Questo contenuto non è disponibile nella lingua selezionata.
Administration And Configuration Guide
The Administration and Configuration Guide for Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite
Abstract
Part I. Introduction
Chapter 1. Business Process Model and Notation
1.1. Components
Execution Engine- provides the runtime environment for Processes and Business Rules. It encompasses a workflow library that can be embedded into a user web application. Runtime manager is the root object and contains the following components:Runtime Engine- implements the core behavior of the computer language and it is provided by the runtime manager.Process Engine- is the environment for business process model execution.Task Service- handles human task lifecycles.
Rule Engine- can be used with the process engine or on its own.Rules Evaluation- executes business rules on the provided set of facts.Complex Event Processing- applies business rules on incoming stream of events.
Business Central- a web-based application that accommodates tooling for asset creation, management, and monitoring by providing an integrated web environment.Asset Repository- is the central sharing location (Knowledge Store) for business assets, processes, rules, forms, etc. Users access this repository through the Project Explorer view of Business Central via → . By default, the product initializes a local GIT repository as its Asset Repository. However, other repositories may be added or removed as necessary.Artifact Repository- is a Maven based repository for storage of project jar artifacts.Execution Server- provides an execution environment for business process instances and tasks.Business Activity Monitor- provides customizable view on business performance.
Note
1.2. Project
pom.xml) with information on how to build the output artifact. It also contains the Module Descriptor file, kmodule.xml, that contains the KIE Base and KIE Session configuration for the assets in the project.
1.3. Creating a project
- Open the Project Authoring perspective: on the main menu, click → .
- In the Project Explorer, select the organizational unit and the repository where you want to create the project.
- In the perspective menu, go to → .
- In the Create new Project dialog window, define the project details:
- In the Project text box, enter the project name.
- The explorer refreshes to show a New Project Wizard pop-up window.
- Define the Project General Settings and Group artifact version details for this new project. These parameters are stored inside the
pom.xmlMaven configuration file.- Project Name: The name for the project; for example
MortgageProject - Project Description: The description of the project which may be useful for the project documentation purpose.
- Group ID: group ID of the project; for example
org.mycompany.commons - Artifact ID: artifact ID unique in the group; for example
myframework. Avoid using a space or any special character that might lead to an invalid name. - Version ID: version of the project; for example
2.1.1
The Project Screen view is updated with the new project details as defined in the pom.xml file. Note, that you can switch between project descriptor files in the drop down-box with Project Settings and Knowledge Base Setting, and edit their contents.
1.4. Adding dependencies
- Open the Project Editor for the given project:
- In the Project Explorer view of the
Project Authoringperspective, open the project directory. - Click on the
 button to open the project view.
button to open the project view.
- In the Project Screen view, select in the Project Settings drop-down box the Dependencies item.
- On the updated Project Screen, click the button to add a maven dependency or click the button to add a dependency from the Knowledge Store (Artifact repository):
- When adding a maven dependency, a user has to define the Group ID, Artifact ID and the Version ID in the new row which is created in the dependency table.
- When adding a dependency from the Knowledge Store, select the dependency in the displayed dialog box: the dependency will be added to the dependency table.
- To apply the various changes, the dependencies must be saved.
Warning
Part II. Configuration
Chapter 2. Business Central Configuration
DEPLOY_DIRECTORY/business-central.war/WEB-INF/web.xml and the referenced files, and if deployed on Red Hat JBoss EAP 6, also in jboss-web.xml and jboss-deployment-structure.xml.
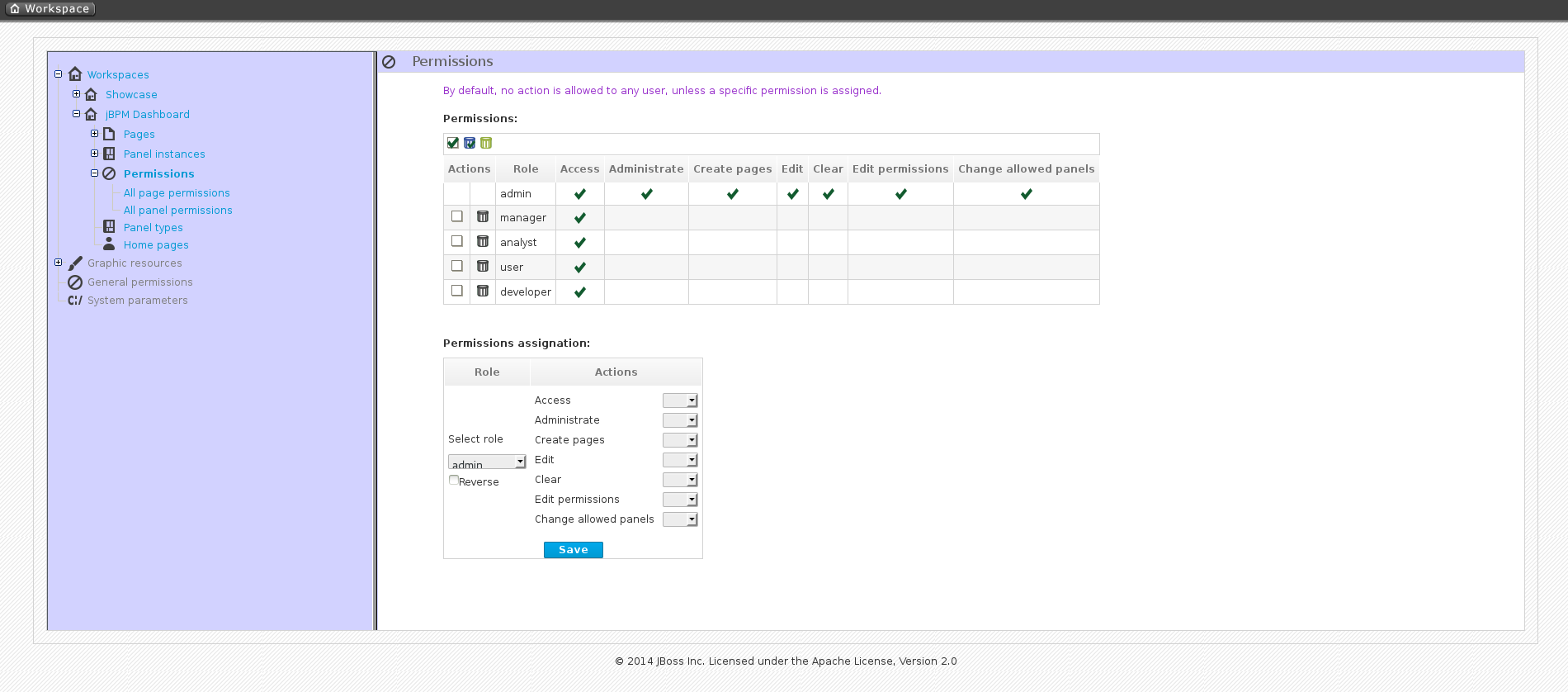
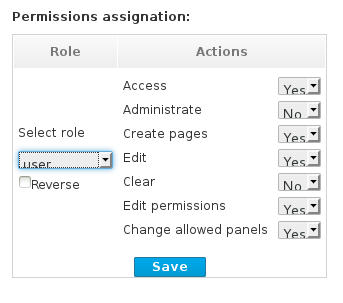
2.1. Access control
$JBOSS_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/WEB-INF/classes/userinfo.properties.
admin: administrates JBoss BPM Suite system and has full access rights to make any changes necessary including the ability to add and remove users from the system.developer: implements code required for processes to work and has access to everything except administration tasks.analyst: creates and designs processes and forms, instantiates the processes and deploys artifacts. This role is the similar to a developer, without access to asset repository and deployments.user: claims, performs, and invokes other actions (such as, escalation, rejection, etc.) on the assigned Tasks and has no access to authoring functions.manager: monitors the system and its statistics and only has access to the dashboard.business user: takes action on business tasks that are required for processes to continue forward. Works primarily with the task list.
$JBOSS_HOME/add-user.sh script and create an Application User in the ApplicationRealm with the respectives roles.
Workbench Configuration
$JBOSS_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/WEB-INF/classes/workbench-policy.propeties.
standalone.xml file in EAP.
Authentication in Human Tasks
UserGroupCallback interface to assign tasks to user.
Warning
2.2. Business Central Profile Configuration
- Full profile - default profile that is active without additional configuration required (UI and remote services e.g. REST).
- Execution server profile - disables completely UI components of the application and allows only remote access e.g. via REST interface.
- UI server profile - disables remote services e.g REST and allows only UI access to the application.
Procedure 2.1. Configuring Business Central Profiles
- Select the desired
web.xmlinside$BPMS_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/WEB-INF/. The following files are provided.web.xml(default) for full profileweb-exec-server.xmlfor execution server profileweb-ui-server.xmlfor UI server profile
- To activate a profile other than the default full profile, the web-<PROFILE>.xml file must be renamed to
web.xml. The following steps demonstrate one way to enable the execution server profile:- Backup the
web.xmlfile from the full profilemv web.xml web-full.xml
$ mv web.xml web-full.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Rename the
web-exec-server.xmlfile:mv web-exec-server.xml web.xml
$ mv web-exec-server.xml web.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Start application server with additional system property to instruct the profile manager to activate given profile.
Dorg.kie.active.profile=full- to activate full profile or skip the property completelyDorg.kie.active.profile=exec-server- to activate execution server profileDorg.kie.active.profile=ui-server- to activate UI server profile
2.3. Branding the Business Central Application
- Login screenYou can customize the following attributes of the Business Central login screen:
- The background image
- The company logo
- The application logo
- Application headerYou can customize the following attributes of the Business Central application header:
- The Business Central header containing the title and banner logo
- Help pop-up windowsYou can customize the following attributes of the splash help pop-up windows:
- The splash help images
- The label text
2.3.1. Customizing Business Central Login Page
Procedure 2.2. Changing the Business Central Login Page Background Image
- Start the EAP server and open http://localhost:8080/business-central in a web browser.
- Copy the new background image to the
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/imagesdirectory in your JBoss BPM Suite installation. - Navigate to
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/stylesdirectory and open thelogin-screen.cssfile in a text editor. - In the
login-screen.cssfile, provide the location of your new background image in the followingbackground-imageattribute.background-image: url("../images/login-screen-background.jpg");background-image: url("../images/login-screen-background.jpg");Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Thebackground-imageattribute points to the defaultlogin-screen-background.jpgimage.In addition to the background image, you can modify other attributes such as image size, position, and background color in thelogin-screen.cssfile.
Procedure 2.3. Changing the Business Central Login Page Company Logo and Project Logo
- Start the EAP server and open http://localhost:8080/business-central in a web browser.
- Navigate to the
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/imagesdirectory in your JBoss BPM Suite installation. - Replace the default image
login-screen-logo.pngwith a new one. This is the company logo that appears on the top right hand corner of the login page. - Replace the default image
RH_JBoss_BPMS_Logo.pngRH_JBoss_BRMS_Logo.pngwith a new one. This is the project logo that appears on the center left hand side of the login page.
2.3.2. Customizing Business Central Application Header
Procedure 2.4. Changing the Business Central Application Header (Banner)
- Start the EAP server and open http://localhost:8080/business-central in a web browser.
- Log in to the Business Central application with your user credentials.
- Copy your new application header image to the
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/bannerdirectory in your JBoss BPM Suite installation. - Open
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/banner/banner.htmlfile in a text editor. - In the
banner.htmlfile, edit the following <img> tag to provide the name of your new header image:<img src="banner/logo.png"/>
<img src="banner/logo.png"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default image islogo.png.
2.3.3. Customizing Business Central Splash Help Windows
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/plugins directory contains the splash pages and the corresponding html files. Each splash page holds the name of the html file, which contains information about the image(s) and the text to be displayed. For example, the authoring_perspective.splash.js splash page points to the authoring_perspective.splash.html file. The authoring_perspective.splash.html contains the names and location of all the image files that appear on the Authoring Perspective splash help and also their captions. You can customize the images and the corresponding captions of the existing splash help pop-up windows.
Procedure 2.5. Changing the Business Central Splash Help Pop-Up Images and Captions
- Start the EAP server and open http://localhost:8080/business-central in a web browser.
- Log in to the Business Central application with your user credentials.
- Copy your new splash help image(s) to the
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/imagesdirectory in your JBoss BPM Suite installation. - Open the corresponding html file from
$EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/pluginsdirectory in a text editor. - Edit the html file to point to your new splash help image. For example, to change the first image that appears in the Authoring Perspective splash help, edit the following <img> tag in the
authoring_perspective.splash.htmlfile to add your new image:<img src="images/authoring_perspective1.png" alt="">
<img src="images/authoring_perspective1.png" alt="">Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default image isauthoring_perspective1.png, which appears on the first page of the Authoring Perspective splash help. - To change the image caption that appears on the splash help, edit the <h4> and <p> tag contents below the <img> tag:
<h4>Authoring</h4> <p>Modularized and customizable workbench</p>
<h4>Authoring</h4> <p>Modularized and customizable workbench</p>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.4. Deployment Descriptors
META-INF directory of the kjar called kmodule.xml can be used to define the knowledge bases and sessions. This kmodule.xml file, by default, is empty.
kmodule.xml to build the runtime representation.
kmodule.xml file. The presence of these descriptors is optional and your deployment will proceed successfully without them. The properties that you can set using these descriptors are purely technical in nature and include meta values like persistence, auditing and runtime strategy.
kie-deployment-descriptor.xml and place this file next to your kmodule.xml file in the META-INF folder. You can change this default location (and the filename) by specifying it as a system parameter:
-Dorg.kie.deployment.desc.location=file:/path/to/file/company-deployment-descriptor.xml
-Dorg.kie.deployment.desc.location=file:/path/to/file/company-deployment-descriptor.xml2.4.1. Deployment Descriptor Configuration
- server level: the main level and the one that applies to all kjars deployed on the server.
- kjar level: this allows you to configure descriptors on a per kjar basis.
- deploy time level: descriptors that apply while a kjar is being deployed.
Note
NONE but the same mode is specified as JPA at the kjar level, the actual mode will be JPA for that kjar. If nothing is specified for the persistence mode in the deployment descriptor for that kjar (or if there is no deployment descriptor), it will fall back to the server level configuration, which in this case is NONE (or to JPA if there is no server level deployment descriptor).
Can you override this hierarchal merge mode behavior?
MERGE_COLLECTIONS mode. But you can change it (Section 2.4.2, “Managing Deployment Descriptors”) if it doesn't suit your environment to one of the following modes:
- KEEP_ALL: in this mode, all higher level values override all lower level values (server level values replace kjar level values)
- OVERRIDE_ALL: in this mode, all lower level values override all higher level values (kjar values replace server level values)
- OVERRIDE_EMPTY: in this mode, all non empty configuration items from lower levels replace those at higher levels, including items that are represented as collections.
- MERGE_COLLECTIONS (DEFAULT): in this mode, all non empty configuration items from lower level replace those from higher levels (like in OVERRIDE_EMPTY), but collection properties are merged (combined).
Do I need to provide a full Deployment Descriptor for all kjars?
What can you configure?
| Configuration | XML Entry | Permissible Values | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistence unit name for runtime data | persistence-unit | Any valid persistence package name | org.jbpm.domain |
| Persistence unit name for audit data | audit-persistence-unit | Any valid persistence package name | org.jbpm.domain |
| Persistence mode | persistence-mode | JPA, NONE | JPA |
| Audit mode | audit-mode | JPA, JMS or NONE | JPA |
| Runtime Strategy | runtime-strategy | SINGLETON, PER_REQUEST or PER_PROCESS_INSTANCE | SINGLETON |
| List of Event Listeners to be registered | event-listeners | Valid listener class names as ObjectModel | No default value |
| List of Task Event Listeners to be registered | task-event-listeners | Valid listener class names as ObjectModel | No default value |
| List of Work Item Handlers to be registered | work-item-handlers | Valid Work Item Handler classes given as NamedObjectHandler | No default value |
| List of Globals to be registered | globals | Valid Global variables given as NamedObjectModel | No default value |
| Marshalling strategies to be registered (for pluggable variable persistence) | marshalling-strategies | Valid ObjectModel classes | No default value |
| Required Roles to be granted access to the resources of the kjar | required-roles | String role names | No default value |
| Additional Environment Entries for Knowledge Session | environment-entries | Valid NamedObjectModel | No default value |
| Additional configuration options of Knowledge Session | configurations | Valid NamedObjectModel | No default value |
How do you provide values for collections based configuration items?
ObjectModel or NamedObjectModel. Both are similar and provide a definition of the object to be built or created at runtime, with the exception that the NamedObjectModel object details name the object to be looked. Both these types are defined using an identifier, optional parameters and resolver (to resolve the object).
- identifier - defines all the information about the object, such as fully qualified class name, Spring bean id or an MVEL expression.
- parameters - optional parameters that should be used while creating instances of objects from this model.
- resolver - identifier of the resolver that will be used to create object instances from the model - (reflection, mvel or Spring).
ObjectModel, with the identifier being com.mycompany.MyStrategy, resolver being reflection (the easiest and the default) and any parameters that are required for your strategy to work. Reflection will then be used to create an instance of this strategy using the fully qualified class name that you have provided as the identifier.
<marshalling-strategy> <resolver>mvel</resolver> <identifier>new com.myCompany.CustomStrategy(runtimeManager)</identifier> </marshalling-strategy>
<marshalling-strategy>
<resolver>mvel</resolver>
<identifier>new com.myCompany.CustomStrategy(runtimeManager)</identifier>
</marshalling-strategy>
<marshalling-strategy> <resolver>spring</resolver> <identifier>customStrategy</identifier> </marshalling-strategy>
<marshalling-strategy>
<resolver>spring</resolver>
<identifier>customStrategy</identifier>
</marshalling-strategy>
2.4.2. Managing Deployment Descriptors
META-INF folder in the File Explorer. Click on the kie-deployment-descriptor.xml file to edit it manually.
kie-deployment-descriptor.xml file is generated with default values as described earlier.
Overriding Hierarchical Merge Mode Behavior
- Set the system property org.kie.dd.mergemode to one of these values. This merge mode will become default for all kjars deployed in the system, unless you override it at a kjar level via the next method.
- When deploying a new deployment unit via Business Central ( → ) you can select what merge mode should be used for that particular kjar.
- When deploying via the REST API, you can add mergemode query parameter to the command URL to one of these modes to set the merge mode for that deployment.
Restricting access to the Runtime Engine
2.5. Managing Deployment Override Policy
false by default. Change it to true to enable overwriting of deployments with the same GAV by providing it at startup time of your server (-Dorg.kie.override.deploy.enabled=true).
2.6. Extending Business Central
Plugin Management.
2.6.1. Plugin Management
Plugin Management screen by clicking on → . This brings up the Plugin Explorer screen that lists all the existing plugins under their respective categories: Perspective Plugin, Screen Plugin, Editor Plugin, Splashscreen Plugin and Dynamic Menu. Open up any of these and you will see the existing plugins in each category, including the uneditable system generated ones.
- Create a new screen
- Create a new perspective (and add the new screen to it)
- Create a new menu (and add the new perspective to it)
- Apps (optional)
Adding a new Screen
Note
<div>My Hello World Screen</div>. This can be any HTML code, and you can use the supplied Angular and Knockout frameworks. For the purposes of this example, we are not using any of those frameworks, but you can choose to by selecting them from the drop down in the Template section.
main, on_close and on_open. For this demo, select the on_open and enter the following: function () { alert('Hello World'); }
Adding a new Perspective
6 6 grid on the right hand side.
HelloWorldJS). Click the button and then click the
 button to save this perspective. Enter
button to save this perspective. Enter HelloWorldPerspective, enter Home in the tag name field (and click the button), and click the button to finish the save.
 button and enter the perspective name.
button and enter the perspective name.
Adding a new menu
Hello World.
Working with Apps (Optional)
HelloWorldPerspective, you entered the tag Home. The Apps directory by default contains a single directory called Home with which you associated your perspective. This is where you will find it when you open the Apps directory. You can click on it to run the perspective now.

2.6.2. The JavaScript (JS) API for Extensions
plugins folder of the Business Central webapp (typically: {INSTALL_DIR}/business-central.war/plugins/) or it can be loaded via regular JavaScript calls.
- Register Perspective API: allows for the dynamic creation of perspectives. The example below creates a panel using the
registerPerspectivemethod:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Editor API: allows you to dynamically create editors and associate them with a file type. The example below creates a sample editor and associates it with
filenamefile type.In addition toCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow on_startupandon_openmethods seen in the previous example, the API exposes the following callback events for managing the editor's lifecycle:You can display this editor via an html template:- on_concurrent_update;
- on_concurrent_delete;
- on_concurrent_rename;
- on_concurrent_copy;
- on_rename;
- on_delete;
- on_copy;
- on_update;
- on_open;
- on_close;
- on_focus;
- on_lost_focus;
- on_may_close;
- on_startup;
- on_shutdown;
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - PlaceManager API: the methods of this API allow you to request that the Business Central display a particular component associated with a target:
$goToPlace("componentIdentifier"); - Register plugin API: the methods of this API allow you to create dynamic plugins (that will be transformed in Business Central screens) via the JS API.The plugin references the
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow angular.sample.htmltemplate:A plugin can be hooked to Business Central events via a series of JavaScript callbacks:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - on_concurrent_update;
- on_concurrent_delete;
- on_concurrent_rename;
- on_concurrent_copy;
- on_rename;
- on_delete;
- on_copy;
- on_update;
- on_open;
- on_close;
- on_focus;
- on_lost_focus;
- on_may_close;
- on_startup;
- on_shutdown;
- Register splash screens API: use the methods in this API to create splash screens.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Virtual File System (VFS) API: with this API, you can read and write a file saved in the file system using an asynchronous call.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.7. Configuring Table Columns
Adding and Removing Columns
 button in the top right corner. Clicking on this button opens up the list of columns that can added or removed to the current table with a checkbox next to each column:
button in the top right corner. Clicking on this button opens up the list of columns that can added or removed to the current table with a checkbox next to each column:

Resizing Columns

Moving Columns
 .
.
 .
.
Sorting Columns
Chapter 3. Command line configuration
kie-config-cli tool is a command line configuration tool that provides capabilities to manage the system repository from the command line and can be used in an online or offline mode.
Online mode(default and recommended) - on startup, the tool connects to a Git repository using a Git server provided bykie-wb. All changes are made locally and published to upstream only after explicitly executing the push-changes command. Use the exit command to publish local changes. To discard local changes on exit, use the discard command.Offline mode(a kind of installer style) - creates and manipulates the system repository directly on the server (there is no discard option).
- Go to the Red Hat Customer Portal and log in.
- Click → .
- In the Product Downloads page that opens, click Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite.
- From the Version drop-down menu, select 6.1.
- In the displayed table, navigate to the Supplementary Tools row and then click Download.
kie-config-cli-6.MINOR_VERSION-redhat-x-dist with file kie-config-cli.sh.
3.1. Starting the kie-config-cli tool in online mode
- To start the kie-config-cli tool in online mode, navigate to the
kie-config-cli-6.MINOR_VERSION-redhat-x-distdirectory where you installed the tool and then execute the following command. - In a Unix environment run:
./kie-config-cli.sh
./kie-config-cli.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a Windows environment run:./kie-config-cli.bat
./kie-config-cli.batCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
git://kie-wb-host:9148/system
3.2. Starting the kie-config-cli tool in offline mode
- Navigate to the
kie-config-cli-6.MINOR_VERSION-redhat-x-distdirectory where you installed the tool. - In a Unix environment, run:
./kie-config-cli.sh offline
./kie-config-cli.sh offlineCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a Windows environment, run:./kie-config-cli.bat offline
./kie-config-cli.bat offlineCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
.niogit) is located. If .niogit does not yet exist, the folder value can be left empty and a brand new setup is created.
3.3. Commands available for the kie-config-cli tool
add-deployment- adds a new deployment unitadd-repo-org-unit- adds a repository to the organizational unitadd-role-org-unit- adds role(s) to an organizational unitadd-role-project- adds role(s) to a projectadd-role-repo- adds role(s) to a repositorycreate-org-unit- creates new organizational unitcreate-repo- creates a new git repositorydiscard- does not publish local changes, cleans up temporary directories and closes the toolexit- publishes work, cleans up temporary directories and closes the toolfetch-changes- fetches changes from upstream repositoryhelp- prints available commands with descriptionslist-deployment- lists available deploymentslist-org-units- lists available organizational unitslist-repo- lists available repositoriespush-changes- pushes changes to upstream repository (in online mode only)remove-deployment- removes existing deploymentremove-org-unit- removes existing organizational unitremove-repo- removes an existing repository from config onlyremove-repo-org-unit- removes a repository from the organizational unitremove-role-org-unit- removes role(s) from an organizational unitremove-role-project- removes role(s) from a projectremove-role-repo- removes role(s) from a repository
Chapter 4. Migration
- Migrate the data first: These are your business assets.
- Next, migrate your runtime processes.
- Finally, convert old API calls to new ones one by one.
4.1. Data Migration
- Download the migration tool by logging in at the Red Hat Customer Portal and then navigating to Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite Software Downloads section. Click on Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite Migration Tool to download the zip archive.
- Unzip the downloaded zip archive in a directory of your choice and navigate to this directory in a command prompt. This directory contains four folders:
bin- contains the launch scripts.jcr-exporter-libs- contains the libs specific to theexport-from-JCRpart of the migration.vfs-importer-libs- contains the libs specific to theimport-into-Gitpart of the migration.conf- contains global migration tool configuration.
- For production databases, copy the JDBC driver for the database that is used by the JCR repository into the
jcr-exporter-libsdirectory of the migration tool. - Execute the following command:
./bin/runMigration.sh -i <source-path> -o <destination-path> -r <repository-name>
./bin/runMigration.sh -i <source-path> -o <destination-path> -r <repository-name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- <source-path> is a path to a source JCR repository.
- <desintation-path> is a path to a destination GIT VFS. This folder must not exist already.
- <repository-name> an arbitrary name for the new repository.
-i command, you can also use -h to print out a help message and -f which forces an overwrite of the output directory, thus eliminating the need for manual deletion of this directory.
Importing the repository in Business Central
Note
Importing the repository in JBDS
- Start JBoss Developer Studio.
- Start the Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite server (if not already running) by selecting the server from the server tab and click the start icon.
- Select → and navigate to the Git folder. Open the Git folder to select and click next.
- Select the repository source as and click next.
- Select the repository that is to be configured from the list of available repositories.
- Import the project as a general project in the next window and click next. Name this project and click Finish.
4.2. Runtime Migration
- Set the system property
jbpm.v5.id.strategyto true in the JBoss BPM Suitestandalone.xmlfile:<property name="jbpm.v5.id.strategy" value="true"/>
<property name="jbpm.v5.id.strategy" value="true"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Load the KieSession as shown here:
KieSession ksession = JPAKnowledgeService.loadStatefulKnowledgeSession(sessionID, kbase, sessionConf, env);
KieSession ksession = JPAKnowledgeService.loadStatefulKnowledgeSession(sessionID, kbase, sessionConf, env);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Continue the normal execution of the process using KieSession methods:
ksession.signalEvent("SomeEvent", null);ksession.signalEvent("SomeEvent", null);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
4.3. API and Backwards Compatibility
Migrating to Version 6.1
knowledge-api JAR file is no longer supported in version 6.1 and is replaced by APIs contained in the kie-api JAR file that were introduced in JBoss BPM Suite 6.0.
knowledge-api.jar), please migrate (rewrite) the API calls to the new KIE API. Please be aware that several other APIs have changed between JBoss BRMS 5.x and JBoss BPM Suite 6.x, namely the task service API and the REST API.
Migrating to Version 6.0
knowledge-api jar for backwards compatible code. This API is the public interface for working with JBoss BPM Suite and JBoss BRMS and is backwards compatible.
4.4. Migrating task service
LocalHTWorkItemHandler.
Chapter 5. Data management
5.1. Data backups
- any customized deployment descriptors (such as,
web.xml,jboss-web.xml,jboss.xml) - any customized properties files
Note
Consider backing up the entirebusiness-central.waranddashbuilder.warfiles.
5.2. Setup Indexes
Setup foreign key indexes
Setup indexes for Process and Task Dashboard
processinstancelog and bamtasksummary.
5.3. Setting up the Database
- Postgres
- The following sql sentence is used to create a Postgres database:
CREATE DATABASE dashbuilder WITH ENCODING='UTF8' OWNER=dashbuilder CONNECTION LIMIT=-1CREATE DATABASE dashbuilder WITH ENCODING='UTF8' OWNER=dashbuilder CONNECTION LIMIT=-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The database encoding must be UTF8 - DB2
- DB2 database can be created using the following sql sentence:
CREATE DATABASE dashb PAGESIZE 16384
CREATE DATABASE dashb PAGESIZE 16384Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
The default pagesize for DB2 systems is 4k which is not enough for the dashbuilder table columns size. The pagesize should be forced to 16384 as shown in the above sentence.
5.4. Editing the Database
java:jboss/datasources/ExampleDS
java:jboss/datasources/ExampleDSstandalone.xml.
Note
Procedure 5.1. Changing Database
- Install the database driver on JBoss (refer to JBoss driver documentation).
- Create an empty database and a JBoss data source which connects to the database driver.
- Modify the file
dashbuilder.war/WEB-INF/jboss-web.xml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Replace the jndi-name parameter value by the JNDI path of the JBoss data source you've just created.
- Modify the file
dashbuilder.war/WEB-INF/jboss-deployment-structure.xml - Add the following snippet of configuration inside the
deploymenttag, wherejdbcDriverModuleNameis the name of the JBoss JDBC driver module:<dependencies> <module name="jdbcDriverModuleName" /> </dependencies><dependencies> <module name="jdbcDriverModuleName" /> </dependencies>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.5. DDL Scripts
ddl-scripts folder. Database scripts are provided for DB2, H2, MySQL5, Oracle, PostgreSQL and SQLServer.
Chapter 6. Asset repository
Project Explorer from the unified environment of Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite.
6.1. Creating a repository
Important
ADMIN role can create a repository.
Procedure 6.1. Creating a New Repository
- Open the Administration perspective: on the main menu, click → .
- On the perspective menu, click → .
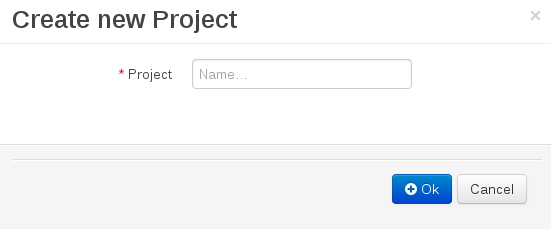
- The Create Repository pop-up window is displayed.
Figure 6.1. Create Repository Pop-up
- Enter the mandatory details:
- Repository name.
Note
Note that the repository name should be a valid filename. Avoid using a space or any special character that might lead to an invalid folder name. - Select an organizational unit in which the repository is to be created from the Organizational Unit drop-down option.
- Click Finish
6.2. Cloning a repository
Important
ADMIN role can clone a repository.
Procedure 6.2. Cloning a repository
- Open the Administration perspective.
- On the Repositories menu, select .
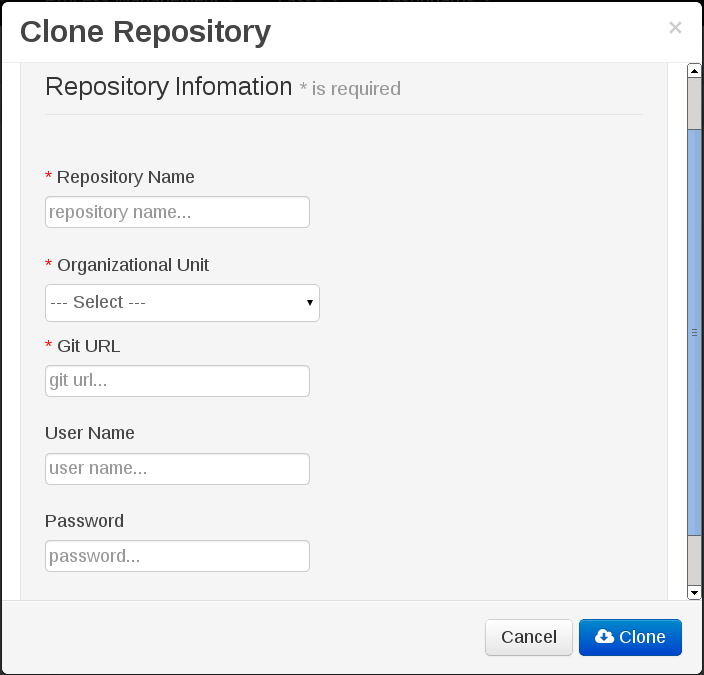
- The Clone Repository pop-up window is displayed.
Figure 6.2. Clone Repository Pop-up
- In the Clone Repository dialog window, enter the repository details:
- Enter the Repository Name to be used as the repository identifier in the Asset repository and select the Organizational Unit it should be added to.
- Enter the URL of the GIT repository:
- For a Local Repository:
file:///path-to-repository/reponame - For a Remote or preexisting Repository:
git://hostname/reponame
Note
The file protocol is only supported for 'READ' operations. 'WRITE' operations are not supported. - If applicable, enter the User Name and Password to be used for authentication when cloning the repository.
- Click Clone.
- A confirmation prompt with an OK button is displayed which notifies the user that the repository is created successfully. Click OK.The repository will be indexed. Some workbench features may be unavailable until indexing has completed.
6.3. Removing a Repository
Removing a Repository from Business Central
Procedure 6.3. Using Business Central to Remove a Repository
- Access the in Business Central → .
- Select from the tree menu on the left.
- In the on the right, locate the repository to be deleted from the list of available repositories.
- Select from the drop-down menu, and click the button.
- The following message will appear:
Are you sure you want to remove Repository "<$RepositoryName>"? Some editors may become inoperable if their content is inaccessible.
Are you sure you want to remove Repository "<$RepositoryName>"? Some editors may become inoperable if their content is inaccessible.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Press to delete.
Removing a Repository using the kie-config-cli Tool
kie-config-cli tool via the remove-repo command.
kie-config-cli tool, see Chapter 3, Command line configuration.
Removing a Repository using the REST API
DELETE REST API call. This call relies on the user having created an authenticated HTTP session before issuing this command.
Example 6.1. Removing a repository using curl
curl -H 'Accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -X DELETE 'localhost:8080/business-central/rest/repositories/REPOSITORY_NAME'
curl -H 'Accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -X DELETE 'localhost:8080/business-central/rest/repositories/REPOSITORY_NAME'
6.4. Managing Assets
Note
kiemgmt.
Managed and Unmanaged Repositories
Managed Branches
Repository Structure
kiemgmt will have a user task appear in this task list to review the assets being promoted. This user can claim this task, and decide to promote all, some or none of the assets. The underlying process will cherry-pick the commits selected by the user to a release branch. This user can also request another review of these assets and this process can be repeated multiple times till all the assets are ready for release. The flow for this process is shown below:
Warning
release
6.5. Maven repository
- Builds
- Documentation
- Reporting
- Dependencies
- Releases
- SCMs
- Distribution
- Local: refers to a local repository where all the project dependencies are stored and is located with the current installation in the default folder as "m2". It is a cache of the remote downloads, and also contains the temporary build artifacts which have not yet been released.
- Remote: refers to any other type of repository that can be accessed by a variety of protocols such as file:// or http://. These repositories can be at a remote location set up by a third-party for downloading of artifacts or an internal repository set up on a file or HTTP server, used to share private artifacts between the development teams for managing internal releases.
6.6. Configuring deployment to a remote Nexus repository
distributionManagement element to your project's pom.xml file as demonstrated in the code example below.
snapshotRepository element is used when the -SNAPSHOT qualifier is appended to the project's current version number. In other cases the repository specified in the repository element is used.
settings-security.xml file, using a master password. By default, this file is in ~/.m2 folder, unless you have changed its location by modifying the kie.maven.settings.custom system property.
pom.xml file.
6.7. System Configuration
Procedure 6.4. Changing System Properties
- Edit the file
$JBOSS_HOME/domain/configuration/host.xml - Locate the XML elements server that belong to the main-server-group and add the system property. For example:
<system-properties> <property name="org.uberfire.nio.git.dir" value="..." boot-time="false"/> ... </system-properties>
<system-properties> <property name="org.uberfire.nio.git.dir" value="..." boot-time="false"/> ... </system-properties>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
org.uberfire.nio.git.dir: Location of the directory .niogit. Default: working directoryorg.uberfire.nio.git.daemon.enabled: Enables/disables GIT daemon. Default: trueorg.uberfire.nio.git.daemon.host: If GIT daemon enabled, uses this property as the localhost identifier. Default: localhostorg.uberfire.nio.git.daemon.port: If GIT daemon is enabled, uses this property as the port number. Default: 9418org.uberfire.nio.git.ssh.enabled: Enables/Disables SSH daemon. Default: trueorg.uberfire.nio.git.ssh.host: If SSH daemon is enabled, uses this property as the localhost identifier. Default: localhostorg.uberfire.nio.git.ssh.port: If SSH daemon is enabled, uses this property as the port number. Default: 8001org.uberfire.nio.git.ssh.cert.dir: Location of the.securitydirectory where local certificates will be stored. Default: working directoryorg.uberfire.metadata.index.dir: Location of the.indexfolder for Lucene. Default: working directoryorg.uberfire.cluster.id: Name of the Helix cluster, for example: kie-clusterorg.uberfire.cluster.zk: Connection string to Zookeeper. This is of the formhost1:port1,host2:port2,host3:port3. For example:localhost:2188.org.uberfire.cluster.local.id: Unique id of the Helix cluster node. Note that ':' is replaced with '_'. For example: node1_12345.org.uberfire.cluster.vfs.lock: Name of the resource defined on the Helix cluster, for example: kie-vfsorg.uberfire.cluster.autostart: Delays VFS clustering until the application is fully initialized to avoid conflicts when all cluster members create local clones. Default: falseorg.uberfire.sys.repo.monitor.disabled: Disable configuration monitor (do not disable unless you know what you're doing). Default: falseorg.uberfire.secure.key: Secret password used by password encryption. Default: org.uberfire.adminorg.uberfire.secure.alg: Crypto algorithm used by password encryption. Default: PBEWithMD5AndDESorg.guvnor.m2repo.dir: Place where Maven repository folder will be stored. Default: working-directory/repositories/kieorg.kie.example.repositories: Folder from where demo repositories will be cloned. The demo repositories need to have been obtained and placed in this folder. This system property takes precedence over org.kie.demo and org.kie.example properties. Default: Not used.org.kie.demo: Enables external clone of a demo application from GitHub. This system property takes precedence over org.kie.example. Default: true.org.kie.example: Enables example structure composed by Repository, Organization Unit and Project. Default: false
Chapter 7. Process export and import
7.1. Creating a Process definition
- Open the Project Authoring perspective ( → ).
- In
Project Explorer( → ), navigate to the project where you want to create the Process definition (in the Project view, select the respective repository and project in the drop-down lists; in the Repository view, navigate toREPOSITORY/PROJECT/src/main/resources/directory).Note
It is recommended to create your resources, including your Process definitions, in a package of a Project to allow importing of resources and their referencing. To create a package, do the following:- In the Repository view of the Project Explorer, navigate to the
REPOSITORY/PROJECT/src/main/resources/directory. - Go to → .
- In the New resource dialog, define the package name and check the location of the package in the repository.
- From the perspective menu, go to → .
- In the New Processes dialog box, enter the Process name and click . Wait until the Process Editor with the Process diagram appears.
7.2. Importing a Process definition
- In the Project Explorer, select a Project and the respective package to which you want to import the Process definition.
- Create a new Business Process to work in by going to → .
- In the Process Designer toolbar, click the Import
 icon in the editor toolbar and pick the format of the imported process definition. Note that you have to choose to overwrite the existing process definition in order to import.
icon in the editor toolbar and pick the format of the imported process definition. Note that you have to choose to overwrite the existing process definition in order to import.
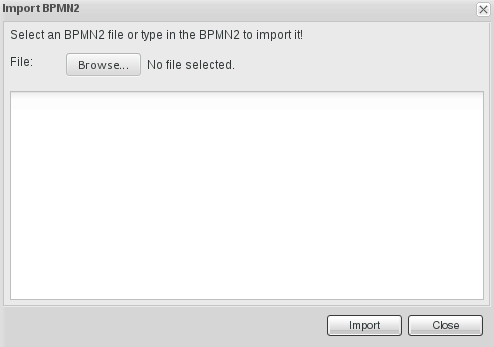
- From the Import window, locate the Process file and click .
Figure 7.1. Import Window
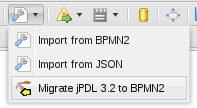
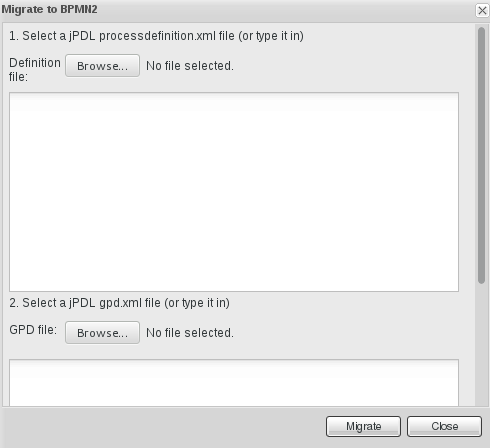
7.3. Importing jPDL 3.2 to BPMN2
Figure 7.2. Migrate jPDL 3.2 to BPMN2
Figure 7.3. Migrate to BPMN2 dialog box
Important
7.4. Exporting a process
Procedure 7.1. Exporting a business process
- Open the Project Authoring perspective: on the main menu, click → .
- Select the business process which is to be exported, to view it in the Process Designer.
- Click on the (
 ) button of the process designer toolbar and select View Process Sources from the drop-down options.
) button of the process designer toolbar and select View Process Sources from the drop-down options.
- The Process Sources window is displayed
- Click on the Download BPMN2 button and save the business process at the desired location.
Part III. Integration
Chapter 8. Deploying Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite artifacts to SOA Repository Artifact Model and Protocol (S-RAMP) repository
8.1. Deploying Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite artifacts to SOA Repository Artifact Model and Protocol (S-RAMP) using Maven
pom.xml file as shown below:
- Clone the git repository where you have saved the BPM Suite project by running this command:
git clone http://localhost:8001/REPOSITORY_NAME
git clone http://localhost:8001/REPOSITORY_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - On the command line, move into the folder that contains the project.
- Follow the instructions in Red Hat JBoss Fuse Service Works 6 Development Guide, Volume 3: Governance, section Deploying to S-RAMP. Use the URL from the example below:With these settings, Maven deployments are sent directly to the S-RAMP repository using the S-RAMP API. Note that artifacts are added to the S-RAMP repository with an artifact type based on the Maven type of the project. You can override this behavior by adding a query parameter to the repository URL in the
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow pom.xmlfile. For example:The above example causes the Maven artifact to be uploaded with an S-RAMP artifact type of KieJarArchive.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Amend the maven plug-in in file
pom.xmland add a dependency to it as follows in case the project does not contain decision tables:If the project contains decision tables, use this dependency for the kie-maven-plugin instead:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Run a clean Maven deployment using the following command:.
mvn -s sramp-settings.xml deploy
mvn -s sramp-settings.xml deployCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
settings.xml file. For further details on the credentials, refer to Red Hat JBoss Fuse Service Works (FSW) documentation on Authentication.
8.2. Deploying Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite artifacts to SOA Repository Artifact Model and Protocol (S-RAMP) using graphical user interface (GUI)
- In a web browser, navigate to http://localhost:8080/s-ramp-ui/. If the user interface has been configured to run from a domain name, substitute
localhostfor the domain name. For example http://www.example.com:8080/s-ramp-ui/. - Click on .
- In the Manage Artifacts section, select .
- Locate the kie archive you want to deploy. In the dialog that opens, fill out
KieJarArchiveas the type, and select . - The deployment then creates these entries in the S-RAMP repository:
KieJarArchive, from which it derives:KieXmlDocument(if the archive containskmodule.xml)BpmnDocument(if the archive containsbpmndefinitions)DroolsDocument(if the archive containsdrldefinitions)
Chapter 9. Integrating Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite with Red Hat JBoss Fuse
features.xml files: one providing core JBoss BPM Suite and JBoss BRMS features, which defines the OSGi features that can be deployed into JBoss Fuse, and the other providing additional support for integration with SwitchYard and Camel.
Note
Important
jboss-brms-bpmsuite<version>-redhat<version>fuse-features.zip:
- drools-common
- drools-module
- drools-templates
- drools-decisiontable
- drools-jpa
- kie
- kie-ci
- kie-spring
- kie-aries-blueprint
- jbpm-commons
- jbpm-human-task
- jbpm
- droolsjbpm-hibernate
- h2
| Feature | Use Case |
|---|---|
drools-module | Use the JBoss BRMS engine for rules evaluation, without requiring persistence, processes, or decision tables. |
drools-jpa | Use the JBoss BRMS engine for rules evaluation with persistence and transactions, but without requiring processes or decision tables. The drools-jpa feature already includes drools-module, however you may also need to install the droolsjbpm-hibernate feature, or ensure there is a compatible hibernate bundle installed. |
drools-decisiontable | Use the JBoss BRMS engine with decision tables. |
jbpm | Use the JBoss BPM Suite (or JBoss BRMS engine with processes). The jbpm feature already includes drools-module and drools-jpa. You may also need to install the droolsjbpm-hibernate feature, or ensure that there is a compatible hibernate bundle installed. |
jbpm and jbpm-human-task | Use the JBoss BPM Suite (or JBoss BRMS engine with processes) with Human Task. |
Core engine jars and kie-ci. | Use JBoss BRMS or JBoss BPM Suite with KieScanner (KIE-CI) to download kJARs from a Maven repository. |
kie-spring | Use KIE-Spring integration. |
kie-spring and kie-aries-blueprint. | Use KIE-Aries-Blueprint integration. |
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-common-knowledge
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-rules
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-bpm
- kie-camel
- jbpm-workitems-camel
installDir/etc/org.ops4j.pax.url.mvn.cfg.
9.1. Install/Update Core Integration Features
Note
jboss-brms-bpmsuite<version>-redhat<version>fuse-features.zip file. For additional integration features, refer to Section 9.2, “Install Additional Integration Features”.
drools-karaf-features-6.2.0.Final-redhat-6-features.xml), you need to remove them and all associated files before installing the most recent features.xml file.
Procedure 9.1. Removing an Existing drools-karaf-features Installation
- Start the Fuse console using:
./installDir/bin/fuse
$ ./installDir/bin/fuseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Unistall old features/apps that used the previous
features.xmlfile. For example:JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:uninstall drools-module JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:uninstall jbpm JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:uninstall kie-ci
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:uninstall drools-module JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:uninstall jbpm JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:uninstall kie-ciCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Search for references of bundles using drools/kie/jbpm and remove them:
list -t 0 -s | grep drools list -t 0 -s | grep kie list -t 0 -s | grep jbpm
list -t 0 -s | grep drools list -t 0 -s | grep kie list -t 0 -s | grep jbpmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove the bundles:karaf@root> osgi:uninstall <BUNDLE_ID>
karaf@root> osgi:uninstall <BUNDLE_ID>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Remove the old drools-karaf-features url:
karaf@root> features:removeurl mvn:org.drools/drools-karaf-features/6.2.0.Final-redhat-<old-version>/xml/features
karaf@root> features:removeurl mvn:org.drools/drools-karaf-features/6.2.0.Final-redhat-<old-version>/xml/featuresCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Restart Fuse
drools-karaf-features:
Procedure 9.2. Install core JBoss BPM Suite and JBoss BRMS features
- Configure required repositories
- Edit the
installDir/etc/org.ops4j.pax.url.mvn.cfgfile in your JBoss Fuse installation and add the following entry to theorg.ops4j.pax.url.mvn.repositoriesvariable, noting that entries are separated by ‘, \’:- http://maven.repository.redhat.com/ga/@id=bxms-product-repo
- Start JBoss Fuse:
./installDir/bin/fuse
$ ./installDir/bin/fuseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add a reference to the core features file by running the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.drools/drools-karaf-features/6.2.0.Final-redhat-<version>/xml/features
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.drools/drools-karaf-features/6.2.0.Final-redhat-<version>/xml/featuresCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You can now install the features provided by this file by running, for example, the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install drools-module
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install drools-moduleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.2. Install Additional Integration Features
Important
Procedure 9.3. SwitchYard and Camel Integration
- Download the
fuse-integrationpackage that is aligned with your version of JBoss FuseNote
For instance, if you want to use the 6.2.0.redhat-117 version of JBoss Fuse, you need to install thefuse-6.2.0.redhat-117JBoss Fuse integration features - Add the Remote Maven Repository that contains the fuse dependencies to your
karafinstance:- Edit the
Fuse_home/etc/org.ops4j.pax.url.mvn.cfg
- Update the Drools features URL:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.switchyard.karaf/mvn:org.switchyard.karaf/switchyard/<SWITCHYARD_VERSION>/xml/core-features JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.drools/drools-karaf-features/<DROOLS_VERSION>/xml/features
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.switchyard.karaf/mvn:org.switchyard.karaf/switchyard/<SWITCHYARD_VERSION>/xml/core-features JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.drools/drools-karaf-features/<DROOLS_VERSION>/xml/featuresCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Add a reference to the features file for additional integration with SwitchYard and Camel by running the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.jboss.integration.fuse/karaf-features/<FUSE_INTEGRATION_PACKAGE_VERSION>/xml/features
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.jboss.integration.fuse/karaf-features/<FUSE_INTEGRATION_PACKAGE_VERSION>/xml/featuresCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You can now install the features provided for SwitchYard and Camel integration by running, for example, the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install fuse-bxms-switchyard-rules JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install kie-camel JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install jbpm-workitems-camel
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install fuse-bxms-switchyard-rules JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install kie-camel JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install jbpm-workitems-camelCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.3. Install JBoss Fuse Integration Quickstart Applications
org/jboss/integration/fuse/quickstarts/karaf-features/<FUSE_INTEGRATION_PACKAGE_VERSION>/karaf-features-<FUSE_INTEGRATION_PACKAGE_VERSION>-features.xml:
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-bpm-service
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-rules-camel-cbr
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-rules-interview
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-rules-interview-container
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-rules-interview-dtable
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-demo-library
- fuse-bxms-switchyard-demo-helpdesk
- fuse-bxms-camel-blueprint-drools-decision-table
- fuse-bxms-camel-spring-drools-decision-table
- fuse-bxms-jbpm-workitems-camel-quickstart
- fuse-bxms-spring-jbpm-osgi-example
installDir/etc/org.ops4j.pax.url.mvn.cfg.
Procedure 9.4. Installing the Quickstart Application
- Add a reference to the features file by running the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.jboss.integration.fuse.quickstarts/karaf-features/1.0.0.redhat-620137/xml/features
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:addurl mvn:org.jboss.integration.fuse.quickstarts/karaf-features/1.0.0.redhat-620137/xml/featuresCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - You can now install the quickstart applications provided by this features file by running, for example, the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-bpm-service
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-bpm-serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Procedure 9.5. Downloading and Installing the Quickstart ZIP Files
- Download the quickstart application ZIP file.
- Unpack the contents of the quickstarts directory into your existing
installDir/quickstartsdirectory. - Unpack the contents of the system directory into your existing
installDir/systemdirectory.
9.3.1. Testing Your First Quickstart Application
Procedure 9.6. Testing the Quickstart Application
- Start JBoss Fuse:
./installDir/bin/fuse
$ ./installDir/bin/fuseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Install and start the switchyard-bpm-service by running the following console command:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-bpm-service
JBossFuse:karaf@root> features:install fuse-bxms-switchyard-quickstart-bpm-serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
Any dependent features specified by the application’s features file will be installed automatically. - Submit a webservice request to invoke the SOAP gateway.
- Open a terminal window and navigate to the associated quickstart directory that was unpacked from the quickstart application ZIP file (in this case, switchyard-bpm-service).
- Run the following command:
mvn clean install
$ mvn clean installCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
You will need the following repositories configured in yoursettings.xmlfile:- http://maven.repository.redhat.com/ga/
- http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/repositories/public/
- Run the following command:
mvn exec:java -Pkaraf
$ mvn exec:java -PkarafCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- You will receive the following response:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 10. Integrating with Spring
10.1. Configuring Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite with Spring
jboss-bpms-engine.zip file and is called kie-spring-VERSION-redhat-MINORVERSION.jar.
As a Self Managed Process Engine
RuntimeManager API, perfect synchronization between process engine and task service is managed internally and the end user does not have to deal with the internal code to make these two work together.
As a Shared Task Service
TaskService, you have more flexibility in configuring the task service instance as it is independent of the RuntimeManager. Once configured it is then used by the RuntimeManager when requested.
org.kie.spring.factorybeans.RuntimeEnvironmentFactoryBean class. This factory class is responsible for producing instances of RuntimeEnvironment that are consumed by RuntimeManager upon creation. Illustrated below is a configured RuntimeEnvironment with the entity manager, transaction manager, and resources for the class org.kie.spring.factorybeans.RuntimeEnvironmentFactoryBean:
- DEFAULT - default (most common) configuration for RuntimeManager
- EMPTY - completely empty environment to be manually populated
- DEFAULT_IN_MEMORY - same as DEFAULT but without persistence of the runtime engine
- DEFAULT_KJAR - same as DEFAULT but knowledge asset are taken from KJAR identified by releaseid or GAV
- DEFAULT_KJAR_CL - build directly from classpath that consists kmodule.xml descriptor
- knowledgeBase
- assets
- releaseId
- groupId, artifactId, version
entity manager factory and transaction manager. Illustrated below is an example RuntimeManager for org.kie.spring.factorybeans.RuntimeManagerFactoryBean:
<bean id="runtimeManager" class="org.kie.spring.factorybeans.RuntimeManagerFactoryBean" destroy-method="close"> <property name="identifier" value="spring-rm"/> <property name="runtimeEnvironment" ref="runtimeEnvironment"/> </bean>
<bean id="runtimeManager" class="org.kie.spring.factorybeans.RuntimeManagerFactoryBean" destroy-method="close">
<property name="identifier" value="spring-rm"/>
<property name="runtimeEnvironment" ref="runtimeEnvironment"/>
</bean>Chapter 11. CDI Integration
11.1. CDI Integration
- entity manager and entity manager factory
- user group callback for human tasks
- identity provider to pass authenticated user information to the services
deployments/business-central.war/WEB-INF/beans.xml file may be configured to change the current settings of the new usergroupcallback implementation.
Note
org.jbpm.services.task.identity.JAASUserGroupCallbackImpl is just an example here to demonstrate the settings of the application server regardless of what it actually is (LDAP, DB, etc).
Chapter 12. Persistence
Note
- Session state: this includes the session ID, date of last modification, the session data that business rules would need for evaluation, state of timer jobs.
- Process instance state: this includes the process instance ID, process ID, date of last modification, date of last read access, process instance start date, runtime data (the execution status including the node being executed, variable values, etc.)and the eventtypes.
- Work item runtime state: this includes the work item ID, creation date, name, process instance ID, and the work item state itself.
12.1. Session
SessionInfo entities. These persist the state of the runtime KIE session, and store the following data:
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
id
|
primary key
|
false
|
|
lastmodificationdate
|
last saved to data store
|
N/A
|
|
rulesbytearray
|
binary dataset with session state (binary blob
|
false
|
|
startdate
|
session start
| |
|
optlock
|
version number used to lock value for optimistic locking
| |
12.2. Process Instance
ProcessInstanceInfo entities, which persist the state of a process instance on runtime and store the following data:
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
instanceid
|
primary key
|
false
|
|
lastmodificationdate
|
last saved to data store
|
N/A
|
|
lastreaddate
|
last read from data store
|
N/A
|
|
processid
|
ID of the process the instance is based on
|
false
|
|
processinstancebytearray
|
binary dataset with process instance state (binary blob)
|
false
|
|
startdate
|
Process instance start date
| |
|
optlock
|
version number used lock value for optimistic locking
| |
|
state
|
Process instance state
|
false
|
ProcessInstanceInfo has a 1:N relationship to the EventTypes entity.
EventTypes entity contains the following data:
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
instanceid
|
reference to the Process instance (foreign key to the
processinstanceinfo)
|
false
|
|
element
|
text field related to an event the Process instance has undergone
| |
Pessimistic Locking Support
12.3. Work Item
workiteminfo entities, which persist the state of the particular work item instance on runtime and store the following data:
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
workitemid
|
primary key
|
false
|
|
name
|
work item name
| |
|
processinstanceid
|
parent Process instance id
|
false
|
|
state
|
integer representing work item state
|
false
|
|
optlock
|
version number used lock value for optimistic locking
| |
|
workitembytearray
|
binary dataset with work item state (binary blob
)
|
false
|
|
creationDate
|
timestampe on which the work item was created
|
false
|
12.4. Persistence configuration
12.4.1. Persistence configuration
JBPMHelper class after you create a session or using the JPAKnowledgeService to create your session. The latter option provides more flexibility, while JBPMHelper has a method to create a session, and uses a configuration file to configure this session.
12.4.2. Configuring persistence using JBPMHelper
- Define your application to use an appropriate JBPMHelper session construtor:
KieSession ksession = JBPMHelper.newKieSession(kbase);KieSession ksession = JBPMHelper.loadKieSession(kbase, sessionId);
- Configure the persistence in the
jBPM.propertiesfile.Example 12.1. A sample jBPM.properties file with persistence for the in-memory H2 database
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
JBPMHelper.startH2Server(); method call and register it with the engine using JBPMHelper.setupDataSource(); method call.
12.4.3. Configuring persistence using JPAKnowledgeService
- Define your application to use the knowledge session created by JPAKnowledgeService:
- Define the session based on a knowledge base, a knowledge session configuration, and an environment. The environment must contain a reference to your Entity Manager Factory:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define the session based on a specific session id.
// recreate the session from database using the sessionId ksession = JPAKnowledgeService.loadKieSession(sessionId, kbase, null, env );
// recreate the session from database using the sessionId ksession = JPAKnowledgeService.loadKieSession(sessionId, kbase, null, env );Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Configure the persistence in the
META-INF/persistence.xmlfile: configure JPA to use Hibernate and the respective database.Information on how to configure data source on your application server should be available in the documentation delivered with the application server. For this information for JBoss Enterprise Application Platform, see the Administration and Configuration Guide for this product.Example 12.2. A sample persistence.xml file with persistence for an H2 data source
jdbc/jbpm-dsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
JBPMHelper.startH2Server(); method call and register it with the engine using JBPMHelper.setupDataSource(); method call.
Note
Chapter 13. Transactions
13.1. Transactions
13.2. Defining transactions
- Register the transaction manager in your environment.
Example 13.1. Code with transaction manager registration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Initialize the KieSession:
// get the KieSession RuntimeManager manager = RuntimeManagerFactory.Factory.get().newPerProcessInstanceRuntimeManager(environment); RuntimeEngine runtime = manager.getRuntimeEngine(ProcessInstanceIdContext.get()); KieSession ksession = runtime.getKieSession();
// get the KieSession RuntimeManager manager = RuntimeManagerFactory.Factory.get().newPerProcessInstanceRuntimeManager(environment); RuntimeEngine runtime = manager.getRuntimeEngine(ProcessInstanceIdContext.get()); KieSession ksession = runtime.getKieSession();Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define the transaction manager in
jndi.properties.Example 13.2. Definition of Bitronix transaction manager in jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=bitronix.tm.jndi.BitronixInitialContextFactory
java.naming.factory.initial=bitronix.tm.jndi.BitronixInitialContextFactoryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note
To use a different JTA transaction manager, edit the hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class, the transaction manager property, in thepersistence.xmlfile to load your transaction manager.Example 13.3. JBoss Transaction Manager set as transaction manager
<property name="hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class" value="org.hibernate.transaction.JBossTransactionManagerLookup"/>
<property name="hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class" value="org.hibernate.transaction.JBossTransactionManagerLookup"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define the start and the end of the transaction.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
13.3. Container Managed Transactions
org.jbpm.persistence.jta.ContainerManagerTransactionManager class. This is because the default implementation of the transaction manager in JBoss BPM Suite is based on the UserTransaction class getting the transaction status. However, some application servers in a CMT mode do not allow accessing the UserTransaction instance from JNDI.
ContainerManagedTransactionManager class expects that the transaction is always active (returning ACTIVE to the getStatus() method).
Note
Configuring the Transaction Manager
ContainerManagedTransactionManager, it needs to be inserted into the environment before you create or load a session:
Environment env = EnvironmentFactory.newEnvironment();
env.set(EnvironmentName.ENTITY_MANAGER_FACTORY, emf);
env.set(EnvironmentName.TRANSACTION_MANAGER, new ContainerManagedTransactionManager());
env.set(EnvironmentName.PERSISTENCE_CONTEXT_MANAGER, new JpaProcessPersistenceContextManager(env));
Environment env = EnvironmentFactory.newEnvironment();
env.set(EnvironmentName.ENTITY_MANAGER_FACTORY, emf);
env.set(EnvironmentName.TRANSACTION_MANAGER, new ContainerManagedTransactionManager());
env.set(EnvironmentName.PERSISTENCE_CONTEXT_MANAGER, new JpaProcessPersistenceContextManager(env));
persistence.xml file. For example if using IBM WebSphere:
<property name="hibernate.transaction.factory_class" value="org.hibernate.transaction.CMTTransactionFactory"/> <property name="hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class" value="org.hibernate.transaction.WebSphereExtendedJTATransactionLookup"/>
<property name="hibernate.transaction.factory_class" value="org.hibernate.transaction.CMTTransactionFactory"/>
<property name="hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class" value="org.hibernate.transaction.WebSphereExtendedJTATransactionLookup"/>
Disposing the KSession in a CMT
dispose() method). Doing so will cause exceptions on transaction completion as the Process Engine needs to clean up the state after the invocation has finished.
org.jbpm.persistence.jta.ContainerManagedTransactionDisposeCommand's execute() method. Using this command ensures that the ksession will be disposed when the transaction is actually complete.
afterDisposal phase of the transaction instead of executing it directly. If there is no active transaction or if there is no active transaction, the ksession is disposed immediately.
Chapter 14. Logging
- Process instance as
processinstancelog - Element instance as
nodeinstancelog - Variable instance as
variableinstancelog
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
id
|
The primary key of the log entity
|
No
|
|
end_date
|
The end date of the process instance
|
Yes
|
|
processid
|
The name (id) of the underlying process
|
Yes
|
|
processinstanceid
|
The id of the process instance
|
No
|
|
start_date
|
The start date of the process instance
|
Yes
|
|
status
|
The status of the process instance
|
Yes
|
|
parentProcessInstanceId
|
The process instance id of the parent process instance if applicable
|
Yes
|
|
outcome
|
The outcome of the process instance (details on the process finish, such as error code)
|
Yes
|
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
id
|
The primary key of the log entity
|
No
|
|
log_date
|
The date of the event
|
Yes
|
|
nodeid
|
The node id of the underlying Process Element
|
Yes
|
|
nodeinstanceid
|
The id of the node instance
|
Yes
|
|
nodename
|
The name of the underlying node
|
Yes
|
|
processid
|
The id of the underlying process
|
Yes
|
|
processinstanceid
|
The id of the parent process instance
|
No
|
|
type
|
The type of the event (
0 = enter event, 1 = exit event)
|
No
|
| Field | Description | Nullable |
|---|---|---|
|
id
|
The primary key of the log entity
|
No
|
|
log_date
|
The date of the event
|
Yes
|
|
processid
|
The name (id) of the underlying process
|
Yes
|
|
processinstanceid
|
The id of the process instance
|
No
|
|
value
|
The value of the variable at log time
|
Yes
|
|
variableid
|
The variable id as defined in the process definition
|
Yes
|
|
variableinstanceid
|
The id of the variable instance
|
Yes
|
|
outcome
|
The outcome of the process instance (details on the process finish, such as error code)
|
Yes
|
14.1. Logging events to database
- Map the Log classes to the data source, so that the given data source accepts the log entries. On Red Hat JBoss EAP, edit the data source properties in the
persistence.xmlfile.Example 14.1. The ProcessInstanceLog, NodeInstanceLog and VariableInstanceLog classes enabled for processInstanceDS
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Register a logger on your Kie Session.
Example 14.2. Import the Loggers
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example 14.3. Registering a Logger to a Kie Session
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optionally, call the method
addFilteron the logger to filter out irrelevant information. Only information accepted by all filters appears in the database. - Logger classes can be viewed in the Audit View:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.2. Logback Functionality
logback functionality for logging configuration.
Note
slf4j-nop and slf4j-simple are ideal for a light environment.
14.3. Configuring Logging
logback.xml file in business-central.war/WEB-INF/classes/logback.xml. To set the logging level of the org.drools package to "debug" for verbose logging, you would need to add the following line to the file:
- org.guvnor
- org.jbpm
- org.kie
- org.slf4j
- org.dashbuilder
- org.uberfire
- org.errai
- etc...
log4j, the log4j.xml can be located at business-central.war/WEB-INF/classes/log4j.xml and can be configured in the following way:
Note
Chapter 15. Localization and customization
15.1. Available Languages
- United States English (
en_US) - Spanish (
es_ES) - Japanese (
ja_JP) - Chinese (
zh_CN) - Portuguese (
pt_BR) - French (
fr_CA) - German (
de_DE)
Note
15.2. Changing language settings
Changing the User Interface Language in Business Central
http://localhost:8080/business-central/?locale=pt_BR
Changing the User Interface Language in Dashbuilder
- Log into the dashbuilder after the server has been successfully started by navigating to http://localhost:8080/dashbuilder in a web browser.
- Select the language of your choice by clicking on the available locales on the top center of the dashbuilder user interface to change the language.
Setting a Default User Interface Language in Dashbuilder
Procedure 15.1. Setting the default language as French
- Navigate to
jboss-eap-6.4/standalone/configurationand define the following in thestandalone.xmlfile.<system-properties> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.installedLocaleIds" value="en,es,de,fr,ja,pt,zh"/> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.defaultLocaleId" value="fr"/> </system-properties><system-properties> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.installedLocaleIds" value="en,es,de,fr,ja,pt,zh"/> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.defaultLocaleId" value="fr"/> </system-properties>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - The default user interface language of the dashbuilder is now set to French.
Defining the Installed Locales in Dashbuilder
Procedure 15.2. Defining the installed locale
- Navigate to
jboss-eap-6.4/standalone/configurationand define the following in thestandalone.xmlfile.<system-properties> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.installedLocaleIds" value="en,es,de,fr,ja,pt"/> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.defaultLocaleId" value="fr"/> </system-properties><system-properties> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.installedLocaleIds" value="en,es,de,fr,ja,pt"/> <property name="org.jboss.dashboard.LocaleManager.defaultLocaleId" value="fr"/> </system-properties>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Note
15.3. Running the JVM with UTF-8 Encoding
Part IV. Execution
Chapter 16. Execution server
16.1. Assignment rules
16.1.1. Defining assignment rules
- Create a file that will contain the rule definition on the Business Central classpath (the recommended location is
$DEPLOY_DIR/standalone/deployments/business-central.war/WEB-INF/classes/):default-add-task.drlwith the rules to be checked when the Human Task is createddefault-complete-task.drlwith the rules to be checked when the Human Task is completed
- Define the rules in the file.
Example 16.1. The default-add-task.drl content
Mary, the task will be automatically assigned to the user mary.
Example 16.2. The default-complete-task.drl content
Mary, the task will be automatically assigned to the user mary.
16.2. Mail session
16.2.1. Setting up mail session
- Open the respective profile configuration file (
standalone.xmlorhost.xml) for editing. - Add the mail session to the
urn:jboss:domain:mail:1.1subsystem.Example 16.3. New mail session on localhost
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Define the session outbound socket in the profile configuration file.
Example 16.4. Outbound socket definition
<outbound-socket-binding name="bpmsMail"> <remote-destination host="localhost" port="12345"/> </outbound-socket-binding><outbound-socket-binding name="bpmsMail"> <remote-destination host="localhost" port="12345"/> </outbound-socket-binding>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 17. Plug-in for Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio
17.1. Plug-in
Part V. Monitoring
Chapter 18. Process monitoring
18.1. JBoss Operations Network
com.sun.management.jmxremote.* parameters must be passed to the JBoss application via the pom.xml configuration file.
18.2. Installing the JBoss BRMS Plug-in into JBoss ON
Procedure 18.1. Copying the JBoss BRMS plug-in JAR files
- Extract the JBoss BRMS plug-in pack archive to a temporary location. This creates a subdirectory with the name jon-plugin-pack-brms-bpms-3.3.0.GA. For example:
unzip jon-plugin-pack-brms-bpms-3.3.0.GA.zip -d /tmp
[root@server rhq-agent]# unzip jon-plugin-pack-brms-bpms-3.3.0.GA.zip -d /tmpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Copy the extracted JBoss BRMS plug-in JAR files from the jon-plugin-pack-brms-bpms-3.2.0.GA/ directory to the JBoss ON server plug-in directory. For example:
cp /tmp/jon-plugin-pack-brms-bpms-3.3.0.GA/*.jar /opt/jon/jon-server-3.3.0.GA1/plugins
[root@server rhq-agent]# cp /tmp/jon-plugin-pack-brms-bpms-3.3.0.GA/*.jar /opt/jon/jon-server-3.3.0.GA1/pluginsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the JBoss Operations Network server to update the JBoss BRMS plug-in.
Procedure 18.2. Uploading the JBoss BRMS plug-in through GUI
- Start the JBoss Operations Network Server and Log in to access the GUI.
- In the top navigation of the GUI, open the Administration menu.
- In the Configuration area on the left, select the Server Plugins link.
- At the bottom of the list of loaded server plug-ins, click the Upload a plugin button and choose the BRMS plugin.
- The JBoss BRMS plug-in for JBoss Operations Network is now uploaded.
18.3. Monitoring Kie Bases and Kie Sessions
-kie.mbeans = enabled
-kie.mbeans = enabledKieBaseConfiguration kbconf = KieServices.Factory.get().newKieBaseConfiguration();
kbconf.setOption(MBeansOption.ENABLED);
KieBaseConfiguration kbconf = KieServices.Factory.get().newKieBaseConfiguration();
kbconf.setOption(MBeansOption.ENABLED);Note
Kie Services have been implemented for JBoss BRMS 6; for JBoss BRMS 5, Drools Services was the naming convention used and it had different measurements on sessions. For example, → renaming occured in the updated version.
Chapter 19. Managing Security for Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite Dashbuilder
19.1. Accessing Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite Dashbuilder
19.2. Managing security
- admin - Administrates the Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite system. Has full access rights to make any changes necessary. Also has the ability to add and remove users from the system.
- developer - Implements code required for process to work. Mostly uses the JBDS connection to view processes, but may use the web tool occasionally.:
- analyst - Responsible for creating and designing processes into the system. Creates process flows and handles process change requests. Needs to test processes that they create. Also creates forms and dashboards.
- user - Daily user of the system to take actions on business tasks that are required for the processes to continue forward. Works primarily with the task lists.
- manager - Viewer of the system that is interested in statistics around the business processes and their performance, business indicators, and other reporting of the system and people who interact with the system.
19.3. Workspace permissions
Procedure 19.1. Accessing Workspace Permissions
- Log into Business Dashboards from Business Central (as described in the Accessing Red Hat JBoss BPM Suite Dashbuilder topic).
- Select the appropriate Dashboard from the Wokspace drop-down.
Figure 19.1. Dashbuilder Workspace
- Click the Edit selected workspace properties
 button to access the Workspace Dashboard.
button to access the Workspace Dashboard.
- Click the Permissions label to view the permission management screen.
Figure 19.2. Permissions Screen
- Access: permission to login into the application.
- Administrate: permission to access the toolbar and system configuration features.
- Create pages: ability to create new project pages.
- Edit: permission to change the workspace properties.
- Clear: ability to delete the workspace.
- Edit permissions: ability to grant/deny permissions.
- Change allowed panels: permission to restrict the type of panels that can be used in this workspace.
Figure 19.3. Permissions Assignation
- Target roles (who): What user will be granted/denied with the permissions defined.
- Allowed actions: depending on the type of the resource we can enable/disable what the user can do on this resource.
- Reverse (optional): when we have a set of roles and we want to grant/deny a permission to all the roles but one.
Note
19.4. Page permissions
- To access Page permissions, locate the Pages drop-down under the jBPM Dashboard (or whatever Dashboard you selected).
- After expanding Pages, expand the Process dashboard option.
- Select the Page permissions option.
Figure 19.4. Page Permissions
- Visualize: permission to make the page visible.
- Edit: ability to change the page properties.
- Clear: ability to delete the page.
- Edit permissions: ability to grant/deny permissions for the page.
19.5. Panel permissions
- To access the Panel permissions page, expand the Panel instances option under the jBPM Dashboard (or whatever Dashboard you are using).
- Expand the Dashboard option and then expand the Process dashboard.
- Expand the Panels choice and select the appropriate process.
- Open the Panel permissions page.
Figure 19.5. Panel permissions configuration screen
- Visualize: make the panel visible.
- Edit: change the panel properties.
- Edit permissions: ability to grant/deny permissions for the panel.
Appendix A. Revision History
| Revision History | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Revision 1.0.0-56 | Thu Dec 17 2015 | ||
| |||