监控
在 OpenShift Container Platform 中配置和使用监控堆栈
摘要
第 1 章 集群监控
1.1. 关于集群监控
OpenShift Container Platform 包括一个预配置、预安装且自助更新的监控堆栈,它基于 Prometheus 开源项目及其更广的生态系统。它提供对集群组件的监控,并且包含一组警报(在发生任何问题时立即通知集群管理员)以及一组 Grafana 仪表板。集群监控堆栈只支持监控 OpenShift Container Platform 集群。
为确保与将来的 OpenShift Container Platform 更新兼容,只有特定的监控堆栈选项配置被支持。
1.1.1. 堆栈组件和受监控目标
监控堆栈包括以下组件:
| 组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Cluster Monitoring Operator | OpenShift Container Platform Cluster Monitoring Operator (CMO) 是堆栈的核心组件。它控制部署的监控组件和资源,并确保它们始终处于最新状态。 |
| Prometheus Operator | Prometheus Operator (PO) 可以创建、配置和管理 Prometheus 和 Alertmanager 实例。还能根据熟悉的 Kubernetes 标签查询来自动生成监控目标配置。 |
| Prometheus | Prometheus 是监控堆栈所依据的系统与服务监控系统。 |
| Prometheus Adapter | Prometheus Adapter 公开用于 Pod 横向自动扩展的集群资源指标 API。资源指标是指 CPU 与内存使用情况。 |
| Alertmanager | Alertmanager 服务处理 Prometheus 发送的警报。 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Thanos querier | Thanos Querier 可在单个多租户接口下启用聚合(Aggregating)以及可选的重复集群和用户工作负载指标。 |
| Grafana | Grafana 分析平台提供用于分析和直观呈现指标的仪表板。由监控堆栈提供的 Grafana 实例及其仪表板是只读的。 |
监控堆栈的所有组件都由堆栈监控,并在 OpenShift Container Platform 更新时自动更新。
除了堆栈本身的组件外,监控堆栈还监控:
- CoreDNS
- Elasticsearch(如果安装了 Logging)
- etcd
- Fluentd(如果安装了 Logging)
- HAProxy
- 镜像 registry
- Kubelets
- Kubernetes apiserver
- Kubernetes 控制器管理器
- Kubernetes 调度程序
- Metering(如果安装了 Metering)
- OpenShift apiserver
- OpenShift 控制器管理器
- Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM)
- Telemeter Client
每个 OpenShift Container Platform 组件负责自己的监控配置。对于组件监控的问题,请在 Bugzilla 中针对具体组件(而非常规的监控组件)创建一个程序错误报告。
其他 OpenShift Container Platform 框架组件也可能会公开指标。如需详细信息,请参阅相应的文档。
1.1.2. 后续步骤
1.2. 配置监控堆栈
在 OpenShift Container Platform 4 之前,Prometheus Cluster Monitoring 堆栈是通过 Ansible 清单文件配置的。为此,堆栈公开了一小部分可用配置选项作为 Ansible 的变量。您需要在安装 OpenShift Container Platform 前配置该堆栈。
在 OpenShift Container Platform 4 中,Ansible 不再是安装 OpenShift Container Platform 的主要方法。安装之前,安装程序只提供非常少的配置选项。大多数 OpenShift 框架组件(包括 Prometheus Cluster Monitoring 堆栈)都在安装后进行配置。
本节介绍支持的配置,演示如何配置监控堆栈,并且展示几个常见的配置情景。
1.2.1. 先决条件
- 监控堆栈会带来额外的资源需求。请参考缩放 Cluster Monitoring Operator 中的计算资源建议,并验证您是否有充足的资源。
1.2.2. 维护和支持
若要配置 OpenShift Container Platform Monitoring,支持的方式是使用本文中介绍的选项。请勿使用其他配置,因为不受支持。各个 Prometheus 发行版本的配置范例可能会有所变化,只有掌握了所有可能的配置,才能稳妥应对这样的配置变化。如果使用并非本节所描述的配置,您的更改可能会丢失,因为 cluster-monitoring-operator 会调节差异。根据设计,Operator 默认将一切还原到定义的状态。
明确不支持的情形包括:
-
在
openshift-*命名空间中创建额外的ServiceMonitor对象。这会扩大集群监控 Prometheus 实例抓取目标的范围,可能会造成无法考量的冲突和负载差异。这些因素可能会导致 Prometheus 设置不稳定。 -
创建非预期的
ConfigMap对象或PrometheusRule对象。这会导致集群监控 Prometheus 实例包含额外的警报和记录规则。 - 修改堆栈的资源。Prometheus 监控堆栈确保其资源始终处于期望的状态。如果修改了资源,堆栈会重置它们。
- 将堆栈资源用于其他目的。Prometheus Cluster Monitoring 堆栈所创建的资源并不是为了供任何其他资源使用,因为不能保证向后兼容性。
- 使 Cluster Monitoring Operator 停止调节监控堆栈。
- 添加新的警报规则。
- 修改监控堆栈 Grafana 实例。
1.2.3. 创建集群监控 ConfigMap
要配置 OpenShift Container Platform 监控堆栈,您必须创建集群监控 ConfigMap。
先决条件
- 您可以使用具有 cluster-admin 角色的用户访问集群。
-
已安装 OpenShift CLI(
oc)。
流程
检查
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象是否存在:oc -n openshift-monitoring get configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring get configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 如果 ConfigMap 不存在:
创建以下 YAML 清单。在本例中,该文件名为
cluster-monitoring-config.yaml:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 应用该配置以创建 ConfigMap:
oc apply -f cluster-monitoring-config.yaml
$ oc apply -f cluster-monitoring-config.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.2.4. 配置集群监控堆栈
您可以使用 ConfigMaps 配置 Prometheus Cluster Monitoring 堆栈。ConfigMaps 配置 Cluster Monitoring Operator,后者配置堆栈的组件。
先决条件
-
您可以使用具有
cluster-admin角色的用户访问集群。 - 已安装 OpenShift CLI(oc)。
-
您已创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
流程
开始编辑
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap:oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 将您的配置以键值对
<component_name>: <component_configuration>的形式放到data/config.yaml下:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 相应地替换
<component>和<configuration_for_the_component>。例如,创建以下 ConfigMap 来为 Prometheus 配置持久性卷声明 (PVC):
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 此处的 prometheusK8s 定义 Prometheus 组件,后面几行则定义其配置。
- 保存文件以使改变生效。受新配置影响的 Pod 会自动重启。
其他资源
-
请参阅创建集群监控 ConfigMap 以了解如何创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
1.2.5. 可配置的监控组件
下表显示了您可以配置的监控组件,以及 ConfigMap 中用来指定这些组件的键:
| 组件 | 键 |
|---|---|
| Prometheus Operator |
|
| Prometheus |
|
| Alertmanager |
|
| kube-state-metrics |
|
| openshift-state-metrics |
|
| Grafana |
|
| Telemeter Client |
|
| Prometheus Adapter |
|
在以上列表中,只有 Prometheus 和 Alertmanager 有许多配置选项。所有其他组件通常仅提供 nodeSelector 字段,用于部署到指定节点。
1.2.6. 将监控组件移到其他节点
您可以将任何监控堆栈组件移到特定的节点。
先决条件
-
您可以使用具有
cluster-admin角色的用户访问集群。 - 已安装 OpenShift CLI(oc)。
-
您已创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
流程
开始编辑
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap:oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 在
data/config.yaml下为组件指定nodeSelector约束:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 相应地替换
<component>,并将<node_key>: <node_value>替换为用于指定目标节点的键值对映射。通常只使用一个键值对。组件只能在以各个指定键值对作为标签的节点上运行。节点也可以有附加标签。
例如,要将组件移到具有
foo: bar标签的节点上,请使用:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 保存文件以使改变生效。受新配置影响的组件会自动移到新节点上。
其他资源
-
请参阅创建集群监控 ConfigMap 以了解如何创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。 - 如需了解更多有关使用节点选择器的信息,请参阅使用节点选择器在特定节点上放置 pod。
-
参阅 Kubernetes 文档来详细了解
nodeSelector约束。
1.2.7. 为监控组件分配容忍(tolerations)
您可以为任何监控堆栈组件分配容忍,以便将其移到污点。
先决条件
-
您可以使用具有
cluster-admin角色的用户访问集群。 - 已安装 OpenShift CLI(oc)。
-
您已创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
流程
开始编辑
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap:oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 为组件指定
tolerations:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 相应地替换
<component>和<toleration_specification>。例如,
oc adm taint nodes node1 key1=value1:NoSchedule污点可以防止调度程序将 Pod 放置到foo: bar节点中。要让alertmanagerMain组件忽略这个污点并且照常将alertmanagerMain放置到foo: bar,请使用以下容忍:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 保存文件以使改变生效。这样就会自动应用新组件放置配置。
其他资源
-
请参阅创建集群监控 ConfigMap 以了解如何创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。 - 参阅 OpenShift Container Platform 文档中有关污点和容忍的内容。
- 参阅 Kubernetes 文档中有关污点和容忍的内容。
1.2.8. 配置持久性存储
如果使用持久性存储运行集群监控,您的指标将保存在持久性卷(PV)中,并可在 Pod 重新启动或重新创建后保留。如果您需要预防指标或警报数据丢失,这是理想方案。在生产环境中,强烈建议配置持久性存储。由于 IO 需求很高,使用本地存储颇有优势。
请参阅建议的可配置存储技术。
1.2.9. 先决条件
- 分配充足的专用本地持久性存储,以确保磁盘不会被填满。您需要的存储量取决于 Pod 的数目。如需有关持久性存储系统要求的信息,请参阅 Prometheus 数据库存储要求。
- 确保持久性卷 (PV) 已准备好以供持久性卷声明 (PVC) 使用,每个副本一个 PV。由于 Prometheus 有两个副本并且 Alertmanager 有三个副本,因此您需要五个 PV 来支持整个监控堆栈。PV 应该从 Local Storage Operator 中提供。如果启用了动态置备的存储,则这项要求不适用。
- 使用块存储类型。
- 配置本地持久性存储。
1.2.9.1. 配置本地持久性卷声明
要让 Prometheus 或 Alertmanager 使用持久性卷 (PV),您首先必须配置持久性卷声明 (PVC)。
先决条件
-
您可以使用具有
cluster-admin角色的用户访问集群。 - 已安装 OpenShift CLI(oc)。
-
您已创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
流程
编辑
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap:oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 将组件的 PVC 配置放在
data/config.yaml下:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 如需有关如何指定
volumeClaimTemplate的信息,请参阅 Kubernetes 文档中与 PersistentVolumeClaim 相关的内容。例如,若要配置一个 PVC 来声明用于 Prometheus 的本地持久性存储,请使用:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 在上例中,由 Local Storage Operator 创建的存储类称为
local-storage。若要配置一个 PVC 来声明用于 Alertmanager 的本地持久性存储,请使用:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 保存文件以使改变生效。受新配置影响的 Pod 会自动重启,并且应用新的存储配置。
1.2.9.2. 修改 Prometheus 指标数据的保留时间
默认情况下,Prometheus Cluster Monitoring 堆栈将 Prometheus 数据的保留时间配置为 15 天。您可以修改保留时间来更改将在多久后删除数据。
先决条件
-
您可以使用具有
cluster-admin角色的用户访问集群。 - 已安装 OpenShift CLI(oc)。
-
您已创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
流程
开始编辑
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap:oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 将保留时间配置放在
data/config.yaml下:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 将
<time_specification>替换为一个数字,后面紧跟ms(毫秒)、s(秒)、m(分钟)、h(小时)、d(天)、w(周)或y(年)。例如,若要将保留时间配置为 24 小时,请使用:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 保存文件以使改变生效。受新配置影响的 Pod 会自动重启。
其他资源
-
请参阅创建集群监控 ConfigMap 以了解如何创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。 - 了解持久性存储
- 优化存储
1.2.10. 配置 Alertmanager
Prometheus Alertmanager 是管理传入警报的组件,其包括:
- 静默警报
- 禁止警报
- 聚合警报
- 可靠数据去重警报
- 分组警报
- 使用电子邮件、PagerDuty 和 HipChat 等接收工具以通知形式发送分组警报
1.2.10.1. Alertmanager 默认配置
OpenShift Container Platform Monitoring Alertmanager 集群的默认配置如下:
OpenShift Container Platform 监控功能附带 Watchdog 警报,它会持续触发。Alertmanager 重复向通知提供程序发送 Watchdog 警报通知,例如: PagerDuty。此提供程序通常会在管理员停止收到 Watchdog 警告时通知管理员。这种机制有助于确保 Prometheus 的继续操作以及 Alertmanager 和通知提供程序之间的持续通信。
1.2.10.2. 应用自定义 Alertmanager 配置
您可以通过编辑 openshift-monitoring 命名空间中的 alertmanager-main secret,覆盖默认的 Alertmanager 配置。
先决条件
-
安装了用来处理 JSON 数据的
jq工具
流程
将当前活跃的 Alertmanager 配置输出到
alertmanager.yaml文件:oc -n openshift-monitoring get secret alertmanager-main --template='{{ index .data "alertmanager.yaml" }}' |base64 -d > alertmanager.yaml$ oc -n openshift-monitoring get secret alertmanager-main --template='{{ index .data "alertmanager.yaml" }}' |base64 -d > alertmanager.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 将
alertmanager.yaml文件中的配置改为您的新配置:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 例如,以下列表配置用于通知的 PagerDuty:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 采用此配置时,由
example-app服务触发的、严重性为critical的警报将使用team-frontend-page接收器发送;即,这些警报将传给选定人员。应用文件中的新配置:
oc -n openshift-monitoring create secret generic alertmanager-main --from-file=alertmanager.yaml --dry-run -o=yaml | oc -n openshift-monitoring replace secret --filename=-
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring create secret generic alertmanager-main --from-file=alertmanager.yaml --dry-run -o=yaml | oc -n openshift-monitoring replace secret --filename=-Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
其他资源
- 参阅 PagerDuty 官方网站来进一步了解 PagerDuty。
-
参阅 PagerDuty Prometheus 集成指南来学习如何检索
service_key。 - 参阅 Alertmanager 配置来配置通过不同警报接收器发送警报。
1.2.10.3. 警报规则
OpenShift Container Platform Cluster Monitoring 默认附带一组预定义的警报规则。
请注意:
- 默认的警报规则专门用于 OpenShift Container Platform 集群,别无它用。例如,您可以获得集群中持久性卷的警报,但不会获得自定义命名空间中持久性卷的警报。
- 目前无法添加自定义警报规则。
- 有些警报规则的名称相同。这是有意设计的。它们发送关于同一事件但具有不同阈值和/或不同严重性的警报。
- 在禁止规则中,触发较高的严重性时会禁止较低严重性。
1.2.10.4. 列出起作用的警报规则
您可以列出当前应用到集群的警报规则。
流程
配置所需的端口转发:
oc -n openshift-monitoring port-forward svc/prometheus-operated 9090
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring port-forward svc/prometheus-operated 9090Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 获取包含作用中警报规则及其属性的 JSON 对象:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
其他资源
- 另请参阅 Alertmanager 文档。
1.2.11. 后续步骤
1.3. 管理集群警报
OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 为 Alertmanager 提供了一个 Web 界面,供您用于管理警报。本节演示如何使用 Alerting UI。
1.3.1. Alerting UI 的内容
本节演示并说明 Alerting UI 的内容,该 UI 是 Alertmanager 的 Web 界面。
Alerting UI 主要有三个页面,即 Alerts、Silences 和 YAML 页面。
若要访问 Alerts 页面,可在 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台中点击 Monitoring → Alerting → Alerts。
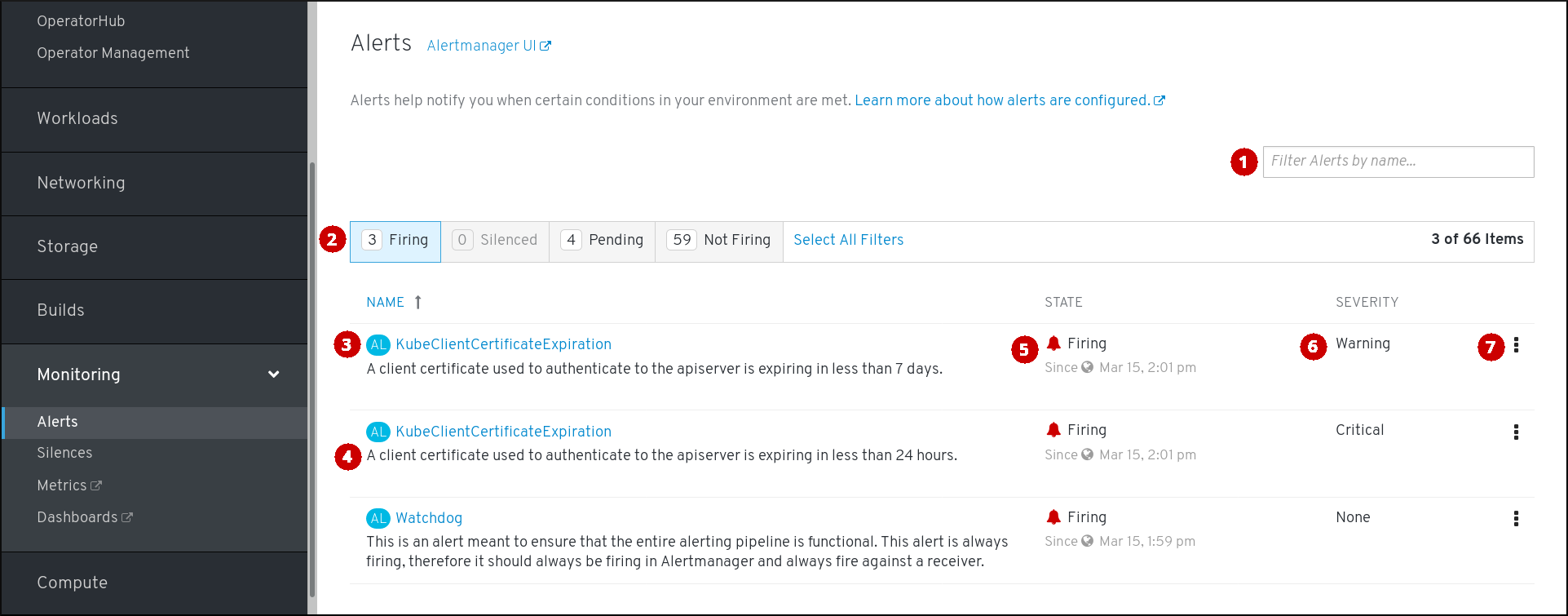
- 按名称过滤警报。
- 按状态过滤警报。若要触发警报,某些警报需要在超时时间内持续满足特定条件。如果警报的某一条件当前为真,但其超时时间尚未结束,那么这个警报处于 Pending 状态。
- 警报的名称。
- 警报的描述。
- 警报的当前状态,以及该警报进入此状态的时间。
- 警报的严重性标签值。
- 您可以对警报执行的操作。
若要访问 Silences 页面,可在 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台中点击 Monitoring → Alerting → Silences。
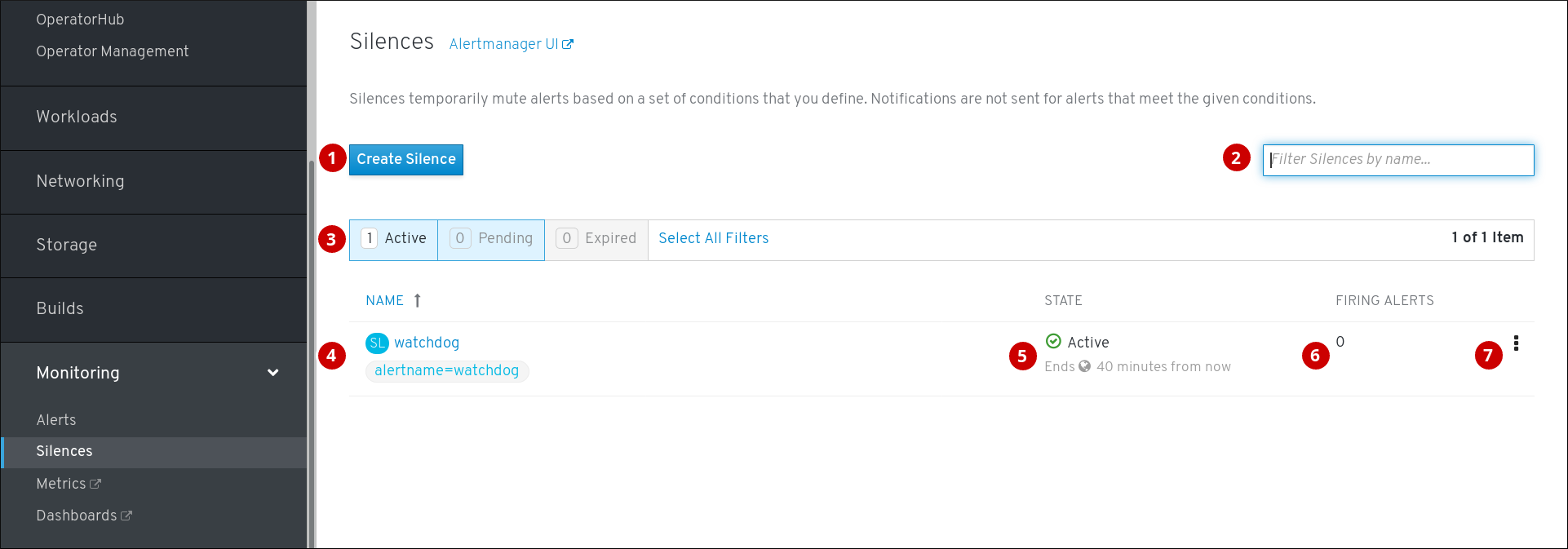
- 为警报创建静默。
- 按名字过滤静默。
- 按状态过滤静默。如果静默为待处理状态,这表示其当前不活跃,因为它已调度到以后的某一时间启动。如果静默已到期,这表示它不再活跃,因为已经达到其结束时间。
- 静默的描述。包括指定与之匹配的警报。
- 静默的当前状态。活跃的静默会显示何时结束,待处理的静默则显示何时启动。
- 被静默时设置为静默的警报数。
- 您可以对静默执行的操作。
若要访问 YAML 页面,可在 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台中点击 Monitoring → Alerting → YAML。
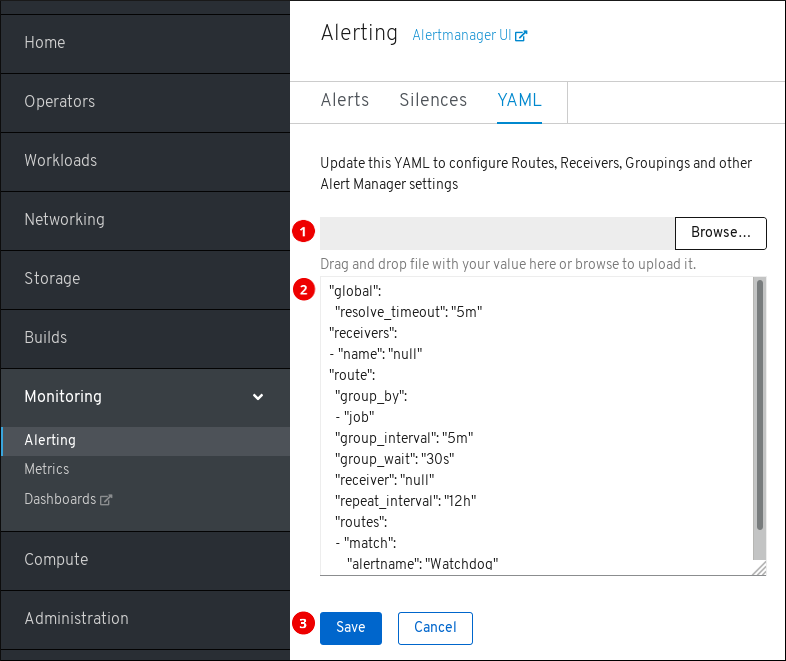
- 上传含有 Alertmanager 配置的文件。
- 检查并编辑当前的 Alertmanager 配置。
- 保存更新的 Alertmanager 配置。
另外,每个页面的标题旁边还有一个 Alertmanager 旧界面链接。
其他资源
- 参阅配置 Alertmanager 以进一步了解如何更改 Alertmanager 配置。
1.3.2. 获取关于警报和警报规则的信息
您可以查找警报,并查看有关这个警报或相关警报规则的信息。
流程
- 打开 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台,并浏览至 Monitoring → Alerting → Alerts 页面。
- 可选:使用 Filter Alerts by name 字段来按照名称过滤警报。
- 可选:使用 Firing、Silenced、Pending 和 Not firing 状态按钮中的一个或多个按钮来根据状态过滤警报。
- 可选:点击 Name、State 和 Severity 列标题中的一个或多个标题对警报进行排序。
在看到所需警报后,您可以查看该警报的详情或相关警报规则的详情。
要查看警报详情,请点击警报的名称。这是包含警报详情的页面:
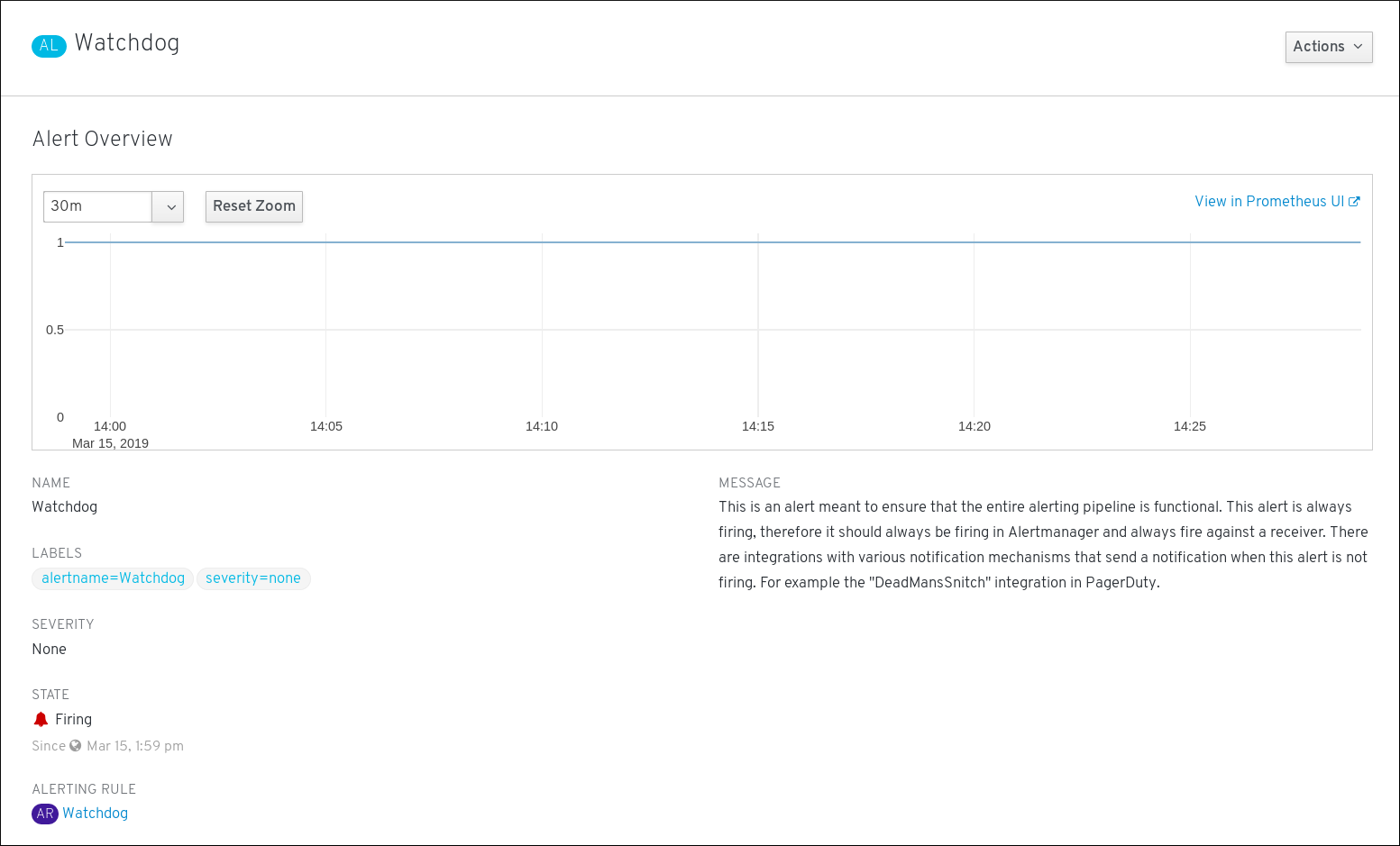
该页面包含注明警报时序的图形。还有与此警报相关的信息,包括:
- 其相关警报规则的链接
- 警报的描述
要查看警报规则详情,请点击最后一列中的按钮并选择 View Alerting Rule。这是包含警报规则详情的页面:
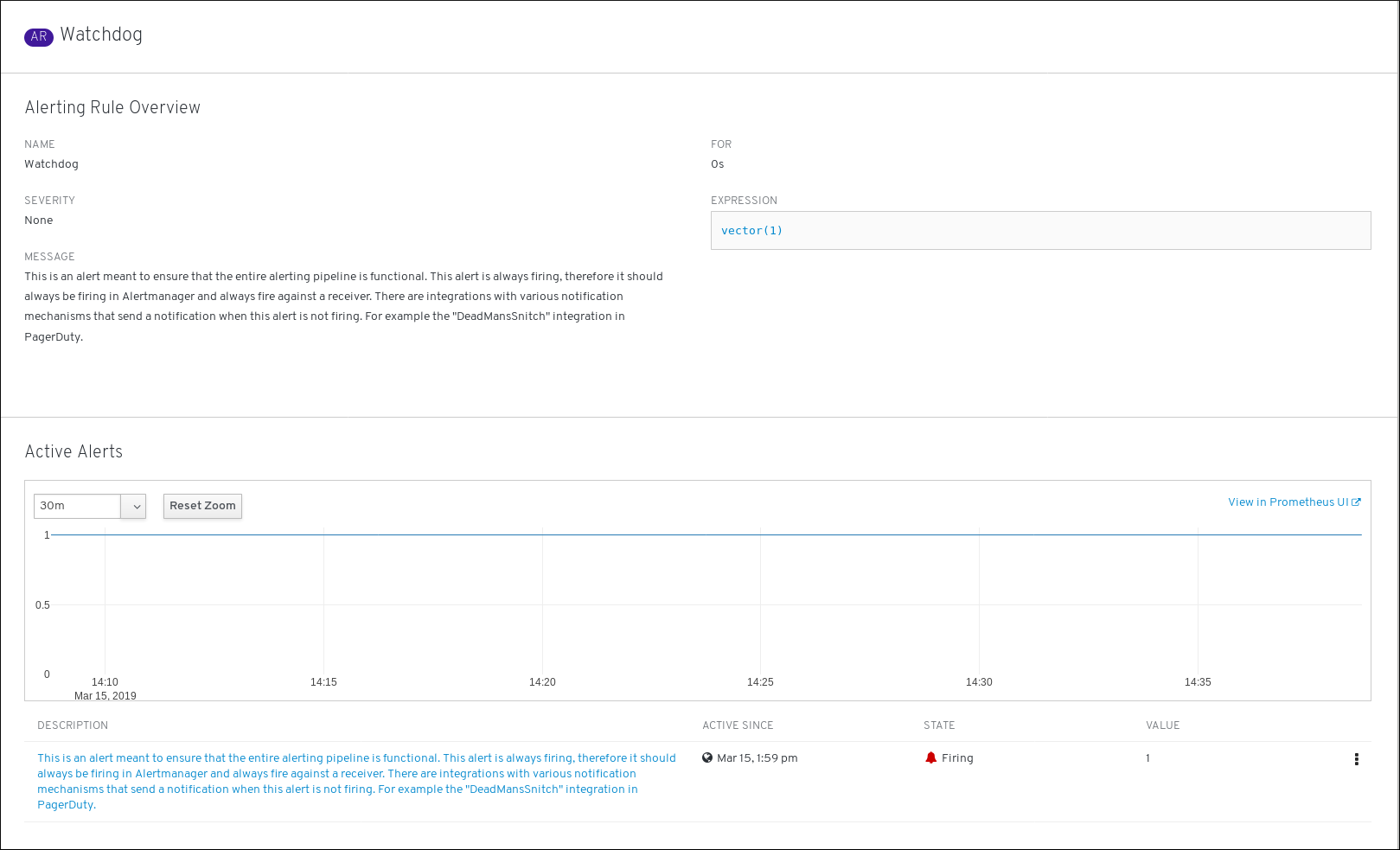
该页面包含与警报规则相关的信息,包括:
- 警报规则名称、严重性和描述
- 定义触发此警报的条件的表达式
- 触发警报的条件得到满足的时间
- 受警报规则约束的各个警报的图形,其中显示了触发该警报的值
- 受警报规则约束的所有警报的列表
1.3.3. 静默警报
您可以静默特定的警报,或者静默符合您定义的指定条件的警报。
流程
通过创建警报指定条件来静默一组警报:
- 浏览到 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台的 Monitoring → Alerting → Silences 页面。
- 点击 Create Silence。
- 填充 Create Silence 表单。
- 若要创建静默,请点击 Create。
静默特定的警报:
- 浏览到 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台的 Monitoring → Alerting → Alerts 页面。
- 针对您想要静默的警报,点击最后一列中的按钮,然后点击 Silence Alert。这时会显示 Create Silence 表单,其中预先填充了所选警报的指定条件。
- 可选:修改静默。
- 若要创建静默,请点击 Create。
1.3.4. 获取有关静默的信息
您可以查找静默并查看其详情。
流程
- 打开 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台,并浏览至 Monitoring → Alerting → Silences 页面。
- 可选:使用 Filter Silences by name 字段来按照名称过滤静默。
- 可选:使用 Active、Pending 和 Expired 状态按钮中的一个或多个按钮,以按状态过滤静默。
- 可选:点击 Name、State 和 Firing alerts 列标题中的一个或多个标题对静默进行排序。
看到所需静默后,您可以点击其名称查看详情,其中包括:
- 警报指定条件
- 状态
- 开始时间
- 结束时间
- 触发警报的数目和列表
1.3.5. 编辑静默
您可以编辑静默,这样会导致现有静默到期,并以更改后的配置创建新静默。
流程
- 浏览到 Monitoring → Alerting → Silences 页面。
针对您想要修改的静默,点击最后一列中的按钮,然后点击 Edit silence。
或者,也可以点击特定静默的 Silence Overview 页中的 Actions → Edit Silence。
- 在 Edit Silence 页中,输入您的更改,再点击 Save 按钮。这会使现有的静默到期,并以所选配置创建新静默。
1.3.6. 使静默到期
您可以让静默到期。让静默到期会永久停用这一静默。
流程
- 浏览到 Monitoring → Alerting → Silences 页面。
针对您想要令其到期的静默,点击最后一列中的按钮,然后点击 Expire Silence。
或者,也可以点击特定静默的 Silence Overview 页面中的 Actions → Expire Silence 按钮。
- 点击 Expire Silence 进行确认。这会使静默到期。
1.3.7. 后续步骤
1.4. 检查集群指标
OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 为 Prometheus 提供了一个 Web 界面,可供您运行 Prometheus Query Language (PromQL) 查询并查看图表中呈现的指标。此功能提供集群状态的综合概览,并可供您用于排查问题。
1.4.1. Metrics UI 的内容
本节演示并说明 Metrics UI 的内容,该 UI 是 Prometheus 的 Web 界面。
若要访问 Metrics 页面,可在 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台中点击 Monitoring → Metrics。
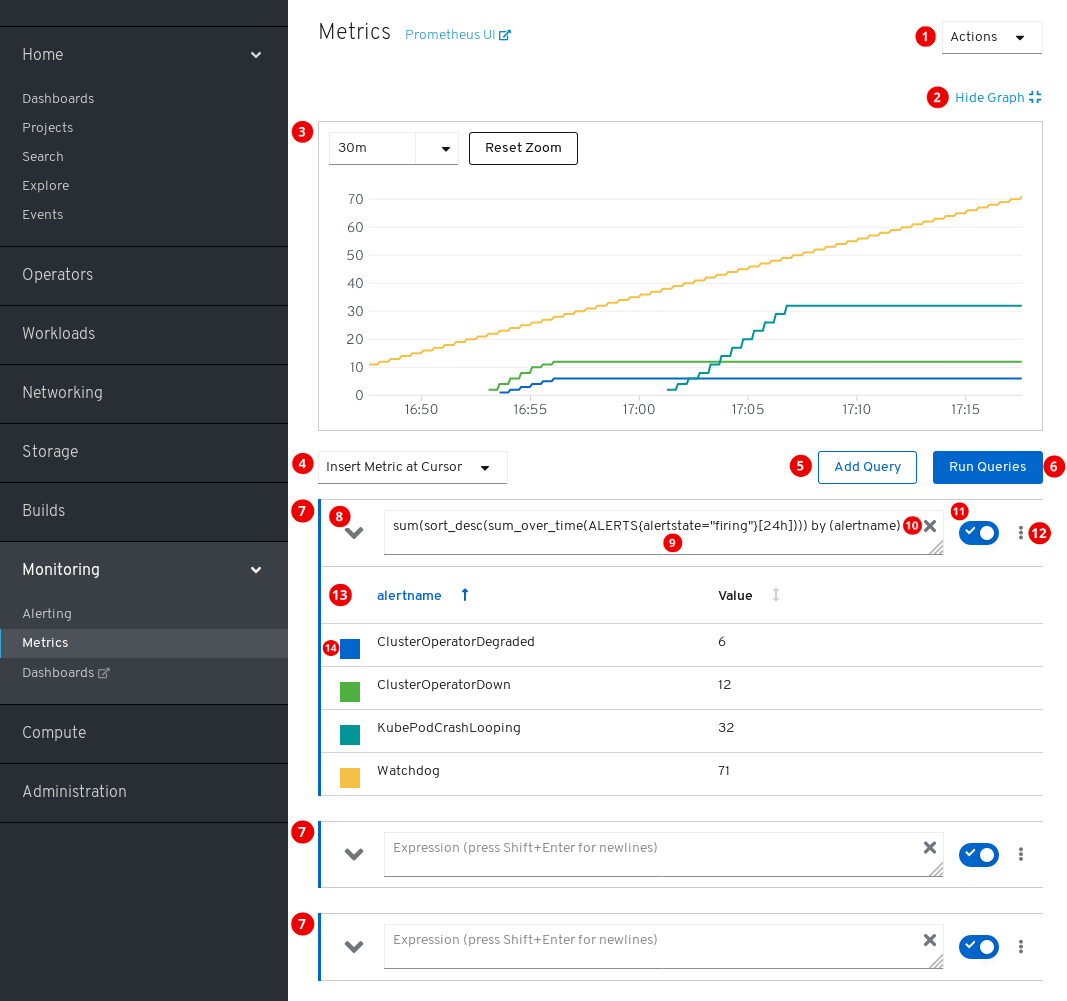
操作。
- 添加查询。
- 展开或折叠所有查询表。
- 删除所有查询。
- 隐藏图表。
- 交互式图表。
- 可用指标的目录。
- 添加查询。
- 运行查询。
- 查询表单。
- 展开或折叠表单。
- 查询。
- 清除查询。
- 启用或禁用查询。
特定查询的操作。
- 启用或禁用查询。
- 在图表中显示或隐藏查询的所有系列。
- 删除查询。
- 查询的指标表。
- 分配给指标图形的颜色。点击方块可以显示或隐藏指标图形。
另外,页面标题旁边也提供 Prometheus 旧界面的链接。
1.4.2. 运行指标查询
您可以通过输入一个或多个 Prometheus Query Language (PromQL) 查询来开始使用指标。
流程
- 打开 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台,并浏览至 Monitoring → Metrics 页面。
在查询字段中,输入您的 PromQL 查询。
- 要显示所有可用的指标和 PromQL 函数,请点击 Insert Metric at Cursor。
- 如需多个查询,请点击 Add Query。
-
要删除查询,请点击查询
 ,然后选择 Delete query。
,然后选择 Delete query。
- 若要保留查询但不运行查询,请点击 Disable query 按钮。
完成创建查询后,点击 Run Queries 按钮。图表中会直观呈现查询的指标。如果查询无效,则 UI 会显示错误消息。
注意如果查询对大量数据进行运算,这可能会在绘制时序图时造成浏览器超时或过载。要避免这种情况,请隐藏图形并且仅使用指标表来校准查询。然后,在找到可行的查询后,启用图表来绘制图形。
- 可选:页面 URL 现在包含您运行的查询。要在以后再次使用这一组查询,请保存这个 URL。
其他资源
1.4.3. 探索视觉化指标
运行查询后,指标会显示在交互式图表中。图表的 X 轴代表时间。Y 轴代表指标值。每个指标都以带颜色的图形显示。您可以操作图表并探索指标。
流程
最初,图表中显示所有启用的查询中的所有指标。您可以要选择显示哪些指标。
-
要隐藏查询的所有指标,请点击
 查询并点击 Hide all series。
查询并点击 Hide all series。
- 要隐藏特定的指标,请转至查询表,然后点击指标名称旁边带颜色的方块。
-
要隐藏查询的所有指标,请点击
要放大图表并更改显示的时间范围,请执行以下操作之一:
- 点击图表并在水平方向上拖动,以可视化方式选择时间范围。
- 使用左上角的菜单来选择时间范围。
要重置时间范围,请点击 Reset Zoom。
- 要显示所有查询在特定时间点的输出,请将鼠标光标停留在图表中的对应点上。弹出框中会显示查询输出。
- 如需有关特定查询的指标的详细信息,请使用下拉按钮展开该查询的表。每个指标均显示其当前的值。
- 要隐藏图表,请点击 Hide Graph。
1.4.4. 非管理员对指标的访问
作为开发者,您可以为项目中的应用程序或服务启用用户工作负载监控。作为管理员,您可以使用相同的功能来启用对基础架构工作负载的监控。在这种情况下,该项目的开发者或管理员可以使用 Web 控制台中的开发者视角来检查公开的指标。
使用开发者视角检查指标只是一项技术预览功能。技术预览功能不被红帽产品服务等级协议 (SLA) 支持,且可能在功能方面有缺陷。红帽不推荐在生产环境中使用它们。这些技术预览功能可以使用户提早试用新的功能,并有机会在开发阶段提供反馈意见。
有关红帽技术预览功能支持范围的详情,请参阅 https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/。
其他资源
请参阅有关监控您自己的服务的文档。它包括以开发者或特权用户身份访问非集群指标的详情。
1.4.5. 后续步骤
1.5. 访问 Prometheus、Alertmanager 和 Grafana。
要使用监控堆栈收集的数据,您可能需要使用 Prometheus、Alertmanager 和 Grafana 界面。它们都默认可用。
1.5.1. 使用 Web 控制台访问 Prometheus、Alerting UI 和 Grafana
您可以使用 Web 浏览器,从 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台访问 Prometheus、Alerting 和 Grafana 的 Web UI。
此过程中访问的 Alerting UI 是 Alertmanager 的新界面。
先决条件
-
根据 OpenShift Container Platform 身份进行身份验证,并使用与 OpenShift Container Platform 其他位置相同的凭证或验证方式。您必须使用具有所有命名空间的读取访问权限的角色,如
cluster-monitoring-view集群角色。
流程
- 浏览到 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台并进行身份验证。
要访问 Prometheus,请浏览到 Monitoring → Metrics 页面。
要访问 Alerting UI,请浏览到 Monitoring → Alerting 页面。
要访问 Grafana,请浏览到 Monitoring → Dashboards 页面。
1.5.2. 直接访问 Prometheus、Alertmanager 和 Grafana
您可以使用 oc 工具和 Web 浏览器来访问 Prometheus、Alertmanager 和 Grafana 的 Web UI。
此过程中访问的 Alertmanager UI 是 Alertmanager 的旧界面。
先决条件
-
根据 OpenShift Container Platform 身份进行身份验证,并使用与 OpenShift Container Platform 其他位置相同的凭证或验证方式。您必须使用具有所有命名空间的读取访问权限的角色,如
cluster-monitoring-view集群角色。
流程
运行:
oc -n openshift-monitoring get routes NAME HOST/PORT ... alertmanager-main alertmanager-main-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com ... grafana grafana-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com ... prometheus-k8s prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com ...
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring get routes NAME HOST/PORT ... alertmanager-main alertmanager-main-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com ... grafana grafana-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com ... prometheus-k8s prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 在地址前附加
https://,您无法使用未加密的连接访问 Web UI。例如,这是为 Alertmanager 生成的 URL:
https://alertmanager-main-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.com
https://alertmanager-main-openshift-monitoring.apps._url_.openshift.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 使用 Web 浏览器浏览到该地址并进行身份验证。
其他资源
- 如需有关 Alertmanager 新界面的文档,请参阅管理集群警报。
监控路由由 Cluster Monitoring Operator 管理,用户不可修改。
第 2 章 监控您自己的服务
除了监控集群外,您还可以为自己的服务使用 OpenShift Monitoring。这样,您不需要使用额外的监控解决方案。这有助于使监控保持集中化。另外,您可以将对服务指标的访问扩展到集群管理员之外。这可让开发者和任意用户访问这些指标。
自定义 Prometheus 实例和通过 Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) 安装的 Prometheus Operator 可能会导致用户定义的工作负载监控(如果启用)出现问题。自定义 Prometheus 实例在 OpenShift Container Platform 中不受支持。
监控您自己的服务只是一个技术预览功能。技术预览功能不被红帽产品服务等级协议 (SLA) 支持,且可能在功能方面有缺陷。红帽不推荐在生产环境中使用它们。这些技术预览功能可以使用户提早试用新的功能,并有机会在开发阶段提供反馈意见。
有关红帽技术预览功能支持范围的详情,请参阅 https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/。
2.1. 启用对您自己的服务的监控
要启用对您自己的服务的监控,您可以在集群监控 ConfigMap 中设置 techPreviewUserWorkload/enabled 标志。
先决条件
-
您可以使用具有
cluster-admin角色的用户访问集群。 - 已安装 OpenShift CLI(oc)。
-
您已创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
流程
开始编辑
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap:oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-config
$ oc -n openshift-monitoring edit configmap cluster-monitoring-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 在
data/config.yaml下将techPreviewUserWorkload设置设为true:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 保存文件以使改变生效。监控您自己的服务会自动启用。
可选:检查是否创建了
prometheus-user-workloadpod:oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE prometheus-operator-85bbb7b64d-7jwjd 1/1 Running 0 3m24s prometheus-user-workload-0 5/5 Running 1 3m13s prometheus-user-workload-1 5/5 Running 1 3m13s
$ oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE prometheus-operator-85bbb7b64d-7jwjd 1/1 Running 0 3m24s prometheus-user-workload-0 5/5 Running 1 3m13s prometheus-user-workload-1 5/5 Running 1 3m13sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
其他资源
-
请参阅创建集群监控 ConfigMap 以了解如何创建
cluster-monitoring-configConfigMap 对象。
2.2. 部署示例服务
要测试监控您自己的服务,您可以部署一个示例服务。
流程
-
为服务配置创建 YAML 文件。在本例中,该文件名为
prometheus-example-app.yaml。 使用用于部署该服务的配置填充该文件:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 此配置会在
ns1项目中部署名为prometheus-example-app的服务。此服务会公开自定义version指标。将配置文件应用到集群:
oc apply -f prometheus-example-app.yaml
$ oc apply -f prometheus-example-app.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 部署该服务需要一些时间。
您可以检查该服务是否正在运行:
oc -n ns1 get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE prometheus-example-app-7857545cb7-sbgwq 1/1 Running 0 81m
$ oc -n ns1 get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE prometheus-example-app-7857545cb7-sbgwq 1/1 Running 0 81mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
2.3. 创建用于设置指标集合的角色
此流程演示了如何创建一个允许用户为服务设置指标集合的角色,如“设置指标集合”中所述。
流程
-
为新角色创建 YAML 文件。在本例中,该文件名为
custom-metrics-role.yaml。 使用
monitor-crd-edit角色的配置填充该文件:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 该角色可让用户为服务设置指标集合。
将配置文件应用到集群:
oc apply -f custom-metrics-role.yaml
$ oc apply -f custom-metrics-role.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 现在角色已创建。
2.4. 为用户授予角色
此流程演示了如何将 monitor-crd-edit 角色分配给用户。
先决条件
- 您需要已创建一个用户。
-
您需要已创建
monitor-crd -edit角色,如“创建用于设置指标集合的角色”中所述。
流程
- 在 Web 控制台中,导航到 User Management → Role Bindings → Create Binding。
- 在 Binding Type 中,选择“Namespace Role Binding”类型。
- 在 Name中,输入绑定的名称。
- 在 Namespace 中,选择要授予访问权限的命名空间。
-
在 Role Name 中,输入
monitor-crd-edit。 - 在 Subject中,选择 User。
-
在 Subject Name 中,输入用户名称,如
johnsmith。 -
确认角色绑定。现在,用户已被分配了
monitor-crd-edit角色,这会允许他为命名空间中的服务设置指标集合。
2.5. 设置指标集合
要使用服务公开的指标,您需要将 OpenShift Monitoring 配置为从 /metrics 端点中提取指标。您可以使用一个 ServiceMonitor 或 PodMonitor 来完成此操作,前者是一个指定应该如何监控服务的自定义资源定义 (CRD),后者是一个指定应该如何监控 pod 的 CRD。前者需要 Service 对象,而后者则不需要,允许 Prometheus 直接从 Pod 公开的指标端点中提取指标。
此流程演示了如何为服务创建 ServiceMonitor。
先决条件
-
以集群管理员或具有
monitor-crd-edit角色的用户身份登录。
流程
-
为 ServiceMonitor 配置创建 YAML 文件。在本例中,该文件名为
example-app-service-monitor.yaml。 使用用于创建 ServiceMonitor 的配置填充该文件:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 此配置可使 OpenShift Monitoring 提取在“部署示例服务”中部署的示例服务所公开的指标,该服务包括单个
version指标。将配置文件应用到集群:
oc apply -f example-app-service-monitor.yaml
$ oc apply -f example-app-service-monitor.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 部署 ServiceMonitor 需要一些时间。
您可以检查 ServiceMonitor 是否正在运行:
oc -n ns1 get servicemonitor NAME AGE prometheus-example-monitor 81m
$ oc -n ns1 get servicemonitor NAME AGE prometheus-example-monitor 81mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
其他资源
有关 ServiceMonitor 和 PodMonitor 的更多信息,请参阅 Prometheus Operator API 文档。
2.6. 创建警报规则
您可以创建警报规则,以根据所选服务指标的值触发警报。
在当前技术预览版本中,只有管理员可以使用 Prometheus UI 和 Web Console 访问警报规则。
流程
-
为警报规则创建 YAML 文件。在本例中,该文件名为
example-app-alerting-rule.yaml。 使用警报规则的配置填充该文件:
注意表达式只能引用由您自己的服务公开的指标。目前无法关联现有的集群指标。
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 此配置会创建一个名为
example-alert的警报规则,它会在示例服务公开的version指标变为0时触发警报。将配置文件应用到集群:
oc apply -f example-app-alerting-rule.yaml
$ oc apply -f example-app-alerting-rule.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 创建警报规则需要一些时间。
2.7. 向用户授予查看访问权限
默认情况下,只有集群管理员用户和开发者可从您的服务访问指标。此流程演示了如何向任意用户授予特定项目的指标访问权限。
先决条件
- 您需要已创建一个用户。
- 您需要以集群管理员身份登录。
流程
运行此命令可向 <user> 授予对 <namespace> 中所有服务指标的访问权限:
oc policy add-role-to-user view <user> -n <namespace>
$ oc policy add-role-to-user view <user> -n <namespace>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 例如,要向用户
bobwilliams提供对ns1命名空间的访问权限,请运行:oc policy add-role-to-user view bobwilliams -n ns1
$ oc policy add-role-to-user view bobwilliams -n ns1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
或者,在 Web 控制台中切换到开发者视角,然后点击 Advanced → Project Access。在这里,您可以选择正确的命名空间,并将
view角色分配给用户。
2.8. 访问您的服务指标
一旦启用了对您自己的服务的监控,部署了服务并为其设置了指标集合,您便能够以集群管理员、开发者或具有项目查看权限的用户身份访问该服务的指标。
OpenShift Container Platform Monitoring 中使用的 Grafana 实例是只读的,仅显示与基础架构相关的仪表板。
先决条件
- 您需要部署要监控的服务。
- 您需要启用对您自己的服务的监控。
- 您需要为该服务设置指标提取。
- 您需要以集群管理员、开发者或具有项目查看权限的用户身份登录。
流程
访问 Prometheus Web 界面:
要以集群管理员身份访问指标,请进入 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台,切换到管理员视角,并点击 Monitoring → Metrics。
注意在使用管理员视角时,集群管理员可访问所有集群指标,并可从所有项目访问自定义服务指标。
注意只有集群管理员可以访问 Alertmanager 和 Prometheus UI。
要以开发者或有权限的用户身份访问指标,请进入 OpenShift Container Platform Web 控制台,切换到开发者视角,然后点击 Advanced → Metrics。选择您要查看指标的项目。
注意开发者只能使用开发者视角。他们只能从单个项目查询指标数据。
- 使用 PromQL 接口为您的服务运行查询。
其他资源
第 3 章 公开用于自动扩展的自定义应用程序指标
您可以为 Pod 横向自动扩展导出自定义应用程序指标。
Prometheus Adapter 只是技术预览功能。技术预览功能不被红帽产品服务等级协议 (SLA) 支持,且可能在功能方面有缺陷。红帽不推荐在生产环境中使用它们。这些技术预览功能可以使用户提早试用新的功能,并有机会在开发阶段提供反馈意见。
有关红帽技术预览功能支持范围的详情,请参阅 https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/。
3.1. 公开用于 Pod 横向自动扩展的自定义应用程序指标
您可以使用 prometheus-adapter 资源,为 Pod 横向自动扩展显示自定义应用程序指标。
先决条件
-
确保安装了自定义 Prometheus 实例。本例中假定 Prometheus 已安装到
default命名空间。 -
确保为应用程序配置了监控功能。本例假定应用程序及服务监控器已安装到
default命名空间。
流程
-
为您的配置创建一个 YAML 文件。本例中称为
deploy.yaml。 添加相应的配置,以便为
prometheus-adapter创建服务帐户、必要角色和角色绑定:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 添加
prometheus-adapter的自定义指标的配置:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 添加将
prometheus-adapter注册为 API 服务的配置:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 显示要使用的 Prometheus Adapter 镜像:
kubectl get -n openshift-monitoring deploy/prometheus-adapter -o jsonpath="{..image}" quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-v4.3-art-dev@sha256:76db3c86554ad7f581ba33844d6a6ebc891236f7db64f2d290c3135ba81c264c$ kubectl get -n openshift-monitoring deploy/prometheus-adapter -o jsonpath="{..image}" quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-v4.3-art-dev@sha256:76db3c86554ad7f581ba33844d6a6ebc891236f7db64f2d290c3135ba81c264cCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow 添加部署
prometheus-adapter的配置:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
image: openshift-release-dev/ocp-v4.3-art-dev指定上一步中找到的 Prometheus Adapter 镜像。
将配置文件应用到集群:
oc apply -f deploy.yaml
$ oc apply -f deploy.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 现在,应用程序的指标已经公开,并可用于配置 Pod 横向自动扩展。
其他资源
Legal Notice
Copyright © Red Hat
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of the OpenJS Foundation.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.