Build an AI-powered virtual agent
Build and deploy a conversational AI virtual agent on Red Hat OpenShift AI to automate customer interactions and provide instant support.
This content is authored by Red Hat experts, but has not yet been tested on every supported configuration.
Build an AI-powered virtual agent
Build and deploy a conversational AI virtual agent on Red Hat OpenShift AI to automate customer interactions and provide instant support.
Detailed description
This platform provides the tools to build and deploy conversational AI agents that can:
- Access knowledge bases - Upload documents and create searchable knowledge bases for RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
- Use tools - Integrate web search, databases, and custom tools through the Model Context Protocol (MCP)
- Apply guardrails - Built-in safety measures and content filtering
- Scale in production - Kubernetes-ready architecture
Key Features
- 🤖 Agent Management - Create and configure AI agents with different capabilities
- 📚 Knowledge Integration - Document search and question answering via RAG
- 💬 Real-time Chat - Streaming conversations with session history
- 🔧 Tool Ecosystem - Built-in tools plus extensible MCP server support
- 🛡️ Safety Controls - Configurable guardrails and content filtering
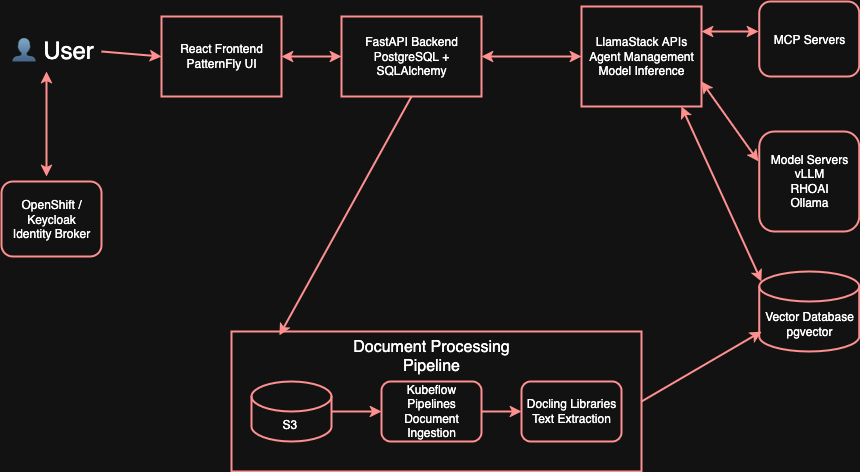
Architecture Overview
The platform integrates several components:
- React Frontend - Web interface for agent and chat management
- FastAPI Backend - API server handling business logic and data persistence
- LlamaStack - AI platform managing models, agents, and inference
- PostgreSQL + pgvector - Data storage with vector search capabilities
- Kubernetes Pipeline - Document processing and knowledge base ingestion
Requirements
Minimum hardware requirements
For a full working version with local inference:
- GPU - Required for running inference locally
- Alternatively, you can deploy without a GPU by using:
- Remote vLLM deployment
- Vertex AI
Minimum software requirements
- Red Hat OpenShift - Container orchestration platform
- Red Hat OpenShift AI - AI/ML platform for model serving and management
- oc CLI - OpenShift command-line tool
- make - Build automation tool
- Hugging Face token - With access to models (some models require authorization)
Required user permissions
- Cluster admin access - Required for installing ClusterRole resources for OAuth authentication
Deploy
Cluster Deployment
For production installation on Kubernetes/OpenShift:
Delete
To remove the application and all associated resources:
cd deploy/cluster make uninstall NAMESPACE=your-namespace
cd deploy/cluster
make uninstall NAMESPACE=your-namespace
This will automatically clean up the Helm chart, deployed resources, and PVCs.
Example Use Case
Creating a Customer Support Agent with Knowledge Base
Advanced Solutions with AI Virtual Agents
Connect Oracle Database for BI Analysts
Integrate AI agents with an Oracle data warehouse using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Oracle MCP Server on OpenShift with the Red Hat AI Virtual Agent
Advanced instructions
Getting Started Guides
👩💻 For Developers
- Local Development Guide - Containerized development environment (without cluster)
- Contributing Guide - Development setup and workflow
- Backend API Reference - Complete API documentation
- Frontend Architecture - UI components and patterns
🚀 For Deployment
- Installation Guide - Production deployment on Kubernetes
- Agent Templates - Pre-built agent configurations
- Knowledge Base Setup - Document processing pipeline
🔧 For Integration
- Testing Guide - Running integration tests
- API Reference - Backend API endpoints
Project Structure
Local Development
For local containerized development (without cluster):
📖 → See Local Development Guide
Note: Local setup has limited functionality compared to OpenShift AI deployment:
- No authentication/authorization
- Knowledge bases not available
- MCP servers not tested
These features are only available with the full OpenShift AI deployment.
Access your app:
- Frontend: http://localhost:5173
- API: http://localhost:8000
- Docs: http://localhost:8000/docs
Cluster Development
Note: All Makefile targets automatically load environment variables from a
.envfile in the repository root if it exists.
Environment setup (.env)
Create a .env file in the repository root to configure your local environment. All Makefile targets will dynamically load this file if present:
cp .env.example .env # then edit `.env` as needed
cp .env.example .env
# then edit `.env` as needed
At minimum, set:
DATABASE_URL=postgresql+asyncpg://admin:password@localhost:5432/ai_virtual_agent
DATABASE_URL=postgresql+asyncpg://admin:password@localhost:5432/ai_virtual_agent
Optional toggles:
Note: If you're not using attachments in local dev, you can set DISABLE_ATTACHMENTS=true in .env to skip attachment-related initialization.
Community & Support
- 🐛 Issues - Report bugs and request features
- 💬 Discussions - Ask questions and share ideas
- 🤝 Contributing - See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines
- 📚 Documentation - Browse
/docsfor detailed guides
License
MIT License - Built with ❤️ by the Red Hat Ecosystem App Engineering team

