Kapitel 1. Device Mapper Multipathing
1.1. Überblick über DM-Multipath
- RedundanzDM-Multipath kann Failover in einer aktiv/passiv-Konfiguration zur Verfügung stellen. In einer aktiv/passiv-Konfiguration wird nur jeweils die Hälfte der Pfade für I/O verwendet. Falls irgendein Element eines I/O-Pfads (das Kabel, der Switch, oder der Kontroller) ausfällt, wechselt DM-Multipath zu einem alternativen Pfad.
- Verbesserte LeistungDM-Multipath kann in aktiv/aktiv-Modus konfiguriert werden, in dem I/O nach Round-Robin-Art über die Pfade verteilt wird. In einigen Konfigurationen kann DM-Multipath die Auslastung auf den I/O-Pfaden ermitteln und diese dynamisch neu ausgleichen.
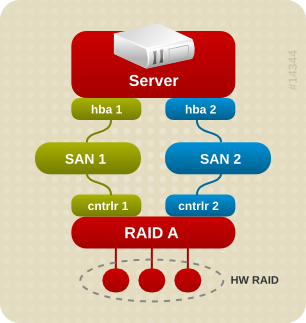
Abbildung 1.1. Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device
- HBA-Ausfall
- FC Kabelausfall
- SAN Switch-Ausfall
- Array-Kontroller Port-Ausfall
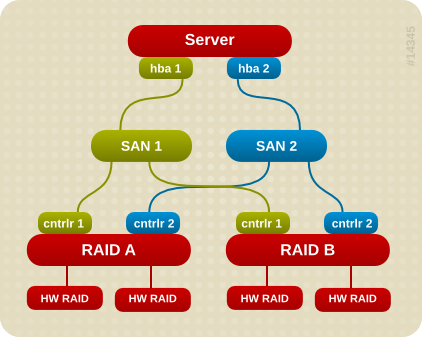
Abbildung 1.2. Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with Two RAID Devices
- hba1 an controller1
- hba1 an controller2
- hba2 an controller1
- hba2 an controller2
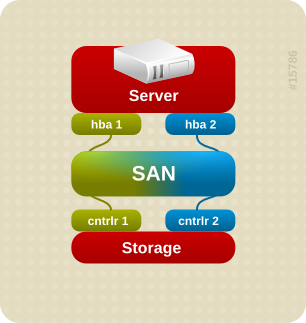
Abbildung 1.3. Active/Active Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device