4.4. GLOBAL SETTINGS
The GLOBAL SETTINGS panel is where the you define the networking details for the primary LVS router's public and private network interfaces.
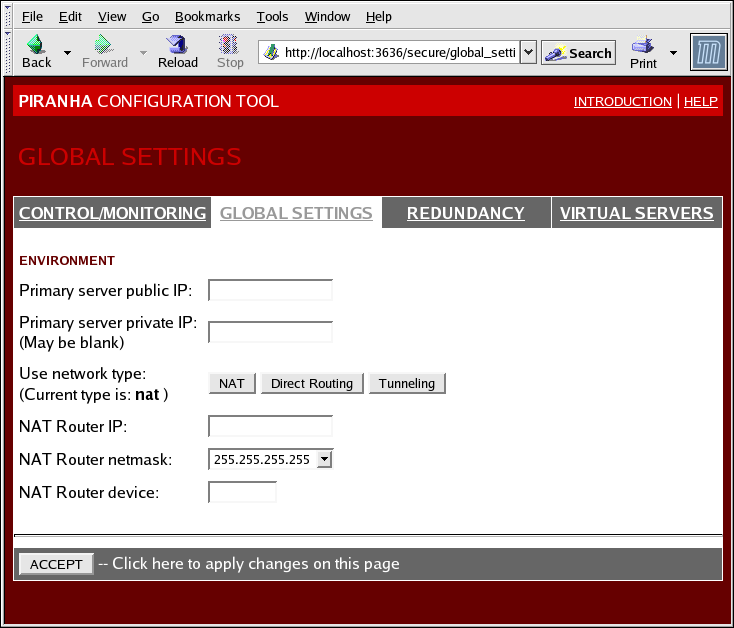
Figura 4.3. The GLOBAL SETTINGS Panel
The top half of this panel sets up the primary LVS router's public and private network interfaces. These are the interfaces already configured in Seção 3.1.1, “Interfaces da Rede Configurada pelo LVS com NAT”.
- Primary server public IP
- Neste campo, entre o endereço IP real que pode ser roteado para o nó LVS primário.
- Primary server private IP
- Enter the real IP address for an alternative network interface on the primary LVS node. This address is used solely as an alternative heartbeat channel for the backup router and does not have to correlate to the real private IP address assigned in Seção 3.1.1, “Interfaces da Rede Configurada pelo LVS com NAT”. You may leave this field blank, but doing so will mean there is no alternate heartbeat channel for the backup LVS router to use and therefore will create a single point of failure.
Nota
O endereço IP privado não é necessário para configurações de , assim como todos os servidores reais e os diretores LVS compartilham os mesmos endereços IP virtuais, e devem possuir a mesma configuração de rota.Nota
The primary LVS router's private IP can be configured on any interface that accepts TCP/IP, whether it be an Ethernet adapter or a serial port. - Use network type
- Clique no botão para selecionar o roteamento NAT.Clique no botão para selecionar o roteamento direto.
The next three fields deal specifically with the NAT router's virtual network interface connecting the private network with the real servers. These fields do not apply to the direct routing network type.
- NAT Router IP
- Entre o IP flutuante privado neste campo. Este IP flutuante deve ser usado como passagem para os servidores reais.
- NAT Router netmask
- If the NAT router's floating IP needs a particular netmask, select it from drop-down list.
- NAT Router device
- Utilize este campo do texto para definir o nome do dispositivo da interface da rede para o endereço IP flutuante, como por exemplo o
eth1:1.Nota
Você deve alias o endereço IP flutuante à Interface Ethernet conectada à rede privada. Neste exemplo, a rede privada está na interfaceeth1, então oeth1:1é o endereço IP flutuante.
Atenção
Após completar esta página, clique no botão para ter certeza de que você não perderá qualquer mudança quando selecionando um painel novo.