 'X-Delete-At: 1392013619' http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test/container1/object1 -T ./localfile
# curl -v -X PUT -H 'X-Delete-At: 1392013619' http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test/container1/object1 -T ./localfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the object expiry time during an object PUT with X-Delete-At header using swift client:swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk99a39aecc3dd4f80b2b1e801d00df846 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test upload container1 ./localfile --header 'X-Delete-At: 1392013619'
# swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk99a39aecc3dd4f80b2b1e801d00df846 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test upload container1 ./localfile --header 'X-Delete-At: 1392013619'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The X-Delete-After header takes an integer number of seconds that represents the amount of time from now when you want the object to be deleted.
- Set the object expiry time with an object PUT with X-Delete-After header using cURL:
curl -v -X PUT -H 'X-Delete-After: 3600' http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test/container1/object1 -T ./localfile
# curl -v -X PUT -H 'X-Delete-After: 3600' http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test/container1/object1 -T ./localfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the object expiry time with an object PUT with X-Delete-At header using swift client:swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk99a39aecc3dd4f80b2b1e801d00df846 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test upload container1 ./localfile --header 'X-Delete-After: 3600'
# swift --os-auth-token=AUTH_tk99a39aecc3dd4f80b2b1e801d00df846 --os-storage-url=http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/AUTH_test upload container1 ./localfile --header 'X-Delete-After: 3600'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.5.7.7.3. Running Object Expirer Service
interval option in /etc/swift/object-expirer.conf file. For every pass it makes, it queries the gsexpiring account for tracker objects. Based on the timestamp and path present in the name of tracker objects, object-expirer deletes the actual object and the corresponding tracker object.
swift-init object-expirer start
# swift-init object-expirer startswift-object-expirer -o -v /etc/swift/object-expirer.conf
# swift-object-expirer -o -v /etc/swift/object-expirer.conf6.5.7.8. Exporting the Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes
Swift on File component.
cd /etc/swift gluster-swift-gen-builders VOLUME [VOLUME...]
# cd /etc/swift
# gluster-swift-gen-builders VOLUME [VOLUME...]cd /etc/swift gluster-swift-gen-builders testvol1 testvol2 testvol3
# cd /etc/swift
# gluster-swift-gen-builders testvol1 testvol2 testvol3/mnt/gluster-object). The default value can be changed to a different path by changing the devices configurable option across all account, container, and object configuration files. The path must contain Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes mounted under directories having the same names as volume names. For example, if devices option is set to /home, it is expected that the volume named testvol1 be mounted at /home/testvol1.
gluster-swift-gen-builders tool even if it was previously added. The gluster-swift-gen-builders tool creates new ring files every time it runs successfully.
gluster-swift-gen-builders only with the volumes which are required to be accessed using the Swift interface.
testvol2 volume, run the following command:
gluster-swift-gen-builders testvol1 testvol3
# gluster-swift-gen-builders testvol1 testvol36.5.7.9. Starting and Stopping Server
- To start the server, run the following command:
swift-init main start
# swift-init main startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To stop the server, run the following command:
swift-init main stop
# swift-init main stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To restart the server, run the following command:
swift-init main restart
# swift-init main restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.5.8. Starting the Services Automatically
systemctl command may require additional configuration. Refer to https://access.redhat.com/solutions/2043773 for details if you encounter problems.
Important
6.5.9. Working with the Object Store
6.5.9.1. Creating Containers and Objects
6.5.9.2. Creating Subdirectory under Containers
Content-Type: application/directory and Content-Length: 0. However, the current behavior of Object Store returns 200 OK on a GET request on subdirectory but this does not list all the objects under that subdirectory.
6.5.9.3. Working with Swift ACLs
6.6. Checking Client Operating Versions
op-version. The cluster.op-version parameter sets the required operating version for all volumes in a cluster on the server side. Each client supports a range of operating versions that are identified by a minimum (min-op-version) and maximum (max-op-version) supported operating version.
- For Red Hat Gluster 3.2 and later
gluster volume status volname clients
# gluster volume status volname clientsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Useallin place of the name of your volume if you want to see the operating versions of clients connected to all volumes in the cluster.
Before Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.2:
- Perform a state dump for the volume whose clients you want to check.
gluster volume statedump volname
# gluster volume statedump volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Locate the state dump directory
gluster --print-statedumpdir
# gluster --print-statedumpdirCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Locate the state dump file and grep for client information.
grep -A4 "identifier=client_ip" statedumpfile
# grep -A4 "identifier=client_ip" statedumpfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 7. Integrating Red Hat Gluster Storage with Windows Active Directory
Figure 7.1. Active Directory Integration
| Information | Example Value |
| DNS domain name / realm | addom.example.com |
| NetBIOS domain name | ADDOM |
| Name of administrative account | administrator |
| RHGS nodes | rhs-srv1.addom.example.com, 192.168.56.10 rhs-srv2.addom.example.com, 192.168.56.11 rhs-srv3.addom.example.com, 192.168.56.12 |
| Netbios name of the cluster | RHS-SMB |
7.1. Prerequisites
- Name Resolution
The Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes must be able to resolve names from the AD domain via DNS. To verify the same you can use the following command:
host dc1.addom.example.com
host dc1.addom.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,addom.example.comis the AD domain and dc1 is the name of a domain controller.For example, the/etc/resolv.conffile in a static network configuration could look like this:domain addom.example.com search addom.example.com nameserver 10.11.12.1 # dc1.addom.example.com nameserver 10.11.12.2 # dc2.addom.example.com
domain addom.example.com search addom.example.com nameserver 10.11.12.1 # dc1.addom.example.com nameserver 10.11.12.2 # dc2.addom.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This example assumes that both the domain controllers are also the DNS servers of the domain. - Kerberos Packages
If you want to use the kerberos client utilities, like kinit and klist, then manually install the krb5-workstation using the following command:
yum -y install krb5-workstation
# yum -y install krb5-workstationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Synchronize Time Service
It is essential that the time service on each Red Hat Gluster Storage node and the Windows Active Directory server are synchronized, else the Kerberos authentication may fail due to clock skew. In environments where time services are not reliable, the best practice is to configure the Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes to synchronize time from the Windows Server.
On each Red Hat Storage node, edit the file /etc/ntp.conf so the time is synchronized from a known, reliable time service:# Enable writing of statistics records. #statistics clockstats cryptostats loopstats peerstats server ntp1.addom.example.com server 10.11.12.3
# Enable writing of statistics records. #statistics clockstats cryptostats loopstats peerstats server ntp1.addom.example.com server 10.11.12.3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Activate the change on each Red Hat Gluster Storage node by stopping the ntp daemon, updating the time, then starting the ntp daemon. Verify the change on both servers using the following commands:service ntpd stop service ntpd start
# service ntpd stop # service ntpd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Samba Packages
Ensure to install the following Samba packages along with its dependencies:
- CTDB
- samba
- samba-client
- samba-winbind
- samba-winbind-modules
7.2. Integration
- Configure Authentication
- Join Active Directory Domain
- Verify/Test Active Directory and Services
7.2.1. Configure Authentication
Note
- Ensure that CTDB is configured before the active directory join. For more information see, Section 6.3.1 Setting up CTDB for Samba in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Administration Guide.
- It is recommended to take backups of the configuration and of Samba’s databases (local and ctdb) before making any changes.
7.2.1.1. Basic Samba Configuration
autorid, not tdb. Red Hat recommends autorid because in addition to automatically calculating user and group identifiers like tdb, it performs fewer database transactions and read operations, and is a prerequisite for supporting secure ID history (SID history).
Warning
/etc/samba/smb.conf must be identical on all nodes, and must contain the relevant parameters for AD. Along with that, a few other settings are required in order to activate mapping of user and group IDs.
Warning
global section required in the smb.conf file. Ensure that nothing else appears in this section in order to prevent gluster mechanisms from changing settings when starting or stopping the ctdb lock volume.
netbios name consists of only one name which has to be the same name on all cluster nodes. Windows clients will only access the cluster via that name (either in this short form or as an FQDN). The individual node hostname (rhs-srv1, rhs-srv2, …) must not be used for the netbios name parameter.
Note
- The idmap
rangedefines the lowerst and hightest identifier numbers that can be used. Specify a range large enough to cover the number of objects specified inrangesize. - The idmap
rangesizespecifies the number of identifiers available for each domain range. In this case there are one million identifiers per domain range, and therangeparameter indicates that there are nearly 19 million identifiers total, meaning that there are a total of 19 possible domain ranges. - If you want to be able to use the individual host names to also access specific nodes, you can add them to the
netbios aliasesparameter ofsmb.conf. - In an AD environment, it is usually not required to run
nmbd. However, if you have to runnmbd, then make sure to set thecluster addressessmb.confoption to the list of public IP addresses of the cluster.
7.2.1.2. Alternative Configuration using ad backend
idmap_ad module in addition to autorid. The idmap_ad module reads the unix IDs from the AD's special unix attributes. This has to be configured by the AD domain's administrator before it can be used by Samba and winbind.
idmap_ad, the AD domain admin has to prepare the AD domain for using the so called unix extensions and assign unix IDs to all users and groups that should be able to access the Samba server.
idmap_ad backend for the ADDOM domain. The default autorid backend catches all objects from domains other than the ADDOM domain.
Note
- The range for the idmap_ad configuration is prescribed by the AD configuration. This has to be obtained by AD administrator.
- Ranges for different idmap configurations must not overlap.
- The schema mode and the winbind nss info setting should have the same value. If the domain is at level 2003R2 or newer, then rfc2307 is the correct value. For older domains, additional values sfu and sfu20 are available. See the manual pages of idmap_ad and smb.conf for further details.
7.2.1.3. Verifying the Samba Configuration
7.2.1.4. nsswitch Configuration
/etc/nsswitch.conf file. Make sure the file contains the winbind entries for the passwd and group databases. For example:
... passwd: files winbind group: files winbind ...
...
passwd: files winbind
group: files winbind
...visible on the individual cluster node once Samba is joined to AD and winbind is started.
7.2.2. Join Active Directory Domain
onnode all service ctdb start onnode all service winbind stop onnode all service smb stop
# onnode all service ctdb start
# onnode all service winbind stop
# onnode all service smb stopNote
- If your configuration has CTDB managing Winbind and Samba, they can be temporarily disabled with the following commands (to be executed prior to the above stop commands) so as to prevent CTDB going into an unhealthy state when they are shut down:
onnode all ctdb event script disable 49.winbind onnode all ctdb event script disable 50.samba
# onnode all ctdb event script disable 49.winbind # onnode all ctdb event script disable 50.sambaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For some versions of RHGS, a bug in the selinux policy prevents 'ctdb disablescript SCRIPT' from succeeding. If this is the case, 'chmod -x /etc/ctdb/events.d/SCRIPT' can be executed as a workaround from a root shell.
- Shutting down winbind and smb is primarily to prevent access to SMB services during this AD integration. These services may be left running but access to them should be prevented through some other means.
net utility from a single node:
Warning
net ads join -U Administrator Enter Administrator's password: Using short domain name -- ADDOM Joined 'RHS-SMB' to dns domain addom.example.com' Not doing automatic DNS update in a clustered setup.
# net ads join -U Administrator
Enter Administrator's password:
Using short domain name -- ADDOM
Joined 'RHS-SMB' to dns domain addom.example.com'
Not doing automatic DNS update in a clustered setup.net utility can be used again:
net ads dns register rhs-smb <PUBLIC IP 1> <PUBLIC IP 2> ...
# net ads dns register rhs-smb <PUBLIC IP 1> <PUBLIC IP 2> ...rhs-smb will resolve to the given public IP addresses. The DNS registrations use the cluster machine account for authentication in AD, which means this operation only can be done after the join has succeeded.
7.2.3. Verify/Test Active Directory and Services
onnode all service nmb start
# onnode all service nmb startonnode all service winbind start onnode all service smb start
# onnode all service winbind start
# onnode all service smb startNote
- If you previously disabled CTDB’s ability to manage Winbind and Samba they can be re-enabled with the following commands:
onnode all ctdb event script enable 50.samba onnode all ctdb event script enable 49.winbind
# onnode all ctdb event script enable 50.samba # onnode all ctdb event script enable 49.winbindCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - For some versions of RHGS, a bug in the selinux polict prevents 'ctdb enablescript SCRIPT' from succeeding. If this is the case, 'chmod +x /etc/ctdb/events.d/SCRIPT' can be executed as a workaround from a root shell.
- Ensure that the winbind starts after a reboot. This is achieved by adding ‘CTDB_MANAGES_WINBIND=yes’ to the /etc/sysconfig/ctdb file on all nodes.
- Verify the join by executing the following stepsVerify the join to check if the created machine account can be used to authenticate to the AD LDAP server using the following command:
net ads testjoin Join is OK
# net ads testjoin Join is OKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to display the machine account’s LDAP object
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to display general information about the AD server:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify if winbind is operating correctly by executing the following stepsExecute the following command to verify if winbindd can use the machine account for authentication to AD
wbinfo -t checking the trust secret for domain ADDOM via RPC calls succeeded
# wbinfo -t checking the trust secret for domain ADDOM via RPC calls succeededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to resolve the given name to a Windows SID
wbinfo --name-to-sid 'ADDOM\Administrator' S-1-5-21-2562125317-1564930587-1029132327-500 SID_USER (1)
# wbinfo --name-to-sid 'ADDOM\Administrator' S-1-5-21-2562125317-1564930587-1029132327-500 SID_USER (1)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to verify authentication:
wbinfo -a 'ADDOM\user' Enter ADDOM\user's password: plaintext password authentication succeeded Enter ADDOM\user's password: challenge/response password authentication succeeded
# wbinfo -a 'ADDOM\user' Enter ADDOM\user's password: plaintext password authentication succeeded Enter ADDOM\user's password: challenge/response password authentication succeededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow or,wbinfo -a 'ADDOM\user%password' plaintext password authentication succeeded challenge/response password authentication succeeded
# wbinfo -a 'ADDOM\user%password' plaintext password authentication succeeded challenge/response password authentication succeededCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to verify if the id-mapping is working properly:
wbinfo --sid-to-uid <SID-OF-ADMIN> 1000000
# wbinfo --sid-to-uid <SID-OF-ADMIN> 1000000Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to verify if the winbind Name Service Switch module works correctly:
getent passwd 'ADDOM\Administrator' ADDOM\administrator:*:1000000:1000004::/home/ADDOM/administrator:/bin/false
# getent passwd 'ADDOM\Administrator' ADDOM\administrator:*:1000000:1000004::/home/ADDOM/administrator:/bin/falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to verify if samba can use winbind and the NSS module correctly:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Part IV. Manage
Chapter 8. Managing Snapshots
Figure 8.1. Snapshot Architecture
- Crash Consistency
A crash consistent snapshot is captured at a particular point-in-time. When a crash consistent snapshot is restored, the data is identical as it was at the time of taking a snapshot.
Note
Currently, application level consistency is not supported. - Online Snapshot
Snapshot is an online snapshot hence the file system and its associated data continue to be available for the clients even while the snapshot is being taken.
- Quorum Based
The quorum feature ensures that the volume is in a good condition while the bricks are down. If any brick that is down for a n way replication, where n <= 2 , quorum is not met. In a n-way replication where n >= 3, quorum is met when m bricks are up, where m >= (n/2 +1) where n is odd and m >= n/2 and the first brick is up where n is even. If quorum is not met snapshot creation fails.
- Barrier
To guarantee crash consistency some of the fops are blocked during a snapshot operation.
These fops are blocked till the snapshot is complete. All other fops is passed through. There is a default time-out of 2 minutes, within that time if snapshot is not complete then these fops are unbarriered. If the barrier is unbarriered before the snapshot is complete then the snapshot operation fails. This is to ensure that the snapshot is in a consistent state.
Note
8.1. Prerequisites
- Snapshot is based on thinly provisioned LVM. Ensure the volume is based on LVM2. Red Hat Gluster Storage is supported on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.7 and later and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.1 and later. Both these versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux is based on LVM2 by default. For more information, see https://access.redhat.com/site/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Logical_Volume_Manager_Administration/thinprovisioned_volumes.html
- Each brick must be independent thinly provisioned logical volume(LV).
- The logical volume which contains the brick must not contain any data other than the brick.
- Only linear LVM is supported with Red Hat Gluster Storage. For more information, see https://access.redhat.com/site/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/4/html-single/Cluster_Logical_Volume_Manager/#lv_overview
- For each volume brick, create a dedicated thin pool that contains the brick of the volume and its (thin) brick snapshots. With the current thin-p design, avoid placing the bricks of different Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes in the same thin pool, as this reduces the performance of snapshot operations, such as snapshot delete, on other unrelated volumes.
- The recommended thin pool chunk size is 256KB. There might be exceptions to this in cases where we have a detailed information of the customer's workload.
- The recommended pool metadata size is 0.1% of the thin pool size for a chunk size of 256KB or larger. In special cases, where we recommend a chunk size less than 256KB, use a pool metadata size of 0.5% of thin pool size.
- Create a physical volume(PV) by using the
pvcreatecommand.pvcreate /dev/sda1
pvcreate /dev/sda1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the correctdataalignmentoption based on your device. For more information, Section 20.2, “Brick Configuration” - Create a Volume Group (VG) from the PV using the following command:
vgcreate dummyvg /dev/sda1
vgcreate dummyvg /dev/sda1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a thin-pool using the following command:
lvcreate --size 1T --thin dummyvg/dummypool --chunksize 256k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --size 1T --thin dummyvg/dummypool --chunksize 256k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A thin pool of size 1 TB is created, using a chunksize of 256 KB. Maximum pool metadata size of 16 G is used. - Create a thinly provisioned volume from the previously created pool using the following command:
lvcreate --virtualsize 1G --thin dummyvg/dummypool --name dummylv
# lvcreate --virtualsize 1G --thin dummyvg/dummypool --name dummylvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a file system (XFS) on this. Use the recommended options to create the XFS file system on the thin LV.For example,
mkfs.xfs -f -i size=512 -n size=8192 /dev/dummyvg/dummylv
mkfs.xfs -f -i size=512 -n size=8192 /dev/dummyvg/dummylvCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Mount this logical volume and use the mount path as the brick.
mount /dev/dummyvg/dummylv /mnt/brick1
mount /dev/dummyvg/dummylv /mnt/brick1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.2. Creating Snapshots
- Red Hat Gluster Storage volume has to be present and the volume has to be in the
Startedstate. - All the bricks of the volume have to be on an independent thin logical volume(LV).
- Snapshot names must be unique in the cluster.
- All the bricks of the volume should be up and running, unless it is a n-way replication where n >= 3. In such case quorum must be met. For more information see Chapter 8, Managing Snapshots
- No other volume operation, like
rebalance,add-brick, etc, should be running on the volume. - Total number of snapshots in the volume should not be equal to Effective snap-max-hard-limit. For more information see Configuring Snapshot Behavior.
- If you have a geo-replication setup, then pause the geo-replication session if it is running, by executing the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL pause
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL pauseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume geo-replication master-vol example.com::slave-vol pause Pausing geo-replication session between master-vol example.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol example.com::slave-vol pause Pausing geo-replication session between master-vol example.com::slave-vol has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure that you take the snapshot of the master volume and then take snapshot of the slave volume.
gluster snapshot create <snapname> <volname> [no-timestamp] [description <description>] [force]
# gluster snapshot create <snapname> <volname> [no-timestamp] [description <description>] [force]- snapname - Name of the snapshot that will be created.
- VOLNAME(S) - Name of the volume for which the snapshot will be created. We only support creating snapshot of single volume.
- description - This is an optional field that can be used to provide a description of the snap that will be saved along with the snap.
force- Snapshot creation will fail if any brick is down. In a n-way replicated Red Hat Gluster Storage volume where n >= 3 snapshot is allowed even if some of the bricks are down. In such case quorum is checked. Quorum is checked only when theforceoption is provided, else by-default the snapshot create will fail if any brick is down. Refer the Overview section for more details on quorum.- no-timestamp: By default a timestamp is appended to the snapshot name. If you do not want to append timestamp then pass no-timestamp as an argument.
Note
activate-on-create parameter to enabled.
gluster snapshot create snap1 vol1 no-timestamp snapshot create: success: Snap snap1 created successfully
# gluster snapshot create snap1 vol1 no-timestamp
snapshot create: success: Snap snap1 created successfullygluster snapshot create snap1 vol1 snapshot create: success: Snap snap1_GMT-2015.07.20-10.02.33 created successfully
# gluster snapshot create snap1 vol1
snapshot create: success: Snap snap1_GMT-2015.07.20-10.02.33 created successfully/var/run/gluster/snaps/<snap-volume-name>/brick<bricknumber>.
0888649a92ea45db8c00a615dfc5ea35 and having two bricks will have the following two mount points:
/var/run/gluster/snaps/0888649a92ea45db8c00a615dfc5ea35/brick1 /var/run/gluster/snaps/0888649a92ea45db8c00a615dfc5ea35/brick2
/var/run/gluster/snaps/0888649a92ea45db8c00a615dfc5ea35/brick1
/var/run/gluster/snaps/0888649a92ea45db8c00a615dfc5ea35/brick2df or mount command.
Note
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL resume
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL resumegluster volume geo-replication master-vol example.com::slave-vol resume Resuming geo-replication session between master-vol example.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol example.com::slave-vol resume
Resuming geo-replication session between master-vol example.com::slave-vol has been successful8.3. Cloning a Snapshot
gluster snapshot clone <clonename> <snapname>
# gluster snapshot clone <clonename> <snapname>Note
- Unlike restoring a snapshot, the original snapshot is still retained, after it has been cloned.
- The snapshot should be in activated state and all the snapshot bricks should be in running state before taking clone. Also the server nodes should be in quorum.
- This is a space efficient clone therefore both the Clone (new volume) and the snapshot LVM share the same LVM backend. The space consumption of the LVM grow as the new volume (clone) diverge from the snapshot.
gluster snapshot clone clone_vol snap1 snapshot clone: success: Clone clone_vol created successfully
# gluster snapshot clone clone_vol snap1
snapshot clone: success: Clone clone_vol created successfullygluster vol info <clonename>
# gluster vol info <clonename>Created state, similar to a newly created volume. This volume should be explicitly started to use this volume.
8.4. Listing of Available Snapshots
gluster snapshot list [VOLNAME]
# gluster snapshot list [VOLNAME]- VOLNAME - This is an optional field and if provided lists the snapshot names of all snapshots present in the volume.
gluster snapshot list snap3 gluster snapshot list test_vol No snapshots present
# gluster snapshot list
snap3
# gluster snapshot list test_vol
No snapshots present8.5. Getting Information of all the Available Snapshots
gluster snapshot info [(<snapname> | volume VOLNAME)]
# gluster snapshot info [(<snapname> | volume VOLNAME)]- snapname - This is an optional field. If the snapname is provided then the information about the specified snap is displayed.
- VOLNAME - This is an optional field. If the VOLNAME is provided the information about all the snaps in the specified volume is displayed.
8.6. Getting the Status of Available Snapshots
gluster snapshot status [(<snapname> | volume VOLNAME)]
# gluster snapshot status [(<snapname> | volume VOLNAME)]- snapname - This is an optional field. If the snapname is provided then the status about the specified snap is displayed.
- VOLNAME - This is an optional field. If the VOLNAME is provided the status about all the snaps in the specified volume is displayed.
Note
8.7. Configuring Snapshot Behavior
snap-max-hard-limit: If the snapshot count in a volume reaches this limit then no further snapshot creation is allowed. The range is from 1 to 256. Once this limit is reached you have to remove the snapshots to create further snapshots. This limit can be set for the system or per volume. If both system limit and volume limit is configured then the effective max limit would be the lowest of the two value.snap-max-soft-limit: This is a percentage value. The default value is 90%. This configuration works along with auto-delete feature. If auto-delete is enabled then it will delete the oldest snapshot when snapshot count in a volume crosses this limit. When auto-delete is disabled it will not delete any snapshot, but it will display a warning message to the user.auto-delete: This will enable or disable auto-delete feature. By default auto-delete is disabled. When enabled it will delete the oldest snapshot when snapshot count in a volume crosses the snap-max-soft-limit. When disabled it will not delete any snapshot, but it will display a warning message to the useractivate-on-create: Snapshots are not activated at creation time by default. If you want created snapshots to immediately be activated after creation, set theactivate-on-createparameter toenabled. Note that all volumes are affected by this setting.
- Displaying the Configuration Values
To display the existing configuration values for a volume or the entire cluster, run the following command:
gluster snapshot config [VOLNAME]
# gluster snapshot config [VOLNAME]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:- VOLNAME: This is an optional field. The name of the volume for which the configuration values are to be displayed.
If the volume name is not provided then the configuration values of all the volume is displayed. System configuration details are displayed irrespective of whether the volume name is specified or not.For Example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Changing the Configuration Values
To change the existing configuration values, run the following command:
gluster snapshot config [VOLNAME] ([snap-max-hard-limit <count>] [snap-max-soft-limit <percent>]) | ([auto-delete <enable|disable>]) | ([activate-on-create <enable|disable>])
# gluster snapshot config [VOLNAME] ([snap-max-hard-limit <count>] [snap-max-soft-limit <percent>]) | ([auto-delete <enable|disable>]) | ([activate-on-create <enable|disable>])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where:- VOLNAME: This is an optional field. The name of the volume for which the configuration values are to be changed. If the volume name is not provided, then running the command will set or change the system limit.
- snap-max-hard-limit: Maximum hard limit for the system or the specified volume.
- snap-max-soft-limit: Soft limit mark for the system.
- auto-delete: This enables or disables the auto-delete feature. By default auto-delete is disabled.
- activate-on-create: This enables or disables the activate-on-create feature for all volumes. By default activate-on-create is disabled.
For Example:gluster snapshot config test_vol snap-max-hard-limit 100 Changing snapshot-max-hard-limit will lead to deletion of snapshots if they exceed the new limit. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y snapshot config: snap-max-hard-limit for test_vol set successfully
# gluster snapshot config test_vol snap-max-hard-limit 100 Changing snapshot-max-hard-limit will lead to deletion of snapshots if they exceed the new limit. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y snapshot config: snap-max-hard-limit for test_vol set successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.8. Activating and Deactivating a Snapshot
gluster snapshot activate <snapname> [force]
# gluster snapshot activate <snapname> [force]- snapname: Name of the snap to be activated.
force: If some of the bricks of the snapshot volume are down then use theforcecommand to start them.
gluster snapshot activate snap1
# gluster snapshot activate snap1gluster snapshot deactivate <snapname>
# gluster snapshot deactivate <snapname>- snapname: Name of the snap to be deactivated.
gluster snapshot deactivate snap1
# gluster snapshot deactivate snap18.9. Deleting Snapshot
- Snapshot with the specified name should be present.
- Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes should be in quorum.
- No volume operation (e.g. add-brick, rebalance, etc) should be running on the original / parent volume of the snapshot.
gluster snapshot delete <snapname>
# gluster snapshot delete <snapname>- snapname - The name of the snapshot to be deleted.
gluster snapshot delete snap2 Deleting snap will erase all the information about the snap. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y snapshot delete: snap2: snap removed successfully
# gluster snapshot delete snap2
Deleting snap will erase all the information about the snap. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y
snapshot delete: snap2: snap removed successfullyNote
8.9.1. Deleting Multiple Snapshots
gluster snapshot delete all
# gluster snapshot delete allgluster snapshot delete volume <volname>
# gluster snapshot delete volume <volname>8.10. Restoring Snapshot
- The specified snapshot has to be present
- The original / parent volume of the snapshot has to be in a stopped state.
- Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes have to be in quorum.
- No volume operation (e.g. add-brick, rebalance, etc) should be running on the origin or parent volume of the snapshot.
gluster snapshot restore <snapname>
# gluster snapshot restore <snapname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,- snapname - The name of the snapshot to be restored.
For Example:gluster snapshot restore snap1 Snapshot restore: snap1: Snap restored successfully
# gluster snapshot restore snap1 Snapshot restore: snap1: Snap restored successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After snapshot is restored and the volume is started, trigger a self-heal by running the following command:gluster volume heal VOLNAME full
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME fullCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- The snapshot will be deleted once it is restored. To restore to the same point again take a snapshot explicitly after restoring the snapshot.
- After restore the brick path of the original volume will change. If you are using
fstabto mount the bricks of the origin volume then you have to fixfstabentries after restore. For more information see, https://access.redhat.com/site/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Installation_Guide/apcs04s07.html
- In the cluster, identify the nodes participating in the snapshot with the snapshot status command. For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the nodes identified above, check if the
geo-replicationrepository is present in/var/lib/glusterd/snaps/snapname. If the repository is present in any of the nodes, ensure that the same is present in/var/lib/glusterd/snaps/snapnamethroughout the cluster. If thegeo-replicationrepository is missing in any of the nodes in the cluster, copy it to/var/lib/glusterd/snaps/snapnamein that node. - Restore snapshot of the volume using the following command:
gluster snapshot restore snapname
# gluster snapshot restore snapnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you have a geo-replication setup, then perform the following steps to restore snapshot:
- Stop the geo-replication session.
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the slave volume and then the master volume.
gluster volume stop VOLNAME
# gluster volume stop VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restore snapshot of the slave volume and the master volume.
gluster snapshot restore snapname
# gluster snapshot restore snapnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the slave volume first and then the master volume.
gluster volume start VOLNAME
# gluster volume start VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the geo-replication session.
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Resume the geo-replication session.
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL resume
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL resumeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.11. Accessing Snapshots
mount -t glusterfs <hostname>:/snaps/<snapname>/parent-VOLNAME /mount_point
mount -t glusterfs <hostname>:/snaps/<snapname>/parent-VOLNAME /mount_point- parent-VOLNAME - Volume name for which we have created the snapshot.For example,
mount -t glusterfs myhostname:/snaps/snap1/test_vol /mnt
# mount -t glusterfs myhostname:/snaps/snap1/test_vol /mntCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
Warning
8.12. Scheduling of Snapshots
8.12.1. Prerequisites
- To initialize snapshot scheduler on all the nodes of the cluster, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py init
snap_scheduler.py initCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command initializes the snap_scheduler and interfaces it with the crond running on the local node. This is the first step, before executing any scheduling related commands from a node.Note
This command has to be run on all the nodes participating in the scheduling. Other options can be run independently from any node, where initialization has been successfully completed. - A shared storage named
gluster_shared_storageis used across nodes to co-ordinate the scheduling operations. This shared storage is mounted at /var/run/gluster/shared_storage on all the nodes. For more information see, Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume” - All nodes in the cluster have their times synced using NTP or any other mechanism. This is a hard requirement for this feature to work.
- If you are on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.1 or later, set the
cron_system_cronjob_use_sharesboolean toonby running the following command:setsebool -P cron_system_cronjob_use_shares on
# setsebool -P cron_system_cronjob_use_shares onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.12.2. Snapshot Scheduler Options
Note
To enable snap scheduler, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py enable
snap_scheduler.py enableNote
snap_scheduler.py enable snap_scheduler: Snapshot scheduling is enabled
# snap_scheduler.py enable
snap_scheduler: Snapshot scheduling is enabledTo enable snap scheduler, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py disable
snap_scheduler.py disable
snap_scheduler.py disable snap_scheduler: Snapshot scheduling is disabled
# snap_scheduler.py disable
snap_scheduler: Snapshot scheduling is disabledTo display the the current status(Enabled/Disabled) of the snap scheduler, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py status
snap_scheduler.py statussnap_scheduler.py status snap_scheduler: Snapshot scheduling status: Disabled
# snap_scheduler.py status
snap_scheduler: Snapshot scheduling status: DisabledTo add a snapshot schedule, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py add "Job Name" "Schedule" "Volume Name"
snap_scheduler.py add "Job Name" "Schedule" "Volume Name"snap_scheduler.py add "Job1" "* * * * *" test_vol snap_scheduler: Successfully added snapshot schedule
# snap_scheduler.py add "Job1" "* * * * *" test_vol
snap_scheduler: Successfully added snapshot scheduleNote
Scheduled-Job1-test_vol_GMT-2015.06.19-09.47.01
Scheduled-Job1-test_vol_GMT-2015.06.19-09.47.01To edit an existing snapshot schedule, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py edit "Job Name" "Schedule" "Volume Name"
snap_scheduler.py edit "Job Name" "Schedule" "Volume Name"
snap_scheduler.py edit "Job1" "*/5 * * * *" gluster_shared_storage snap_scheduler: Successfully edited snapshot schedule
# snap_scheduler.py edit "Job1" "*/5 * * * *" gluster_shared_storage
snap_scheduler: Successfully edited snapshot scheduleTo list the existing snapshot schedule, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py list
snap_scheduler.py list
snap_scheduler.py list JOB_NAME SCHEDULE OPERATION VOLUME NAME -------------------------------------------------------------------- Job0 * * * * * Snapshot Create test_vol
# snap_scheduler.py list
JOB_NAME SCHEDULE OPERATION VOLUME NAME
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Job0 * * * * * Snapshot Create test_vol
To delete an existing snapshot schedule, execute the following command:
snap_scheduler.py delete "Job Name"
snap_scheduler.py delete "Job Name"snap_scheduler.py delete Job1 snap_scheduler: Successfully deleted snapshot schedule
# snap_scheduler.py delete Job1
snap_scheduler: Successfully deleted snapshot schedule8.13. User Serviceable Snapshots
test.txt which was in the Home directory a couple of months earlier and was deleted accidentally. You can now easily go to the virtual .snaps directory that is inside the home directory and recover the test.txt file using the cp command.
Note
- User Serviceable Snapshot is not the recommended option for bulk data access from an earlier snapshot volume. For such scenarios it is recommended to mount the Snapshot volume and then access the data. For more information see, Chapter 8, Managing Snapshots
- Each activated snapshot volume when initialized by User Serviceable Snapshots, consumes some memory. Most of the memory is consumed by various house keeping structures of gfapi and xlators like DHT, AFR, etc. Therefore, the total memory consumption by snapshot depends on the number of bricks as well. Each brick consumes approximately 10MB of space, for example, in a 4x2 replica setup the total memory consumed by snapshot is around 50MB and for a 6x2 setup it is roughly 90MB.Therefore, as the number of active snapshots grow, the total memory footprint of the snapshot daemon (snapd) also grows. Therefore, in a low memory system, the snapshot daemon can get
OOMkilled if there are too many active snapshots
8.13.1. Enabling and Disabling User Serviceable Snapshot
gluster volume set VOLNAME features.uss enable
# gluster volume set VOLNAME features.uss enablegluster volume set test_vol features.uss enable volume set: success
# gluster volume set test_vol features.uss enable
volume set: successgluster volume set VOLNAME features.uss disable
# gluster volume set VOLNAME features.uss disablegluster volume set test_vol features.uss disable volume set: success
# gluster volume set test_vol features.uss disable
volume set: success8.13.2. Viewing and Retrieving Snapshots using NFS / FUSE
.snaps directory of every directory of the mounted volume.
Note
mount -t nfs -o vers=3 server1:/test-vol /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t nfs -o vers=3 server1:/test-vol /mnt/glusterfsmount -t glusterfs server1:/test-vol /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-vol /mnt/glusterfs.snaps directory is a virtual directory which will not be listed by either the ls command, or the ls -a option. The .snaps directory will contain every snapshot taken for that given volume as individual directories. Each of these snapshot entries will in turn contain the data of the particular directory the user is accessing from when the snapshot was taken.
- Go to the folder where the file was present when the snapshot was taken. For example, if you had a test.txt file in the root directory of the mount that has to be recovered, then go to that directory.
cd /mnt/glusterfs
# cd /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Since every directory has a virtual.snapsdirectory, you can enter the.snapsdirectory from here. Since.snapsis a virtual directory,lsandls -acommand will not list the.snapsdirectory. For example:ls -a ....Bob John test1.txt test2.txt# ls -a ....Bob John test1.txt test2.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Go to the
.snapsfoldercd .snaps
# cd .snapsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the
lscommand to list all the snapsFor example:ls -p snapshot_Dec2014/ snapshot_Nov2014/ snapshot_Oct2014/ snapshot_Sept2014/
# ls -p snapshot_Dec2014/ snapshot_Nov2014/ snapshot_Oct2014/ snapshot_Sept2014/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Go to the snapshot directory from where the file has to be retrieved.For example:
cd snapshot_Nov2014
cd snapshot_Nov2014Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ls -p John/ test1.txt test2.txt# ls -p John/ test1.txt test2.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Copy the file/directory to the desired location.
cp -p test2.txt $HOME
# cp -p test2.txt $HOMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.13.3. Viewing and Retrieving Snapshots using CIFS for Windows Client
.snaps folder of every folder in the root of the CIFS share. The .snaps folder is a hidden folder which will be displayed only when the following option is set to ON on the volume using the following command:
gluster volume set volname features.show-snapshot-directory on
# gluster volume set volname features.show-snapshot-directory onON, every Windows client can access the .snaps folder by following these steps:
- In the
Folderoptions, enable theShow hidden files, folders, and drivesoption. - Go to the root of the CIFS share to view the
.snapsfolder.Note
The.snapsfolder is accessible only in the root of the CIFS share and not in any sub folders. - The list of snapshots are available in the
.snapsfolder. You can now access the required file and retrieve it.
8.14. Troubleshooting
- Situation
Snapshot creation fails.
Step 1Check if the bricks are thinly provisioned by following these steps:
- Execute the
mountcommand and check the device name mounted on the brick path. For example:mount /dev/mapper/snap_lvgrp-snap_lgvol on /rhgs/brick1 type xfs (rw) /dev/mapper/snap_lvgrp1-snap_lgvol1 on /rhgs/brick2 type xfs (rw)
# mount /dev/mapper/snap_lvgrp-snap_lgvol on /rhgs/brick1 type xfs (rw) /dev/mapper/snap_lvgrp1-snap_lgvol1 on /rhgs/brick2 type xfs (rw)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the following command to check if the device has a LV pool name.
lvs device-name
lvs device-nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If thePoolfield is empty, then the brick is not thinly provisioned. - Ensure that the brick is thinly provisioned, and retry the snapshot create command.
Step 2Check if the bricks are down by following these steps:
- Execute the following command to check the status of the volume:
gluster volume status VOLNAME
# gluster volume status VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If any bricks are down, then start the bricks by executing the following command:
gluster volume start VOLNAME force
# gluster volume start VOLNAME forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To verify if the bricks are up, execute the following command:
gluster volume status VOLNAME
# gluster volume status VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Retry the snapshot create command.
Step 3Check if the node is down by following these steps:
- Execute the following command to check the status of the nodes:
gluster volume status VOLNAME
# gluster volume status VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If a brick is not listed in the status, then execute the following command:
gluster pool list
# gluster pool listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the status of the node hosting the missing brick is
Disconnected, then power-up the node. - Retry the snapshot create command.
Step 4Check if rebalance is in progress by following these steps:
- Execute the following command to check the rebalance status:
gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME status
gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If rebalance is in progress, wait for it to finish.
- Retry the snapshot create command.
- Situation
Snapshot delete fails.
Step 1Check if the server quorum is met by following these steps:
- Execute the following command to check the peer status:
gluster pool list
# gluster pool listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If nodes are down, and the cluster is not in quorum, then power up the nodes.
- To verify if the cluster is in quorum, execute the following command:
gluster pool list
# gluster pool listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Retry the snapshot delete command.
- Situation
Snapshot delete command fails on some node(s) during commit phase, leaving the system inconsistent.
Solution- Identify the node(s) where the delete command failed. This information is available in the delete command's error output. For example:
gluster snapshot delete snapshot1 Deleting snap will erase all the information about the snap. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y snapshot delete: failed: Commit failed on 10.00.00.02. Please check log file for details. Snapshot command failed
# gluster snapshot delete snapshot1 Deleting snap will erase all the information about the snap. Do you still want to continue? (y/n) y snapshot delete: failed: Commit failed on 10.00.00.02. Please check log file for details. Snapshot command failedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On the node where the delete command failed, bring down glusterd using the following command:
service glusterd stop
# service glusterd stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Ifglusterdcrashes, there is no functionality impact to this crash as it occurs during the shutdown. For more information, see Section 23.3, “ResolvingglusterdCrash” - Delete that particular snaps repository in
/var/lib/glusterd/snaps/from that node. For example:rm -rf /var/lib/glusterd/snaps/snapshot1
# rm -rf /var/lib/glusterd/snaps/snapshot1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start glusterd on that node using the following command:
service glusterd start.
# service glusterd start.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Repeat the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th steps on all the nodes where the commit failed as identified in the 1st step.
- Retry deleting the snapshot. For example:
gluster snapshot delete snapshot1
# gluster snapshot delete snapshot1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Situation
Snapshot restore fails.
Step 1Check if the server quorum is met by following these steps:
- Execute the following command to check the peer status:
gluster pool list
# gluster pool listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If nodes are down, and the cluster is not in quorum, then power up the nodes.
- To verify if the cluster is in quorum, execute the following command:
gluster pool list
# gluster pool listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Retry the snapshot restore command.
Step 2Check if the volume is in
Stopstate by following these steps:- Execute the following command to check the volume info:
gluster volume info VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the volume is in
Startedstate, then stop the volume using the following command:gluster volume stop VOLNAME
gluster volume stop VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Retry the snapshot restore command.
- Situation
Snapshot commands fail.
Step 1Check if there is a mismatch in the operating versions by following these steps:
- Open the following file and check for the operating version:
/var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info
/var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If theoperating-versionis lesser than 30000, then the snapshot commands are not supported in the version the cluster is operating on. - Upgrade all nodes in the cluster to Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.2 or higher.
- Retry the snapshot command.
- Situation
After rolling upgrade, snapshot feature does not work.
SolutionYou must ensure to make the following changes on the cluster to enable snapshot:
- Restart the volume using the following commands.
gluster volume stop VOLNAME gluster volume start VOLNAME
# gluster volume stop VOLNAME # gluster volume start VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart glusterd services on all nodes.
service glusterd restart
# service glusterd restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 9. Managing Directory Quotas
9.1. Enabling and Disabling Quotas
gluster volume quota VOLNAME enable
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME enablegluster volume quota VOLNAME disable
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME disableImportant
quota-remove-xattr.sh. If you re-enable quotas while the cleanup process is still running, the extended attributes that enable quotas may be removed by the cleanup process. This has negative effects on quota accounting.
9.2. Before Setting a Quota on a Directory
- When specifying a directory to limit with the
gluster volume quotacommand, the directory's path is relative to the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume mount point, not the root directory of the server or client on which the volume is mounted. That is, if the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume is mounted at/mnt/glusterfsand you want to place a limit on the/mnt/glusterfs/dirdirectory, use/diras the path when you run thegluster volume quotacommand, like so:gluster volume quota VOLNAME limit-usage /dir hard_limit
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME limit-usage /dir hard_limitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that at least one brick is available per replica set when you run the
gluster volume quotacommand. A brick is available if aYappears in theOnlinecolumn ofgluster volume statuscommand output, like so:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.3. Limiting Disk Usage
9.3.1. Setting Disk Usage Limits
gluster volume quota VOLNAME limit-usage path hard_limit
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME limit-usage path hard_limit/dir directory on the data volume to 100 GB, run the following command:
gluster volume quota data limit-usage /dir 100GB
# gluster volume quota data limit-usage /dir 100GB/dir directory and all files and directories underneath it from containing more than 100 GB of data cumulatively.
data volume to 1 TB, set a 1 TB limit on the root directory of the volume, like so:
gluster volume quota data limit-usage / 1TB
# gluster volume quota data limit-usage / 1TBgluster volume quota data limit-usage / 1TB 75
# gluster volume quota data limit-usage / 1TB 75/var/log/glusterfs/bricks/BRICKPATH.log.
default-soft-limit subcommand. For example, to set a default soft limit of 90% on the data volume, run the following command:
gluster volume quota data default-soft-limit 90
# gluster volume quota data default-soft-limit 90gluster volume quota VOLNAME list
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME listlimit-usage subcommand.
9.3.2. Viewing Current Disk Usage Limits
gluster volume quota VOLNAME list
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME listgluster volume quota VOLNAME list /<directory_name>
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME list /<directory_name>gluster volume quota test-volume list /dir Path Hard-limit Soft-limit Used Available ------------------------------------------------- /dir 10.0GB 75% 0Bytes 10.0GB
# gluster volume quota test-volume list /dir
Path Hard-limit Soft-limit Used Available
-------------------------------------------------
/dir 10.0GB 75% 0Bytes 10.0GBgluster volume quota VOLNAME list DIR1 DIR2
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME list DIR1 DIR29.3.2.1. Viewing Quota Limit Information Using the df Utility
df utility does not take quota limits into account when reporting disk usage. This means that clients accessing directories see the total space available to the volume, rather than the total space allotted to their directory by quotas. You can configure a volume to display the hard quota limit as the total disk space instead by setting quota-deem-statfs parameter to on.
quota-deem-statfs parameter to on, run the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME quota-deem-statfs on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME quota-deem-statfs ondf to to display the hard quota limit as the total disk space for a client.
quota-deem-statfs is set to off:
df -hT /home Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on server1:/test-volume fuse.glusterfs 400G 12G 389G 3% /home
# df -hT /home
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
server1:/test-volume fuse.glusterfs 400G 12G 389G 3% /homequota-deem-statfs is set to on:
df -hT /home Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on server1:/test-volume fuse.glusterfs 300G 12G 289G 4% /home
# df -hT /home
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
server1:/test-volume fuse.glusterfs 300G 12G 289G 4% /home9.3.3. Setting Quota Check Frequency (Timeouts)
soft-timeout parameter specifies how often Red Hat Gluster Storage checks space usage when usage has, so far, been below the soft limit set on the directory or volume. The default soft timeout frequency is every 60 seconds.
gluster volume quota VOLNAME soft-timeout seconds
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME soft-timeout secondshard-timeout parameter specifies how often Red Hat Gluster Storage checks space usage when usage is greater than the soft limit set on the directory or volume. The default hard timeout frequency is every 5 seconds.
gluster volume quota VOLNAME hard-timeout seconds
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME hard-timeout secondsImportant
9.3.4. Setting Logging Frequency (Alert Time)
alert-time parameter configures how frequently usage information is logged after the soft limit has been reached. You can configure alert-time with the following command:
gluster volume quota VOLNAME alert-time time
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME alert-time time1w).
| Unit of time | Format 1 | Format 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Second(s) | [integer]s | [integer]sec |
| Minute(s) | [integer]m | [integer]min |
| Hour(s) | [integer]h | [integer]hr |
| Day(s) | [integer]d | [integer]days |
| Week(s) | [integer]w | [integer]wk |
gluster volume quota test-vol alert-time 10m
# gluster volume quota test-vol alert-time 10mgluster volume quota test-vol alert-time 10days
# gluster volume quota test-vol alert-time 10days9.3.5. Removing Disk Usage Limits
gluster volume quota VOLNAME remove DIR
# gluster volume quota VOLNAME remove DIRgluster volume quota test-volume remove /data volume quota : success
# gluster volume quota test-volume remove /data
volume quota : successgluster vol quota VOLNAME remove /
# gluster vol quota VOLNAME remove /Chapter 10. Managing Geo-replication
10.1. About Geo-replication
- Master – the primary Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
- Slave – a secondary Red Hat Gluster Storage volume. A slave volume can be a volume on a remote host, such as
remote-host::volname.
10.2. Replicated Volumes vs Geo-replication
| Replicated Volumes | Geo-replication |
|---|---|
| Works between all bricks in a replica set, so that changes are synced in both directions. | Works only from the primary (master) volume to the secondary (slave) volume. |
| Mirrors data across bricks within one trusted storage pool. | Mirrors data across geographically distributed trusted storage pools. |
| Provides high-availability. | Provides data back-up for disaster recovery. |
| Synchronous replication: each and every file operation is applied to all the bricks. | Asynchronous replication: checks for changes in files periodically, and syncs them on detecting differences. |
10.3. Preparing to Deploy Geo-replication
10.3.1. Exploring Geo-replication Deployment Scenarios
- Geo-replication over LAN
- Geo-replication over WAN
- Geo-replication over the Internet
- Multi-site cascading geo-replication
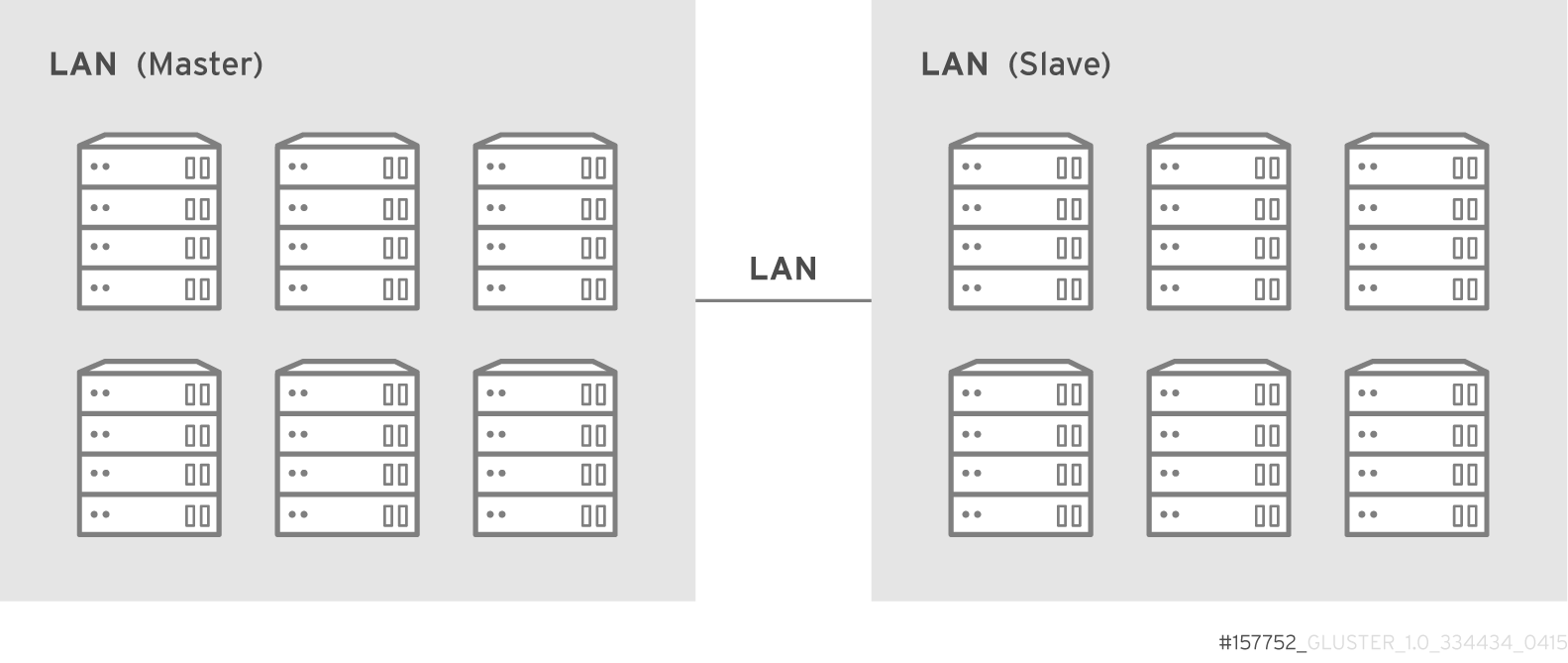

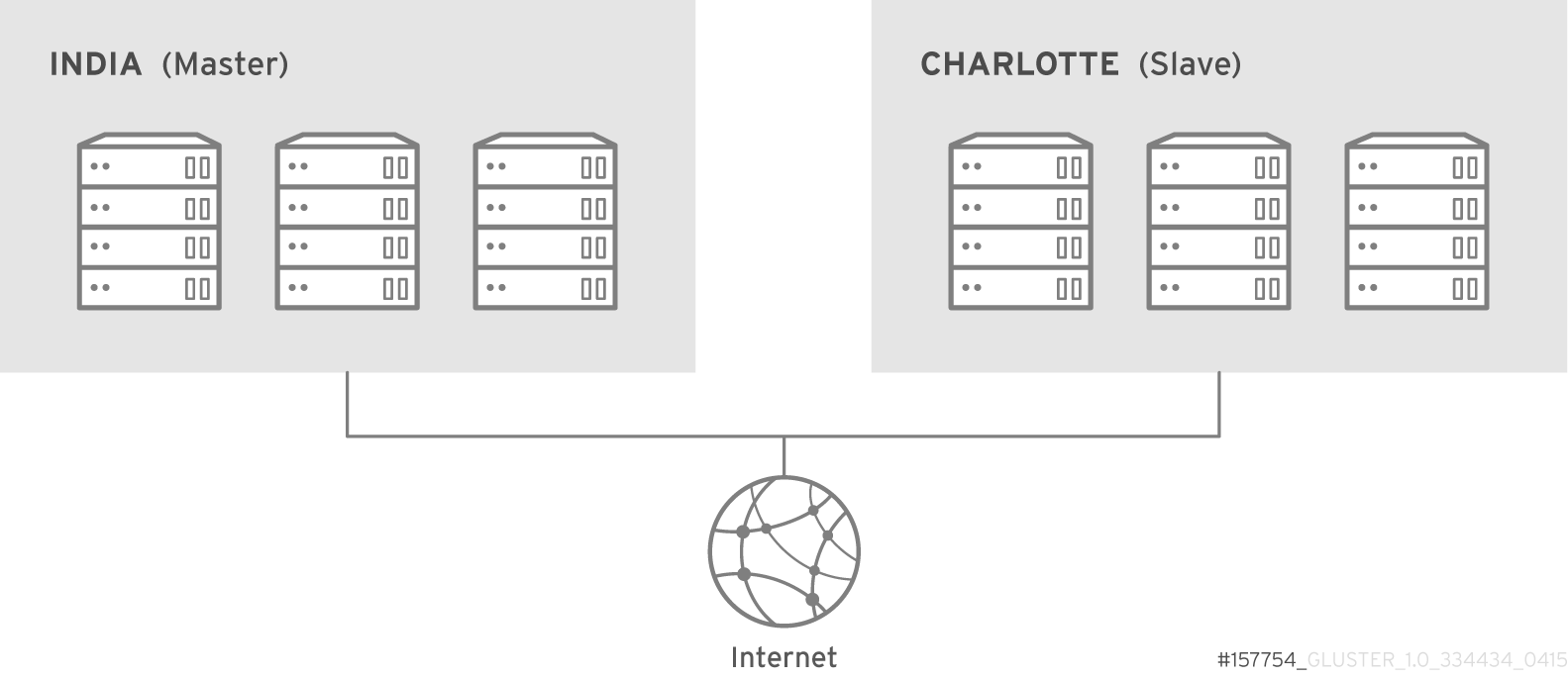

10.3.2. Geo-replication Deployment Overview
- Verify that your environment matches the minimum system requirements. See Section 10.3.3, “Prerequisites”.
- Determine the appropriate deployment scenario. See Section 10.3.1, “Exploring Geo-replication Deployment Scenarios”.
- Start geo-replication on the master and slave systems. See Section 10.4, “Starting Geo-replication”.
10.3.3. Prerequisites
- The master and slave volumes must use the same version of Red Hat Gluster Storage.
- Nodes in the slave volume must not be part of the master volume. Two separate trusted storage pools are required.
- Disable the
performance.quick-readoption in the slave volume using the following command:gluster volume set slavevol performance.quick-read off
[slave ~]# gluster volume set slavevol performance.quick-read offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Time must be synchronized between all master and slave nodes before geo-replication is configured. Red Hat recommends setting up a network time protocol service to keep time synchronized between bricks and servers, and avoid out-of-time synchronization errors.See Network Time Protocol Setup for more information.
- Add the required port for geo-replication from the ports listed in the Section 3.1.2, “Port Access Requirements”.
- Key-based SSH authentication without a password is required between one node of the master volume (the node from which the
geo-replication createcommand will be executed), and one node of the slave volume (the node whose IP/hostname will be mentioned in the slave name when running thegeo-replication createcommand).Create the public and private keys usingssh-keygen(without passphrase) on the master node:ssh-keygen
# ssh-keygenCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the public key to the slave node using the following command:ssh-copy-id -i identity_file root@slave_node_IPaddress/Hostname
# ssh-copy-id -i identity_file root@slave_node_IPaddress/HostnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you are setting up a non-root geo-replicaton session, then copy the public key to the respectiveuserlocation.Note
- Key-based SSH authentication without a password is only required from the master node to the slave node; the slave node does not need this level of access. - ssh-copy-idcommand does not work ifssh authorized_keysfile is configured in the custom location. You must copy the contents of.ssh/id_rsa.pubfile from the Master and paste it to authorized_keys file in the custom location on the Slave node.Gsyncd also requires key-based SSH authentication without a password between every node in the master cluster to every node in the slave cluster. Thegluster system:: execute gsec_createcommand createssecret-pemfiles on all the nodes in the master, and is used to implement the SSH authentication connection. Thepush-pemoption in thegeo-replication createcommand pushes these keys to all slave nodes.For more information on thegluster system::execute gsec_createandpush-pemcommands, see Section 10.3.4.1, “Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session”.
10.3.4. Setting Up your Environment
- Section 10.3.4.1, “Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session” - In this method, the slave mount is owned by the root user.
- Section 10.3.4.2, “Setting Up your Environment for a Secure Geo-replication Slave” - This method is more secure as the slave mount is owned by a normal user.
10.3.4.1. Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session
Creating Geo-replication Sessions
- To create a common
pem pubfile, run the following command on the master node where the key-based SSH authentication connection is configured:gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create the geo-replication session using the following command. The
push-pemoption is needed to perform the necessarypem-filesetup on the slave nodes.gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem [force]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem [force]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol create push-pem
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol create push-pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- There must be key-based SSH authentication access between the node from which this command is run, and the slave host specified in the above command. This command performs the slave verification, which includes checking for a valid slave URL, valid slave volume, and available space on the slave. If the verification fails, you can use the
forceoption which will ignore the failed verification and create a geo-replication session. - The slave volume is in read-only mode by default. However, in case of a failover-failback situation, the original master is made read-only by default as the session is from the original slave to the original master.
- Enable shared storage for master and slave volumes:
gluster volume set all cluster.enable-shared-storage enable
# gluster volume set all cluster.enable-shared-storage enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on shared storage, see Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume”. - Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”. - Start the geo-replication by running the following command on the master node:For example,
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start [force]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start [force]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of the created session by running the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.3.4.2. Setting Up your Environment for a Secure Geo-replication Slave
mountbroker, an internal service of glusterd which manages the mounts for unprivileged slave accounts. You must perform additional steps to configure glusterd with the appropriate mountbroker's access control directives. The following example demonstrates this process:
- In all the slave nodes, create a new group. For example,
geogroup.Note
You must not use multiple groups for themountbrokersetup. You can create multiple user accounts but the group should be same for all the non-root users. - In all the slave nodes, create a unprivileged account. For example,
geoaccount. Addgeoaccountas a member ofgeogroupgroup. - On any one of the Slave nodes, run the following command to set up mountbroker root directory and group.
gluster-mountbroker setup <MOUNT ROOT> <GROUP>
# gluster-mountbroker setup <MOUNT ROOT> <GROUP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster-mountbroker setup /var/mountbroker-root geogroup
# gluster-mountbroker setup /var/mountbroker-root geogroupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On any one of the Slave nodes, run the following commands to add volume and user to the mountbroker service.
gluster-mountbroker add <VOLUME> <USER>
# gluster-mountbroker add <VOLUME> <USER>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster-mountbroker add slavevol geoaccount
# gluster-mountbroker add slavevol geoaccountCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check the status of the setup by running the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output displays the mountbroker status for every peer node in the slave cluster. - Restart
glusterdservice on all the Slave nodes.service glusterd restart
# service glusterd restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you setup an auxiliary glusterFS mount for the unprivileged account on all the Slave nodes, perform the following steps to setup a non-root geo-replication session.: - Setup key-based SSH authentication from one of the master nodes to the
useron one of the slave nodes.For example, to setup key-based SSH authentication to the user geoaccount.ssh-keygen ssh-copy-id -i identity_file geoaccount@slave_node_IPaddress/Hostname
# ssh-keygen # ssh-copy-id -i identity_file geoaccount@slave_node_IPaddress/HostnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a common pem pub file by running the following command on the master nodes, where the key-based SSH authentication connection is configured to the
useron the slave nodes:gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a geo-replication relationship between the master and the slave to the
userby running the following command on the master node:For example,gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol create push-pem
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol create push-pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you have multiple slave volumes and/or multiple accounts, create a geo-replication session with that particular user and volume.For example,gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount2@SLAVENODE::slavevol2 create push-pem
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount2@SLAVENODE::slavevol2 create push-pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On the slave node, which is used to create relationship, run
/usr/libexec/glusterfs/set_geo_rep_pem_keys.shas a root with user name, master volume name, and slave volume names as the arguments.For example,/usr/libexec/glusterfs/set_geo_rep_pem_keys.sh geoaccount MASTERVOL SLAVEVOL_NAME
# /usr/libexec/glusterfs/set_geo_rep_pem_keys.sh geoaccount MASTERVOL SLAVEVOL_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”. - Start the geo-replication with slave user by running the following command on the master node:For example,
gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol start
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of geo-replication session by running the following command on the master node:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol status
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
After mountbroker geo-replicaton session is deleted, use the following command to remove volumes per mountbroker user.
gluster-mountbroker remove [--volume volume] [--user user]
# gluster-mountbroker remove [--volume volume] [--user user]gluster-mountbroker remove --volume slavevol --user geoaccount gluster-mountbroker remove --user geoaccount gluster-mountbroker remove --volume slavevol
# gluster-mountbroker remove --volume slavevol --user geoaccount
# gluster-mountbroker remove --user geoaccount
# gluster-mountbroker remove --volume slavevol
Important
gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol status
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTERVOL geoaccount@SLAVENODE::slavevol statusgeoaccount is the name of the unprivileged user account.
10.3.5. Configuring a Meta-Volume
gluster_shared_storage is created in the cluster, and is mounted at /var/run/gluster/shared_storage on all the nodes in the cluster. For more information on setting up shared storage volume, see Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume”.
- Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.4. Starting Geo-replication
10.4.1. Starting a Geo-replication Session
Important
- To start the geo-replication session between the hosts:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol start Starting geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol start Starting geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command will start distributed geo-replication on all the nodes that are part of the master volume. If a node that is part of the master volume is down, the command will still be successful. In a replica pair, the geo-replication session will be active on any of the replica nodes, but remain passive on the others.After executing the command, it may take a few minutes for the session to initialize and become stable.Note
If you attempt to create a geo-replication session and the slave already has data, the following error message will be displayed:slave-node::slave is not empty. Please delete existing files in slave-node::slave and retry, or use force to continue without deleting the existing files. geo-replication command failed
slave-node::slave is not empty. Please delete existing files in slave-node::slave and retry, or use force to continue without deleting the existing files. geo-replication command failedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- To start the geo-replication session forcefully between the hosts:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol start force Starting geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol start force Starting geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command will force start geo-replication sessions on the nodes that are part of the master volume. If it is unable to successfully start the geo-replication session on any node which is online and part of the master volume, the command will still start the geo-replication sessions on as many nodes as it can. This command can also be used to re-start geo-replication sessions on the nodes where the session has died, or has not started.
10.4.2. Verifying a Successful Geo-replication Deployment
status command to verify the status of geo-replication in your environment:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL statusgluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol status
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol status10.4.3. Displaying Geo-replication Status Information
status command can be used to display information about a specific geo-replication master session, master-slave session, or all geo-replication sessions. The status output provides both node and brick level information.
- To display information about all geo-replication sessions, use the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication status [detail]
# gluster volume geo-replication status [detail]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To display information on all geo-replication sessions from a particular master volume, use the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL status [detail]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL status [detail]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- To display information of a particular master-slave session, use the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status [detail]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status [detail]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
There will be a mismatch between the outputs of thedfcommand (including-hand-k) and inode of the master and slave volumes when the data is in full sync. This is due to the extra inode and size consumption by thechangelogjournaling data, which keeps track of the changes done on the file system on themastervolume. Instead of running thedfcommand to verify the status of synchronization, use# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status detailinstead. - The geo-replication status command output provides the following information:
- Master Node: Master node and Hostname as listed in the
gluster volume infocommand output - Master Vol: Master volume name
- Master Brick: The path of the brick
- Slave User: Slave user name
- Slave: Slave volume name
- Slave Node: IP address/hostname of the slave node to which master worker is connected to.
- Status: The status of the geo-replication worker can be one of the following:
- Initializing: This is the initial phase of the Geo-replication session; it remains in this state for a minute in order to make sure no abnormalities are present.
- Created: The geo-replication session is created, but not started.
- Active: The
gsyncdaemon in this node is active and syncing the data. - Passive: A replica pair of the active node. The data synchronization is handled by the active node. Hence, this node does not sync any data.
- Faulty: The geo-replication session has experienced a problem, and the issue needs to be investigated further. For more information, see Section 10.11, “Troubleshooting Geo-replication” section.
- Stopped: The geo-replication session has stopped, but has not been deleted.
- Crawl Status: Crawl status can be one of the following:
- Changelog Crawl: The
changelogtranslator has produced the changelog and that is being consumed bygsyncddaemon to sync data. - Hybrid Crawl: The
gsyncddaemon is crawling the glusterFS file system and generating pseudo changelog to sync data. - History Crawl: The
gsyncddaemon consumes the history changelogs produced by the changelog translator to sync data.
- Last Synced: The last synced time.
- Entry: The number of pending entry (CREATE, MKDIR, RENAME, UNLINK etc) operations per session.
- Data: The number of
Dataoperations pending per session. - Meta: The number of
Metaoperations pending per session. - Failures: The number of failures. If the failure count is more than zero, view the log files for errors in the Master bricks.
- Checkpoint Time: Displays the date and time of the checkpoint, if set. Otherwise, it displays as N/A.
- Checkpoint Completed: Displays the status of the checkpoint.
- Checkpoint Completion Time: Displays the completion time if Checkpoint is completed. Otherwise, it displays as N/A.
10.4.4. Configuring a Geo-replication Session
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config [Name] [Value]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config [Name] [Value]gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_tarssh true
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_tarssh truegluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config! (exclamation mark). For example, to reset log-level to the default value:
gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config '!log-level'
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config '!log-level'Warning
Connected (online) state. If you change the configuration when any of the peer is down, the geo-replication cluster would be in inconsistent state when the node comes back online.
The following table provides an overview of the configurable options for a geo-replication setting:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| gluster-log-file LOGFILE | The path to the geo-replication glusterfs log file. |
| gluster-log-level LOGFILELEVEL | The log level for glusterfs processes. |
| log-file LOGFILE | The path to the geo-replication log file. |
| log-level LOGFILELEVEL | The log level for geo-replication. |
| changelog-log-level LOGFILELEVEL | The log level for the changelog. The default log level is set to INFO. |
| changelog-batch-size SIZEINBYTES | The total size for the changelog in a batch. The default size is set to 727040 bytes. |
| ssh-command COMMAND | The SSH command to connect to the remote machine (the default is SSH). |
| rsync-command COMMAND | The rsync command to use for synchronizing the files (the default is rsync). |
| use-tarssh [true | false] | The use-tarssh command allows tar over Secure Shell protocol. Use this option to handle workloads of files that have not undergone edits. |
| volume_id=UID | The command to delete the existing master UID for the intermediate/slave node. |
| timeout SECONDS | The timeout period in seconds. |
| sync-jobs N |
The number of sync-jobs represents the maximum number of syncer threads (rsync processes or tar over ssh processes for syncing) inside each worker. The number of workers is always equal to the number of bricks in the Master volume. For example, a distributed-replicated volume of (3 x 2) with sync-jobs configured at 3 results in 9 total sync-jobs (aka threads) across all nodes/servers.
Active and Passive Workers: The number of active workers is based on the volume configuration. In case of a distribute volume, all bricks (workers) will be active and participate in syncing. In case of replicate or dispersed volume, one worker from each replicate/disperse group (subvolume) will be active and participate in syncing. This is to avoid duplicate syncing from other bricks. The remaining workers in each replicate/disperse group (subvolume) will be passive. In case the active worker goes down, one of the passive worker from the same replicate/disperse group will become an active worker.
|
| ignore-deletes | If this option is set to 1, a file deleted on the master will not trigger a delete operation on the slave. As a result, the slave will remain as a superset of the master and can be used to recover the master in the event of a crash and/or accidental delete. |
| checkpoint [LABEL|now] | Sets a checkpoint with the given option LABEL. If the option is set as now, then the current time will be used as the label. |
| sync-acls [true | false] | Syncs acls to the Slave cluster. By default, this option is enabled.
Note
Geo-replication can sync acls only with rsync as the sync engine and not with tarssh as the sync engine.
|
| sync-xattrs [true | false] | Syncs extended attributes to the Slave cluster. By default, this option is enabled.
Note
Geo-replication can sync extended attributes only with rsync as the sync engine and not with tarssh as the sync engine.
|
| log-rsync-performance [true | false] | If this option is set to enable, geo-replication starts recording the rsync performance in log files. By default, this option is disabled. |
| rsync-options | Additional options to rsync. For example, you can limit the rsync bandwidth usage "--bwlimit=<value>". |
| use-meta-volume [true | false] | Set this option to enable, to use meta volume in Geo-replication. By default, this option is disabled.
Note
For more information on meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”.
|
| meta-volume-mnt PATH | The path of the meta volume mount point. |
| gfid-conflict-resolution [true | false] | Auto GFID conflict resolution feature provides an ability to automatically detect and fix the GFID conflicts between master and slave. This configuration option provides an ability to enable or disable this feature. By default, this option is true. |
10.4.4.1. Geo-replication Checkpoints
10.4.4.1.1. About Geo-replication Checkpoints
10.4.4.1.2. Configuring and Viewing Geo-replication Checkpoint Information
- To set a checkpoint on a geo-replication session, use the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config checkpoint [now|LABEL]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config checkpoint [now|LABEL]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to set checkpoint betweenVolume1andstorage.backup.com:/data/remote_dir:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config checkpoint now geo-replication config updated successfully
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config checkpoint now geo-replication config updated successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The label for a checkpoint can be set as the current time usingnow, or a particular label can be specified, as shown below:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config checkpoint NEW_ACCOUNTS_CREATED geo-replication config updated successfully.
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config checkpoint NEW_ACCOUNTS_CREATED geo-replication config updated successfully.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To display the status of a checkpoint for a geo-replication session, use the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status detail
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status detailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To delete checkpoints for a geo-replication session, use the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config '!checkpoint'
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config '!checkpoint'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to delete the checkpoint set betweenVolume1andstorage.backup.com::slave-vol:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config '!checkpoint' geo-replication config updated successfully
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config '!checkpoint' geo-replication config updated successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.4.5. Stopping a Geo-replication Session
- To stop a geo-replication session between the hosts:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol stop Stopping geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol stop Stopping geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Thestopcommand will fail if:- any node that is a part of the volume is offline.
- if it is unable to stop the geo-replication session on any particular node.
- if the geo-replication session between the master and slave is not active.
- To stop a geo-replication session forcefully between the hosts:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol stop force Stopping geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol stop force Stopping geo-replication session between Volume1 & storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Usingforcewill stop the geo-replication session between the master and slave even if any node that is a part of the volume is offline. If it is unable to stop the geo-replication session on any particular node, the command will still stop the geo-replication sessions on as many nodes as it can. Usingforcewill also stop inactive geo-replication sessions.
10.4.6. Deleting a Geo-replication Session
Important
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL delete [reset-sync-time]
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL delete [reset-sync-time]reset-sync-time: The geo-replication delete command retains the information about the last synchronized time. Due to this, if the same geo-replication session is recreated, then the synchronization will continue from the time where it was left before deleting the session. For the geo-replication session to not maintain any details about the deleted session, use the reset-sync-time option with the delete command. Now, when the session is recreated, it starts synchronization from the beginning just like a new session.
gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol delete geo-replication command executed successfully
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol delete
geo-replication command executed successfullyNote
delete command will fail if:
- any node that is a part of the volume is offline.
- if it is unable to delete the geo-replication session on any particular node.
- if the geo-replication session between the master and slave is still active.
Important
pem files which contain the SSH keys from the /var/lib/glusterd/geo-replication/ directory.
10.5. Starting Geo-replication on a Newly Added Brick, Node, or Volume
10.5.1. Starting Geo-replication for a New Brick or New Node
- Run the following command on the master node where key-based SSH authentication connection is configured, in order to create a common
pem pubfile.gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create the geo-replication session using the following command. The
push-pemandforceoptions are required to perform the necessarypem-filesetup on the slave nodes.gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol create push-pem force
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol create push-pem forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
There must be key-based SSH authentication access between the node from which this command is run, and the slave host specified in the above command. This command performs the slave verification, which includes checking for a valid slave URL, valid slave volume, and available space on the slave. - After successfully setting up the shared storage volume, when a new node is added to the cluster, the shared storage is not mounted automatically on this node. Neither is the
/etc/fstabentry added for the shared storage on this node. To make use of shared storage on this node, execute the following commands:mount -t glusterfs <local node's ip>:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage cp /etc/fstab /var/run/gluster/fstab.tmp echo "<local node's ip>:/gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/ glusterfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
# mount -t glusterfs <local node's ip>:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage # cp /etc/fstab /var/run/gluster/fstab.tmp # echo "<local node's ip>:/gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/ glusterfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstabCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on setting up shared storage volume, see Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume”. - Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”. - If a node is added at slave, stop the geo-replication session using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the geo-replication session between the slave and master forcefully, using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of the created session, using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.5.2. Starting Geo-replication for a New Brick on an Existing Node
10.5.3. Starting Geo-replication for a New Volume
Prerequisites
- There must be key-based SSH authentication without a password access between the master volume node and the slave volume node.
- Create the geo-replication session using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol create
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
This command performs the slave verification, which includes checking for a valid slave URL, valid slave volume, and available space on the slave. - Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”. - Start the geo-replication session between the slave and master, using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of the created session, using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.6. Scheduling Geo-replication as a Cron Job
- Stops the geo-replication session, if started
- Starts the geo-replication session
- Sets the Checkpoint
- Checks the status of checkpoint until it is complete
- After the checkpoint is complete, stops the geo-replication session
To run a geo-reolication session only when required, run the following script:
python /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py MASTERVOL SLAVEHOST SLAVEVOL
# python /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py MASTERVOL SLAVEHOST SLAVEVOLpython /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py Volume1 storage.backup.com slave-vol
# python /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py Volume1 storage.backup.com slave-volpython /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py --help
# python /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py --helpTo schedule geo-replication to run automatically using Cron:
minute hour day month day-of-week directory_and_script-to-execute MASTERVOL SLAVEHOST SLAVEVOL >> log_file_for_script_output
minute hour day month day-of-week directory_and_script-to-execute MASTERVOL SLAVEHOST SLAVEVOL >> log_file_for_script_output30 20 * * * root python /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py --no-color Volume1 storage.backup.com slave-vol >> /var/log/glusterfs/schedule_georep.log 2>&1
30 20 * * * root python /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts/schedule_georep.py --no-color Volume1 storage.backup.com slave-vol >> /var/log/glusterfs/schedule_georep.log 2>&110.7. Disaster Recovery
failover procedure so that a slave can replace the master. When this happens, all the I/O operations, including reads and writes, are done on the slave which is now acting as the master. When the original master is back online, you can perform a failback procedure on the original slave so that it synchronizes the differences back to the original master.
10.7.1. Failover: Promoting a Slave to Master
- Disable read-only on the slave volume by running the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME features.read-only off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME features.read-only offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the following commands on the slave machine to promote it to be the master:
gluster volume set VOLNAME geo-replication.indexing on # gluster volume set VOLNAME changelog on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME geo-replication.indexing on # gluster volume set VOLNAME changelog onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For examplegluster volume set slave-vol geo-replication.indexing on volume set: success # gluster volume set slave-vol changelog on volume set: success
# gluster volume set slave-vol geo-replication.indexing on volume set: success # gluster volume set slave-vol changelog on volume set: successCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.7.2. Failback: Resuming Master and Slave back to their Original State
- Stop the existing geo-rep session from original master to orginal slave using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL ORIGINAL_SLAVE_HOST::ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL stop force
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL ORIGINAL_SLAVE_HOST::ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL stop forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol stop force Stopping geo-replication session between Volume1 and storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol stop force Stopping geo-replication session between Volume1 and storage.backup.com::slave-vol has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a new geo-replication session with the original slave as the new master, and the original master as the new slave with
forceoption. Detailed information on creating geo-replication session is available at: . - Start the special synchronization mode to speed up the recovery of data from slave. This option adds capability to geo-replication to ignore the files created before enabling
indexingoption. With this option, geo-replication will synchronize only those files which are created after making Slave volume as Master volume.gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL config special-sync-mode recover
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL config special-sync-mode recoverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 config special-sync-mode recover geo-replication config updated successfully
# gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 config special-sync-mode recover geo-replication config updated successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Disable the gfid-conflict-resolution option:
gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL config gfid-conflict-resolution false
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL config gfid-conflict-resolution falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 config gfid-conflict-resolution false geo-replication config updated successfully
# gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 config gfid-conflict-resolution false geo-replication config updated successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the new geo-replication session using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 start Starting geo-replication session between slave-vol and master.com::Volume1 has been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 start Starting geo-replication session between slave-vol and master.com::Volume1 has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the I/O operations on the original slave and set the checkpoint. By setting a checkpoint, synchronization information is available on whether the data that was on the master at that point in time has been replicated to the slaves.
gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL config checkpoint now
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL config checkpoint nowCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 config checkpoint now geo-replication config updated successfully
# gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 config checkpoint now geo-replication config updated successfullyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Checkpoint completion ensures that the data from the original slave is restored back to the original master. But since the IOs were stopped at slave before checkpoint was set, we need to touch the slave mount for checkpoint to be completed
touch orginial_slave_mount
# touch orginial_slave_mountCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL status detail
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL status detailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,touch /mnt/gluster/slavevol gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 status detail
# touch /mnt/gluster/slavevol # gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol master.com::Volume1 status detailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After the checkpoint is complete, stop and delete the current geo-replication session between the original slave and original master
gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL stop
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL delete
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL ORIGINAL_MASTER_HOST::ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL deleteCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Disable read-only on the master volume by running the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME features.read-only off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME features.read-only offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Reset the options that were set for promoting the slave volume as the master volume by running the following commands:
gluster volume reset ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL geo-replication.indexing force gluster volume reset ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL changelog
# gluster volume reset ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL geo-replication.indexing force # gluster volume reset ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL changelogCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Resume the original roles by starting the geo-rep session from the original master using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL ORIGINAL_SLAVE_HOST::ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication ORIGINAL_MASTER_VOL ORIGINAL_SLAVE_HOST::ORIGINAL_SLAVE_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol start Starting geo-replication session between slave-vol and master.com::Volume1 been successful
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 storage.backup.com::slave-vol start Starting geo-replication session between slave-vol and master.com::Volume1 been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.8. Creating a Snapshot of Geo-replicated Volume
gluster snapshot create snap1 master snapshot create: failed: geo-replication session is running for the volume master. Session needs to be stopped before taking a snapshot. Snapshot command failed
# gluster snapshot create snap1 master
snapshot create: failed: geo-replication session is running for the volume master. Session needs to be stopped before taking a snapshot.
Snapshot command failed10.9. Example - Setting up Cascading Geo-replication
- Verify that your environment matches the minimum system requirements listed in Section 10.3.3, “Prerequisites”.
- Determine the appropriate deployment scenario. For more information on deployment scenarios, see Section 10.3.1, “Exploring Geo-replication Deployment Scenarios”.
- Configure the environment and create a geo-replication session between master-vol and interimmaster-vol.
- Create a common pem pub file, run the following command on the master node where the key-based SSH authentication connection is configured:
gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create the geo-replication session using the following command. The push-pem option is needed to perform the necessary pem-file setup on the interimmaster nodes.
gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol create push-pem
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol create push-pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of the created session by running the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost::interimmaster-vol status
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost::interimmaster-vol statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”. - Start a Geo-replication session between the hosts:
gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol start
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command will start distributed geo-replication on all the nodes that are part of the master volume. If a node that is part of the master volume is down, the command will still be successful. In a replica pair, the geo-replication session will be active on any of the replica nodes, but remain passive on the others. After executing the command, it may take a few minutes for the session to initialize and become stable. - Verifying the status of geo-replication session by running the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol status
# gluster volume geo-replication master-vol interimhost.com::interimmaster-vol statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a geo-replication session between interimmaster-vol and slave-vol.
- Create a common pem pub file by running the following command on the interimmaster master node where the key-based SSH authentication connection is configured:
gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On interimmaster node, create the geo-replication session using the following command. The push-pem option is needed to perform the necessary pem-file setup on the slave nodes.
gluster volume geo-replication interimmaster-vol slave_host.com::slave-vol create push-pem
# gluster volume geo-replication interimmaster-vol slave_host.com::slave-vol create push-pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of the created session by running the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host::slave-vol status
# gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host::slave-vol statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host::slave-vol config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host::slave-vol config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”. - Start a geo-replication session between interrimaster-vol and slave-vol by running the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host.com::slave-vol start
# gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host.com::slave-vol startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the status of geo-replication session by running the following:
gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host.com::slave-vol status
# gluster volume geo-replication interrimmaster-vol slave_host.com::slave-vol statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.10. Recommended Practices
If you have to change the time on the bricks manually, then the geo-replication session and indexing must be disabled when setting the time on all the bricks. All bricks in a geo-replication environment must be set to the same time, as this avoids the out-of-time sync issue described in Section 10.3.4.1, “Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session”. Bricks not operating on the same time setting, or changing the time while the geo-replication is running, will corrupt the geo-replication index. The recommended way to set the time manually is using the following procedure.
Manually Setting the Time on Bricks in a Geo-replication Environment
- Stop geo-replication between the master and slave, using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop geo-replication indexing, using the following command:
gluster volume set MASTER_VOL geo-replication.indexing off
# gluster volume set MASTER_VOL geo-replication.indexing offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Set a uniform time on all the bricks.
- Restart the geo-replication sessions, using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When the following option is set, it has been observed that there is an increase in geo-replication performance. On the slave volume, run the following command:
gluster volume set SLAVE_VOL batch-fsync-delay-usec 0
# gluster volume set SLAVE_VOL batch-fsync-delay-usec 0For replicating large volumes to a slave in a remote location, it may be useful to do the initial replication to disks locally on a local area network (LAN), and then physically transport the disks to the remote location. This eliminates the need of doing the initial replication of the whole volume over a slower and more expensive wide area network (WAN) connection. The following procedure provides instructions for setting up a local geo-replication session, physically transporting the disks to the remote location, and then setting up geo-replication over a WAN.
Initially Replicating to a Remote Slave Locally using a LAN
- Create a geo-replication session locally within the LAN. For information on creating a geo-replication session, see Section 10.3.4.1, “Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session”.
Important
You must remember the order in which the bricks/disks are specified when creating the slave volume. This information is required later for configuring the remote geo-replication session over the WAN. - Ensure that the initial data on the master is synced to the slave volume. You can verify the status of the synchronization by using the
statuscommand, as shown in Section 10.4.3, “Displaying Geo-replication Status Information”. - Stop and delete the geo-replication session.For information on stopping and deleting the the geo-replication session, see Section 10.4.5, “Stopping a Geo-replication Session” and Section 10.4.6, “Deleting a Geo-replication Session”.
Important
You must ensure that there are no stale files in/var/lib/glusterd/geo-replication/. - Stop and delete the slave volume.For information on stopping and deleting the volume, see Section 11.13, “Stopping Volumes” and Section 11.14, “Deleting Volumes”.
- Remove the disks from the slave nodes, and physically transport them to the remote location. Make sure to remember the order in which the disks were specified in the volume.
- At the remote location, attach the disks and mount them on the slave nodes. Make sure that the file system or logical volume manager is recognized, and that the data is accessible after mounting it.
- Configure a trusted storage pool for the slave using the
peer probecommand.For information on configuring a trusted storage pool, see Chapter 4, Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool. - Delete the glusterFS-related attributes on the bricks. This should be done before creating the volume. You can remove the glusterFS-related attributes by running the following command:
for i in `getfattr -d -m . ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_BRICK 2>/dev/null | grep trusted | awk -F = '{print $1}'`; do setfattr -x $i ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_BRICK; done# for i in `getfattr -d -m . ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_BRICK 2>/dev/null | grep trusted | awk -F = '{print $1}'`; do setfattr -x $i ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_BRICK; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command to ensure that there are noxattrsstill set on the brick:getfattr -d -m . ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_BRICK
# getfattr -d -m . ABSOLUTE_PATH_TO_BRICKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After creating the trusted storage pool, create the Red Hat Gluster Storage volume with the same configuration that it had when it was on the LAN. For information on creating volumes, see Chapter 5, Setting Up Storage Volumes.
Important
Make sure to specify the bricks in same order as they were previously when on the LAN. A mismatch in the specification of the brick order may lead to data loss or corruption. - Start and mount the volume, and check if the data is intact and accessible.For information on starting and mounting volumes, see Section 5.11, “Starting Volumes” and Chapter 6, Creating Access to Volumes.
- Configure the environment and create a geo-replication session from the master to this remote slave.For information on configuring the environment and creating a geo-replication session, see Section 10.3.4.1, “Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session”.
- Start the geo-replication session between the master and the remote slave.For information on starting the geo-replication session, see Section 10.4, “Starting Geo-replication”.
- Use the
statuscommand to verify the status of the session, and check if all the nodes in the session are stable.For information on thestatus, see Section 10.4.3, “Displaying Geo-replication Status Information”.
10.11. Troubleshooting Geo-replication
10.11.1. Tuning Geo-replication performance with Change Log
rollover-time option sets the rate at which the change log is consumed. The default rollover time is 15 seconds, but it can be configured to a faster rate. A recommended rollover-time for geo-replication is 10-15 seconds. To change the rollover-time option, use following the command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME rollover-time 15
# gluster volume set VOLNAME rollover-time 15fsync-interval option determines the frequency that updates to the change log are written to disk. The default interval is 5, which means that updates to the change log are written synchronously as they occur, and this may negatively impact performance in a geo-replication environment. Configuring fsync-interval to a non-zero value will write updates to disk asynchronously at the specified interval. To change the fsync-interval option, use following the command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME fsync-interval 5
# gluster volume set VOLNAME fsync-interval 510.11.2. Triggering Explicit Sync on Entries
glusterfs.geo-rep.trigger-sync is provided to accomplish the same.
setfattr -n glusterfs.geo-rep.trigger-sync -v "1" <file-path>
# setfattr -n glusterfs.geo-rep.trigger-sync -v "1" <file-path>10.11.3. Synchronization Is Not Complete
The geo-replication status is displayed as Stable, but the data has not been completely synchronized.
A full synchronization of the data can be performed by erasing the index and restarting geo-replication. After restarting geo-replication, it will begin a synchronization of the data using checksums. This may be a long and resource intensive process on large data sets. If the issue persists, contact Red Hat Support.
10.11.4. Issues with File Synchronization
The geo-replication status is displayed as Stable, but only directories and symlinks are synchronized. Error messages similar to the following are in the logs:
[2011-05-02 13:42:13.467644] E [master:288:regjob] GMaster: failed to sync ./some_file`
[2011-05-02 13:42:13.467644] E [master:288:regjob] GMaster: failed to sync ./some_file`
Geo-replication requires rsync v3.0.0 or higher on the host and the remote machines. Verify if you have installed the required version of rsync.
10.11.5. Geo-replication Status is Often Faulty
The geo-replication status is often displayed as Faulty, with a backtrace similar to the following:
012-09-28 14:06:18.378859] E [syncdutils:131:log_raise_exception] <top>: FAIL: Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/python/syncdaemon/syncdutils.py", line 152, in twraptf(*aa) File "/usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/python/syncdaemon/repce.py", line 118, in listen rid, exc, res = recv(self.inf) File "/usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/python/syncdaemon/repce.py", line 42, in recv return pickle.load(inf) EOFError
012-09-28 14:06:18.378859] E [syncdutils:131:log_raise_exception] <top>: FAIL: Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/python/syncdaemon/syncdutils.py", line 152, in twraptf(*aa) File "/usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/python/syncdaemon/repce.py", line 118, in listen rid, exc, res = recv(self.inf) File "/usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/python/syncdaemon/repce.py", line 42, in recv return pickle.load(inf) EOFErrorThis usually indicates that RPC communication between the master gsyncd module and slave gsyncd module is broken. Make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
- Key-based SSH authentication is set up properly between the host and remote machines.
- FUSE is installed on the machines. The geo-replication module mounts Red Hat Gluster Storage volumes using FUSE to sync data.
10.11.6. Intermediate Master is in a Faulty State
In a cascading environment, the intermediate master is in a faulty state, and messages similar to the following are in the log:
raise RuntimeError ("aborting on uuid change from %s to %s" % \ RuntimeError: aborting on uuid change from af07e07c-427f-4586-ab9f- 4bf7d299be81 to de6b5040-8f4e-4575-8831-c4f55bd41154
raise RuntimeError ("aborting on uuid change from %s to %s" % \ RuntimeError: aborting on uuid change from af07e07c-427f-4586-ab9f- 4bf7d299be81 to de6b5040-8f4e-4575-8831-c4f55bd41154
In a cascading configuration, an intermediate master is loyal to its original primary master. The above log message indicates that the geo-replication module has detected that the primary master has changed. If this change was deliberate, delete the volume-id configuration option in the session that was initiated from the intermediate master.
10.11.7. Remote gsyncd Not Found
The master is in a faulty state, and messages similar to the following are in the log:
[2012-04-04 03:41:40.324496] E [resource:169:errfail] Popen: ssh> bash: /usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/gsyncd: No such file or directory
[2012-04-04 03:41:40.324496] E [resource:169:errfail] Popen: ssh> bash: /usr/local/libexec/glusterfs/gsyncd: No such file or directoryThe steps to configure a SSH connection for geo-replication have been updated. Use the steps as described in Section 10.3.4.1, “Setting Up your Environment for Geo-replication Session”
Chapter 11. Managing Red Hat Gluster Storage Volumes
11.1. Configuring Volume Options
Note
gluster volume info VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAMEgluster volume set VOLNAME OPTION PARAMETER
# gluster volume set VOLNAME OPTION PARAMETERtest-volume:
gluster volume set test-volume performance.cache-size 256MB Set volume successful
# gluster volume set test-volume performance.cache-size 256MB
Set volume successful11.2. Setting Multiple Volume Option
Creating a group configuration file
- Create a new file in the
/var/lib/glusterd/groups/directory.touch /var/lib/glusterd/groups/filename
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/groups/filenameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the parameters and values that you want to set on the volume to the created file as key-value pairs, placing each parameter on a new line:
domain1.key1=value1 domain1.key2=value2 domain2.key3=value3
domain1.key1=value1 domain1.key2=value2 domain2.key3=value3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,changelog.changelog=on client.event-threads=6 cluster.brick-multiplex=on
changelog.changelog=on client.event-threads=6 cluster.brick-multiplex=onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Adding configurations to volumes
gluster volume set volname group filename
# gluster volume set volname group filenamegluster volume set volume1 group virt gluster volume set volume2 group virt gluster volume set volume3 group dbgroup
# gluster volume set volume1 group virt
# gluster volume set volume2 group virt
# gluster volume set volume3 group dbgroupNote
11.3. Supported Volume Options
Important
| Option | Value Description | Allowed Values | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| auth.allow | IP addresses or hostnames of the clients which are allowed to access the volume. | Valid hostnames or IP addresses, which includes wild card patterns including *. For example, 192.168.1.*. A list of comma separated addresses is acceptable, but a single hostname must not exceed 256 characters. | * (allow all) |
| auth.reject | IP addresses or hostnames of FUSE clients that are denied access to a volume. For NFS access control, use nfs.rpc-auth-* options instead. | Valid hostnames or IP addresses, which includes wild card patterns including *. For example, 192.168.1.*. A list of comma separated addresses is acceptable, but a single hostname must not exceed 256 characters. | none (reject none) |
| changelog | Enables the changelog translator to record all the file operations. | on | off | off |
| client.event-threads | Specifies the number of network connections to be handled simultaneously by the client processes accessing a Red Hat Gluster Storage node. | 1 - 32 | 2 |
| cluster.background-self-heal-count | The maximum number of heal operations that can occur simultaneously. Requests in excess of this number are stored in a queue whose length is defined by cluster.heal-wait-queue-leng. | 0–256 | 8 |
| cluster.brick-multiplex |
Available as of Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.3 and later. Controls whether to use brick multiplexing on all volumes. Red Hat recommends restarting volumes after enabling or disabling brick multiplexing. When set to
off (the default), each brick has its own process and uses its own port. When set to on, bricks that are compatible with each other use the same process and the same port. This reduces per-brick memory usage and port consumption.
Brick compatibility is determined at volume start, and depends on volume options shared between bricks. When multiplexing is enabled, restart volumes whenever volume configuration is changed in order to maintain the compatibility of the bricks grouped under a single process.
| on | off | off |
| cluster.consistent-metadata |
If set to
on, the readdirp function in Automatic File Replication feature will always fetch metadata from their respective read children as long as it holds the good copy (the copy that does not need healing) of the file/directory. However, this could cause a reduction in performance where readdirps are involved.
This option requires that the volume is remounted on the client to take effect.
| on | off | off |
| cluster.granular-entry-heal |
If set to enable, stores more granular information about the entries which were created or deleted from a directory while a brick in a replica was down. This helps in faster self-heal of directories, especially in use cases where directories with large number of entries are modified by creating or deleting entries. If set to disable, it only stores that the directory needs heal without information about what entries within the directories need to be healed, and thereby requires entire directory crawl to identify the changes.
| enable | disable | disable |
| Important
Execute the gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.granular-entry-heal [enable | disable] command only if the volume is in Created state. If the volume is in any other state other than Created, for example, Started, Stopped, and so on, execute gluster volume heal VOLNAME granular-entry-heal [enable | disable] command to enable or disable granular-entry-heal option.
| |||
| cluster.heal-wait-queue-leng | The maximum number of requests for heal operations that can be queued when heal operations equal to cluster.background-self-heal-count are already in progress. If more heal requests are made when this queue is full, those heal requests are ignored. | 0-10000 | 128 |
| cluster.lookup-optimize |
If this option is set to
on, when a hashed sub-volume does not return a lookup result, negative lookups are optimized by not continuing to look on non-hashed subvolumes.
For existing volumes, any directories created after the upgrade will have lookup-optimize behavior enabled. Rebalance operation has to be performed on all existing directories before they can use the lookup optimization.
For new volumes, the lookup-optimize behavior is enabled by default, except for the root of the volume. Run a rebalance operation in order to enable lookup-optimize for the root of the volume.
| on|off | on (in version 3.4 onward) |
| cluster.max-bricks-per-process |
The maximum number of bricks that can run on a single instance of glusterfsd process.
As of Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 Batch 2 Update, the default value of this option is set to
250. This provides better control of resource usage for container-based workloads. In earlier versions, the default value was 0, which used a single process for all bricks on the node.
Updating the value of this option does not affect currently running bricks. Restart the volume to change this setting for existing bricks.
| 0 to system maximum (any positive integer greater than 1) | 250 |
| cluster.min-free-disk | Specifies the percentage of disk space that must be kept free. This may be useful for non-uniform bricks. | Percentage of required minimum free disk space. | 10% |
| cluster.op-version | Allows you to set the operating version of the cluster. The op-version number cannot be downgraded and is set for all volumes in the cluster. The op-version is not listed as part of gluster volume info command output. | 30708 | 30712 | 31001 | 31101 | 31302 | 31303 | 31304 | 31305 | 31306 | Default value depends on Red Hat Gluster Storage version first installed. For Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4.4 async Update the value is set to 31306 for a new deployment. |
| cluster.read-freq-threshold | Specifies the number of reads, in a promotion/demotion cycle, that would mark a file HOT for promotion. Any file that has read hits less than this value will be considered as COLD and will be demoted. | 0-20 | 0 |
| cluster.self-heal-daemon | Specifies whether proactive self-healing on replicated volumes is activated. | on | off | on |
| cluster.data-self-heal | Specifies whether proactive data self-healing on replicated volumes is activated. | on | off | on |
| cluster.entry-self-heal | Specifies whether proactive self-healing of the contents of a directory on replicated volumes is activated. | on | off | on |
| cluster.metadata-self-heal | Specifies whether proactive metadata self-healing on replicated volumes is activated. | on | off | on |
| Important
By default, cluster.data-self-heal, cluster.entry-self-heal, and cluster.metadata-self-heal options are turned on. These options are for client-side, that is, mounts, healing of files. These will not affect the self-heal daemon. As a file is accessed healing gets triggered on it without waiting for the Self-heal-daemon to select and heal the file. This maximizes the client-side I/O throughput. It is recommended to turn these options off, with the help of Red Hat support, in the case of severe CPU or memory consumption. When turned off, self-heal is not triggered when the client accesses the file and the entire network bandwidth is available for I/O from the clients (client-side healing and accessing files pending heal consumed some). The self-heal daemon will still heal the file during its crawl.
| |||
| cluster.server-quorum-ratio | Sets the quorum percentage for the trusted storage pool. | 0 - 100 | >50% |
| cluster.server-quorum-type | If set to server, this option enables the specified volume to participate in the server-side quorum. For more information on configuring the server-side quorum, see Section 11.15.1.1, “Configuring Server-Side Quorum” | none | server | none |
| cluster.shd-max-threads | Specifies the number of entries that can be self healed in parallel on each replica by self-heal daemon. | 1 - 64 | 1 |
| cluster.shd-max-threads | Specifies the number of entries that can be self healed in parallel on each replica by self-heal daemon. | 1 - 64 | 1 |
| cluster.shd-wait-qlength | Specifies the number of entries that must be kept in the queue for self-heal daemon threads to take up as soon as any of the threads are free to heal. This value should be changed based on how much memory self-heal daemon process can use for keeping the next set of entries that need to be healed. | 1 - 655536 | 1024 |
| cluster.shd-wait-qlength | Specifies the number of entries that must be kept in the dispersed subvolume's queue for self-heal daemon threads to take up as soon as any of the threads are free to heal. This value should be changed based on how much memory self-heal daemon process can use for keeping the next set of entries that need to be healed. | 1 - 655536 | 1024 |
| cluster.tier-demote-frequency | Specifies how frequently the tier daemon must check for files to demote. | 1 - 172800 seconds | 3600 seconds |
| cluster.tier-max-files | Specifies the maximum number of files that may be migrated in any direction from each node in a given cycle. | 1-100000 files | 10000 |
| cluster.tier-max-mb | Specifies the maximum number of MB that may be migrated in any direction from each node in a given cycle. | 1 -100000 (100 GB) | 4000 MB |
| cluster.tier-mode | If set to cache mode, promotes or demotes files based on whether the cache is full or not, as specified with watermarks. If set to test mode, periodically demotes or promotes files automatically based on access. | test | cache | cache |
| cluster.tier-promote-frequency | Specifies how frequently the tier daemon must check for files to promote. | 1- 172800 seconds | 120 seconds |
| cluster.use-compound-fops | When enabled, write transactions that occur as part of Automatic File Replication are modified so that network round trips are reduced, improving performance. | on | off | off |
| cluster.watermark-hi | Upper percentage watermark for promotion. If hot tier fills above this percentage, no promotion will happen and demotion will happen with high probability. | 1- 99 % | 90% |
| cluster.watermark-low | Lower percentage watermark. If hot tier is less full than this, promotion will happen and demotion will not happen. If greater than this, promotion/demotion will happen at a probability relative to how full the hot tier is. | 1- 99 % | 75% |
| cluster.write-freq-threshold | Specifies the number of writes, in a promotion/demotion cycle, that would mark a file HOT for promotion. Any file that has write hits less than this value will be considered as COLD and will be demoted. | 0-20 | 0 |
| config.transport | Specifies the type of transport(s) volume would support communicating over. | tcp OR rdma OR tcp,rdma | tcp |
| diagnostics.brick-log-buf-size | The maximum number of unique log messages that can be suppressed until the timeout or buffer overflow, whichever occurs first on the bricks. | 0 and 20 (0 and 20 included) | 5 |
| diagnostics.brick-log-flush-timeout | The length of time for which the log messages are buffered, before being flushed to the logging infrastructure (gluster or syslog files) on the bricks. | 30 - 300 seconds (30 and 300 included) | 120 seconds |
| diagnostics.brick-log-format | Allows you to configure the log format to log either with a message id or without one on the brick. | no-msg-id | with-msg-id | with-msg-id |
| diagnostics.brick-log-level | Changes the log-level of the bricks. | INFO | DEBUG | WARNING | ERROR | CRITICAL | NONE | TRACE | info |
| diagnostics.brick-sys-log-level | Depending on the value defined for this option, log messages at and above the defined level are generated in the syslog and the brick log files. | INFO | WARNING | ERROR | CRITICAL | CRITICAL |
| diagnostics.client-log-buf-size | The maximum number of unique log messages that can be suppressed until the timeout or buffer overflow, whichever occurs first on the clients. | 0 and 20 (0 and 20 included) | 5 |
| diagnostics.client-log-flush-timeout | The length of time for which the log messages are buffered, before being flushed to the logging infrastructure (gluster or syslog files) on the clients. | 30 - 300 seconds (30 and 300 included) | 120 seconds |
| diagnostics.client-log-format | Allows you to configure the log format to log either with a message ID or without one on the client. | no-msg-id | with-msg-id | with-msg-id |
| diagnostics.client-log-level | Changes the log-level of the clients. | INFO | DEBUG | WARNING | ERROR | CRITICAL | NONE | TRACE | info |
| diagnostics.client-sys-log-level | Depending on the value defined for this option, log messages at and above the defined level are generated in the syslog and the client log files. | INFO | WARNING | ERROR | CRITICAL | CRITICAL |
| disperse.eager-lock | Before a file operation starts, a lock is placed on the file. The lock remains in place until the file operation is complete. After the file operation completes, if eager-lock is on, the lock remains in place either until lock contention is detected, or for 1 second in order to check if there is another request for that file from the same client. If eager-lock is off, locks release immediately after file operations complete, improving performance for some operations, but reducing access efficiency. | on | off | on |
| disperse.other-eager-lock | This option is equivalent to the disperse.eager-lock option but applicable only for non regular files. When multiple clients access a particular directory, disabling disperse.other-eager-lockoption for the volume can improve performance for directory access without compromising performance of I/O's for regular files. | on | off | off |
| disperse.shd-max-threads | Specifies the number of entries that can be self healed in parallel on each disperse subvolume by self-heal daemon. | 1 - 64 | 1 |
| disperse.shd-wait-qlength | Specifies the number of entries that must be kept in the dispersed subvolume's queue for self-heal daemon threads to take up as soon as any of the threads are free to heal. This value should be changed based on how much memory self-heal daemon process can use for keeping the next set of entries that need to be healed. | 1 - 655536 | 1024 |
| features.ctr_link_consistency | Enables a crash consistent way of recording hardlink updates by Change Time Recorder translator. When recording in a crash consistent way the data operations will experience more latency. | on | off | off |
| features.ctr-enabled | Enables Change Time Recorder (CTR) translator for a tiered volume. This option is used in conjunction with features.record-counters option to enable recording write and read heat counters. | on | off | on |
| features.quota-deem-statfs | When this option is set to on, it takes the quota limits into consideration while estimating the filesystem size. The limit will be treated as the total size instead of the actual size of filesystem. | on | off | on |
| features.read-only | Specifies whether to mount the entire volume as read-only for all the clients accessing it. | on | off | off |
| features.record-counters | If set to enabled, cluster.write-freq-thresholdand cluster.read-freq-thresholdoptions defines the number of writes and reads to a given file that are needed before triggering migration. | on | off | on |
| features.shard | Enables or disables sharding on the volume. Affects files created after volume configuration. | enable | disable | disable |
| features.shard-block-size | Specifies the maximum size of file pieces when sharding is enabled. Affects files created after volume configuration. | 512MB | 512MB |
| geo-replication.indexing | Enables the marker translator to track the changes in the volume. | on | off | off |
| network.ping-timeout | The time the client waits for a response from the server. If a timeout occurs, all resources held by the server on behalf of the client are cleaned up. When the connection is reestablished, all resources need to be reacquired before the client can resume operations on the server. Additionally, locks are acquired and the lock tables are updated. A reconnect is a very expensive operation and must be avoided. | 42 seconds | 42 seconds |
| nfs.acl | Disabling nfs.acl will remove support for the NFSACL sideband protocol. This is enabled by default. | enable | disable | enable |
| nfs.addr-namelookup | Specifies whether to lookup names for incoming client connections. In some configurations, the name server can take too long to reply to DNS queries, resulting in timeouts of mount requests. This option can be used to disable name lookups during address authentication. Note that disabling name lookups will prevent you from using hostnames in nfs.rpc-auth-*options. | on | off | off |
| nfs.disable | Specifies whether to disable NFS exports of individual volumes. | on | off | off |
| nfs.enable-ino32 | For nfs clients or applciatons that do not support 64-bit inode numbers, use this option to make NFS return 32-bit inode numbers instead. Disabled by default, so NFS returns 64-bit inode numbers. This value is global and applies to all the volumes in the trusted storage pool. | enable | disable | disable |
| nfs.export-volumes | Enables or disables exporting entire volumes. If this option is disabled and the nfs.export-diroption is enabled, you can set subdirectories as the only exports. | on | off | on |
| nfs.mount-rmtab | Path to the cache file that contains a list of NFS-clients and the volumes they have mounted. Change the location of this file to a mounted (with glusterfs-fuse, on all storage servers) volume to gain a trusted pool wide view of all NFS-clients that use the volumes. The contents of this file provide the information that can get obtained with the showmount command. | Path to a directory | /var/lib/glusterd/nfs/rmtab |
| nfs.mount-udp | Enable UDP transport for the MOUNT sideband protocol. By default, UDP is not enabled, and MOUNT can only be used over TCP. Some NFS-clients (certain Solaris, HP-UX and others) do not support MOUNT over TCP and enabling nfs.mount-udpmakes it possible to use NFS exports provided by Red Hat Gluster Storage. | disable | enable | disable |
| nfs.nlm | By default, the Network Lock Manager (NLMv4) is enabled. Use this option to disable NLM. Red Hat does not recommend disabling this option. | on|off | on |
| nfs.port | Associates glusterFS NFS with a non-default port. | 1025-65535 | 38465- 38467 |
| nfs.ports-insecure | Allows client connections from unprivileged ports. By default only privileged ports are allowed. This is a global setting for allowing insecure ports for all exports using a single option. | on | off | off |
| nfs.rdirplus | The default value is on. When this option is turned off, NFS falls back to standard readdir instead of readdirp. Turning this off would result in more lookup and stat requests being sent from the client which may impact performance. | on|off | on |
| nfs.rpc-auth-allow IP_ADRESSES | A comma separated list of IP addresses allowed to connect to the server. By default, all clients are allowed. | Comma separated list of IP addresses | accept all |
| nfs.rpc-auth-reject IP_ADRESSES | A comma separated list of addresses not allowed to connect to the server. By default, all connections are allowed. | Comma separated list of IP addresses | reject none |
| nfs.server-aux-gids | When enabled, the NFS-server will resolve the groups of the user accessing the volume. NFSv3 is restricted by the RPC protocol (AUTH_UNIX/AUTH_SYS header) to 16 groups. By resolving the groups on the NFS-server, this limits can get by-passed. | on|off | off |
| nfs.transport-type | Specifies the transport used by GlusterFS NFS server to communicate with bricks. | tcp OR rdma | tcp |
| open-behind | It improves the application's ability to read data from a file by sending success notifications to the application whenever it receives an open call. | on | off | on |
| performance.cache-max-file-size | Sets the maximum file size cached by the io-cache translator. Can be specified using the normal size descriptors of KB, MB, GB, TB, or PB (for example, 6 GB). | Size in bytes, or specified using size descriptors. | 2 ^ 64-1 bytes |
| performance.cache-min-file-size | Sets the minimum file size cached by the io-cache translator. Can be specified using the normal size descriptors of KB, MB, GB, TB, or PB (for example, 6 GB). | Size in bytes, or specified using size descriptors. | 0 |
| performance.cache-refresh-timeout | The number of seconds cached data for a file will be retained. After this timeout, data re-validation will be performed. | 0 - 61 seconds | 1 second |
| performance.cache-size | Size of the read cache. | Size in bytes, or specified using size descriptors. | 32 MB |
| performance.client-io-threads | Improves performance for parallel I/O from a single mount point for dispersed (erasure-coded) volumes by allowing up to 16 threads to be used in parallel. When enabled, 1 thread is used by default, and further threads up to the maximum of 16 are created as required by client workload. This is useful for dispersed and distributed dispersed volumes. This feature is not recommended for distributed, replicated or distributed-replicated volumes. It is disabled by default on replicated and distributed-replicated volume types. | on | off | on, except for replicated and distributed-replicated volumes |
| performance.flush-behind | Specifies whether the write-behind translator performs flush operations in the background by returning (false) success to the application before flush file operations are sent to the backend file system. | on | off | on |
| performance.io-thread-count | The number of threads in the I/O threads translator. | 0 - 65 | 16 |
| performance.lazy-open | This option requires open-behind to be on. Perform an open in the backend only when a necessary FOP arrives (for example, write on the file descriptor, unlink of the file). When this option is disabled, perform backend open immediately after an unwinding open. | Yes/No | Yes |
| performance.md-cache-timeout | The time period in seconds which controls when metadata cache has to be refreshed. If the age of cache is greater than this time-period, it is refreshed. Every time cache is refreshed, its age is reset to 0. | 0-600 seconds | 1 second |
| performance.nfs-strict-write-ordering | Specifies whether to prevent later writes from overtaking earlier writes for NFS, even if the writes do not relate to the same files or locations. | on | off | off |
| performance.nfs.flush-behind | Specifies whether the write-behind translator performs flush operations in the background for NFS by returning (false) success to the application before flush file operations are sent to the backend file system. | on | off | on |
| performance.nfs.strict-o-direct | Specifies whether to attempt to minimize the cache effects of I/O for a file on NFS. When this option is enabled and a file descriptor is opened using the O_DIRECT flag, write-back caching is disabled for writes that affect that file descriptor. When this option is disabled, O_DIRECT has no effect on caching. This option is ignored if performance.write-behind is disabled. | on | off | off |
| performance.nfs.write-behind-trickling-writes | Enables and disables trickling-write strategy for the write-behind translator for NFS clients. | on | off | on |
| performance.nfs.write-behind-window-size | Specifies the size of the write-behind buffer for a single file or inode for NFS. | 512 KB - 1 GB | 1 MB |
| performance.quick-read | To enable/disable quick-read translator in the volume. | on | off | on |
| performance.rda-cache-limit | The value specified for this option is the maximum size of cache consumed by the readdir-ahead translator. This value is global and the total memory consumption by readdir-ahead is capped by this value, irrespective of the number/size of directories cached. | 0-1GB | 10MB |
| performance.rda-request-size | The value specified for this option will be the size of buffer holding directory entries in readdirp response. | 4KB-128KB | 128KB |
| performance.resync-failed-syncs-after-fsync | If syncing cached writes that were issued before an fsync operation fails, this option configures whether to reattempt the failed sync operations. | on | off | off |
| performance.strict-o-direct | Specifies whether to attempt to minimize the cache effects of I/O for a file. When this option is enabled and a file descriptor is opened using the O_DIRECT flag, write-back caching is disabled for writes that affect that file descriptor. When this option is disabled, O_DIRECT has no effect on caching. This option is ignored if performance.write-behind is disabled. | on | off | off |
| performance.strict-write-ordering | Specifies whether to prevent later writes from overtaking earlier writes, even if the writes do not relate to the same files or locations. | on | off | off |
| performance.use-anonymous-fd | This option requires open-behind to be on. For read operations, use anonymous file descriptor when the original file descriptor is open-behind and not yet opened in the backend. | Yes | No | Yes |
| performance.write-behind | Enables and disables write-behind translator. | on | off | on |
| performance.write-behind-trickling-writes | Enables and disables trickling-write strategy for the write-behind translator for FUSE clients. | on | off | on |
| performance.write-behind-window-size | Specifies the size of the write-behind buffer for a single file or inode. | 512 KB - 1 GB | 1 MB |
| rebal-throttle | Rebalance process is made multithreaded to handle multiple files migration for enhancing the performance. During multiple file migration, there can be a severe impact on storage system performance. The throttling mechanism is provided to manage it. | lazy, normal, aggressive | normal |
| server.allow-insecure | Allows FUSE-based client connections from unprivileged ports. By default, this is enabled, meaning that ports can accept and reject messages from insecure ports. When disabled, only privileged ports are allowed. This is a global setting for allowing insecure ports to be enabled for all FUSE-based exports using a single option. Use nfs.rpc-auth-* options for NFS access control. | on | off | on |
| server.anongid | Value of the GID used for the anonymous user when root-squash is enabled. When root-squash is enabled, all the requests received from the root GID (that is 0) are changed to have the GID of the anonymous user. | 0 - 4294967295 | 65534 (this UID is also known as nfsnobody) |
| server.anonuid | Value of the UID used for the anonymous user when root-squash is enabled. When root-squash is enabled, all the requests received from the root UID (that is 0) are changed to have the UID of the anonymous user. | 0 - 4294967295 | 65534 (this UID is also known as nfsnobody) |
| server.event-threads | Specifies the number of network connections to be handled simultaneously by the server processes hosting a Red Hat Gluster Storage node. | 1 - 32 | 1 |
| server.gid-timeout | The time period in seconds which controls when cached groups has to expire. This is the cache that contains the groups (GIDs) where a specified user (UID) belongs to. This option is used only when server.manage-gids is enabled. | 0-4294967295 seconds | 2 seconds |
| server.manage-gids | Resolve groups on the server-side. By enabling this option, the groups (GIDs) a user (UID) belongs to gets resolved on the server, instead of using the groups that were send in the RPC Call by the client. This option makes it possible to apply permission checks for users that belong to bigger group lists than the protocol supports (approximately 93). | on|off | off |
| server.root-squash | Prevents root users from having root privileges, and instead assigns them the privileges of nfsnobody. This squashes the power of the root users, preventing unauthorized modification of files on the Red Hat Gluster Storage servers. This option is used only for glusterFS NFS protocol. | on | off | off |
| server.statedump-path | Specifies the directory in which the statedumpfiles must be stored. | /var/run/gluster (for a default installation) | Path to a directory |
| storage.fips-mode-rchecksum | If enabled, posix_rchecksum uses the FIPS compliant SHA256 checksum, else it uses MD5. | on | off | off |
| Important
Do not enable fips-mode-rchecksum on volumes with clients that use Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 or earlier.
| |||
| storage.create-mask | Maximum set (upper limit) of permission for the files that will be created. | 0000 - 0777 | 0777 |
| storage. create-directory-mask | Maximum set (upper limit) of permission for the directories that will be created. | 0000 - 0777 | 0777 |
| storage.force-create-mode | Minimum set (lower limit) of permission for the files that will be created. | 0000 - 0777 | 0000 |
| storage.force-create-directory | Minimum set (lower limit) of permission for the directories that will be created. | 0000 - 0777 | 0000 |
| Important
Behavior is undefined in terms of calculated file access mode when both a mask and a matching forced mode are set simultaneously, create-directory-mask and force-directory-mode or create-mask and force-create-mode.
| |||
| storage.health-check-interval | Sets the time interval in seconds for a filesystem health check. You can set it to 0 to disable. The POSIX translator on the bricks performs a periodic health check. If this check fails, the file system exported by the brick is not usable anymore and the brick process (glusterfsd) logs a warning and exits. | 0-4294967295 seconds | 30 seconds |
| storage.owner-gid | Sets the GID for the bricks of the volume. This option may be required when some of the applications need the brick to have a specific GID to function correctly. Example: For QEMU integration the UID/GID must be qemu:qemu, that is, 107:107 (107 is the UID and GID of qemu). | Any integer greater than or equal to -1. | The GID of the bricks are not changed. This is denoted by -1. |
| storage.owner-uid | Sets the UID for the bricks of the volume. This option may be required when some of the applications need the brick to have a specific UID to function correctly. Example: For QEMU integration the UID/GID must be qemu:qemu, that is, 107:107 (107 is the UID and GID of qemu). | Any integer greater than or equal to -1. | The UID of the bricks are not changed. This is denoted by -1. |
| storage.reserve | As of Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.5, the POSIX translator includes an option storage.reserve to reserve storage space at the brick. This option accepts size in form of MB and also in form of percentage. If user has configured the storage.reserve option using size in MB earlier, and then wants to give the size in percentage, it can be done using the same option. Also, the newest set value is considered, if it was in MB before and then if it sent in percentage, the percentage value becomes new value and the older one is over-written | 0-100 | 1 (1% of the brick size) |
| transport.listen-backlog | The maximum number of established TCP socket requests queued and waiting to be accepted at any one time. | 0 to system maximum | 1024 |
11.4. Configuring a volume to be mounted read-only
gluster volume set volname read-only enable
# gluster volume set volname read-only enable11.5. Configuring Transport Types for a Volume
- Unmount the volume on all the clients using the following command:
umount mount-point
# umount mount-pointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the volumes using the following command:
gluster volume stop volname
# gluster volume stop volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change the transport type. For example, to enable both tcp and rdma execute the followimg command:
gluster volume set volname config.transport tcp,rdma OR tcp OR rdma
# gluster volume set volname config.transport tcp,rdma OR tcp OR rdmaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Mount the volume on all the clients. For example, to mount using rdma transport, use the following command:
mount -t glusterfs -o transport=rdma server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs -o transport=rdma server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.6. Reserving Storage on a Volume
gluster volume set volname storage.reserve percentage
# gluster volume set volname storage.reserve percentagestorage.reserve option takes a percentage value. The default value for the option is 1(1% of the brick size). If set to 0 this option is disabled.
Note
11.7. Expanding Volumes
Warning
Important
Expanding a Volume
- From any server in the trusted storage pool, use the following command to probe the server on which you want to add a new brick:
gluster peer probe HOSTNAME
# gluster peer probe HOSTNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster peer probe server5 Probe successful gluster peer probe server6 Probe successful
# gluster peer probe server5 Probe successful # gluster peer probe server6 Probe successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the bricks using the following command:
gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEW_BRICK
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEW_BRICKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume add-brick test-volume server5:/rhgs/brick5/ server6:/rhgs/brick6/ Add Brick successful
# gluster volume add-brick test-volume server5:/rhgs/brick5/ server6:/rhgs/brick6/ Add Brick successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check the volume information using the following command:
gluster volume info
# gluster volume infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command output displays information similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Rebalance the volume to ensure that files will be distributed to the new brick. Use the rebalance command as described in Section 11.11, “Rebalancing Volumes”.The
add-brickcommand should be followed by arebalanceoperation to ensure better utilization of the added bricks.
11.7.1. Expanding a Tiered Volume
11.7.1.1. Expanding a Cold Tier Volume
- Detach the tier by performing the steps listed in Section 16.7, “Detaching a Tier from a Volume”
- From any server in the trusted storage pool, use the following command to probe the server on which you want to add a new brick :
gluster peer probe HOSTNAME
# gluster peer probe HOSTNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster peer probe server5 Probe successful gluster peer probe server6 Probe successful
# gluster peer probe server5 Probe successful # gluster peer probe server6 Probe successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the bricks using the following command:
gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEW_BRICK
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEW_BRICKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume add-brick test-volume server5:/rhgs/brick5/ server6:/rhgs/brick6/
# gluster volume add-brick test-volume server5:/rhgs/brick5/ server6:/rhgs/brick6/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Rebalance the volume to ensure that files will be distributed to the new brick. Use the rebalance command as described in Section 11.11, “Rebalancing Volumes”.The
add-brickcommand should be followed by arebalanceoperation to ensure better utilization of the added bricks. - Reattach the tier to the volume with both old and new (expanded) bricks:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME attach [replica COUNT] NEW-BRICK...Important
When you reattach a tier, an internal process called fix-layout commences internally to prepare the hot tier for use. This process takes time and there will a delay in starting the tiering activities.If you are reusing the brick, be sure to clearly wipe the existing data before attaching it to the tiered volume.
11.7.1.2. Expanding a Hot Tier Volume
- Detach the tier by performing the steps listed in Section 16.7, “Detaching a Tier from a Volume”
- Reattach the tier to the volume with both old and new (expanded) bricks:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME attach [replica COUNT] NEW-BRICK...For example,gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/tier5 server2:/rhgs/tier6 server1:/rhgs/tier7 server2:/rhgs/tier8
# gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/tier5 server2:/rhgs/tier6 server1:/rhgs/tier7 server2:/rhgs/tier8Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
When you reattach a tier, an internal process called fix-layout commences internally to prepare the hot tier for use. This process takes time and there will a delay in starting the tiering activities.If you are reusing the brick, be sure to clearly wipe the existing data before attaching it to the tiered volume.
11.7.2. Expanding a Dispersed or Distributed-dispersed Volume
Note
Dispersed volume, it will be converted to a Distributed-Dispersed volume, and the existing dispersed volume will be treated as dispersed subvolume.
- From any server in the trusted storage pool, use the following command to probe the server on which you want to add new bricks:
gluster peer probe HOSTNAME
# gluster peer probe HOSTNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the bricks using the following command:
gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEW_BRICK
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEW_BRICKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume add-brick test-volume server4:/rhgs/brick7 server4:/rhgs/brick8 server5:/rhgs/brick9 server5:/rhgs/brick10 server6:/rhgs/brick11 server6:/rhgs/brick12
# gluster volume add-brick test-volume server4:/rhgs/brick7 server4:/rhgs/brick8 server5:/rhgs/brick9 server5:/rhgs/brick10 server6:/rhgs/brick11 server6:/rhgs/brick12Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - (Optional) View the volume information after adding the bricks:
gluster volume info VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Rebalance the volume to ensure that the files will be distributed to the new brick. Use the rebalance command as described in Section 11.11, “Rebalancing Volumes”.The
add-brickcommand should be followed by arebalanceoperation to ensure better utilization of the added bricks.
11.7.3. Expanding Underlying Logical Volume
lvextend command.
Warning
gluster volume status kill -9 brick-process-id
# gluster volume status
# kill -9 brick-process-id- Stop all volumes using the brick with the following command:
gluster volume stop VOLNAME
# gluster volume stop VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check if new disk is visible using
lsblkcommand:lsblk
# lsblkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create new physical volume using following command:
pvcreate /dev/PHYSICAL_VOLUME_NAME
# pvcreate /dev/PHYSICAL_VOLUME_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Use the following command to verify if the physical volume is created:
pvs
# pvsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Extend the existing volume group:
vgextend VOLUME_GROUP_NAME /dev/PHYSICAL_VOLUME_NAME
# vgextend VOLUME_GROUP_NAME /dev/PHYSICAL_VOLUME_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Use the following commands to check the size of volume group, and verify if it reflects the new addition:
vgscan
# vgscanCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure the volume group created has enough space to extend the logical volume:
vgdisplay VOLUME_GROUP_NAME
vgdisplay VOLUME_GROUP_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Retrieve the file system name using the following command:df -h
# df -hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Extend the logical volume using the following command:
lvextend -L+nG /dev/mapper/ LOGICAL_VOLUME_NAME-VOLUME_GROUP_NAME
# lvextend -L+nG /dev/mapper/ LOGICAL_VOLUME_NAME-VOLUME_GROUP_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In case of thin pool, extend the pool using the following command:lvextend -L+nG VOLUME_GROUP_NAME/POOL_NAME
# lvextend -L+nG VOLUME_GROUP_NAME/POOL_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above commands, n is the additional size in GB to be extended.Execute the#lvdisplaycommand to fetch the pool name.Use the following command to check if the logical volume is extended:lvdisplay VOLUME_GROUP_NAME
# lvdisplay VOLUME_GROUP_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command to expand the filesystem to accommodate the extended logical volume:
xfs_growfs /dev/VOLUME_GROUP_NAME/LOGICAL_VOLUME_NAME
# xfs_growfs /dev/VOLUME_GROUP_NAME/LOGICAL_VOLUME_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Remount the file system using the following command:
mount -o remount /dev/VOLUME_GROUP_NAME/LOGICAL_VOLUME_NAME /bricks/path_to_brick
# mount -o remount /dev/VOLUME_GROUP_NAME/LOGICAL_VOLUME_NAME /bricks/path_to_brickCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start all the volumes with
forceoption:gluster volume start VOLNAME force
# gluster volume start VOLNAME forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.8. Shrinking Volumes
Shrinking a Volume
- Remove a brick using the following command:
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK start
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successful# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
If theremove-brickcommand is run withforceor without any option, the data on the brick that you are removing will no longer be accessible at the glusterFS mount point. When using thestartoption, the data is migrated to other bricks, and on a successful commit the removed brick's information is deleted from the volume configuration. Data can still be accessed directly on the brick. - You can view the status of the remove brick operation using the following command:
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK status
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the data migration shown in the previous
statuscommand is complete, run the following command to commit the brick removal:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK commit
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 commit
# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After the brick removal, you can check the volume information using the following command:
gluster volume info
# gluster volume infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command displays information similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.8.1. Shrinking a Geo-replicated Volume
- Remove a brick using the following command:
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK start
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume remove-brick MASTER_VOL MASTER_HOST:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successful
# gluster volume remove-brick MASTER_VOL MASTER_HOST:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
If theremove-brickcommand is run withforceor without any option, the data on the brick that you are removing will no longer be accessible at the glusterFS mount point. When using thestartoption, the data is migrated to other bricks, and on a successful commit the removed brick's information is deleted from the volume configuration. Data can still be accessed directly on the brick. - Use geo-replication
config checkpointto ensure that all the data in that brick is synced to the slave.- Set a checkpoint to help verify the status of the data synchronization.
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config checkpoint now
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config checkpoint nowCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the checkpoint completion for the geo-replication session using the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status detail
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status detailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- You can view the status of the remove brick operation using the following command:
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK status
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume remove-brick MASTER_VOL MASTER_HOST:/rhgs/brick2 status
# gluster volume remove-brick MASTER_VOL MASTER_HOST:/rhgs/brick2 statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the geo-replication session between the master and the slave:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the data migration shown in the previous
statuscommand is complete, run the following command to commit the brick removal:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK commit
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume remove-brick MASTER_VOL MASTER_HOST:/rhgs/brick2 commit
# gluster volume remove-brick MASTER_VOL MASTER_HOST:/rhgs/brick2 commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After the brick removal, you can check the volume information using the following command:
gluster volume info
# gluster volume infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the geo-replication session between the hosts:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.8.2. Shrinking a Tiered Volume
11.8.2.1. Shrinking a Cold Tier Volume
- Detach the tier by performing the steps listed in Section 16.7, “Detaching a Tier from a Volume”
- Remove a brick using the following command:
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK start
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successful
# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
If theremove-brickcommand is run withforceor without any option, the data on the brick that you are removing will no longer be accessible at the glusterFS mount point. When using thestartoption, the data is migrated to other bricks, and on a successful commit the removed brick's information is deleted from the volume configuration. Data can still be accessed directly on the brick. - You can view the status of the remove brick operation using the following command:
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK status
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 status Node Rebalanced-files size scanned failures status --------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ------------ localhost 16 16777216 52 0 in progress 192.168.1.1 13 16723211 47 0 in progress# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 status Node Rebalanced-files size scanned failures status --------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ------------ localhost 16 16777216 52 0 in progress 192.168.1.1 13 16723211 47 0 in progressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the data migration shown in the previous
statuscommand is complete, run the following command to commit the brick removal:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK commit
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 commit
# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Rerun the attach-tier command only with the required set of bricks:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME attach [replica COUNT] BRICK...For example,gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/tier1 server2:/rhgs/tier2 server1:/rhgs/tier3 server2:/rhgs/tier4
# gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/tier1 server2:/rhgs/tier2 server1:/rhgs/tier3 server2:/rhgs/tier4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
When you attach a tier, an internal process called fix-layout commences internally to prepare the hot tier for use. This process takes time and there will a delay in starting the tiering activities.
11.8.2.2. Shrinking a Hot Tier Volume
- Detach the tier by performing the steps listed in Section 16.7, “Detaching a Tier from a Volume”
- Rerun the attach-tier command only with the required set of bricks:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME attach [replica COUNT] brick...Important
When you reattach a tier, an internal process called fix-layout commences internally to prepare the hot tier for use. This process takes time and there will a delay in starting the tiering activities.
11.8.3. Stopping a remove-brick Operation
remove-brick operation that is in progress can be stopped by using the stop command.
Note
remove-brick operation will not be migrated back to the same brick when the operation is stopped.
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK stop
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME BRICK stop11.9. Migrating Volumes
Note
replace-brick operation, review the known issues related to replace-brick operation in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Release Notes.
11.9.1. Replacing a Subvolume on a Distribute or Distribute-replicate Volume
- Add the new bricks to the volume.
gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] NEW-BRICK
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] NEW-BRICKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 11.1. Adding a Brick to a Distribute Volume
gluster volume add-brick test-volume server5:/rhgs/brick5 Add Brick successful
# gluster volume add-brick test-volume server5:/rhgs/brick5 Add Brick successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the volume information using the command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
In case of a Distribute-replicate volume, you must specify the replica count in theadd-brickcommand and provide the same number of bricks as the replica count to theadd-brickcommand. - Remove the bricks to be replaced from the subvolume.
- Start the
remove-brickoperation using the command:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] <BRICK> start
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] <BRICK> startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 11.2. Start a remove-brick operation on a distribute volume
gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successful
# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 start Remove Brick start successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - View the status of the
remove-brickoperation using the command:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] BRICK status
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] BRICK statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 11.3. View the Status of remove-brick Operation
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Keep monitoring theremove-brickoperation status by executing the above command. In the above example, the estimated time for rebalance to complete is 10 minutes. When the value of the status field is set tocompletein the output ofremove-brickstatus command, proceed further. - Commit the
remove-brickoperation using the command:gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] <BRICK> commit
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME [replica <COUNT>] <BRICK> commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 11.4. Commit the remove-brick Operation on a Distribute Volume
gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 commit
# gluster volume remove-brick test-volume server2:/rhgs/brick2 commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the volume information using the command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the content on the brick after committing the
remove-brickoperation on the volume. If there are any files leftover, copy it through FUSE or NFS mount.- Verify if there are any pending files on the bricks of the subvolume.Along with files, all the application-specific extended attributes must be copied. glusterFS also uses extended attributes to store its internal data. The extended attributes used by glusterFS are of the form
trusted.glusterfs.*,trusted.afr.*, andtrusted.gfid. Any extended attributes other than ones listed above must also be copied.To copy the application-specific extended attributes and to achieve a an effect similar to the one that is described above, use the following shell script:Syntax:copy.sh <glusterfs-mount-point> <brick>
# copy.sh <glusterfs-mount-point> <brick>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 11.5. Code Snippet Usage
If the mount point is/mnt/glusterfsand brick path is/rhgs/brick1, then the script must be run as:copy.sh /mnt/glusterfs /rhgs/brick1
# copy.sh /mnt/glusterfs /rhgs/brick1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To identify a list of files that are in a split-brain state, execute the command:
gluster volume heal test-volume info split-brain
# gluster volume heal test-volume info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If there are any files listed in the output of the above command, compare the files across the bricks in a replica set, delete the bad files from the brick and retain the correct copy of the file. Manual intervention by the System Administrator would be required to choose the correct copy of file.
11.9.2. Replacing an Old Brick with a New Brick on a Replicate or Distribute-replicate Volume
- Ensure that the new brick (
server5:/rhgs/brick1) that replaces the old brick (server0:/rhgs/brick1) is empty. Ensure that all the bricks are online. The brick that must be replaced can be in an offline state. - Execute the
replace-brickcommand with theforceoption:gluster volume replace-brick test-volume server0:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 commit force volume replace-brick: success: replace-brick commit successful
# gluster volume replace-brick test-volume server0:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 commit force volume replace-brick: success: replace-brick commit successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Check if the new brick is online.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Data on the newly added brick would automatically be healed. It might take time depending upon the amount of data to be healed. It is recommended to check heal information after replacing a brick to make sure all the data has been healed before replacing/removing any other brick.
gluster volume heal VOL_NAME info
# gluster volume heal VOL_NAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The value ofNumber of entriesfield will be displayed as zero if the heal is complete.
11.9.3. Replacing an Old Brick with a New Brick on a Distribute Volume
- Before making any changes, check the contents of the brick that you want to remove from the volume.
ls /mount/point/OLDBRICK file1 file2 ... file5
# ls /mount/point/OLDBRICK file1 file2 ... file5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the new brick to the volume.
gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEWSERVER:NEWBRICK
# gluster volume add-brick VOLNAME NEWSERVER:NEWBRICKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start removing the old brick.
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME OLDSERVER:OLDBRICK start
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME OLDSERVER:OLDBRICK startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Wait until the remove-brick status command shows that the removal is complete.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Finish removing the old brick.
gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME OLDSERVER:OLDBRICK commit
# gluster volume remove-brick VOLNAME OLDSERVER:OLDBRICK commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify that all files that were on the removed brick are still present on the volume.
11.9.4. Replacing an Old Brick with a New Brick on a Dispersed or Distributed-dispersed Volume
- Ensure that the new brick that replaces the old brick is empty. The brick that must be replaced can be in an offline state but all other bricks must be online.
- Execute the replace-brick command with the
forceoption:gluster volume replace-brick VOL_NAME old_brick_path new_brick_path commit force
# gluster volume replace-brick VOL_NAME old_brick_path new_brick_path commit forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume replace-brick test-volume server1:/rhgs/brick2 server1:/rhgs/brick2new commit force volume replace-brick: success: replace-brick commit successful
# gluster volume replace-brick test-volume server1:/rhgs/brick2 server1:/rhgs/brick2new commit force volume replace-brick: success: replace-brick commit successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The new brick you are adding could be from the same server or you can add a new server and then a new brick. - Check if the new brick is online.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Data on the newly added brick would automatically be healed. It might take time depending upon the amount of data to be healed. It is recommended to check heal information after replacing a brick to make sure all the data has been healed before replacing/removing any other brick.
gluster volume heal VOL_NAME info
# gluster volume heal VOL_NAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The value ofNumber of entriesfield will be displayed as zero if the heal is complete. - Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 introduces the ‘summary’ option of ‘heal info’ command. This command displays the statistics of entries pending heal in split-brain and the entries undergoing healing. This command prints only the entry count and not the actual file-names or gfids.To get the summary of a volume, run the following command:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info summary
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info summaryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The ‘summary’ option provides a detailed information about the brick unlike the ‘info’ command. The summary information is obtained in a similar way as the ‘info’ command.The --xml parameter provides the output of the summary option in XML formatCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.9.5. Reconfiguring a Brick in a Volume
reset-brick subcommand is useful when you want to reconfigure a brick rather than replace it. reset-brick lets you replace a brick with another brick of the same location and UUID. For example, if you initially configured bricks so that they were identified with a hostname, but you want to use that hostname somewhere else, you can use reset-brick to stop the brick, reconfigure it so that it is identified by an IP address instead of the hostname, and return the reconfigured brick to the cluster.
- Ensure that the quorum minimum will still be met when the brick that you want to reset is taken offline.
- If possible, Red Hat recommends stopping I/O, and verifying that no heal operations are pending on the volume.
- Run the following command to kill the brick that you want to reset.
gluster volume reset-brick VOLNAME HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH start
# gluster volume reset-brick VOLNAME HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Configure the offline brick according to your needs.
- Check that the volume's
Volume IDdisplayed bygluster volume infomatches thevolume-id(if any) of the offline brick.gluster volume info VOLNAME cat /var/lib/glusterd/vols/VOLNAME/VOLNAME.HOSTNAME.BRICKPATH.vol | grep volume-id
# gluster volume info VOLNAME # cat /var/lib/glusterd/vols/VOLNAME/VOLNAME.HOSTNAME.BRICKPATH.vol | grep volume-idCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, in the following dispersed volume, theVolume IDand thevolume-idare bothab8a981a-a6d9-42f2-b8a5-0b28fe2c4548.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow cat /var/lib/glusterd/vols/vol/vol.myhost.brick-gluster-vol-1.vol | grep volume-id option volume-id ab8a981a-a6d9-42f2-b8a5-0b28fe2c4548
# cat /var/lib/glusterd/vols/vol/vol.myhost.brick-gluster-vol-1.vol | grep volume-id option volume-id ab8a981a-a6d9-42f2-b8a5-0b28fe2c4548Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Bring the reconfigured brick back online. There are two options for this:
- If your brick did not have a
volume-idin the previous step, run:gluster volume reset-brick VOLNAME HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH commit
# gluster volume reset-brick VOLNAME HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH commitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If your brick's
volume-idmatches your volume's identifier, Red Hat recommends adding theforcekeyword to ensure that the operation succeeds.gluster volume reset-brick VOLNAME HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH commit force
# gluster volume reset-brick VOLNAME HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH HOSTNAME:BRICKPATH commit forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.10. Replacing Hosts
11.10.1. Replacing a Host Machine with a Different Hostname
Important
server0.example.com and the replacement machine is server5.example.com. The brick with an unrecoverable failure is server0.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 and the replacement brick is server5.example.com:/rhgs/brick1.
- Stop the geo-replication session if configured by executing the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Probe the new peer from one of the existing peers to bring it into the cluster.
gluster peer probe server5.example.com
# gluster peer probe server5.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that the new brick
(server5.example.com:/rhgs/brick1)that is replacing the old brick(server0.example.com:/rhgs/brick1)is empty. - If the geo-replication session is configured, perform the following steps:
- Setup the geo-replication session by generating the ssh keys:
gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create geo-replication session again with
forceoption to distribute the keys from new nodes to Slave nodes.gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After successfully setting up the shared storage volume, when a new node is replaced in the cluster, the shared storage is not mounted automatically on this node. Neither is the
/etc/fstabentry added for the shared storage on this node. To make use of shared storage on this node, execute the following commands:mount -t glusterfs local node's ip:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage cp /etc/fstab /var/run/gluster/fstab.tmp echo local node's ip:/gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/ glusterfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
# mount -t glusterfs local node's ip:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage # cp /etc/fstab /var/run/gluster/fstab.tmp # echo local node's ip:/gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/ glusterfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstabCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on setting up shared storage volume, see Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume”. - Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring meta-volume, see Section 10.3.5, “Configuring a Meta-Volume”.
- Retrieve the brick paths in
server0.example.comusing the following command:gluster volume info <VOLNAME>
# gluster volume info <VOLNAME>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Brick path inserver0.example.comis/rhgs/brick1. This has to be replaced with the brick in the newly added host,server5.example.com. - Create the required brick path in server5.example.com.For example, if /rhs/brick is the XFS mount point in server5.example.com, then create a brick directory in that path.
mkdir /rhgs/brick1
# mkdir /rhgs/brick1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the
replace-brickcommand with the force option:gluster volume replace-brick vol server0.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 server5.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 commit force volume replace-brick: success: replace-brick commit successful
# gluster volume replace-brick vol server0.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 server5.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 commit force volume replace-brick: success: replace-brick commit successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify that the new brick is online.
gluster volume status Status of volume: vol Gluster process Port Online Pid Brick server5.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 49156 Y 5731 Brick server1.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 49153 Y 5354
# gluster volume status Status of volume: vol Gluster process Port Online Pid Brick server5.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 49156 Y 5731 Brick server1.example.com:/rhgs/brick1 49153 Y 5354Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Initiate self-heal on the volume. The status of the heal process can be seen by executing the command:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME
# gluster volume heal VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The status of the heal process can be seen by executing the command:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Detach the original machine from the trusted pool.
gluster peer detach server0.example.com
# gluster peer detach server0.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that after the self-heal completes, the extended attributes are set to zero on the other bricks in the replica.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the extended attributestrusted.afr.vol-client-0andtrusted.afr.vol-client-1have zero values. This means that the data on the two bricks is identical. If these attributes are not zero after self-heal is completed, the data has not been synchronised correctly. - Start the geo-replication session using
forceoption:gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.10.2. Replacing a Host Machine with the Same Hostname
/var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info file.
- Stop the geo-replication session if configured by executing the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the
glusterdservice on the server0.example.com.service glusterd stop
# service glusterd stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Ifglusterdcrashes, there is no functionality impact to this crash as it occurs during the shutdown. For more information, see Section 23.3, “ResolvingglusterdCrash” - Retrieve the UUID of the failed host (server0.example.com) from another of the Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool by executing the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the UUID of the failed host isb5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b - Edit the
glusterd.infofile in the new host and include the UUID of the host you retrieved in the previous step.cat /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info UUID=b5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b operating-version=30703
# cat /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info UUID=b5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b operating-version=30703Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The operating version of this node must be same as in other nodes of the trusted storage pool. - Select any host (say for example, server1.example.com) in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool and retrieve its UUID from the
glusterd.infofile.grep -i uuid /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info UUID=8cc6377d-0153-4540-b965-a4015494461c
# grep -i uuid /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info UUID=8cc6377d-0153-4540-b965-a4015494461cCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Gather the peer information files from the host (server1.example.com) in the previous step. Execute the following command in that host (server1.example.com) of the cluster.
cp -a /var/lib/glusterd/peers /tmp/
# cp -a /var/lib/glusterd/peers /tmp/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Remove the peer file corresponding to the failed host (server0.example.com) from the
/tmp/peersdirectory.rm /tmp/peers/b5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b
# rm /tmp/peers/b5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the UUID corresponds to the UUID of the failed host (server0.example.com) retrieved in Step 3. - Archive all the files and copy those to the failed host(server0.example.com).
cd /tmp; tar -cvf peers.tar peers
# cd /tmp; tar -cvf peers.tar peersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Copy the above created file to the new peer.
scp /tmp/peers.tar root@server0.example.com:/tmp
# scp /tmp/peers.tar root@server0.example.com:/tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Copy the extracted content to the
/var/lib/glusterd/peersdirectory. Execute the following command in the newly added host with the same name (server0.example.com) and IP Address.tar -xvf /tmp/peers.tar cp peers/* /var/lib/glusterd/peers/
# tar -xvf /tmp/peers.tar # cp peers/* /var/lib/glusterd/peers/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Select any other host in the cluster other than the node (server1.example.com) selected in step 5. Copy the peer file corresponding to the UUID of the host retrieved in Step 5 to the new host (server0.example.com) by executing the following command:
scp /var/lib/glusterd/peers/<UUID-retrieved-from-step5> root@Example1:/var/lib/glusterd/peers/
# scp /var/lib/glusterd/peers/<UUID-retrieved-from-step5> root@Example1:/var/lib/glusterd/peers/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Retrieve the brick directory information, by executing the following command in any host in the cluster.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above example, the brick path in server0.example.com is,/rhgs/brick1. If the brick path does not exist in server0.example.com, perform steps a, b, and c.- Create a brick path in the host, server0.example.com.
mkdir /rhgs/brick1
mkdir /rhgs/brick1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Retrieve the volume ID from the existing brick of another host by executing the following command on any host that contains the bricks for the volume.
getfattr -d -m. -ehex <brick-path>
# getfattr -d -m. -ehex <brick-path>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the volume-id.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above example, the volume id is 0x8f16258c88a0498fbd53368706af7496 - Set this volume ID on the brick created in the newly added host and execute the following command on the newly added host (server0.example.com).
setfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.volume-id -v <volume-id> <brick-path>
# setfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.volume-id -v <volume-id> <brick-path>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Example:setfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.volume-id -v 0x8f16258c88a0498fbd53368706af7496 /rhs/brick2/drv2
# setfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.volume-id -v 0x8f16258c88a0498fbd53368706af7496 /rhs/brick2/drv2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Data recovery is possible only if the volume type is replicate or distribute-replicate. If the volume type is plain distribute, you can skip steps 12 and 13. - Create a FUSE mount point to mount the glusterFS volume.
mount -t glusterfs <server-name>:/VOLNAME <mount>
# mount -t glusterfs <server-name>:/VOLNAME <mount>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Perform the following operations to change the Automatic File Replication extended attributes so that the heal process happens from the other brick (server1.example.com:/rhgs/brick1) in the replica pair to the new brick (server0.example.com:/rhgs/brick1). Note that /mnt/r2 is the FUSE mount path.
- Create a new directory on the mount point and ensure that a directory with such a name is not already present.
mkdir /mnt/r2/<name-of-nonexistent-dir>
# mkdir /mnt/r2/<name-of-nonexistent-dir>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Delete the directory and set the extended attributes.
rmdir /mnt/r2/<name-of-nonexistent-dir> setfattr -n trusted.non-existent-key -v abc /mnt/r2 setfattr -x trusted.non-existent-key /mnt/r2
# rmdir /mnt/r2/<name-of-nonexistent-dir> # setfattr -n trusted.non-existent-key -v abc /mnt/r2 # setfattr -x trusted.non-existent-key /mnt/r2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Ensure that the extended attributes on the other bricks in the replica (in this example,
trusted.afr.vol-client-0) is not set to zero.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
You must ensure to perform steps 12, 13, and 14 for all the volumes having bricks fromserver0.example.com. - Start the
glusterdservice.service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Perform the self-heal operation on the restored volume.
gluster volume heal VOLNAME
# gluster volume heal VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You can view the gluster volume self-heal status by executing the following command:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the geo-replication session is configured, perform the following steps:
- Setup the geo-replication session by generating the ssh keys:
gluster system:: execute gsec_create
# gluster system:: execute gsec_createCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create geo-replication session again with
forceoption to distribute the keys from new nodes to Slave nodes.gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL create push-pem forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After successfully setting up the shared storage volume, when a new node is replaced in the cluster, the shared storage is not mounted automatically on this node. Neither is the
/etc/fstabentry added for the shared storage on this node. To make use of shared storage on this node, execute the following commands:mount -t glusterfs <local node's ip>:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage # cp /etc/fstab /var/run/gluster/fstab.tmp # echo "<local node's ip>:/gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/ glusterfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
# mount -t glusterfs <local node's ip>:gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage # cp /etc/fstab /var/run/gluster/fstab.tmp # echo "<local node's ip>:/gluster_shared_storage /var/run/gluster/shared_storage/ glusterfs defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstabCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on setting up shared storage volume, see Section 11.12, “Setting up Shared Storage Volume”. - Configure the meta-volume for geo-replication:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume true
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config use_meta_volume trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the geo-replication session using
forceoption:gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL start forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If there are only 2 hosts in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool where the host server0.example.com must be replaced, perform the following steps:
- Stop the geo-replication session if configured by executing the following command:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop force
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stop forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the
glusterdservice on server0.example.com.service glusterd stop
# service glusterd stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Ifglusterdcrashes, there is no functionality impact to this crash as it occurs during the shutdown. For more information, see Section 23.3, “ResolvingglusterdCrash” - Retrieve the UUID of the failed host (server0.example.com) from another peer in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool by executing the following command:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the UUID of the failed host isb5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b - Edit the
glusterd.infofile in the new host (server0.example.com) and include the UUID of the host you retrieved in the previous step.cat /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info UUID=b5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b operating-version=30703
# cat /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info UUID=b5ab2ec3-5411-45fa-a30f-43bd04caf96b operating-version=30703Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The operating version of this node must be same as in other nodes of the trusted storage pool. - Create the peer file in the newly created host (server0.example.com) in /var/lib/glusterd/peers/<uuid-of-other-peer> with the name of the UUID of the other host (server1.example.com).UUID of the host can be obtained with the following:
gluster system:: uuid get
# gluster system:: uuid getCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 11.6. Example to obtain the UUID of a host
For example, # gluster system:: uuid get UUID: 1d9677dc-6159-405e-9319-ad85ec030880
For example, # gluster system:: uuid get UUID: 1d9677dc-6159-405e-9319-ad85ec030880Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this case the UUID of other peer is1d9677dc-6159-405e-9319-ad85ec030880 - Create a file
/var/lib/glusterd/peers/1d9677dc-6159-405e-9319-ad85ec030880in server0.example.com, with the following command:touch /var/lib/glusterd/peers/1d9677dc-6159-405e-9319-ad85ec030880
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/peers/1d9677dc-6159-405e-9319-ad85ec030880Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The file you create must contain the following information:UUID=<uuid-of-other-node> state=3 hostname=<hostname>
UUID=<uuid-of-other-node> state=3 hostname=<hostname>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Continue to perform steps 12 to 18 as documented in the previous procedure.
11.11. Rebalancing Volumes
add-brick or remove-brick commands, the data on the volume needs to be rebalanced among the servers.
Note
rebalance operation using the start option. In a replicated volume, at least one of the bricks in the replica should be online.
gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME start
# gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME startgluster volume rebalance test-volume start Starting rebalancing on volume test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume rebalance test-volume start
Starting rebalancing on volume test-volume has been successfulforce option, the rebalance command attempts to balance the space utilized across nodes. Files whose migration would cause the target node to have less available space than the source node are skipped. This results in linkto files being retained, which may cause slower access when a large number of linkto files are present.
Warning
Rebalance command can be executed with the force option even when the older clients are connected to the cluster. However, this could lead to a data loss situation.
rebalance operation with force, balances the data based on the layout, and hence optimizes or does away with the link files, but may lead to an imbalanced storage space used across bricks. This option is to be used only when there are a large number of link files in the system.
gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME start force
# gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME start forcegluster volume rebalance test-volume start force Starting rebalancing on volume test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume rebalance test-volume start force
Starting rebalancing on volume test-volume has been successful11.11.1. Rebalance Throttling
normal mode. Configure the throttling modes to adjust the rate at which the files must be migrated
gluster volume set VOLNAME rebal-throttle lazy|normal|aggressive
# gluster volume set VOLNAME rebal-throttle lazy|normal|aggressivegluster volume set test-volume rebal-throttle lazy
# gluster volume set test-volume rebal-throttle lazy11.11.2. Displaying Rebalance Progress
gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME status
# gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME status| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Node | The name of the node. |
| Rebalanced-files | The number of files that were successfully migrated. |
| size | The total size of the files that were migrated. |
| scanned | The number of files scanned on the node. This includes the files that were migrated. |
| failures | The number of files that could not be migrated because of errors. |
| skipped | The number of files which were skipped because of various errors or reasons. |
| status | The status of the rebalance operation on the node is in progress, completed, or failed. |
| run time in h:m:s | The amount of time for which the process has been running on the node. |
>2 months and the user is advised to check again later.
completed. For example:
rebalance log with the message ID 109126. You can search for the message ID from the log file and get the list of all the skipped files:
11.11.3. Stopping a Rebalance Operation
gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME stop
# gluster volume rebalance VOLNAME stop11.13. Stopping Volumes
gluster volume stop VOLNAME
# gluster volume stop VOLNAMEgluster volume stop test-volume Stopping volume will make its data inaccessible. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y Stopping volume test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume stop test-volume
Stopping volume will make its data inaccessible. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
Stopping volume test-volume has been successful11.14. Deleting Volumes
Important
/etc/fstab file after the volume has been deleted.
gluster volume delete VOLNAME
# gluster volume delete VOLNAMEgluster volume delete test-volume Deleting volume will erase all information about the volume. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y Deleting volume test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume delete test-volume
Deleting volume will erase all information about the volume. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
Deleting volume test-volume has been successful11.15. Managing Split-brain
- Data split-brain: Contents of the file under split-brain are different in different replica pairs and automatic healing is not possible.Red Hat allows the user to resolve Data split-brain from the mount point and from the CLI.For information on how to recover from data split-brain from the mount point, see Section 11.15.2.1, “ Recovering File Split-brain from the Mount Point”.For information on how to recover from data split-brain using CLIS, see Section 11.15.2.2, “Recovering File Split-brain from the gluster CLI”.
- Metadata split-brain: The metadata of the files like user defined extended attribute are different and automatic healing is not possible.Like Data split-brain, Metadata split-brain can also be resolved from both mount point and CLI.For information on how to recover from metadata split-brain from the mount point, see Section 11.15.2.1, “ Recovering File Split-brain from the Mount Point”.para>For information on how to recover from metadata split-brain using CLI, see Section 11.15.2.2, “Recovering File Split-brain from the gluster CLI”.
- Entry split-brain: Entry split-brain can be of two types:
- GlusterFS Internal File Identifier or GFID split-Brain: This happen when files or directories in different replica pairs have different GFIDs.
- Type Mismatch Split-Brain: This happen when the files/directories stored in replica pairs are of different types but with the same names.
Red Hat Gluster Storage 3.4 allows you to resolve GFID split-brain from gluster CLI. For more information, see Section 11.15.3, “Recovering GFID Split-brain from the gluster CLI”.You can resolve split-brain manually by inspecting the file contents from the backend and deciding which is the true copy (source) and modifying the appropriate extended attributes such that healing can happen automatically.
11.15.1. Preventing Split-brain
11.15.1.1. Configuring Server-Side Quorum
cluster.server-quorum-type volume option as server. For more information on this volume option, see Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options”.
glusterd service. Whenever the glusterd service on a machine observes that the quorum is not met, it brings down the bricks to prevent data split-brain. When the network connections are brought back up and the quorum is restored, the bricks in the volume are brought back up. When the quorum is not met for a volume, any commands that update the volume configuration or peer addition or detach are not allowed. It is to be noted that both, the glusterd service not running and the network connection between two machines being down are treated equally.
gluster volume set all cluster.server-quorum-ratio PERCENTAGE
# gluster volume set all cluster.server-quorum-ratio PERCENTAGEgluster volume set all cluster.server-quorum-ratio 51%
# gluster volume set all cluster.server-quorum-ratio 51%gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.server-quorum-type server
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.server-quorum-type serverImportant
11.15.1.2. Configuring Client-Side Quorum
Client-Side Quorum Options
- cluster.quorum-count
- The minimum number of bricks that must be available in order for writes to be allowed. This is set on a per-volume basis. Valid values are between
1and the number of bricks in a replica set. This option is used by thecluster.quorum-typeoption to determine write behavior. - cluster.quorum-type
- Determines when the client is allowed to write to a volume. Valid values are
fixedandauto.Ifcluster.quorum-typeisfixed, writes are allowed as long as the number of bricks available in the replica set is greater than or equal to the value of thecluster.quorum-countoption.Ifcluster.quorum-typeisauto, writes are allowed when at least 50% of the bricks in a replica set are be available. In a replica set with an even number of bricks, if exactly 50% of the bricks are available, the first brick in the replica set must be available in order for writes to continue.In a three-way replication setup, it is recommended to setcluster.quorum-typetoautoto avoid split-brains. If the quorum is not met, the replica pair becomes read-only.
Example 11.7. Client-Side Quorum

A, only replica group A becomes read-only. Replica groups B and C continue to allow data modifications.
cluster.quorum-type and cluster.quorum-count options.
Important
gluster volume set VOLNAME group virt command. If on a two replica set up, if the first brick in the replica pair is offline, virtual machines will be paused because quorum is not met and writes are disallowed.
gluster volume reset VOLNAME quorum-type
# gluster volume reset VOLNAME quorum-typeThis example provides information on how to set server-side and client-side quorum on a Distribute Replicate volume to avoid split-brain scenario. The configuration of this example has 2 X 2 ( 4 bricks) Distribute Replicate setup.
gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.server-quorum-type server
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.server-quorum-type servergluster volume set all cluster.server-quorum-ratio 51%
# gluster volume set all cluster.server-quorum-ratio 51%quorum-typeoption to auto to allow writes to the file only if the percentage of active replicate bricks is more than 50% of the total number of bricks that constitute that replica.
gluster volume set VOLNAME quorum-type auto
# gluster volume set VOLNAME quorum-type autoImportant
n) in a replica set is an even number, it is mandatory that the n/2 count must consist of the primary brick and it must be up and running. If n is an odd number, the n/2 count can have any brick up and running, that is, the primary brick need not be up and running to allow writes.
11.15.2. Recovering from File Split-brain
- See Section 11.15.2.1, “ Recovering File Split-brain from the Mount Point” for information on how to recover from data and meta-data split-brain from the mount point.
- See Section 11.15.2.2, “Recovering File Split-brain from the gluster CLI” for information on how to recover from data and meta-data split-brain using CLI
11.15.2.1. Recovering File Split-brain from the Mount Point
Steps to recover from a split-brain from the mount point
- You can use a set of
getfattrandsetfattrcommands to detect the data and meta-data split-brain status of a file and resolve split-brain from the mount point.Important
This process for split-brain resolution from mount will not work on NFS mounts as it does not provide extended attributes support.In this example, thetest-volumevolume has bricksbrick0,brick1,brick2andbrick3.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Directory structure of the bricks is as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the following output, some of the files in the volume are in split-brain.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To know data or meta-data split-brain status of a file:getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status <path-to-file>
# getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The above command executed from mount provides information if a file is in data or meta-data split-brain. This command is not applicable to entry/type-mismatch split-brain.For example,file100is in meta-data split-brain. Executing the above mentioned command forfile100gives :getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file100 file: file100 replica.split-brain-status="data-split-brain:no metadata-split-brain:yes Choices:test-client-0,test-client-1"
# getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file100 # file: file100 replica.split-brain-status="data-split-brain:no metadata-split-brain:yes Choices:test-client-0,test-client-1"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow file1is in data split-brain.getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file1 file: file1 replica.split-brain-status="data-split-brain:yes metadata-split-brain:no Choices:test-client-2,test-client-3"
# getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file1 # file: file1 replica.split-brain-status="data-split-brain:yes metadata-split-brain:no Choices:test-client-2,test-client-3"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow file99is in both data and meta-data split-brain.getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file99 file: file99 replica.split-brain-status="data-split-brain:yes metadata-split-brain:yes Choices:test-client-2,test-client-3"
# getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file99 # file: file99 replica.split-brain-status="data-split-brain:yes metadata-split-brain:yes Choices:test-client-2,test-client-3"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow diris inentry/type-mismatchsplit-brain but as mentioned earlier, the above command is does not display if the file is inentry/type-mismatchsplit-brain. Hence, the command displaysThe file is not under data or metadata split-brain. For information on resolving entry/type-mismatch split-brain, see Chapter 25, Manually Recovering File Split-brain .getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status dir file: dir replica.split-brain-status="The file is not under data or metadata split-brain"
# getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status dir # file: dir replica.split-brain-status="The file is not under data or metadata split-brain"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow file2is not in any kind of split-brain.getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file2 file: file2 replica.split-brain-status="The file is not under data or metadata split-brain"
# getfattr -n replica.split-brain-status file2 # file: file2 replica.split-brain-status="The file is not under data or metadata split-brain"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Analyze the files in data and meta-data split-brain and resolve the issue
When you perform operations like
cat,getfattr, and more from the mount on files in split-brain, it throws an input/output error. For further analyzing such files, you can usesetfattrcommand.setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice -v "choiceX" <path-to-file>
# setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice -v "choiceX" <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Using this command, a particular brick can be chosen to access the file in split-brain.For example,file1is in data-split-brain and when you try to read from the file, it throws input/output error.cat file1 cat: file1: Input/output error
# cat file1 cat: file1: Input/output errorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Split-brain choices provided for file1 weretest-client-2andtest-client-3.Settingtest-client-2as split-brain choice for file1 serves reads fromb2for the file.setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice -v test-client-2 file1
# setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice -v test-client-2 file1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now, you can perform operations on the file. For example, read operations on the file:cat file1 xyz
# cat file1 xyzCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Similarly, to inspect the file from other choice,replica.split-brain-choiceis to be set totest-client-3.Trying to inspect the file from a wrong choice errors out. You can undo the split-brain-choice that has been set, the above mentionedsetfattrcommand can be used withnoneas the value for extended attribute.For example,setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice -v none file1
# setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice -v none file1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Now performingcatoperation on the file will again result in input/output error, as before.cat file cat: file1: Input/output error
# cat file cat: file1: Input/output errorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After you decide which brick to use as a source for resolving the split-brain, it must be set for the healing to be done.setfattr -n replica.split-brain-heal-finalize -v <heal-choice> <path-to-file>
# setfattr -n replica.split-brain-heal-finalize -v <heal-choice> <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Examplesetfattr -n replica.split-brain-heal-finalize -v test-client-2 file1
# setfattr -n replica.split-brain-heal-finalize -v test-client-2 file1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The above process can be used to resolve data and/or meta-data split-brain on all the files.Setting the split-brain-choice on the fileAfter setting the split-brain-choice on the file, the file can be analyzed only for five minutes. If the duration of analyzing the file needs to be increased, use the following command and set the required time intimeout-in-minuteargument.setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice-timeout -v <timeout-in-minutes> <mount_point/file>
# setfattr -n replica.split-brain-choice-timeout -v <timeout-in-minutes> <mount_point/file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This is a global timeout and is applicable to all files as long as the mount exists. The timeout need not be set each time a file needs to be inspected but for a new mount it will have to be set again for the first time. This option becomes invalid if the operations like add-brick or remove-brick are performed.Note
Iffopen-keep-cacheFUSE mount option is disabled, then inode must be invalidated each time before selecting a newreplica.split-brain-choiceto inspect a file using the following command:setfattr -n inode-invalidate -v 0 <path-to-file>
# setfattr -n inode-invalidate -v 0 <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.2.2. Recovering File Split-brain from the gluster CLI
- Use bigger-file as source
- Use the file with latest mtime as source
- Use one replica as source for a particular file
- Use one replica as source for all files
Note
Theentry/type-mismatchsplit-brain resolution is not supported using CLI. For information on resolvingentry/type-mismatchsplit-brain, see Chapter 25, Manually Recovering File Split-brain .
This method is useful for per file healing and where you can decided that the file with bigger size is to be considered as source.
- Run the following command to obtain the list of files that are in split-brain:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the command output, identify the files that are in split-brain.You can find the differences in the file size and md5 checksums by performing a stat and md5 checksums on the file from the bricks. The following is the stat and md5 checksum output of a file:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can notice the differences in the file size and md5 checksums. - Execute the following command along with the full file name as seen from the root of the volume (or) the gfid-string representation of the file, which is displayed in the heal info command's output.
gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain bigger-file <FILE>
# gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain bigger-file <FILE>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain bigger-file /dir/file1 Healed /dir/file1.
# gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain bigger-file /dir/file1 Healed /dir/file1.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This method is useful for per file healing and if you want the file with latest mtime has to be considered as source.
- Run the following command to obtain the list of files that are in split-brain:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the command output, identify the files that are in split-brain.You can find the differences in the file size and md5 checksums by performing a stat and md5 checksums on the file from the bricks. The following is the stat and md5 checksum output of a file:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can notice the differences in the md5 checksums, and the modify time. - Execute the following command
gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain latest-mtime <FILE>
# gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain latest-mtime <FILE>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, FILE can be either the full file name as seen from the root of the volume or the gfid-string representation of the file.For example,#gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain latest-mtime /file4 Healed /file4
#gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain latest-mtime /file4 Healed /file4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the healing is complete, the md5 checksum, file size, and modify time on both bricks must be same. The following is a sample output of the stat and md5 checksums command after completion of healing the file. You can notice that the file has been healed using the brick having the latest mtime (brick b1, in this example) as the source.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This method is useful if you know which file is to be considered as source.
- Run the following command to obtain the list of files that are in split-brain:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the command output, identify the files that are in split-brain.You can find the differences in the file size and md5 checksums by performing a stat and md5 checksums on the file from the bricks. The following is the stat and md5 checksum output of a file:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can notice the differences in the file size and md5 checksums. - Execute the following command
gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain source-brick <HOSTNAME:BRICKNAME> <FILE>
# gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain source-brick <HOSTNAME:BRICKNAME> <FILE>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, FILE present in <HOSTNAME:BRICKNAME> is taken as source for healing.For example,gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain source-brick test-host:b1 /file4 Healed /file4
# gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain source-brick test-host:b1 /file4 Healed /file4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the healing is complete, the md5 checksum and file size on both bricks must be same. The following is a sample output of the stat and md5 checksums command after completion of healing the file.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This method is useful if you know want to use a particular brick as a source for the split-brain files in that replica pair.
- Run the following command to obtain the list of files that are in split-brain:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the command output, identify the files that are in split-brain. - Execute the following command
gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain source-brick <HOSTNAME:BRICKNAME>
# gluster volume heal <VOLNAME> split-brain source-brick <HOSTNAME:BRICKNAME>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, for all the files that are in split-brain in this replica, <HOSTNAME:BRICKNAME> is taken as source for healing.For example,gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain source-brick test-host:b1
# gluster volume heal test-volume split-brain source-brick test-host:b1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.3. Recovering GFID Split-brain from the gluster CLI
- Use bigger-file as source
- Use the file with latest mtime as source
- Use one replica as source for a particular file
Note
This method is useful for per file healing and where you can decided that the file with bigger size is to be considered as source.
- Run the following command to obtain the path of the file that is in split-brain:
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the output, identify the files for which file operations performed from the client failed with input/output error.For example,gluster volume heal 12 info split-brain
# gluster volume heal 12 info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above command, 12 is the volume name, b0 and b1 are the bricks. - Execute the below command on the brick to fetch information if a file is in GFID split-brain. The
getfattrcommand is used to obtain and verify the AFR changelog extended attributes of the files.#getfattr -d -e hex -m. <path-to-file>
#getfattr -d -e hex -m. <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can notice the difference in GFID for the file f5 in both the bricks.You can find the differences in the file size by executingstatcommand on the file from the bricks. The following is the output of the file f5 in bricks b0 and b1:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command along with the full filename as seen from the root of the volume which is displayed in the
heal infocommand's output:#gluster volume heal VOLNAME split-brain bigger-file FILE
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME split-brain bigger-file FILECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume heal12 split-brain bigger-file /f5 GFID split-brain resolved for file /f5
# gluster volume heal12 split-brain bigger-file /f5 GFID split-brain resolved for file /f5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the healing is complete, the file size on both bricks must be the same as that of the file which had the bigger size. The following is a sample output of thegetfattrcommand after completion of healing the file.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This method is useful for per file healing and if you want the file with latest mtime has to be considered as source.
- Run the following command to obtain the list of files that are in split-brain:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the output, identify the files for which file operations performed from the client failed with input/output error.For example,gluster volume heal 12 info split-brain
# gluster volume heal 12 info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above command, 12 is the volume name, b0 and b1 are the bricks. - The below command executed from backend provides information if a file is in GFID split-brain.
getfattr -d -e hex -m. <path-to-file>
# getfattr -d -e hex -m. <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can notice the difference in GFID for the file f4 in both the bricks.You can find the difference in the modify time by executingstatcommand on the file from the bricks. The following is the output of the file f4 in bricks b0 and b1:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Execute the following command:
#gluster volume healVOLNAME split-brain latest-mtime FILE
#gluster volume healVOLNAME split-brain latest-mtime FILECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,gluster volume heal 12 split-brain latest-mtime /f4 GFID split-brain resolved for file /f4
# gluster volume heal 12 split-brain latest-mtime /f4 GFID split-brain resolved for file /f4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the healing is complete, the GFID of the files on both bricks must be same. The following is a sample output of thegetfattrcommand after completion of healing the file. You can notice that the file has been healed using the brick having the latest mtime as the source.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This method is useful if you know which file is to be considered as source.
- Run the following command to obtain the list of files that are in split-brain:
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the output, identify the files for which file operations performed from the client failed with input/output error.For example,gluster volume heal 12 info split-brain
# gluster volume heal 12 info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above command, 12 is the volume name, b0 and b1 are the bricks.Note
With one replica as source option, there is no way to resolve all the GFID split-brain in one shot by not specifying any file-path in the CLI as done for data/metadata split-brain resolutions.For each file in GFID split-brain, you have to run thehealcommand separately. - The below command executed from backend provides information if a file is in GFID split-brain.
getfattr -d -e hex -m. <path-to-file>
# getfattr -d -e hex -m. <path-to-file>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can notice the difference in GFID for the file f3 in both the bricks. - Execute the following command:
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME split-brain source-brick HOSTNAME : export-directory-absolute-path FILE
#gluster volume heal VOLNAME split-brain source-brick HOSTNAME : export-directory-absolute-path FILECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, FILE present in HOSTNAME : export-directory-absolute-path is taken as source for healing.For example,gluster volume heal 12 split-brain source-brick 10.70.47.144:/bricks/brick2/b1 /f3 GFID split-brain resolved for file /f3
# gluster volume heal 12 split-brain source-brick 10.70.47.144:/bricks/brick2/b1 /f3 GFID split-brain resolved for file /f3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the healing is complete, the GFID of the file on both the bricks should be same as that of the file which had bigger size. The following is a sample output of thegetfattrcommand after the file is healed.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
You can not use the GFID of the file as an argument with any of the CLI options to resolve GFID split-brain. It should be the absolute path as seen from the mount point to the file considered as source.With source-brick option there is no way to resolve all the GFID split-brain in one shot by not specifying any file-path in the CLI as done while resolving data or metadata split-brain. For each file in GFID split-brain, run the CLI with the policy you want to use.Resolving directory GFID split-brain using CLI with the "source-brick" option in a "distributed-replicated" volume needs to be done on all the volumes explicitly. Since directories get created on all the subvolumes, using one particular brick as source for directory GFID split-brain, heal the directories for that subvolume. In this case, other subvolumes must be healed using the brick which has same GFID as that of the previous brick which was used as source for healing other subvolume. For information on resolvingentry/type-mismatchsplit-brain, see Chapter 25, Manually Recovering File Split-brain .
11.15.4. Triggering Self-Healing on Replicated Volumes
Self-heal daemon has the capability to handle multiple heals in parallel and is supported on Replicate and Distribute-replicate volumes. However, increasing the number of heals has impact on I/O performance so the following options have been provided. The cluster.shd-max-threads volume option controls the number of entries that can be self healed in parallel on each replica by self-heal daemon using. Using cluster.shd-wait-qlength volume option, you can configure the number of entries that must be kept in the queue for self-heal daemon threads to take up as soon as any of the threads are free to heal.
cluster.shd-max-threads and cluster.shd-wait-qlength volume set options, see Section 11.1, “Configuring Volume Options”.
- To view the list of files that need healing:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to view the list of files on test-volume that need healing:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To trigger self-healing only on the files which require healing:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME
# gluster volume heal VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to trigger self-healing on files which require healing on test-volume:gluster volume heal test-volume Heal operation on volume test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume heal test-volume Heal operation on volume test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To trigger self-healing on all the files on a volume:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME full
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME fullCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to trigger self-heal on all the files on test-volume:gluster volume heal test-volume full Heal operation on volume test-volume has been successful
# gluster volume heal test-volume full Heal operation on volume test-volume has been successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To view the list of files on a volume that are in a split-brain state:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to view the list of files on test-volume that are in a split-brain state:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.16. Recommended Configurations - Dispersed Volume
The following table lists the brick layout details of multiple server/disk configurations for dispersed and distributed dispersed volumes.
| Redundancy Level | Supported Configurations | Bricks per Server per Subvolume | Node Loss | Max brick failure count within a subvolume | Compatible Server Node count | Increment Size (no. of nodes) | Min number of sub-volumes | Total Spindles | Tolerated HDD Failure Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 HDD Chassis | |||||||||
| 2 | 4 + 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 36 | 33.33% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 72 | 33.33% | ||
| 2 | 8+2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 60 | 20.00% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 120 | 20.00% | ||
| 3 | 8 + 3 | 1-2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 72 | 25.00% |
| 4 | 8 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 36 | 33.33% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 72 | 33.33% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 144 | 33.33% | ||
| 4 | 16 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 60 | 20.00% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 6 | 120 | 20.00% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 20 | 12 | 240 | 20.00% | ||
| 24 HDD Chassis | |||||||||
| 2 | 4 + 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 72 | 33.33% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 24 | 144 | 33.33% | ||
| 2 | 8+ 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 120 | 20.00% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 10 | 24 | 240 | 20.00% | ||
| 4 | 8 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 72 | 33.33% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 144 | 33.33% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 12 | 12 | 24 | 288 | 33.33% | ||
| 4 | 16 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 120 | 20.00% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 240 | 20.00% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 20 | 24 | 480 | 20.00% | ||
| 36 HDD Chassis | |||||||||
| 2 | 4 + 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 18 | 108 | 33.33% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 36 | 216 | 33.33% | ||
| 2 | 8 + 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 18 | 180 | 20.00% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 10 | 36 | 360 | 20.00% | ||
| 3 | 8 + 3 | 1-2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 19 | 216 | 26.39% |
| 4 | 8 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 108 | 33.33% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 18 | 216 | 33.33% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 12 | 12 | 36 | 432 | 33.33% | ||
| 4 | 16 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 180 | 20.00% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 18 | 360 | 20.00% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 20 | 36 | 720 | 20.00% | ||
| 60 HDD Chassis | |||||||||
| 2 | 4 + 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 30 | 180 | 33.33% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 60 | 360 | 33.33% | ||
| 2 | 8 + 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 30 | 300 | 20.00% |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 10 | 60 | 600 | 20.00% | ||
| 3 | 8 + 3 | 1-2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 32 | 360 | 26.67% |
| 4 | 8 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 15 | 180 | 33.33% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 30 | 360 | 33.33% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 12 | 12 | 60 | 720 | 33.33% | ||
| 4 | 16 + 4 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 300 | 20.00% |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 600 | 20.00% | ||
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 1200 | 20.00% | ||
This example describes a compact configuration of three servers, with each server attached to a 12 HDD chassis to create a dispersed volume. In this example, each HDD is assumed to contain a single brick.
gluster volume create test_vol disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server1:/rhgs/brick2 server2:/rhgs/brick3 server2:/rhgs/brick4 server3:/rhgs/brick5 server3:/rhgs/brick6 --force
# gluster volume create test_vol disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server1:/rhgs/brick2 server2:/rhgs/brick3 server2:/rhgs/brick4 server3:/rhgs/brick5 server3:/rhgs/brick6 --force--force parameter is required because this configuration is not optimal in terms of fault tolerance. Since each server provides two bricks, this configuration has a greater risk to data availability if a server goes offline than it would if each brick was provided by a separate server.
gluster volume info command to view the volume information.
gluster volume add-brick test_vol server1:/rhgs/brick7 server1:/rhgs/brick8 server2:/rhgs/brick9 server2:/rhgs/brick10 server3:/rhgs/brick11 server3:/rhgs/brick12
# gluster volume add-brick test_vol server1:/rhgs/brick7 server1:/rhgs/brick8 server2:/rhgs/brick9 server2:/rhgs/brick10 server3:/rhgs/brick11 server3:/rhgs/brick12gluster volume info command to view distributed dispersed volume information.
The following diagram illustrates a dispersed 8+4 configuration on three servers as explained in the row 3 of Table 11.3, “Brick Configurations for Dispersed and Distributed Dispersed Volumes” The command to create the disperse volume for this configuration:
gluster volume create test_vol disperse-data 8 redundancy 4 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server1:/rhgs/brick2 server1:/rhgs/brick3 server1:/rhgs/brick4 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick2 server2:/rhgs/brick3 server2:/rhgs/brick4 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick2 server3:/rhgs/brick3 server3:/rhgs/brick4 server1:/rhgs/brick5 server1:/rhgs/brick6 server1:/rhgs/brick7 server1:/rhgs/brick8 server2:/rhgs/brick5 server2:/rhgs/brick6 server2:/rhgs/brick7 server2:/rhgs/brick8 server3:/rhgs/brick5 server3:/rhgs/brick6 server3:/rhgs/brick7 server3:/rhgs/brick8 server1:/rhgs/brick9 server1:/rhgs/brick10 server1:/rhgs/brick11 server1:/rhgs/brick12 server2:/rhgs/brick9 server2:/rhgs/brick10 server2:/rhgs/brick11 server2:/rhgs/brick12 server3:/rhgs/brick9 server3:/rhgs/brick10 server3:/rhgs/brick11 server3:/rhgs/brick12 --force
# gluster volume create test_vol disperse-data 8 redundancy 4 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server1:/rhgs/brick2 server1:/rhgs/brick3 server1:/rhgs/brick4 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick2 server2:/rhgs/brick3 server2:/rhgs/brick4 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick2 server3:/rhgs/brick3 server3:/rhgs/brick4 server1:/rhgs/brick5 server1:/rhgs/brick6 server1:/rhgs/brick7 server1:/rhgs/brick8 server2:/rhgs/brick5 server2:/rhgs/brick6 server2:/rhgs/brick7 server2:/rhgs/brick8 server3:/rhgs/brick5 server3:/rhgs/brick6 server3:/rhgs/brick7 server3:/rhgs/brick8 server1:/rhgs/brick9 server1:/rhgs/brick10 server1:/rhgs/brick11 server1:/rhgs/brick12 server2:/rhgs/brick9 server2:/rhgs/brick10 server2:/rhgs/brick11 server2:/rhgs/brick12 server3:/rhgs/brick9 server3:/rhgs/brick10 server3:/rhgs/brick11 server3:/rhgs/brick12 --force--force parameter is required because this configuration is not optimal in terms of fault tolerance. Since each server provides more than one brick, this configuration has a greater risk to data availability if a server goes offline than it would if each brick was provided by a separate server.
Figure 11.1. Example Configuration of 8+4 Dispersed Volume Configuration
m bricks (refer to section Section 5.9, “Creating Dispersed Volumes” for information on n = k+m equation) from a dispersed subvolume on each server. If you add more than m bricks from a dispersed subvolume on server S, and if the server S goes down, data will be unavailable.
S (a single column in the above diagram) goes down, there is no data loss, but if there is any additional hardware failure, either another node going down or a storage device failure, there would be immediate data loss.
The following diagram illustrates dispersed 4+2 configuration on six servers and each server with 12-disk-per-server configuration as explained in the row 2 of Table 11.3, “Brick Configurations for Dispersed and Distributed Dispersed Volumes”. The command to create the disperse volume for this configuration:
gluster volume create test_vol disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 server6:/rhgs/brick1server1:/rhgs/brick2 server2:/rhgs/brick2 server3:/rhgs/brick2 server4:/rhgs/brick2 server5:/rhgs/brick2 server6:/rhgs/brick2 server1:/rhgs/brick3 server2:/rhgs/brick3 server3:/rhgs/brick3 server4:/rhgs/brick3 server5:/rhgs/brick3 server6:/rhgs/brick3 server1:/rhgs/brick4 server2:/rhgs/brick4 server3:/rhgs/brick4 server4:/rhgs/brick4 server5:/rhgs/brick4 server6:/rhgs/brick4 server1:/rhgs/brick5 server2:/rhgs/brick5 server3:/rhgs/brick5 server4:/rhgs/brick5 server5:/rhgs/brick5 server6:/rhgs/brick5 server1:/rhgs/brick6 server2:/rhgs/brick6 server3:/rhgs/brick6 server4:/rhgs/brick6 server5:/rhgs/brick6 server6:/rhgs/brick6 server1:/rhgs/brick7 server2:/rhgs/brick7 server3:/rhgs/brick7 server4:/rhgs/brick7 server5:/rhgs/brick7 server6:/rhgs/brick7 server1:/rhgs/brick8 server2:/rhgs/brick8 server3:/rhgs/brick8 server4:/rhgs/brick8 server5:/rhgs/brick8 server6:/rhgs/brick8 server1:/rhgs/brick9 server2:/rhgs/brick9 server3:/rhgs/brick9 server4:/rhgs/brick9 server5:/rhgs/brick9 server6:/rhgs/brick9 server1:/rhgs/brick10 server2:/rhgs/brick10 server3:/rhgs/brick10 server4:/rhgs/brick10 server5:/rhgs/brick10 server6:/rhgs/brick10 server1:/rhgs/brick11 server2:/rhgs/brick11 server3:/rhgs/brick11 server4:/rhgs/brick11 server5:/rhgs/brick11 server6:/rhgs/brick11 server1:/rhgs/brick12 server2:/rhgs/brick12 server3:/rhgs/brick12 server4:/rhgs/brick12 server5:/rhgs/brick12 server6:/rhgs/brick12
# gluster volume create test_vol disperse-data 4 redundancy 2 transport tcp server1:/rhgs/brick1 server2:/rhgs/brick1 server3:/rhgs/brick1 server4:/rhgs/brick1 server5:/rhgs/brick1 server6:/rhgs/brick1server1:/rhgs/brick2 server2:/rhgs/brick2 server3:/rhgs/brick2 server4:/rhgs/brick2 server5:/rhgs/brick2 server6:/rhgs/brick2 server1:/rhgs/brick3 server2:/rhgs/brick3 server3:/rhgs/brick3 server4:/rhgs/brick3 server5:/rhgs/brick3 server6:/rhgs/brick3 server1:/rhgs/brick4 server2:/rhgs/brick4 server3:/rhgs/brick4 server4:/rhgs/brick4 server5:/rhgs/brick4 server6:/rhgs/brick4 server1:/rhgs/brick5 server2:/rhgs/brick5 server3:/rhgs/brick5 server4:/rhgs/brick5 server5:/rhgs/brick5 server6:/rhgs/brick5 server1:/rhgs/brick6 server2:/rhgs/brick6 server3:/rhgs/brick6 server4:/rhgs/brick6 server5:/rhgs/brick6 server6:/rhgs/brick6 server1:/rhgs/brick7 server2:/rhgs/brick7 server3:/rhgs/brick7 server4:/rhgs/brick7 server5:/rhgs/brick7 server6:/rhgs/brick7 server1:/rhgs/brick8 server2:/rhgs/brick8 server3:/rhgs/brick8 server4:/rhgs/brick8 server5:/rhgs/brick8 server6:/rhgs/brick8 server1:/rhgs/brick9 server2:/rhgs/brick9 server3:/rhgs/brick9 server4:/rhgs/brick9 server5:/rhgs/brick9 server6:/rhgs/brick9 server1:/rhgs/brick10 server2:/rhgs/brick10 server3:/rhgs/brick10 server4:/rhgs/brick10 server5:/rhgs/brick10 server6:/rhgs/brick10 server1:/rhgs/brick11 server2:/rhgs/brick11 server3:/rhgs/brick11 server4:/rhgs/brick11 server5:/rhgs/brick11 server6:/rhgs/brick11 server1:/rhgs/brick12 server2:/rhgs/brick12 server3:/rhgs/brick12 server4:/rhgs/brick12 server5:/rhgs/brick12 server6:/rhgs/brick12
Figure 11.2. Example Configuration of 4+2 Dispersed Volume Configuration
The following chart illustrates the redundancy comparison of all supported dispersed volume configurations.
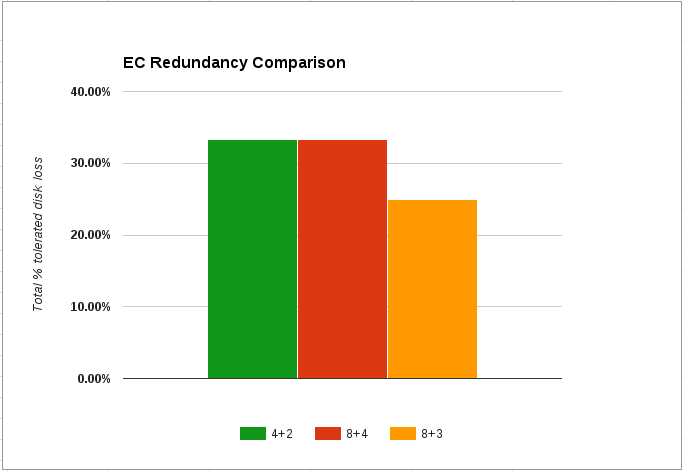
Figure 11.3. Illustration of the redundancy comparison
Chapter 12. Managing Red Hat Gluster Storage Logs
log-file-name.epoch-time-stamp.The components for which the log messages are generated with message-ids are glusterFS Management Service, Distributed Hash Table (DHT), and Automatic File Replication (AFR).
12.1. Log Rotation
12.2. Red Hat Gluster Storage Component Logs and Location
/var/log directory.
| Component/Service Name | Location of the Log File | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| glusterd | /var/log/glusterfs/glusterd.log | One glusterd log file per server. This log file also contains the snapshot and user logs. |
| gluster commands | /var/log/glusterfs/cmd_history.log | Gluster commands executed on a node in a Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool is logged in this file. |
| bricks | /var/log/glusterfs/bricks/<path extraction of brick path>.log | One log file per brick on the server |
| rebalance | /var/log/glusterfs/VOLNAME-rebalance.log | One log file per volume on the server |
| self heal deamon | /var/log/glusterfs/glustershd.log | One log file per server |
| quota |
| One log file per server (and per volume from quota-mount. |
| Gluster NFS | /var/log/glusterfs/nfs.log | One log file per server |
| SAMBA Gluster | /var/log/samba/glusterfs-VOLNAME-<ClientIP>.log | If the client mounts this on a glusterFS server node, the actual log file or the mount point may not be found. In such a case, the mount outputs of all the glusterFS type mount operations need to be considered. |
| NFS - Ganesha | /var/log/ganesha/ganesha.log, /var/log/ganesha/ganesha-gfapi.log | One log file per server |
| FUSE Mount | /var/log/ glusterfs/<mountpoint path extraction>.log | |
| Geo-replication | /var/log/glusterfs/geo-replication/<master> /var/log/glusterfs/geo-replication-slaves | |
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info command | /var/log/glusterfs/glfsheal-VOLNAME.log | One log file per server on which the command is executed. |
| gluster-swift | /var/log/messages | |
| SwiftKrbAuth | /var/log/httpd/error_log | |
| Command Line Interface logs | /var/log/glusterfs/cli.log | This file captures log entries for every command that is executed on the Command Line Interface(CLI). |
12.3. Configuring the Log Format
gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-format <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-format <value>Example 12.1. Generate log files with with-msg-id:
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-format with-msg-id
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-format with-msg-idExample 12.2. Generate log files with no-msg-id:
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-format no-msg-id
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-format no-msg-idgluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-format <value>
gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-format <value>Example 12.3. Generate log files with with-msg-id:
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-format with-msg-id
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-format with-msg-idExample 12.4. Generate log files with no-msg-id:
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-format no-msg-id
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-format no-msg-idglusterd:
glusterd --log-format=<value>
# glusterd --log-format=<value>Example 12.5. Generate log files with with-msg-id:
glusterd --log-format=with-msg-id
# glusterd --log-format=with-msg-idExample 12.6. Generate log files with no-msg-id:
glusterd --log-format=no-msg-id
# glusterd --log-format=no-msg-id12.4. Configuring the Log Level
INFO, only CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, and INFO messages are logged.
- CRITICAL
- ERROR
- WARNING
- INFO
- DEBUG
- TRACE
Important
gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-level <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-level <value>Example 12.7. Set the log level to warning on a brick
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-level WARNING
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-level WARNINGgluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-sys-log-level <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-sys-log-level <value>Example 12.8. Set the syslog level to warning on a brick
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-sys-log-level WARNING
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-sys-log-level WARNINGgluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-level <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-level <value>Example 12.9. Set the log level to error on a client
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-level ERROR
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-level ERRORgluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-sys-log-level <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-sys-log-level <value>Example 12.10. Set the syslog level to error on a client
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-sys-log-level ERROR
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-sys-log-level ERRORglusterd persistently
/etc/sysconfig/glusterd file, and set the value of the LOG_LEVEL parameter to the log level that you want glusterd to use.
## Set custom log file and log level (below are defaults) #LOG_FILE='/var/log/glusterfs/glusterd.log' LOG_LEVEL='VALUE'
## Set custom log file and log level (below are defaults)
#LOG_FILE='/var/log/glusterfs/glusterd.log'
LOG_LEVEL='VALUE'service or systemctl command.
Example 12.11. Set the log level to WARNING on glusterd
/etc/sysconfig/glusterd file, locate the LOG_LEVEL parameter and set its value to WARNING.
## Set custom log file and log level (below are defaults) #LOG_FILE='/var/log/glusterfs/glusterd.log' LOG_LEVEL='WARNING'
## Set custom log file and log level (below are defaults)
#LOG_FILE='/var/log/glusterfs/glusterd.log'
LOG_LEVEL='WARNING'systemctl restart glusterd.service
# systemctl restart glusterd.serviceservice glusterd restart
# service glusterd restartgluster --log-level=ERROR VOLNAME COMMAND
# gluster --log-level=ERROR VOLNAME COMMANDExample 12.12. Run volume status with a log level of ERROR
gluster --log-level=ERROR volume status
# gluster --log-level=ERROR volume status12.5. Suppressing Repetitive Log Messages
log-flush-timeout period and by defining a log-buf-size buffer size options with the gluster volume set command.
gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-flush-timeout <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-flush-timeout <value>Example 12.13. Set a timeout period on the bricks
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-flush-timeout 200 volume set: success
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-flush-timeout 200
volume set: successgluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-flush-timeout <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-flush-timeout <value>Example 12.14. Set a timeout period on the clients
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-flush-timeout 180 volume set: success
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-flush-timeout 180
volume set: successglusterd:
glusterd --log-flush-timeout=<value>
# glusterd --log-flush-timeout=<value>Example 12.15. Set a timeout period on the glusterd
glusterd --log-flush-timeout=60
# glusterd --log-flush-timeout=60The maximum number of unique log messages that can be suppressed until the timeout or buffer overflow, whichever occurs first on the bricks.
gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-buf-size <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.brick-log-buf-size <value>Example 12.16. Set a buffer size on the bricks
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-buf-size 10 volume set: success
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.brick-log-buf-size 10
volume set: successgluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-buf-size <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME diagnostics.client-log-buf-size <value>Example 12.17. Set a buffer size on the clients
gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-buf-size 15 volume set: success
# gluster volume set testvol diagnostics.client-log-buf-size 15
volume set: successglusterd:
glusterd --log-buf-size=<value>
# glusterd --log-buf-size=<value>Example 12.18. Set a log buffer size on the glusterd
glusterd --log-buf-size=10
# glusterd --log-buf-size=10Note
12.6. Geo-replication Logs
Master-log-file- log file for the process that monitors the master volume.Slave-log-file- log file for process that initiates changes on a slave.Master-gluster-log-file- log file for the maintenance mount point that the geo-replication module uses to monitor the master volume.Slave-gluster-log-file- If the slave is a Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume, this log file is the slave's counterpart ofMaster-gluster-log-file.
12.6.1. Viewing the Geo-replication Master Log Files
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config log-file
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config log-filegluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol config log-file
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol config log-file12.6.2. Viewing the Geo-replication Slave Log Files
glusterd must be running on slave machine.
- On the master, run the following command to display the session-owner details:
gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config session-owner
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config session-ownerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol config session-owner 5f6e5200-756f-11e0-a1f0-0800200c9a66
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol config session-owner 5f6e5200-756f-11e0-a1f0-0800200c9a66Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On the slave, run the following command with the session-owner value from the previous step:
gluster volume geo-replication SLAVE_VOL config log-file /var/log/gluster/SESSION_OWNER:remote-mirror.log
# gluster volume geo-replication SLAVE_VOL config log-file /var/log/gluster/SESSION_OWNER:remote-mirror.logCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol config log-file /var/log/gluster/5f6e5200-756f-11e0-a1f0-0800200c9a66:remote-mirror.log
# gluster volume geo-replication slave-vol config log-file /var/log/gluster/5f6e5200-756f-11e0-a1f0-0800200c9a66:remote-mirror.logCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 13. Managing Red Hat Gluster Storage Volume Life-Cycle Extensions
- Creating a volume
- Starting a volume
- Adding a brick
- Removing a brick
- Tuning volume options
- Stopping a volume
- Deleting a volume
Note
13.1. Location of Scripts
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/create/
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/delete/
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/start/
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/stop/
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/set/
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/add-brick/
- /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/remove-brick/
--volname=VOLNAME to specify the volume. Command-specific additional arguments are provided for the following volume operations:
- Start volume
--first=yes, if the volume is the first to be started--first=no, for otherwise
- Stop volume
--last=yes, if the volume is to be stopped last.--last=no, for otherwise
- Set volume
-o key=valueFor every key, value is specified in volume set command.
13.2. Prepackaged Scripts
/var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/start/post and /var/lib/glusterd/hooks/1/stop/pre. By default, the scripts are enabled.
# gluster volume start VOLNAME
S30samba-start.sh script performs the following:
- Adds Samba share configuration details of the volume to the
smb.conffile - Mounts the volume through FUSE and adds an entry in
/etc/fstabfor the same. - Restarts Samba to run with updated configuration
# gluster volume stop VOLNAME
S30samba-stop.sh script performs the following:
- Removes the Samba share details of the volume from the
smb.conffile - Unmounts the FUSE mount point and removes the corresponding entry in
/etc/fstab - Restarts Samba to run with updated configuration
Chapter 14. Detecting BitRot
gluster volume bitrot command scans all the bricks in a volume for BitRot issues in a process known as scrubbing. The process calculates the checksum for each file or object, and compares that checksum against the actual data of the file. When BitRot is detected in a file, that file is marked as corrupted, and the detected errors are logged in the following files:
- /var/log/glusterfs/bitd.log
- /var/log/glusterfs/scrub.log
14.1. Enabling and Disabling the BitRot daemon
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME enable- Enable the BitRot daemon for the specified volume.
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME disable- Disable the BitRot daemon for the specified volume.
14.2. Modifying BitRot Detection Behavior
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME scrub ondemand- Starts the scrubbing process and the scrubber will start crawling the file system immediately. Ensure to keep the scrubber in 'Active (Idle)' state, where the scrubber is waiting for it's next frequency cycle to start scrubbing, for on demand scrubbing to be successful. On demand scrubbing does not work when the scrubber is in 'Paused' state or already running.
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME scrub pause- Pauses the scrubbing process on the specified volume. Note that this does not stop the BitRot daemon; it stops the process that cycles through the volume checking files.
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME scrub resume- Resumes the scrubbing process on the specified volume. Note that this does not start the BitRot daemon; it restarts the process that cycles through the volume checking files.
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME scrub status- This command prints a summary of scrub status on the specified volume, including various configuration details and the location of the bitrot and scrubber error logs for this volume. It also prints details each node scanned for errors, along with identifiers for any corrupted objects located.
gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME scrub-throttle rate- Because the BitRot daemon scrubs the entire file system, scrubbing can have a severe performance impact. This command changes the rate at which files and objects are verified. Valid rates are
lazy,normal, andaggressive. By default, the scrubber process is started inlazymode. gluster volume bitrot VOLNAME scrub-frequency frequency- This command changes how often the scrub operation runs when the BitRot daemon is enabled. Valid options are
daily,weekly,biweekly, andmonthly.By default, the scrubber process is set to runbiweekly.
14.3. Restoring a bad file
Important
-oaux-gfid-mount mount option, and enable GFID-to-path translation on each volume by running the following command.
gluster volume set VOLNAME build-pgfid on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME build-pgfid onfind command.
Procedure 14.1. Restoring a bad file from a replicate volume
Note the identifiers of bad files
Check the output of thescrub statuscommand to determine the identifiers of corrupted files.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Determine the path of each corrupted object
For files created after GFID-to-path translation was enabled, use thegetfattrcommand to determine the path of the corrupted files.getfattr -n glusterfs.ancestry.path -e text /mnt/VOLNAME/.gfid/GFID ... glusterfs.ancestry.path="/path/to/corrupted_file"
# getfattr -n glusterfs.ancestry.path -e text /mnt/VOLNAME/.gfid/GFID ... glusterfs.ancestry.path="/path/to/corrupted_file"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For files created before GFID-to-path translation was enabled, use thefindcommand to determine the path of the corrupted file and the index file that match the identifying GFID.find /rhgs/brick*/.glusterfs -name GFID /rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/path/to/GFID
# find /rhgs/brick*/.glusterfs -name GFID /rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/path/to/GFIDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow find /rhgs -samefile /rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/path/to/GFID /rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/path/to/GFID /rhgs/brick1/path/to/corrupted_file
# find /rhgs -samefile /rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/path/to/GFID /rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/path/to/GFID /rhgs/brick1/path/to/corrupted_fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the corrupted files
Delete the corrupted files from the path output by thegetfattrorfindcommand.Delete the GFID file
Delete the GFID file from the/rhgs/brickN/.glusterfsdirectory.Restore the file
Follow these steps to safely restore corrupt files.Disable metadata caching
If the metadata cache is enabled, disable it by running the following command:gluster volume set VOLNAME stat-prefetch off
# gluster volume set VOLNAME stat-prefetch offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a recovery mount point
Create a mount point to use for the recovery process. For example,/mnt/recovery.mkdir /mnt/recovery
# mkdir /mnt/recoveryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount the volume with timeouts disabled
mount -t glusterfs -o attribute-timeout=0,entry-timeout=0 hostname:volume-path /mnt/recovery
# mount -t glusterfs -o attribute-timeout=0,entry-timeout=0 hostname:volume-path /mnt/recoveryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Heal files and hard links
Access files and hard links to heal them. For example, run thestatcommand on the files and hard links you need to heal.stat /mnt/recovery/corrupt-file
$ stat /mnt/recovery/corrupt-fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you do not have client self-heal enabled, you must manually heal the volume with the following command.gluster volume heal VOLNAME
# gluster volume heal VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Unmount and optionally remove the recovery mount point
umount /mnt/recovery rmdir /mnt/recovery
# umount /mnt/recovery # rmdir /mnt/recoveryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Re-enable metadata caching
If the metadata cache was enabled previously, re-enable it by running the following command:gluster volume set VOLNAME stat-prefetch on
# gluster volume set VOLNAME stat-prefetch onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 15. Incremental Backup Assistance using Glusterfind
15.1. Glusterfind Configuration Options
- Glusterfind Create
- Glusterfind Pre
- Glusterfind Post
- Glusterfind Query
- Glusterfind List
- Glusterfind Delete
Note
To create a session for a particular instance in the volume, execute the following command:
glusterfind create [-h] [--debug] [--force] <SessionName> <volname> [--reset-session-time]
# glusterfind create [-h] [--debug] [--force] <SessionName> <volname> [--reset-session-time]create command is executed.
glusterfind create sess_vol1 vol1 Session sess_vol1 created with volume vol1
# glusterfind create sess_vol1 vol1
Session sess_vol1 created with volume vol1
To retrieve the list of modified files and directories and store it in the outfile, execute the following command:
glusterfind pre [--debug] [--disable-partial] [--output-prefix OUTPUT_PREFIX] [--no-encode] [--regenerate-outfile] [--field-separator FIELD_SEPARATOR] [-h] <session> <volname> <outfile>
# glusterfind pre [--debug] [--disable-partial] [--output-prefix OUTPUT_PREFIX] [--no-encode] [--regenerate-outfile] [--field-separator FIELD_SEPARATOR] [-h] <session> <volname> <outfile>
pre command is executed.
glusterfind pre sess_vol1 vol1 /tmp/outfile.txt Generated output file /tmp/outfile.txt
# glusterfind pre sess_vol1 vol1 /tmp/outfile.txt
Generated output file /tmp/outfile.txt
Note
NEW file1 NEW dir1%2Ffile2 MODIFY dir3%2Fdir4%2Ftest3 RENAME test1 dir1%2F%2Ftest1new DELETE test2
NEW file1
NEW dir1%2Ffile2
MODIFY dir3%2Fdir4%2Ftest3
RENAME test1 dir1%2F%2Ftest1new
DELETE test2--no-encode option
The following command is run to update the session time:
glusterfind post [-h] [--debug] <SessionName> <volname>
# glusterfind post [-h] [--debug] <SessionName> <volname>
post command is executed.
glusterfind post sess_vol1 vol1 Session sess_vol1 with volume vol1 updated
# glusterfind post sess_vol1 vol1
Session sess_vol1 with volume vol1 updatedTo list all the active sessions and the corresponding volumes present in the cluster, execute the following command:
glusterfind list [-h] [--session SESSION] [--volume VOLUME] [--debug]
# glusterfind list [-h] [--session SESSION] [--volume VOLUME] [--debug]
glusterfind list SESSION VOLUME SESSION TIME -------------------------------------------------- sess_vol1 vol1 2015-06-22 22:22:53
# glusterfind list
SESSION VOLUME SESSION TIME
--------------------------------------------------
sess_vol1 vol1 2015-06-22 22:22:53
The glusterfind query subcommand provides a list of changed files based on a specified time stamp. These commands do not check any change log information. Use the glusterfind query subcommand when your backup software maintains its own checkpoints and time stamps outside glusterfind.
glusterfind query volname --since-time timestamp1 --end-time timestamp2 output_file.txt
# glusterfind query volname --since-time timestamp1 --end-time timestamp2 output_file.txtecho $(date +'%s') on the command line.
glusterfind query volname --full output_file.txt
# glusterfind query volname --full output_file.txtglusterfind query volname --full --tag-for-full-find NEW output_file.txt
# glusterfind query volname --full --tag-for-full-find NEW output_file.txt--field-separator option. The following command sets the field separator to ==.
gluster query volname --full output_file.txt --field-separator "=="
# gluster query volname --full output_file.txt --field-separator "=="To clear out all the session information associated with that particular session, execute the following command:
glusterfind delete [-h] [--debug] <SessionName> <volname>
# glusterfind delete [-h] [--debug] <SessionName> <volname>delete command is executed.
glusterfind delete sess_vol1 vol1 Session sess_vol1 with volume vol1 deleted
# glusterfind delete sess_vol1 vol1
Session sess_vol1 with volume vol1 deleted15.1.1. Adding or Replacing a Brick from an Existing Glusterfind Session
glusterfind create command with force for the existing session to work. For example:
glusterfind create existing-session volname --force
# glusterfind create existing-session volname --forceChapter 16. Managing Tiering
Important
The hot tier is the tiering volume created using better performing subvolumes, an example of which could be SSDs. Frequently accessed data is placed in the highest performance and most expensive hot tier. Hot tier volume could be a distributed volume or distributed-replicated volume.
Warning
The cold tier is the existing Red Hat Gluster Storage volume created using slower storage such as Spinning disks. Inactive or infrequently accessed data is placed in the lowest-cost cold tier.
Tiering automatically migrates files between hot tier and cold tier to improve the storage performance and resource use.
16.1. Tiering Architecture
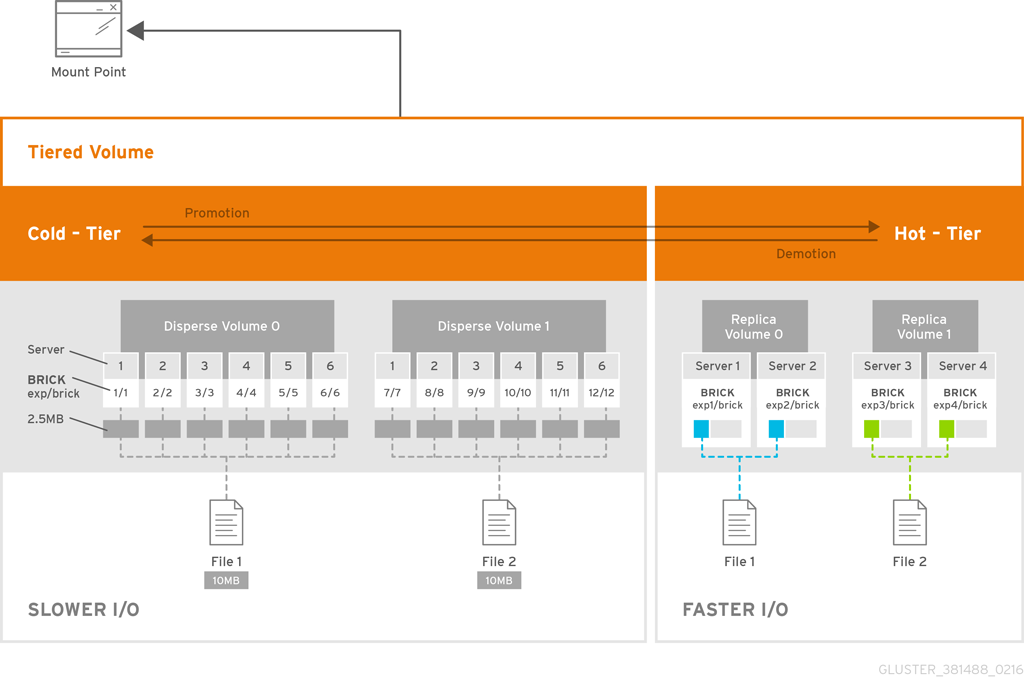
Figure 16.1. Tiering Architecture
16.2. Key Benefits of Tiering
- Automatic classification and movement of files based on the access patterns
- Faster response time and reduced latency
- Better I/O performance
- Improved data-storage efficiency
- Reduced deployment and operating costs
16.3. Tiering Limitations
- Native client support for tiering is limited to Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 6.7, 6.8 and 7.x clients. Tiered volumes cannot be mounted by Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.x clients.
- Tiering works only with
cache friendlyworkloads. Attaching a tier volume to a cache unfriendly workload will lead to slow performance. In acache friendlyworkload, most of the reads and writes are accessing a subset of the total amount of data. And, this subset fits on the hot tier. This subset should change only infrequently. - Tiering feature is supported only on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based Red Hat Gluster Storage. Tiering feature is not supported on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based Red Hat Gluster Storage.
- Only Fuse and gluster-nfs access is supported. Server Message Block (SMB) and nfs-ganesha access to tiered volume is not supported.
- Creating snapshot of a tiered volume is supported. Snapshot clones are not supported with the tiered volumes.
- When you run
tier detach commitortier detach force, ongoing I/O operations may fail with a Transport endpoint is not connected error. - Files with hardlinks and softlinks are not migrated.
- Files on which POSIX locks has been taken are not migrated until all locks are released.
- Add brick, remove brick, and rebalance operations are not supported on the tiered volume. For information on expanding a tiered volume, see Section 11.7.1, “Expanding a Tiered Volume” and for information on shrinking a tiered volume, see Section 11.8.2, “Shrinking a Tiered Volume ”
16.4. Attaching a Tier to a Volume
attach command will declare an existing volume as cold tier and creates a new hot tier volume which is appended to it. Together, the combination is a single tiered volume.
- Attach the tier to the volume by executing the following command:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME attach [replica COUNT] NEW-BRICK...For example,gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/brick5/b1 server2:/rhgs/brick6/b2 server1:/rhgs/brick7/b3 server2:/rhgs/brick8/b4
# gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/brick5/b1 server2:/rhgs/brick6/b2 server1:/rhgs/brick7/b3 server2:/rhgs/brick8/b4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run
gluster volume infocommand to optionally display the volume information.The command output displays information similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
gluster volume tier VOLNAME start force command.
16.4.1. Attaching a Tier to a Geo-replicated Volume
Important
performance.quick-read option is enabled and geo-replicated from a tiered master volume. If the master volume is a tiered volume, you must disable the performance.quick-read option in the Slave Volume using the following command:
gluster volume set Slavevol performance.quick-read off
# gluster volume set Slavevol performance.quick-read off- Stop geo-replication between the master and slave, using the following command:
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopFor example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol stop
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Attach the tier to the volume using the following command:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME attach [replica COUNT] NEW-BRICK...For example, to create a distributed-replicated tier volume with replica count two:gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/brick1/b1 server2:/rhgs/brick2/b2 server1:/rhgs/brick3/b3 server2:/rhgs/brick4/b4
# gluster volume tier test-volume attach replica 2 server1:/rhgs/brick1/b1 server2:/rhgs/brick2/b2 server1:/rhgs/brick3/b3 server2:/rhgs/brick4/b4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the geo-replication sessions, using the following command:
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startFor examplegluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol start
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify whether geo-replication session has started with tier's bricks, using the following command:
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL statusFor example,gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol status
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.5. Configuring a Tiering Volume
# gluster volume set VOLNAME key value
16.5.1. Configuring Watermarks
cache mode, the configured watermark values and the percentage of the hot tier that is full determine whether a file will be promoted or demoted. The cluster.watermark-low and cluster.watermark-hi volume options set the lower and upper watermark values respectively for a tier volume.
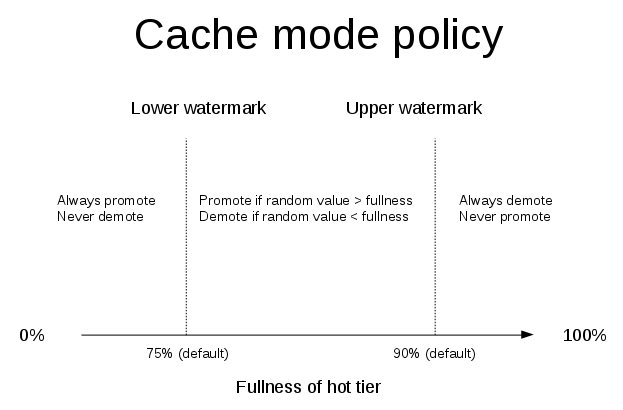
Figure 16.2. Tiering Watermarks
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.watermark-hi value
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.watermark-low value
16.5.2. Configuring Promote and Demote Frequency
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.tier-demote-frequency value_in_seconds
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.tier-promote-frequency value_in_seconds
16.5.3. Configuring Read and Write Frequency
HOT for promotion. Any file that has read or write hits less than this value will be considered as COLD and will be demoted. If the read/write access count is not set, then the default count is set to 0.
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.write-freq-threshold value
Note
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.read-freq-threshold value
Note
16.5.4. Configuring Target Data Size
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.tier-max-mb value_in_mb
cluster.tier-max-mb count is not set, then the default data size is set to 4000 MB.
16.5.5. Configuring the File Count per Cycle
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.tier-max-files count
cluster.tier-max-files count is not set, then the default count is set to 10000.
16.6. Displaying Tiering Status Information
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME status
16.7. Detaching a Tier from a Volume
- Start the detach tier by executing the following command:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME detach startFor example,gluster volume tier test-volume detach start
# gluster volume tier test-volume detach startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Monitor the status of detach tier until the status displays the status as complete.
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME detach statusFor example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
It is possible that some files are not migrated to the cold tier on a detach operation for various reasons like POSIX locks being held on them. Check for files on the hot tier bricks and you can either manually move the files, or turn off applications (which would presumably unlock the files) and stop/start detach tier, to retry. - When the tier is detached successfully as shown in the previous status command, run the following command to commit the tier detach:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME detach commitFor example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
tier detach commit or tier detach force, ongoing I/O operations may fail with a Transport endpoint is not connected error.
gluster volume info command.
16.7.1. Detaching a Tier of a Geo-replicated Volume
- Start the detach tier by executing the following command:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME detach startFor example,gluster volume tier test-volume detach start
# gluster volume tier test-volume detach startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Monitor the status of detach tier until the status displays the status as complete.
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME detach statusFor example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
There could be some number of files that were not moved. Such files may have been locked by the user, and that prevented them from moving to the cold tier on the detach operation. You must check for such files. If you find any such files, you can either manually move the files, or turn off applications (which would presumably unlock the files) and stop/start detach tier, to retry. - Set a checkpoint on a geo-replication session to ensure that all the data in that cold-tier is synced to the slave. For more information on geo-replication checkpoints, see Section 10.4.4.1, “Geo-replication Checkpoints”.
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL config checkpoint nowFor example,gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol config checkpoint now
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol config checkpoint nowCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Use the following command to verify the checkpoint completion for the geo-replication session
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL status detail - Stop geo-replication between the master and slave, using the following command:
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL stopFor example:gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol stop
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Commit the detach tier operation using the following command:
# gluster volume tier VOLNAME detach commitFor example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After the detach tier commit is completed, you can verify that the volume is no longer a tier volume by runninggluster volume infocommand. - Restart the geo-replication sessions, using the following command:
# gluster volume geo-replication MASTER_VOL SLAVE_HOST::SLAVE_VOL startFor example,gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol start
# gluster volume geo-replication Volume1 example.com::slave-vol startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Part V. Monitor and Tune
Chapter 17. Monitoring Red Hat Gluster Storage
- Red Hat Gluster Storage Web Administration Monitoring Guide
- Red Hat Gluster Storage Web Administration Quick Start Guide
Warning
- Nagios deployed on Red Hat Gluster Storage node.
- Nagios deployed on Red Hat Gluster Storage Console node.
- Nagios deployed on Red Hat Enterprise Linux node.

Figure 17.1. Nagios deployed on Red Hat Gluster Storage node
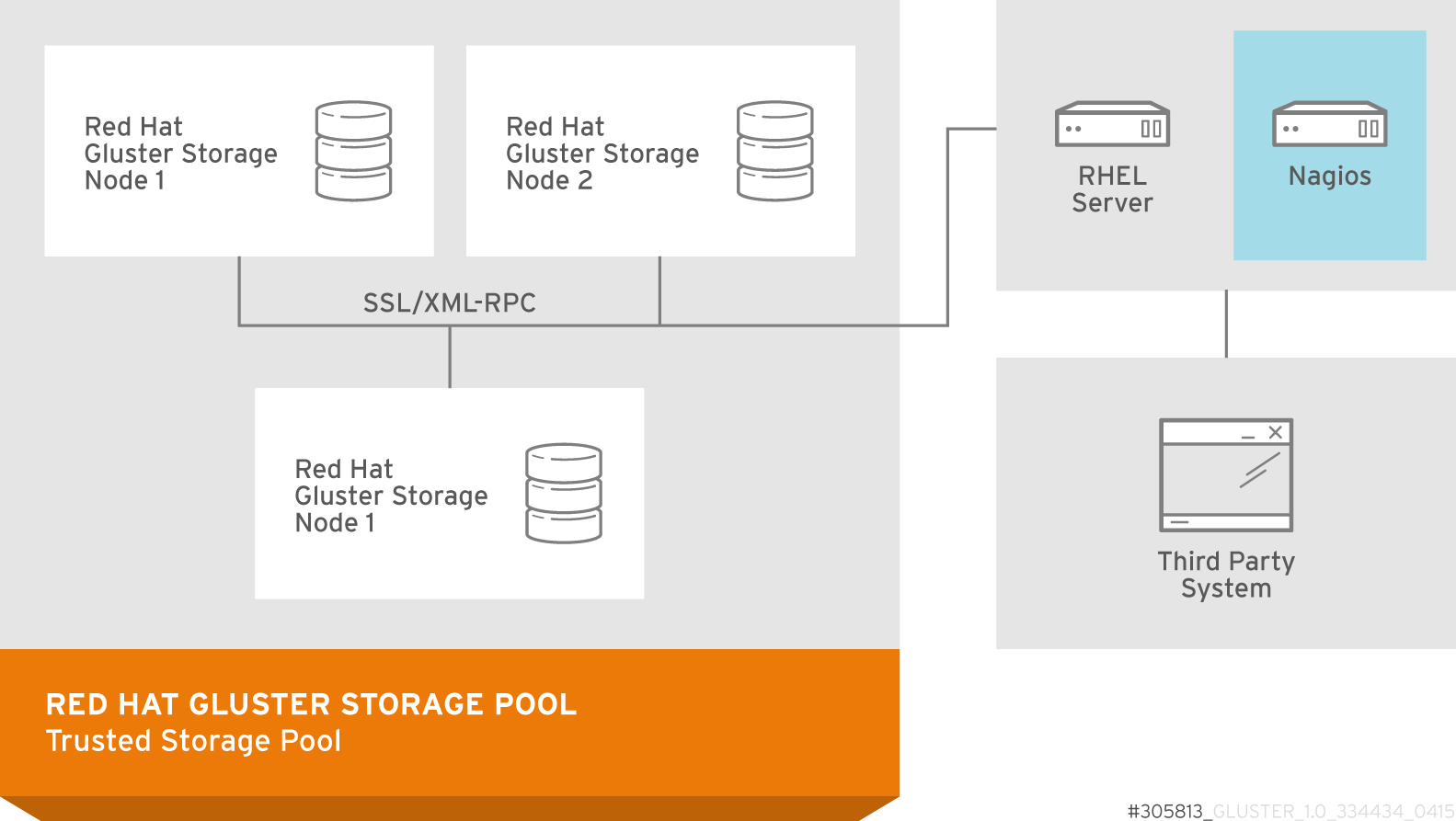
Figure 17.2. Nagios deployed on Red Hat Enterprise Linux node
17.1. Prerequisites
Note
- Registering using Subscription Manager and enabling Nagios repositories
- To install Nagios on Red Hat Gluster Storage node, subscribe to
rhs-nagios-3-for-rhel-6-server-rpmsrepository. - To install Nagios on Red Hat Enterprise Linux node, subscribe to
rhel-6-server-rpms,rhs-nagios-3-for-rhel-6-server-rpmsrepositories. - To install Nagios on Red Hat Gluster Storage node based on RHEL7, subscribe to
rh-gluster-3-nagios-for-rhel-7-server-rpmsrepository. - To install Nagios on Red Hat Enterprise Linux node, subscribe to
rhel-7-server-rpms,rh-gluster-3-nagios-for-rhel-7-server-rpmsrepositories.
- Registering using Red Hat Network (RHN) Classic and subscribing to Nagios channels
- To install Nagios on Red Hat Gluster Storage node, subscribe to
rhel-x86_64-server-6-rhs-nagios-3channel. - To install Nagios on Red Hat Gluster Storage node, subscribe to
rhel-x86_64-server-7-rh-gluster-3-nagioschannel. - To install Nagios on Red Hat Enterprise Linux node, subscribe to
rhel-x86_64-server-6,rhel-x86_64-server-6-rhs-nagios-3channels. - To install Nagios on Red Hat Enterprise Linux node, subscribe to
rhel-x86_64-server-7,rhel-x86_64-server-7-rh-gluster-3-nagioschannels.
Note
getsebool -a | grep nagios command:
nagios_run_sudo --> onnagios_run_pnp4nagios --> on
17.2. Installing Nagios
- nagios
- Core program, web interface and configuration files for Nagios server.
- python-cpopen
- Python package for creating sub-process in simple and safe manner.
- python-argparse
- Command line parser for python.
- libmcrypt
- Encryptions algorithm library.
- rrdtool
- Round Robin Database Tool to store and display time-series data.
- pynag
- Python modules and utilities for Nagios plugins and configuration.
- check-mk
- General purpose Nagios-plugin for retrieving data.
- mod_python
- An embedded Python interpreter for the Apache HTTP Server.
- nrpe
- Monitoring agent for Nagios.
- nsca
- Nagios service check acceptor.
- nagios-plugins
- Common monitoring plug-ins for nagios.
- gluster-nagios-common
- Common libraries, tools, configurations for Gluster node and Nagios server add-ons.
- nagios-server-addons
- Gluster node management add-ons for Nagios.
17.2.1. Installing Nagios Server
yum install nagios-server-addons
# yum install nagios-server-addons17.2.2. Configuring Red Hat Gluster Storage Nodes for Nagios
Note
setsebool -P logging_syslogd_run_nagios_plugins on setsebool -P nagios_run_sudo on
# setsebool -P logging_syslogd_run_nagios_plugins on
# setsebool -P nagios_run_sudo on- In
/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfgfile, add the central Nagios server IP address as shown below:allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1, NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1, NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the
NRPEservice using the following command:service nrpe restart
# service nrpe restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- The host name of the node is used while configuring Nagios server using auto-discovery. To view the host name, run
hostnamecommand. - Ensure that the host names are unique.
- Start the
glusterpmdservice using the following command:service glusterpmd start
# service glusterpmd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To startglusterpmdservice automatically when the system reboots, runchkconfig --add glusterpmdcommand.You can start theglusterpmdservice usingservice glusterpmd startcommand and stop the service usingservice glusterpmd stopcommand.Theglusterpmdservice is a Red Hat Gluster Storage process monitoring service running in every Red Hat Gluster Storage node to monitor glusterd, self heal, smb, quotad, ctdbd and brick services and to alert the user when the services go down. Theglusterpmdservice sends its managing services detailed status to the Nagios server whenever there is a state change on any of its managing services.This service uses/etc/nagios/nagios_server.conffile to get the Nagios server name and the local host name given in the Nagios server. Thenagios_server.confis configured by auto-discovery.
17.3. Monitoring Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool
17.3.1. Configuring Nagios
Note
configure-gluster-nagios command, ensure that all the Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes are configured as mentioned in Section 17.2.2, “Configuring Red Hat Gluster Storage Nodes for Nagios”.
- Execute the
configure-gluster-nagioscommand manually on the Nagios server using the following command:configure-gluster-nagios -c cluster-name -H HostName-or-IP-address
# configure-gluster-nagios -c cluster-name -H HostName-or-IP-addressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For-c, provide a cluster name (a logical name for the cluster) and for-H, provide the host name or ip address of a node in the Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool. - Perform the steps given below when
configure-gluster-nagioscommand runs:- Confirm the configuration when prompted.
- Enter the current Nagios server host name or IP address to be configured all the nodes.
- Confirm restarting Nagios server when prompted.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow All the hosts, volumes and bricks are added and displayed.
- Login to the Nagios server GUI using the following URL.
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
- The default Nagios user name and password is nagiosadmin / nagiosadmin.
- You can manually update/discover the services by executing the
configure-gluster-nagioscommand or by runningCluster Auto Configservice through Nagios Server GUI. - If the node with which auto-discovery was performed is down or removed from the cluster, run the
configure-gluster-nagioscommand with a different node address to continue discovering or monitoring the nodes and services. - If new nodes or services are added, removed, or if snapshot restore was performed on Red Hat Gluster Storage node, run
configure-gluster-nagioscommand.
17.3.2. Verifying the Configuration
- Verify the updated configurations using the following command:
nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
# nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If error occurs, verify the parameters set in/etc/nagios/nagios.cfgand update the configuration files. - Restart Nagios server using the following command:
service nagios restart
# service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Log into the Nagios server GUI using the following URL with the Nagios Administrator user name and password.
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
To change the default password, see Changing Nagios Password section in Red Hat Gluster Storage Administration Guide. - Click Services in the left pane of the Nagios server GUI and verify the list of hosts and services displayed.

Figure 17.3. Nagios Services
17.3.3. Using Nagios Server GUI
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
Figure 17.4. Nagios Login
To view the overview of the hosts and services being monitored, click Tactical Overview in the left pane. The overview of Network Outages, Hosts, Services, and Monitoring Features are displayed.
Figure 17.5. Tactical Overview
To view the status summary of all the hosts, click Summary under Host Groups in the left pane.
Figure 17.6. Host Groups Summary
Figure 17.7. Host Status
Note
To view the list of all hosts and their service status click Services in the left pane.
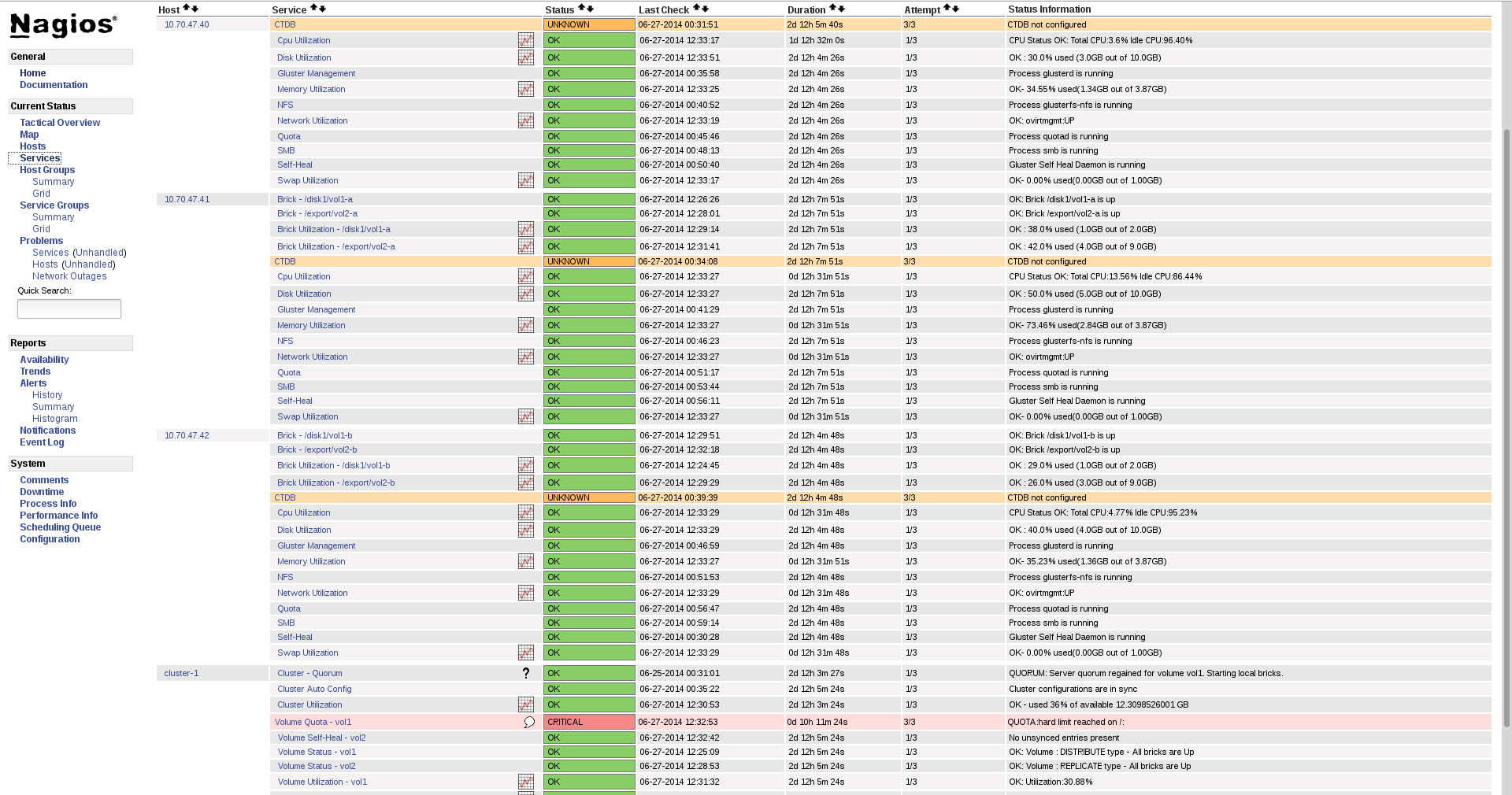
Figure 17.8. Service Status
Note
- Click
Hostsin the left pane. The list of hosts are displayed. - Click
 corresponding to the host name to view the host details.
corresponding to the host name to view the host details.
- Select the service name to view the Service State Information. You can view the utilization of the following services:
- Memory
- Swap
- CPU
- Network
- Brick
- DiskThe Brick/Disk Utilization Performance data has four sets of information for every mount point which are brick/disk space detail, inode detail of a brick/disk, thin pool utilization and thin pool metadata utilization if brick/disk is made up of thin LV.The Performance data for services is displayed in the following format: value[UnitOfMeasurement];warningthreshold;criticalthreshold;min;max.For Example,Performance Data: /bricks/brick2=31.596%;80;90;0;0.990 /bricks/brick2.inode=0.003%;80;90;0;1048064 /bricks/brick2.thinpool=19.500%;80;90;0;1.500 /bricks/brick2.thinpool-metadata=4.100%;80;90;0;0.004As part of disk utilization service, the following mount points will be monitored:
/ , /boot, /home, /var and /usrif available.
- To view the utilization graph, click
 corresponding to the service name. The utilization graph is displayed.
corresponding to the service name. The utilization graph is displayed.
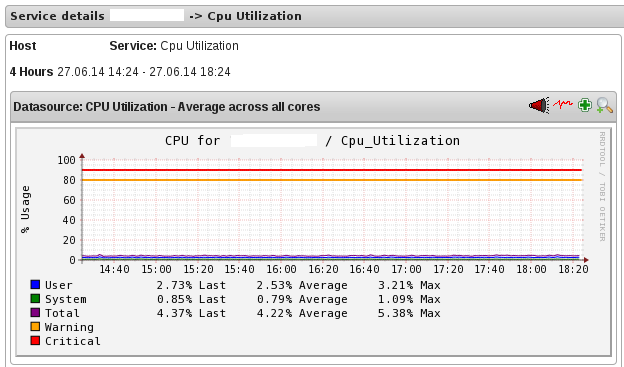
Figure 17.9. CPU Utilization
- To monitor status, click on the service name. You can monitor the status for the following resources:
- Disk
- Network
- To monitor process, click on the process name. You can monitor the following processes:
- Gluster NFS (Network File System)
- Self-Heal (Self-Heal)
- Gluster Management (glusterd)
- Quota (Quota daemon)
- CTDB
- SMB
Note
Monitoring Openstack Swift operations is not supported.
- Click
Hostsin the left pane. The list of hosts and clusters are displayed. - Click
 corresponding to the cluster name to view the cluster details.
corresponding to the cluster name to view the cluster details.
- To view utilization graph, click
 corresponding to the service name. You can monitor the following utilizations:
corresponding to the service name. You can monitor the following utilizations:
- Cluster
- Volume
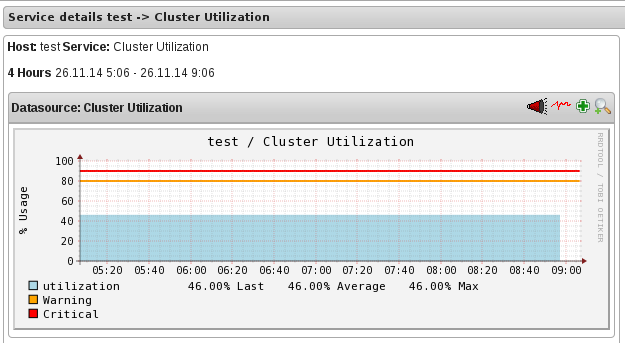
Figure 17.10. Cluster Utilization
- To monitor status, click on the service name. You can monitor the status for the following resources:
- Host
- Volume
- Brick
- To monitor cluster services, click on the service name. You can monitor the following:
- Volume Quota
- Volume Geo-replication
- Volume Split-Brain
- Cluster Quorum (A cluster quorum service would be present only when there are volumes in the cluster.)
If new nodes or services are added or removed, or if snapshot restore is performed on Red Hat Gluster Storage node, reschedule the Cluster Auto config service using Nagios Server GUI or execute the configure-gluster-nagios command. To synchronize the configurations using Nagios Server GUI, perform the steps given below:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI using the following URL in your browser with nagiosadmin user name and password.
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Services in left pane of Nagios server GUI and click Cluster Auto Config.
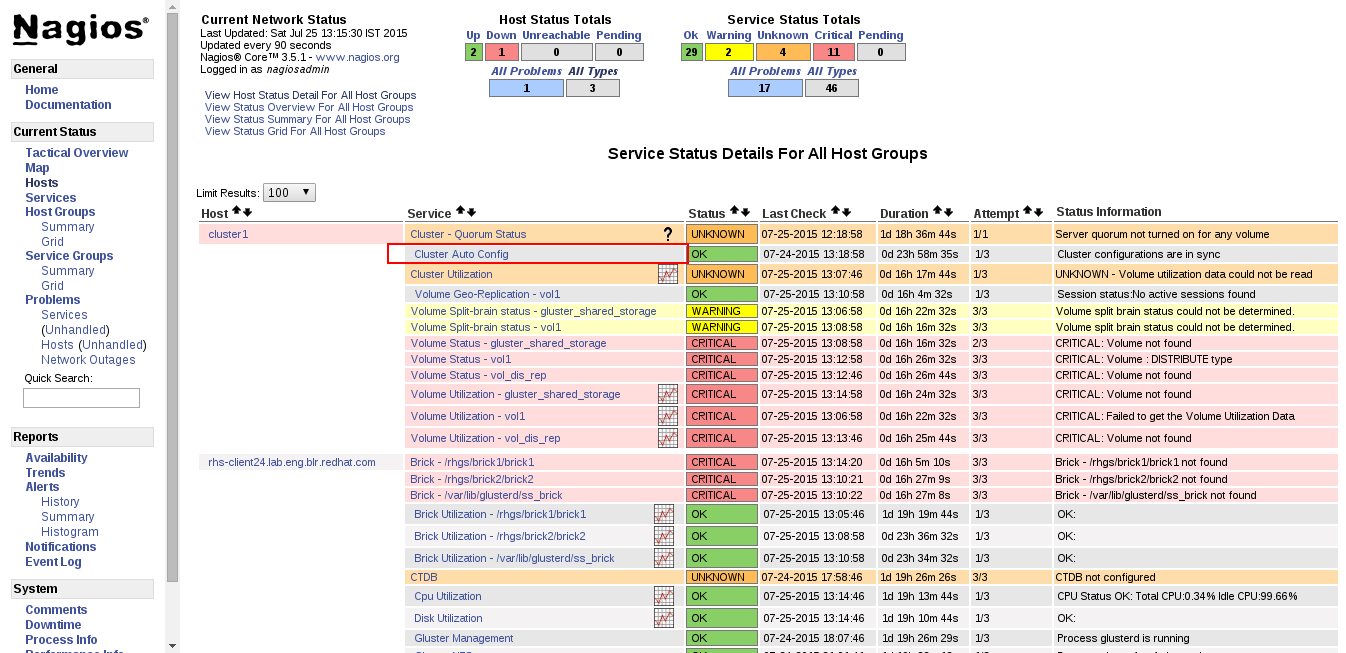
Figure 17.11. Nagios Services
- In Service Commands, click Re-schedule the next check of this service. The Command Options window is displayed.
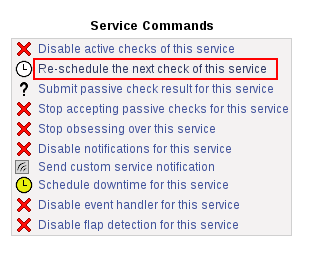
Figure 17.12. Service Commands
- In Command Options window, click .
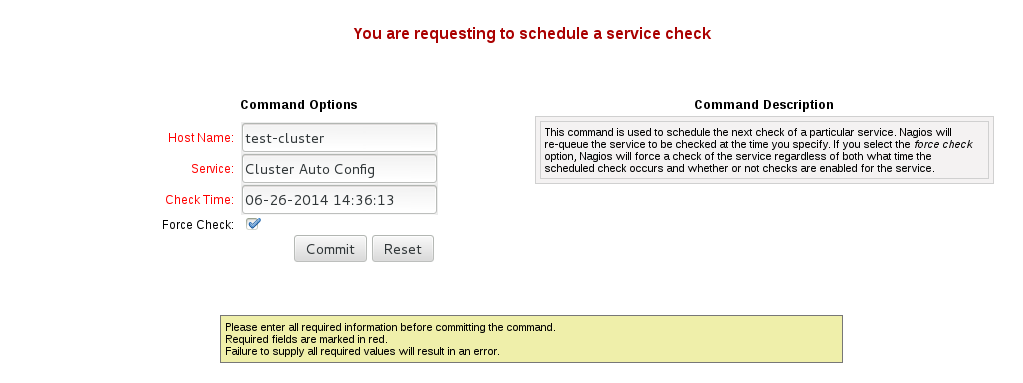
Figure 17.13. Command Options
You can enable or disable Host and Service notifications through Nagios GUI.
- To enable and disable Host Notifcations:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI using the following URL in your browser with
nagiosadminuser name and password.https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Hosts in left pane of Nagios server GUI and select the host.
- Click Enable notifications for this host or Disable notifications for this host in Host Commands section.
- Click Commit to enable or disable notification for the selected host.
- To enable and disable Service Notification:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI.
- Click Services in left pane of Nagios server GUI and select the service to enable or disable.
- Click Enable notifications for this service or Disable notifications for this service from the Service Commands section.
- Click Commit to enable or disable the selected service notification.
- To enable and disable all Service Notifications for a host:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI.
- Click Hosts in left pane of Nagios server GUI and select the host to enable or disable all services notifications.
- Click Enable notifications for all services on this host or Disable notifications for all services on this host from the Service Commands section.
- Click Commit to enable or disable all service notifications for the selected host.
- To enable or disable all Notifications:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI.
- Click Process Info under Systems section from left pane of Nagios server GUI.
- Click Enable notifications or Disable notifications in Process Commands section.
- Click Commit.
You can enable a service to monitor or disable a service you have been monitoring using the Nagios GUI.
- To enable Service Monitoring:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI using the following URL in your browser with
nagiosadminuser name and password.https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Services in left pane of Nagios server GUI and select the service to enable monitoring.
- Click Enable active checks of this service from the Service Commands and click Commit.
- Click Start accepting passive checks for this service from the Service Commands and click Commit.Monitoring is enabled for the selected service.
- To disable Service Monitoring:
- Login to the Nagios Server GUI using the following URL in your browser with
nagiosadminuser name and password.https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Services in left pane of Nagios server GUI and select the service to disable monitoring.
- Click Disable active checks of this service from the Service Commands and click Commit.
- Click Stop accepting passive checks for this service from the Service Commands and click Commit.Monitoring is disabled for the selected service.
Note
| Service Name | Status | Messsage | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMB | OK | OK: No gluster volume uses smb | When no volumes are exported through smb. |
| OK | Process smb is running | When SMB service is running and when volumes are exported using SMB. | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL: Process smb is not running | When SMB service is down and one or more volumes are exported through SMB. | |
| CTDB | UNKNOWN | CTDB not configured | When CTDB service is not running, and smb or nfs service is running. |
| CRITICAL | Node status: BANNED/STOPPED | When CTDB service is running but Node status is BANNED/STOPPED. | |
| WARNING | Node status: UNHEALTHY/DISABLED/PARTIALLY_ONLINE | When CTDB service is running but Node status is UNHEALTHY/DISABLED/PARTIALLY_ONLINE. | |
| OK | Node status: OK | When CTDB service is running and healthy. | |
| Gluster Management | OK | Process glusterd is running | When glusterd is running as unique. |
| WARNING | PROCS WARNING: 3 processes | When there are more then one glusterd is running. | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL: Process glusterd is not running | When there is no glusterd process running. | |
| UNKNOWN | NRPE: Unable to read output | When unable to communicate or read output | |
| Gluster NFS | OK | OK: No gluster volume uses nfs | When no volumes are configured to be exported through NFS. |
| OK | Process glusterfs-nfs is running | When glusterfs-nfs process is running. | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL: Process glusterfs-nfs is not running | When glusterfs-nfs process is down and there are volumes which requires NFS export. | |
| Auto-Config | OK | Cluster configurations are in sync | When auto-config has not detected any change in Gluster configuration. This shows that Nagios configuration is already in synchronization with the Gluster configuration and auto-config service has not made any change in Nagios configuration. |
| OK | Cluster configurations synchronized successfully from host host-address | When auto-config has detected change in the Gluster configuration and has successfully updated the Nagios configuration to reflect the change Gluster configuration. | |
| CRITICAL | Can't remove all hosts except sync host in 'auto' mode. Run auto discovery manually. | When the host used for auto-config itself is removed from the Gluster peer list. Auto-config will detect this as all host except the synchronized host is removed from the cluster. This will not change the Nagios configuration and the user need to manually run the auto-config. | |
| QUOTA | OK | OK: Quota not enabled | When quota is not enabled in any volumes. |
| OK | Process quotad is running | When glusterfs-quota service is running. | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL: Process quotad is not running | When glusterfs-quota service is down and quota is enabled for one or more volumes. | |
| CPU Utilization | OK | CPU Status OK: Total CPU:4.6% Idle CPU:95.40% | When CPU usage is less than 80%. |
| WARNING | CPU Status WARNING: Total CPU:82.40% Idle CPU:17.60% | When CPU usage is more than 80%. | |
| CRITICAL | CPU Status CRITICAL: Total CPU:97.40% Idle CPU:2.6% | When CPU usage is more than 90%. | |
| Memory Utilization | OK | OK- 65.49% used(1.28GB out of 1.96GB) | When used memory is below warning threshold. (Default warning threshold is 80%) |
| WARNING | WARNING- 85% used(1.78GB out of 2.10GB) | When used memory is below critical threshold (Default critical threshold is 90%) and greater than or equal to warning threshold (Default warning threshold is 80%). | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL- 92% used(1.93GB out of 2.10GB) | When used memory is greater than or equal to critical threshold (Default critical threshold is 90% ) | |
| Brick Utilization | OK | OK | When used space of any of the four parameters, space detail, inode detail, thin pool, and thin pool-metadata utilizations, are below threshold of 80%. |
| WARNING | WARNING:mount point /brick/brk1 Space used (0.857 / 1.000) GB | If any of the four parameters, space detail, inode detail, thin pool utilization, and thinpool-metadata utilization, crosses warning threshold of 80% (Default is 80%). | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL : mount point /brick/brk1 (inode used 9980/1000) | If any of the four parameters, space detail, inode detail, thin pool utilization, and thinpool-metadata utilizations, crosses critical threshold 90% (Default is 90%). | |
| Disk Utilization | OK | OK | When used space of any of the four parameters, space detail, inode detail, thin pool utilization, and thinpool-metadata utilizations, are below threshold of 80%. |
| WARNING | WARNING:mount point /boot Space used (0.857 / 1.000) GB | When used space of any of the four parameters, space detail, inode detail, thin pool utilization, and thinpool-metadata utilizations, are above warning threshold of 80%. | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL : mount point /home (inode used 9980/1000) | If any of the four parameters, space detail, inode detail, thin pool utilization, and thinpool-metadata utilizations, crosses critical threshold 90% (Default is 90%). | |
| Network Utilization | OK | OK: tun0:UP,wlp3s0:UP,virbr0:UP | When all the interfaces are UP. |
| WARNING | WARNING: tun0:UP,wlp3s0:UP,virbr0:DOWN | When any of the interfaces is down. | |
| UNKNOWN | UNKNOWN | When network utilization/status is unknown. | |
| Swap Utilization | OK | OK- 0.00% used(0.00GB out of 1.00GB) | When used memory is below warning threshold (Default warning threshold is 80%). |
| WARNING | WARNING- 83% used(1.24GB out of 1.50GB) | When used memory is below critical threshold (Default critical threshold is 90%) and greater than or equal to warning threshold (Default warning threshold is 80%). | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL- 83% used(1.42GB out of 1.50GB) | When used memory is greater than or equal to critical threshold (Default critical threshold is 90%). | |
| Cluster Quorum | PENDING | When cluster.server-quorum-type is not set to server; or when there are no problems in the cluster identified. | |
| OK | Quorum regained for volume | When quorum is regained for volume. | |
| CRITICAL | Quorum lost for volume | When quorum is lost for volume. | |
| Volume Geo-replication | OK | "Session Status: slave_vol1-OK .....slave_voln-OK. | When all sessions are active. |
| OK | Session status :No active sessions found | When Geo-replication sessions are deleted. | |
| CRITICAL | Session Status: slave_vol1-FAULTY slave_vol2-OK | If one or more nodes are Faulty and there's no replica pair that's active. | |
| WARNING | Session Status: slave_vol1-NOT_STARTED slave_vol2-STOPPED slave_vol3- PARTIAL_FAULTY |
| |
| WARNING | Geo replication status could not be determined. | When there's an error in getting Geo replication status. This error occurs when volfile is locked as another transaction is in progress. | |
| UNKNOWN | Geo replication status could not be determined. | When glusterd is down. | |
| Volume Quota | OK | QUOTA: not enabled or configured | When quota is not set |
| OK | QUOTA:OK | When quota is set and usage is below quota limits. | |
| WARNING | QUOTA:Soft limit exceeded on path of directory | When quota exceeds soft limit. | |
| CRITICAL | QUOTA:hard limit reached on path of directory | When quota reaches hard limit. | |
| UNKNOWN | QUOTA: Quota status could not be determined as command execution failed | When there's an error in getting Quota status. This occurs when
| |
| Volume Status | OK | Volume : volume type - All bricks are Up | When all volumes are up. |
| WARNING | Volume :volume type Brick(s) - list of bricks is|are down, but replica pair(s) are up | When bricks in the volume are down but replica pairs are up. | |
| UNKNOWN | Command execution failed Failure message | When command execution fails. | |
| CRITICAL | Volume not found. | When volumes are not found. | |
| CRITICAL | Volume: volume-type is stopped. | When volumes are stopped. | |
| CRITICAL | Volume : volume type - All bricks are down. | When all bricks are down. | |
| CRITICAL | Volume : volume type Bricks - brick list are down, along with one or more replica pairs | When bricks are down along with one or more replica pairs. | |
|
Volume Self-Heal
(available in Red Hat Gluster Storage version 3.1.0 and earlier)
| OK | When volume is not a replicated volume, there is no self-heal to be done. | |
| OK | No unsynced entries present | When there are no unsynched entries in a replicated volume. | |
| WARNING | Unsynched entries present : There are unsynched entries present. | If self-heal process is turned on, these entries may be auto healed. If not, self-heal will need to be run manually. If unsynchronized entries persist over time, this could indicate a split brain scenario. | |
| WARNING | Self heal status could not be determined as the volume was deleted | When self-heal status can not be determined as the volume is deleted. | |
| UNKNOWN |
When there's an error in getting self heal status. This error occurs when:
| ||
|
Volume Self-Heal Info
(available in Red Hat Gluster Storage version 3.1.3 and later)
| OK | No unsynced entries found. | Displayed when there are no entries in a replicated volume that haven't been synced. |
| WARNING | Unsynced entries found. | Displayed when there are entries in a replicated volume that still need to be synced. If self-heal is enabled, these may heal automatically. If self-heal is not enabled, healing must be run manually. | |
| WARNING | Volume heal information could not be determined. | Displayed when self-heal status cannot be determined, usually because the volume has been deleted. | |
| UNKNOWN | Glusterd cannot be queried. | Displayed when self-heal status cannot be retrieved. usually because the volume has been stopped, the glusterd service is down, or the volfile is locked because another transaction is in progress. | |
|
Volume Split-Brain Status
(available in Red Hat Gluster Storage version 3.1.1 and later)
| OK | No split-brain entries found. | Displayed when files are present and do not have split-brain issues. |
| UNKNOWN | Glusterd cannot be queried. | Displayed when split-brain status cannot be retrieved, usually because the volume has been stopped, the glusterd service is down, or the volfile is locked because another transaction is in progress. | |
| WARNING | Volume split-brain status could not be determined. | Displayed when split-brain status cannot be determined, usually because the volume no longer exists. | |
| CRITICAL |
14 entries found in split-brain state.
| Displays the number of files in a split-brain state when files in split-brain state are detected. | |
| Cluster Utilization | OK | OK : 28.0% used (1.68GB out of 6.0GB) | When used % is below the warning threshold (Default warning threshold is 80%). |
| WARNING | WARNING: 82.0% used (4.92GB out of 6.0GB) | Used% is above the warning limit. (Default warning threshold is 80%) | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL : 92.0% used (5.52GB out of 6.0GB) | Used% is above the warning limit. (Default critical threshold is 90%) | |
| UNKNOWN | Volume utilization data could not be read | When volume services are present, but the volume utilization data is not available as it's either not populated yet or there is error in fetching volume utilization data. | |
| Volume Utilization | OK | OK: Utilization: 40 % | When used % is below the warning threshold (Default warning threshold is 80%). |
| WARNING | WARNING - used 84% of available 200 GB | When used % is above the warning threshold (Default warning threshold is 80%). | |
| CRITICAL | CRITICAL - used 96% of available 200 GB | When used % is above the critical threshold (Default critical threshold is 90%). | |
| UNKNOWN | UNKNOWN - Volume utilization data could not be read | When all the bricks in the volume are killed or if glusterd is stopped in all the nodes in a cluster. |
17.4. Monitoring Notifications
17.4.1. Configuring Nagios Server to Send Mail Notifications
- In the
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-contacts.cfgfile, add contacts to send mail in the format shown below:Modifycontact_name,alias, andemail.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Theservice_notification_optionsdirective is used to define the service states for which notifications can be sent out to this contact. Valid options are a combination of one or more of the following:w: Notify on WARNING service statesu: Notify on UNKNOWN service statesc: Notify on CRITICAL service statesr: Notify on service RECOVERY (OK states)f: Notify when the service starts and stops FLAPPINGn (none): Do not notify the contact on any type of service notifications
Thehost_notification_optionsdirective is used to define the host states for which notifications can be sent out to this contact. Valid options are a combination of one or more of the following:d: Notify on DOWN host statesu: Notify on UNREACHABLE host statesr: Notify on host RECOVERY (UP states)f: Notify when the host starts and stops FLAPPINGs: Send notifications when host or service scheduled downtime starts and endsn (none): Do not notify the contact on any type of host notifications.
Note
By default, a contact and a contact group are defined for administrators incontacts.cfgand all the services and hosts will notify the administrators. Add suitable email id for administrator incontacts.cfgfile. - To add a group to which the mail need to be sent, add the details as given below:
define contactgroup{ contactgroup_name Group1 alias GroupAlias members Contact1,Contact2 }define contactgroup{ contactgroup_name Group1 alias GroupAlias members Contact1,Contact2 }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-templates.cfgfile specify the contact name and contact group name for the services for which the notification need to be sent, as shown below:Addcontact_groupsname andcontactsname.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can configure notification for individual services by editing the corresponding node configuration file. For example, to configure notification for brick service, edit the corresponding node configuration file as shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To receive detailed information on every update when Cluster Auto-Config is run, edit
/etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfgfile add$NOTIFICATIONCOMMENT$\nafter$SERVICEOUTPUT$\noption innotify-service-by-emailandnotify-host-by-emailcommand definition as shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the Nagios server using the following command:
service nagios restart
# service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
- By default, the system ensures three occurences of the event before sending mail notifications.
- By default, Nagios Mail notification is sent using
/bin/mailcommand. To change this, modify the definition fornotify-host-by-emailcommand andnotify-service-by-emailcommand in/etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfgfile and configure the mail server accordingly. - Ensure that the mail server is setup and configured.
17.4.2. Configuring Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Notification
- Log in as root user.
- In the
/etc/nagios/gluster/snmpmanagers.conffile, specify the Host Name or IP address and community name of the SNMP managers to whom the SNMP traps need to be sent as shown below:HostName-or-IP-address public
HostName-or-IP-address publicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-contacts.cfgfile specify the contacts name as +snmp as shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can download the required Management Information Base (MIB) files from the URLs given below: - Restart Nagios using the following command:
service nagios restart
# service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.5. Nagios Advanced Configuration
17.5.1. Creating Nagios User
- Login as
rootuser. - Run the command given below with the new user name and type the password when prompted.
htpasswd /etc/nagios/passwd newUserName
# htpasswd /etc/nagios/passwd newUserNameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add permissions for the new user in
/etc/nagios/cgi.cfgfile as shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
To setread onlypermission for users, addauthorized_for_read_only=usernamein the/etc/nagios/cgi.cfgfile. - Start
nagiosandhttpdservices using the following commands:service httpd restart service nagios restart
# service httpd restart # service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify Nagios access by using the following URL in your browser, and using the user name and password.
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 
Figure 17.14. Nagios Login
17.5.2. Changing Nagios Password
nagiosadmin. This value is available in the /etc/nagios/cgi.cfg file.
- Login as
rootuser. - To change the default password for the Nagios Administrator user, run the following command with the new password:
htpasswd -c /etc/nagios/passwd nagiosadmin
# htpasswd -c /etc/nagios/passwd nagiosadminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start
nagiosandhttpdservices using the following commands:service httpd restart service nagios restart
# service httpd restart # service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify Nagios access by using the following URL in your browser, and using the user name and password that was set in Step 2:
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagios
https://NagiosServer-HostName-or-IPaddress/nagiosCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 
Figure 17.15. Nagios Login
17.5.3. Configuring SSL
- Create a 1024 bit RSA key using the following command:
openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/private/{cert-file-name.key} 1024openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/private/{cert-file-name.key} 1024Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create an SSL certificate for the server using the following command:
openssl req -key nagios-ssl.key -new | openssl x509 -out nagios-ssl.crt -days 365 -signkey nagios-ssl.key -req
openssl req -key nagios-ssl.key -new | openssl x509 -out nagios-ssl.crt -days 365 -signkey nagios-ssl.key -reqCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the server's host name which is used to access the Nagios Server GUI as Common Name. - Edit the
/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conffile and add path to SSL Certificate and key files correspondingly forSSLCertificateFileandSSLCertificateKeyFilefields as shown below:SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/nagios-ssl.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/nagios-ssl.key
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/nagios-ssl.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/nagios-ssl.keyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Edit the
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conffile and comment the port 80 listener as shown below:Listen 80
# Listen 80Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conffile, ensure that the following line is not commented:<Directory "/var/www/html">
<Directory "/var/www/html">Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the
httpdservice on thenagiosserver using the following command:service httpd restart
# service httpd restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.5.4. Integrating LDAP Authentication with Nagios
- In apache configuration file
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf, ensure that LDAP is installed and LDAP apache module is enabled.The configurations are displayed as given below if the LDAP apache module is enabled.You can enable the LDAP apache module by deleting the # symbol.LoadModule ldap_module modules/mod_ldap.so LoadModule authnz_ldap_module modules/mod_authnz_ldap.so
LoadModule ldap_module modules/mod_ldap.so LoadModule authnz_ldap_module modules/mod_authnz_ldap.soCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Edit the
nagios.conffile in/etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.confwith the corresponding values for the following:- AuthBasicProvider
- AuthLDAPURL
- AuthLDAPBindDN
- AuthLDAPBindPassword
- Edit the CGI authentication file
/etc/nagios/cgi.cfgas given below with the path where Nagios is installed.nagiosinstallationdir = /usr/local/nagios/ or /etc/nagios/
nagiosinstallationdir = /usr/local/nagios/ or /etc/nagios/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Uncomment the lines shown below by deleting # and set permissions for specific users:
Note
Replacenagiosadminand user names with * to give any LDAP user full functionality of Nagios.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Enable the
httpd_can_connect_ldapboolean, if not enabled.getsebool httpd_can_connect_ldap setsebool httpd_can_connect_ldap on
# getsebool httpd_can_connect_ldap # setsebool httpd_can_connect_ldap onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart
httpdservice andnagiosserver using the following commands:service httpd restart service nagios restart
# service httpd restart # service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.6. Configuring Nagios Manually
Note
- In the
/etc/nagios/glusterdirectory, create a directory with the cluster name. All configurations for the cluster are added in this directory. - In the
/etc/nagios/gluster/cluster-namedirectory, create a file with nameclustername.cfgto specify thehostandhostgroupconfigurations. The service configurations for all the cluster and volume level services are added in this file.Note
Cluster is configured as host and host group in Nagios.In theclustername.cfgfile, add the following definitions:- Define a host group with cluster name as shown below:
define hostgroup{ hostgroup_name cluster-name alias cluster-name }define hostgroup{ hostgroup_name cluster-name alias cluster-name }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define a host with cluster name as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define Cluster-Quorum service to monitor cluster quorum status as shown below:
define service { service_description Cluster - Quorum use gluster-passive-service host_name cluster-name }define service { service_description Cluster - Quorum use gluster-passive-service host_name cluster-name }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define the Cluster Utilization service to monitor cluster utilization as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the following service definitions for each volume in the cluster:
- Volume Status service to monitor the status of the volume as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Volume Utilization service to monitor the volume utilization as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Volume Split-brain service to monitor split brain status as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Volume Quota service to monitor the volume quota status as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Volume Geo-Replication service to monitor Geo Replication status as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- In the
/etc/nagios/gluster/cluster-namedirectory, create a file with namehost-name.cfg. The host configuration for the node and service configuration for all the brick from the node are added in this file.Inhost-name.cfgfile, add following definitions:- Define Host for the node as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create the following services for each brick in the node:
- Add Brick Utilization service as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add Brick Status service as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Add host configurations and service configurations for all nodes in the cluster as shown in Step 3.
- In
/etc/nagiosdirectory of each Red Hat Gluster Storage node, editnagios_server.conffile by setting the configurations as shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Thenagios_server.conffile is used byglusterpmdservice to get server name, host name, and the process monitoring interval time. - Start the
glusterpmdservice using the following command:service glusterpmd start
# service glusterpmd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
By default, the active Red Hat Gluster Storage services are monitored every 10 minutes. You can change the time interval for monitoring by editing the gluster-templates.cfg file.
- In
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-templates.cfgfile, edit the service withgluster-servicename. - Add
normal_check_intervaland set the time interval to 1 to check all Red Hat Gluster Storage services every 1 minute as shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - To change this on individual service, add this property to the required service definition as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Thecheck_intervalis controlled by the global directiveinterval_length. This defaults to 60 seconds. This can be changed in/etc/nagios/nagios.cfgas shown below:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.7. Troubleshooting Nagios
17.7.1. Troubleshooting NSCA and NRPE Configuration Issues
- Check Firewall and Port Settings on Nagios ServerIf port 5667 is not opened on the server host's firewall, a timeout error is displayed. Ensure that port 5667 is opened.
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
- Log in as root and run the following command on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node to get the list of current iptables rules:
iptables -L
# iptables -LCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The output is displayed as shown below:
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:5667
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:5667Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
- Run the following command on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node as root to get a listing of the current firewall rules:
firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
# firewall-cmd --list-all-zonesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the port is open,
5667/tcpis listed besideports:under one or more zones in your output.
- If the port is not open, add a firewall rule for the port:
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
- If the port is not open, add an iptables rule by adding the following line in
/etc/sysconfig/iptablesfile:-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5667 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5667 -j ACCEPTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the iptables service using the following command:
service iptables restart
# service iptables restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the NSCA service using the following command:
service nsca restart
# service nsca restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
- Run the following commands to open the port:
firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5667/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5667/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5667/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5667/tcp --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Check the Configuration File on Red Hat Gluster Storage NodeMessages cannot be sent to the NSCA server, if Nagios server IP or FQDN, cluster name and hostname (as configured in Nagios server) are not configured correctly.Open the Nagios server configuration file /etc/nagios/nagios_server.conf and verify if the correct configurations are set as shown below:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If Host name is updated, restart the NSCA service using the following command:service nsca restart
# service nsca restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- CHECK_NRPE: Error - Could Not Complete SSL HandshakeThis error occurs if the IP address of the Nagios server is not defined in the
nrpe.cfgfile of the Red Hat Gluster Storage node. To fix this issue, follow the steps given below:- Add the Nagios server IP address in
/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfgfile in theallowed_hostsline as shown below:allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1, NagiosServerIP
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1, NagiosServerIPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Theallowed_hostsis the list of IP addresses which can execute NRPE commands. - Save the
nrpe.cfgfile and restart NRPE service using the following command:service nrpe restart
# service nrpe restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- CHECK_NRPE: Socket Timeout After n SecondsTo resolve this issue perform the steps given below:On Nagios Server:The default timeout value for the NRPE calls is 10 seconds and if the server does not respond within 10 seconds, Nagios Server GUI displays an error that the NRPE call has timed out in 10 seconds. To fix this issue, change the timeout value for NRPE calls by modifying the command definition configuration files.
- Changing the NRPE timeout for services which directly invoke check_nrpe.For the services which directly invoke check_nrpe (check_disk_and_inode, check_cpu_multicore, and check_memory), modify the command definition configuration file
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-commands.cfgby adding -t Time in Seconds as shown below:define command { command_name check_disk_and_inode command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c check_disk_and_inode -t TimeInSeconds }define command { command_name check_disk_and_inode command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c check_disk_and_inode -t TimeInSeconds }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Changing the NRPE timeout for the services in
nagios-server-addonspackage which invoke NRPE call through code.The services which invoke/usr/lib64/nagios/plugins/gluster/check_vol_server.py(check_vol_utilization, check_vol_status, check_vol_quota_status, check_vol_heal_status, and check_vol_georep_status) make NRPE call to the Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes for the details through code. To change the timeout for the NRPE calls, modify the command definition configuration file/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-commands.cfgby adding -t No of seconds as shown below:define command { command_name check_vol_utilization command_line $USER1$/gluster/check_vol_server.py $ARG1$ $ARG2$ -w $ARG3$ -c $ARG4$ -o utilization -t TimeInSeconds }define command { command_name check_vol_utilization command_line $USER1$/gluster/check_vol_server.py $ARG1$ $ARG2$ -w $ARG3$ -c $ARG4$ -o utilization -t TimeInSeconds }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The auto configuration servicegluster_auto_discoverymakes NRPE calls for the configuration details from the Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes. To change the NRPE timeout value for the auto configuration service, modify the command definition configuration file/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-commands.cfgby adding -t TimeInSeconds as shown below:define command{ command_name gluster_auto_discovery command_line sudo $USER1$/gluster/configure-gluster-nagios.py -H $ARG1$ -c $HOSTNAME$ -m auto -n $ARG2$ -t TimeInSeconds }define command{ command_name gluster_auto_discovery command_line sudo $USER1$/gluster/configure-gluster-nagios.py -H $ARG1$ -c $HOSTNAME$ -m auto -n $ARG2$ -t TimeInSeconds }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart Nagios service using the following command:
service nagios restart
# service nagios restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
On Red Hat Gluster Storage node:- Add the Nagios server IP address as described in CHECK_NRPE: Error - Could Not Complete SSL Handshake section in Troubleshooting NRPE Configuration Issues section.
- Edit the
nrpe.cfgfile using the following command:vi /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
# vi /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Search for the
command_timeoutandconnection_timeoutsettings and change the value. Thecommand_timeoutvalue must be greater than or equal to the timeout value set in Nagios server.The timeout on checks can be set as connection_timeout=300 and the command_timeout=60 seconds. - Restart the NRPE service using the following command:
service nrpe restart
# service nrpe restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Check the NRPE Service StatusThis error occurs if the NRPE service is not running. To resolve this issue perform the steps given below:
- Log in as root to the Red Hat Gluster Storage node and run the following command to verify the status of NRPE service:
service nrpe status
# service nrpe statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If NRPE is not running, start the service using the following command:
service nrpe start
# service nrpe startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Check Firewall and Port SettingsThis error is associated with firewalls and ports. The timeout error is displayed if the NRPE traffic is not traversing a firewall, or if port 5666 is not open on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node.Ensure that port 5666 is open on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node.
- Run
check_nrpecommand from the Nagios server to verify if the port is open and if NRPE is running on the Red Hat Gluster Storage Node . - Log into the Nagios server as root and run the following command:
/usr/lib64/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H RedHatStorageNodeIP
# /usr/lib64/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H RedHatStorageNodeIPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The output is displayed as given below:
NRPE v2.14
NRPE v2.14Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If not, ensure the that port 5666 is opened on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node.On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6:
- Run the following command on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node as root to get a listing of the current iptables rules:
iptables -L
# iptables -LCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the port is open, the following appears in your output.
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:5666
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:5666Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
- Run the following command on the Red Hat Gluster Storage node as root to get a listing of the current firewall rules:
firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
# firewall-cmd --list-all-zonesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If the port is open,
5666/tcpis listed besideports:under one or more zones in your output.
- If the port is not open, add an iptables rule for the port.
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6:
- To add iptables rule, edit the
iptablesfile as shown below:vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
# vi /etc/sysconfig/iptablesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the following line in the file:
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5666 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 5666 -j ACCEPTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the iptables service using the following command:
service iptables restart
# service iptables restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file and restart the NRPE service:
service nrpe restart
# service nrpe restartCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
On Red Hat Gluster Storage based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7:
- Run the following commands to open the port:
firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5666/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5666/tcp --permanent
# firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5666/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=zone_name --add-port=5666/tcp --permanentCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Checking Port 5666 From the Nagios Server with TelnetUse telnet to verify the Red Hat Gluster Storage node's ports. To verify the ports of the Red Hat Gluster Storage node, perform the steps given below:
- Log in as root on Nagios server.
- Test the connection on port 5666 from the Nagios server to the Red Hat Gluster Storage node using the following command:
telnet RedHatStorageNodeIP 5666
# telnet RedHatStorageNodeIP 5666Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The output displayed is similar to:
telnet 10.70.36.49 5666 Trying 10.70.36.49... Connected to 10.70.36.49. Escape character is '^]'.
telnet 10.70.36.49 5666 Trying 10.70.36.49... Connected to 10.70.36.49. Escape character is '^]'.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Connection Refused By HostThis error is due to port/firewall issues or incorrectly configured allowed_hosts directives. See the sections CHECK_NRPE: Error - Could Not Complete SSL Handshake and CHECK_NRPE: Socket Timeout After n Seconds for troubleshooting steps.
Chapter 18. Monitoring Red Hat Gluster Storage Gluster Workload
volume top and volume profile commands to view vital performance information and identify bottlenecks on each brick of a volume.
Note
profile and top information will be reset.
18.1. Profiling volumes
18.1.1. Server-side volume profiling using volume profile
volume profile command provides an interface to get the per-brick or NFS server I/O information for each File Operation (FOP) of a volume. This information helps in identifying the bottlenecks in the storage system.
volume profile command.
18.1.1.1. Start Profiling
# gluster volume profile VOLNAME start
gluster volume profile test-volume start Profiling started on test-volume
# gluster volume profile test-volume start
Profiling started on test-volumeImportant
profile command can affect system performance while the profile information is being collected. Red Hat recommends that profiling should only be used for debugging.
volume info command:
diagnostics.count-fop-hits: on diagnostics.latency-measurement: on
diagnostics.count-fop-hits: on
diagnostics.latency-measurement: on18.1.1.2. Displaying the I/O Information
# gluster volume profile VOLNAME info
# gluster volume profile VOLNAME info nfs
18.1.1.3. Stop Profiling
# gluster volume profile VOLNAME stop
gluster volume profile test-volume stop
Profiling stopped on test-volume
# gluster volume profile test-volume stop
Profiling stopped on test-volume18.1.2. Client-side volume profiling (FUSE only)
setfattr -n trusted.io-stats-dump -v output_file_id mount_point
# setfattr -n trusted.io-stats-dump -v output_file_id mount_point/var/run/gluster directory. The output_file_id is not the whole file name, but is used as part of the name of the generated files.
18.2. Running the Volume Top Command
volume top command allows you to view the glusterFS bricks’ performance metrics, including read, write, file open calls, file read calls, file write calls, directory open calls, and directory real calls. The volume top command displays up to 100 results.
volume top command.
18.2.1. Viewing Open File Descriptor Count and Maximum File Descriptor Count
volume top command. The volume top command also displays the maximum open file descriptor count of files that are currently open, and the maximum number of files opened at any given point of time since the servers are up and running. If the brick name is not specified, then the open file descriptor metrics of all the bricks belonging to the volume displays.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME open [nfs | brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
18.2.2. Viewing Highest File Read Calls
volume top command. If the brick name is not specified, a list of 100 files are displayed by default.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME read [nfs | brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
18.2.3. Viewing Highest File Write Calls
volume top command. If the brick name is not specified, a list of 100 files displays by default.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME write [nfs | brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
18.2.4. Viewing Highest Open Calls on a Directory
volume top command. If the brick name is not specified, the metrics of all bricks belonging to that volume displays.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME opendir [brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
18.2.5. Viewing Highest Read Calls on a Directory
volume top command. If the brick name is not specified, the metrics of all bricks belonging to that volume displays.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME readdir [nfs | brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
18.2.6. Viewing Read Performance
volume top command. If the brick name is not specified, the metrics of all the bricks belonging to that volume is displayed. The output is the read throughput.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME read-perf [bs blk-size count count] [nfs | brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
server:/export/ of test-volume, specifying a 256 block size, and list the top 10 results:
18.2.7. Viewing Write Performance
volume top command. If brick name is not specified, then the metrics of all the bricks belonging to that volume will be displayed. The output will be the write throughput.
# gluster volume top VOLNAME write-perf [bs blk-size count count] [nfs | brick BRICK-NAME] [list-cnt cnt]
server:/export/ of test-volume, specifying a 256 block size, and list the top 10 results:
18.3. gstatus Command
18.3.1. gstatus Command
gstatus provides an overview of the health of a Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool for distributed, replicated, distributed-replicated, dispersed, and distributed-dispersed volumes.
gstatus command provides an easy-to-use, high-level view of the health of a trusted storage pool with a single command. By executing the glusterFS commands, it gathers information about the statuses of the Red Hat Gluster Storage nodes, volumes, and bricks. The checks are performed across the trusted storage pool and the status is displayed. This data can be analyzed to add further checks and incorporate deployment best-practices and free-space triggers.
Note
18.3.1.1. Prerequisites
- Python 2.6 or above
18.3.2. Executing the gstatus command
gstatus command can be invoked in different ways. The table below shows the optional switches that can be used with gstatus.
gstatus -h Usage: gstatus [options]
# gstatus -h
Usage: gstatus [options]| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| --version | Displays the program's version number and exits. |
| -h, --help | Displays the help message and exits. |
| -s, --state | Displays the high level health of the Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool. |
| -v, --volume | Displays volume information of all the volumes, by default. Specify a volume name to display the volume information of a specific volume. |
| -b, --backlog | Probes the self heal state. |
| -a, --all | Displays the detailed status of volume health. (This output is aggregation of -s and -v). |
| -l, --layout | Displays the brick layout when used in combination with -v, or -a . |
| -o OUTPUT_MODE, --output-mode=OUTPUT_MODE | Produces outputs in various formats such as - json, keyvalue, or console(default). |
| -D, --debug | Enables the debug mode. |
| -w, --without-progress | Disables progress updates during data gathering. |
| -u UNITS, --units=UNITS | Displays capacity units in decimal or binary format (GB vs GiB). |
| -t TIMEOUT, --timeout=TIMEOUT | Specify the command timeout value in seconds. |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
gstatus -s | An overview of the trusted storage pool. |
gstatus -a | View detailed status of the volume health. |
gstatus -vl VOLNAME | View the volume details, including the brick layout. |
gstatus -o <keyvalue> | View the summary output for Nagios and Logstash. |
gstatus provides a header section, which provides a high level view of the state of the Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool. The Status field within the header offers two states; Healthy and Unhealthy. When problems are detected, the status field changes to Unhealthy(n), where n denotes the total number of issues that have been detected.
gstatus command output for both healthy and unhealthy Red Hat Gluster Storage environments.
Example 18.1. Example 1: Trusted Storage Pool is in a healthy state; all nodes, volumes and bricks are online
Example 18.2. Example 2: A node is down within the trusted pool
-l option is used. The brick layout mode shows the brick and node relationships. This provides a simple means of checking the replication relationships for bricks across nodes is as intended.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Volume State | Up – The volume is started and available, and all the bricks are up . |
Up (Degraded) - This state is specific to replicated volumes, where at least one brick is down within a replica set. Data is still 100% available due to the alternate replicas, but the resilience of the volume to further failures within the same replica set flags this volume as degraded. | |
Up (Partial) - Effectively, this means that all though some bricks in the volume are online, there are others that are down to a point where areas of the file system will be missing. For a distributed volume, this state is seen if any brick is down, whereas for a replicated volume a complete replica set needs to be down before the volume state transitions to PARTIAL. | |
| Down - Bricks are down, or the volume is yet to be started. | |
| Capacity Information | This information is derived from the brick information taken from the volume status detail command. The accuracy of this number hence depends on the nodes and bricks all being online - elements missing from the configuration are not considered in the calculation. |
| Over-commit Status | The physical file system used by a brick could be re-used by multiple volumes, this field indicates whether a brick is used by multiple volumes. But this exposes the system to capacity conflicts across different volumes when the quota feature is not in use. Reusing a brick for multiple volumes is not recommended. |
| Connections | Displays a count of connections made to the trusted pool and each of the volumes. |
| Nodes / Self Heal / Bricks X/Y | This indicates that X components of Y total/expected components within the trusted pool are online. In Example 2, note that 3/4 is displayed against all of these fields, indicating 3 nodes are available out of 4 nodes. A node, brick, and the self-heal daemon are also unavailable. |
| Tasks Active | Active background tasks such as rebalance, remove-brick are displayed here against individual volumes. |
| Protocols | Displays which protocols have been enabled for the volume. |
| Snapshots | Displays a count of the number of snapshots taken for the volume. The snapshot count for each volume is rolled up to the trusted storage pool to provide a high level view of the number of snapshots in the environment. |
| Status Messages | After the information is gathered, any errors detected are reported in the Status Messages section. These descriptions provide a view of the problem and the potential impact of the condition. |
18.4. Listing Volumes
# gluster volume list
gluster volume list test-volume volume1 volume2 volume3
# gluster volume list
test-volume
volume1
volume2
volume318.5. Displaying Volume Information
# gluster volume info VOLNAME
18.6. Obtaining Node Information
get-state command outputs information about a node to a specified file.
The get-state command outputs information about a node to a specified file and can be invoked in different ways. The table below shows the options that can be used with the get-state command.
gluster get-state [odir path_to_output_dir] [file filename] [detail|volumeoptions] Usage: get-state [options]
# gluster get-state [odir path_to_output_dir] [file filename] [detail|volumeoptions]
Usage: get-state [options]
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
gluster get-state | glusterd state information is saved in the /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestamp file. |
gluster get-state file filename | glusterd state information is saved in the /var/run/gluster/ directory with the filename as specified in the command. |
gluster get-state odir directory file filename | glusterd state information is saved in the directory and in the file name as specified in the command. |
gluster get-state detail | glusterd state information is saved in the /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestamp file, and all clients connected per brick are included in the output. |
gluster get-state volumeoptions | glusterd state information is saved in the /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestamp file, and all values for all the volume options are included in the output. |
Invocation of the get-state command saves the information that reflects the node level status of the trusted storage pool as maintained in glusterd (no other daemons are supported as of now) to a file specified in the command. By default, the output will be dumped to /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestamp file .
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Global | Displays the UUID and the op-version of the glusterd. |
| Global options | Displays cluster specific options that have been set explicitly through the volume set command. |
| Peers | Displays the peer node information including its hostname and connection status. |
| Volumes | Displays the list of volumes created on this node along with the detailed information on each volume. |
| Services | Displays the list of the services configured on this node along with its status. |
| Misc | Displays miscellaneous information about the node. For example, configured ports. |
gluster get-state:
gluster get-state glusterd state dumped to /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestamp
# gluster get-state
glusterd state dumped to /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestampcat state_dump_file_path command:
gluster get-state volumeoptions lists all volume options irrespective of whether the volume option has been explicitly set or not.
gluster get-state volumeoptions:
gluster get-state volumeoptions glusterd state dumped to /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestamp
# gluster get-state volumeoptions
glusterd state dumped to /var/run/gluster/glusterd_state_timestampcat state_dump_file_path command:
18.7. Retrieving Current Volume Option Settings
gluster volume get command. If a volume option is reconfigured for a volume, then the same value is displayed. If the volume option is not reconfigured, the default value is displayed.
# gluster volume get <VOLNAME|all> <key|all>
18.7.1. Retrieving Value of a Specific Volume Option
gluster volume get <VOLNAME> <key>
# gluster volume get <VOLNAME> <key>gluster volume get test-vol nfs.disable Option Value ------ ----- nfs.disable on
# gluster volume get test-vol nfs.disable
Option Value
------ -----
nfs.disable on18.7.2. Retrieving all Options of a Volume
gluster volume get <VOLNAME> all
# gluster volume get <VOLNAME> all18.7.3. Retrieving all Global Options
gluster volume get all all
# gluster volume get all all18.8. Viewing complete volume state with statedump
statedump subcommand writes out details of the current state of a specified process, including internal variables and other information that is useful for troubleshooting.
gluster volume statedump VOLNAME [[nfs|quotad] [all|mem|iobuf|callpool|priv|fd|inode|history] | [client hostname:pid]]
# gluster volume statedump VOLNAME [[nfs|quotad] [all|mem|iobuf|callpool|priv|fd|inode|history] | [client hostname:pid]]18.8.1. Gathering information from the server
- all
- Dumps all available state information.
- mem
- Dumps the memory usage and memory pool details of the bricks.
- iobuf
- Dumps iobuf details of the bricks.
- priv
- Dumps private information of loaded translators.
- callpool
- Dumps the pending calls of the volume.
- fd
- Dumps the open file descriptor tables of the volume.
- inode
- Dumps the inode tables of the volume.
- history
- Dumps the event history of the volume
data volume, run the following command on the server:
gluster volume statedump data all
# gluster volume statedump data allgluster volume statedump data history
# gluster volume statedump data historynfs parameter is required to gather details about volumes shared via NFS. It can be combined with any of the above parameters to filter output.
gluster volume statedump VOLNAME nfs all
# gluster volume statedump VOLNAME nfs allquotad parameter is required to gather details about the quota daemon. The following command writes out the state of the quota daemon across all nodes.
gluster volume statedump VOLNAME quotad
# gluster volume statedump VOLNAME quotadkill -SIGUSR1 pid
# kill -SIGUSR1 pid18.8.2. Gathering information from the client
statedump subcommand writes out details of the current state of a specified process, including internal variables and other information that is useful for troubleshooting.
gluster volume statedump VOLNAME client hostname:pid
# gluster volume statedump VOLNAME client hostname:pidImportant
gluster volume statedump VOLNAME client localhost:pid
# gluster volume statedump VOLNAME client localhost:pidkill -SIGUSR1 pid
# kill -SIGUSR1 pidImportant
gluster group. For example, if your gfapi application is run by user qemu, ensure that qemu is added to the gluster group by running the following command:
usermod -a -G gluster qemu
# usermod -a -G gluster qemu18.8.3. Controlling statedump output location
/var/run/gluster directory by default. Output files are named according to the following conventions:
- For brick processes,
brick_path.brick_pid.dump - For volume processes and
killcommand results,glusterdump-glusterd_pid.dump.timestamp
server.statedump-path parameter, like so:
gluster volume set VOLNAME server.statedump-path PATH
# gluster volume set VOLNAME server.statedump-path PATH18.9. Displaying Volume Status
- detail - Displays additional information about the bricks.
- clients - Displays the list of clients connected to the volume.
- mem - Displays the memory usage and memory pool details of the bricks.
- inode - Displays the inode tables of the volume.
- fd - Displays the open file descriptor tables of the volume.
- callpool - Displays the pending calls of the volume.
When you try to obtain information of a specific volume, the command may get timed out from the CLI if the originator glusterd takes longer than 120 seconds, the default time out, to aggregate the results from all the other glusterds and report back to CLI.
--timeout option to ensure that the commands do not get timed out by 120 seconds.
gluster volume status --timeout=500 VOLNAME inode
# gluster volume status --timeout=500 VOLNAME inode--timeout option when obtaining information about the inodes or clients or details as they frequently get timed out.
# gluster volume status --timeout=value_in_seconds [all|VOLNAME [nfs | shd | BRICKNAME]] [detail |clients | mem | inode | fd |callpool]
# gluster volume status all
# gluster volume status VOLNAME detail
# gluster volume status VOLNAME clients
# gluster volume status VOLNAME mem
# gluster volume status VOLNAME inode
# gluster volume status VOLNAME fd
# gluster volume status VOLNAME callpool
18.10. Troubleshooting issues in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool
18.10.1. Troubleshooting a network issue in the Red Hat Gluster Storage Trusted Storage Pool
ping from one Red Hat Gluster Storage node to another.
ping command times out and displays the following error:
ping -s 1600 '-Mdo' local error: Message too long, mtu=1500
# ping -s 1600 '-Mdo'
local error: Message too long, mtu=1500Chapter 19. Managing Resource Usage
Procedure 19.1. Limiting glusterd resources on RHEL7 based Red Hat Gluster Storage
- Stop all gluster processes
systemctl stop glusterd
# systemctl stop glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Ifglusterdcrashes, there is no functionality impact to this crash as it occurs during the shutdown. For more information, see Section 23.3, “ResolvingglusterdCrash” - Create a service configuration directory for glusterd
mkdir /etc/systemd/system/glusterd.service.d
# mkdir /etc/systemd/system/glusterd.service.dCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a service configuration file
echo "[Service] CPUAccounting=yes Slice=glusterfs.slice" >> /etc/systemd/system/glusterd.service.d/99-cpu.conf
# echo "[Service] CPUAccounting=yes Slice=glusterfs.slice" >> /etc/systemd/system/glusterd.service.d/99-cpu.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a slice fileThe following defines a slice that sets
CPUQuotato the recommended value of400%(four cores).echo "[Slice] CPUQuota=400%" >> /etc/systemd/system/glusterfs.slice
# echo "[Slice] CPUQuota=400%" >> /etc/systemd/system/glusterfs.sliceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can alter the percentage to suit your environment by editing the value in the slice file:systemctl set-property glusterfs.slice CPUQuota=value
# systemctl set-property glusterfs.slice CPUQuota=valueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart the system daemon
systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl daemon-reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start gluster processes
systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure 19.2. Controlling CPU Usage for a Gluster Daemon
control-cpu-load script provides a utility to control CPU utilization for any Gluster daemon by using the cgroup framework to configure CPU quota for a process.
- Navigate to the scripts folder by using the following command:
cd /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts
# cd /usr/share/glusterfs/scriptsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Determine the PID of the required gluster daemon by using the following command:
ps -aef | grep daemon_name
# ps -aef | grep daemon_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will be in the following format:root 1565...output omitted...grep --color=auto daemon_name
root 1565...output omitted...grep --color=auto daemon_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this output, 1565 represents the PID of the daemon service. PIDs are unlikely to be the same on different systems, or for different instances of the daemon, so ensure that you check for the relevant PID every time you perform this process. - Execute the
control-cpu-loadscript by using the following command:sh control-cpu-load.sh
# sh control-cpu-load.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts you with the following input, type the PID of the daemon acquired from the previous step and press
Enter:sh control-cpu-load.sh Enter gluster daemon pid for which you want to control CPU. 1565
[root@XX-XX scripts]# sh control-cpu-load.sh Enter gluster daemon pid for which you want to control CPU. 1565Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts you with the following input, type
yand pressEnter:If you want to continue the script to attach 1565 with new cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup Press (y/n)?
If you want to continue the script to attach 1565 with new cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup Press (y/n)?Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts the following notification, enter the required quota value to be assigned to the daemon and press
Enter:Creating child cgroup directory 'cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup' for daemon_name.service. Enter quota value in range [10,100]: 25
Creating child cgroup directory 'cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup' for daemon_name.service. Enter quota value in range [10,100]: 25Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, quota value for the daemon service is set to25.The system displays the following message once the quota value has been successfully set:Entered quota value is 25 Setting 25000 to cpu.cfs_quota_us for gluster_cgroup. Tasks are attached successfully specific to 1565 to cgroup_gluster_1565.
Entered quota value is 25 Setting 25000 to cpu.cfs_quota_us for gluster_cgroup. Tasks are attached successfully specific to 1565 to cgroup_gluster_1565.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Important
Procedure 19.3. Controlling memory usage for a Gluster daemon
control-mem script provides a utility to control memory utilization for any Gluster daemon by using the cgroup framework to configure memory limit for a process.
- Navigate to the scripts folder by using the following command:
cd /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts
# cd /usr/share/glusterfs/scriptsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Determine the PID of the required gluster daemon by using the following command:
ps -aef | grep daemon_name
# ps -aef | grep daemon_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will be in the following format:root 1565 1 0 Feb05 ? 00:09:17 /usr/sbin/glusterfs -s localhost --volfile-id gluster/daemon_name -p /var/run/gluster/daemon_name/daemon_name.pid -l /var/log/glusterfs/daemon_name.log -S /var/run/gluster/ed49b959a0dc9b2185913084e3b2b339.socket --xlator-option *replicate*.node-uuid=13dbfa1e-ebbf-4cee-a1ac-ca6763903c55 root 16766 14420 0 19:00 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto daemon_name
root 1565 1 0 Feb05 ? 00:09:17 /usr/sbin/glusterfs -s localhost --volfile-id gluster/daemon_name -p /var/run/gluster/daemon_name/daemon_name.pid -l /var/log/glusterfs/daemon_name.log -S /var/run/gluster/ed49b959a0dc9b2185913084e3b2b339.socket --xlator-option *replicate*.node-uuid=13dbfa1e-ebbf-4cee-a1ac-ca6763903c55 root 16766 14420 0 19:00 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto daemon_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this output, 1565 represents the PID of the daemon service. - Execute the
control-memscript by using the following command:sh control-mem.sh
# sh control-mem.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts for the following input, type the PID of the daemon acquired from the previous step and press
Enter:sh control-mem.sh Enter gluster daemon pid for which you want to control CPU. 1565
[root@XX-XX scripts]# sh control-mem.sh Enter gluster daemon pid for which you want to control CPU. 1565Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, 1565 represents the PID of the daemon service. The PID of the daemon services can vary from system to system. - When the system prompts for the following input, type
yand pressEnter:If you want to continue the script to attach daeomon with new cgroup. Press (y/n)?
If you want to continue the script to attach daeomon with new cgroup. Press (y/n)?Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The system prompts the following notification:Creating child cgroup directory 'cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup' for daemon_name.service.
Creating child cgroup directory 'cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup' for daemon_name.service.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts for the following input, enter the required memory value to be assigned to the daemon and press
Enter:Enter Memory value in Mega bytes [100,8000000000000]:
Enter Memory value in Mega bytes [100,8000000000000]:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the memory value is set to5000. The system prompts the following message once the memory value has been successfully set:Entered memory limit value is 5000. Setting 5242880000 to memory.limit_in_bytes for /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/daemon_name.service/cgroup_gluster_1565. Tasks are attached successfully specific to 1565 to cgroup_gluster_1565.
Entered memory limit value is 5000. Setting 5242880000 to memory.limit_in_bytes for /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/system.slice/daemon_name.service/cgroup_gluster_1565. Tasks are attached successfully specific to 1565 to cgroup_gluster_1565.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Important
Chapter 20. Tuning for Performance
20.1. Disk Configuration
20.1.1. Hardware RAID
20.1.2. JBOD
raw drives to the operating system using a pass-through mode.
20.2. Brick Configuration
Procedure 20.1. Brick Configuration
LVM layer
The steps for creating a brick from a physical device is listed below. An outline of steps for creating multiple bricks on a physical device is listed as Example - Creating multiple bricks on a physical device below.- Creating the Physical VolumeThe
pvcreatecommand is used to create the physical volume. The Logical Volume Manager can use a portion of the physical volume for storing its metadata while the rest is used as the data portion.Align the I/O at the Logical Volume Manager (LVM) layer using--dataalignmentoption while creating the physical volume.The command is used in the following format:pvcreate --dataalignment alignment_value disk
# pvcreate --dataalignment alignment_value diskCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For JBOD, use an alignment value of256K.In case of hardware RAID, the alignment_value should be obtained by multiplying the RAID stripe unit size with the number of data disks. If 12 disks are used in a RAID 6 configuration, the number of data disks is 10; on the other hand, if 12 disks are used in a RAID 10 configuration, the number of data disks is 6.For example, the following command is appropriate for 12 disks in a RAID 6 configuration with a stripe unit size of 128 KiB:pvcreate --dataalignment 1280k disk
# pvcreate --dataalignment 1280k diskCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following command is appropriate for 12 disks in a RAID 10 configuration with a stripe unit size of 256 KiB:pvcreate --dataalignment 1536k disk
# pvcreate --dataalignment 1536k diskCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the previously configured physical volume settings for--dataalignment, run the following command:pvs -o +pe_start disk PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree 1st PE /dev/sdb lvm2 a-- 9.09t 9.09t 1.25m
# pvs -o +pe_start disk PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree 1st PE /dev/sdb lvm2 a-- 9.09t 9.09t 1.25mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Creating the Volume GroupThe volume group is created using the
vgcreatecommand.For hardware RAID, in order to ensure that logical volumes created in the volume group are aligned with the underlying RAID geometry, it is important to use the-- physicalextentsizeoption. Execute thevgcreatecommand in the following format:vgcreate --physicalextentsize extent_size VOLGROUP physical_volume
# vgcreate --physicalextentsize extent_size VOLGROUP physical_volumeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The extent_size should be obtained by multiplying the RAID stripe unit size with the number of data disks. If 12 disks are used in a RAID 6 configuration, the number of data disks is 10; on the other hand, if 12 disks are used in a RAID 10 configuration, the number of data disks is 6.For example, run the following command for RAID-6 storage with a stripe unit size of 128 KB, and 12 disks (10 data disks):vgcreate --physicalextentsize 1280k VOLGROUP physical_volume
# vgcreate --physicalextentsize 1280k VOLGROUP physical_volumeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the case of JBOD, use thevgcreatecommand in the following format:vgcreate VOLGROUP physical_volume
# vgcreate VOLGROUP physical_volumeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Creating the Thin PoolA thin pool provides a common pool of storage for thin logical volumes (LVs) and their snapshot volumes, if any.Execute the following commands to create a thin pool of a specific size:
lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/POOLNAME --size POOLSIZE --chunksize CHUNKSIZE --poolmetadatasize METASIZE --zero n
# lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/POOLNAME --size POOLSIZE --chunksize CHUNKSIZE --poolmetadatasize METASIZE --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also create a thin pool of the maximum possible size for your device by executing the following command:lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/POOLNAME --extents 100%FREE --chunksize CHUNKSIZE --poolmetadatasize METASIZE --zero n
# lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/POOLNAME --extents 100%FREE --chunksize CHUNKSIZE --poolmetadatasize METASIZE --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Recommended parameter values for thin pool creation
- poolmetadatasize
- Internally, a thin pool contains a separate metadata device that is used to track the (dynamically) allocated regions of the thin LVs and snapshots. The
poolmetadatasizeoption in the above command refers to the size of the pool metadata device.The maximum possible size for a metadata LV is 16 GiB. Red Hat Gluster Storage recommends creating the metadata device of the maximum supported size. You can allocate less than the maximum if space is a concern, but in this case you should allocate a minimum of 0.5% of the pool size.Warning
If your metadata pool runs out of space, you cannot create data. This includes the data required to increase the size of the metadata pool or to migrate data away from a volume that has run out of metadata space. Monitor your metadata pool using thelvs -o+metadata_percentcommand and ensure that it does not run out of space. - chunksize
- An important parameter to be specified while creating a thin pool is the chunk size,which is the unit of allocation. For good performance, the chunk size for the thin pool and the parameters of the underlying hardware RAID storage should be chosen so that they work well together.For JBOD, use a thin pool chunk size of 256 KiB.For RAID 6 storage, the striping parameters should be chosen so that the full stripe size (stripe_unit size * number of data disks) is between 1 MiB and 2 MiB, preferably in the low end of the range. The thin pool chunk size should be chosen to match the RAID 6 full stripe size. Matching the chunk size to the full stripe size aligns thin pool allocations with RAID 6 stripes, which can lead to better performance. Limiting the chunk size to below 2 MiB helps reduce performance problems due to excessive copy-on-write when snapshots are used.For example, for RAID 6 with 12 disks (10 data disks), stripe unit size should be chosen as 128 KiB. This leads to a full stripe size of 1280 KiB (1.25 MiB). The thin pool should then be created with the chunk size of 1280 KiB.For RAID 10 storage, the preferred stripe unit size is 256 KiB. This can also serve as the thin pool chunk size. Note that RAID 10 is recommended when the workload has a large proportion of small file writes or random writes. In this case, a small thin pool chunk size is more appropriate, as it reduces copy-on-write overhead with snapshots.If the addressable storage on the device is smaller than the device itself, you need to adjust the recommended chunk size. Calculate the adjustment factor using the following formula:
adjustment_factor = device_size_in_tb / (preferred_chunk_size_in_kb * 4 / 64 )
adjustment_factor = device_size_in_tb / (preferred_chunk_size_in_kb * 4 / 64 )Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Round the adjustment factor up. Then calculate the new chunk size using the following:chunk_size = preferred_chunk_size * rounded_adjustment_factor
chunk_size = preferred_chunk_size * rounded_adjustment_factorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - block zeroing
- By default, the newly provisioned chunks in a thin pool are zeroed to prevent data leaking between different block devices. In the case of Red Hat Gluster Storage, where data is accessed via a file system, this option can be turned off for better performance with the
--zero noption. Note thatndoes not need to be replaced.The following example shows how to create the thin pool:lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --size 2T --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --size 2T --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also use--extents 100%FREEto ensure the thin pool takes up all available space once the metadata pool is created.lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --extents 100%FREE --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --extents 100%FREE --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The following example shows how to create a 2 TB thin pool:lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --size 2T --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --size 2T --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example creates a thin pool that takes up all remaining space once the metadata pool has been created.lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --extents 100%FREE --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin VOLGROUP/thin_pool --extents 100%FREE --chunksize 1280k --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Creating a Thin Logical VolumeAfter the thin pool has been created as mentioned above, a thinly provisioned logical volume can be created in the thin pool to serve as storage for a brick of a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.
lvcreate --thin --name LV_name --virtualsize LV_size VOLGROUP/thin_pool
# lvcreate --thin --name LV_name --virtualsize LV_size VOLGROUP/thin_poolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Example - Creating multiple bricks on a physical deviceThe steps above (LVM Layer) cover the case where a single brick is being created on a physical device. This example shows how to adapt these steps when multiple bricks need to be created on a physical device.
Note
In this following steps, we are assuming the following:- Two bricks must be created on the same physical device
- One brick must be of size 4 TiB and the other is 2 TiB
- The device is
/dev/sdb, and is a RAID-6 device with 12 disks - The 12-disk RAID-6 device has been created according to the recommendations in this chapter, that is, with a stripe unit size of 128 KiB
- Create a single physical volume using pvcreate
pvcreate --dataalignment 1280k /dev/sdb
# pvcreate --dataalignment 1280k /dev/sdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a single volume group on the device
vgcreate --physicalextentsize 1280k vg1 /dev/sdb
# vgcreate --physicalextentsize 1280k vg1 /dev/sdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create a separate thin pool for each brick using the following commands:
lvcreate --thin vg1/thin_pool_1 --size 4T --chunksize 1280K --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin vg1/thin_pool_1 --size 4T --chunksize 1280K --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow lvcreate --thin vg1/thin_pool_2 --size 2T --chunksize 1280K --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero n
# lvcreate --thin vg1/thin_pool_2 --size 2T --chunksize 1280K --poolmetadatasize 16G --zero nCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the examples above, the size of each thin pool is chosen to be the same as the size of the brick that will be created in it. With thin provisioning, there are many possible ways of managing space, and these options are not discussed in this chapter. - Create a thin logical volume for each brick
lvcreate --thin --name lv1 --virtualsize 4T vg1/thin_pool_1
# lvcreate --thin --name lv1 --virtualsize 4T vg1/thin_pool_1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow lvcreate --thin --name lv2 --virtualsize 2T vg1/thin_pool_2
# lvcreate --thin --name lv2 --virtualsize 2T vg1/thin_pool_2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Follow the XFS Recommendations (next step) in this chapter for creating and mounting filesystems for each of the thin logical volumes
mkfs.xfs options /dev/vg1/lv1
# mkfs.xfs options /dev/vg1/lv1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow mkfs.xfs options /dev/vg1/lv2
# mkfs.xfs options /dev/vg1/lv2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow mount options /dev/vg1/lv1 mount_point_1
# mount options /dev/vg1/lv1 mount_point_1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow mount options /dev/vg1/lv2 mount_point_2
# mount options /dev/vg1/lv2 mount_point_2Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
XFS Recommendataions
- XFS Inode SizeAs Red Hat Gluster Storage makes extensive use of extended attributes, an XFS inode size of 512 bytes works better with Red Hat Gluster Storage than the default XFS inode size of 256 bytes. So, inode size for XFS must be set to 512 bytes while formatting the Red Hat Gluster Storage bricks. To set the inode size, you have to use -i size option with the
mkfs.xfscommand as shown in the following Logical Block Size for the Directory section. - XFS RAID AlignmentWhen creating an XFS file system, you can explicitly specify the striping parameters of the underlying storage in the following format:
mkfs.xfs other_options -d su=stripe_unit_size,sw=stripe_width_in_number_of_disks device
# mkfs.xfs other_options -d su=stripe_unit_size,sw=stripe_width_in_number_of_disks deviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For RAID 6, ensure that I/O is aligned at the file system layer by providing the striping parameters. For RAID 6 storage with 12 disks, if the recommendations above have been followed, the values must be as following:mkfs.xfs other_options -d su=128k,sw=10 device
# mkfs.xfs other_options -d su=128k,sw=10 deviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For RAID 10 and JBOD, the-d su=<>,sw=<>option can be omitted. By default, XFS will use the thin-p chunk size and other parameters to make layout decisions. - Logical Block Size for the DirectoryAn XFS file system allows to select a logical block size for the file system directory that is greater than the logical block size of the file system. Increasing the logical block size for the directories from the default 4 K, decreases the directory I/O, which in turn improves the performance of directory operations. To set the block size, you need to use
-n sizeoption with themkfs.xfscommand as shown in the following example output.Following is the example output of RAID 6 configuration along with inode and block size options:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Allocation Strategyinode32 and inode64 are two most common allocation strategies for XFS. With inode32 allocation strategy, XFS places all the inodes in the first 1 TiB of disk. With larger disk, all the inodes would be stuck in first 1 TiB. inode32 allocation strategy is used by default.With inode64 mount option inodes would be replaced near to the data which would be minimize the disk seeks.To set the allocation strategy to inode64 when file system is being mounted, you need to use
-o inode64option with themountcommand as shown in the following Access Time section. - Access TimeIf the application does not require to update the access time on files, than file system must always be mounted with
noatimemount option. For example:mount -t xfs -o inode64,noatime <logical volume> <mount point>
# mount -t xfs -o inode64,noatime <logical volume> <mount point>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This optimization improves performance of small-file reads by avoiding updates to the XFS inodes when files are read./etc/fstab entry for option E + F <logical volume> <mount point>xfs inode64,noatime 0 0
/etc/fstab entry for option E + F <logical volume> <mount point>xfs inode64,noatime 0 0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Allocation groupsEach XFS file system is partitioned into regions called allocation groups. Allocation groups are similar to the block groups in ext3, but allocation groups are much larger than block groups and are used for scalability and parallelism rather than disk locality. The default allocation for an allocation group is 1 TiB.Allocation group count must be large enough to sustain the concurrent allocation workload. In most of the cases allocation group count chosen by
mkfs.xfscommand would give the optimal performance. Do not change the allocation group count chosen bymkfs.xfs, while formatting the file system. - Percentage of space allocation to inodesIf the workload is very small files (average file size is less than 10 KB ), then it is recommended to set
maxpctvalue to10, while formatting the file system.
Performance tuning option in Red Hat Gluster Storage
A tuned profile is designed to improve performance for a specific use case by tuning system parameters appropriately. Red Hat Gluster Storage includes tuned profiles tailored for its workloads. These profiles are available in both Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.Expand Table 20.1. Recommended Profiles for Different Workloads Workload Profile Name Large-file, sequential I/O workloads rhgs-sequential-ioSmall-file workloads rhgs-random-ioRandom I/O workloads rhgs-random-ioEarlier versions of Red Hat Gluster Storage on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 recommended tuned profilesrhs-high-throughputandrhs-virtualization. These profiles are still available on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. However, switching to the new profiles is recommended.To apply tunings contained in the tuned profile, run the following command after creating a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume.tuned-adm profile profile-name
# tuned-adm profile profile-nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:tuned-adm profile rhgs-sequential-io
# tuned-adm profile rhgs-sequential-ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Writeback Caching
For small-file and random write performance, we strongly recommend writeback cache, that is, non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) in your storage controller. For example, normal Dell and HP storage controllers have it. Ensure that NVRAM is enabled, that is, the battery is working. Refer your hardware documentation for details on enabling NVRAM.Do not enable writeback caching in the disk drives, this is a policy where the disk drive considers the write is complete before the write actually made it to the magnetic media (platter). As a result, the disk write cache might lose its data during a power failure or even loss of metadata leading to file system corruption.
20.2.1. Many Bricks per Node
Configuring Brick Multiplexing
- Set
cluster.brick-multiplextoon. This option affects all volumes.gluster volume set all cluster.brick-multiplex on
# gluster volume set all cluster.brick-multiplex onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart all volumes for brick multiplexing to take effect.
gluster volume stop VOLNAME gluster volume start VOLNAME
# gluster volume stop VOLNAME # gluster volume start VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Important
20.2.2. Port Range Configuration
glusterd.vol file. The base-port and max-port options can be used to set the port range. By default, base-port is set to 49152, and max-port is set to 65535.
Important
base-port and max-port, newer bricks and volumes fail to start.
Configuring Port Range
- Edit the
glusterd.volfile on all the nodes.vi /etc/glusterfs/glusterd.vol
# vi /etc/glusterfs/glusterd.volCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Remove the comment marker
#corresponding to thebase-portandmax-portoptions.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define the port number in the
base-port, andmax-portoptions.option base-port 49152 option max-port 65535
option base-port 49152 option max-port 65535Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the
glusterd.volfile and restart theglusterdservice on each Red Hat Gluster Storage node.
20.3. Network
20.4. Memory
20.4.1. Virtual Memory Parameters
- vm.dirty_ratio
- vm.dirty_background_ratio
- Large-file sequential I/O workloads benefit from higher values for these parameters.
- For small-file and random I/O workloads it is recommended to keep these parameter values low.
20.5. Small File Performance Enhancements
Metadata-intensive workload is the term used to identify such workloads. A few performance enhancements can be made to optimize the network and storage performance and minimize the effect of slow throughput and response time for small files in a Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool.
Note
rhgs-random-io tuned profile.
You can set the client.event-thread and server.event-thread values for the client and server components. Setting the value to 4, for example, would enable handling four network connections simultaneously.
gluster volume set VOLNAME client.event-threads <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME client.event-threads <value>Example 20.1. Tuning the event threads for a client accessing a volume
gluster volume set test-vol client.event-threads 4
# gluster volume set test-vol client.event-threads 4gluster volume set VOLNAME server.event-threads <value>
# gluster volume set VOLNAME server.event-threads <value>Example 20.2. Tuning the event threads for a server accessing a volume
gluster volume set test-vol server.event-threads 4
# gluster volume set test-vol server.event-threads 4gluster volume info VOLNAME
# gluster volume info VOLNAMEIt is possible to see performance gains with the Red Hat Gluster Storage stack by tuning the number of threads processing events from network connections. The following are the recommended best practices to tune the event thread values.
- As each thread processes a connection at a time, having more threads than connections to either the brick processes (
glusterfsd) or the client processes (glusterfsorgfapi) is not recommended. Due to this reason, monitor the connection counts (using thenetstatcommand) on the clients and on the bricks to arrive at an appropriate number for the event thread count. - Configuring a higher event threads value than the available processing units could again cause context switches on these threads. As a result reducing the number deduced from the previous step to a number that is less that the available processing units is recommended.
- If a Red Hat Gluster Storage volume has a high number of brick processes running on a single node, then reducing the event threads number deduced in the previous step would help the competing processes to gain enough concurrency and avoid context switches across the threads.
- If a specific thread consumes more number of CPU cycles than needed, increasing the event thread count would enhance the performance of the Red Hat Gluster Storage Server.
- In addition to the deducing the appropriate event-thread count, increasing the
server.outstanding-rpc-limiton the storage nodes can also help to queue the requests for the brick processes and not let the requests idle on the network queue. - Another parameter that could improve the performance when tuning the event-threads value is to set the
performance.io-thread-count(and its related thread-counts) to higher values, as these threads perform the actual IO operations on the underlying file system.
20.5.1. Enabling Lookup Optimization
cluster.lookup-optimize configuration option enables DHT lookup optimization. To enable this option run the following command:
gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.lookup-optimize <on/off>\
# gluster volume set VOLNAME cluster.lookup-optimize <on/off>\Note
20.6. Replication
20.7. Directory Operations
- Listing of directories (recursive)
- Creating files
- Deleting files
- Renaming files
20.7.1. Enabling Metadata Caching
Note
- Execute the following command to enable metadata caching and cache invalidation:
gluster volume set <volname> group metadata-cache
# gluster volume set <volname> group metadata-cacheCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This is group set option which sets multiple volume options in a single command. - To increase the number of files that can be cached, execute the following command:
gluster volume set <VOLNAME> network.inode-lru-limit <n>
# gluster volume set <VOLNAME> network.inode-lru-limit <n>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow n, is set to 50000. It can be increased if the number of active files in the volume is very high. Increasing this number increases the memory footprint of the brick processes.
20.8. LVM Cache for Red Hat Gluster Storage
Important
20.8.1. About LVM Cache
20.8.1.1. LVM Cache vs. DM-Cache
dm-cache refers to the Linux kernel-level device-mapper subsystem that is responsible for all I/O transactions. For most usual operations, the administrator interfaces with the logical volume manager (LVM) as a much simpler abstraction layer above device-mapper. As such, lvmcache is simply part of the LVM system acting as an abstraction layer for the dm-cache subsystem.
20.8.1.2. LVM Cache vs. Gluster Tiered Volumes
20.8.1.3. Arbiter Bricks
20.8.1.4. Writethrough vs. Writeback
Note
20.8.1.5. Cache-Friendly Workloads
20.8.2. Choosing the Size and Speed of Your Cache Devices
20.8.3. Configuring LVM Cache
Warning
/dev/nvme0n1. A SATA/SAS device will likely present with a device path such as /dev/sdb. The following example naming has been used:
- Physical Volume (PV) Name:
/dev/nvme0n1 - Volume Group (VG) Name:
GVG - Thin pool name:
GTP - Logical Volume (LV) name:
GLV
Note
lvmcache(7).
- Create a PV for your fast data device.
pvcreate /dev/nvme0n1
# pvcreate /dev/nvme0n1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add the fast data PV to the VG that hosts the LV you intend to cache.
vgextend GVG /dev/nvme0n1
# vgextend GVG /dev/nvme0n1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Create the cache pool from your fast data device, reserving space required for metadata during the cache conversion process of your LV.
lvcreate --type cache-pool -l 100%FREE -n cpool GVG /dev/nvme0n1
# lvcreate --type cache-pool -l 100%FREE -n cpool GVG /dev/nvme0n1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Convert your existing data thin pool LV into a cache LV.
lvconvert --type cache --cachepool GVG/cpool GVG/GTP
# lvconvert --type cache --cachepool GVG/cpool GVG/GTPCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
20.8.4. Managing LVM Cache
20.8.4.1. Changing the Mode of an Existing Cache Pool
lvchange command. For thin LVs, the command must be run against the tdata subvolume.
lvchange --cachemode writeback GVG/GTP_tdata
# lvchange --cachemode writeback GVG/GTP_tdata20.8.4.2. Checking Your Configuration
lsblk command to view the new virtual block device layout.
lvs command displays a number of valuable columns to show the status of your cache pool and volume. For more details, see lvs(8).
lvs command that can be used to monitor the effectiveness of the cache and to aid in sizing decisions are:
- CacheTotalBlocks
- CacheUsedBlocks
- CacheDirtyBlocks
- CacheReadHits
- CacheReadMisses
- CacheWriteHits
- CacheWriteMisses
lvs -a -o devices,cachetotalblocks,cacheusedblocks, \ cachereadhits,cachereadmisses | egrep 'Devices|cdata' Devices CacheTotalBlocks CacheUsedBlocks CacheReadHits CacheReadMisses cpool_cdata(0) 998850 2581 1 192
# lvs -a -o devices,cachetotalblocks,cacheusedblocks, \
cachereadhits,cachereadmisses | egrep 'Devices|cdata'
Devices CacheTotalBlocks CacheUsedBlocks CacheReadHits CacheReadMisses
cpool_cdata(0) 998850 2581 1 19220.8.4.3. Detaching a Cache Pool
lvconvert --splitcache GVG/cpool
# lvconvert --splitcache GVG/cpoolChapter 21. Nagios Configuration Files
- In
/etc/nagios/gluster/directory, a new directoryCluster-Nameis created with the name provided asCluster-Namewhile executingconfigure-gluster-nagioscommand for auto-discovery. All configurations created by auto-discovery for the cluster are added in this folder. - In
/etc/nagios/gluster/Cluster-Namedirectory, a configuration file,Cluster-Name.cfgis generated. This file has the host and hostgroup configurations for the cluster. This also contains service configuration for all the cluster/volume level services.The following Nagios object definitions are generated inCluster-Name.cfgfile:- A hostgroup configuration with
hostgroup_nameas cluster name. - A host configuration with
host_nameas cluster name. - The following service configurations are generated for cluster monitoring:
- A Cluster - Quorum service to monitor the cluster quorum.
- A Cluster Utilization service to monitor overall utilization of volumes in the cluster. This is created only if there is any volume present in the cluster.
- A Cluster Auto Config service to periodically synchronize the configurations in Nagios with Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool.
- The following service configurations are generated for each volume in the trusted storage pool:
- A Volume Status- Volume-Name service to monitor the status of the volume.
- A Volume Utilization - Volume-Name service to monitor the utilization statistics of the volume.
- A Volume Quota - Volume-Name service to monitor the Quota status of the volume, if Quota is enabled for the volume.
- A Volume Self-Heal - Volume-Name service to monitor the Self-Heal status of the volume, if the volume is of type replicate or distributed-replicate.
- A Volume Geo-Replication - Volume-Name service to monitor the Geo Replication status of the volume, if Geo-replication is configured for the volume.
- In
/etc/nagios/gluster/Cluster-Namedirectory, a configuration file with nameHost-Name.cfgis generated for each node in the cluster. This file has the host configuration for the node and service configuration for bricks from the particular node. The following Nagios object definitions are generated inHost-name.cfg.- A host configuration which has Cluster-Name in the
hostgroupsfield. - The following services are created for each brick in the node:
- A Brick Utilization - brick-path service to monitor the utilization of the brick.
- A Brick - brick-path service to monitor the brick status.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
/etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
Main Nagios configuration file.
|
/etc/nagios/cgi.cfg
|
CGI configuration file.
|
/etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf
|
Nagios configuration for httpd.
|
/etc/nagios/passwd
|
Password file for Nagios users.
|
/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
|
NRPE configuration file.
|
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-contacts.cfg
|
Email notification configuration file.
|
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-host-services.cfg
|
Services configuration file that's applied to every Red Hat Gluster Storage node.
|
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-host-groups.cfg
|
Host group templates for a Red Hat Gluster Storage trusted storage pool.
|
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-commands.cfg
|
Command definitions file for Red Hat Gluster Storage Monitoring related commands.
|
/etc/nagios/gluster/gluster-templates.cfg
|
Template definitions for Red Hat Gluster Storage hosts and services.
|
/etc/nagios/gluster/snmpmanagers.conf
|
SNMP notification configuration file with the IP address and community name of SNMP managers where traps need to be sent.
|
Part VI. Security
Chapter 22. Configuring Network Encryption in Red Hat Gluster Storage
- I/O encryption
- Encryption of the I/O connections between the Red Hat Gluster Storage clients and servers.
- Management encryption
- Encryption of management (
glusterd) connections within a trusted storage pool, and betweenglusterdand NFS Ganesha or SMB clients.
/etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem- Certificate file containing the system's uniquely signed TLS certificate. This file is unique for each system and must not be shared with others.
/etc/ssl/glusterfs.key- This file contains the system's unique private key. This file must not be shared with others.
/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca- This file contains the certificates of the Certificate Authorities (CA) who have signed the certificates. The
glusterfs.cafile must be identical on all servers in the trusted pool, and must contain the certificates of the signing CA for all servers and all clients. All clients should also have a.cafile that contains the certificates of the signing CA for all the servers.Red Hat Gluster Storage does not use the global CA certificates that come with the system, so you need to either create your own self-signed certificates, or create certificates and have them signed by a Certificate Authority. If you are using self-signed certificates, the CA file for the servers is a concatenation of the relevant.pemfiles of every server and every client. The client CA file is a concatenation of the certificate files of every server. /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access- This file is required for management encryption. It enables encryption on the management (
glusterd) connections betweenglusterdof all servers and the connection between clients, and contains any configuration required by the Certificate Authority. Theglusterdservice of all servers uses this file to fetch volfiles and notify the clients with the volfile changes. This file must be present on all servers and all clients for management encryption to work correctly. It can be empty, but most configurations require at least one line to set the certificate depth (transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth) required by the Certificate Authority.
22.1. Preparing Certificates
- Self-signed certificate
- Generating and signing the certificate yourself.
- Certificate Authority (CA) signed certificate
- Generating the certificate and then requesting that a Certificate Authority sign it.
Procedure 22.1. Preparing a self-signed certificate
Generate and sign certificates for each server and client
Perform the following steps on each server and client.Generate a private key for this machine
openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048
# openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate a self-signed certificate for this machine
The following command generates a signed certificate that expires in 365 days, instead of the default 30 days. Provide a short name for this machine in place of COMMONNAME. This is generally a hostname, FQDN, or IP address.openssl req -new -x509 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj "/CN=COMMONNAME" -days 365 -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem
# openssl req -new -x509 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj "/CN=COMMONNAME" -days 365 -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Generate client-side certificate authority lists
From the first server, concatenate the/etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemfiles from all servers into a single file calledglusterfs.ca, and place this file in the/etc/ssldirectory on all clients.For example, running the following commands fromserver1creates a certificate authority list (.cafile) that contains the certificates (.pemfiles) of two servers, and copies the certificate authority list (.cafile) to three clients.cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem > /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca ssh user@server2 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca client1:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca client2:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca client3:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca
# cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem > /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # ssh user@server2 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca client1:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca client2:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca client3:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate server-side
glusterfs.cafilesFrom the first server, append the certificates (/etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemfiles) from all clients to the end of the certificate authority list (/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile) generated in the previous step.For example, running the following commands fromserver1appends the certificates (.pemfiles) of three clients to the certificate authority list (.cafile) onserver1, and then copies that certificate authority list (.cafile) to one other server.ssh user@client1 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca ssh user@client2 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca ssh user@client3 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca server2:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca
# ssh user@client1 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # ssh user@client2 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # ssh user@client3 cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca server2:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify server certificates
Run the following command in the/etc/ssldirectory on the servers to verify the certificate on that machine against the Certificate Authority list.openssl verify -verbose -CAfile glusterfs.ca glusterfs.pem
# openssl verify -verbose -CAfile glusterfs.ca glusterfs.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your certificate is correct if the output of this command isglusterfs.pem: OK.Note
This process does not work for self-signed client certificates.
Procedure 22.2. Preparing a Common Certificate Authority certificate
Generate a private key
openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048
# openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate a certificate signing request
The following command generates a certificate signing request for a certificate that expires in 365 days, instead of the default 30 days. Provide a short name for this machine in place of COMMONNAME. This is generally a hostname, FQDN, or IP address.openssl req -new -sha256 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj '/CN=<COMMONNAME>' -days 365 -out glusterfs.csr
# openssl req -new -sha256 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj '/CN=<COMMONNAME>' -days 365 -out glusterfs.csrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Send the generated glusterfs.csr file to your Certificate Authority
Your Certificate Authority provides a signed certificate for this machine in the form of a.pemfile, and the certificates of the Certificate Authority in the form of a.cafile.Place the
.pemfile provided by the Certificate AuthorityEnsure that the.pemfile is calledglusterfs.pem. Place this file in the/etc/ssldirectory of this server only.Place the
.cafile provided by the Certificate AuthorityEnsure that the.cafile is calledglusterfs.ca. Place the.cafile in the/etc/ssldirectory of all servers.Verify your certificates
Run the following command in the/etc/ssldirectory on all clients and servers to verify the certificate on that machine against the Certificate Authority list.openssl verify -verbose -CAfile glusterfs.ca glusterfs.pem
# openssl verify -verbose -CAfile glusterfs.ca glusterfs.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your certificate is correct if the output of this command isglusterfs.pem: OK.
22.2. Configuring Network Encryption for a New Trusted Storage Pool
22.2.1. Enabling Management Encryption
Procedure 22.3. Enabling management encryption on servers
Create and edit the secure-access file
Create a new/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile. This file can be empty if you are using the default settings.touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your Certificate Authority may require changes to the SSL certificate depth setting,transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth, in order to work correctly. To edit this setting, add the following line to thesecure-accessfile, replacing n with the certificate depth required by your Certificate Authority.echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start
glusterdOn Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based servers, run:systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based servers, run:service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Continue storage configuration
Proceed with the normal configuration process by setting up the trusted storage pool, formatting bricks, and creating volumes. For more information, see Chapter 4, Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool and Chapter 5, Setting Up Storage Volumes.
Procedure 22.4. Enabling management encryption on clients
Prerequisites
- You must have configured a trusted storage pool, bricks, and volumes before following this process. For more information, see Chapter 4, Adding Servers to the Trusted Storage Pool and Chapter 5, Setting Up Storage Volumes.
Create and edit the secure-access file
Create the/var/lib/glusterddirectory, and create a new/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile. This file can be empty if you are using the default settings.touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your Certificate Authority may require changes to the SSL certificate depth setting,transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth, in order to work correctly. To edit this setting, add the following line to thesecure-accessfile, replacing n with the certificate depth required by your Certificate Authority.echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the volume
On the server, start the volume.gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount the volume
The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using. The following command mounts a volume calledtestvolusing the native FUSE protocol.mount -t glusterfs server1:testvol /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:testvol /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.2.2. Enabling I/O Encryption
Procedure 22.5. Enabling I/O encryption
Prerequisites
- You must have volumes configured, but not started, to perform this process. See Chapter 5, Setting Up Storage Volumes for information on creating volumes. To stop a volume, run the following command:
gluster volume stop volname
# gluster volume stop volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Specify servers and clients to allow
Provide a list of the common names of servers and clients that are allowed to access the volume. The common names provided must be exactly the same as the common name specified when you created theglusterfs.pemfile for that server or client.gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'
# gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This provides an additional check in case you want to leave keys in place, but temporarily restrict a client or server by removing it from this list, as shown in Section 22.7, “Deauthorizing a Client”.You can also use the default value of*, which indicates that any TLS authenticated machine can mount and access the volume.Enable TLS/SSL on the volume
gluster volume set volname client.ssl on gluster volume set volname server.ssl on
# gluster volume set volname client.ssl on # gluster volume set volname server.ssl onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the volume
gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify
Verify that the volume can be mounted on authorized clients, and that the volume cannot be mounted by unauthorized clients. The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using.The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using. The following command mounts a volume calledtestvolusing the native FUSE protocol.mount -t glusterfs server1:testvol /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:testvol /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.3. Configuring Network Encryption for an existing Trusted Storage Pool
22.3.1. Enabling I/O Encryption
Procedure 22.6. Enabling I/O encryption
Unmount the volume from all clients
Unmount the volume by running the following command on all clients.umount mountpoint
# umount mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop the volume
Stop the volume by running the following command from any server.gluster volume stop VOLNAME
# gluster volume stop VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify servers and clients to allow
Provide a list of the common names of servers and clients that are allowed to access the volume. The common names provided must be exactly the same as the common name specified when you created theglusterfs.pemfile for that server or client.gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'
# gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This provides an additional check in case you want to leave keys in place, but temporarily restrict a client or server by removing it from this list, as shown in Section 22.7, “Deauthorizing a Client”.You can also use the default value of*, which indicates that any TLS authenticated machine can mount and access the volume.Enable TLS/SSL encryption on the volume
Run the following command from any server to enable TLS/SSL encryption.gluster volume set volname client.ssl on gluster volume set volname server.ssl on
# gluster volume set volname client.ssl on # gluster volume set volname server.ssl onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the volume
gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify
Verify that the volume can be mounted only on authorized clients. The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using.The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol. Ensure that this command works on authorized clients, and does not work on unauthorized clients.mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.4. Enabling Management Encryption
Prerequisites
- Enabling management encryption requires that storage servers are offline. Schedule an outage window for volumes, applications, clients, and other end users before beginning this process. Be aware that features such as snapshots and geo-replication may also be affected by this outage.
Procedure 22.7. Enabling management encryption
Prepare to enable encryption
Unmount all volumes from all clients
Run the following command on each client, for each volume mounted on that client.umount mount-point
# umount mount-pointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop NFS Ganesha or SMB services, if used
Run the following command on any gluster server to disable NFS-Ganesha.systemctl stop nfs-ganesha
# systemctl stop nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command on any gluster server to stop SMB.systemctl stop ctdb
# systemctl stop ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Unmount shared storage, if used
Run the following command on all servers to unmount shared storage.umount /var/run/gluster/shared_storage
# umount /var/run/gluster/shared_storageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Features that require shared storage, such as snapshots and geo-replication, may not work until after this process is complete.Stop all volumes
Run the following command on any server to stop all volumes, including the shared storage volume.for vol in `gluster volume list`; do gluster --mode=script volume stop $vol; sleep 2s; done
# for vol in `gluster volume list`; do gluster --mode=script volume stop $vol; sleep 2s; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop gluster services on all servers
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations:systemctl stop glusterd pkill glusterfs
# systemctl stop glusterd # pkill glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations:service glusterd stop pkill glusterfs
# service glusterd stop # pkill glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Bug 1635071 may cause glusterd to crash during shutdown, but there is no functionality impact to this crash. See Resolving glusterd crash for details.
Create and edit the secure-access file on all servers and clients
Create a new/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile. This file can be empty if you are using the default settings.touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your Certificate Authority may require changes to the SSL certificate depth setting,transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth, in order to work correctly. To edit this setting, add the following line to thesecure-accessfile, replacing n with the certificate depth required by your Certificate Authority.echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Clean up after configuring management encryption
Start the glusterd service on all servers
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations:systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations:service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start all volumes
Run the following command on any host to start all volumes including shared storage.for vol in `gluster volume list`; do gluster --mode=script volume start $vol; sleep 2s; done
# for vol in `gluster volume list`; do gluster --mode=script volume start $vol; sleep 2s; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount shared storage, if used
Run the following command on all servers to mount shared storage.mount -t glusterfs hostname:/gluster_shared_storage /run/gluster/shared_storage
# mount -t glusterfs hostname:/gluster_shared_storage /run/gluster/shared_storageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart NFS Ganesha or SMB services, if used
Run the following command on any gluster server to start NFS-Ganesha.systemctl start nfs-ganesha
# systemctl start nfs-ganeshaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following command on any gluster server to start SMB.systemctl start ctdb
# systemctl start ctdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount volumes on clients
The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using. The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol.mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.5. Expanding Volumes
22.5.1. Certificate signed by a Common Certificate Authority
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have followed the steps in Section 22.1, “Preparing Certificates” before following this section.
Procedure 22.8. Expanding a pool that uses common Certificate Authority signed certificates
Import the common Certificate Authority list
Copy the/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile from an existing server into the/etc/ssldirectory of the new server.For management encryption, create and edit the secure-access file
Create a new/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile. This file can be empty if you are using the default settings.touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your Certificate Authority may require changes to the SSL certificate depth setting,transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth, in order to work correctly. To edit this setting, add the following line to thesecure-accessfile, replacing n with the certificate depth required by your Certificate Authority.echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start glusterd on the new server
systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify servers and clients to allow
Provide a list of the common names of servers and clients that are allowed to access the volume. The common names provided must be exactly the same as the common name specified when you created theglusterfs.pemfile for that server or client.gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'
# gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This provides an additional check in case you want to leave keys in place, but temporarily restrict a client or server by removing it from this list, as shown in Section 22.7, “Deauthorizing a Client”.Note
Thegluster volume setcommand does not append to existing values of the options. To append the new name to the list, get the existing list usinggluster volume infocommand, append the new name to the list and set the option again usinggluster volume setcommand.You can also use the default value of*, which indicates that any TLS authenticated machine can mount and access the volume.Expand volumes to the new server
Follow the instructions in Section 11.7, “Expanding Volumes” to expand existing volumes using the newly trusted server.
22.5.2. Self-signed Certificates
Prerequisites
- Because self-signed certificates are not automatically generated and updated, the trusted storage pool must be offline for this process. Schedule an outage window for volumes, applications, clients, and other end users before beginning this process.
Procedure 22.9. Expanding a pool that uses self-signed certificates
Generate the key and self-signed certificate for the new server
Follow the steps in Section 22.1, “Preparing Certificates” to generate a private key and a self-signed certificate for the new server.Update server Certificate Authority list files
Append the contents of the new server's/etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemfile to the/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile on all existing servers in the trusted storage pool.Update client Certificate Authority list files
Append the contents of the new server's/etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemfile to the/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile on all authorized clients in the trusted storage pool.Stop all gluster processes
Run the following commands on all servers.systemctl stop glusterd pkill glusterfs
# systemctl stop glusterd # pkill glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Bug 1635071 may cause glusterd to crash during shutdown, but there is no functionality impact to this crash. See Resolving glusterd crash for details.(Optional) Enable management encryption on the new server
Copy the/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile from an existing server to the new server.Start glusterd on the new server
systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update servers and clients to allow
Run the following command from any server to specify the common names of servers and clients that are allowed to access the volume. The common names provided must be exactly the same as the common name specified when you created theglusterfs.pemfile for that server or client.gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'
# gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Thegluster volume setcommand does not append to existing values of the options. To append the new name to the list, get the existing list usinggluster volume infocommand, append the new name to the list and set the option again usinggluster volume setcommand.You can also use the default value of*, which indicates that any TLS authenticated machine can mount and access the volume.Restart the glusterfs processes on existing servers and clients
On all clients, unmount all volumes
umount mountpoint
# umount mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On any server, stop all volumes
for vol in `gluster volume list`; do gluster --mode=script volume stop $vol; sleep 2s; done
# for vol in `gluster volume list`; do gluster --mode=script volume stop $vol; sleep 2s; doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On all servers, restart glusterd
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations:systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations:service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On any server, start all volumes
gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Mount the volume on all clients
The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using. The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol.mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/test-volume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expand volumes to the new server
Follow the instructions in Section 11.7, “Expanding Volumes” to expand existing volumes using the newly trusted server.
22.6. Authorizing a New Client
22.6.1. Certificate Signed by a Common Certificate Authority
Procedure 22.10. Authorizing a new client using a CA-signed certificate
Generate a key for the client
Run the following command on the client.openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048
# openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate a certificate signing request
The following command generates a certificate signing request for a certificate that expires in 365 days, instead of the default 30 days. Provide a short name for this machine in place of COMMONNAME. This is generally a hostname, FQDN, or IP address.openssl req -new -sha256 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj '/CN=<COMMONNAME>' -days 365 -out glusterfs.csr
# openssl req -new -sha256 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj '/CN=<COMMONNAME>' -days 365 -out glusterfs.csrCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Send the generated glusterfs.csr file to your Certificate Authority
Your Certificate Authority provides a signed certificate for this machine in the form of a.pemfile, and the Certificate Authority list in the form of a.cafile.Add provided certificate file on the client
Place the.pemfile provided by the Certificate Authority in the/etc/ssldirectory on the client. Ensure that the.pemfile is calledglusterfs.pem.Add the Certificate Authority list to the client
Copy the/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile from an existing client to your new client.scp existingclient/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca newclient:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca
# scp existingclient/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca newclient:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify your certificate
Run the following command in the/etc/ssldirectory to verify the certificate on that machine against the Certificate Authority list.openssl verify -verbose -CAfile glusterfs.ca glusterfs.pem
# openssl verify -verbose -CAfile glusterfs.ca glusterfs.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your certificate is correct if the output of this command isglusterfs.pem: OK.Configure management encryption, if used
On the client, create the/var/lib/glusterddirectory, and create a new/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile. This file can be empty if you are using the default settings.touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your Certificate Authority may require changes to the SSL certificate depth setting,transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth, in order to work correctly. To edit this setting, add the following line to thesecure-accessfile, replacing n with the certificate depth required by your Certificate Authority.echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the list of servers and clients to allow
Run the following command from any server to specify the common names of servers and clients that are allowed to access the volume. The common names provided must be exactly the same as the common name specified when you created theglusterfs.pemfile for that server or client.gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'
# gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Thegluster volume setcommand does not append to existing values of the options. To append the new name to the list, get the existing list usinggluster volume infocommand, append the new name to the list and set the option again usinggluster volume setcommand.You can also use the default value of*, which indicates that any TLS authenticated machine can mount and access the volume.Start the volume
gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify
Verify that the volume can be mounted from the new client. The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using.The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol. Ensure that this command works on authorized clients, and does not work on unauthorized clients.mount -t glusterfs server1:testvolume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:testvolume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.6.2. Self-signed Certificates
Prerequisites
- Because self-signed certificates are not automatically generated and updated, the trusted storage pool must be offline for this process. Schedule an outage window for volumes, applications, clients, and other end users before beginning this process.
Procedure 22.11. Authorizing a new client using a self-signed certificate
Generate a key for the client
Run the following command on the client.openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048
# openssl genrsa -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key 2048Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate a self-signed certificate for the client
The following command generates a signed certificate that expires in 365 days, instead of the default 30 days. Provide a short name for this machine in place of COMMONNAME. This is generally a hostname, FQDN, or IP address.openssl req -new -x509 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj "/CN=COMMONNAME" -days 365 -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem
# openssl req -new -x509 -key /etc/ssl/glusterfs.key -subj "/CN=COMMONNAME" -days 365 -out /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Certificate Authority list to the client
Copy the/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile from an existing client to your new client. Run the following command from the new client.scp existingclient:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca
# scp existingclient:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca /etc/ssl/glusterfs.caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Generate new server
glusterfs.cafilesOn any server, append the value of the new client's/etc/ssl/glusterfs.pemfile to the end of the server's/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile.Place the updated/etc/ssl/glusterfs.cafile in the/etc/ssldirectory of all servers in the trusted storage pool.For example, running the following commands on any server updates theglusterfs.cafile with the.pemfile from the new client, and then copies thatglusterfs.cafile to all servers.ssh user@newclient cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca server1:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca server2:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca
# ssh user@newclient cat /etc/ssl/glusterfs.pem >> /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca server1:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca # scp /etc/ssl/glusterfs.ca server2:/etc/ssl/glusterfs.caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure management encryption on the new client, if used
On the client, create the/var/lib/glusterddirectory, and create a new/var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessfile. This file can be empty if you are using the default settings.touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# touch /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Your Certificate Authority may require changes to the SSL certificate depth setting,transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth, in order to work correctly. To edit this setting, add the following line to thesecure-accessfile, replacing n with the certificate depth required by your Certificate Authority.echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
echo "option transport.socket.ssl-cert-depth n" > /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the list of servers and clients to allow
Run the following command from any server to specify the common names of servers and clients that are allowed to access the volume. The common names provided must be exactly the same as the common name specified when you created theglusterfs.pemfile for that server or client.gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'
# gluster volume set volname auth.ssl-allow 'server1,server2,client1,client2,client3'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Thegluster volume setcommand does not append to existing values of the options. To append the new name to the list, get the existing list usinggluster volume infocommand, append the new name to the list and set the option again usinggluster volume setcommand.You can also use the default value of*, which indicates that any TLS authenticated machine can mount and access the volume.Start the volume
Run the following command from any server to start the volume.gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If management encryption is used, restart glusterd on all servers
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations:systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations:service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify
Verify that the volume can be mounted from the new client. The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using.The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol. Ensure that this command works on authorized clients, and does not work on unauthorized clients.mount -t glusterfs server1:testvolume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:testvolume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.7. Deauthorizing a Client
Procedure 22.12. Removing an authorized client from the allowed list
List currently authorized clients and servers
gluster volume get VOLNAME auth.ssl-allow
$ gluster volume get VOLNAME auth.ssl-allowCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the following command shows that there are three authorized servers and five authorized clients.gluster volume get sample_volname auth.ssl-allow server1,server2,server3,client1,client2,client3,client4,client5
$ gluster volume get sample_volname auth.ssl-allow server1,server2,server3,client1,client2,client3,client4,client5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove clients to deauthorize from the output
For example, if you want to deauthorize client2 and client4, copy the string and remove those clients from the list.server1,server2,server3,client1,client3,client5
server1,server2,server3,client1,client3,client5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the new list of authorized clients and servers
Set the value ofauth.ssl-allowto your updated string.gluster volume set VOLNAME auth.ssl-allow <list_of_systems>
$ gluster volume set VOLNAME auth.ssl-allow <list_of_systems>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the updated list shows three servers and three clients.gluster volume set sample_volname auth.ssl-allow server1,server2,server3,client1,client3,client5
$ gluster volume set sample_volname auth.ssl-allow server1,server2,server3,client1,client3,client5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.8. Disabling Network Encryption
Procedure 22.13. Disabling I/O encryption
Unmount volumes from all clients
Run the following command on each client for any volume that should have encryption disabled.umount /mountpoint
# umount /mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop encrypted volumes
Run the following command on any server to stop volumes that should have encryption disabled.gluster volume stop volname
# gluster volume stop volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable server and client SSL usage
Run the following commands for each volume that should have encryption disabled.gluster volume set volname server.ssl off gluster volume set volname client.ssl off
# gluster volume set volname server.ssl off # gluster volume set volname client.ssl offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start volumes
gluster volume start volname
# gluster volume start volnameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount volumes on clients
The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using. The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol.mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure 22.14. Disabling management encryption
Unmount volumes from all clients
Run the following command on each client for any volume that should have encryption disabled.umount /mountpoint
# umount /mountpointCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop glusterd on all nodes
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations:systemctl stop glusterd
# systemctl stop glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations:service glusterd stop
# service glusterd stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Bug 1635071 may cause glusterd to crash during shutdown, but there is no functionality impact to this crash. See Resolving glusterd crash for details.Remove the secure-access file
Run the following command on all servers and clients to remove the secure-access file. You can just rename the file if you are only disabling encryption temporarily.rm -f /var/lib/glusterd/secure-access
# rm -f /var/lib/glusterd/secure-accessCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start glusterd on all nodes
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 based installations:systemctl start glusterd
# systemctl start glusterdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 based installations:service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Mount volumes on clients
The process for mounting a volume depends on the protocol your client is using. The following command mounts a volume using the native FUSE protocol.mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfs
# mount -t glusterfs server1:/testvolume /mnt/glusterfsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Important
Part VII. Troubleshoot
Chapter 23. Resolving Common Issues
23.1. Identifying locked file and clear locks
statedump command to list the locks held on files. The statedump output also provides information on each lock with its range, basename, and PID of the application holding the lock, and so on. You can analyze the output to find the locks whose owner/application is no longer running or interested in that lock. After ensuring that no application is using the file, you can clear the lock using the following clear-locks command:
# gluster volume clear-locks VOLNAME path kind {blocked | granted | all}{inode range | entry basename | posix range}
statedump, see Section 18.8, “Viewing complete volume state with statedump”
- Perform
statedumpon the volume to view the files that are locked using the following command:# gluster volume statedump VOLNAMEFor example, to displaystatedumpof test-volume:gluster volume statedump test-volume Volume statedump successful
# gluster volume statedump test-volume Volume statedump successfulCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Thestatedumpfiles are created on the brick servers in the/tmpdirectory or in the directory set using theserver.statedump-pathvolume option. The naming convention of the dump file isbrick-path.brick-pid.dump. - Clear the entry lock using the following command:
# gluster volume clear-locks VOLNAME path kind granted entry basenameThe following are the sample contents of thestatedumpfile indicating entry lock (entrylk). Ensure that those are stale locks and no resources own them.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to clear the entry lock onfile1of test-volume:gluster volume clear-locks test-volume / kind granted entry file1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: entry blocked locks=0 granted locks=1
# gluster volume clear-locks test-volume / kind granted entry file1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: entry blocked locks=0 granted locks=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Clear the inode lock using the following command:
# gluster volume clear-locks VOLNAME path kind granted inode rangeThe following are the sample contents of thestatedumpfile indicating there is an inode lock (inodelk). Ensure that those are stale locks and no resources own them.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to clear the inode lock onfile1of test-volume:gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind granted inode 0,0-0 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: inode blocked locks=0 granted locks=1
# gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind granted inode 0,0-0 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: inode blocked locks=0 granted locks=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Clear the granted POSIX lock using the following command:
# gluster volume clear-locks VOLNAME path kind granted posix rangeThe following are the sample contents of thestatedumpfile indicating there is a granted POSIX lock. Ensure that those are stale locks and no resources own them.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to clear the granted POSIX lock onfile1of test-volume:gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind granted posix 0,8-1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=0 granted locks=1 test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=0 granted locks=1 test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=0 granted locks=1
# gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind granted posix 0,8-1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=0 granted locks=1 test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=0 granted locks=1 test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=0 granted locks=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Clear the blocked POSIX lock using the following command:
# gluster volume clear-locks VOLNAME path kind blocked posix rangeThe following are the sample contents of thestatedumpfile indicating there is a blocked POSIX lock. Ensure that those are stale locks and no resources own them.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to clear the blocked POSIX lock onfile1of test-volume:gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind blocked posix 0,0-1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=28 granted locks=0 test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=1 granted locks=0 No locks cleared.
# gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind blocked posix 0,0-1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=28 granted locks=0 test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=1 granted locks=0 No locks cleared.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Clear all POSIX locks using the following command:
# gluster volume clear-locks VOLNAME path kind all posix rangeThe following are the sample contents of thestatedumpfile indicating that there are POSIX locks. Ensure that those are stale locks and no resources own them.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to clear all POSIX locks onfile1of test-volume:gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind all posix 0,0-1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=1 granted locks=0 No locks cleared. test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=4 granted locks=1
# gluster volume clear-locks test-volume /file1 kind all posix 0,0-1 Volume clear-locks successful test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=1 granted locks=0 No locks cleared. test-volume-locks: posix blocked locks=4 granted locks=1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
statedump on test-volume again to verify that all the above locks are cleared.
23.2. Retrieving File Path from the Gluster Volume
getfattr utility. The getfattr utility enables you to locate a file residing on a gluster volume brick. You can retrieve the path of a file even if the filename is unknown.
23.2.1. Retrieving Known File Name
getfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo -e text <path_to_fuse_mount/filename>
# getfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo -e text <path_to_fuse_mount/filename>23.2.2. Retrieving Unknown File Name
Note
getfattr -d -m. -e hex /path/to/file/on/the/brick
# getfattr -d -m. -e hex /path/to/file/on/the/brick23.2.3. Retrieving File Path using gfid String
- Fuse mount the volume with the aux-gfid option enabled.
mount -t glusterfs -o aux-gfid-mount hostname:volume-name <path_to_fuse_mnt>
# mount -t glusterfs -o aux-gfid-mount hostname:volume-name <path_to_fuse_mnt>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where,path_to_fuse_mount: The fuse mount where the gluster volume is mounted.For example:mount -t glusterfs -o aux-gfid-mount 127.0.0.2:testvol /mnt/aux_mount
# mount -t glusterfs -o aux-gfid-mount 127.0.0.2:testvol /mnt/aux_mountCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After mounting the volume, execute the following command
getfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo -e text <path-to-fuse-mnt>/.gfid/<GFID string>
# getfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo -e text <path-to-fuse-mnt>/.gfid/<GFID string>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where,path_to_fuse_mount: The fuse mount where the gluster volume is mounted.GFID string: The GFID string.For example:getfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo -e text /mnt/aux_mount/.gfid/80b0b164-2ea4-478b-a4cd-a9f76c1e6efd getfattr: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names file: mnt/aux_mount/.gfid/80b0b164-2ea4-478b-a4cd-a9f76c1e6efd trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo="(<DISTRIBUTE:testvol-dht> (<REPLICATE:testvol-replicate-0> <POSIX(/rhgs/brick2):tuxpad:/rhgs/brick2/File1> <POSIX(/rhgs/brick1):tuxpad:/rhgs/brick1/File1>))
# getfattr -n trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo -e text /mnt/aux_mount/.gfid/80b0b164-2ea4-478b-a4cd-a9f76c1e6efd getfattr: Removing leading '/' from absolute path names # file: mnt/aux_mount/.gfid/80b0b164-2ea4-478b-a4cd-a9f76c1e6efd trusted.glusterfs.pathinfo="(<DISTRIBUTE:testvol-dht> (<REPLICATE:testvol-replicate-0> <POSIX(/rhgs/brick2):tuxpad:/rhgs/brick2/File1> <POSIX(/rhgs/brick1):tuxpad:/rhgs/brick1/File1>))Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command output displays the brick pathinfo under the <POSIX> tag. In this example output, two paths are displayed as the file is replicated twice and resides on a two-way replicated volume.
23.2.4. Controlling Self-heal for Dispersed Volumes
- Navigate to the scripts folder using the following command:
cd /usr/share/glusterfs/scripts
# cd /usr/share/glusterfs/scriptsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Determine the PID of the self-heal daemon using the following command:
ps -aef | grep glustershd
# ps -aef | grep glustershdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will be in the following format:root 1565 1 0 Feb05 ? 00:09:17 /usr/sbin/glusterfs -s localhost --volfile-id gluster/glustershd -p /var/run/gluster/glustershd/glustershd.pid -l /var/log/glusterfs/glustershd.log -S /var/run/gluster/ed49b959a0dc9b2185913084e3b2b339.socket --xlator-option *replicate*.node-uuid=13dbfa1e-ebbf-4cee-a1ac-ca6763903c55 root 16766 14420 0 19:00 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto glustershd
root 1565 1 0 Feb05 ? 00:09:17 /usr/sbin/glusterfs -s localhost --volfile-id gluster/glustershd -p /var/run/gluster/glustershd/glustershd.pid -l /var/log/glusterfs/glustershd.log -S /var/run/gluster/ed49b959a0dc9b2185913084e3b2b339.socket --xlator-option *replicate*.node-uuid=13dbfa1e-ebbf-4cee-a1ac-ca6763903c55 root 16766 14420 0 19:00 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto glustershdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this output, 1565 represents the PID of the selfheald service. - Execute the
control-cpu-loadscript using the following command:sh control-cpu-load.sh
# sh control-cpu-load.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts for the following input, type the PID of the self-heal daemon acquired from the previous step and press
Enter:sh control-cpu-load.sh Enter gluster daemon pid for which you want to control CPU. 1565
[root@XX-XX scripts]# sh control-cpu-load.sh Enter gluster daemon pid for which you want to control CPU. 1565Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - When the system prompts for the following input, type
yand pressEnter:If you want to continue the script to attach 1565 with new cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup Press (y/n)?
If you want to continue the script to attach 1565 with new cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup Press (y/n)?Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, 1565 represents the PID of the selfheald service. The PID of the selfheald service can vary from system to system. - When the system prompts for the following input, enter the required quota value to be assigned to the self-heal daemon and press
Enter:Creating child cgroup directory 'cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup' for glustershd.service. Enter quota value in range [10,100]: 25
Creating child cgroup directory 'cgroup_gluster_1565 cgroup' for glustershd.service. Enter quota value in range [10,100]: 25Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the quota value for the self-heal daemon is set as25.Note
The recommended quota value for a self-heal daemon is 25. However, the quota value can be set by the user on a run-time basis.The system prompts the following notification once the quota value is successfully set:Entered quota value is 25 Setting 25000 to cpu.cfs_quota_us for gluster_cgroup. Tasks are attached successfully specific to 1565 to cgroup_gluster_1565.
Entered quota value is 25 Setting 25000 to cpu.cfs_quota_us for gluster_cgroup. Tasks are attached successfully specific to 1565 to cgroup_gluster_1565.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
top command.
Important
23.3. Resolving glusterd Crash
glusterd crash is observed in the following scenarios:
glusterdrecieves a Termination Signal orSIGTERM.Segmentation faulterror message when upgrading Red Hat Gluster Storage.glusterdservice is being stopped.
Important
glusterd.
glusterd crash is persistent in any other scenarios, contact Red Hat Support
23.4. Restarting a dead/failed brick
Note
gluster volume start VOLNAME force
# gluster volume start VOLNAME forcePart VIII. Appendices
Chapter 24. Starting and Stopping the glusterd service
glusterd command line, logical storage volumes can be decoupled from physical hardware. Decoupling allows storage volumes to be grown, resized, and shrunk, without application or server downtime.
glusterd service is started automatically on all servers in the trusted storage pool. The service can also be manually started and stopped as required.
- Run the following command to start glusterd manually.
service glusterd start
# service glusterd startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run the following command to stop glusterd manually.
service glusterd stop
# service glusterd stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Important
Ifglusterdcrashes, there is no functionality impact to this crash as it occurs during the shutdown. For more information, see Section 23.3, “ResolvingglusterdCrash”
Chapter 25. Manually Recovering File Split-brain
- Run the following command to obtain the path of the file that is in split-brain:
gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brain
# gluster volume heal VOLNAME info split-brainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the command output, identify the files for which file operations performed from the client keep failing with Input/Output error. - Close the applications that opened split-brain file from the mount point. If you are using a virtual machine, you must power off the machine.
- Obtain and verify the AFR changelog extended attributes of the file using the
getfattrcommand. Then identify the type of split-brain to determine which of the bricks contains the 'good copy' of the file.getfattr -d -m . -e hex <file-path-on-brick>
getfattr -d -m . -e hex <file-path-on-brick>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The extended attributes withtrusted.afr.VOLNAMEvolname-client-<subvolume-index>are used by AFR to maintain changelog of the file. The values of thetrusted.afr.VOLNAMEvolname-client-<subvolume-index>are calculated by the glusterFS client (FUSE or NFS-server) processes. When the glusterFS client modifies a file or directory, the client contacts each brick and updates the changelog extended attribute according to the response of the brick.subvolume-indexis thebrick number - 1ofgluster volume info VOLNAMEoutput.For example,Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the example above:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Each file in a brick maintains the changelog of itself and that of the files present in all the other bricks in it's replica set as seen by that brick.In the example volume given above, all files in brick-a will have 2 entries, one for itself and the other for the file present in it's replica pair. The following is the changelog for brick2,- trusted.afr.vol-client-0=0x000000000000000000000000 - is the changelog for itself (brick1)
- trusted.afr.vol-client-1=0x000000000000000000000000 - changelog for brick2 as seen by brick1
Likewise, all files in brick2 will have the following:- trusted.afr.vol-client-0=0x000000000000000000000000 - changelog for brick1 as seen by brick2
- trusted.afr.vol-client-1=0x000000000000000000000000 - changelog for itself (brick2)
Note
These files do not have entries for themselves, only for the other bricks in the replica. For example,brick1will only havetrusted.afr.vol-client-1set andbrick2will only havetrusted.afr.vol-client-0set. Interpreting the changelog remains same as explained below.The same can be extended for other replica pairs.Interpreting changelog (approximate pending operation count) valueEach extended attribute has a value which is 24 hexa decimal digits. First 8 digits represent changelog of data. Second 8 digits represent changelog of metadata. Last 8 digits represent Changelog of directory entries.
Pictorially representing the same is as follows:0x 000003d7 00000001 00000000110 | | | | | \_ changelog of directory entries | \_ changelog of metadata \ _ changelog of data0x 000003d7 00000001 00000000110 | | | | | \_ changelog of directory entries | \_ changelog of metadata \ _ changelog of dataCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For directories, metadata and entry changelogs are valid. For regular files, data and metadata changelogs are valid. For special files like device files and so on, metadata changelog is valid. When a file split-brain happens it could be either be data split-brain or meta-data split-brain or both.The following is an example of both data, metadata split-brain on the same file:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Scrutinize the changelogsThe changelog extended attributes on file/rhgs/brick1/aare as follows:- The first 8 digits of
trusted.afr.vol-client-0 are all zeros (0x00000000................),The first 8 digits oftrusted.afr.vol-client-1are not all zeros (0x000003d7................).So the changelog on/rhgs/brick-a/aimplies that some data operations succeeded on itself but failed on/rhgs/brick2/a. - The second 8 digits of
trusted.afr.vol-client-0 are all zeros (0x........00000000........), and the second 8 digits oftrusted.afr.vol-client-1are not all zeros (0x........00000001........).So the changelog on/rhgs/brick1/aimplies that some metadata operations succeeded on itself but failed on/rhgs/brick2/a.
The changelog extended attributes on file/rhgs/brick2/aare as follows:- The first 8 digits of
trusted.afr.vol-client-0are not all zeros (0x000003b0................).The first 8 digits oftrusted.afr.vol-client-1are all zeros (0x00000000................).So the changelog on/rhgs/brick2/aimplies that some data operations succeeded on itself but failed on/rhgs/brick1/a. - The second 8 digits of
trusted.afr.vol-client-0are not all zeros (0x........00000001........)The second 8 digits oftrusted.afr.vol-client-1are all zeros (0x........00000000........).So the changelog on/rhgs/brick2/aimplies that some metadata operations succeeded on itself but failed on/rhgs/brick1/a.
Here, both the copies have data, metadata changes that are not on the other file. Hence, it is both data and metadata split-brain.Deciding on the correct copyYou must inspect
statandgetfattroutput of the files to decide which metadata to retain and contents of the file to decide which data to retain. To continue with the example above, here, we are retaining the data of/rhgs/brick1/aand metadata of/rhgs/brick2/a.Resetting the relevant changelogs to resolve the split-brainResolving data split-brainYou must change the changelog extended attributes on the files as if some data operations succeeded on
/rhgs/brick1/abut failed on /rhgs/brick-b/a. But/rhgs/brick2/ashouldnothave any changelog showing data operations succeeded on/rhgs/brick2/abut failed on/rhgs/brick1/a. You must reset the data part of the changelog ontrusted.afr.vol-client-0of/rhgs/brick2/a.Resolving metadata split-brainYou must change the changelog extended attributes on the files as if some metadata operations succeeded on/rhgs/brick2/abut failed on/rhgs/brick1/a. But/rhgs/brick1/ashouldnothave any changelog which says some metadata operations succeeded on/rhgs/brick1/abut failed on/rhgs/brick2/a. You must reset metadata part of the changelog ontrusted.afr.vol-client-1of/rhgs/brick1/aRun the following commands to reset the extended attributes.- On
/rhgs/brick2/a, fortrusted.afr.vol-client-0 0x000003b00000000100000000to0x000000000000000100000000, execute the following command:setfattr -n trusted.afr.vol-client-0 -v 0x000000000000000100000000 /rhgs/brick2/a
# setfattr -n trusted.afr.vol-client-0 -v 0x000000000000000100000000 /rhgs/brick2/aCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On
/rhgs/brick1/a, fortrusted.afr.vol-client-1 0x0000000000000000ffffffffto0x000003d70000000000000000, execute the following command:setfattr -n trusted.afr.vol-client-1 -v 0x000003d70000000000000000 /rhgs/brick1/a
# setfattr -n trusted.afr.vol-client-1 -v 0x000003d70000000000000000 /rhgs/brick1/aCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
After you reset the extended attributes, the changelogs would look similar to the following:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Resolving Directory entry split-brainAFR has the ability to conservatively merge different entries in the directories when there is a split-brain on directory. If on one brick directory
storagehas entries1,2and has entries3,4on the other brick then AFR will merge all of the entries in the directory to have1, 2, 3, 4entries in the same directory. But this may result in deleted files to re-appear in case the split-brain happens because of deletion of files on the directory. Split-brain resolution needs human intervention when there is at least one entry which has same file name but differentgfidin that directory.For example:Onbrick-athe directory has 2 entriesfile1withgfid_xandfile2. Onbrick-bdirectory has 2 entriesfile1withgfid_yandfile3. Here the gfid's offile1on the bricks are different. These kinds of directory split-brain needs human intervention to resolve the issue. You must remove eitherfile1onbrick-aor thefile1onbrick-bto resolve the split-brain.In addition, the correspondinggfid-linkfile must be removed. Thegfid-linkfiles are present in the .glusterfsdirectory in the top-level directory of the brick. If the gfid of the file is0x307a5c9efddd4e7c96e94fd4bcdcbd1b(the trusted.gfid extended attribute received from thegetfattrcommand earlier), the gfid-link file can be found at/rhgs/brick1/.glusterfs/30/7a/307a5c9efddd4e7c96e94fd4bcdcbd1b.Warning
Before deleting thegfid-link, you must ensure that there are no hard links to the file present on that brick. If hard-links exist, you must delete them. - Trigger self-heal by running the following command:
ls -l <file-path-on-gluster-mount>
# ls -l <file-path-on-gluster-mount>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow orgluster volume heal VOLNAME
# gluster volume heal VOLNAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Appendix A. Revision History
| Revision History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revision 3.4-4 | Wed Mar 27 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revision 3.4-3 | Mon Feb 04 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revision 3.4-2 | Wed Oct 31 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revision 3.4-1 | Tue Sep 04 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||