Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 1. Eclipse 4.19
Red Hat Developer Tools on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 is an offering for developers on the RHEL platform that includes Eclipse 4.19, which is based on the Eclipse Foundation’s 2021-03 release train.
The Eclipse development environment provides tools for each phase of the development process. Eclipse 4.19 on RHEL 7 supports Java development.
Note that this is the last update of Software Collections on RHEL 7. To upgrade Eclipse in the future, install the module eclipse for RHEL 8. It is possible that this module will not contain the same set of plugins as Eclipse Software Collections on RHEL 7.
To learn more about Eclipse, see the main Eclipse foundation page.
Sample Eclipse session
Eclipse provides a graphical development environment providing an alternative to using the command-line interface.
For an overview of how to develop applications for Red Hat JBoss Middleware or for support of OpenShift Tools, see Red Hat Developer Studio.
1.1. Enabling access to Eclipse RPMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
Eclipse is part of the Red Hat Developer Tools content set for RHEL 7. To install Eclipse, enable the Red Hat Developer Tools, Red Hat Software Collections, and Optional repositories using the Red Hat Subscription Management utility.
Prerequisites
The host must be registered and attached to a subscription.
For more information on registering your system using Red Hat Subscription Management and associating it with subscriptions, see the Red Hat Subscription Management collection of guides.
Procedure
Choose the system variant, either workstation or server, to use in the following commands. Red Hat recommends to choose server for access to the widest range of development tools.
Enable the
rhel-7-variant-devtools-rpmsrepository to access Red Hat Developer Tools:# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-variant-devtools-rpmsEnable the
rhel-variant-rhscl-7-rpmsrepository to access Red Hat Software Collections:# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-variant-rhscl-7-rpmsEnable the
rhel-7-variant-optional-rpmsrepository to access additional components:# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-variant-optional-rpms
Optional: Enabling the Red Hat Developer Tools debuginfo repositories
The Red Hat Developer Tools offering also provides debuginfo packages for all architecture-dependent RPMs in the repositories. These packages are useful for core-file analysis and for debugging Eclipse itself.
Procedure
Enable the Red Hat Developer Tools
debuginforepositories and replace variant with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system variant (serverorworkstation):# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-variant-devtools-debug-rpms- Enable the Red Hat Software Collections debuginfo repository:
# subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-__variant__-rhscl-7-debug-rpms
Additional resources
-
For details on installing, understanding, and using the
debuginfopackages, refer to Debugging a Running Application. - For more information on registering your system using Red Hat Subscription Management and associating it with subscriptions, see the Red Hat Subscription Management collection of guides.
- For detailed instructions on managing a subscription to Red Hat Software Collections, see the Red Hat Developer Toolset User Guide Section 1.4. Getting Access to Red Hat Developer Toolset.
1.2. Installing Eclipse
The following section describes how to install Eclipse.
Eclipse is available only on the AMD64 and Intel 64 architecture.
Prerequisites
- On RHEL 7, the repositories must be enabled as per Section 1.1, “Enabling access to Eclipse RPMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7”.
Procedure
- On RHEL 7, run the following command:
# yum install rh-eclipse
1.2.1. Installing additional Eclipse components
Eclipse 4.19 on RHEL 7 supports Java development. To install more components from the upstream repositories, for example to support the C and C++ languages, use the Install New Software wizard, Eclipse Marketplace Client, or the command-line interface.
Installing additional Eclipse components is not possible without access to the internet.
1.2.1.1. Installing additional Eclipse components using the Install New Software wizard
Procedure
- To use the Install New Software wizard for the installation of additional components, in the main menu click Help > Install New Software and follow the instructions on the screen.
1.2.1.2. Installing additional Eclipse components using Eclipse Marketplace
To use the Marketplace Client for the installation of additional components, follow the instructions in Section 1.2.1.2.1, “Example: Installing C and C++ Development Tooling (CDT) using the Eclipse Marketplace Client”.
1.2.1.2.1. Example: Installing C and C++ Development Tooling (CDT) using the Eclipse Marketplace Client
Procedure
- From the main menu, select Help > Eclipse Marketplace.
In Eclipse Marketplace, use the Find field to search for the wanted component, in this case CDT, and press Go.
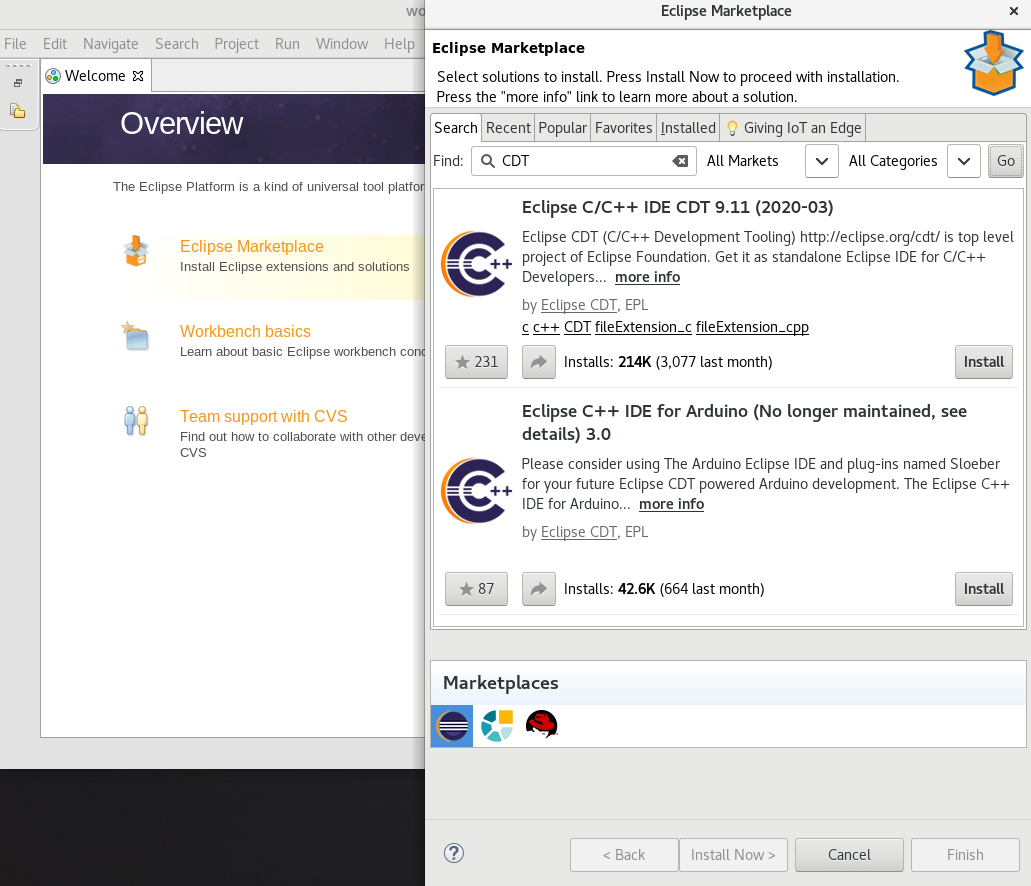
- Click the Install button to start the installation and follow the instructions on the screen.
1.2.1.3. Installing additional Eclipse components using the command-line interface
Red Hat recommends using Eclipse Marketplace or the Install New Software wizard to install additional components to Eclipse. However, it is possible to install components from the command line using the p2 director application.
To use the command-line interface for the installation of additional components, follow the instructions in Section 1.2.1.3.1, “Example: Installing Eclipse C and C++ Development Tools using the command-line interface”.
1.2.1.3.1. Example: Installing Eclipse C and C++ Development Tools using the command-line interface
Prerequisites
- Eclipse is not running.
Procedure
In the command-line interface, run the following command:
$ scl enable rh-eclipse 'eclipse -noSplash -application org.eclipse.equinox.p2.director -repository https://download.eclipse.org/releases/2021-03 -i org.eclipse.cdt.feature.group'
- Start Eclipse.
Eclipse C/C++ Development Tools is installed.
Running the p2 director application as root causes significant problems for the RPM consistency. Never run the p2 director application as root.
Additional resources
- For a list of available components, see Section 1.4, “Eclipse Components”.
- For further information on the p2 director application, see Installing software using the p2 director application in the online documentation or the built-in help system of Eclipse.
1.3. Starting Eclipse
1.3.1. Starting Eclipse from the GUI
To start Eclipse from the GUI, complete the following steps:
- Click Applications > Programming > Red Hat Eclipse.
1.3.2. Starting Eclipse from the command-line interface
To start Eclipse from the command-line, type the following at a shell prompt:
On RHEL 7:
$ scl enable rh-eclipse eclipse
While starting, Eclipse prompts you to select a workspace directory for your projects. You can use ~/workspace/, the default option, or click Browse and select a custom directory. You can also select Use this as the default and do not ask again to prevent Eclipse from displaying this dialog box again. Click OK to confirm the selection and proceed with the start.
1.4. Eclipse Components
The Eclipse development environment is provided as a set of RPM packages. The set contains the following Eclipse components:
| Package | Description |
|---|---|
|
| EGit, a team provider for Eclipse, provides features and plug-ins for interaction with Git repositories. |
|
| The Eclipse Modeling Framework (EMF) enables you to build applications based on a structured data model. |
|
| The Graphical Editing Framework (GEF) enables you to create a rich graphical editor from an existing application model. |
|
| The Eclipse Java development tools (JDT) plug-in. |
|
| JGit, a Java implementation of the Git revision control system. |
|
| The Eclipse Marketplace Client. |
|
| The Plugin Development Environment for developing Eclipse plug-ins. |
|
| The Eclipse Webtools plug-ins. |
Additional resources
A detailed description of Eclipse and all its features is beyond the scope of this document. For more information, see the following resources.
Installed documentation
- Eclipse includes a built-in help system that provides extensive documentation for each integrated feature and tool. It is accessible from Eclipse’s main menu: Help > Help Contents.
Other resources
- For a list of selected features and improvements in the latest version of the Eclipse development environment, see Section 1.5, “Changes in Eclipse 4.19”.
1.5. Changes in Eclipse 4.19
Eclipse 4.19 ships with Red Hat Developer Tools and plug-ins from the 2021-03 release train that provide a number of bug fixes and feature enhancements.
This section lists notable new features and compatibility changes in this release.
Significant package updates on RHEL 7
eclipse4.184.19 Eclipse IDE and JDT/PDE plug-ins have been updated to version 4.19. For a more complete list of changes, see the Eclipse 4.19 - New and Noteworthy pages. Notable enhancements include:
- In the Run Configurations menu, it is now possible to configure whether child processes should be terminated along with the launched operating system process.
- The new Equinox Linux Security JNA fragment has been added to improve password security on Linux.
- The Java editor has been improved through a number of new clean up options.
- Parallel index search is now the default option for all index based Java search operations.
eclipse-egit/jgit5.10.05.11.0 The Git integration plug-ins have been updated to version 5.11.0. For details, see the upstream EGit 5.11.0 Release Notes and JGit 5.11.0 Release Notes. Notable enhancements include:
- EGit 5.11 now uses the Apache MINA sshd SSH library as default. Support for the JSch library for SSH connections has been removed.
- In EGit 5.11 it is now possible to create OpenPGP-signed tags. Signed tags must be annotated.
- In EGit 5.11 it is now possible to verify OpenPGP signatures of commits.
- In EGit 5.11 it is now possible to use the external GPG executable installed on the system to sign commits and tags. Before, it was only possible to use the signing support provided by JGit.
Deprecated functionality on RHEL 7
Subclipse is no longer supported as part of Eclipse.
Additional resources
For details on how to use the new features, see Eclipse Installed documentation.
1.6. Known issues in Eclipse 4.19
This section details the known issues in Eclipse 4.19.
Known issues on RHEL 7
Initializing Eclipse Error Reporting SystemerrorThis error occurs when running a workspace created in an older version of Eclipse.
To work around this problem, start Eclipse with the
-cleanoption to clear its dependency resolution cache:$ scl enable rh-eclipse "eclipse -clean"
Eclipse will start without this error message.
- NullPointerExceptions
NullPointerExceptions can occur when you install a plug-in from a third-party update site. In that case, Eclipse fails to start with a
NullPointerExceptionin the workspace log file.To work around this problem, restart Eclipse with the
-cleanoption to clear its dependency resolution cache:On RHEL 7:
$ scl enable rh-eclipse "eclipse -clean"
Eclipse will start normally.
- The
rh-eclipse-tychopackage conflicts with the same package from earlier collections For example:
rh-eclipse48-tycho:As a result, the installation of the
rh-eclipse-tychopackage may fail when therh-eclipse48-tychopackage is already installed.You only need Tycho if you want to build or rebuild Eclipse or its plug-ins need Tycho. If needed, uninstall the
rh-eclipse48-tychopackage before installing therh-eclipse-tychopackage using this command:$ yum remove rh-eclipse48-tycho
The installation of the
rh-eclipse-tychopackage will now succeed.- The
rh-eclipse-scldevelpackage conflicts with packages from earlier collections For example:
rh-maven36-scldevel:As a result, the installation of the
rh-maven36-scldevelpackage may fail when therh-maven35-scldevelpackage is already installed.To solve this problem, uninstall the
rh-maven35-scldevelpackage before installing the new version ofrh-eclipse-scldevelusing this command:$ yum remove rh-maven35-scldevel
The installation of
rh-eclipse-scldevelwill now succeed.