Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
3.2. Shared JDBC Master/Slave
Overview
- The shared database is a single point of failure. This disadvantage can be mitigated by using a database with built in high availability(HA) functionality. The database will handle replication and fail over of the data store.
- You cannot enable high speed journaling. This has a significant impact on performance.
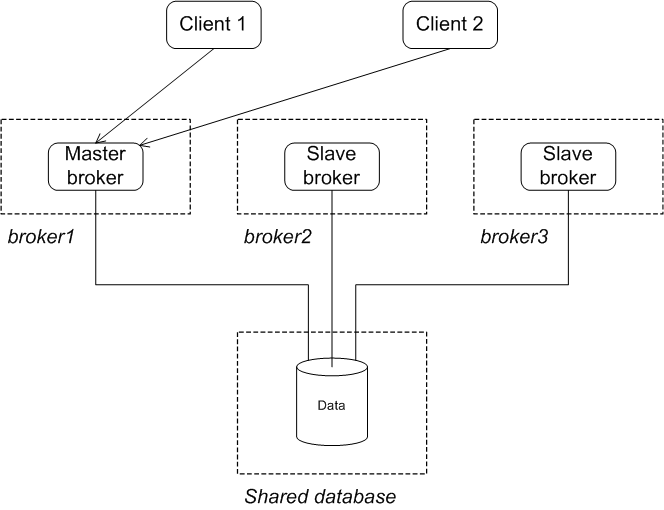
Initial state
Figure 3.4. JDBC Master/Slave Initial State
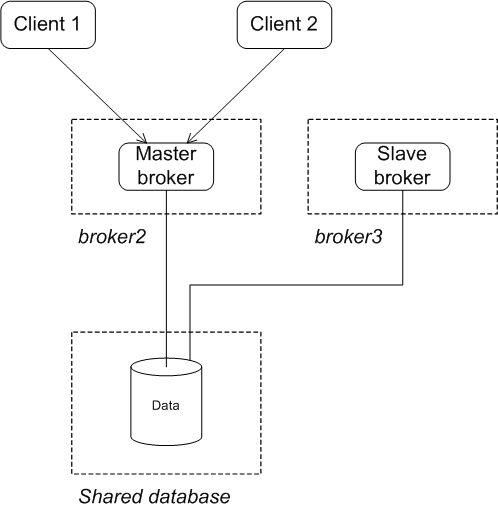
After failure of the master
Figure 3.5. JDBC Master/Slave after Master Failure
Configuring the brokers
Example 3.3. JDBC Master/Slave Broker Configuration
schedulerDirectory as shown below:
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core” schedulerSupport="true" schedulerDirectory="{activemq.data}/broker/scheduler”/>
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core” schedulerSupport="true" schedulerDirectory="{activemq.data}/broker/scheduler”/>
Configuring the clients
broker1, broker2, and broker3.
Example 3.4. Client URL for a Shared JDBC Master/Slave Group
failover:(tcp://broker1:61616,tcp://broker2:61616,tcp://broker3:61616)
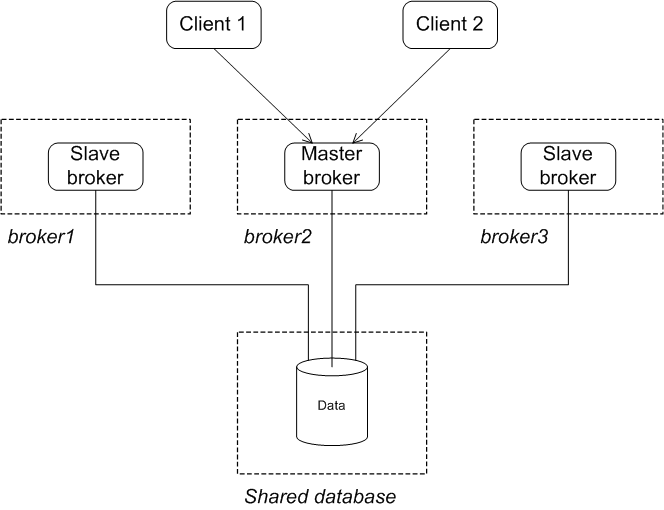
failover:(tcp://broker1:61616,tcp://broker2:61616,tcp://broker3:61616)Reintroducing a failed node
Figure 3.6. JDBC Master/Slave after Master Restart