이 콘텐츠는 선택한 언어로 제공되지 않습니다.
Rules Development Guide
Create custom rules to enhance migration coverage.
Abstract
Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code, documentation, and web properties. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Because of the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be implemented gradually over several upcoming releases. For more details, see our CTO Chris Wright’s message.
Chapter 1. Introduction
All customers using this product should start their transition to Migration Toolkit for Applications.
Migration Toolkit for Applications is fully backwards compatible with all features and rulesets available in Migration Toolkit for Runtimes and will be maintained in the long term.
1.1. About the Rule Development Guide
This guide is intended for software engineers who want to create custom YAML-based rules for Migration Toolkit for Runtimes (MTR) tools.
See the Introduction to the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes for an overview and the CLI Guide for details.
1.1.1. Use of in this guide
This guide uses the <MTR_HOME> replaceable variable to denote the path to your MTR installation. The installation directory is the mtr-1.2.7.GA-offline directory where you extracted the MTR .zip file.
When you encounter <MTR_HOME> in this guide, replace it with the actual path to your MTR installation.
1.2. The MTR rules
The Migration Toolkit for Runtimes (MTR) contains rule-based migration tools (analyzers) that you can use to analyze the application user interfaces (APIs), technologies, and architectures used by the applications you plan to migrate. MTR analyzer rules use the following rule pattern:
when(condition) message(message) tag(tags)
when(condition)
message(message)
tag(tags)You can use the MTR rules internally to perform the following tasks:
- Extract files from archives.
- Decompile files.
- Scan and classify file types.
- Analyze XML and other file content.
- Analyze the application code.
- Build the reports.
MTR builds a data model based on the rule execution results and stores component data and relationships in a graph database. This database can then be queried and updated as required by the migration rules and for reporting purposes.
You can create your own custom analyzer rules. You can use custom rules to identify the use of custom libraries or other components that might not be covered by the provided standard migration rules.
For instructions on how to write custom rules, see [Rule Development Guide].
Chapter 2. Getting started with rules
You can get started creating custom MTR rules by creating a rule or by reviewing the quickstarts.
2.1. Creating your first XML rule
This section guides you through the process of creating and testing your first MTR XML-based rule. This assumes that you have already installed MTR. See Installing and running the CLI in the CLI Guide for installation instructions.
In this example, you will write a rule to discover instances where an application defines a jboss-web.xml file containing a <class-loading> element and provide a link to the documentation that describes how to migrate the code.
2.1.1. Creating the directory structure for the rule
Create a directory structure to contain your first rule and the data file to use for testing.
mkdir -p /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/rules mkdir -p /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/data
$ mkdir -p /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/rules
$ mkdir -p /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/dataThis directory structure will also be used to hold the generated MTR reports.
2.1.2. Creating data to test the rule
-
Create a
jboss-web.xmlfile in the/home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/data/subdirectory. Copy in the following content.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.1.3. Creating the rule
MTR XML-based rules use the following rule pattern:
when(condition) perform(action) otherwise(action)
when(condition)
perform(action)
otherwise(action)Procedure
In the
/home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/rules/directory, create a file namedJBoss5-web-class-loading.windup.xmlthat contains the following content:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe XML file name must include the
.windup.xmlextension. Otherwise, MTR does not evaluate the new rule.Add a unique identifier for the ruleset and rule:
-
Replace
<UNIQUE_RULESET_ID>with an appropriate ruleset ID, for example,JBoss5-web-class-loading. -
Replace
<UNIQUE_RULE_ID>with an appropriate rule ID, for example,JBoss5-web-class-loading_001.
-
Replace
Add the following ruleset add-on dependencies:
<dependencies> <addon id="org.jboss.windup.rules,windup-rules-javaee,3.0.0.Final"/> <addon id="org.jboss.windup.rules,windup-rules-java,3.0.0.Final"/> </dependencies>
<dependencies> <addon id="org.jboss.windup.rules,windup-rules-javaee,3.0.0.Final"/> <addon id="org.jboss.windup.rules,windup-rules-java,3.0.0.Final"/> </dependencies>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the source and target technologies:
-
Replace
<SOURCE_ID>witheap. -
Replace
<TARGET_ID>witheap.
-
Replace
Set the source and target technology versions.
-
Replace
<SOURCE_VERSION_RANGE>with(4,5). -
Replace
<TARGET_VERSION_RANGE>with(6,).
See the Apache Maven version range specification for more information.
-
Replace
Complete the
whencondition. Because this rule tests for a match in an XML file,xmlfileis used to evaluate the files.To match on the
class-loadingelement that is a child ofjboss-web, use the xpath expressionjboss-web/class-loading.<when> <xmlfile matches="jboss-web/class-loading" /> </when><when> <xmlfile matches="jboss-web/class-loading" /> </when>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Complete the
performaction for this rule.-
Add a classification with a descriptive title and a level of effort of
1. Provide a hint with an informative message and a link to documentation that describes the migration details.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Add a classification with a descriptive title and a level of effort of
The rule is now complete and should look like the following example.
2.1.4. Installing the rule
An MTR rule is installed by placing the rule into the appropriate directory.
Copy the JBoss5-web-class-loading.windup.xml file to the <MTR_HOME>/rules/ directory.
cp /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/rules/JBoss5-web-class-loading.windup.xml <MTR_HOME>/rules/
$ cp /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/rules/JBoss5-web-class-loading.windup.xml <MTR_HOME>/rules/2.1.5. Testing the rule
Open a terminal and run the following command, passing the test file as an input argument and a directory for the output report.
<MTR_HOME>/bin/mta-cli --sourceMode --input /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/data --output /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports --target eap:6
$ <MTR_HOME>/bin/mta-cli --sourceMode --input /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/data --output /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports --target eap:6You should see the following result.
Report created: /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports/index.html
Access it at this URL: file:///home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports/index.html
Report created: /home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports/index.html
Access it at this URL: file:///home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports/index.html2.1.6. Reviewing the reports
Review the report to be sure that it provides the expected results. For a more detailed walkthrough of MTR reports, see the Reviewing the reports section of the MTR CLI Guide.
-
Open
/home/<USER_NAME>/migration-rules/reports/index.htmlin a web browser. Verify that the rule ran successfully.
- From the main landing page, click the Rule providers execution overview link to open the Rule Providers Execution Overview.
Find the
JBoss5-web-class-loading_001rule and verify that its Status? isCondition metand its Result? issuccess.Figure 2.1. Test rule execution
Verify that the rule matches the test data:
-
From the main landing page, click the name of the application or input folder, which is
datain this example. - Click the Application Details report link.
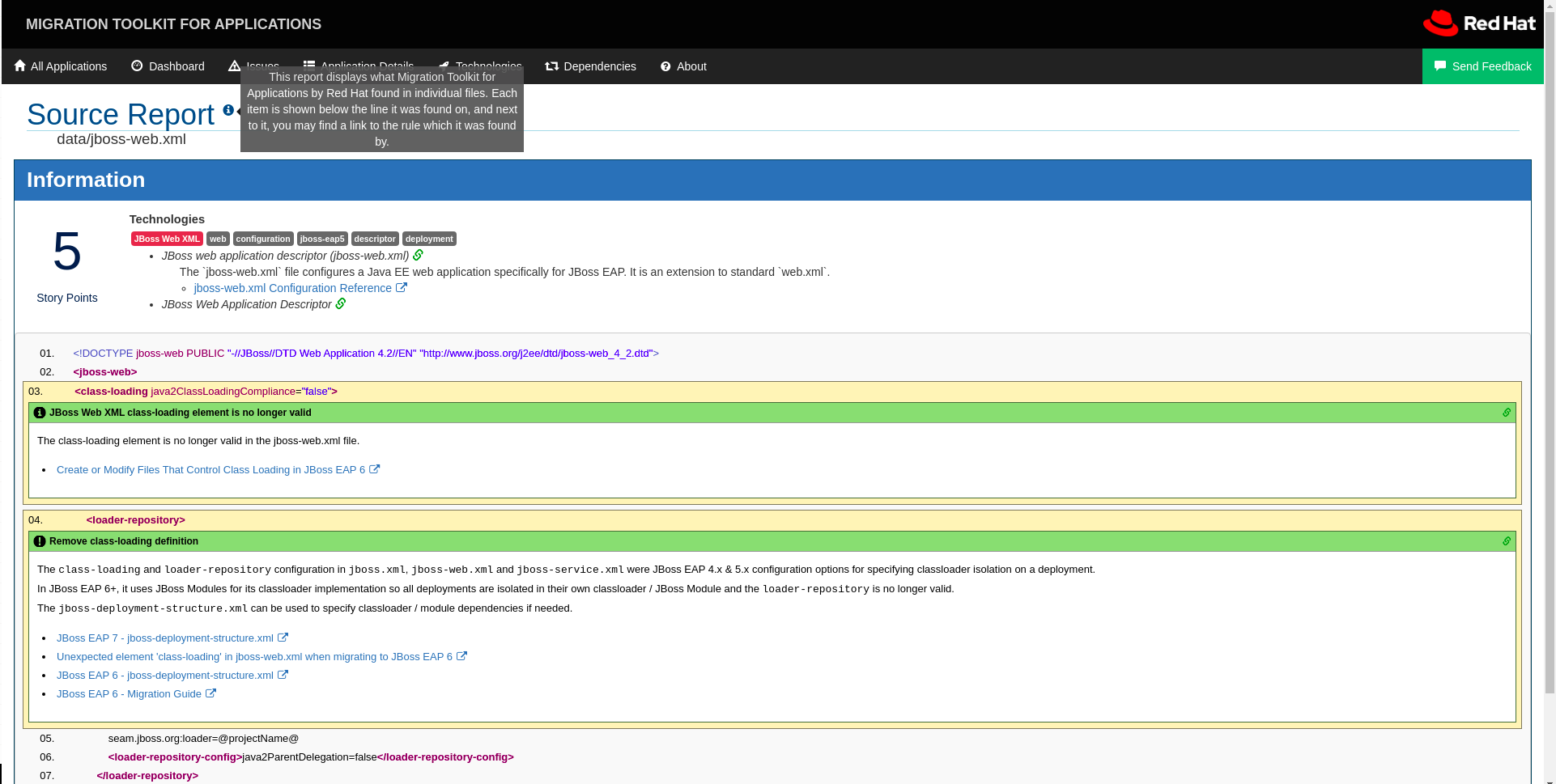
Click the jboss-web.xml link to view the Source Report.
You can see that the
<class-loading>line is highlighted, and the hint from the custom rule is shown inline.Figure 2.2. Rule match
The top of the file lists the classifications for matching rules. You can use the link icon to view the details for that rule. Notice that in this example, the
jboss-web.xmlfile matched on another rule (JBoss web application descriptor (jboss-web.xml)) that produced1story point. This story point, combined with the1story point from our custom rule, brings the total story points for this file to2.
-
From the main landing page, click the name of the application or input folder, which is
2.2. Reviewing the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes quickstarts
The Migration Toolkit for Runtimes quickstarts provide working examples of how to create custom Java-based rule add-ons and XML rules. You can use them as a starting point for creating your own custom rules.
Each quickstart has a README.adoc file that contains instructions for that quickstart.
You can download a .zip file of the latest version of the quickstarts. If you prefer to work with the source code, you can fork and clone the windup-quickstarts project repository.
2.2.1. Downloading the latest quickstart
You can download the latest release of a quickstart.
Procedure
- Launch a browser and navigate to https://github.com/windup/windup-quickstarts/releases.
-
Click the latest release to download the
.zipfile to your local file system. Extract the archive files to a local directory.
You can review the quickstart
README.adocfile.
2.2.2. Forking and cloning the quickstart GitHub project
You can fork and clone the Quickstart Github project on your local machine.
Prerequisites
-
You must have
gitclient installed.
Procedure
-
Click Fork on the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes quickstart GitHub page to create the project in your own Git. The forked GitHub repository URL should look like this:
https://github.com/<YOUR_USER_NAME>/windup-quickstarts.git. Clone the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes quickstart repository to your local file system:
git clone https://github.com/<YOUR_USER_NAME>/windup-quickstarts.git
$ git clone https://github.com/<YOUR_USER_NAME>/windup-quickstarts.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This creates a
windup-quickstartsdirectory on your local file system.Navigate to the newly created directory:
cd windup-quickstarts/
$ cd windup-quickstarts/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To retrieve the latest code updates, add the remote
upstreamrepository so that you can fetch changes to the original forked repository:git remote add upstream https://github.com/windup/windup-quickstarts.git
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/windup/windup-quickstarts.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download the latest files from the
upstreamrepository:git fetch upstream
$ git fetch upstreamCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 3. Creating XML rules
3.1. XML rule structure
This section describes the basic structure of XML rules. All XML rules are defined as elements within rulesets. For more details, see the MTR XML rule schema.
3.1.1. Rulesets
A ruleset is a group of one or more rules that targets a specific area of migration. This is the basic structure of the <ruleset> element.
<ruleset id="<UNIQUE_RULESET_ID>">: Defines this as an MTR ruleset and gives it a unique ruleset ID.
<metadata>: The metadata about the ruleset.
- <description>: The description of the ruleset.
- <dependencies/>: The rule add-ons required by this ruleset.
- <sourceTechnology/>: The source technology.
- <targetTechnology/>: The target technology.
<overrideRules/>: Setting to
trueindicates that rules in this ruleset override rules with the same ID from the core ruleset distributed with MTR. Both the ruleset id and the rule id must match a rule within the core ruleset, or the rule will be ignored. In addition, the target technology in this ruleset must match one of the targets that you specified for running the analysis.This is
falseby default.
<rules>: A set of individual rules.
<rule id="<UNIQUE_RULE_ID>">: Defines the rule and gives it a unique ID. It is recommended to include the ruleset ID as part of the rule ID, for example,
<UNIQUE_RULESET_ID_UNIQUE_RULE_ID>. One or more rules can be defined for a ruleset.- <when>: The conditions to match on.
- <perform>: The action to be performed when the rule condition is matched.
-
<otherwise>: The action to be performed when the rule condition is not matched. This element takes the same child elements as the
<perform>element. - <where>: A string pattern defined as a parameter, which can be used elsewhere in the rule definition.
- <file-mapping/>: Maps an extension to a graph type.
- <package-mapping/>: Maps from a package pattern (regular expression) to an organization name.
3.1.2. Predefined rules
MTR provides predefined rules for common migration requirements. These core MTR rules are located in the MTR installation at <MTR_HOME>/rules/migration-core/.
The following is an example of a core MTR rule that matches on a proprietary utility class.
3.2. Creating a basic XML rule
This section describes how to create an MTR XML rule. This assumes that you already have MTR installed. See the MTR CLI Guide for installation instructions.
3.2.1. Creating a basic XML rule template
MTR XML rules consist of conditions and actions and use the following rule pattern:
when(condition) perform(action) otherwise(action)
when(condition)
perform(action)
otherwise(action)Create a file with the following contents, which is the basic syntax for XML rules.
The XML file name must include the .windup.xml extension. Otherwise, MTR does not evaluate the new rule.
3.2.2. Creating the ruleset metadata
The XML ruleset metadata element provides additional information about the ruleset such as a description, the source and target technologies, and add-on dependencies. The metadata also allows for specification of tags, which allow you to provide additional information about a ruleset.
<metadata> example
3.2.3. Creating a rule
Individual rules are contained within the <rules> element. They comprise one or more when conditions and perform actions.
See the XML rule schema for valid rule syntax.
3.2.3.1. Creating a condition
The XML rule <when> element tests for a condition. The following is a list of valid <when> conditions.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <and> | The standard logical and operator. |
| <filecontent> | Find strings or text within files, for example, properties files. |
| <file-mapping> | Define file names to internal stored File model. |
| <javaclass> | Test for a match in a Java class. |
| <javaclass-ignore> | Exclude javaclass that you would like to ignore in processing discovery. |
| <not> | The standard logical not operator. |
| <or> | The standard logical or operator. |
| <package-mapping> | Define package names to organization or libraries. |
| <project> | Test for project characteristics, such as dependencies. |
| <true> | Always match. |
| <xmlfile> | Test for a match in an XML file. |
The specific syntax is dependent on whether you are creating a rule to evaluate Java class, an XML file, a project, or file content.
3.2.3.2. Creating a action
The XML rule <perform> element performs the action when the condition is met. Operations allowed in this section of the rule include the classification of application resources, in-line hints for migration steps, links to migration information, and project line item reporting. The following is a list of valid <perform> actions.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <classification> | This operation adds metadata that you want to apply to the entire file. For example, if the Java Class is a JMS Message Listener, you can add a Classification with the title "JMS Message Listener" that includes information that applies to the entire file. You can also set an effort level for the entire file. |
| <hint> | This operation adds metadata to a line within the file. This provides a hint or inline information about how to migrate a section of code. |
| <iteration> | This specifies to iterate over an implicit or explicit variable defined within the rule. |
| <lineitem> | This provides a high-level message that is displayed in the application overview page. |
| <link> | This provides an HTML link to additional information or documentation about the migration task. |
| <xslt> | This specifies how to transform an XML file. |
3.3. XML rule syntax
3.3.1. syntax
Conditions allowed in the when portion of a rule must extend GraphOperation and currently include evaluation of Java classes, XML files, projects, and file content. Because XML rules are modeled after the Java-based rule add-ons, links to JavaDocs for the related Java classes are provided for a better understanding of how they behave.
The complete XML rule schema is located here: http://windup.jboss.org/schema/windup-jboss-ruleset.xsd.
The following sections describe the more common XML when rule conditions.
- <javaclass> condition syntax
- <xmlfile> condition syntax
- <project> condition syntax
- <filecontent> condition syntax
- <file> condition syntax
- <has-hint> condition syntax
- <has-classification> condition syntax
- <graph-query> condition syntax
- <dependency> condition syntax
By default, if more than one when rule condition is provided, then all conditions must be met for the rule to match.
3.3.1.1. syntax
3.3.1.1.1. Summary
Use the <javaclass> element to find imports, methods, variable declarations, annotations, class implementations, and other items related to Java classes. For a better understanding of the <javaclass> condition, see the JavaDoc for the JavaClass class.
The following is an example of a rule that tests for WebLogic-specific Apache XML packages:
3.3.1.1.2. Construct a element
3.3.1.1.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| references | CLASS_NAME | The package or class name to match on. Wildcard characters can be used. This attribute is required. Note
For performance reasons, you should not start the reference with wildcard characters. For example, use references="weblogic.apache.xml.{*}"
|
| matchesSource | STRING | An exact regex to match. This is useful to distinguish hard-coded strings. This attribute is required. matchesSource="log4j.logger" |
| as | VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
| from | VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
| in | PATH_FILTER | Filter input files matching this regex (regular expression) naming pattern. Wildcard characters can be used. in="{*}File1"
|
3.3.1.1.2.2. child elements
| Child Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <location> | The location where the reference was found in a Java class. Location can refer to annotations, field and variable declarations, imports, and methods. For the complete list of valid values, see the JavaDoc for TypeReferenceLocation. <location>IMPORT</location> |
| <annotation-literal> | Match on literal values inside of annotations.
The following example matches on <javaclass references="org.package.MyAnnotation">
<location>ANNOTATION</location>
<annotation-literal name="myvalue" pattern="test"/>
</javaclass>
Note that in this case, the |
| <annotation-type> | Match on a particular annotation type. You can supply subconditions to be matched against the annotation elements.
The below example would match on a |
| <annotation-list> | Match on an item in an array within an annotation. If an array index is not specified, the condition will be matched if it applies to any item in the array. You can supply subconditions to be matched against this element.
The below example would match on
Note that in this case, the |
3.3.1.2. syntax
3.3.1.2.1. Summary
Use the <xmlfile> element to find information in XML files. For a better understanding of the <xmlfile> condition, see the JavaDoc for the XmlFile class.
The following is an example of a rule that tests for an XML file:
3.3.1.2.2. Construct an element
3.3.1.2.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| matches | XPATH | Match on an XML file condition. matches="/w:web-app/w:resource-ref/w:res-auth[text() = 'Container']" |
| xpathResultMatch | XPATH_RESULT_STRING | Return results that match the given regex. <xmlfile matches="//foo/text()" xpathResultMatch="Text from foo."/> |
| as | VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
| in | PATH_FILTER | Used to filter input files matching this regex (regular expression) naming pattern. Wildcard characters can be used. in="{*}File1"
|
| from | VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
| public-id | PUBLIC_ID | The DTD public-id regex. public-id="public" |
3.3.1.2.2.2. matches custom functions
The matches attribute may use several built-in custom XPath functions, which may have useful side effects, like setting the matched value on the rule variables stack.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Match a XPath expression against a string, possibly containing MTR parameterization placeholders. matches="windup:matches(//foo/@class, '{javaclassname}')"
This will match all |
3.3.1.2.2.3. child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
| <namespace> |
The namespace referenced in XML files. This element contains two optional attributes: The <namespace prefix="abc" uri="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"/> |
3.3.1.3. syntax
3.3.1.3.1. Summary
Use the <project> element to query the Maven POM file for the project characteristics. For a better understanding of the <project> condition, see the JavaDoc for the Project class.
The following is an example of a rule that checks for a JUnit dependency version between 2.0.0.Final and 2.2.0.Final.
3.3.1.3.2. Construct a element
3.3.1.3.2.1. element attributes
The <project> element is used to match against the project’s Maven POM file. You can use this condition to query for dependencies of the project. It does not have any attributes itself.
3.3.1.3.2.2. child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
| <artifact> |
Subcondition used within |
3.3.1.3.2.3. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| groupId | PROJECT_GROUP_ID |
Match on the project |
| artifactId | PROJECT_ARTIFACT_ID |
Match on the project |
| fromVersion | FROM_VERSION |
Specify the lower version bound of the artifact. For example |
| toVersion | TO_VERSION |
Specify the upper version bound of the artifact. For example |
It is possible to qualify the element within the POM file that contains the artifact that the rule is searching for. This is achieved using the optional <location> element. The example below shows a rule that is searching for an artifact within the <plugins> element of the POM file.
The valid list of locations is as follows:
- DEPENDENCY_MANAGEMENT
- DEPENDENCIES
- PLUGIN_MANAGEMENT
- PLUGINS
- PARENT
3.3.1.4. syntax
3.3.1.4.1. Summary
Use the <filecontent> element to find strings or text within files, for example, a line in a Properties file. For a better understanding of the <filecontent> condition, see the JavaDoc for the FileContent class.
3.3.1.4.2. Construct a element
3.3.1.4.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| pattern | String | Match the file contents against the provided parameterized string. This attribute is required. |
| filename | String | Match the file names against the provided parameterized string. |
| as | VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
| from | VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
3.3.1.5. syntax
3.3.1.5.1. Summary
Use the <file> element to find the existence of files with a specific name, for example, an ibm-webservices-ext.xmi file. For a better understanding of the <file> condition, see the JavaDoc for the File class.
3.3.1.5.2. Construct a element
3.3.1.5.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filename | String | Match the file names against the provided parameterized string. This attribute is required. |
| as | VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
| from | VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its Example: from="MyEjbRule" |
3.3.1.6. syntax
3.3.1.6.1. Summary
Use the <has-hint> element to test whether a file or line has a hint already associated with it. It is primarily used to prevent firing if a hint already exists, or to implement rules for default execution when no other conditions apply. For a better understanding of the <has-hint> condition, see the JavaDoc for the HasHint class.
The following is an example of a rule that checks to see if a hint exists for an IBM JMS destination message, and if not, includes it.
3.3.1.6.2. Construct a
The <has-hint> element is used to determine if a hint exists for a file or line. It does not have any child elements.
3.3.1.6.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| message | String | An optional argument allowing you to match the hint against the provided message string. |
3.3.1.7. syntax
3.3.1.7.1. Summary
Use the <has-classification> element to test whether a file or line has a classification. It is primarily used to prevent firing if a classification already exists, or to implement rules for default execution when no other conditions apply. For a better understanding of the <has-classification> condition, see the JavaDoc for the HasClassification class.
3.3.1.7.2. Construct a
The has-classification element is used to determine if a specified classification exists. It does not have any child elements.
3.3.1.7.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | String | An optional title to match the classification against. |
3.3.1.8. syntax
3.3.1.8.1. Summary
Use the <graph-query> element to search the generated graph for any elements. This element is primarily used to search for specific archives. For a better understanding of the <graph-query> condition, see the JavaDoc for the QueryHandler class.
The following is an example of a rule that tests to determine if any ehcache packages are found.
3.3.1.8.2. Construct a
3.3.1.8.2.1. element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| discriminator | MODEL_TYPE |
The type of model to use for searching. This can be any valid model; however, it is recommended to use the |
| as | VARIABLE_NAME |
A variable name assigned to the rule so that it can be used as a reference in later processing. See the as="MyEjbRule" |
| from | VARIABLE_NAME |
Begin the search query with the filtered result from a previous search identified by its from="MyEjbRule" |
3.3.1.8.2.2. properties
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | String |
The name of the attribute to match against within the chosen model. When using any file-based models, it is recommended to match on |
| type | property-type |
Defines the expected type of property, either |
| searchType | property-search-type |
Defines how the condition is matched. If set to |
3.3.1.9. syntax
3.3.1.9.1. Summary
Use the <dependency> element to search dependencies defined within the application’s POM file to determine whether they are supported by the target runtime.
The following is an example of a rule that checks for all artifacts belonging to the org.springframework.boot group that have a version up to, and including, 1.6.0.
3.3.2. syntax
Operations available in the perform section of the rule include the classification of application resources, in-line hints for migration steps, links to migration information, and project lineitem reporting. Because XML rules are modeled after the Java-based rule add-ons, links to JavaDocs for the related Java classes are provided for a better understanding of how they behave.
You can view the complete XML rule schema.
The following sections describe the more common XML rule perform actions.
3.3.2.1. syntax
3.3.2.1.1. Summary
The <classification> element is used to identify or classify application resources that match the rule. It provides a title that is displayed in the report, a level of effort, and it can also provide links to additional information about how to migrate this resource classification. For a better understanding of the <classification> action, see the JavaDoc for the Classification class.
The following is an example of a rule that classifies a resource as a WebLogic EAR application deployment descriptor file.
3.3.2.1.2. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | STRING | The title given to this resource. This attribute is required. title="JBoss Seam Components" |
| effort | BYTE | The level of effort assigned to this resource. effort="2" |
| category-id | STRING |
A reference to a category as defined in category-id="mandatory" |
| of | VARIABLE_NAME | Create a new classification for the given reference. of="MySeamRule" |
3.3.2.1.3. child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
| <link> | Provides a link URI and text title for additional information. <classification title="Websphere Startup Service" effort="4"> <link href="http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/6/api/javax/ejb/Singleton.html" title="EJB3.1 Singleton Bean"/> <link href="http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/6/api/javax/ejb/Startup.html" title="EJB3.1 Startup Bean"/> </classification> |
| <tag> | Provides additional custom information for the classification. <tag>Seam3</tag> |
| <description> | Description of this resource <description>JBoss Seam components must be replaced</description> |
3.3.2.2. syntax
3.3.2.2.1. Summary
The <link> element is used in classifications or hints to provide links to informational content. For a better understanding of the <link> action, see the JavaDoc for the Link class.
The following is an example of a rule that creates links to additional information.
3.3.2.2.2. element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| href | URI | The URI for the referenced link. href="https://access.redhat.com/articles/1249423" |
| title | STRING | A title for the link. title="Migrate WebLogic Proprietary Servlet Annotations" |
3.3.2.3. syntax
3.3.2.3.1. Summary
The <hint> element is used to provide a hint or inline information about how to migrate a section of code. For a better understanding of the <hint> action, see the JavaDoc for the Hint class.
The following is an example of a rule that creates a hint.
3.3.2.3.2. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | STRING | Title this hint using the specified string. This attribute is required. title="JBoss Seam Component Hint" |
| category-id | STRING |
A reference to a category as defined in category-id="mandatory" |
| in | VARIABLE_NAME | Create a new Hint in the FileLocationModel resolved by the given variable. in="Foo" |
| effort | BYTE | The level of effort assigned to this resource. effort="2" |
3.3.2.3.3. child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
| <message> | A message describing the migration hint. <message>EJB 2.0 is deprecated</message> |
| <link> | Identify or classify links to informational content. <link href="http://docs.oracle.com/javaee/6/api/" title="Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 6 API Specification" /> |
| <tag> |
Define a custom tag for this <tag>Needs review</tag> |
| <quickfix> | Contains information to be used by the MTR plugin to perform quick fixes when the rule condition is met. <quickfix name="slink-qf" type="REPLACE">
<replacement>h:link</replacement>
<search>s:link</search>
</quickfix>
|
3.3.2.4. syntax
3.3.2.4.1. Summary
The <xslt> element specifies how to transform an XML file. For a better understanding of the <xslt> action, see the JavaDoc for the XSLTTransformation class.
The following is an example of rule that defines an XSLT action.
3.3.2.4.2. element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | STRING | Sets the title for this XSLTTransformation in the report. This attribute is required. title="XSLT Transformed Output" |
| of | STRING | Create a new transformation for the given reference. of="testVariable_instance" |
| extension | STRING | Sets the extension for this XSLTTransformation. This attribute is required. extension="-result.html" |
| template | STRING | Sets the XSL template. This attribute is required. template="simpleXSLT.xsl" |
| effort | BYTE | The level of effort required for the transformation. |
3.3.2.4.3. child elements
| Child element | Description |
|---|---|
| <xslt-parameter> | Specify XSLTTransformation parameters as property value pairs <xslt-parameter property="title" value="EJB Transformation"/> |
3.3.2.5. syntax
3.3.2.5.1. Summary
The <lineitem> element is used to provide general migration requirements for the application, such as the need to replace deprecated libraries or the need to resolve potential class loading issues. This information is displayed on the project or application overview page. For a better understanding of the <lineitem> action, see the JavaDoc for the LineItem class.
The following is an example of a rule that creates a lineitem message.
3.3.2.5.2. element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| message | STRING | A lineitem message. message="Proprietary code found." |
3.3.2.6. syntax
3.3.2.6.1. Summary
The <iteration> element specifies to iterate over an implicit or explicit variable defined within the rule. For a better understanding of the <iteration> action, see the JavaDoc for the Iteration class.
The following is an example of a rule that performs an iteration.
3.3.2.6.2. element attributes
| Attribute name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| over | VARIABLE_NAME | Iterate over the condition identified by this VARIABLE_NAME. over="jboss-app" |
3.3.2.6.3. child elements
| Child Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <iteration> |
Child elements include a |
3.3.3. syntax
You can define parameters that specify a matching pattern to be used in other elements of an XML rule. This can help simplify the patterns for complex matching expressions.
Use the <where> element to define a parameter. Specify the parameter name using the param attribute and supply the pattern using the <matches> element. This parameter can then be referenced elsewhere in the rule definition using the syntax {<PARAM_NAME>}.
You can view the complete XML rule schema.
The following example rule defines a parameter named subpackage that specifies a pattern of (activeio|activemq).
The pattern defined by subpackage will then be substituted in the <javaclass> references attribute. This causes the rule to match on org.apache.activeio.* and org.apache.activemq.* packages.
3.4. Adding a rule to the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes
A Migration Toolkit for Runtimes rule is installed by copying the rule to the appropriate MTR folder. MTR scans for rules, which are files with the .windup.xml extension in the following locations:
-
Directory specified by the
--userRulesDirectoryargument on the MTR command line. -
<MTR_HOME>/rules/directory.<MTR_HOME>is the directory where you install and run the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes executable. ${user.home}/.mtr/rules/directory. This directory is created by MTR the first time it is run. it contains rules, add-ons, and the MTR log.NoteIn a Windows operating system, the rules are located in
\Documents and Settings\<USER_NAME>\.mtr\rules\or\Users\<USER_NAME>\.mtr\rules\.
Chapter 4. Testing XML rules
After you have created an XML rule, you should create a test rule to ensure that it works.
4.1. Creating a test rule
Test rules are created using a process similar to the process for creating an XML rule, with the following differences:
-
Test rules should be placed in a
tests/directory beneath the rule to be tested. -
Any data, such as test classes, should be placed in a
data/directory beneath thetests/directory. -
Test rules should use the
.windup.test.xmlextension. - These rules use the structure defined in the Test XML Rule Structure.
In addition, it is recommended to create a test rule that follows the name of the rule it tests. For example, if a rule were created with a filename of proprietary-rule.mtr.xml, the test rule should be called proprietary-rule.windup.test.xml.
4.1.1. Test XML rule structure
All test XML rules are defined as elements within ruletests which contain one or more rulesets. For more details, see the MTR XML rule schema.
A ruletest is a group of one or more tests that targets a specific area of migration. This is the basic structure of the <ruletest> element.
<ruletest id="<RULE_TOPIC>-test">: Defines this as a unique MTR ruletest and gives it a unique ruletest id.-
<testDataPath>: Defines the path to any data, such as classes or files, used for testing. -
<sourceMode>: Indicates if the passed in data only contains source files. If an archive, such as an EAR, WAR, or JAR, is in use, then this should be set tofalse. Defaults totrue. -
<rulePath>: The path to the rule to be tested. This should end in the name of the rule to test. -
<ruleset>: Rulesets containing the logic of the test cases. These are identical to the ones defined in Rulesets.
-
4.1.2. Test XML rule syntax
In addition to the tags in the standard XML rule syntax, the following when conditions are commonly used for creating test rules:
-
<not> -
<iterable-filter> -
<classification-exists> -
<hint-exists>
In addition to the tags in the standard perform action syntax, the following perform conditions are commonly used as actions in test rules:
-
<fail>
4.1.2.1. syntax
Summary
The <not> element is the standard logical not operator, and is commonly used to perform a <fail> if the condition is not met.
The following is an example of a test rule that fails if only a specific message exists at the end of the analysis.
The <not> element has no unique attributes or child elements.
4.1.2.2. syntax
Summary
The <iterable-filter> element counts the number of times a condition is verified. For additional information, see the IterableFilter class.
The following is an example that looks for four instances of the specified message.
The <iterable-filter> element has no unique child elements.
<iterable-filter> element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| size | integer | The number of times to be verified. |
4.1.2.3. syntax
The <classification-exists> element determines if a specific classification title has been included in the analysis. For additional information, see the ClassificationExists class.
When testing for a message that contains special characters, such as [ or ', you must escape each special character with a backslash (\) to correctly match.
The following is an example that searches for a specific classification title.
The <classification-exists> has no unique child elements.
<classification-exists> element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| classification | String |
The |
| in | String | An optional argument that restricts matching to files that contain the defined filename. |
4.1.2.4. syntax
The <hint-exists> element determines if a specific hint has been included in the analysis. It searches for any instances of the defined message, and is typically used to search for the beginning or a specific class inside of a <message> element. For additional information, see the HintExists class.
When testing for a message that contains special characters, such as [ or ', you must escape each special character with a backslash (\) to correctly match.
The following is an example that searches for a specific hint.
The <hint-exists> element has no unique child elements.
<hint-exists> element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| message | String |
The |
| in | String |
An optional argument that restricts matching to |
4.1.2.5. syntax
The <fail> element reports the execution as a failure and displays the associated message. It is commonly used in conjunction with the <not> condition to display a message only if the conditions are not met.
The <fail> element has no unique child elements.
<fail> element attributes
| Attribute Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| message | String | The message to be displayed. |
4.2. Manually testing an XML rule
You can run an XML rule against your application file to test it:
<MTR_HOME>/mta-cli [--sourceMode] --input <INPUT_ARCHIVE_OR_FOLDER> --output <OUTPUT_REPORT_DIRECTORY> --target <TARGET_TECHNOLOGY> --packages <PACKAGE_1> <PACKAGE_2> <PACKAGE_N>
$ <MTR_HOME>/mta-cli [--sourceMode] --input <INPUT_ARCHIVE_OR_FOLDER> --output <OUTPUT_REPORT_DIRECTORY> --target <TARGET_TECHNOLOGY> --packages <PACKAGE_1> <PACKAGE_2> <PACKAGE_N>You should see the following result:
Report created: <OUTPUT_REPORT_DIRECTORY>/index.html
Access it at this URL: file:///<OUTPUT_REPORT_DIRECTORY>/index.html
Report created: <OUTPUT_REPORT_DIRECTORY>/index.html
Access it at this URL: file:///<OUTPUT_REPORT_DIRECTORY>/index.htmlMore examples of how to run MTR are located in the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes CLI Guide.
4.3. Testing the rules by using JUnit
Once a test rule has been created, it can be analyzed as part of a JUnit test to confirm that the rule meets all criteria for execution. The WindupRulesMultipleTests class in the MTR rules repository is designed to test multiple rules simultaneously, and provides feedback on any missing requirements.
Prerequisites
- Fork and clone the MTR XML rules. The location of this repository will be referred to as <RULESETS_REPO>.
- Create a test XML rule.
Creating the JUnit test configuration
The following instructions detail creating a JUnit test using Eclipse. When using a different IDE, it is recommended to consult your IDE’s documentation for instructions on creating a JUnit test.
- Import the MTR rulesets repository into your IDE.
Copy the custom rules, along with the corresponding tests and data, into
</path/to/RULESETS_REPO>/rules-reviewed/<RULE_NAME>/. This should create the following directory structure.Directory structure
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Select Run from the top menu bar.
- Select Run Configurations… from the drop down that appears.
- Right-click JUnit from the options on the left side and select New.
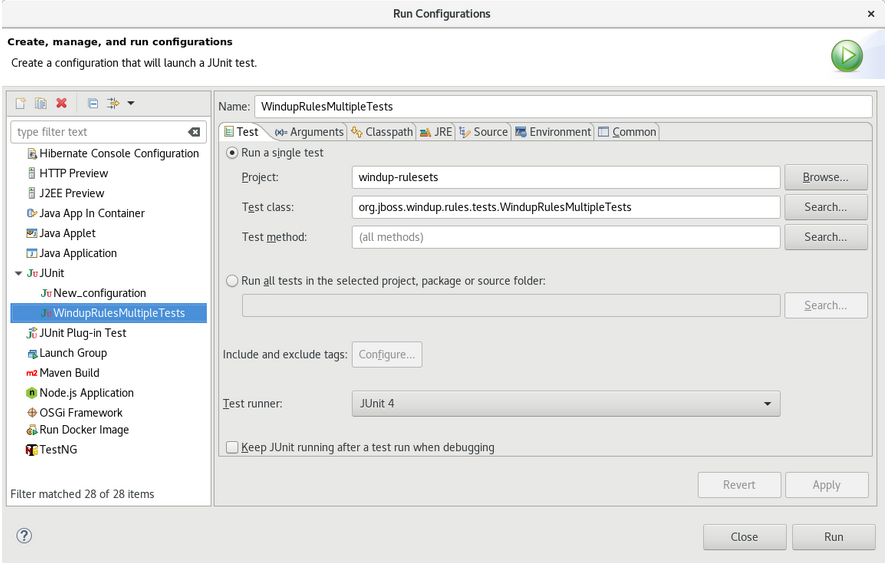
Enter the following:
-
Name: A name for your JUnit test, such as
WindupRulesMultipleTests. -
Project: Ensure this is set to
windup-rulesets. Test class: Set this to
org.jboss.windup.rules.tests.WindupRulesMultipleTests.
-
Name: A name for your JUnit test, such as
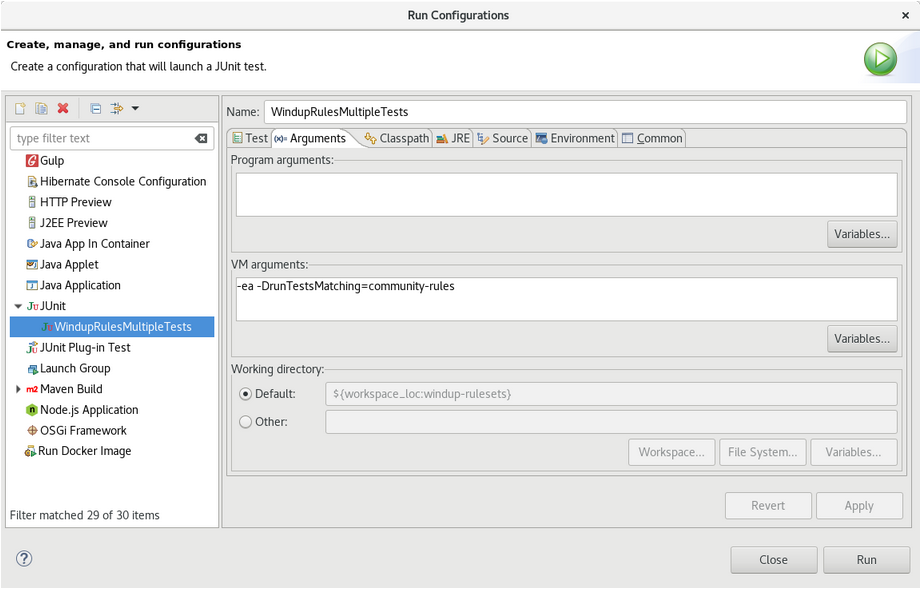
Select the Arguments tab, and add the
-DrunTestsMatching=<RULE_NAME>VM argument. For instance, if your rule name wascommunity-rules, then you would add-DrunTestsMatching=community-rulesas seen in the following image.Click Run in the bottom right corner to begin the test.
When the execution completes, the results are available for analysis. If all tests passed, then the test rule is correctly formatted. If all tests did not pass, it is recommended to address each of the issues raised in the test failures.
4.4. About validation reports
Validation reports provide details about test rules and failures and contain the following sections:
Summary
This section contains the total number of tests run and reports the number of errors and failures. It displays the total success rate and the time taken, in seconds, for the report to be generated.
Package List
This section contains the number of tests executed for each package and reports the number of errors and failures. It displays the success rate and the time taken, in seconds, for each package to be analyzed.
A single package named
org.jboss.windup.rules.testsis displayed unless additional test cases have been defined.Test Cases
This section describes the test cases. Each failure includes a Details section that can be expanded to show the stack trace for the assertion, including a human-readable line indicating the source of the error.
4.4.1. Creating a validation report
You can create a validation report for your custom rules.
Prerequisites
- You must fork and clone the MTR XML rules.
- You must have one or more test XML rules to validate.
Procedure
-
Navigate to the local
windup-rulesetsrepository. -
Create a directory for your custom rules and tests:
windup-rulesets/rules-reviewed/myTests. -
Copy your custom rules and tests to the
windup-rulesets/rules-reviewed/<myTests>directory. Run the following command from the root directory of the
windup-rulesetsrepository:mvn -Dtest=WindupRulesMultipleTests -DrunTestsMatching=<myTests> clean <myReport>:report
$ mvn -Dtest=WindupRulesMultipleTests -DrunTestsMatching=<myTests> clean <myReport>:report1 2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The validation report is created in the
windup-rulesets/target/site/repository.
4.4.2. Validation report error messages
Validation reports contain errors encountered while running the rules and tests.
The following table contains error messages and how to resolve the errors.
| Error message | Description | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| No test file matching rule | This error occurs when a rule file exists without a corresponding test file. | Create a test file for the existing rule. |
| Test rule Ids <RULE_NAME> not found! | This error is thrown when a rule exists without a corresponding ruletest. | Create a test for the existing rule. |
| XML parse fail on file <FILE_NAME> | The syntax in the XML file is invalid, and unable to be parsed successfully by the rule validator. | Correct the invalid syntax. |
|
Test file path from |
No files are found in the path defined in the |
Create the path defined in the |
| The rule with id="<RULE_ID>" has not been executed. | The rule with the provided id has not been executed during this validation. | Ensure that a test data file exists that matches the conditions defined in the specified rule. |
Chapter 5. Overriding rules
You can override core rules distributed with MTR or even custom rules. For example, you can change the matching conditions, effort, or hint text for a rule. This is done by making a copy of the original rule, marking it as a rule override, and making the necessary adjustments.
You can disable a rule by creating a rule override with an empty <rule> element.
5.1. Overriding a rule
You can override a core or custom rule.
Procedure
Copy the XML file that contains the rule you want to override to the custom rules directory.
Custom rules can be placed in
<MTR_HOME>/rules,${user.home}/.mtr/rules/, or a directory specified by the--userRulesDirectorycommand-line argument.Edit the XML file so that it contains only the
<rule>elements for the rules that you want to override.NoteRules from the original ruleset that are not overridden by the new ruleset are run as normal.
- Ensure that you keep the same rule and ruleset IDs. When you copy the original rule XML, this ensures that the IDs match.
- Ensure that the target technology in the override ruleset matches one of the targets that you specified for running the analysis.
-
Add the
<overrideRules>true</overrideRules>element to the ruleset metadata. Update the rule definition.
You can change anything in the rule definition. The new rule overrides the original rule in its entirety.
The following rule override example changes the effort of the weblogic-02000 rule in the weblogic ruleset from 1 to 3:
Rule override definition example
When you run MTR, this rule overrides the original rule with the same rule ID. You can verify that the new rule was used by viewing the contents of the Rule Provider Executions Overview.
5.2. Disabling a rule
To disable a rule, create a rule override definition with an empty <rule> element according to the following example:
Rule override definition example to disable a rule
- 1
- The
<rule>element is empty so that theweblogic-02000rule in theweblogicruleset is disabled.
Chapter 6. Using custom rule categories
You can create custom rule categories and assign MTR rules to them.
Although MTR processes rules with the legacy severity field, you must update your custom rules to use the new category-id field.
6.1. Adding a custom category
You can add a custom category to the rule category file.
Procedure
-
Edit the rule category file, which is located at
<MTR_HOME>/rules/migration-core/core.windup.categories.xml. Add a new
<category>element and fill in the following parameters:-
id: The ID that MTR rules use to reference the category. -
priority: The sorting priority relative to other categories. The category with the lowest value is displayed first. -
name: The display name of the category. description: The description of the category.Custom rule category example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This category is ready to be referenced by MTR rules.
-
6.2. Assigning a rule to a custom category
You can assign a rule to your new custom category.
Procedure
In your MTR rule, update the category-id field as in the following example.
If this rule condition is met, incidents identified by this rule use your custom category. The custom category is displayed on the dashboard and in the Issues report.
Figure 6.1. Custom category on the dashboard
Appendix A. Reference material
A.1. About rule story points
A.1.1. What are story points?
Story points are an abstract metric commonly used in Agile software development to estimate the level of effort needed to implement a feature or change.
The Migration Toolkit for Runtimes uses story points to express the level of effort needed to migrate particular application constructs, and the application as a whole. It does not necessarily translate to man-hours, but the value should be consistent across tasks.
A.1.2. How story points are estimated in rules
Estimating the level of effort for the story points for a rule can be tricky. The following are the general guidelines MTR uses when estimating the level of effort required for a rule.
| Level of Effort | Story Points | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Information | 0 | An informational warning with very low or no priority for migration. |
| Trivial | 1 | The migration is a trivial change or a simple library swap with no or minimal API changes. |
| Complex | 3 | The changes required for the migration task are complex, but have a documented solution. |
| Redesign | 5 | The migration task requires a redesign or a complete library change, with significant API changes. |
| Rearchitecture | 7 | The migration requires a complete rearchitecture of the component or subsystem. |
| Unknown | 13 | The migration solution is not known and may need a complete rewrite. |
A.1.3. Task category
In addition to the level of effort, you can categorize migration tasks to indicate the severity of the task. The following categories are used to group issues to help prioritize the migration effort.
- Mandatory
- The task must be completed for a successful migration. If the changes are not made, the resulting application will not build or run successfully. Examples include replacement of proprietary APIs that are not supported in the target platform.
- Optional
- If the migration task is not completed, the application should work, but the results may not be optimal. If the change is not made at the time of migration, it is recommended to put it on the schedule soon after your migration is completed.
- Potential
- The task should be examined during the migration process, but there is not enough detailed information to determine if the task is mandatory for the migration to succeed. An example of this would be migrating a third-party proprietary type where there is no directly compatible type.
- Information
- The task is included to inform you of the existence of certain files. These may need to be examined or modified as part of the modernization effort, but changes are typically not required.
For more information on categorizing tasks, see Using custom rule categories.
A.2. Additional resources
A.2.1. Reviewing existing MTR XML rules
MTR XML-based rules are located on GitHub at the following location: https://github.com/windup/windup-rulesets/tree/master/rules/rules-reviewed.
You can fork and clone the MTR XML rules on your local machine.
Rules are grouped by target platform and function. When you create a new rule, it is helpful to find a rule that is similar to the one you need and use it as a starting template.
New rules are continually added, so it is a good idea to check back frequently to review the updates.
A.2.1.1. Forking and cloning the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes XML rules
The Migration Toolkit for Runtimes windup-rulesets repository provides working examples of how to create custom Java-based rule add-ons and XML rules. You can use them as a starting point for creating your own custom rules.
You must have the git client installed on your machine.
-
Click the
Forklink on the Migration Toolkit for Runtimes Rulesets GitHub page to create the project in your own Git. The forked GitHub repository URL created by the fork should look like this:https://github.com/<YOUR_USER_NAME>/windup-rulesets.git. Clone your Migration Toolkit for Runtimes rulesets repository to your local file system:
git clone https://github.com/<YOUR_USER_NAME>/windup-rulesets.git
$ git clone https://github.com/<YOUR_USER_NAME>/windup-rulesets.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This creates and populates a
windup-rulesetsdirectory on your local file system. Navigate to the newly created directory, for examplecd windup-rulesets/
$ cd windup-rulesets/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you want to be able to retrieve the latest code updates, add the remote
upstreamrepository so you can fetch any changes to the original forked repository.git remote add upstream https://github.com/windup/windup-rulesets.git
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/windup/windup-rulesets.gitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the latest files from the
upstreamrepository.git fetch upstream
$ git fetch upstreamCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
A.2.2. Additional resources
- MTR Jira issue tracker: https://issues.redhat.com/projects/WINDUP
- MTR mailing list: windup-eng@redhat.com
Revised on 2024-09-12 13:52:54 UTC