Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 21. Enabling Tracing
This chapter is describing a feature which is currently in preview. Please provide your feedback while we’re continuing to work on this.
This chapter explains how you can enable and configure distributed tracing in Red Hat build of Keycloak by utilizing OpenTelemetry (OTel). Tracing allows for detailed monitoring of each request’s lifecycle, which helps quickly identify and diagnose issues, leading to more efficient debugging and maintenance.
It also provides valuable insights into performance bottlenecks and can help optimize the system’s overall efficiency. Red Hat build of Keycloak uses a supported Quarkus OTel extension that provides smooth integration and exposure of application traces.
21.1. Enable tracing
It is possible to enable exposing traces using the build time option tracing-enabled, and enabling opentelemetry feature as follows:
bin/kc.[sh|bat] start --tracing-enabled=true --features=opentelemetry
bin/kc.[sh|bat] start --tracing-enabled=true --features=opentelemetry
By default, the trace exporters send out data in batches, using the gRPC protocol and endpoint http://localhost:4317.
The default service name is keycloak, specified via the tracing-service-name property, which takes precedence over service.name defined in the tracing-resource-attributes property.
For more information about resource attributes that can be provided via the tracing-resource-attributes property, see the Quarkus OpenTelemetry Resource guide.
For more tracing settings, see all possible configurations below.
21.2. Development setup
In order to see the captured Red Hat build of Keycloak traces, the basic setup with leveraging the Jaeger tracing platform might be used. For development purposes, the Jaeger-all-in-one can be used to see traces as easily as possible.
Jaeger-all-in-one includes the Jaeger agent, an OTel collector, and the query service/UI. You do not need to install a separate collector, as you can directly send the trace data to Jaeger.
podman run --name jaeger \ -p 16686:16686 \ -p 4317:4317 \ -p 4318:4318 \ jaegertracing/all-in-one
podman run --name jaeger \
-p 16686:16686 \
-p 4317:4317 \
-p 4318:4318 \
jaegertracing/all-in-one21.2.1. Exposed ports
-
:16686- Jaeger UI -
:4317- OpenTelemetry Protocol gRPC receiver (default) -
:4318- OpenTelemetry Protocol HTTP receiver
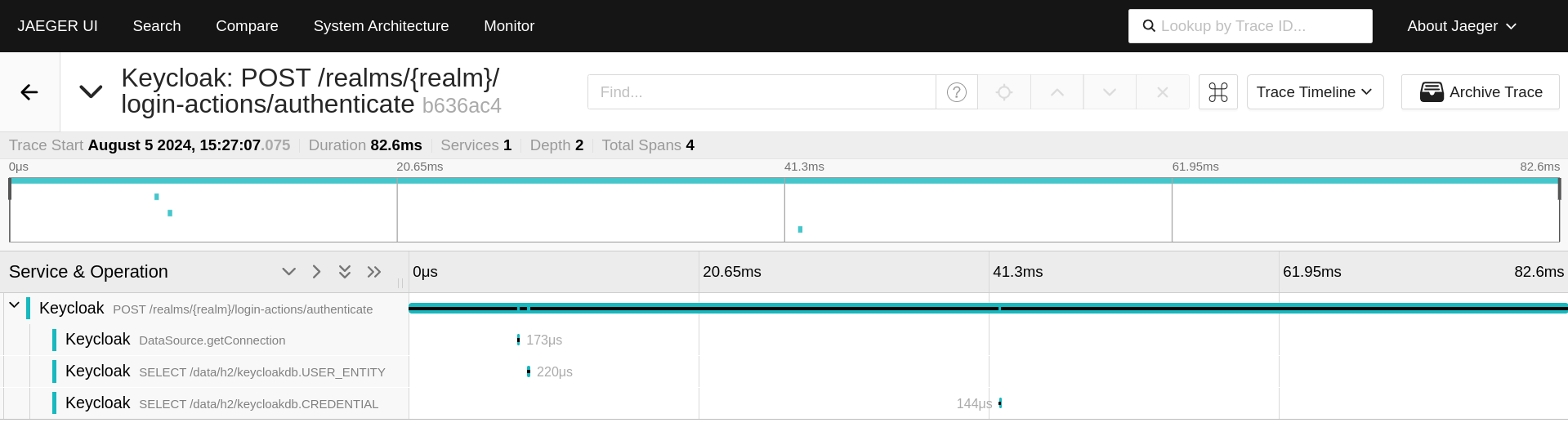
You can visit the Jaeger UI on http://localhost:16686/ to see the tracing information. The Jaeger UI might look like this with an arbitrary Red Hat build of Keycloak trace:
21.3. Traces in logs
When tracing is enabled, the trace information is included in the log messages of all enabled log handlers (see more in Configuring logging). It can be useful for associating log events to request execution, which might provide better traceability and debugging. All log lines originating from the same request will have the same traceId in the log.
The log message also contains a sampled flag, which relates to the sampling described below and indicates whether the span was sampled - sent to the collector.
The format of the log records may start as follows:
2024-08-05 15:27:07,144 traceId=b636ac4c665ceb901f7fdc3fc7e80154, parentId=d59cea113d0c2549, spanId=d59cea113d0c2549, sampled=true WARN [org.keycloak.events] ...
2024-08-05 15:27:07,144 traceId=b636ac4c665ceb901f7fdc3fc7e80154, parentId=d59cea113d0c2549, spanId=d59cea113d0c2549, sampled=true WARN [org.keycloak.events] ...21.3.1. Hide trace info in logs
You can hide tracing information in specific log handlers by specifying their associated Red Hat build of Keycloak option log-<handler-name>-include-trace, where <handler-name> is the name of the log handler. For instance, to disable trace info in the console log, you can turn it off as follows:
bin/kc.[sh|bat] start --tracing-enabled=true --features=opentelemetry --log=console --log-console-include-trace=false
bin/kc.[sh|bat] start --tracing-enabled=true --features=opentelemetry --log=console --log-console-include-trace=false
When you explicitly override the log format for the particular log handlers, the *-include-trace options do not have any effect, and no tracing is included.
21.4. Sampling
Sampler decides whether a trace should be discarded or forwarded, effectively reducing overhead by limiting the number of collected traces sent to the collector. It helps manage resource consumption, which leads to avoiding the huge storage costs of tracing every single request and potential performance penalty.
For a production-ready environment, sampling should be properly set to minimize infrastructure costs.
Red Hat build of Keycloak supports several built-in OpenTelemetry samplers, such as:
- always_on
- always_off
- traceidratio (default)
- parentbased_always_on
- parentbased_always_off
- parentbased_traceidratio
The used sampler can be changed via the tracing-sampler-type property.
21.4.1. Default sampler
The default sampler for Red Hat build of Keycloak is traceidratio, which controls the rate of trace sampling based on a specified ratio configurable via the tracing-sampler-ratio property.
21.4.1.1. Trace ratio
The default trace ratio is 1.0, which means all traces are sampled - sent to the collector. The ratio is a floating number in the range (0,1]. For instance, when the ratio is 0.1, only 10% of the traces are sampled.
For a production-ready environment, the trace ratio should be a smaller number to prevent the massive cost of trace store infrastructure and avoid performance overhead.
21.4.1.2. Rationale
The sampler makes its own sampling decisions based on the current ratio of sampled spans, regardless of the decision made on the parent span, as with using the parentbased_traceidratio sampler.
The parentbased_traceidratio sampler could be the preferred default type as it ensures the sampling consistency between parent and child spans. Specifically, if a parent span is sampled, all its child spans will be sampled as well - the same sampling decision for all. It helps to keep all spans together and prevents storing incomplete traces.
However, it might introduce certain security risks leading to DoS attacks. External callers can manipulate trace headers, parent spans can be injected, and the trace store can be overwhelmed. Proper HTTP headers (especially tracestate) filtering and adequate measures of caller trust would need to be assessed.
For more information, see the W3C Trace context document.
21.5. Tracing in Kubernetes environment
When the tracing is enabled when using the Red Hat build of Keycloak Operator, certain information about the deployment is propagated to the underlying containers.
There is no support for tracing configuration in Red Hat build of Keycloak CR yet, so the additionalOptions can be used to the tracing-enabled property and other tracing options.
You can filter out the required traces in your tracing backend based on their tags:
-
service.name- Red Hat build of Keycloak deployment name -
k8s.namespace.name- Namespace -
host.name- Pod name
Red Hat build of Keycloak Operator automatically sets the KC_TRACING_SERVICE_NAME and KC_TRACING_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES environment variables for each Red Hat build of Keycloak container included in pods it manages.
21.6. Relevant options
| Value | |
|---|---|
|
Available only when Console log handler and Tracing is activated |
|
|
Available only when File log handler and Tracing is activated |
|
|
Available only when Syslog handler and Tracing is activated |
|
|
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled |
|
| 🛠
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature is enabled |
|
|
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled | (default) |
| 🛠
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled |
|
|
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled |
|
|
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled | |
|
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled | (default) |
| 🛠
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled |
|
|
Available only when 'opentelemetry' feature and Tracing is enabled | (default) |