OpenShift Container Storage is now OpenShift Data Foundation starting with version 4.9.
Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 4. OpenShift Container Storage deployed using local storage devices
4.1. Replacing failed storage devices on Amazon EC2 infrastructure
When you need to replace a storage device on an Amazon EC2 (storage-optimized I3) infrastructure, you must replace the storage node. For information about how to replace nodes, see Replacing failed storage nodes on Amazon EC2 infrastructure.
4.2. Replacing failed storage devices on VMware and bare metal infrastructures using user interface
Use this procedure to replace a storage device that has failed due to I/O errors. You can initiate the replacement of a failed storage device from the Cluster or the Persistent Storage dashboards, Nodes page, or the Notifications.
However, if the failure has removed the disk, you need to replace the object storage device (OSD) using the command line steps described in the Replacing operational or failed storage devices on clusters backed by local storage devices section.
For encrypted cluster, replacing a failed device from user interface is not supported. To replace the device from the command-line interface, follow the steps from chapter Replacing operational or failed storage devices on clusters backed by local storage devices section.
Prerequisites
- Red Hat recommends that replacement nodes are configured with similar infrastructure, resources, and disks to the node being replaced.
- If you upgraded to OpenShift Container Storage 4.6 from a previous version, ensure to add annotations to storage cluster to enable failed device replacement from the user interface. See Adding annotations.
-
If you upgraded to OpenShift Container Storage 4.6 from a previous version, ensure that you have followed post-upgrade procedures to create the
LocalVolumeDiscoveryobject. See Post-update configuration changes for details. -
If you upgraded to OpenShift Container Storage 4.6 from a previous version, ensure that you have followed post-upgrade procedures to create the
LocalVolumeSetobject. See Post-update configuration changes for details."
Procedure
- From the Cluster or Persistent Storage dashboard
Open either the Cluster or the Persistent Storage dashboard.
Click Home
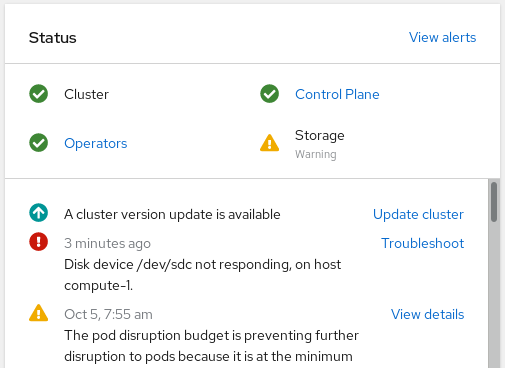
Overview Cluster from the left navigation bar of the OpenShift Web Console. Figure 4.1. Cluster dashboard with the alert
Click Home
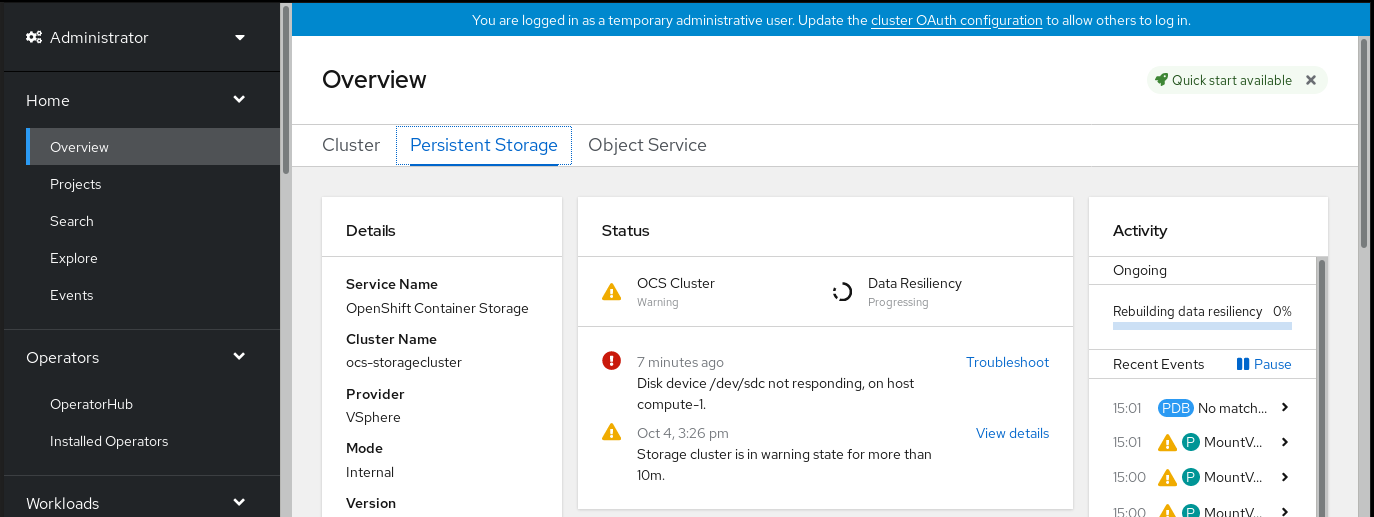
Overview Persistent Storage from the left navigation bar of the OpenShift Web Console. Figure 4.2. Persistent Storage dashboard with the alert
Click Troubleshoot in the
Disk <disk1> not respondingor theDisk <disk1> not accessiblealert.NoteIn case the disk failure has removed the disk, you might not see the failed disk when you click the link. In such a scenario, you need to perform command line steps as described in the Replacing operational or failed storage devices on clusters backed by local storage devices section.
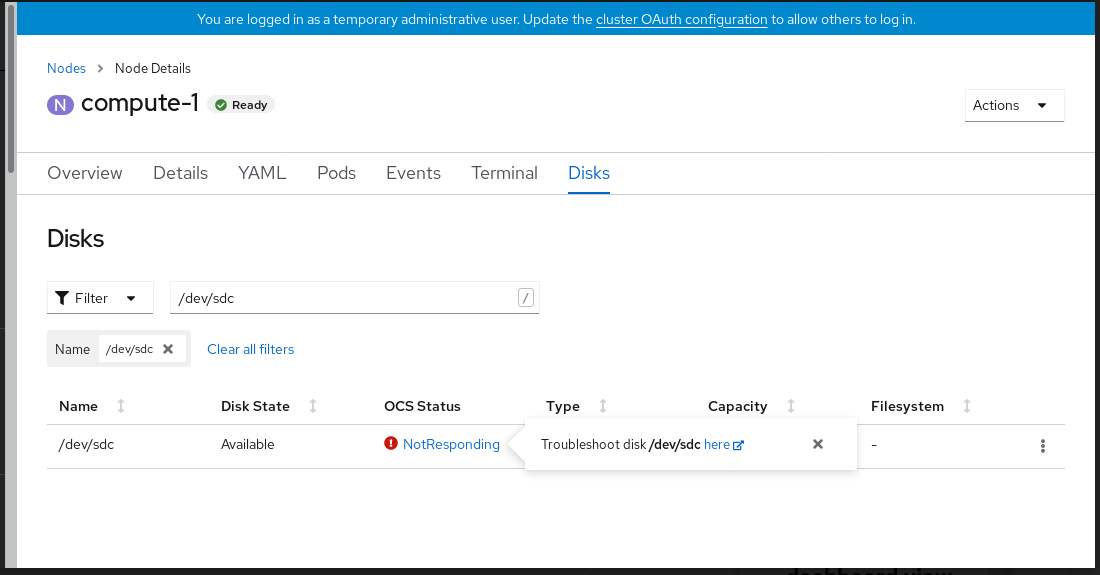
Figure 4.3. Disks page to replace failed disk
On the Disks page, you can do one of the following:
- Click the here link in the Troubleshoot popover dialog and follow the steps in the Troubleshooting OpenShift Container Storage guide to confirm that the disk has actually failed.
- From the Action (⋮) menu of the failed disk, click Start Disk Replacement.
-
OpenShift Container Storage Statusfield of the disk changes toPreparingToReplace. Wait for theOpenShift Container Storage Statusfield to change toReplacementReady. - Confirm that the disk alert no longer appears by clicking the notification bell.
- Replace the disk and wait for it to appear in the inventory list.
Delete the ocs-osd-removal job for the replaced disk.
- On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Workloads→Jobs.
- Use the search by Name filter to look for ocs-osd-removal . Ensure that the Project selected is openshift-storage.
- For the listed job, click the Action (⋮) menu and select Delete Job .
- Confirm that the job is deleted.
Delete the PersistentVolume resource associated with the replaced disk.
-
On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Storage
PersistentVolumes. - Use the search by Name filter to look for the PersistentVolume in Released status.
-
For the listed PersistentVolume from the storage class created as part of the LocalVolumeSet creation, for example,
localblock, click the Action (⋮) menu and select Delete PersistentVolume.
-
On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Storage
-
Verify that the
OpenShift Container Storage StatusshowsOnlinefor the newly added disk.
- From the inventory list
Click Compute
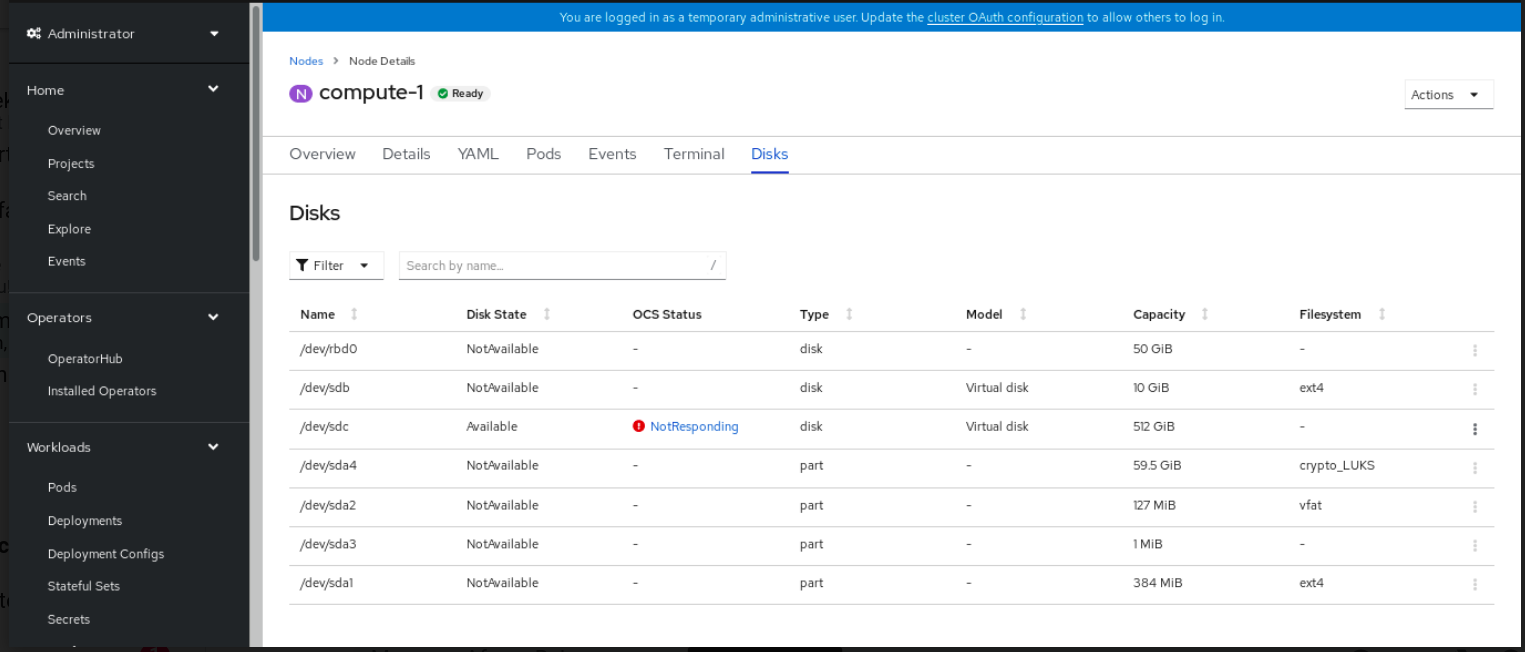
Nodes from the OpenShift Web Console. Figure 4.4. Inventory list of disks in the Nodes page
- Click the Disks tab. From the Action (:) menu of the failed disk, click Start Disk Replacement.
-
OpenShift Container Storage Statusfield of the disk changes toPreparingToReplace. Wait for theOpenShift Container Storage Statusfield to change toReplacementReady. - Confirm that the disk alert no longer appears by clicking the notification bell.
- Replace the disk and wait for it to appear in the inventory list.
Delete the ocs-osd-removal job for the replaced disk.
- On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Workloads→Jobs.
- Use the search by Name filter to look for ocs-osd-removal . Ensure that the Project selected is openshift-storage.
- For the listed job, click the Action (⋮) menu and select Delete Job .
- Confirm that the job is deleted.
Delete the PersistentVolume resource associated with the replaced disk.
-
On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Storage
PersistentVolumes. - Use the search by Name filter to look for the PersistentVolume in Released status.
-
For the listed PersistentVolume from the storage class created as part of the LocalVolumeSet creation, for example,
localblock, click the Action (⋮) menu and select Delete PersistentVolume.
-
On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Storage
-
Verify that the
OpenShift Container Storage StatusshowsOnlinefor the newly added disk.
- From the Notifications
-
Click Home
Overview Persistent Storage or Cluster dashboard or click Compute Nodes Disks tab. Look for one of the following alerts in the Notifications of the Cluster or the Persistent Storage dashboard or in the Nodes page:
-
CephOSDDiskUnavailable -
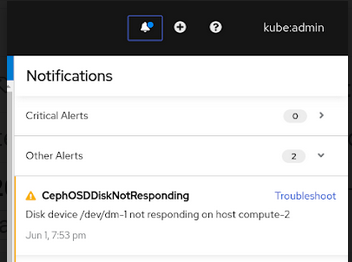
CephOSDDiskNotResponding
-
Click Troubleshoot in the alert notification.
NoteIn case the disk failure has removed the disk, you might not see the failed disk when you click the link. In such a scenario, you need to perform command line steps as described in the Replacing operational or failed storage devices on clusters backed by local storage devices section.
Figure 4.5. Notification of disk failure
In the Disks page, you can do one of the following:
- Click the here link in the Troubleshoot popover dialog and follow the steps in the Troubleshooting OpenShift Container Storage guide to confirm that the disk has actually failed.
- From the Action (⋮) menu of the failed disk, click Start Disk Replacement.
-
OpenShift Container Storage Statusof the disk changes toPreparingToReplaceand once it is ready to be replaced, the status changes toReplacementReady. - Confirm that the disk alert no longer appears by clicking the notification bell.
- Replace the disk and wait for it to appear in the inventory list.
Delete the ocs-osd-removal job for the replaced disk.
- On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Workloads→Jobs.
- Use the search by Name filter to look for ocs-osd-removal . Ensure that the Project selected is openshift-storage.
- For the listed job, click the Action (⋮) menu and select Delete Job .
- Confirm that the job is deleted.
Delete the PersistentVolume resource associated with the replaced disk.
-
On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Storage
PersistentVolumes. - Use the search by Name filter to look for the PersistentVolume in Released status.
-
For the listed PersistentVolume from the storage class created as part of the LocalVolumeSet creation, for example,
localblock, click the Action (⋮) menu and select Delete PersistentVolume.
-
On the OpenShift Web Console, navigate to Storage
-
Verify that the
OpenShift Container Storage StatusshowsOnlinefor the newly added disk.
-
Click Home
4.3. Replacing operational or failed storage devices on clusters backed by local storage devices
You can replace an object storage device (OSD) in OpenShift Container Storage deployed using local storage devices on bare metal and VMware infrastructures. Use this procedure when one or more underlying storage devices need to be replaced.
Prerequisites
- Red Hat recommends that replacement nodes are configured with similar infrastructure and resources to the node being replaced.
-
If you upgraded to OpenShift Container Storage 4.6 from a previous version, ensure that you have followed post-upgrade procedures to create the
LocalVolumeDiscoveryobject. See Post-update configuration changes for details. -
If you upgraded to OpenShift Container Storage 4.6 from a previous version, ensure that you have followed post-upgrade procedures to create the
LocalVolumeSetobject. See Post-update configuration changes for details.
Procedure
Identify the OSD that needs to be replaced and the OpenShift Container Platform node that has the OSD scheduled on it.
oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd -o wide
$ oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 0 24h 10.129.0.16 compute-2 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-1-85d99fb95f-2svc7 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.128.2.24 compute-0 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-2-6c66cdb977-jp542 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.130.0.18 compute-1 <none> <none>
rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 0 24h 10.129.0.16 compute-2 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-1-85d99fb95f-2svc7 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.128.2.24 compute-0 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-2-6c66cdb977-jp542 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.130.0.18 compute-1 <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example,
rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6needs to be replaced andcompute-2is the OpenShift Container platform node on which the OSD is scheduled.NoteIf the OSD to be replaced is healthy, the status of the pod will be
Running.Scale down the OSD deployment for the OSD to be replaced.
osd_id_to_remove=0 oc scale -n openshift-storage deployment rook-ceph-osd-${osd_id_to_remove} --replicas=0$ osd_id_to_remove=0 $ oc scale -n openshift-storage deployment rook-ceph-osd-${osd_id_to_remove} --replicas=0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
osd_id_to_removeis the integer in the pod name immediately after therook-ceph-osdprefix. In this example, the deployment name isrook-ceph-osd-0.Example output:
deployment.extensions/rook-ceph-osd-0 scaled
deployment.extensions/rook-ceph-osd-0 scaledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
rook-ceph-osdpod is terminated.oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l ceph-osd-id=${osd_id_to_remove}$ oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l ceph-osd-id=${osd_id_to_remove}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.
No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf the
rook-ceph-osdpod is interminatingstate for more than a few minutes, use theforceoption to delete the pod.oc delete -n openshift-storage pod rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6 --grace-period=0 --force
$ oc delete -n openshift-storage pod rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6 --grace-period=0 --forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
warning: Immediate deletion does not wait for confirmation that the running resource has been terminated. The resource may continue to run on the cluster indefinitely. pod "rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6" force deleted
warning: Immediate deletion does not wait for confirmation that the running resource has been terminated. The resource may continue to run on the cluster indefinitely. pod "rook-ceph-osd-0-6d77d6c7c6-m8xj6" force deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the old OSD from the cluster so that a new OSD can be added.
Delete any old
ocs-osd-removaljobs.oc delete -n openshift-storage job ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove}$ oc delete -n openshift-storage job ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
job.batch "ocs-osd-removal-0" deleted
job.batch "ocs-osd-removal-0" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change to the
openshift-storageproject.oc project openshift-storage
$ oc project openshift-storageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the old OSD from the cluster.
oc process -n openshift-storage ocs-osd-removal -p FAILED_OSD_IDS=${osd_id_to_remove} |oc create -n openshift-storage -f -$ oc process -n openshift-storage ocs-osd-removal -p FAILED_OSD_IDS=${osd_id_to_remove} |oc create -n openshift-storage -f -Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningThis step results in OSD being completely removed from the cluster. Ensure that the correct value of
osd_id_to_removeis provided.
Verify that the OSD is removed successfully by checking the status of the
ocs-osd-removalpod. A status ofCompletedconfirms that the OSD removal job succeeded.oc get pod -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storage$ oc get pod -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf
ocs-osd-removalfails and the pod is not in the expectedCompletedstate, check the pod logs for further debugging. For example:oc logs -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storage --tail=-1$ oc logs -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storage --tail=-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If encryption was enabled at the time of install, remove
dm-cryptmanageddevice-mappermapping from the OSD devices that are removed from the respective OpenShift Container Storage nodes.Get PVC name(s) of the replaced OSD(s) from the logs of
ocs-osd-removal-jobpod :oc logs -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-job -n openshift-storage --tail=-1 |egrep -i ‘pvc|deviceset’
$ oc logs -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-job -n openshift-storage --tail=-1 |egrep -i ‘pvc|deviceset’Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
2021-05-12 14:31:34.666000 I | cephosd: removing the OSD PVC "ocs-deviceset-xxxx-xxx-xxx-xxx"
2021-05-12 14:31:34.666000 I | cephosd: removing the OSD PVC "ocs-deviceset-xxxx-xxx-xxx-xxx"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For each of the nodes identified in step #1, do the following:
Create a
debugpod andchrootto the host on the storage node.oc debug node/<node name> chroot /host
$ oc debug node/<node name> $ chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find relevant device name based on the PVC names identified in the previous step
dmsetup ls| grep <pvc name>
sh-4.4# dmsetup ls| grep <pvc name> ocs-deviceset-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-block-dmcrypt (253:0)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the mapped device.
cryptsetup luksClose --debug --verbose ocs-deviceset-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-block-dmcrypt
$ cryptsetup luksClose --debug --verbose ocs-deviceset-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-block-dmcryptCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf the above command gets stuck due to insufficient privileges, run the following commands:
-
Press
CTRL+Zto exit the above command. Find PID of the process which was stuck.
ps -ef | grep crypt
$ ps -ef | grep cryptCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Terminate the process using
killcommand.kill -9 <PID>
$ kill -9 <PID>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the device name is removed.
dmsetup ls
$ dmsetup lsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Press
Find the persistent volume (PV) that need to be deleted by the command:
oc get pv -L kubernetes.io/hostname | grep localblock | grep Released
$ oc get pv -L kubernetes.io/hostname | grep localblock | grep Released local-pv-d6bf175b 1490Gi RWO Delete Released openshift-storage/ocs-deviceset-0-data-0-6c5pw localblock 2d22h compute-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the persistent volume.
oc delete pv local-pv-d6bf175b
$ oc delete pv local-pv-d6bf175bCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Physically add a new device to the node.
You can also remove the old device (optional).
Use the following command to track provisioning of persistent volumes for devices that match the
deviceInclusionSpec. It can take a few minutes to provision persistent volumes.oc -n openshift-local-storage describe localvolumeset localblock
$ oc -n openshift-local-storage describe localvolumeset localblockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Once the persistent volume is provisioned, a new OSD pod is automatically created for the provisioned volume.
Delete the
ocs-osd-removaljob(s).oc delete -n openshift-storage job ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove}$ oc delete -n openshift-storage job ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verfication steps
Verify that there is a new OSD running.
oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd
$ oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
rook-ceph-osd-0-5f7f4747d4-snshw 1/1 Running 0 4m47s rook-ceph-osd-1-85d99fb95f-2svc7 1/1 Running 0 1d20h rook-ceph-osd-2-6c66cdb977-jp542 1/1 Running 0 1d20h
rook-ceph-osd-0-5f7f4747d4-snshw 1/1 Running 0 4m47s rook-ceph-osd-1-85d99fb95f-2svc7 1/1 Running 0 1d20h rook-ceph-osd-2-6c66cdb977-jp542 1/1 Running 0 1d20hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf the new OSD does not show as
Runningafter a few minutes, restart therook-ceph-operatorpod to force a reconciliation.oc delete pod -n openshift-storage -l app=rook-ceph-operator
$ oc delete pod -n openshift-storage -l app=rook-ceph-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
pod "rook-ceph-operator-6f74fb5bff-2d982" deleted
pod "rook-ceph-operator-6f74fb5bff-2d982" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that a new PVC is created.
oc get -n openshift-storage pvc | grep localblock
# oc get -n openshift-storage pvc | grep localblockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
ocs-deviceset-0-0-c2mqb Bound local-pv-b481410 1490Gi RWO localblock 5m ocs-deviceset-1-0-959rp Bound local-pv-414755e0 1490Gi RWO localblock 1d20h ocs-deviceset-2-0-79j94 Bound local-pv-3e8964d3 1490Gi RWO localblock 1d20h
ocs-deviceset-0-0-c2mqb Bound local-pv-b481410 1490Gi RWO localblock 5m ocs-deviceset-1-0-959rp Bound local-pv-414755e0 1490Gi RWO localblock 1d20h ocs-deviceset-2-0-79j94 Bound local-pv-3e8964d3 1490Gi RWO localblock 1d20hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow (Optional) If data encryption is enabled on the cluster, verify that the new OSD devices are encrypted.
Identify the node(s) where the new OSD pod(s) are running.
oc get -o=custom-columns=NODE:.spec.nodeName pod/<OSD pod name>
$ oc get -o=custom-columns=NODE:.spec.nodeName pod/<OSD pod name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
oc get -o=custom-columns=NODE:.spec.nodeName pod/rook-ceph-osd-0-544db49d7f-qrgqm
oc get -o=custom-columns=NODE:.spec.nodeName pod/rook-ceph-osd-0-544db49d7f-qrgqmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For each of the nodes identified in previous step, do the following:
Create a debug pod and open a chroot environment for the selected host(s).
oc debug node/<node name> chroot /host
$ oc debug node/<node name> $ chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run “lsblk” and check for the “crypt” keyword beside the
ocs-devicesetname(s)lsblk
$ lsblkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Log in to OpenShift Web Console and check the OSD status on the storage dashboard.
Figure 4.6. OSD status in OpenShift Container Platform storage dashboard after device replacement
A full data recovery may take longer depending on the volume of data being recovered.
4.4. Replacing operational or failed storage devices on IBM Power Systems
You can replace an object storage device (OSD) in OpenShift Container Storage deployed using local storage devices on IBM Power Systems. Use this procedure when an underlying storage device needs to be replaced.
Procedure
Identify the OSD that needs to be replaced and the OpenShift Container Platform node that has the OSD scheduled on it.
oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd -o wide
# oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd -o wideCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5t 0/1 crashLoopBackOff 0 24h 10.129.2.26 worker-0 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-1-7c99657cfb-jdzvz 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.128.2.46 worker-1 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-2-5f9f6dfb5b-2mnw9 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.131.0.33 worker-2 <none> <none>
rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5t 0/1 crashLoopBackOff 0 24h 10.129.2.26 worker-0 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-1-7c99657cfb-jdzvz 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.128.2.46 worker-1 <none> <none> rook-ceph-osd-2-5f9f6dfb5b-2mnw9 1/1 Running 0 24h 10.131.0.33 worker-2 <none> <none>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example,
rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5tneeds to be replaced andworker-0is the RHOCP node on which the OSD is scheduled.NoteIf the OSD to be replaced is healthy, the status of the pod will be
Running.Scale down the OSD deployment for the OSD to be replaced.
osd_id_to_remove=0 oc scale -n openshift-storage deployment rook-ceph-osd-${osd_id_to_remove} --replicas=0# osd_id_to_remove=0 # oc scale -n openshift-storage deployment rook-ceph-osd-${osd_id_to_remove} --replicas=0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where
osd_id_to_removeis the integer in the pod name immediately after therook-ceph-osdprefix. In this example, the deployment name isrook-ceph-osd-0.Example output:
deployment.apps/rook-ceph-osd-0 scaled
deployment.apps/rook-ceph-osd-0 scaledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
rook-ceph-osdpod is terminated.oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l ceph-osd-id=${osd_id_to_remove}# oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l ceph-osd-id=${osd_id_to_remove}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.
No resources found in openshift-storage namespace.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf the
rook-ceph-osdpod is interminatingstate, use theforceoption to delete the pod.oc delete pod rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5t --grace-period=0 --force
# oc delete pod rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5t --grace-period=0 --forceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
warning: Immediate deletion does not wait for confirmation that the running resource has been terminated. The resource may continue to run on the cluster indefinitely. pod "rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5t" force deleted
warning: Immediate deletion does not wait for confirmation that the running resource has been terminated. The resource may continue to run on the cluster indefinitely. pod "rook-ceph-osd-0-86bf8cdc8-4nb5t" force deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the old OSD from the cluster so that a new OSD can be added.
Identify the
DeviceSetassociated with the OSD to be replaced.oc get -n openshift-storage -o yaml deployment rook-ceph-osd-${osd_id_to_remove} | grep ceph.rook.io/pvc# oc get -n openshift-storage -o yaml deployment rook-ceph-osd-${osd_id_to_remove} | grep ceph.rook.io/pvcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
ceph.rook.io/pvc: ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl ceph.rook.io/pvc: ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjlceph.rook.io/pvc: ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl ceph.rook.io/pvc: ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the PVC name is
ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl.Remove the old OSD from the cluster
oc process -n openshift-storage ocs-osd-removal -p FAILED_OSD_IDS=${osd_id_to_remove} | oc -n openshift-storage create -f -# oc process -n openshift-storage ocs-osd-removal -p FAILED_OSD_IDS=${osd_id_to_remove} | oc -n openshift-storage create -f -Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example Output:
job.batch/ocs-osd-removal-0 created
job.batch/ocs-osd-removal-0 createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningThis step results in OSD being completely removed from the cluster. Make sure that the correct value of
osd_id_to_removeis provided.
Verify that the OSD is removed successfully by checking the status of the
ocs-osd-removalpod. A status ofCompletedconfirms that the OSD removal job completed successfully.oc get pod -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storage# oc get pod -l job-name=ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf
ocs-osd-removalfails and the pod is not in the expectedCompletedstate, check the pod logs for further debugging. For example:oc logs ${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storage --tail=-1# oc logs ${osd_id_to_remove} -n openshift-storage --tail=-1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the persistent volume claim (PVC) resources associated with the OSD to be replaced.
Identify the PV associated with the PVC.
oc get -n openshift-storage pvc ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix>
# oc get -n openshift-storage pvc ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,
x,y, andpvc-suffixare the values in theDeviceSetidentified in an step 4(a).Example output:
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl Bound local-pv-8137c873 256Gi RWO localblock 24h
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl Bound local-pv-8137c873 256Gi RWO localblock 24hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the associated PV is
local-pv-8137c873.Identify the name of the device to be replaced.
oc get pv local-pv-<pv-suffix> -o yaml | grep path
# oc get pv local-pv-<pv-suffix> -o yaml | grep pathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,
pv-suffixis the value in the PV name identified in an earlier step.Example output:
path: /mnt/local-storage/localblock/vdc
path: /mnt/local-storage/localblock/vdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the device name is
vdc.Identify the
prepare-podassociated with the OSD to be replaced.oc describe -n openshift-storage pvc ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix> | grep Mounted
# oc describe -n openshift-storage pvc ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix> | grep MountedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,
x,y, andpvc-suffixare the values in theDeviceSetidentified in an earlier step.Example output:
Mounted By: rook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64knzkc
Mounted By: rook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64knzkcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example the
prepare-podname isrook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64knzkc.Delete the
osd-preparepod before removing the associated PVC.oc delete -n openshift-storage pod rook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix>-<pod-suffix>
# oc delete -n openshift-storage pod rook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix>-<pod-suffix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,
x,y,pvc-suffix, andpod-suffixare the values in theosd-preparepod name identified in an earlier step.Example output:
pod "rook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64knzkc" deleted
pod "rook-ceph-osd-prepare-ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64knzkc" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the PVC associated with the OSD to be replaced.
oc delete -n openshift-storage pvc ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix>
# oc delete -n openshift-storage pvc ocs-deviceset-<x>-<y>-<pvc-suffix>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where,
x,y, andpvc-suffixare the values in theDeviceSetidentified in an earlier step.Example output:
persistentvolumeclaim "ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl" deleted
persistentvolumeclaim "ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-64xjl" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Replace the old device and use the new device to create a new OpenShift Container Platform PV.
Log in to OpenShift Container Platform node with the device to be replaced. In this example, the OpenShift Container Platform node is
worker-0.oc debug node/worker-0
# oc debug node/worker-0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Starting pod/worker-0-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` Pod IP: 192.168.88.21 If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. # chroot /host
Starting pod/worker-0-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` Pod IP: 192.168.88.21 If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. # chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Record the
/dev/diskthat is to be replaced using the device name,vdc, identified earlier.ls -alh /mnt/local-storage/localblock
# ls -alh /mnt/local-storage/localblockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 17 Nov 18 15:23 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 24 Nov 18 15:23 .. lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 8 Nov 18 15:23 vdc -> /dev/vdc
total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 17 Nov 18 15:23 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 24 Nov 18 15:23 .. lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 8 Nov 18 15:23 vdc -> /dev/vdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Find the name of the
LocalVolumeSetCR, and remove or comment out the device/dev/diskthat is to be replaced.oc get -n openshift-local-storage localvolumeset
# oc get -n openshift-local-storage localvolumeset NAME AGE localblock 25hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Log in to OpenShift Container Platform node with the device to be replaced and remove the old
symlink.oc debug node/worker-0
# oc debug node/worker-0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Starting pod/worker-0-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` Pod IP: 192.168.88.21 If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. # chroot /host
Starting pod/worker-0-debug ... To use host binaries, run `chroot /host` Pod IP: 192.168.88.21 If you don't see a command prompt, try pressing enter. # chroot /hostCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Identify the old
symlinkfor the device name to be replaced. In this example, the device name isvdc.ls -alh /mnt/local-storage/localblock
# ls -alh /mnt/local-storage/localblockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 17 Nov 18 15:23 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 24 Nov 18 15:23 .. lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 8 Nov 18 15:23 vdc -> /dev/vdc
total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 17 Nov 18 15:23 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 24 Nov 18 15:23 .. lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 8 Nov 18 15:23 vdc -> /dev/vdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the
symlink.rm /mnt/local-storage/localblock/vdc
# rm /mnt/local-storage/localblock/vdcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the
symlinkis removed.ls -alh /mnt/local-storage/localblock
# ls -alh /mnt/local-storage/localblockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 18 17:11 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 24 Nov 18 15:23 ..
total 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Nov 18 17:11 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 24 Nov 18 15:23 ..Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantFor new deployments of OpenShift Container Storage 4.5 or later, LVM is not in use,
ceph-volumeraw mode is in play instead. Therefore, additional validation is not needed and you can proceed to the next step.
Delete the PV associated with the device to be replaced, which was identified in earlier steps. In this example, the PV name is
local-pv-8137c873.oc delete pv local-pv-8137c873
# oc delete pv local-pv-8137c873Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
persistentvolume "local-pv-8137c873" deleted
persistentvolume "local-pv-8137c873" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Replace the device with the new device.
Log back into the correct OpenShift Cotainer Platform node and identify the device name for the new drive. The device name must change unless you are reseating the same device.
lsblk
# lsblkCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the new device name is
vdd.-
After the new
/dev/diskis available ,it will be auto detected by localvolumeset. Verify that there is a new PV in
Availablestate and of the correct size.oc get pv | grep 256Gi
# oc get pv | grep 256GiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
local-pv-1e31f771 256Gi RWO Delete Bound openshift-storage/ocs-deviceset-localblock-2-data-0-6xhkf localblock 24h local-pv-ec7f2b80 256Gi RWO Delete Bound openshift-storage/ocs-deviceset-localblock-1-data-0-hr2fx localblock 24h local-pv-8137c873 256Gi RWO Delete Available localblock 32m
local-pv-1e31f771 256Gi RWO Delete Bound openshift-storage/ocs-deviceset-localblock-2-data-0-6xhkf localblock 24h local-pv-ec7f2b80 256Gi RWO Delete Bound openshift-storage/ocs-deviceset-localblock-1-data-0-hr2fx localblock 24h local-pv-8137c873 256Gi RWO Delete Available localblock 32mCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create new OSD for new device.
Deploy the new OSD by restarting the
rook-ceph-operatorto force operator reconciliation.Identify the name of the
rook-ceph-operator.oc get -n openshift-storage pod -l app=rook-ceph-operator
# oc get -n openshift-storage pod -l app=rook-ceph-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62v 1/1 Running 0 1d20h
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62v 1/1 Running 0 1d20hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the
rook-ceph-operator.oc delete -n openshift-storage pod rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62v
# oc delete -n openshift-storage pod rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62vCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
pod "rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62v" deleted
pod "rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62v" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, the rook-ceph-operator pod name is
rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-sg62v.Verify that the
rook-ceph-operatorpod is restarted.oc get -n openshift-storage pod -l app=rook-ceph-operator
# oc get -n openshift-storage pod -l app=rook-ceph-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-wx9xx 1/1 Running 0 50s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE rook-ceph-operator-85f6494db4-wx9xx 1/1 Running 0 50sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Creation of the new OSD may take several minutes after the operator restarts.
Delete the
ocs-osd-removaljob(s).oc delete -n openshift-storage job ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove}$ oc delete -n openshift-storage job ocs-osd-removal-${osd_id_to_remove}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verfication steps
Verify that there is a new OSD running and a new PVC created.
oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd
# oc get -n openshift-storage pods -l app=rook-ceph-osdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
rook-ceph-osd-0-76d8fb97f9-mn8qz 1/1 Running 0 23m rook-ceph-osd-1-7c99657cfb-jdzvz 1/1 Running 1 25h rook-ceph-osd-2-5f9f6dfb5b-2mnw9 1/1 Running 0 25h
rook-ceph-osd-0-76d8fb97f9-mn8qz 1/1 Running 0 23m rook-ceph-osd-1-7c99657cfb-jdzvz 1/1 Running 1 25h rook-ceph-osd-2-5f9f6dfb5b-2mnw9 1/1 Running 0 25hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow oc get -n openshift-storage pvc | grep localblock
# oc get -n openshift-storage pvc | grep localblockCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-q4q6b Bound local-pv-8137c873 256Gi RWO localblock 10m ocs-deviceset-localblock-1-data-0-hr2fx Bound local-pv-ec7f2b80 256Gi RWO localblock 1d20h ocs-deviceset-localblock-2-data-0-6xhkf Bound local-pv-1e31f771 256Gi RWO localblock 1d20h
ocs-deviceset-localblock-0-data-0-q4q6b Bound local-pv-8137c873 256Gi RWO localblock 10m ocs-deviceset-localblock-1-data-0-hr2fx Bound local-pv-ec7f2b80 256Gi RWO localblock 1d20h ocs-deviceset-localblock-2-data-0-6xhkf Bound local-pv-1e31f771 256Gi RWO localblock 1d20hCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in to OpenShift Web Console and view the storage dashboard.
Figure 4.7. OSD status in OpenShift Container Platform storage dashboard after device replacement
4.5. Replacing operational or failed storage devices on IBM Z or LinuxONE infrastructure
You can replace operational or failed storage devices on IBM Z or LinuxONE infrastructure with new SCSI disks.
IBM Z or LinuxONE supports SCSI FCP disk logical units (SCSI disks) as persistent storage devices from external disk storage. A SCSI disk can be identified by using its FCP Device number, two target worldwide port names (WWPN1 and WWPN2), and the logical unit number (LUN). For more information, see https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSB27U_6.4.0/com.ibm.zvm.v640.hcpa5/scsiover.html
Procedure
List all the disks with the following command.
lszdev
$ lszdevCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A SCSI disk is represented as a
zfcp-lunwith the structure<device-id>:<wwpn>:<lun-id>in theIDsection. The first disk is used for the operating system. If one storage device fails, it can be replaced with a new disk.Remove the disk.
Run the following command on the disk, replacing
scsi-idwith the SCSI disk identifier of the disk to be replaced.chzdev -d scsi-id
$ chzdev -d scsi-idCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the following command removes one disk with the device ID
0.0.8204, the WWPN0x500507630a0b50a4, and the LUN0x4002403000000000with the following command:chzdev -d 0.0.8204:0x500407630c0b50a4:0x3002b03000000000
$ chzdev -d 0.0.8204:0x500407630c0b50a4:0x3002b03000000000Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Append a new SCSI disk with the following command:
chzdev -e 0.0.8204:0x500507630b1b50a4:0x4001302a00000000
$ chzdev -e 0.0.8204:0x500507630b1b50a4:0x4001302a00000000Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe device ID for the new disk must be the same as the disk to be replaced. The new disk is identified with its WWPN and LUN ID.
List all the FCP devices to verify the new disk is configured.
lszdev zfcp-lun
$ lszdev zfcp-lun TYPE ID ON PERS NAMES zfcp-lun 0.0.8204:0x102107630b1b5060:0x4001402900000000 yes no sda sg0 zfcp-lun 0.0.8204:0x500507630b1b50a4:0x4001302a00000000 yes yes sdb sg1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow