Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 1. Introduction to RHEL for Edge images
A RHEL for Edge image is an rpm-ostree image that includes system packages to remotely install RHEL on Edge servers.
The system packages include:
-
Base OSpackage - Podman as the container engine
- Additional RPM Package Manager (RPM) content
RHEL for Edge is an immutable operating system that contains a read-only root directory, and has following characteristics:
- The packages are isolated from the root directory.
- Each version of the operating system is a separate deployment. Therefore, you can roll back the system to a previous deployment when needed.
-
The
rpm-ostreeimage offers efficient updates over the network. - RHEL for Edge supports multiple operating system branches and repositories.
-
The image contains a hybrid
rpm-ostreepackage system.
You can compose customized RHEL for Edge images by using the RHEL image builder tool. You can also create RHEL for Edge images by accessing the edge management application in the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console platform and configure automated management.
Use the edge management application to simplify provisioning and registering your images. To learn more about the edge management, see the Create RHEL for Edge images and configure automated management documentation.
Using RHEL for Edge customized images that were created by using the RHEL image builder on-premise version is not supported in the edge management application. See Edge management supportability.
The edge management application supports building and managing only the edge-commit and edge-installer image types.
Additionally, you cannot use the FIDO Device Onboarding (FDO) process with images that you create by using the edge management application.
With a RHEL for Edge image, you can achieve the following benefits:
- Atomic upgrades
- You know the state of each update, and no changes are seen until you reboot your system.
- Custom health checks and intelligent rollbacks
- You can create custom health checks, and if a health check fails, the operating system rolls back to the previous stable state.
- Container-focused workflow
- The image updates are staged in the background, minimizing any workload interruptions to the system.
- Optimized Over-the-Air updates
- You can make sure that your systems are up-to-date, even with intermittent connectivity, thanks to efficient over-the-air (OTA) delta updates.
1.1. RHEL for Edge—supported architecture
Currently, you can deploy RHEL for Edge images on AMD and Intel 64-bit systems.
RHEL for Edge does not support ARM systems in RHEL 8.
1.2. RHEL for Edge image types and their deployments
Composing and deploying a RHEL for Edge image involves two phases:
-
Composing a RHEL
rpm-ostreeimage using the RHEL image builder tool. You can access RHEL image builder through a command-line interface in thecomposer-clitool, or use a graphical user interface in the RHEL web console. - Deploying the image by using RHEL installer.
The image types vary in terms of their contents, and are therefore suitable for different types of deployment environments. While composing a RHEL for Edge image, you can select any of the following image types:
- RHEL for Edge Commit
-
This image type delivers atomic and safe updates to a system. The
edge-commit(.tar) image contains a full operating system, but it is not directly bootable. To boot theedge-commitimage type, you must deploy it by using one of the other disk image types. You can also buildedge-commitimages on the edge management application. - RHEL for Edge Container
-
This image type serves the OSTree commits by using an integrated HTTP server. The
edge-containercreates anOSTreecommit and embeds it into an OCI container with a web server. When theedge-commitimage starts, the web server serves the commit as an OSTree repository. - RHEL for Edge Installer
-
The
edge-installerimage type is an Anaconda-based installer image that deploys a RHEL for Edge OSTree commit that is embedded in the installer. Besides building.isoimages by using the RHEL image builder tool, you can also build RHEL for Edge installer (edge-installer) on the edge management application. Theedge-installerimage type is an Anaconda-based installer image that deploys a RHEL for Edge ostree commit that is embedded in the installer image. - RHEL for Edge Raw Image
-
Use for bare metal platforms by flashing the RHEL Raw Images on a hard disk or boot the Raw image on a virtual machine. The
edge-raw-imageis a compressed raw images that consist of a file containing a partition layout with an existing deployed OSTree commit in it. - RHEL for Edge Simplified Installer
-
Use the
edge-simplified-installerimage type for unattended installations, where user configuration is provided via FDO or Ignition. Theedge-simplified-installerimage can use Ignition to inject the user configuration into the images at an early stage of the boot process. Additionally, it is possible to use FDO as a way to inject user configuration during an early stage of the boot process. After booting the Edge Simplified Installer, it provisions the RHEL for Edge image to a device with the injected user configuration. - RHEL for Edge AMI
-
Use this image to launch an EC2 instance in AWS cloud. The
edge-amiimage uses the Ignition tool to inject the user configuration into the images at an early stage of the boot process. You can upload the.amiimage to AWS and boot an EC2 instance in AWS. - RHEL for Edge VMDK
-
Use this image to load the image on vSphere and boot the image in a vSphere VM. The
edge-vsphereimage uses the Ignition tool to inject the user configuration into the images at an early stage of the boot process.
| Image type | File type | Suitable for network-based deployments | Suitable for non-network-based deployments |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHEL for Edge Commit |
| Yes | No |
| RHEL for Edge Container |
| No | Yes |
| RHEL for Edge Installer |
| No | Yes |
| RHEL for Edge Raw Image | .raw.xz | Yes | Yes |
| RHEL for Edge Simplified Installer |
| Yes | Yes |
| RHEL for Edge AMI |
| Yes | Yes |
| RHEL for Edge VMDK |
| Yes | Yes |
Additional resources
1.3. Non-network-based deployments
Use RHEL image builder to create flexible RHEL rpm-ostree images to suit your requirements, and then use Anaconda to deploy them in your environment.
You can access RHEL image builder through a command-line interface in the composer-cli tool, or use a graphical user interface in the RHEL web console.
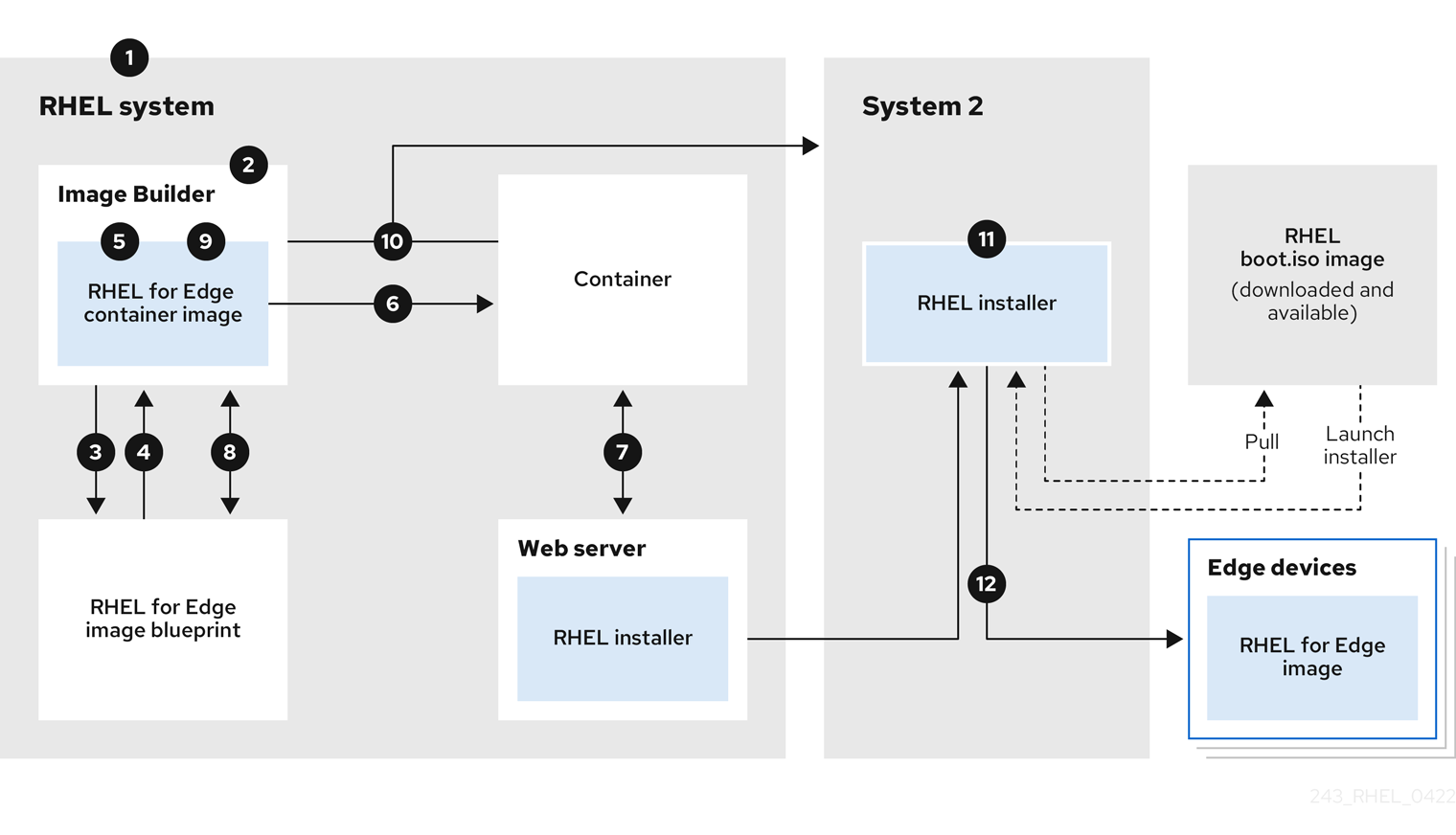
Composing and deploying a RHEL for Edge image in non-network-based deployments involves the following high-level steps:
- Install and register a RHEL system
- Install RHEL image builder
- Using RHEL image builder, create a blueprint with customizations for RHEL for Edge Container image
- Import the RHEL for Edge blueprint in RHEL image builder
- Create a RHEL for Edge image embed in an OCI container with a webserver ready to deploy the commit as an OSTree repository
- Download the RHEL for Edge Container image file
- Deploy the container serving a repository with the RHEL for Edge Container commit
- Using RHEL image builder, create another blueprint for RHEL for Edge Installer image
- Create a RHEL for Edge Installer image configured to pull the commit from the running container embedded with RHEL for Edge Container image
- Download the RHEL for Edge Installer image
- Run the installation
The following diagram represents the RHEL for Edge image non-network deployment workflow:
Figure 1.1. Deploying RHEL for Edge in non-network environment
1.4. Network-based deployments
Use RHEL image builder to create flexible RHEL rpm-ostree images to suit your requirements, and then use Anaconda to deploy them in your environment. RHEL image builder automatically identifies the details of your deployment setup and generates the image output as an edge-commit as a .tar file.
You can access RHEL image builder through a command-line interface in the composer-cli tool, or use a graphical user interface in the RHEL web console.
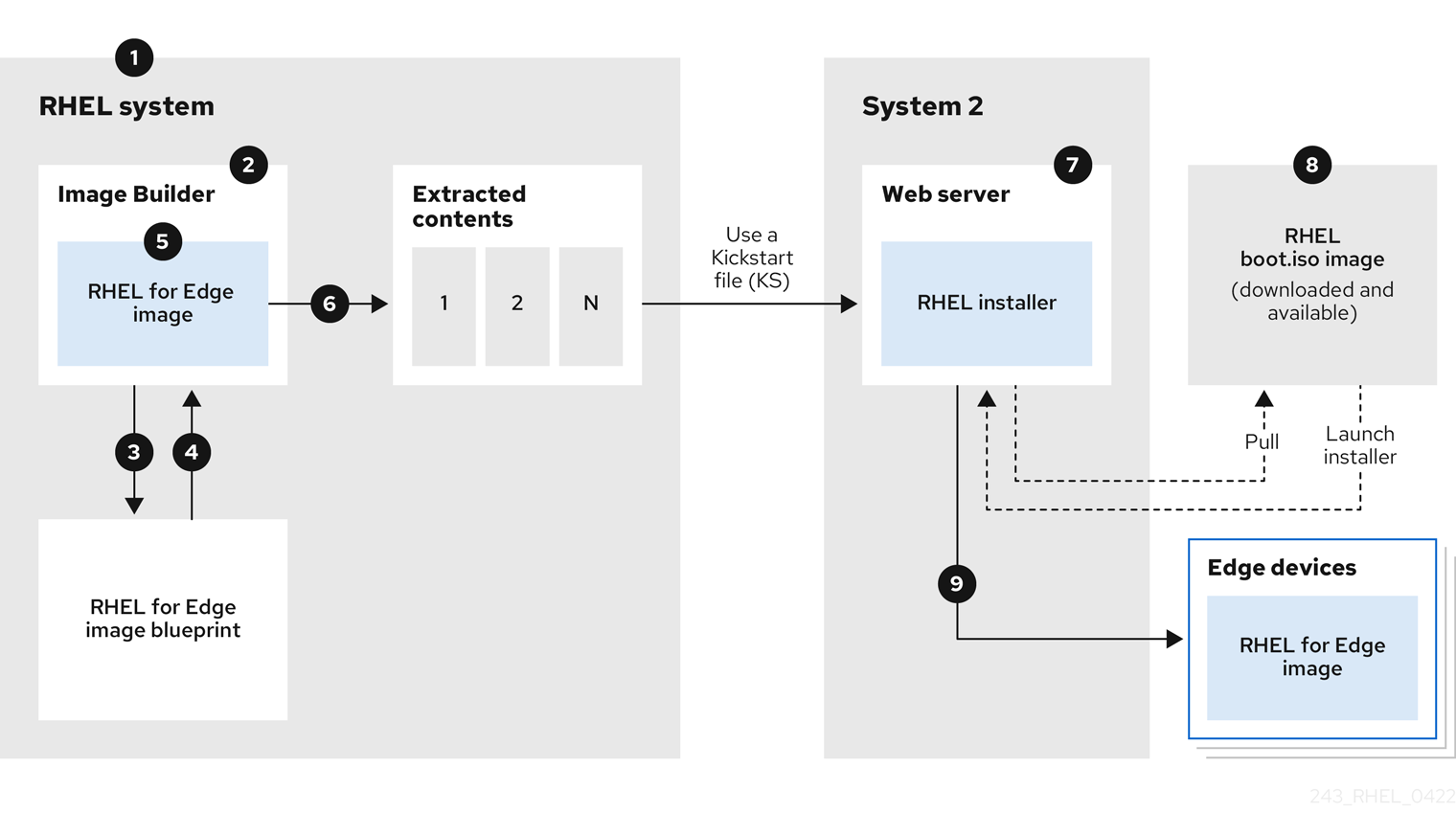
You can compose and deploy the RHEL for Edge image by performing the following high-level steps:
For an attended installation
- Install and register a RHEL system
- Install RHEL image builder
- Using RHEL image builder, create a blueprint for RHEL for Edge image
- Import the RHEL for Edge blueprint in RHEL image builder
-
Create a RHEL for Edge Commit (
.tar) image - Download the RHEL for Edge image file
- On the same system where you have installed RHEL image builder, install a web server that you want to serve the RHEL for Edge Commit content. For instructions, see Setting up and configuring NGINX
-
Extract the RHEL for Edge Commit (
.tar) content to the running web server - Create a Kickstart file that pulls the OSTree content from the running web server. For details on how to modify the Kickstart to pull the OSTree content, see Extracting the RHEL for Edge image commit
- Boot the RHEL installer ISO on the edge device and provide the Kickstart to it.
For an unattended installation, you can customize the RHEL installation ISO and embed the Kickstart file to it.
The following diagram represents the RHEL for Edge network image deployment workflow:
Figure 1.2. Deploying RHEL for Edge in network-base environment
1.5. Difference between RHEL RPM images and RHEL for Edge images
You can create RHEL system images in traditional package-based RPM format and also as RHEL for Edge (rpm-ostree) images.
You can use the traditional package-based RPMs to deploy RHEL on traditional data centers. However, with RHEL for Edge images you can deploy RHEL on servers other than traditional data centers. These servers include systems where processing of large amounts of data is done closest to the source where data is generated, the Edge servers.
The RHEL for Edge (rpm-ostree) images are not a package manager. They only support complete bootable file system trees, not individual files. These images do not have information regarding the individual files such as how these files were generated or anything related to their origin.
The rpm-ostree images need a separate mechanism, the package manager, to install additional applications in the /var directory. With that, the rpm-ostree image keeps the operating system unchanged, while maintaining the state of the /var and /etc directories. The atomic updates enable rollbacks and background staging of updates.
Refer to the following table to know how RHEL for Edge images differ from the package-based RHEL RPM images.
| Key attributes | RHEL RPM image | RHEL for Edge image |
|
| You can assemble the packages locally to form an image. | The packages are assembled in an OSTree which you can install on a system. |
|
|
You can use |
You can use |
|
| The package contains YUM repositories | The package contains OSTree remote repository |
|
| Read write |
Read-only ( |
|
|
You can mount the image to any non |
|