Audit AI apps to meet compliance goals
Deploy a financial audit system with insights into the performance, cost, and usage of your large language models in real time.
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
Audit AI apps to meet compliance goals
Deploy a financial audit system with insights into the performance, cost, and usage of your large language models in real time.
Table of Contents
Detailed description
This quickstart features a Financial Services Industry (FSI) compliance demo that demonstrates auditability and traceability for AI-powered financial applications.
As AI workloads become more complex, organizations need robust telemetry and observability of Large Language Model (LLM) infrastructure. This quickstart demonstrates those needs by providing:
- AI observability for model performance, resource utilization, and distributed tracing
- Standardized deployment patterns for consistent, scalable AI service delivery
- Enterprise-grade monitoring using OpenShift-native observability tools
This repository provides helm charts for both the monitoring infrastructure and AI service deployments needed to run Llama Stack reliably in OpenShift AI.
Architecture
The proposed observability & telemetry architecture:
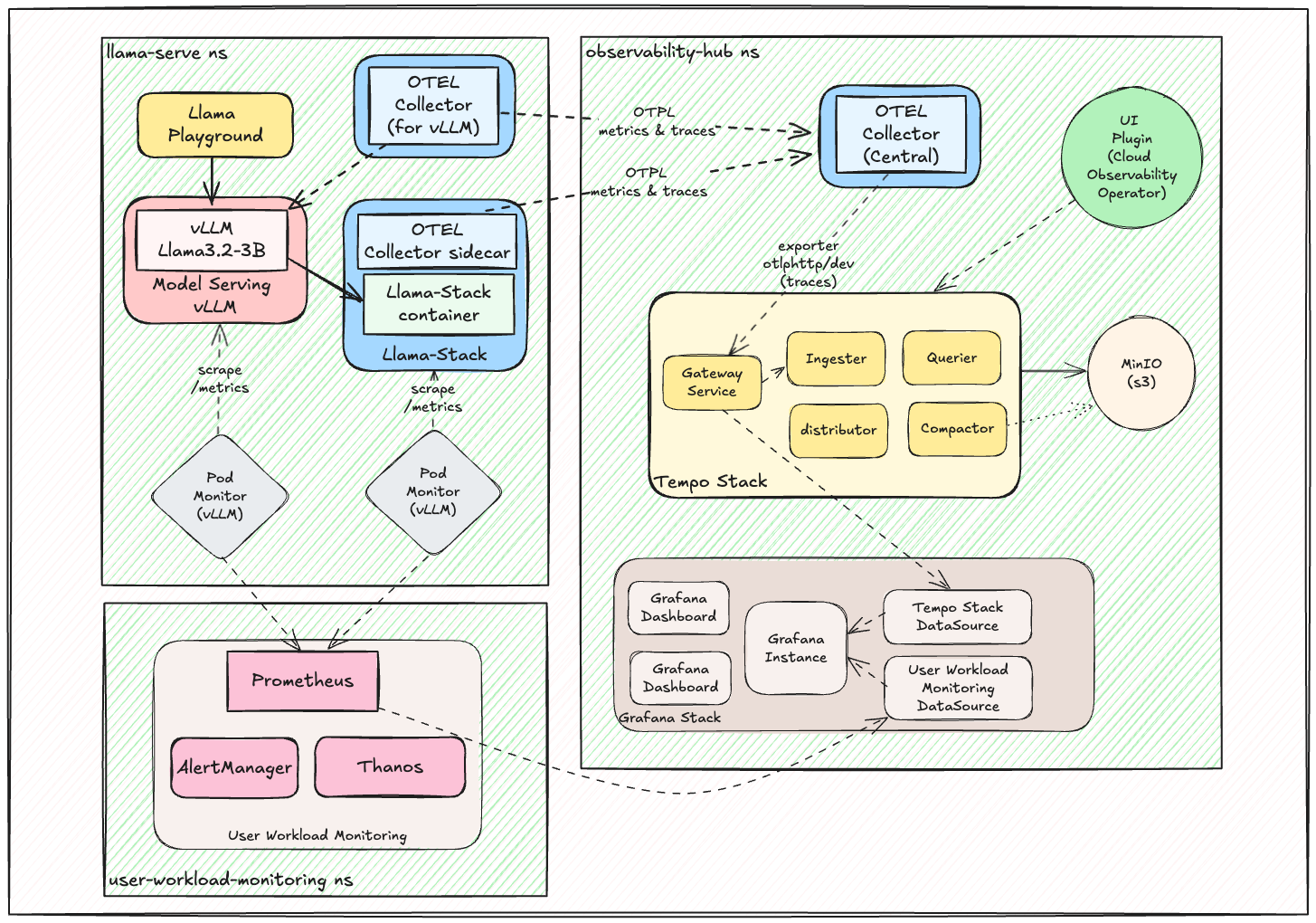
This architecture demonstrates the complete observability ecosystem, from AI workload telemetry collection through distributed tracing to comprehensive monitoring dashboards.
Components
All components are organized by dependency layers in the ./helm/ directory:
Phase 1: Operators (./helm/01-operators/)
cluster-observability-operator- PodMonitor/ServiceMonitor CRDs and UI pluginsgrafana-operator- Grafana operator for visualization and dashboard managementotel-operator- Red Hat Build of OpenTelemetry operatortempo-operator- Distributed tracing backend operator
Phase 2: Observability Infrastructure (./helm/02-observability/)
tempo- Distributed tracing backend with S3-compatible storageotel-collector- OpenTelemetry collector configurations for telemetry collection and processinggrafana- Visualization and dashboard management with pre-built dashboardsuwm- User Workload Monitoring with PodMonitors for VLLM and AI workloadsdistributed-tracing-ui-plugin- OpenShift console integration for tracing
Phase 3: AI Services (./helm/03-ai-services/)
llama-stack-instance- Complete Llama Stack Instance with configurable endpointsllama3.2-3b- Llama 3.2 3B model deployment on vLLMllama-stack-playground- Interactive Llama-Stack web interface for testingllama-guard- Llama Guard 1B for providing Safety / Shield mechanisms
Phase 4: MCP Servers (./helm/04-mcp-servers/)
mcp-weather- MCP weather servicehr-api- MCP HR API demonstration serviceopenshift-mcp- MCP OpenShift/Kubernetes operations service
Observability in Action
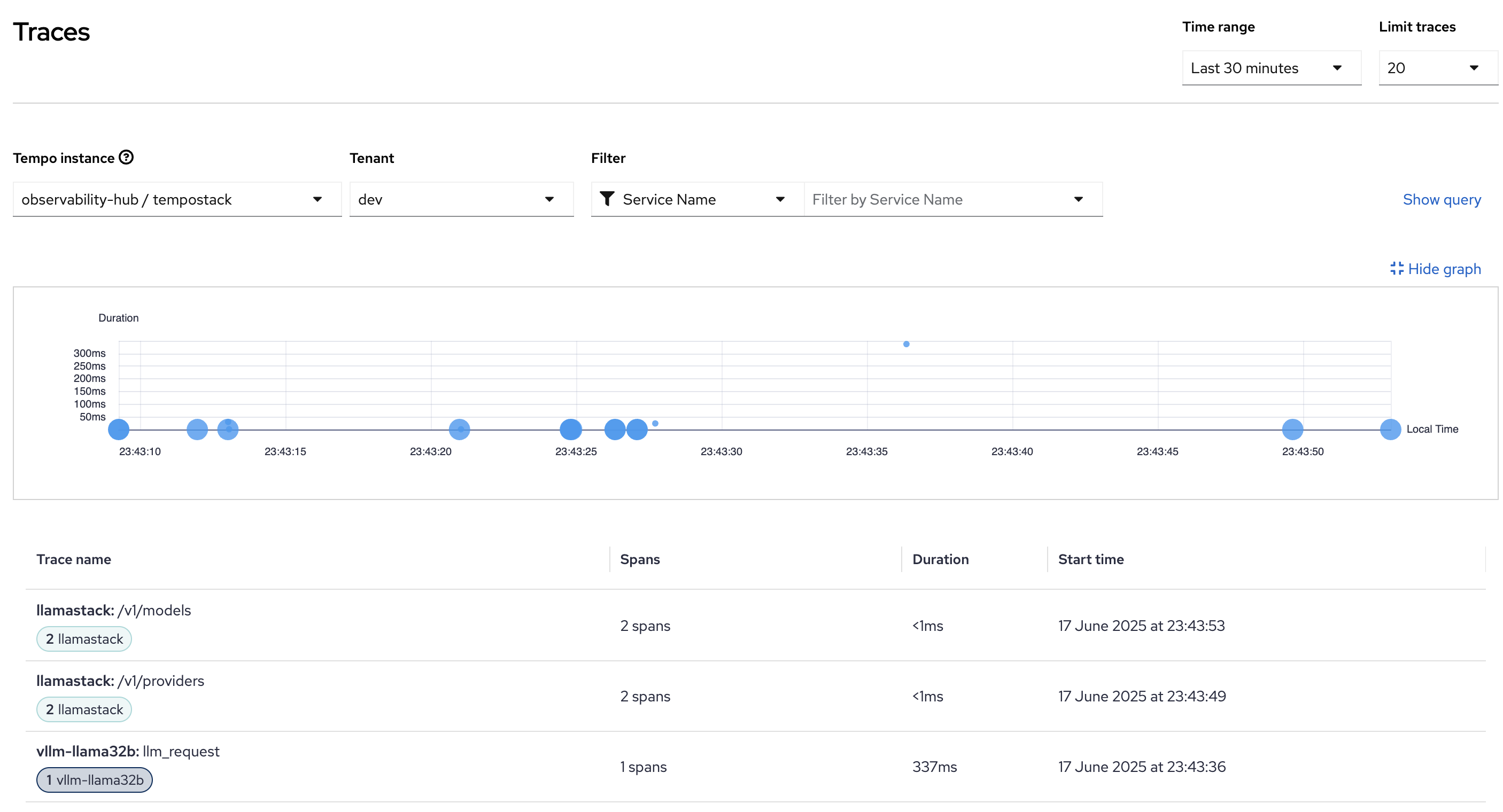
The telemetry and observability stack provides comprehensive visibility into AI workload performance and distributed system behavior.
Distributed Tracing Examples
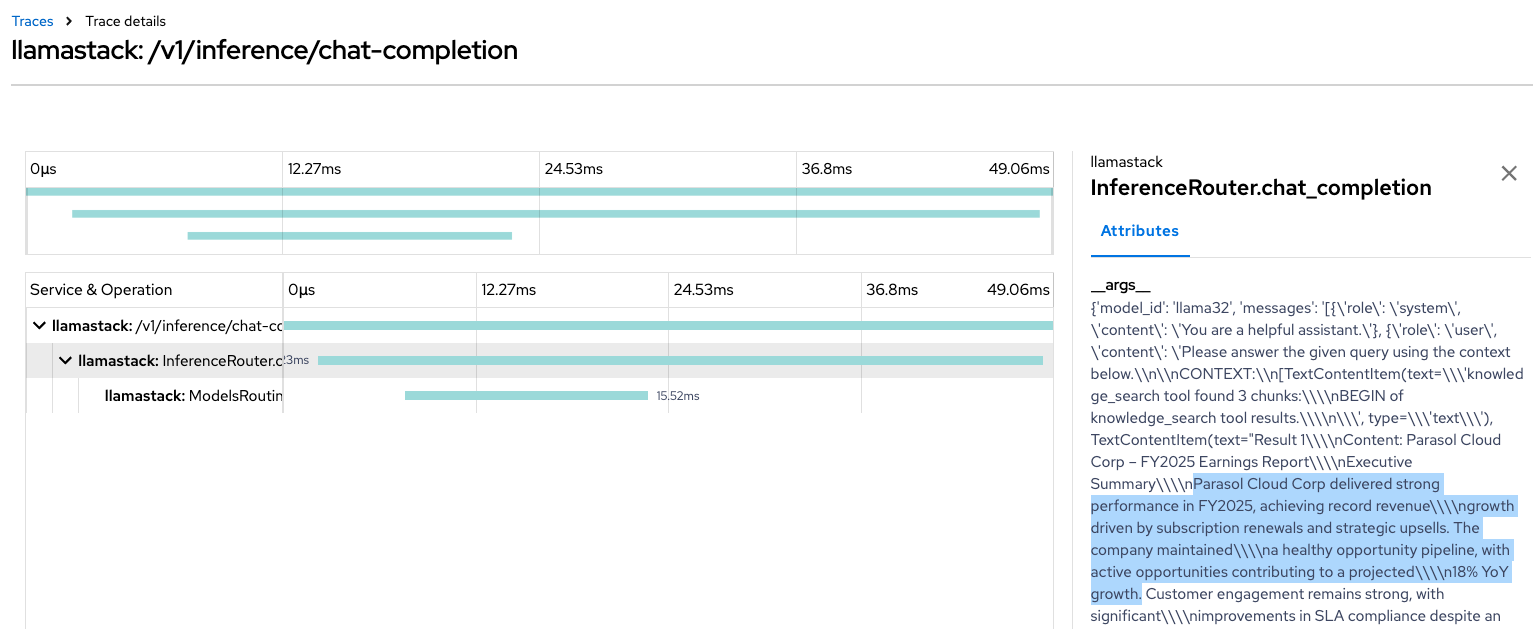
End-to-End Request Tracing: Complete visibility into AI inference request flows through the Llama Stack infrastructure.
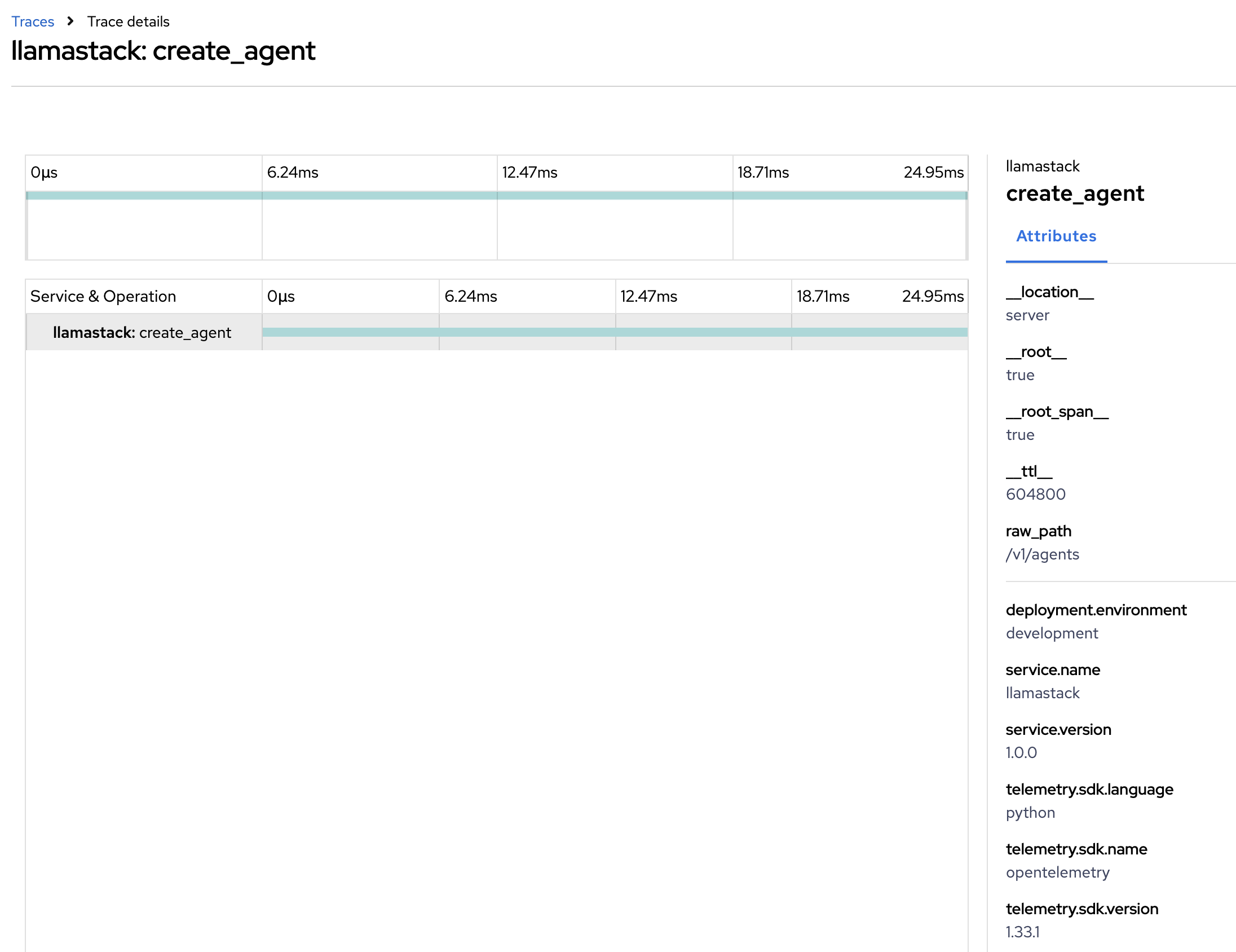
Create Agent from LlamaStack Tracing: Detailed trace view showing complex interactions between different services in the AI stack.
These traces provide insights into:
- Request latency and service dependencies
- Error tracking and performance bottlenecks
- Load distribution across model endpoints
Requirements
Minimum hardware requirements
- CPU: 8+ cores recommended for full stack deployment
- Memory: 16GB+ RAM for monitoring stack, additional memory based on AI workload requirements
- Storage: 100GB+ for observability data retention
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU required for AI model inference (varies by model size)
Minimum software requirements
- OpenShift 4.12+ or Kubernetes 1.24+
- OpenShift AI 2.19 onwards
- Helm 3.8+ for chart deployment
- oc CLI or kubectl for cluster management
Required user permissions
- Cluster Admin - Required for operator installation and observability stack setup
- GPU Access - Required for AI workload deployment
Deploy
step 0 - git clone https://github.com/rh-ai-quickstart/lls-observability.git && \ cd lls-observability
# step 0 - git clone
https://github.com/rh-ai-quickstart/lls-observability.git && \
cd lls-observability
Quick Start - Automated Installation
Option 1: Complete Stack (Recommended)
# Run the full installation script ./scripts/install-full-stack.sh
# Run the full installation script
./scripts/install-full-stack.sh
Option 2: Phase-by-Phase Installation
Option 3: Using Makefile (Optional)
Advanced Usage
Manual Step-by-Step Installation
For users who prefer to understand each step or need to customize the installation.
Set these environment variables before running the installation commands:
export OBSERVABILITY_NAMESPACE="observability-hub" export UWM_NAMESPACE="openshift-user-workload-monitoring" export AI_SERVICES_NAMESPACE="llama-serve"
export OBSERVABILITY_NAMESPACE="observability-hub"
export UWM_NAMESPACE="openshift-user-workload-monitoring"
export AI_SERVICES_NAMESPACE="llama-serve"
Launch this instructions:
MaaS Integration (Optional)
Model-as-a-Service (MaaS) Remote Models
The Llama Stack can optionally integrate with external MaaS (Models as a Server) to access remote models without local GPU requirements.
Configuration Options:
Uninstall
Complete Stack Uninstall
# Uninstall everything in reverse order make clean
# Uninstall everything in reverse order
make clean