此内容没有您所选择的语言版本。
2.4 Release Notes
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4
Release Notes for Red Hat Software Collections 2.4
Abstract
The Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Release Notes document the major features and contain important information about known problems in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4.
The Red Hat Developer Toolset collection is documented in the Red Hat Developer Toolset Release Notes and the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide.
Chapter 1. Red Hat Software Collections 2.4
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This chapter serves as an overview of the Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 content set. It provides a list of components and their descriptions, sums up changes in this version, documents relevant compatibility information, and lists known issues.
1.1. About Red Hat Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
For certain applications, more recent versions of some software components are often needed in order to use their latest new features. Red Hat Software Collections is a Red Hat offering that provides a set of dynamic programming languages, database servers, and various related packages that are either more recent than their equivalent versions included in the base Red Hat Enterprise Linux system, or are available for this system for the first time.
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 is be available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7; selected new components and previously released components also for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. For a complete list of components that are distributed as part of Red Hat Software Collections and a brief summary of their features, see Section 1.2, “Main Features”.
Red Hat Software Collections does not replace the default system tools provided with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 or Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Instead, a parallel set of tools is installed in the
/opt/ directory and can be optionally enabled per application by the user using the supplied scl utility. The default versions of Perl or PostgreSQL, for example, remain those provided by the base Red Hat Enterprise Linux system.
All Red Hat Software Collections components are fully supported under Red Hat Enterprise Linux Subscription Level Agreements, are functionally complete, and are intended for production use. Important bug fix and security errata are issued to Red Hat Software Collections subscribers in a similar manner to Red Hat Enterprise Linux for at least two years from the release of each major version. In each major release stream, each version of a selected component remains backward compatible. For detailed information about length of support for individual components, refer to the Red Hat Software Collections Product Life Cycle document.
1.1.1. Red Hat Developer Toolset
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Developer Toolset is a part of Red Hat Software Collections, included as a separate Software Collection. For more information about Red Hat Developer Toolset, refer to the Red Hat Developer Toolset Release Notes and the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide.
1.2. Main Features
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 provides recent stable versions of the tools listed in Table 1.1, “Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Components”.
| Component | Software Collection | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Developer Toolset 6.1 | devtoolset-6 | Red Hat Developer Toolset is designed for developers working on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform. It provides current versions of the GNU Compiler Collection, GNU Debugger, and other development, debugging, and performance monitoring tools. For a complete list of components, see the Red Hat Developer Toolset Components table in the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide. |
| Eclipse 4.6.3[a] | rh-eclipse46 | A release of the Eclipse integrated development environment that is based on the Eclipse Foundation's Neon release train. Eclipse was previously available as a Red Hat Developer Toolset component. This Software Collection depends on the rh-java-common component. |
| Perl 5.20.1 | rh-perl520 | A release of Perl, a high-level programming language that is commonly used for system administration utilities and web programming. The rh-perl520 Software Collection provides additional utilities, scripts, and database connectors for MySQL and PostgreSQL. Also, it includes the DateTime Perl module and the mod_perl Apache httpd module, which is supported only with the httpd24 Software Collection. |
| Perl 5.24.0 | rh-perl524 | A release of Perl, a high-level programming language that is commonly used for system administration utilities and web programming. The rh-perl524 Software Collection provides additional utilities, scripts, and database connectors for MySQL and PostgreSQL. It includes the DateTime Perl module and the mod_perl Apache httpd module, which is supported only with the httpd24 Software Collection. Additionally, it provides the cpanm utility for easy installation of CPAN modules. |
| PHP 5.6.25 | rh-php56 | A release of PHP with PEAR 1.9.5 and enhanced language features including constant expressions, variadic functions, arguments unpacking, and the interactive debugger. The memcache, mongo, and XDebug extensions are also included. |
| PHP 7.0.10 | rh-php70 | A release of PHP 7 with PEAR 1.10, enhanced language features and performance improvement. |
| Python 2.7.13 | python27 | A release of Python 2.7 with a number of additional utilities. This Python version provides various features and enhancements, including an ordered dictionary type, faster I/O operations, and improved forward compatibility with Python 3. The python27 Software Collections contains the Python 2.7.13 interpreter, a set of extension libraries useful for programming web applications and mod_wsgi (only supported with the httpd24 Software Collection), MySQL and PostgreSQL database connectors, and numpy and scipy. |
| Python 3.4.2 | rh-python34 | A release of Python 3 with a number of additional utilities. This Software Collection gives developers on Red Hat Enterprise Linux access to Python 3 and allows them to benefit from various advantages and new features of this version. The rh-python34 Software Collection contains Python 3.4.2 interpreter, a set of extension libraries useful for programming web applications and mod_wsgi (only supported with the httpd24 Software Collection), PostgreSQL database connector, and numpy and scipy. |
| Python 3.5.1 | rh-python35 | The rh-python35 Software Collection contains Python 3.5.1 interpreter, a set of extension libraries useful for programming web applications and mod_wsgi (only supported with the httpd24 Software Collection), PostgreSQL database connector, and numpy and scipy. |
| Ruby 2.2.2 | rh-ruby22 | A release of Ruby 2.2. This version provides substantial performance and reliability improvements, including incremental and symbol garbage collection and many others, while maintaining source level backward compatibility with Ruby 2.0.0 and Ruby 1.9.3. |
| Ruby 2.3.1 | rh-ruby23 | A release of Ruby 2.3. This version introduces a command-line option to freeze all string literals in the source files, a safe navigation operator, and multiple performance enhancements, while maintaining source-level backward compatibility with Ruby 2.2.2, Ruby 2.0.0, and Ruby 1.9.3. |
| Ruby 2.4.0 | rh-ruby24 | A release of Ruby 2.4. This version provides multiple performance improvements and enhancements, for example improved hash table, new debugging features, support for Unicode case mappings, and support for OpenSSL 1.1.0. Ruby 2.4.0 maintains source-level backward compatibility with Ruby 2.3.1, Ruby 2.2.2, Ruby 2.0.0, and Ruby 1.9.3. |
| Ruby on Rails 4.1.5 | rh-ror41 | A release of Ruby on Rails 4.1, a web application development framework written in the Ruby language. This version provides a number of new features including Spring application preloader, config/secrets.yml, Action Pack variants, and Action Mailer previews. This Software Collection is supported together with the rh-ruby22 Collection. |
| Ruby on Rails 4.2.6 | rh-ror42 | A release of Ruby on Rails 4.2, a web application framework written in the Ruby language. Highlights in this release include Active Job, asynchronous mails, Adequate Record, Web Console, and foreign key support. This Software Collection is supported together with the rh-ruby23 and rh-nodejs4 Collections. |
| Ruby on Rails 5.0.1 | rh-ror50 | A release of Ruby on Rails 5.0, the latest version of the web application framework written in the Ruby language. Notable new features include Action Cable, API mode, exclusive use of rails CLI over Rake, and ActionRecord attributes. This Software Collection is supported together with the rh-ruby24 and rh-nodejs6 Collections. |
| Scala 2.10.6 [a] | rh-scala210 | A release of Scala, a general purpose programming language for the Java platform, which integrates features of object-oriented and functional languages. |
| MariaDB 10.0.26 | rh-mariadb100 | A release of MariaDB, an alternative to MySQL for users of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. For all practical purposes, MySQL is binary compatible with MariaDB and can be replaced with it without any data conversions. This version adds the PAM authentication plugin to MariaDB. |
| MariaDB 10.1.16 | rh-mariadb101 | A release of MariaDB, an alternative to MySQL for users of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. For all practical purposes, MySQL is binary compatible with MariaDB and can be replaced with it without any data conversions. This version adds the Galera Cluster support. |
| MongoDB 2.6.9 | rh-mongodb26 | A release of MongoDB, a cross-platform document-oriented database system classified as a NoSQL database. This Software Collection includes the mongo-java-driver package version 2.14.1. |
| MongoDB 3.2.10 | rh-mongodb32 | A release of MongoDB, a cross-platform document-oriented database system classified as a NoSQL database. This Software Collection includes the mongo-java-driver package version 3.2.1. |
| MongoDB 3.0.11 upgrade collection | rh-mongodb30upg | A limited version of MongoDB 3.0 is available to provide an upgrade path from MongoDB 2.6 to MongoDB 3.2 for customers with existing MongoDB databases. |
| MySQL 5.6.34 | rh-mysql56 | A release of MySQL, which provides a number of new features and enhancements, including improved performance. |
| MySQL 5.7.16 | rh-mysql57 | A release of MySQL, which provides a number of new features and enhancements, including improved performance. |
| PostgreSQL 9.4.9 | rh-postgresql94 | A release of PostgreSQL, which provides a new data type to store JSON more efficiently and a new SQL command for changing configuration files, reduces lock strength for some commands, allows materialized views without blocking concurrent reads, supports logical decoding of WAL data to allow stream changes in a customizable format and enable background worker processes to be dynamically registered, started, and terminated. |
| PostgreSQL 9.5.4 | rh-postgresql95 | A release of PostgreSQL, which provides a number of enhancements, including row-level security control, introduces replication progress tracking, improves handling of large tables with high number of columns, and improves performance for sorting and multi-CPU machines. |
| Node.js 4.6.2 | rh-nodejs4 | A release of Node.js, which provides a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine and npm 2.15.1, a package manager for JavaScript. This version includes an enhanced API, multiple security and bug fixes, and support for the SPDY protocol version 3.1 |
| Node.js 6.9.1 | rh-nodejs6 | A release of Node.js, which provides multiple API enhancements, performance and security improvements, ECMAScript 2015 support, and npm 3.10.9. |
| rh-nginx 1.8.1 | rh-nginx18 | A release of nginx, a web and proxy server with a focus on high concurrency, performance and low memory usage. This version introduces a number of new features, including back-end SSL certificate verification, logging to syslog, thread pools support for offloading I/O requests, or hash load balancing method. |
| rh-nginx 1.10.2 | rh-nginx110 | A release of nginx, a web and proxy server with a focus on high concurrency, performance and low memory usage. This version introduces a number of new features, including dynamic module support, HTTP/2 support, Perl integration, and numerous performance improvements. |
| Apache httpd 2.4.25 | httpd24 | A release of the Apache HTTP Server (httpd), including a high performance event-based processing model, enhanced SSL module and FastCGI support. The mod_auth_kerb module is also included. |
| Varnish Cache 4.0.3 | rh-varnish4 | A release of Varnish Cache, a high-performance HTTP reverse proxy. Varnish Cache stores files or fragments of files in memory that are used to reduce the response time and network bandwidth consumption on future equivalent requests. |
| Thermostat 1.6.6 | rh-thermostat16 | A release of Thermostat, a monitoring and instrumentation tool for the OpenJDK HotSpot JVM, with support for monitoring multiple JVM instances. This Software Collection depends on the rh-mongodb32 and rh-java-common components. |
| Maven 3.3.9 | rh-maven33 | A release of Maven, a software project management and comprehension tool used primarily for Java projects. This version provides various enhancements, for example, improved core extension mechanism. |
| Passenger 4.0.50 | rh-passenger40 | A release of Phusion Passenger, a web and application server, designed to be fast, robust, and lightweight. It supports Ruby using the ruby193, ruby200, or rh-ruby22 Software Collections together with Ruby on Rails using the ror40 or rh-ror41 Collections. It can also be used with nginx 1.6 from the nginx16 Software Collection and with Apache httpd from the httpd24 Software Collection. |
| Git 2.9.3 | rh-git29 | A release of Git, a distributed revision control system with a decentralized architecture. As opposed to centralized version control systems with a client-server model, Git ensures that each working copy of a Git repository is its exact copy with complete revision history. |
| Redis 3.2.4 | rh-redis32 | A release of Redis 3.2, a persistent key-value database. |
| Common Java Packages 1.1 | rh-java-common | This Software Collection provides common Java libraries and tools used by other collections. The rh-java-common Software Collection is required by the devtoolset-4, devtoolset-3, rh-maven33, maven30, rh-mongodb32, rh-mongodb26, thermostat1, rh-thermostat16, and rh-eclipse46 components and it is not supposed to be installed directly by users. |
| V8 3.14.5.10 | v8314 | This Software Collection provides the V8 JavaScript engine and is supported only as a dependency for the mongodb24, rh-mongodb26, rh-mongodb30upg, ruby193, ror40, rh-ror41, and nodejs010 Software Collections. |
[a]
This Software Collection is available only for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
| ||
Previously released Software Collections remain available in the same distribution channels. All currently available Software Collections are listed in the Table 1.2, “All Available Software Collections”.
See the Red Hat Software Collections Product Life Cycle document for information on the length of support for individual components. For detailed information regarding previously released components, refer to the Release Notes for earlier versions of Red Hat Software Collections.
| Component | Software Collection | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Components New in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 | ||
| Scala 2.10.6 | rh-scala210 | RHEL7 |
| nginx 1.10.2 | rh-nginx110 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Node.js 6.9.1 | rh-nodejs6 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby 2.4.0 | rh-ruby24 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby on Rails 5.0.1 | rh-ror50 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Components Updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Developer Toolset 6.1 | devtoolset-6 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Eclipse 4.6.3 | rh-eclipse46 | RHEL7 |
| Python 2.7.13 | python27 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Apache httpd 2.4.25 | httpd24 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Thermostat 1.6.6 | rh-thermostat16 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Maven 3.3.9 | rh-maven33 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Common Java Packages 1.1 | rh-java-common | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Components Last Updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Git 2.9.3 | rh-git29 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Redis 3.2.4 | rh-redis32 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Perl 5.24.0 | rh-perl524 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PHP 7.0.10 | rh-php70 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MySQL 5.7.16 | rh-mysql57 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Python 3.5.1 | rh-python35 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MongoDB 3.2.10 | rh-mongodb32 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby 2.3.1 | rh-ruby23 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PHP 5.6.25 | rh-php56 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Components Last Updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Developer Toolset 4.1 | devtoolset-4 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MariaDB 10.1.19 | rh-mariadb101 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MongoDB 3.0.11 upgrade collection | rh-mongodb30upg | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Node.js 4.6.2 | rh-nodejs4 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PostgreSQL 9.5.4 | rh-postgresql95 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby on Rails 4.2.6 | rh-ror42 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MongoDB 2.6.9 | rh-mongodb26 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Thermostat 1.4.4 | thermostat1 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Components Last Updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Varnish Cache 4.0.3 | rh-varnish4 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| nginx 1.8.1 | rh-nginx18 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Node.js 0.10 | nodejs010 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Maven 3.0.5 | maven30 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| V8 3.14.5.10 | v8314 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Components Last Updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.0 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Developer Toolset 3.1 | devtoolset-3 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Perl 5.20.1 | rh-perl520 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Python 3.4.2 | rh-python34 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby 2.2.2 | rh-ruby22 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby on Rails 4.1.5 | rh-ror41 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MariaDB 10.0.28 | rh-mariadb100 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MySQL 5.6.34 | rh-mysql56 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PostgreSQL 9.4.9 | rh-postgresql94 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Passenger 4.0.50 | rh-passenger40 | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PHP 5.4.40 | php54 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PHP 5.5.21 | php55 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| nginx 1.6.2 | nginx16 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| DevAssistant 0.9.3 | devassist09 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Components Last Updated in Red Hat Software Collections 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Git 1.9.4 | git19 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Perl 5.16.3 | perl516 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Python 3.3.2 | python33 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby 1.9.3 | ruby193 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby 2.0.0 | ruby200 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| Ruby on Rails 4.0.2 | ror40 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MariaDB 5.5.53 | mariadb55 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MongoDB 2.4.9 | mongodb24 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| MySQL 5.5.52 | mysql55 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
| PostgreSQL 9.2.18 | postgresql92 * | RHEL6, RHEL7 |
RHEL6 — Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
RHEL7 — Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
* Retired component — this Software Collection is no longer supported
The tables above list the latest versions available through asynchronous updates.
Note that Software Collections released in Red Hat Software Collections 2.0 and later include a
rh- prefix in their names.
1.3. Changes in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
1.3.1. Overview
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
New Software Collections
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 adds these new Software Collections:
- rh-scala210 — This new Software Collection, available only for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, provides Scala 2.10.6, a general purpose programming language, designed to express common programming patterns in a concise, elegant, and type-safe way. It integrates features of object-oriented and functional languages. It is also fully interoperable with Java. For more information, see the upstream documentation.
- rh-nginx110 — see Section 1.3.4, “Changes in nginx”
- rh-nodejs6 — see Section 1.3.5, “Changes in Node.js”
- rh-ruby24 — see Section 1.3.6, “Changes in Ruby”
- rh-ror50 — see Section 1.3.7, “Changes in Ruby on Rails”
Updated Software Collections
The following components have been updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4:
- devtoolset-6 — see Section 1.3.2, “Changes in Red Hat Developer Toolset”
- rh-eclipse46 — see Section 1.3.3, “Changes in Eclipse”
- pyton27 — see Section 1.3.8, “Changes in Python”
- httpd24 — see Section 1.3.9, “Changes in Apache httpd”
- thermostat16 — see Section 1.3.10, “Changes in Thermostat”
- rh-maven33 — see Section 1.3.11, “Changes in Maven”
- rh-java-common — see Section 1.3.12, “Changes in the Common Java Packages”
Red Hat Software Collections Container Images
The following container images are new in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4:
- rhscl/nginx-110-rhel7
- rhscl/nodejs-6-rhel7
- rhscl/ruby-24-rhel7
- rhscl/ror-50-rhel7
The following container images have been updated in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4:
- rhscl/devtoolset-6-toolchain-rhel7
- rhscl/devtoolset-6-perftools-rhel7
- rhscl/httpd-24-rhel7
- rhscl/python-27-rhel7
- rhscl/thermostat-16-agent-rhel7
- rhscl/thermostat-16-storage-rhel7
For detailed information regarding Red Hat Software Collections container images, see Section 3.4, “Red Hat Software Collections Container Images”.
1.3.2. Changes in Red Hat Developer Toolset
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The following components have been upgraded in Red Hat Developer Toolset 6.1 compared to the previous release of Red Hat Developer Toolset:
- GCC to version 6.3.1
- elfutils to version 0.168
- GDB to version 7.12.1
Additionally, a bug fix update is available for ltrace.
For detailed information on changes in 6.1, see the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide.
1.3.3. Changes in Eclipse
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-eclipse46 Software Collection, available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, has been upgraded to version 4.6.3, which is based on the Eclipse Foundation's Neon release train. This update contains a number of bug fixes and two new plug-ins:
- The
m2eplug-in provides support for developing maven-based projects - The
TestNGplug-in provides support for writing and executing tests using the TestNG framework.
Most other plug-ins have received incremental updates to consume bug fixes from upstream. For details, see the upstream documentation.
For information on usage of the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection, see Section 4.2, “Eclipse 4.6.3”.
1.3.4. Changes in nginx
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The new rh-nginx110 Software Collection includes nginx 1.10.2. This version provides a number of new features, including dynamic module support, HTTP/2 support, and numerous performance improvements. For more information on changes in nginx 1.10, see the upstream release notes.
Note that the rh-nginx110 Software Collection does not support integration with Phusion Passenger. Users requiring nginx with Passenger support should continue using the rh-nginx18 Software Collection, which provides nginx version 1.8.
The rh-nginx110 Software Collection has optional support for Perl in conjunction with the rh-perl524 Software Collection. To be able to configure Perl handlers and call Perl functions from SSI scripts, install the rh-nginx110-nginx-mod-http-perl package. For more information, see the upstream documentation.
1.3.5. Changes in Node.js
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The new rh-nodejs6 Software Collection includes Node.js 6.9.1 and npm 3.10.9. This version provides numerous new features and bug fixes, including multiple API enhancements, performance and security improvements, and support for the
ECMAScript 2015 language specification.
For details, see the upstream release notes and upstream documentation.
The rh-nodejs4 Software Collection has been upgraded to version 4.6.2 with security and bug fixes through an asynchronous update. For more information about Node.js version 4.6.2, see the upstream release notes.
1.3.6. Changes in Ruby
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Ruby 2.4.0, provided by the new rh-ruby24Software Collection, introduces performance improvements and the following notable enhancements:
- Improved hash table performance
- The new
binding#irbmethod starts a read–eval–print loop (REPL) session allowing easier debugging and introspection of variables during runtime - Improved debugging of threads and better deadlock detection
- The
FixnumandBignumclasses integrated into theIntegerclass - Support for Unicode case mappings
- Support for the OpenSSL 1.1.0 library.
For details, see the upstream release notes and upstream documentation.
Ruby 2.4 is backward compatible with Ruby 2.3.1, Ruby 2.2.2, Ruby 2.2.2, Ruby 2.0.0, and Ruby 1.9.3. The rh-ruby23 and rh-ruby22 Software Collections are still supported. For information about length of support for these components, refer to the Red Hat Software Collections Product Life Cycle document.
1.3.7. Changes in Ruby on Rails
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The new rh-ror50 Software Collection includes Ruby on Rails 5.0.1. It provides a number of bug fixes and new features, for example:
- Action Cable framework for handling
WebSocketsin Rails - API mode to create a Rails application for an API server more easily
- Exclusive use of
railsCLI over Rake ActionRecordattributes – users can now overrideActiveRecordattributes if needed.
For details, see the upstream release notes.
The rh-ror50 Software Collection is supported together with the rh-ruby24 and rh-nodejs6 Collections.
1.3.8. Changes in Python
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The python27 Software Collection has been upgraded to upstream version 2.7.13, which provides a number of bug fixes and enhancements over the previous version. Among others:
- New per-application and per-process configuration options for SSL/TLS certificate verification have been added for the HTTP clients in the Python standard library. The options are described in the 493 Python Enhancement Proposal (PEP). In addition, the default global setting has been changed to verify certificates. Customers that opted out using the file-based configuration will not be affected. For details, see the relevant Knowledgebase article.
- The python27-mod_wsgi package has been upgraded to version 4.5.13.
- The python27-python-pip package has been upgraded to version 8.1.2.
1.3.9. Changes in Apache httpd
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The httpd24 Software Collection has been upgraded to upstream version 2.4.25, which provides a number of bug fixes and enhancements over the previous version, including multiple improvements to HTTP/2 support, fixes for both SSL/TLS support and the proxy modules. For more information on changes in httpd 2.4.25, see the upstream release notes.
1.3.10. Changes in Thermostat
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-thermostat16 Software Collection has been upgraded to upstream version 1.6.6, which provides the following notable changes:
- Support for Tomcat 8 has been added
- The profiler table has been fixed
- JDK used by Thermostat is now runtime-configurable
- The
gccommand has been fixed - Thermostat now uses the JDK version selected by the
alternativescommand by default.
For detailed changes, see the upstream change log. For information on usage, refer to the Thermostat User Guide.
1.3.11. Changes in Maven
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-maven33 Software Collection has been updated with several bug fixes.
1.3.12. Changes in the Common Java Packages
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-java-common Software Collection has been updated and extended to comply with the changes in the dependent components.
1.4. Compatibility Information
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 is available for all supported releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 on AMD64 and Intel 64 architectures. Certain components are available also for all supported releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 on AMD64 and Intel 64 architectures.
For a full list of available components, see Table 1.2, “All Available Software Collections”.
1.5. Known Issues
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
rh-eclipse46component- When a plug-in from a third-party update site is installed, Eclipse sometimes fails to start with a
NullPointerExceptionin the workspace log file. To work around this problem, restart Eclipse with the-cleanoption. For example:scl enable rh-eclipse46 "eclipse -clean"
~]$ scl enable rh-eclipse46 "eclipse -clean"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow httpd24component, BZ#1440858- When the
service httpd24-httpd gracefulcommand is used on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 while thehttpd24-httpdservice is not running, the daemon is started in an incorrect SELinux domain. As a consequence, the daemon is not tracked bysystemd. To work around this problem, restart the service using thesystemctl reload-or-restart httpd24-httpdcommand. httpd24component, BZ#1418395- On a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 system, when the
httpdservice is stopped twice in a row by running theservice httpd stop, a misleading message is returned:Stopping httpd: [FAILED]
Stopping httpd: [FAILED]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This message can be safely ignored. rh-thermostat16component- Due to typos in the desktop application file, users are unable to launch Thermostat using the desktop icon. To work around this problem, modify the
/usr/share/applications/rh-thermostat16-thermostat.desktopfile from:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, run Thermostat from command line:scl enable rh-thermostat16 "thermostat local"
$ scl enable rh-thermostat16 "thermostat local"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow rh-ruby24,rh-ruby23components- Determination of
RubyGeminstallation paths is dependent on the order in which multiple Software Collections are enabled. The required order has been changed since Ruby 2.3.1 shipped in Red Hat Software Collections 2.3 to support dependent Collections. As a consequence,RubyGempaths, which are used forgeminstallation during an RPM build, are invalid when the Software Collections are supplied in an incorrect order. For example, the build now fails if the RPM spec file containsscl enable rh-ror50 rh-nodejs6. To work around this problem, enable the rh-ror50 Software Collection last, for example,scl enable rh-nodejs6 rh-ror50. httpd24component, BZ#1382706- When SELinux is enabled, the
LD_LIBRARY_PATHenvironment variable is not passed through to CGI scripts invoked by httpd. As a consequence, in some cases it is impossible to invoke executables from Software Collections enabled in the/opt/rh/httpd24/service-environmentfile from CGI scripts run by httpd. To work around this problem, setLD_LIBRARY_PATHas desired from within the CGI script. eclipsecomponent- The Eclipse Docker Tooling introduces a Dockerfile editor with syntax highlighting and a basic command auto-completion. When the Build Image Wizard is open and the button is pressed, the Dockerfile editor opens the file in a detached editor window. However, this window does not contain the and buttons. To work around this problem, press Ctrl+S to save your changes or right-click in the editor to launch a context menu, which offers the option. To cancel your changes, close the window.
eclipsecomponent- On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2, a bug in the perf tool, which is used to populate the
Perf Profile Viewin Eclipse, causes some of the items in the view not to be properly linked to their respective positions in the Eclipse Editor. While the profiling works as expected, it is not possible to navigate to related positions in the Editor by clicking on parts of thePerl Profile View. python27component, BZ#1330489- The python27-python-pymongo package has been updated to version 3.2.1. Note that this version is not fully compatible with the previously shipped version 2.5.2. For details, see https://api.mongodb.org/python/current/changelog.html.
httpd24component, BZ#1327548- The
mod_sslmodule does not support the Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation (ALPN) protocol on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Consequently, clients that support upgrading TLS connections to HTTP/2 only using ALPN are limited to HTTP/1.1 support. Clients that support the NPN protocol in addition to ALPN are able to successfully upgrade to HTTP/2. rh-maven33component- When the user has installed both the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system version of maven-local package and the rh-maven33-maven-local package, XMvn, a tool used for building Java RPM packages, run from the rh-maven33 Software Collection tries to read the configuration file from the base system and fails. To work around this problem, uninstall the maven-local package from the base Red Hat Enterprise Linux system.
rh-nodejs4component, BZ#1316626- The
/opt/rh/rh-nodejs4/root/usr/share/licenses/directory is not owned by any package. Consequently, when the rh-nodejs4 collection is uninstalled, this directory is not removed. To work around this problem, remove the directory manually after uninstalling rh-nodejs4. -
rh-mysql57,rh-mysql56,rh-mariadb100,rh-mariadb101components, BZ#1194611 - The rh-mysql57-mysql-server, rh-mysql56-mysql-server, rh-mariadb100-mariadb-server, and rh-mariadb101-mariadb-server packages no longer provide the
testdatabase by default. Although this database is not created during initialization, the grant tables are prefilled with the same values as whentestwas created by default. As a consequence, upon a later creation of thetestortest_*databases, these databases have less restricted access rights than is default for new databases.Additionally, when running benchmarks, therun-all-testsscript no longer works out of the box with example parameters. You need to create a test database before running the tests and specify the database name in the--databaseparameter. If the parameter is not specified,testis taken by default but you need to make sure thetestdatabase exist. -
httpd24component, BZ#1224763 - When using the
mod_proxy_fcgimodule with FastCGI Process Manager (PHP-FPM), httpd uses port8000for the FastCGI protocol by default instead of the correct port9000. To work around this problem, specify the correct port explicitly in configuration. -
mongodb24component - The mongodb24 Software Collection from Red Hat Software Collections 1.2 cannot be rebuilt with the rh-java-common and maven30 Software Collections shipped with Red Hat Software Collections 2.4. Additionally, the mongodb24-build and mongodb24-scldevel packages cannot be installed with Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 due to unsatisfied requires on the maven30-javapackages-tools and maven30-maven-local packages. When the mongodb24-scldevel package is installed, broken dependencies are reported and the
yum --skip-brokencommand skips too many packages. Users are advised to update to the rh-mongodb26 Software Collection. -
perlcomponent - It is impossible to install more than one
mod_perl.solibrary. As a consequence, it is not possible to use themod_perlmodule from more than one Perl Software Collection. -
nodejs010component - Shared libraries provided by the nodejs010 Software Collection, namely
libcares,libhttp_parser, andlibuv, are not properly prefixed with the Collection name. As a consequence, conflicts with the corresponding system libraries might occur. -
nodejs-hawkcomponent - The nodejs-hawk package uses an implementation of the SHA-1 and SHA-256 algorithms adopted from the CryptoJS project. In this release, the client-side JavaScript is obfuscated. The future fix will involve using crypto features directly from the CryptoJS library.
-
postgresqlcomponent - The postgresql92, rh-postgresql94, and rh-postgresql95 packages for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 do not provide the
sepgsqlmodule as this feature requires installation of libselinux version 2.0.99, which is not available in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. -
httpd,mariadb,mongodb,mysql,nodejs,perl,php55,rh-php56,python,ruby,ror,thermostat, andv8314components, BZ#1072319 - When uninstalling the httpd24, mariadb55, rh-mariadb100, mongodb24, rh-mongodb26, mysql55, rh-mysql56, nodejs010, perl516, rh-perl520, php55, rh-php56, python27, python33, rh-python34, ruby193, ruby200, rh-ruby22, ror40, rh-ror41, thermostat1, or v8314 packages, the order of uninstalling can be relevant due to ownership of dependent packages. As a consequence, some directories and files might not be removed properly and might remain on the system.
-
mariadb,mysql,postgresql,mongodbcomponents - Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 contains the MySQL 5.7, MySQL 5.6, MariaDB 10.0, MariaDB 10.1, PostgreSQL 9.4, PostgreSQL 9.5, MongoDB 2.6, and MongoDB 3.2 databases. The core Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 provides earlier versions of the MySQL and PostgreSQL databases (client library and daemon). The core Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 provides earlier versions of the MariaDB and PostgreSQL databases (client library and daemon). Client libraries are also used in database connectors for dynamic languages, libraries, and so on.The client library packaged in the Red Hat Software Collections database packages in the PostgreSQL component is not supposed to be used, as it is included only for purposes of server utilities and the daemon. Users are instead expected to use the system library and the database connectors provided with the core system.A protocol, which is used between the client library and the daemon, is stable across database versions, so, for example, using the PostgreSQL 9.2 client library with the PostgreSQL 9.4 or 9.5 daemon works as expected.The core Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 do not include the client library for MongoDB. In order to use this client library for your application, you should use the client library from Red Hat Software Collections and always use the
scl enable ...call every time you run an application linked against this MongoDB client library. -
mariadb,mysql,mongodbcomponents - MariaDB, MySQL, and MongoDB do not make use of the
/opt/provider/collection/rootprefix when creating log files. Note that log files are saved in the/var/opt/provider/collection/log/directory, not in/opt/provider/collection/root/var/log/. -
httpdcomponent - Compiling external applications against the Apache Portable Runtime (APR) and APR-util libraries from the httpd24 Software Collection is not supported. The LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable is not set in httpd24 because it is not required by any application in this Software Collection.
-
python27component - In Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, when the user tries to install the python27-python-debuginfo package, the
/usr/src/debug/Python-2.7.5/Modules/socketmodule.cfile conflicts with the corresponding file from the python-debuginfo package installed on the core system. Consequently, installation of the python27-python-debuginfo fails. To work around this problem, uninstall the python-debuginfo package and then install the python27-python-debuginfo package.
Other Notes
eclipsecomponent- The Eclipse SWT graphical library on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 uses GTK 3.x. Eclipse
Dark Themeis not yet fully stable on GTK 3.x, so this theme is considered a Technology Preview and not supported. For more information about Red Hat Technology Previews, see https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/. -
rh-ruby22,rh-ruby23,rh-python34,rh-python35,rh-php56,rh-php70components - Using Software Collections on a read-only NFS has several limitations.
- Ruby gems cannot be installed while the rh-ruby22 or rh-ruby23 Software Collection is on a read-only NFS. Consequently, for example, when the user tries to install the ab gem using the
gem install abcommand, an error message is displayed, for example:ERROR: While executing gem ... (Errno::EROFS) Read-only file system @ dir_s_mkdir - /opt/rh/rh-ruby22/root/usr/local/share/gemsERROR: While executing gem ... (Errno::EROFS) Read-only file system @ dir_s_mkdir - /opt/rh/rh-ruby22/root/usr/local/share/gemsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The same problem occurs when the user tries to update or install gems from an external source by running thebundle updateorbundle installcommands. - When installing Python packages on a read-only NFS using the Python Package Index (PyPI), running the
pipcommand fails with an error message similar to this:Read-only file system: '/opt/rh/rh-python34/root/usr/lib/python3.4/site-packages/ipython-3.1.0.dist-info'
Read-only file system: '/opt/rh/rh-python34/root/usr/lib/python3.4/site-packages/ipython-3.1.0.dist-info'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Installing packages from PHP Extension and Application Repository (PEAR) on a read-only NFS using the
pearcommand fails with the error message:Cannot install, php_dir for channel "pear.php.net" is not writeable by the current user
Cannot install, php_dir for channel "pear.php.net" is not writeable by the current userCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This is an expected behavior. -
httpdcomponent - Language modules for Apache are supported only with the Red Hat Software Collections version of Apache httpd and not with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system versions of httpd. For example, the
mod_wsgimodule from the rh-python35 Collection can be used only with the httpd24 Collection. - all components
- Since Red Hat Software Collections 2.0, configuration files, variable data, and runtime data of individual Collections are stored in different directories than in previous versions of Red Hat Software Collections.
-
coreutils,util-linux,screencomponents - Some utilities, for example, su, login, or screen, do not export environment settings in all cases, which can lead to unexpected results. It is therefore recommended to use sudo instead of su and set the
env_keepenvironment variable in the/etc/sudoersfile. Alternatively, you can run commands in a reverse order; for example:su -l postgres -c "scl enable rh-postgresql94 psql"
su -l postgres -c "scl enable rh-postgresql94 psql"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow instead ofscl enable rh-postgresql94 bash su -l postgres -c psql
scl enable rh-postgresql94 bash su -l postgres -c psqlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When using tools like screen or login, you can use the following command to preserve the environment settings:source /opt/rh/<collection_name>/enable
source /opt/rh/<collection_name>/enableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
php54component - Note that Alternative PHP Cache (APC) in Red Hat Software Collections is provided only for user data cache. For opcode cache, Zend OPcache is provided.
-
pythoncomponent - When the user tries to install more than one scldevel package from the python27, python33, rh-python34, and rh-python35 Software Collections, a transaction check error message is returned. This is an expected behavior because the user can install only one set of the macro files provided by the packages (
%scl_python,%scl_prefix_python). -
phpcomponent - When the user tries to install more than one scldevel package from the php54, php55, rh-php56, and rh-php70 Software Collections, a transaction check error message is returned. This is an expected behavior because the user can install only one set of the macro files provided by the packages (
%scl_php,%scl_prefix_php). -
rubycomponent - When the user tries to install more than one scldevel package from the ruby193, ruby200, rh-ruby22, and rh-ruby23 Software Collections, a transaction check error message is returned. This is an expected behavior because the user can install only one set of the macro files provided by the packages (
%scl_ruby,%scl_prefix_ruby). -
perlcomponent - When the user tries to install more than one scldevel package from the perl516, rh-perl520, and rh-perl524 Software Collections, a transaction check error message is returned. This is an expected behavior because the user can install only one set of the macro files provided by the packages (
%scl_perl,%scl_prefix_perl). -
nginxcomponent - When the user tries to install more than one scldevel package from the nginx16 and rh-nginx18 Software Collections, a transaction check error message is returned. This is an expected behavior because the user can install only one set of the macro files provided by the packages (
%scl_nginx,%scl_prefix_nginx). -
nodejscomponent - When installing the nodejs010 Software Collection, nodejs010 installs GCC in the base Red Hat Enterprise Linux system as a dependency, unless the gcc packages are already installed.
1.6. Deprecated Functionality
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
httpd24component, BZ#1434053- Previously, in an SSL/TLS configuration requiring name-based SSL virtual host selection, the
mod_sslmodule rejected requests with a400 Bad Requesterror, if the host name provided in theHost:header did not match the host name provided in a Server Name Indication (SNI) header. Such requests are no longer rejected if the configured SSL/TLS security parameters are identical between the selected virtual hosts, in-line with the behavior of upstreammod_ssl.
Chapter 2. Installation
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This chapter describes in detail how to get access to the content set, install Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 on the system, and rebuild Red Hat Software Collections.
2.1. Getting Access to Red Hat Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The Red Hat Software Collections content set is available to customers with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 subscriptions listed at https://access.redhat.com/solutions/472793. Depending on the subscription management service with which you registered your Red Hat Enterprise Linux system, you can either enable Red Hat Software Collections by using Red Hat Subscription Management, or by using RHN Classic. For detailed instructions on how to enable Red Hat Software Collections using RHN Classic or Red Hat Subscription Management, see the respective section below. For information on how to register your system with one of these subscription management services, see Using and Configuring Red Hat Subscription Manager.
Since Red Hat Software Collections 2.2, the Red Hat Software Collections and Red Hat Developer Toolset content is available also in the ISO format at https://access.redhat.com/downloads, specifically for Server and Workstation. Note that packages that require the
Optional channel, which are listed in Section 2.1.3, “Packages from the Optional Channel”, cannot be installed from the ISO image.
Note
Packages that require the
Optional channel cannot be installed from the ISO image. A list of packages that require enabling of the Optional channel is provided in Section 2.1.3, “Packages from the Optional Channel”.
Beta content is unavailable in the ISO format.
2.1.1. Using Red Hat Subscription Management
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
If your system is registered with Red Hat Subscription Management, complete the following steps to attach the subscription that provides access to the repository for Red Hat Software Collections and enable the repository:
- Display a list of all subscriptions that are available for your system and determine the pool ID of a subscription that provides Red Hat Software Collections. To do so, type the following at a shell prompt as
root:subscription-manager list --available
subscription-manager list --availableCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For each available subscription, this command displays its name, unique identifier, expiration date, and other details related to it. The pool ID is listed on a line beginning withPool Id. - Attach the appropriate subscription to your system by running the following command as
root:subscription-manager attach --pool=pool_id
subscription-manager attach --pool=pool_idCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace pool_id with the pool ID you determined in the previous step. To verify the list of subscriptions your system has currently attached, type asroot:subscription-manager list --consumed
subscription-manager list --consumedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Display the list of available Yum list repositories to retrieve repository metadata and determine the exact name of the Red Hat Software Collections repositories. As
root, type:subscription-manager repos --list
subscription-manager repos --listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Or alternatively, runyum repolist allfor a brief list.The repository names depend on the specific version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux you are using and are in the following format:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace variant with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system variant, that is,serverorworkstation. Note that Red Hat Software Collections is supported neither on theClientnor on theComputeNodevariant. - Enable the appropriate repository by running the following command as
root:subscription-manager repos --enable repository
subscription-manager repos --enable repositoryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Once the subscription is attached to the system, you can install Red Hat Software Collections as described in Section 2.2, “Installing Red Hat Software Collections”. For more information on how to register your system using Red Hat Subscription Management and associate it with subscriptions, see Using and Configuring Red Hat Subscription Manager.
2.1.2. Using RHN Classic
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
If your system is registered with RHN Classic, complete the following steps to subscribe to Red Hat Software Collections:
- Display a list of all channels that are available to you and determine the exact name of the Red Hat Software Collections channel. To do so, type the following at a shell prompt as
root:rhn-channel --available-channels
rhn-channel --available-channelsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The name of the channel depends on the specific version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux you are using and is in the following format, where variant is the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system variant (serverorworkstation):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 channels are accessible only through Red Hat Satellite instances.Note
Red Hat Software Collections 2.x are distributed in the same channels as Red Hat Software Collections 1.x. - Subscribe the system to the Red Hat Software Collections channel by running the following command as
root:rhn-channel --add --channel=channel_name
rhn-channel --add --channel=channel_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace channel_name with the name you determined in the previous step. - Verify the list of channels you are subscribed to. As
root, type:rhn-channel --list
rhn-channel --listCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When the system is subscribed, you can install Red Hat Software Collections as described in Section 2.2, “Installing Red Hat Software Collections”. For more information on how to register your system with RHN Classic, see Using and Configuring Red Hat Subscription Manager.
2.1.3. Packages from the Optional Channel
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Some of the Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 packages require the
Optional channel to be enabled in order to complete the full installation of these packages. For detailed instructions on how to subscribe your system to this channel, see the relevant Knowledgebase articles at https://access.redhat.com/solutions/392003 for Red Hat Subscription Management or at https://access.redhat.com/solutions/70019 if your system is registered with RHN Classic.
Packages from Software Collections for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 that require the
Optional channel to be enabled are listed in the following table.
| Package from a Software Collection | Required Package from the Optional Channel |
|---|---|
| devtoolset-4-dyninst-testsuite | glibc-static |
| devtoolset-4-elfutils-devel | xz-devel |
| devtoolset-4-gcc-plugin-devel | mpfr, mpfr-devel |
| devtoolset-4-libgccjit | mpfr |
| devtoolset-6-dyninst-testsuite | glibc-static |
| devtoolset-6-elfutils-devel | xz-devel |
| devtoolset-6-gcc-plugin-devel | mpfr, mpfr-devel |
| devtoolset-6-libgccjit | mpfr |
| rh-git29-git-all | cvsps |
| rh-git29-git-cvs | cvsps |
| rh-git29-perl-Git-SVN | perl-YAML, subversion-perl |
| rh-mariadb101-boost-devel | libicu-devel |
| rh-mariadb101-boost-examples | libicu-devel |
| rh-mariadb101-boost-static | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb30upg-boost-devel | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb30upg-boost-examples | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb30upg-boost-static | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb30upg-yaml-cpp-devel | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb32-boost-devel | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb32-boost-examples | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb32-boost-static | libicu-devel |
| rh-mongodb32-yaml-cpp-devel | libicu-devel |
| rh-php56-php-imap | libc-client |
| rh-php56-php-recode | recode |
| rh-php70-php-imap | libc-client |
| rh-php70-php-recode | recode |
Software Collections packages that require the
Optional channel in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 are listed in the table below.
| Package from a Software Collection | Required Package from the Optional Channel |
|---|---|
| devtoolset-6-build | scl-utils-build |
| devtoolset-6-dyninst-testsuite | glibc-static |
| devtoolset-6-gcc-plugin-devel | libmpc-devel |
| httpd24-mod_ldap | apr-util-ldap |
| rh-eclipse46 | ruby-doc |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-dltk-ruby | ruby-doc |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-dltk-sdk | ruby-doc |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-dltk-tests | ruby-doc |
| rh-git29-git-all | cvsps |
| rh-git29-git-cvs | cvsps |
| rh-git29-perl-Git-SVN | subversion-perl |
| rh-perl520-perl-Pod-Perldoc | groff |
Note that packages from the
Optional channel are not supported. For details, see the Knowledgebase article at https://access.redhat.com/articles/1150793.
2.2. Installing Red Hat Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Software Collections is distributed as a collection of RPM packages that can be installed, updated, and uninstalled by using the standard package management tools included in Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Note that a valid subscription is required to install Red Hat Software Collections on your system. For detailed instructions on how to associate your system with an appropriate subscription and get access to Red Hat Software Collections, see Section 2.1, “Getting Access to Red Hat Software Collections”.
Use of Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 requires the removal of any earlier pre-release versions, including Beta releases. If you have installed any previous version of Red Hat Software Collections 2.4, uninstall it from your system and install the new version as described in the Section 2.3, “Uninstalling Red Hat Software Collections” and Section 2.2.1, “Installing Individual Software Collections” sections.
The in-place upgrade from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 is not supported by Red Hat Software Collections. As a consequence, the installed Software Collections might not work correctly after the upgrade. If you want to upgrade from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 to Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, it is strongly recommended to remove all Red Hat Software Collections packages, perform the in-place upgrade, update the Red Hat Software Collections repository, and install the Software Collections packages again. It is advisable to back up all data before upgrading.
2.2.1. Installing Individual Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To install any of the Software Collections that are listed in Table 1.1, “Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Components”, install the corresponding meta package by typing the following at a shell prompt as
root:
yum install software_collection...
yum install software_collection...
Replace software_collection with a space-separated list of Software Collections you want to install. For example, to install php54 and rh-mariadb100, type as
root:
yum install rh-php56 rh-mariadb100
~]# yum install rh-php56 rh-mariadb100
This installs the main meta package for the selected Software Collection and a set of required packages as its dependencies. For information on how to install additional packages such as additional modules, see Section 2.2.2, “Installing Optional Packages”.
2.2.2. Installing Optional Packages
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Each component of Red Hat Software Collections is distributed with a number of optional packages that are not installed by default. To list all packages that are part of a certain Software Collection but are not installed on your system, type the following at a shell prompt:
yum list available software_collection-\*
yum list available software_collection-\*
To install any of these optional packages, type as
root:
yum install package_name...
yum install package_name...
Replace package_name with a space-separated list of packages that you want to install. For example, to install the rh-perl520-perl-CPAN and rh-perl520-perl-Archive-Tar, type:
yum install rh-perl524-perl-CPAN rh-perl524-perl-Archive-Tar
~]# yum install rh-perl524-perl-CPAN rh-perl524-perl-Archive-Tar2.2.3. Installing Debugging Information
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To install debugging information for any of the Red Hat Software Collections packages, make sure that the yum-utils package is installed and type the following command as
root:
debuginfo-install package_name
debuginfo-install package_name
For example, to install debugging information for the rh-ruby22-ruby package, type:
debuginfo-install rh-ruby22-ruby
~]# debuginfo-install rh-ruby22-ruby
Note that in order to use this command, you need to have access to the repository with these packages. If your system is registered with Red Hat Subscription Management, enable the
rhel-variant-rhscl-6-debug-rpms or rhel-variant-rhscl-7-debug-rpms repository as described in Section 2.1.1, “Using Red Hat Subscription Management”. If your system is registered with RHN Classic, subscribe the system to the rhel-x86_64-variant-6-rhscl-1-debuginfo or rhel-x86_64-variant-7-rhscl-1-debuginfo channel as described in Section 2.1.2, “Using RHN Classic”. For more information on how to get access to debuginfo packages, see https://access.redhat.com/solutions/9907.
2.3. Uninstalling Red Hat Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To uninstall any of the Software Collections components, type the following at a shell prompt as
root:
yum remove software_collection\*
yum remove software_collection\*
Replace software_collection with the Software Collection component you want to uninstall.
Note that uninstallation of the packages provided by Red Hat Software Collections does not affect the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system versions of these tools.
2.4. Rebuilding Red Hat Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
<collection>-build packages are not provided by default. If you wish to rebuild a collection and do not want or cannot use the
rpmbuild --define 'scl foo' command, you first need to rebuild the metapackage, which provides the <collection>-build package.
Note that existing collections should not be rebuilt with different content. To add new packages into an existing collection, you need to create a new collection containing the new packages and make it dependent on packages from the original collection. The original collection has to be used without changes.
For detailed information on building Software Collections, refer to the Red Hat Software Collections Packaging Guide.
Chapter 3. Usage
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This chapter describes the necessary steps for rebuilding and using Red Hat Software Collections 2.4, and deploying applications that use Red Hat Software Collections.
3.1. Using Red Hat Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
3.1.1. Running an Executable from a Software Collection
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To run an executable from a particular Software Collection, type the following command at a shell prompt:
scl enable software_collection... 'command...'
scl enable software_collection... 'command...'
Or, alternatively, use the following command:
scl enable software_collection... -- command...
scl enable software_collection... -- command...
Replace software_collection with a space-separated list of Software Collections you want to use and command with the command you want to run. For example, to execute a Perl program stored in a file named
hello.pl with the Perl interpreter from the perl516 Software Collection, type:
scl enable rh-perl524 'perl hello.pl' Hello, World!
~]$ scl enable rh-perl524 'perl hello.pl'
Hello, World!
You can execute any command using the
scl utility, causing it to be run with the executables from a selected Software Collection in preference to their possible Red Hat Enterprise Linux system equivalents. For a complete list of Software Collections that are distributed with Red Hat Software Collections, see Table 1.1, “Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Components”.
To start a new shell session with executables from a selected Software Collection in preference to their Red Hat Enterprise Linux equivalents, type the following at a shell prompt:
scl enable software_collection... bash
scl enable software_collection... bash
Replace software_collection with a space-separated list of Software Collections you want to use. For example, to start a new shell session with the python27 and rh-postgresql95 Software Collections as default, type:
scl enable python27 rh-postgresql95 bash
~]$ scl enable python27 rh-postgresql95 bash
The list of Software Collections that are enabled in the current session is stored in the
$X_SCLS environment variable, for instance:
echo $X_SCLS python27 rh-postgresql95
~]$ echo $X_SCLS
python27 rh-postgresql95
For a complete list of Software Collections that are distributed with Red Hat Software Collections, see Table 1.1, “Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Components”.
Software Collections that include system services install corresponding init scripts in the
/etc/rc.d/init.d/ directory. To start such a service in the current session, type the following at a shell prompt as root:
service software_collection-service_name start
service software_collection-service_name start
Replace software_collection with the name of the Software Collection and service_name with the name of the service you want to start. To configure this service to start automatically at boot time, type the following command as
root:
chkconfig software_collection-service_name on
chkconfig software_collection-service_name on
For example, to start the
postgresql service from the rh-postgresql95 Software Collection and enable it in runlevels 2, 3, 4, and 5, type as root:
service rh-postgresql95-postgresql start Starting rh-postgresql95-postgresql service: [ OK ] chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql on
~]# service rh-postgresql95-postgresql start
Starting rh-postgresql95-postgresql service: [ OK ]
~]# chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql on
For more information on how to manage system services in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6, refer to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Deployment Guide. For a complete list of Software Collections that are distributed with Red Hat Software Collections, see Table 1.1, “Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Components”.
3.2. Accessing a Manual Page from a Software Collection
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Every Software Collection contains a general manual page that describes the content of this component. Each manual page has the same name as the component and it is located in the
/opt/rh directory.
To read a manual page for a Software Collection, type the following command:
scl enable software_collection 'man software_collection'
scl enable software_collection 'man software_collection'
Replace software_collection with the particular Red Hat Software Collections component. For example, to display the manual page for rh-mariadb101, type:
scl enable rh-mariadb101 "man rh-mariadb101"
~]$ scl enable rh-mariadb101 "man rh-mariadb101"
In general, you can use one of the following two approaches to deploy an application that depends on a component from Red Hat Software Collections in production:
- Install all required Software Collections and packages manually and then deploy your application, or
- Create a new Software Collection for your application and specify all required Software Collections and other packages as dependencies.
For more information on how to manually install individual Red Hat Software Collections components, see Section 2.2, “Installing Red Hat Software Collections”. For further details on how to use Red Hat Software Collections, see Section 3.1, “Using Red Hat Software Collections”. For a detailed explanation of how to create a custom Software Collection or extend an existing one, read the Red Hat Software Collections Packaging Guide.
3.4. Red Hat Software Collections Container Images
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Container images based on Red Hat Software Collections include applications, daemons, and databases. The images can be run on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Server and Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host. For information about their usage, see Using Red Hat Software Collections Container Images.
The following container images are available with Red Hat Software Collections 2.4:
- rhscl/devtoolset-6-toolchain-rhel7
- rhscl/devtoolset-6-perftools-rhel7
- rhscl/httpd-24-rhel7
- rhscl/nginx-110-rhel7
- rhscl/nodejs-6-rhel7
- rhscl/python-27-rhel7
- rhscl/ruby-24-rhel7
- rhscl/ror-50-rhel7
- rhscl/thermostat-16-agent-rhel7
- rhscl/thermostat-16-storage-rhel7
The following container images are based on Red Hat Software Collections 2.3:
- rhscl/mysql-57-rhel7
- rhscl/perl-524-rhel7
- rhscl/php-70-rhel7
- rhscl/redis-32-rhel7
- rhscl/mongodb-32-rhel7
- rhscl/php-56-rhel7
- rhscl/python-35-rhel7
- rhscl/ruby-23-rhel7
The following container images are based on Red Hat Software Collections 2.2:
- rhscl/devtoolset-4-toolchain-rhel7
- rhscl/devtoolset-4-perftools-rhel7
- rhscl/mariadb-101-rhel7
- rhscl/nginx-18-rhel7
- rhscl/nodejs-4-rhel7
- rhscl/postgresql-95-rhel7
- rhscl/ror-42-rhel7
- rhscl/thermostat-1-agent-rhel7
- rhscl/varnish-4-rhel7
The following container images are based on Red Hat Software Collections 2.0:
- rhscl/mariadb-100-rhel7
- rhscl/mongodb-26-rhel7
- rhscl/mysql-56-rhel7
- rhscl/nginx-16-rhel7
- rhscl/passenger-40-rhel7
- rhscl/perl-520-rhel7
- rhscl/postgresql-94-rhel7
- rhscl/python-34-rhel7
- rhscl/ror-41-rhel7
- rhscl/ruby-22-rhel7
- rhscl/s2i-base-rhel7
Chapter 4. Specifics of Individual Software Collections
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This chapter is focused on the specifics of certain Software Collections and provides additional details concerning these components.
4.1. Red Hat Developer Toolset
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Developer Toolset is designed for developers working on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform. Red Hat Developer Toolset provides current versions of the GNU Compiler Collection, GNU Debugger, and other development, debugging, and performance monitoring tools. Similarly to other Software Collections, an additional set of tools is installed into the
/opt/ directory. These tools are enabled by the user on demand using the supplied scl utility. Similarly to other Software Collections, these do not replace the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system versions of these tools, nor will they be used in preference to those system versions unless explicitly invoked using the scl utility.
For an overview of features, refer to the Main Features section of the Red Hat Developer Toolset Release Notes.
For a complete list of components, see the Red Hat Developer Toolset Components table in the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide.
Note that since Red Hat Developer Toolset 3.1, Red Hat Developer Toolset requires the rh-java-common Software Collection.
4.2. Eclipse 4.6.3
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-eclipse46 Software Collection, available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, includes Eclipse 4.6.3, which is based on the Eclipse Foundation's Neon release train. This integrated development environment was previously available as a part of Red Hat Developer Toolset. Note that the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection requires the rh-java-common Collection.
Eclipse is a powerful development environment that provides tools for each phase of the development process. It integrates a variety of disparate tools into a unified environment to create a rich development experience, provides a fully configurable user interface, and features a pluggable architecture that allows for an extension in a variety of ways. For instance, the Valgrind plug-in allows programmers to perform memory profiling, otherwise performed on the command line, through the Eclipse user interface.
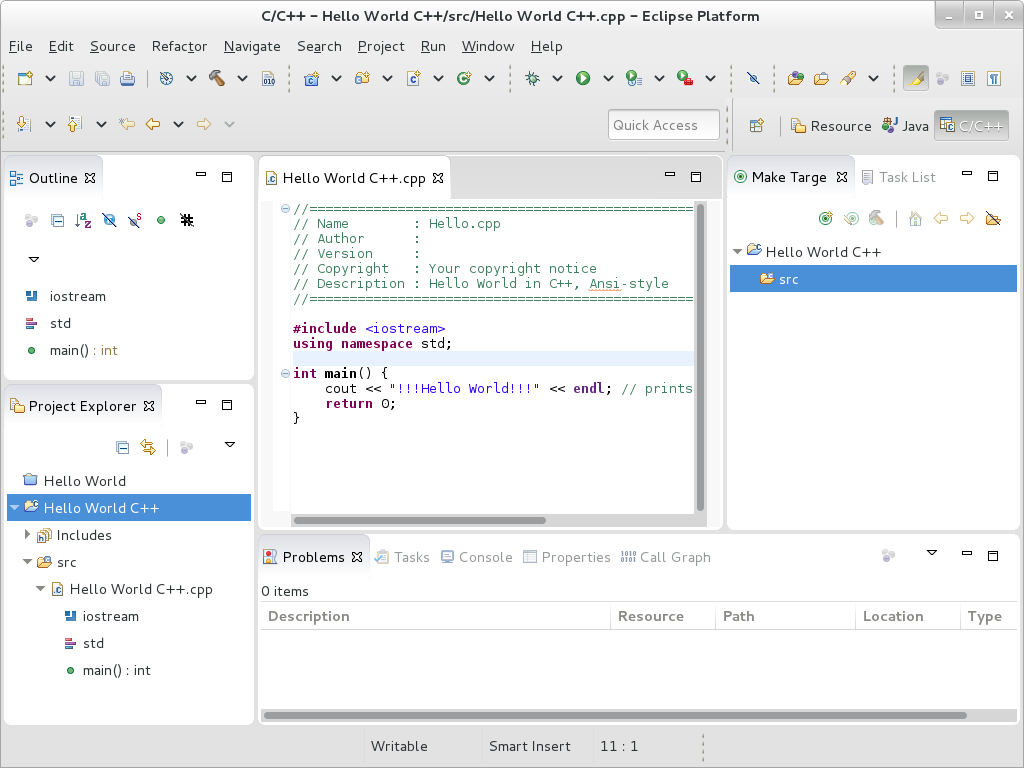
Figure 4.1. Sample Eclipse Session
Eclipse provides a graphical development environment alternative to traditional interaction with command line tools and as such, it is a welcome alternative to developers who do not want to use the command line interface. The traditional, mostly command line-based Linux tools suite (such as
gcc or gdb) and Eclipse offer two distinct approaches to programming.
Note that if you intend to develop applications for Red Hat JBoss Middleware or require support for OpenShift Tools, it is recommended that you use Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio.
| Package | Description |
|---|---|
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-cdt | The C/C++ Development Tooling (CDT), which provides features and plug-ins for development in C and C++. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-changelog | The ChangeLog plug-in, which allows you to create and maintain changelog files. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-egit | EGit, a team provider for Eclipse that provides features and plug-ins for interaction with Git repositories. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-emf | The Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF), which allows you to build applications based on a structured data model. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-epp-logging | The Eclipse error reporting tool. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-gcov | The GCov plug-in, which integrates the GCov test coverage program with Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-gef | The Graphical Editing Framework (GEF), which allows you to create a rich graphical editor from an existing application model. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-gprof | The Gprof plug-in, which integrates the Gprof performance analysis utility with Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-jdt | The Eclipse Java development tools (JDT) plug-in. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-jgit | JGit, a Java implementation of the Git revision control system. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-manpage | The Man Page plug-in, which allows you to view manual pages in Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-mpc | The Eclipse Marketplace Client. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-mylyn | Mylyn, a task management system for Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-oprofile | The OProfile plug-in, which integrates OProfile with Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-pde | The Plugin Development Environment for developing Eclipse plugins. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-perf | The Perf plug-in, which integrates the perf tool with Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-ptp | A subset of the PTP project providing support for synchronized projects. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-pydev | A full featured Python IDE for Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-remote | The Remote Services plug-in, which provides an extensible remote-services framework. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-rpm-editor | The Eclipse Spec File Editor, which allows you to maintain RPM spec files. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-rse | The Remote System Explorer (RSE) framework, which allows you to work with remote systems from Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-systemtap | The SystemTap plug-in, which integrates SystemTap with Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-valgrind | The Valgrind plug-in, which integrates Valgrind with Eclipse. |
| rh-eclipse46-eclipse-webtools | The Eclipse Webtools plug-ins. |
4.2.1. Installing Eclipse
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The Eclipse development environment is provided as a collection of RPM packages. To install the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection, type the following command as
root:
yum install rh-eclipse46
yum install rh-eclipse46
For a list of available components, see Table 4.1, “Eclipse Components Included in the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection”.
Note
The rh-eclipse46 Software Collection fully supports C, C++, and Java development, but does not provide support for the Fortran programming language.
4.2.2. Using Eclipse
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To start the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection, either select → → from the panel, or type the following at a shell prompt:
scl enable rh-eclipse46 eclipse
scl enable rh-eclipse46 eclipse
During its startup, Eclipse prompts you to select a workspace, that is, a directory in which you want to store your projects. You can either use
~/workspace/, which is the default option, or click the button to browse your file system and select a custom directory. Additionally, you can select the Use this as the default and do not ask again check box to prevent Eclipse from displaying this dialog box the next time you run this development environment. When you are done, click the button to confirm the selection and proceed with the startup.
4.2.2.1. Using the Red Hat Developer Toolset Toolchain
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To use the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection with support for the GNU Compiler Collection and binutils from Red Hat Developer Toolset, make sure that the devtoolset-6-toolchain package is installed and run the application as described in Section 4.2.2, “Using Eclipse”. The rh-eclipse46 Collection uses the Red Hat Developer Toolset toolchain by default.
For detailed instructions on how to install the devtoolset-6-toolchain package in your system, see the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide.
Important
If you are working on a project that you previously built with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux version of the GNU Compiler Collection, make sure that you discard all previous build results. To do so, open the project in Eclipse and select → from the menu.
4.2.2.2. Using the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Toolchain
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To use the rh-eclipse46 Software Collection with support for the toolchain distributed with Red Hat Enterprise Linux, change the configuration of the project to use absolute paths to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system versions of
gcc, g++, and as.
To configure Eclipse to explicitly use the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system versions of the tools for the current project, complete the following steps:
- In the C/C++ perspective, choose → from the main menu bar to open the project properties.
- In the menu on the left-hand side of the dialog box, click → .
- Select the Tool Settings tab.
- If you are working on a C project:
- select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/gcc
/usr/bin/gccCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/gcc
/usr/bin/gccCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/as
/usr/bin/asCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you are working on a C++ project:- select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/g++
/usr/bin/g++Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/gcc
/usr/bin/gccCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/g++
/usr/bin/g++Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - select or and change the value of the Command field to:
/usr/bin/as
/usr/bin/asCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Click the button to save the configuration changes.
4.2.3. Additional Resources
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
A detailed description of Eclipse and all its features is beyond the scope of this book. For more information, see the resources listed below.
Installed Documentation
- Eclipse includes a built-in system, which provides extensive documentation for each integrated feature and tool. This greatly decreases the initial time investment required for new developers to become fluent in its use. The use of this Help section is detailed in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Developer Guide linked below.
See Also
- Section 1.3.3, “Changes in Eclipse” provides a comprehensive list of features and improvements over the Eclipse development environment included in the previous release of Red Hat Developer Toolset.
- The Red Hat Developer Toolset chapter in the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide provides an overview of Red Hat Developer Toolset and more information on how to install it on your system.
- The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) chapter in the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide provides information on how to compile programs written in C, C++, and Fortran on the command line.
4.3. Thermostat
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-thermostat16 Software Collection provides a monitoring and instrumentation tool for the OpenJDK HotSpot JVM, with support for monitoring multiple JVM instances. The system is made up of two components: an
Agent, which collects data, and a Client, which allows users to visualize collected data. These components communicate via a storage layer: either directly via MongoDB or indirectly via a Web layer for increased security. A pluggable agent and GUI framework allows for collection and visualization of performance data beyond what is included out of the box.
To install the rh-thermostat16 collection, type the following command as
root:
yum install rh-thermostat16
yum install rh-thermostat16
Note that the rh-thermostat16 Software Collection requires the rh-java-common Collection.
To enable the rh-thermostat16 collection, type the following command at a shell prompt:
scl enable rh-thermostat16 bash
scl enable rh-thermostat16 bash
For more information, refer to the Thermostat User Guide. In order to deploy Thermostat securely, see the Configuration and Administration Guide.
4.4. Ruby on Rails 5.0
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 provides the rh-ruby24 Software Collection together with the rh-ror50 Collection.
To install Ruby on Rails 5.0, type the following command as
root:
yum install rh-ror50
yum install rh-ror50
Installing any package from the rh-ror50 Software Collection automatically pulls in rh-ruby24 and rh-nodejs6 as dependencies.
The rh-nodejs6 Collection is used by certain gems in an asset pipeline to post-process web resources, for example, sass or coffee-script source files. Additionally, the Action Cable framework uses rh-nodejs6 for handling
WebSockets in Rails.
To run the
rails s command without requiring rh-nodejs6, disable the coffee-rails and uglifier gems in the Gemfile.
To run Ruby on Rails without Node.js, run the following command, which will automatically enable rh-ruby24:
Copy to Clipboard
Copied!
Toggle word wrap
Toggle overflow
scl enable rh-ror50 bash
scl enable rh-ror50 bash
To run Ruby on Rails with all features, enable also the rh-nodejs6 Software Collection:
Copy to Clipboard
Copied!
Toggle word wrap
Toggle overflow
scl enable rh-ror50 rh-nodejs6 bash
scl enable rh-ror50 rh-nodejs6 bash
The rh-ror50 Software Collection is supported together with the rh-ruby24 and rh-nodejs6 components.
4.5. MongoDB 3.2
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
To install the rh-mongodb32 collection, type the following command as
root:
yum install rh-mongodb32
yum install rh-mongodb32
Note that the rh-mongodb32 Software Collection requires the rh-java-common Collection.
To run the MongoDB shell utility, type the following command:
scl enable rh-mongodb32 'mongo'
scl enable rh-mongodb32 'mongo'MongoDB 3.2 on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
If you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6, the following instructions apply to your system.
To start the MongoDB daemon, type the following command as
root:
service rh-mongodb32-mongod start
service rh-mongodb32-mongod start
To start the MongoDB daemon on boot, type this command as
root:
chkconfig rh-mongodb32-mongod on
chkconfig rh-mongodb32-mongod on
To start the MongoDB sharding server, type this command as
root:
service rh-mongodb32-mongos start
service rh-mongodb32-mongos start
To start the MongoDB sharding server on boot, type the following command as
root:
chkconfig rh-mongodb32-mongos on
chkconfig rh-mongodb32-mongos on
Note that the MongoDB sharding server does not work unless the user starts at least one configuration server and specifies it in the
mongos.conf file.
MongoDB 3.2 on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
When using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, the following commands are applicable.
To start the MongoDB daemon, type the following command as
root:
systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongod.service
systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongod.service
To start the MongoDB daemon on boot, type this command as
root:
systemctl enable rh-mongodb32-mongod.service
systemctl enable rh-mongodb32-mongod.service
To start the MongoDB sharding server, type the following command as
root:
systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongos.service
systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongos.service
To start the MongoDB sharding server on boot, type this command as
root:
systemctl enable rh-mongodb32-mongos.service
systemctl enable rh-mongodb32-mongos.service
Note that the MongoDB sharding server does not work unless the user starts at least one configuration server and specifies it in the
mongos.conf file.
4.6. Git
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Git is a distributed revision control system with a decentralized architecture. As opposed to centralized version control systems with a client-server model, Git ensures that each working copy of a Git repository is an exact copy with complete revision history. This not only allows you to work on and contribute to projects without the need to have permission to push your changes to their official repositories, but also makes it possible for you to work with no network connection. For detailed information, see the Git chapter in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Developer Guide.
4.7. Maven
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-maven33 Software Collection provides a software project management and comprehension tool. Based on the concept of a project object model (POM), Maven can manage a project's build, reporting, and documentation from a central piece of information.
To install the rh-maven33 Collection, type the following command as
root:
yum install rh-maven33
yum install rh-maven33
To enable this collection, type the following command at a shell prompt:
scl enable rh-maven33 bash
scl enable rh-maven33 bash
Global Maven settings, such as remote repositories or mirrors, can be customized by editing the
/opt/rh/rh-maven33/root/etc/maven/settings.xml file.
For more information about using Maven, refer to the Maven documentation. Usage of plug-ins is described in this section; to find documentation regarding individual plug-ins, see the index of plug-ins.
4.8. Passenger
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The rh-passenger40 Software Collection provides Phusion Passenger, a web and application server designed to be fast, robust and lightweight.
The rh-passenger40 Collection supports multiple versions of Ruby, particularly the ruby193, ruby200, and rh-ruby22 Software Collections together with Ruby on Rails using the ror40 or rh-ror41 Collections. Prior to using Passenger with any of the Ruby Software Collections, install the corresponding package from the rh-passenger40 Collection: the rh-passenger-ruby193, rh-passenger-ruby200, or rh-passenger-ruby22 package.
The rh-passenger40 Software Collection can also be used with Apache httpd from the httpd24 Software Collection. To do so, install the rh-passenger40-mod_passenger package. Refer to the default configuration file
/opt/rh/httpd24/root/etc/httpd/conf.d/passenger.conf for an example of Apache httpd configuration, which shows how to use multiple Ruby versions in a single Apache httpd instance.
Additionally, the rh-passenger40 Software Collection can be used with the nginx 1.6 web server from the nginx16 Software Collection. To use nginx 1.6 with rh-passenger40, you can run Passenger in Standalone mode using the following command in the web appplication's directory:
scl enable nginx16 rh-passenger40 'passenger start'
scl enable nginx16 rh-passenger40 'passenger start'
Alternatively, edit the nginx16 configuration files as described in the upstream Passenger documentation.
Chapter 5. Migration
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This chapter provides information on migrating to versions of components included in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4.
5.1. Migrating to MariaDB 10.1
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 contains MySQL 5.1 as the default MySQL implementation. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 includes MariaDB 5.5 as the default MySQL implementation. MariaDB is a community-developed drop-in replacement for MySQL. MariaDB 10.0 has been available as a Software Collection since Red Hat Software Collections 2.0; Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 is distributed with MariaDB 10.1.
The rh-mariadb101 Software Collection, available for both Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, does not conflict with the mysql or mariadb packages from the core systems, so it is possible to install the rh-mariadb101 Software Collection together with the mysql or mariadb packages. It is also possible to run both versions at the same time, however, the port number and the socket in the
my.cnf files need to be changed to prevent these specific resources from conflicting. Additionally, it is possible to install the rh-mariadb101 Software Collection while the rh-mariadb100 Collection is still installed and even running.
Note that if you are using an MariaDB 5.5, it is necessary to upgrade to the rh-mariadb100 Software Collection first, which is described in the Red Hat Software Collections 2.0 Release Notes.
For more information about MariaDB 10.1, see the upstream documentation about changes in version 10.1 and about upgrading.
Note
The rh-mariadb101 Software Collection supports neither mounting over NFS nor dynamical registering using the
scl register command.
- Galera Cluster, a synchronous multi-master cluster, which is a standard part of MariaDB 10.1. See the Knowledgebase article about setting up Galera Cluster with the rh-mariadb101 Software Collection.
- Since MariaDB 10.1.7, the
SQL_MODEvariable is by default set toNO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USERwhile in earlier versions of MariaDB no default was set. Consequently, theGRANTstatement does not create a user by default. The setting of theSQL_MODEvariable can be changed in the configuration file. See the upstream documentation for details.
Important
Prior to upgrading, back up all your data, including any MariaDB databases.
- Install the rh-mariadb101 Software Collection.
yum install rh-mariadb101-mariadb-server
yum install rh-mariadb101-mariadb-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Inspect the configuration of rh-mariadb101, which is stored in the
/etc/opt/rh/rh-mariadb101/my.cnffile and the/etc/opt/rh/rh-mariadb101/my.cnf.d/directory. Compare it with the configuration of rh-mariadb100 stored in/etc/opt/rh/rh-mariadb100/my.cnfand/etc/opt/rh/rh-mariadb100/my.cnf.d/and adjust it if necessary. - Stop the rh-mariadb100 database server, if it is still running.
service rh-mariadb100-mariadb stop
service rh-mariadb100-mariadb stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - All the data of the rh-mariadb100 Software Collection is stored in the
/var/opt/rh/rh-mariadb100/lib/mysql/directory. Copy the whole content of this directory to/var/opt/rh/rh-mariadb101/lib/mysql/. You can also move the content but remember to back up your data before you continue to upgrade. - Start the rh-mariadb101 database server.
service rh-mariadb101-mariadb start
service rh-mariadb101-mariadb startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Perform the data migration.
scl enable rh-mariadb101 mysql_upgrade
scl enable rh-mariadb101 mysql_upgradeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If therootuser has a non-empty password defined (it should have a password defined), it is necessary to call the mysql_upgrade utility with the-poption and specify the password.scl enable rh-mariadb101 -- mysql_upgrade -p
scl enable rh-mariadb101 -- mysql_upgrade -pCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.2. Migrating to MongoDB 3.2
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 is shipped with MongoDB 3.2, provided by the rh-mongodb32 Software Collection and available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Previously released MongoDB Software Collections, mongodb24 and rh-mongodb26 are available for both Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. See the Red Hat Software Collections 2.0 Release Notes if you need to upgrade to MongoDB 2.6.
Note that when migrating from the rh-mongodb26 to the rh-mongodb32 Software Collection, it is necessary to first upgrade to the 3.0-series release of MongoDB, which is provided by the rh-mongodb30upg Collection.
General Changes
The rh-mongodb32 Software Collection introduces several general changes listed below.
- MongoDB now ships configuration files in the YAML format
- MongoDB server and tools are no longer shipped in a single package; MongoDB tools are packaged in rh-mongodb32-mongo-tools
- Improved MongoDB testsuite provided by the rh-mongodb32-mongodb-test package. For more information about usage, install this package and read the
/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/root/usr/share/mongodb-test/READMEfile.
Compatibility Changes
MongoDB 3.2 includes various minor changes that can affect compatibility with previous versions of MongoDB.
Compatibility Changes in MongoDB 3.0
- Configuration file options changes due to inclusion of additional storage engines
- Data files must correspond to the configured storage engine; if files in the
dbPathdirectory were created by a storage engine other than the current one, an error is returned - Changes due to using the WiredTiger storage engine:
oplogentries generated by versions of MongoDB earlier than 2.2.1 are overwritten - Replica set configuration validation
- The
w:majoritysemantics has been changed so that thew:majorityvalue is satisfied when a majority of the voting members replicates a write operation - The
local.slavescollection has been removed - The FATAL replica set state no longer exists
- The
mongodump,mongorestore,mongoexport,mongoimport,mongofiles, andmongooplogtools must connect to a running MongoDB instance - The MongoDB 2.4 user model has been removed
- The localhost exception has been changed so that it allows to create only the first user on the admin database
- The
db.addUser()function has been removed; usedb.createUser()anddb.updateUser()instead - TLS/SSL changes
- The
mongoshell versions earlier than 3.0 are not compatible with 3.0 deployments of MongoDB - Index changes
- Direct access to the
system.indexesandsystem.namespacescollections has been deprecated - The following commands have been deprecated:
closeAllDatabases,getoptime,text,indexStats,db.collection.getIndexStats(), anddb.collection.indexStats() - The
DateandTimestampdata types are no longer equivalent for comparison purposes
For details regarding compatibility changes in Mongodb 3.0, refer to the upstream release notes.
Compatibility Changes in MongoDB 3.2
- The WiredTiger storage engine is now the default one
- The JavaScript engine has been changed from V8 to SpiderMonkey
- Creation of version 0 indexes is now disallowed
- Aggregation compatibility changes
For detailed compatibility changes in MongoDB 3.2, see the upstream release notes.
Note that once you have upgraded to MongoDB 3.2 and started using new features, you cannot downgrade to any earlier version.
Important
Before migrating from the rh-mongodb26 to the rh-mongodb32 Software Collection, back up all your data, including any MongoDB databases, which are by default stored in the
/var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb26/lib/mongodb/ directory.
To upgrade to the rh-mongodb32 Software Collection, perform the following steps.
- Install the MongoDB servers and shells from the rh-mongodb30upg and rh-mongodb32 Software Collections:
yum install rh-mongodb30upg rh-mongodb30upg-mongodb rh-mongodb32 rh-mongodb32-mongodb
~]# yum install rh-mongodb30upg rh-mongodb30upg-mongodb rh-mongodb32 rh-mongodb32-mongodbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Connect the
mongoshell from the rh-mongodb26 Collection to your MongoDB 2.6 server (for example, running onlocalhost, port27017).scl enable rh-mongodb26 'mongo --host localhost --port 27017 admin'
~]$ scl enable rh-mongodb26 'mongo --host localhost --port 27017 admin'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the
mongoshell, check your data set for compatibility issues mentioned above and fix the ones that affect your application. - Stop the MongoDB 2.6 server:
systemctl stop rh-mongodb26-mongod.service
~]# systemctl stop rh-mongodb26-mongod.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use theservice rh-mongodb26-mongodb stopcommand if you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. - Copy your data to the new location:
cp -a /var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb26/lib/mongodb/* /var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/lib/mongodb
~]# cp -a /var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb26/lib/mongodb/* /var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/lib/mongodbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Change the
dbpathvariable in the/etc/opt/rh/rh-mongodb30upg/mongod.conffile to/var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/lib/mongodb/. - Start the MongoDB server from the rh-mongodb30upg Software Collection:
systemctl start rh-mongodb30upg-mongod.service
~]# systemctl start rh-mongodb30upg-mongod.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use theservice rh-mongodb30upg-mongodb startcommand if you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. - Connect the
mongoshell from the rh-mongodb32 Collection to your MongoDB 3.0 server (for example, running onlocalhost, port27017).scl enable rh-mongodb30upg 'mongo --host localhost --port 27017 admin'
~]$ scl enable rh-mongodb30upg 'mongo --host localhost --port 27017 admin'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the
mongoshell, check your data set for compatibility issues mentioned above and fix the ones that affect your application. - Stop the MongoDB 3.0 server.
systemctl stop rh-mongodb30upg-mongod.service
~]# systemctl stop rh-mongodb30upg-mongod.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use theservice rh-mongodb30upg-mongodb stopcommand if you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. - Configure the
rh-mongodb32-mongoddaemon in the/etc/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/mongod.conffile. - MongoDB 3.2 has the new default storage engine, WiredTiger, which introduces performance improvements. To be able to run the MongoDB server with old data, configure the
rh-mongodb32-mongoddaemon to use the old storage engine. Uncomment theengineproperty in thestoragesection in the/etc/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/mongod.conffile and change its value tommapv1. - Start the MongoDB 3.2 server.
systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongod.service
~]# systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongod.serviceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use theservice rh-mongodb32-mongodb startcommand if you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. - If you want to use the WiredTiger storage engine, you have to perform additional migration steps described in the MongoDB documentation.
yum install rh-mongodb32-mongo-tools scl enable rh-mongodb32 'mongodump --out ~/mongodb.dump' systemctl stop rh-mongodb32-mongod.service rm -rf /var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/lib/mongodb/*
~]# yum install rh-mongodb32-mongo-tools ~]$ scl enable rh-mongodb32 'mongodump --out ~/mongodb.dump' ~]# systemctl stop rh-mongodb32-mongod.service ~]# rm -rf /var/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/lib/mongodb/*Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change theengineproperty in the/etc/opt/rh/rh-mongodb32/mongod.conftowiredTiger. Use theservice rh-mongodb32-mongodb stopcommand if you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongod.service scl enable rh-mongodb32 'mongorestore ~/mongodb.dump'
~]# systemctl start rh-mongodb32-mongod.service ~]$ scl enable rh-mongodb32 'mongorestore ~/mongodb.dump'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use theservice rh-mongodb32-mongodb startcommand if you are using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.
For detailed information about upgrading, see the upstream MongoDB 3.0 and MongoDB 3.2 release notes.
For information about upgrading a Replica Set, see the upstream MongoDB Manual.
For information about upgrading a Sharded Cluster, see the upstream MongoDB Manual.
5.3. Migrating to MySQL 5.7
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 contains MySQL 5.1 as the default MySQL implementation. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 includes MariaDB 5.5 as the default MySQL implementation. In addition to these basic versions, MySQL 5.6 has been available as a Software Collection for both Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 since Red Hat Software Collections 2.0.
The rh-mysql57 Software Collection, available for both Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, conflicts neither with the mysql or mariadb packages from the core systems nor with the rh-mysql56 Software Collection, so it is possible to install the rh-mysql57 Software Collection together with the mysql, mariadb, or rh-mysql56 packages. It is also possible to run multiple versions at the same time; however, the port number and the socket in the
my.cnf files need to be changed to prevent these specific resources from conflicting.
Note that it is possible to upgrade to MySQL 5.7 only from MySQL 5.6. If you need to upgrade from an earlier version, upgrade to MySQL 5.6 first. Instructions how to upgrade to MySQL 5.6 are available in the Red Hat Software Collections 2.2 Release Notes.
- The mysql-bench subpackage is not included in the rh-mysql57 Software Collection.
- Since MySQL 5.7.7, the default SQL mode includes
NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER. Therefore it is necessary to create MySQL accounts using theCREATE USERstatement because theGRANTstatement no longer creates a user by default. See the upstream documentation for details.
To find out about more detailed changes in MySQL 5.7 compared to earlier versions, see the upstream documentation: What Is New in MySQL 5.7 and Changes Affecting Upgrades to MySQL 5.7.
5.3.2. Upgrading to the rh-mysql57 Software Collection
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Important
Prior to upgrading, back-up all your data, including any MySQL databases.
- Install the rh-mysql57 Software Collection.
yum install rh-mysql57-mysql-server
yum install rh-mysql57-mysql-serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Inspect the configuration of rh-mysql57, which is stored in the
/etc/opt/rh/rh-mysql57/my.cnffile and the/etc/opt/rh/rh-mysql57/my.cnf.d/directory. Compare it with the configuration of rh-mysql56 stored in/etc/opt/rh/rh-mysql56/my.cnfand/etc/opt/rh/rh-mysql56/my.cnf.d/and adjust it if necessary. - Stop the rh-mysql56 database server, if it is still running.
service rh-mysql56-mysqld stop
service rh-mysql56-mysqld stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - All data of the rh-mysql56 Software Collection is stored in the
/var/opt/rh/rh-mysql56/lib/mysql/directory. Copy the whole content of this directory to/var/opt/rh/rh-mysql57/lib/mysql/. You can also move the content but remember to back up your data before you continue to upgrade. - Start the rh-mysql57 database server.
service rh-mysql57-mysqld start
service rh-mysql57-mysqld startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Perform the data migration.
scl enable rh-mysql57 mysql_upgrade
scl enable rh-mysql57 mysql_upgradeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If therootuser has a non-empty password defined (it should have a password defined), it is necessary to call the mysql_upgrade utility with the-poption and specify the password.scl enable rh-mysql57 -- mysql_upgrade -p
scl enable rh-mysql57 -- mysql_upgrade -pCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.4. Migrating to PostgreSQL 9.5
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 is distributed with PostgreSQL 9.5, which can be safely installed on the same machine in parallel with PostgreSQL 8.4 from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6, PostgreSQL 9.2 from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 or Red Hat Software Collections 1, or PostgreSQL 9.4 from Red Hat Software Collections 2. It is also possible to run more than one version of PostgreSQL on a machine at the same time, but you need to use different ports or IP addresses and adjust SELinux policy.
The most notable changes between PostgreSQL 9.4 and PostgreSQL 9.5 are desribed in the upstream release notes for versions 9.5, 9.5.1, and 9.5.2.
The following table provides an overview of different paths in a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system version of PostgreSQL (postgresql) and in the postgresql92, rh-postgresql94, and rh-postgresql95 Software Collections. Note that the paths of PostgreSQL 8.4 distributed with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and the system version of PostgreSQL 9.2 shipped with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 are the same.
| Content | postgresql | postgresql92 | rh-postgresql94 | rh-postgresql95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Executables | /usr/bin/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/bin/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/bin/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/bin/ |
| Libraries | /usr/lib64/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/lib64/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/lib64/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/lib64/ |
| Documentation | /usr/share/doc/postgresql/html/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql/html/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql/html/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql/html/ |
| PDF documentation | /usr/share/doc/postgresql-docs/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql-docs/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql-docs/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql-docs/ |
| Contrib documentation | /usr/share/doc/postgresql-contrib/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql-contrib/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql-contrib/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/share/doc/postgresql-contrib/ |
| Source | not installed | not installed | not installed | not installed |
| Data | /var/lib/pgsql/data/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/var/lib/pgsql/data/ | /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/lib/pgsql/data/ | /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/ |
| Backup area | /var/lib/pgsql/backups/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/var/lib/pgsql/backups/ | /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/lib/pgsql/backups/ | /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/backups/ |
| Templates | /usr/share/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/share/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/share/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/share/pgsql/ |
| Procedural Languages | /usr/lib64/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/lib64/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/lib64/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/lib64/pgsql/ |
| Development Headers | /usr/include/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/include/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/include/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/include/pgsql/ |
| Other shared data | /usr/share/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/share/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/share/pgsql/ | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/share/pgsql/ |
| Regression tests | /usr/lib64/pgsql/test/regress/ (in the -test package) | /opt/rh/postgresql92/root/usr/lib64/pgsql/test/regress/ (in the -test package) | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/root/usr/lib64/pgsql/test/regress/ (in the -test package) | /opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/lib64/pgsql/test/regress/ (in the -test package) |
For detailed changes, see the upstream PostgreSQL 9.5 Release Notes. For changes between PostgreSQL 8.4 and PostgreSQL 9.2, refer to the Red Hat Software Collections 1.2 Release Notes. Notable changes between PostgreSQL 9.2 and PostgreSQL 9.4 are described in Red Hat Software Collections 2.0 Release Notes.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 includes PostgreSQL 8.4, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 is distributed with PostgreSQL 9.2. To migrate your data from a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system version of PostgreSQL to the rh-postgresql95 Software Collection, you can either perform a fast upgrade using the
pg_upgrade tool (recommended), or dump the database data into a text file with SQL commands and import it in the new database. Note that the second method is usually significantly slower and may require manual fixes; see the PostgreSQL documentation for more information about this upgrade method. The following procedures are applicable for both Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 system versions of PostgreSQL.
Important
Before migrating your data from a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system version of PostgreSQL to PostgreSQL 9.5, make sure that you back up all your data, including the PostgreSQL database files, which are by default located in the
/var/lib/pgsql/data/ directory.
Procedure 5.1. Fast Upgrade Using the pg_upgrade Tool
To perform a fast upgrade of your PostgreSQL server, complete the following steps:
- Stop the old PostgreSQL server to ensure that the data is not in an inconsistent state. To do so, type the following at a shell prompt as
root:service postgresql stop
service postgresql stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the server is not running, type:service postgresql status
service postgresql statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify that the old directory
/var/lib/pgsql/data/exists:file /var/lib/pgsql/data/
file /var/lib/pgsql/data/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow and back up your data. - Verify that the new data directory
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/does not exist:file /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/
file /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you are running a fresh installation of PostgreSQL 9.5, this directory should not be present in your system. If it is, back it up by running the following command asroot:mv /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data{,-scl-backup}mv /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data{,-scl-backup}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Upgrade the database data for the new server by running the following command as
root:scl enable rh-postgresql95 -- postgresql-setup --upgrade
scl enable rh-postgresql95 -- postgresql-setup --upgradeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, you can use the/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/bin/postgresql-setup --upgradecommand.Note that you can use the--upgrade-fromoption for upgrade from different versions of PostgreSQL. The list of possible upgrade scenarios is available using the--upgrade-idsoption.It is recommended that you read the resulting/var/lib/pgsql/upgrade_rh-postgresql95-postgresql.loglog file to find out if any problems occurred during the upgrade. - Start the new server as
root:service rh-postgresql95-postgresql start
service rh-postgresql95-postgresql startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow It is also advised that you run theanalyze_new_cluster.shscript as follows:su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 ~/analyze_new_cluster.sh'
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 ~/analyze_new_cluster.sh'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optionally, you can configure the PostgreSQL 9.5 server to start automatically at boot time. To disable the old system PostgreSQL server, type the following command as
root:chkconfig postgresql off
chkconfig postgresql offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To enable the PostgreSQL 9.5 server, type asroot:chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql on
chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If your configuration differs from the default one, make sure to update configuration files, especially the
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.confconfiguration file. Otherwise only thepostgresuser will be allowed to access the database.
Procedure 5.2. Performing a Dump and Restore Upgrade
To perform a dump and restore upgrade of your PostgreSQL server, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that the old PostgreSQL server is running by typing the following at a shell prompt as
root:service postgresql start
service postgresql startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Dump all data in the PostgreSQL database into a script file. As
root, type:su - postgres -c 'pg_dumpall > ~/pgdump_file.sql'
su - postgres -c 'pg_dumpall > ~/pgdump_file.sql'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the old server by running the following command as
root:service postgresql stop
service postgresql stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Initialize the data directory for the new server as
root:scl enable rh-postgresql95-postgresql -- postgresql-setup --initdb
scl enable rh-postgresql95-postgresql -- postgresql-setup --initdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the new server as
root:service rh-postgresql95-postgresql start
service rh-postgresql95-postgresql startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Import data from the previously created SQL file:
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 "psql -f ~/pgdump_file.sql postgres"'
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 "psql -f ~/pgdump_file.sql postgres"'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optionally, you can configure the PostgreSQL 9.5 server to start automatically at boot time. To disable the old system PostgreSQL server, type the following command as
root:chkconfig postgresql off
chkconfig postgresql offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To enable the PostgreSQL 9.5 server, type asroot:chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql on
chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If your configuration differs from the default one, make sure to update configuration files, especially the
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.confconfiguration file. Otherwise only thepostgresuser will be allowed to access the database.
To migrate your data from the rh-postgresql94 Software Collection to the rh-postgresql95 Collection included in Red Hat Software Collections 2.4, you can either perform a fast upgrade using the
pg_upgrade tool (recommended), or dump the database data into a text file with SQL commands and import it in the new database. Note that the second method is usually significantly slower and may require manual fixes; see the PostgreSQL documentation for more information about this upgrade method.
Important
Before migrating your data from PostgreSQL 9.4 to PostgreSQL 9.5, make sure that you back up all your data, including the PostgreSQL database files, which are by default located in the
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/lib/pgsql/data/ directory.
Procedure 5.3. Fast Upgrade Using the pg_upgrade Tool
To perform a fast upgrade of your PostgreSQL server, complete the following steps:
- Stop the old PostgreSQL server to ensure that the data is not in an inconsistent state. To do so, type the following at a shell prompt as
root:service rh-postgresql94-postgresql stop
service rh-postgresql94-postgresql stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To verify that the server is not running, type:service rh-postgresql94-postgresql status
service rh-postgresql94-postgresql statusCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify that the old directory
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/lib/pgsql/data/exists:file /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/lib/pgsql/data/
file /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql94/lib/pgsql/data/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow and back up your data. - Verify that the new data directory
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/does not exist:file /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/
file /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you are running a fresh installation of PostgreSQL 9.5, this directory should not be present in your system. If it is, back it up by running the following command asroot:mv /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data{,-scl-backup}mv /var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data{,-scl-backup}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Upgrade the database data for the new server by running the following command as
root:scl enable rh-postgresql95 -- postgresql-setup --upgrade --upgrade-from=rh-postgresql94-postgresql
scl enable rh-postgresql95 -- postgresql-setup --upgrade --upgrade-from=rh-postgresql94-postgresqlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, you can use the/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/root/usr/bin/postgresql-setup --upgrade --upgrade-from=rh-postgresql94-postgresqlcommand.Note that you can use the--upgrade-fromoption for upgrading from different versions of PostgreSQL. The list of possible upgrade scenarios is available using the--upgrade-idsoption.It is recommended that you read the resulting/var/lib/pgsql/upgrade_rh-postgresql95-postgresql.loglog file to find out if any problems occurred during the upgrade. - Start the new server as
root:service rh-postgresql95-postgresql start
service rh-postgresql95-postgresql startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow It is also advised that you run theanalyze_new_cluster.shscript as follows:su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 ~/analyze_new_cluster.sh'
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 ~/analyze_new_cluster.sh'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optionally, you can configure the PostgreSQL 9.5 server to start automatically at boot time. To disable the old PostgreSQL 9.4 server, type the following command as
root:chkconfig rh-postgresql94-postgreqsql off
chkconfig rh-postgresql94-postgreqsql offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To enable the PostgreSQL 9.5 server, type asroot:chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql on
chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If your configuration differs from the default one, make sure to update configuration files, especially the
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.confconfiguration file. Otherwise only thepostgresuser will be allowed to access the database.
Procedure 5.4. Performing a Dump and Restore Upgrade
To perform a dump and restore upgrade of your PostgreSQL server, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that the old PostgreSQL server is running by typing the following at a shell prompt as
root:service rh-postgresql94-postgresql start
service rh-postgresql94-postgresql startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Dump all data in the PostgreSQL database into a script file. As
root, type:su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql94 "pg_dumpall > ~/pgdump_file.sql"'
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql94 "pg_dumpall > ~/pgdump_file.sql"'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Stop the old server by running the following command as
root:service rh-postgresql94-postgresql stop
service rh-postgresql94-postgresql stopCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Initialize the data directory for the new server as
root:scl enable rh-postgresql95-postgresql -- postgresql-setup --initdb
scl enable rh-postgresql95-postgresql -- postgresql-setup --initdbCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the new server as
root:service rh-postgresql95-postgresql start
service rh-postgresql95-postgresql startCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Import data from the previously created SQL file:
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 "psql -f ~/pgdump_file.sql postgres"'
su - postgres -c 'scl enable rh-postgresql95 "psql -f ~/pgdump_file.sql postgres"'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Optionally, you can configure the PostgreSQL 9.5 server to start automatically at boot time. To disable the old PostgreSQL 9.4 server, type the following command as
root:chkconfig rh-postgresql94-postgresql off
chkconfig rh-postgresql94-postgresql offCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To enable the PostgreSQL 9.5 server, type asroot:chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql on
chkconfig rh-postgresql95-postgresql onCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - If your configuration differs from the default one, make sure to update configuration files, especially the
/var/opt/rh/rh-postgresql95/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.confconfiguration file. Otherwise only thepostgresuser will be allowed to access the database.
If you need to migrate from the postgresql92 Software Collection, refer to Red Hat Software Collections 2.0 Release Notes; the procedure is the same, you just need to adjust the version of the new Collection.
5.5. Migrating to nginx 1.10
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The root directory for the rh-nginx110 Software Collection is located in
/opt/rh/rh-nginx110/root/. The error log is stored in /var/opt/rh/rh-nginx110/log/nginx by default, and the init script is called rh-nginx110-nginx.
Configuration files are stored in the
/etc/opt/rh/rh-nginx110/nginx/ directory. Configuration files in nginx 1.10 have the same syntax and largely the same format as previous nginx Software Collections, with some minor changes:
- Duplicate
http,mail, andstreamblocks are now disallowed. - Some deprecated directives are no longer supported.
A new directory,
/etc/opt/rh/rh-nginx110/nginx/default.d/, has also been introduced. Configuration files (with a .conf extension) in this directory are included in the default server block configuration for port 80.
Important
Before upgrading from nginx 1.8 to nginx 1.10, back up all your data, including web pages and configuration files located in the
/opt/rh/nginx18/root/ tree.
If you have made any specific changes, such as changing configuration files or setting up web applications, in the
/opt/rh/nginx18/root/ tree, replicate those changes in the new /opt/rh/rh-nginx110/root/ and /etc/opt/rh/rh-nginx110/nginx/ directories, too.
You can use this procedure to upgrade directly from nginx 1.4 or nginx 1.6 to nginx 1.8 or nginx 1.10. Use the appropriate paths in this case.
For the official nginx documentation, refer to http://nginx.org/en/docs/.
Chapter 6. Additional Resources
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
This chapter provides references to other relevant sources of information about Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
6.1. Red Hat Product Documentation
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
The following documents are directly or indirectly relevant to this book:
- Red Hat Software Collections 2.4 Packaging Guide — The Packaging Guide for Red Hat Software Collections explains the concept of Software Collections, documents the
sclutility, and provides a detailed explanation of how to create a custom Software Collection or extend an existing one. - Red Hat Developer Toolset 6.1 Release Notes — The Release Notes for Red Hat Developer Toolset document known problems, possible issues, changes, and other important information about this Software Collection.
- Red Hat Developer Toolset 6.1 User Guide — The User Guide for Red Hat Developer Toolset contains more information about installing and using this Software Collection.
- Using Red Hat Software Collections Container Images — This book provides information on how to use container images based on Red Hat Software Collections. The available container images include applications, daemons, databases, as well as the Red Hat Developer Toolset container images. The images can be run on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Server and Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host.
- Get Started with Docker Formatted Container Images — This guide contains a comprehensive overview of information about building and using docker-formatted container images on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host.
- Using and Configuring Red Hat Subscription Manager — The Using and Configuring Red Hat Subscription Manager book provides detailed information on how to register Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems, manage subscriptions, and view notifications for the registered systems.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Deployment Guide — The Deployment Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 provides relevant information regarding the deployment, configuration, and administration of this system.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 System Administrator's Guide — The System Administrator's Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 provides information on deployment, configuration, and administration of this system.
6.2. Red Hat Developer Blog
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Developer Blog content is directed to designers and developers of applications based on Red Hat technologies. It contains links to product team blogs and other relevant internal and external resources. Its goal is to inform and engage the developer community with up-to-date information, best practices, opinion, product and program announcements as well as pointers to sample code and other resources.
6.3. Red Hat Developers Portal
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Red Hat Developers Portal provides an overview of Red Hat Software Collections and offers getting started content, including Hello world! examples.
Appendix A. Revision History
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
| Revision History | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Revision 2.4-4 | Tue Dec 18 2018 | ||
| |||
| Revision 2.4-3 | Wed Apr 26 2017 | ||
| |||
| Revision 2.4-2 | Thu Apr 06 2017 | ||
| |||
| Revision 2.4-1 | Wed Apr 05 2017 | ||
| |||
Legal Notice
复制链接链接已复制到粘贴板!
Copyright © 2017-2018 Red Hat, Inc.
This document is licensed by Red Hat under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you distribute this document, or a modified version of it, you must provide attribution to Red Hat, Inc. and provide a link to the original. If the document is modified, all Red Hat trademarks must be removed.
Red Hat, as the licensor of this document, waives the right to enforce, and agrees not to assert, Section 4d of CC-BY-SA to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of Joyent. Red Hat Software Collections is not formally related to or endorsed by the official Joyent Node.js open source or commercial project.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation's permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.