Dieser Inhalt ist in der von Ihnen ausgewählten Sprache nicht verfügbar.
Chapter 6. Custom resource API reference
6.1. Common configuration properties
Common configuration properties apply to more than one resource.
6.1.1. replicas
Use the replicas property to configure replicas.
The type of replication depends on the resource.
-
KafkaTopicuses a replication factor to configure the number of replicas of each partition within a Kafka cluster. - Kafka components use replicas to configure the number of pods in a deployment to provide better availability and scalability.
When running a Kafka component on OpenShift it may not be necessary to run multiple replicas for high availability. When the node where the component is deployed crashes, OpenShift will automatically reschedule the Kafka component pod to a different node. However, running Kafka components with multiple replicas can provide faster failover times as the other nodes will be up and running.
6.1.2. bootstrapServers
Use the bootstrapServers property to configure a list of bootstrap servers.
The bootstrap server lists can refer to Kafka clusters that are not deployed in the same OpenShift cluster. They can also refer to a Kafka cluster not deployed by AMQ Streams.
If on the same OpenShift cluster, each list must ideally contain the Kafka cluster bootstrap service which is named CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-bootstrap and a port number. If deployed by AMQ Streams but on different OpenShift clusters, the list content depends on the approach used for exposing the clusters (routes, ingress, nodeports or loadbalancers).
When using Kafka with a Kafka cluster not managed by AMQ Streams, you can specify the bootstrap servers list according to the configuration of the given cluster.
6.1.3. ssl
You can incorporate SSL configuration and cipher suite specifications to further secure TLS-based communication between your client application and a Kafka cluster. In addition to the standard TLS configuration, you can specify a supported TLS version and enable cipher suites in the configuration for the Kafka broker. You can also add the configuration to your clients if you wish to limit the TLS versions and cipher suites they use. The configuration on the client must only use protocols and cipher suites that are enabled on the broker.
A cipher suite is a set of security mechanisms for secure connection and data transfer. For example, the cipher suite TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 is composed of the following mechanisms, which are used in conjunction with the TLS protocol:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) encryption (256-bit key)
- GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) authenticated encryption
- SHA384 (Secure Hash Algorithm) data integrity protection
The combination is encapsulated in the TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 cipher suite specification.
The ssl.enabled.protocols property specifies the available TLS versions that can be used for secure communication between the cluster and its clients. The ssl.protocol property sets the default TLS version for all connections, and it must be chosen from the enabled protocols. Use the ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm property to enable or disable hostname verification.
Example SSL configuration
- 1
- Cipher suite specifications enabled.
- 2
- TLS versions supported.
- 3
- Default TLS version is
TLSv1.3. If a client only supports TLSv1.2, it can still connect to the broker and communicate using that supported version, and vice versa if the configuration is on the client and the broker only supports TLSv1.2. - 4
- Hostname verification is enabled by setting to
HTTPS. An empty string disables the verification.
6.1.4. trustedCertificates
Having set tls to configure TLS encryption, use the trustedCertificates property to provide a list of secrets with key names under which the certificates are stored in X.509 format.
You can use the secrets created by the Cluster Operator for the Kafka cluster, or you can create your own TLS certificate file, then create a Secret from the file:
oc create secret generic MY-SECRET \ --from-file=MY-TLS-CERTIFICATE-FILE.crt
oc create secret generic MY-SECRET \
--from-file=MY-TLS-CERTIFICATE-FILE.crtExample TLS encryption configuration
If certificates are stored in the same secret, it can be listed multiple times.
If you want to enable TLS encryption, but use the default set of public certification authorities shipped with Java, you can specify trustedCertificates as an empty array:
Example of enabling TLS with the default Java certificates
tls: trustedCertificates: []
tls:
trustedCertificates: []
For information on configuring mTLS authentication, see the KafkaClientAuthenticationTls schema reference.
6.1.5. resources
Configure resource requests and limits to control resources for AMQ Streams containers. You can specify requests and limits for memory and cpu resources. The requests should be enough to ensure a stable performance of Kafka.
How you configure resources in a production environment depends on a number of factors. For example, applications are likely to be sharing resources in your OpenShift cluster.
For Kafka, the following aspects of a deployment can impact the resources you need:
- Throughput and size of messages
- The number of network threads handling messages
- The number of producers and consumers
- The number of topics and partitions
The values specified for resource requests are reserved and always available to the container. Resource limits specify the maximum resources that can be consumed by a given container. The amount between the request and limit is not reserved and might not be always available. A container can use the resources up to the limit only when they are available. Resource limits are temporary and can be reallocated.
Resource requests and limits

If you set limits without requests or vice versa, OpenShift uses the same value for both. Setting equal requests and limits for resources guarantees quality of service, as OpenShift will not kill containers unless they exceed their limits.
You can configure resource requests and limits for one or more supported resources.
Example resource configuration
Resource requests and limits for the Topic Operator and User Operator are set in the Kafka resource.
If the resource request is for more than the available free resources in the OpenShift cluster, the pod is not scheduled.
AMQ Streams uses the OpenShift syntax for specifying memory and cpu resources. For more information about managing computing resources on OpenShift, see Managing Compute Resources for Containers.
- Memory resources
When configuring memory resources, consider the total requirements of the components.
Kafka runs inside a JVM and uses an operating system page cache to store message data before writing to disk. The memory request for Kafka should fit the JVM heap and page cache. You can configure the
jvmOptionsproperty to control the minimum and maximum heap size.Other components don’t rely on the page cache. You can configure memory resources without configuring the
jvmOptionsto control the heap size.Memory requests and limits are specified in megabytes, gigabytes, mebibytes, and gibibytes. Use the following suffixes in the specification:
-
Mfor megabytes -
Gfor gigabytes -
Mifor mebibytes -
Gifor gibibytes
Example resources using different memory units
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more details about memory specification and additional supported units, see Meaning of memory.
-
- CPU resources
A CPU request should be enough to give a reliable performance at any time. CPU requests and limits are specified as cores or millicpus/millicores.
CPU cores are specified as integers (
5CPU core) or decimals (2.5CPU core). 1000 millicores is the same as1CPU core.Example CPU units
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The computing power of 1 CPU core may differ depending on the platform where OpenShift is deployed.
For more information on CPU specification, see Meaning of CPU.
6.1.6. image
Use the image property to configure the container image used by the component.
Overriding container images is recommended only in special situations where you need to use a different container registry or a customized image.
For example, if your network does not allow access to the container repository used by AMQ Streams, you can copy the AMQ Streams images or build them from the source. However, if the configured image is not compatible with AMQ Streams images, it might not work properly.
A copy of the container image might also be customized and used for debugging.
You can specify which container image to use for a component using the image property in the following resources:
-
Kafka.spec.kafka -
Kafka.spec.zookeeper -
Kafka.spec.entityOperator.topicOperator -
Kafka.spec.entityOperator.userOperator -
Kafka.spec.entityOperator.tlsSidecar -
KafkaConnect.spec -
KafkaMirrorMaker.spec -
KafkaMirrorMaker2.spec -
KafkaBridge.spec
Configuring the image property for Kafka, Kafka Connect, and Kafka MirrorMaker
Kafka, Kafka Connect, and Kafka MirrorMaker support multiple versions of Kafka. Each component requires its own image. The default images for the different Kafka versions are configured in the following environment variables:
-
STRIMZI_KAFKA_IMAGES -
STRIMZI_KAFKA_CONNECT_IMAGES -
STRIMZI_KAFKA_MIRROR_MAKER_IMAGES
These environment variables contain mappings between the Kafka versions and their corresponding images. The mappings are used together with the image and version properties:
-
If neither
imagenorversionare given in the custom resource then theversionwill default to the Cluster Operator’s default Kafka version, and the image will be the one corresponding to this version in the environment variable. -
If
imageis given butversionis not, then the given image is used and theversionis assumed to be the Cluster Operator’s default Kafka version. -
If
versionis given butimageis not, then the image that corresponds to the given version in the environment variable is used. -
If both
versionandimageare given, then the given image is used. The image is assumed to contain a Kafka image with the given version.
The image and version for the different components can be configured in the following properties:
-
For Kafka in
spec.kafka.imageandspec.kafka.version. -
For Kafka Connect and Kafka MirrorMaker in
spec.imageandspec.version.
It is recommended to provide only the version and leave the image property unspecified. This reduces the chance of making a mistake when configuring the custom resource. If you need to change the images used for different versions of Kafka, it is preferable to configure the Cluster Operator’s environment variables.
Configuring the image property in other resources
For the image property in the other custom resources, the given value will be used during deployment. If the image property is missing, the image specified in the Cluster Operator configuration will be used. If the image name is not defined in the Cluster Operator configuration, then the default value will be used.
For Topic Operator:
-
Container image specified in the
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_TOPIC_OPERATOR_IMAGEenvironment variable from the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/strimzi-rhel8-operator:2.4.0container image.
-
Container image specified in the
For User Operator:
-
Container image specified in the
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_USER_OPERATOR_IMAGEenvironment variable from the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/strimzi-rhel8-operator:2.4.0container image.
-
Container image specified in the
For Entity Operator TLS sidecar:
-
Container image specified in the
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_TLS_SIDECAR_ENTITY_OPERATOR_IMAGEenvironment variable from the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/kafka-34-rhel8:2.4.0container image.
-
Container image specified in the
For Kafka Exporter:
-
Container image specified in the
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_KAFKA_EXPORTER_IMAGEenvironment variable from the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/kafka-34-rhel8:2.4.0container image.
-
Container image specified in the
For Kafka Bridge:
-
Container image specified in the
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_KAFKA_BRIDGE_IMAGEenvironment variable from the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/bridge-rhel8:2.4.0container image.
-
Container image specified in the
For Kafka broker initializer:
-
Container image specified in the
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_KAFKA_INIT_IMAGEenvironment variable from the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/strimzi-rhel8-operator:2.4.0container image.
-
Container image specified in the
Example container image configuration
6.1.7. livenessProbe and readinessProbe healthchecks
Use the livenessProbe and readinessProbe properties to configure healthcheck probes supported in AMQ Streams.
Healthchecks are periodical tests which verify the health of an application. When a Healthcheck probe fails, OpenShift assumes that the application is not healthy and attempts to fix it.
For more details about the probes, see Configure Liveness and Readiness Probes.
Both livenessProbe and readinessProbe support the following options:
-
initialDelaySeconds -
timeoutSeconds -
periodSeconds -
successThreshold -
failureThreshold
Example of liveness and readiness probe configuration
For more information about the livenessProbe and readinessProbe options, see the Probe schema reference.
6.1.8. metricsConfig
Use the metricsConfig property to enable and configure Prometheus metrics.
The metricsConfig property contains a reference to a ConfigMap that has additional configurations for the Prometheus JMX Exporter. AMQ Streams supports Prometheus metrics using Prometheus JMX exporter to convert the JMX metrics supported by Apache Kafka and ZooKeeper to Prometheus metrics.
To enable Prometheus metrics export without further configuration, you can reference a ConfigMap containing an empty file under metricsConfig.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key. When referencing an empty file, all metrics are exposed as long as they have not been renamed.
Example ConfigMap with metrics configuration for Kafka
Example metrics configuration for Kafka
When metrics are enabled, they are exposed on port 9404.
When the metricsConfig (or deprecated metrics) property is not defined in the resource, the Prometheus metrics are disabled.
For more information about setting up and deploying Prometheus and Grafana, see Introducing Metrics to Kafka in the Deploying and Upgrading AMQ Streams on OpenShift guide.
6.1.9. jvmOptions
The following AMQ Streams components run inside a Java Virtual Machine (JVM):
- Apache Kafka
- Apache ZooKeeper
- Apache Kafka Connect
- Apache Kafka MirrorMaker
- AMQ Streams Kafka Bridge
To optimize their performance on different platforms and architectures, you configure the jvmOptions property in the following resources:
-
Kafka.spec.kafka -
Kafka.spec.zookeeper -
Kafka.spec.entityOperator.userOperator -
Kafka.spec.entityOperator.topicOperator -
Kafka.spec.cruiseControl -
KafkaConnect.spec -
KafkaMirrorMaker.spec -
KafkaMirrorMaker2.spec -
KafkaBridge.spec
You can specify the following options in your configuration:
-Xms- Minimum initial allocation heap size when the JVM starts
-Xmx- Maximum heap size
-XX- Advanced runtime options for the JVM
javaSystemProperties- Additional system properties
gcLoggingEnabled- Enables garbage collector logging
The units accepted by JVM settings, such as -Xmx and -Xms, are the same units accepted by the JDK java binary in the corresponding image. Therefore, 1g or 1G means 1,073,741,824 bytes, and Gi is not a valid unit suffix. This is different from the units used for memory requests and limits, which follow the OpenShift convention where 1G means 1,000,000,000 bytes, and 1Gi means 1,073,741,824 bytes.
-Xms and -Xmx options
In addition to setting memory request and limit values for your containers, you can use the -Xms and -Xmx JVM options to set specific heap sizes for your JVM. Use the -Xms option to set an initial heap size and the -Xmx option to set a maximum heap size.
Specify heap size to have more control over the memory allocated to your JVM. Heap sizes should make the best use of a container’s memory limit (and request) without exceeding it. Heap size and any other memory requirements need to fit within a specified memory limit. If you don’t specify heap size in your configuration, but you configure a memory resource limit (and request), the Cluster Operator imposes default heap sizes automatically. The Cluster Operator sets default maximum and minimum heap values based on a percentage of the memory resource configuration.
The following table shows the default heap values.
| Component | Percent of available memory allocated to the heap | Maximum limit |
|---|---|---|
| Kafka | 50% | 5 GB |
| ZooKeeper | 75% | 2 GB |
| Kafka Connect | 75% | None |
| MirrorMaker 2 | 75% | None |
| MirrorMaker | 75% | None |
| Cruise Control | 75% | None |
| Kafka Bridge | 50% | 31 Gi |
If a memory limit (and request) is not specified, a JVM’s minimum heap size is set to 128M. The JVM’s maximum heap size is not defined to allow the memory to increase as needed. This is ideal for single node environments in test and development.
Setting an appropriate memory request can prevent the following:
- OpenShift killing a container if there is pressure on memory from other pods running on the node.
-
OpenShift scheduling a container to a node with insufficient memory. If
-Xmsis set to-Xmx, the container will crash immediately; if not, the container will crash at a later time.
In this example, the JVM uses 2 GiB (=2,147,483,648 bytes) for its heap. Total JVM memory usage can be a lot more than the maximum heap size.
Example -Xmx and -Xms configuration
# ... jvmOptions: "-Xmx": "2g" "-Xms": "2g" # ...
# ...
jvmOptions:
"-Xmx": "2g"
"-Xms": "2g"
# ...
Setting the same value for initial (-Xms) and maximum (-Xmx) heap sizes avoids the JVM having to allocate memory after startup, at the cost of possibly allocating more heap than is really needed.
Containers performing lots of disk I/O, such as Kafka broker containers, require available memory for use as an operating system page cache. For such containers, the requested memory should be significantly higher than the memory used by the JVM.
-XX option
-XX options are used to configure the KAFKA_JVM_PERFORMANCE_OPTS option of Apache Kafka.
Example -XX configuration
JVM options resulting from the -XX configuration
-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=20 -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=35 -XX:+ExplicitGCInvokesConcurrent -XX:-UseParNewGC
-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=20 -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=35 -XX:+ExplicitGCInvokesConcurrent -XX:-UseParNewGC
When no -XX options are specified, the default Apache Kafka configuration of KAFKA_JVM_PERFORMANCE_OPTS is used.
javaSystemProperties
javaSystemProperties are used to configure additional Java system properties, such as debugging utilities.
Example javaSystemProperties configuration
jvmOptions:
javaSystemProperties:
- name: javax.net.debug
value: ssl
jvmOptions:
javaSystemProperties:
- name: javax.net.debug
value: ssl
For more information about the jvmOptions, see the JvmOptions schema reference.
6.1.10. Garbage collector logging
The jvmOptions property also allows you to enable and disable garbage collector (GC) logging. GC logging is disabled by default. To enable it, set the gcLoggingEnabled property as follows:
Example GC logging configuration
# ... jvmOptions: gcLoggingEnabled: true # ...
# ...
jvmOptions:
gcLoggingEnabled: true
# ...6.2. Schema properties
6.2.1. Kafka schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the Kafka and ZooKeeper clusters, and Topic Operator. |
| status | The status of the Kafka and ZooKeeper clusters, and Topic Operator. |
6.2.2. KafkaSpec schema reference
Used in: Kafka
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| kafka | Configuration of the Kafka cluster. |
| zookeeper | Configuration of the ZooKeeper cluster. |
| entityOperator | Configuration of the Entity Operator. |
| clusterCa | Configuration of the cluster certificate authority. |
| clientsCa | Configuration of the clients certificate authority. |
| cruiseControl | Configuration for Cruise Control deployment. Deploys a Cruise Control instance when specified. |
| kafkaExporter | Configuration of the Kafka Exporter. Kafka Exporter can provide additional metrics, for example lag of consumer group at topic/partition. |
| maintenanceTimeWindows | A list of time windows for maintenance tasks (that is, certificates renewal). Each time window is defined by a cron expression. |
| string array |
6.2.3. KafkaClusterSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaSpec
Full list of KafkaClusterSpec schema properties
Configures a Kafka cluster.
6.2.3.1. listeners
Use the listeners property to configure listeners to provide access to Kafka brokers.
Example configuration of a plain (unencrypted) listener without authentication
6.2.3.2. config
Use the config properties to configure Kafka broker options as keys.
Standard Apache Kafka configuration may be provided, restricted to those properties not managed directly by AMQ Streams.
Configuration options that cannot be configured relate to:
- Security (Encryption, Authentication, and Authorization)
- Listener configuration
- Broker ID configuration
- Configuration of log data directories
- Inter-broker communication
- ZooKeeper connectivity
The values can be one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Apache Kafka documentation with the exception of those options that are managed directly by AMQ Streams. Specifically, all configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
listeners -
advertised. -
broker. -
listener. -
host.name -
port -
inter.broker.listener.name -
sasl. -
ssl. -
security. -
password. -
principal.builder.class -
log.dir -
zookeeper.connect -
zookeeper.set.acl -
authorizer. -
super.user
When a forbidden option is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message is printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other supported options are passed to Kafka.
There are exceptions to the forbidden options. For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties. You can also configure the zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms property to set the maximum time allowed for establishing a ZooKeeper connection.
Example Kafka broker configuration
6.2.3.3. brokerRackInitImage
When rack awareness is enabled, Kafka broker pods use init container to collect the labels from the OpenShift cluster nodes. The container image used for this container can be configured using the brokerRackInitImage property. When the brokerRackInitImage field is missing, the following images are used in order of priority:
-
Container image specified in
STRIMZI_DEFAULT_KAFKA_INIT_IMAGEenvironment variable in the Cluster Operator configuration. -
registry.redhat.io/amq-streams/strimzi-rhel8-operator:2.4.0container image.
Example brokerRackInitImage configuration
Overriding container images is recommended only in special situations, where you need to use a different container registry. For example, because your network does not allow access to the container registry used by AMQ Streams. In this case, you should either copy the AMQ Streams images or build them from the source. If the configured image is not compatible with AMQ Streams images, it might not work properly.
6.2.3.4. logging
Kafka has its own configurable loggers:
-
log4j.logger.org.I0Itec.zkclient.ZkClient -
log4j.logger.org.apache.zookeeper -
log4j.logger.kafka -
log4j.logger.org.apache.kafka -
log4j.logger.kafka.request.logger -
log4j.logger.kafka.network.Processor -
log4j.logger.kafka.server.KafkaApis -
log4j.logger.kafka.network.RequestChannel$ -
log4j.logger.kafka.controller -
log4j.logger.kafka.log.LogCleaner -
log4j.logger.state.change.logger -
log4j.logger.kafka.authorizer.logger
Kafka uses the Apache log4j logger implementation.
Use the logging property to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Any available loggers that are not configured have their level set to OFF.
If Kafka was deployed using the Cluster Operator, changes to Kafka logging levels are applied dynamically.
If you use external logging, a rolling update is triggered when logging appenders are changed.
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.3.5. KafkaClusterSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The kafka broker version. Defaults to 3.4.0. Consult the user documentation to understand the process required to upgrade or downgrade the version. |
| string | |
| replicas | The number of pods in the cluster. |
| integer | |
| image |
The docker image for the pods. The default value depends on the configured |
| string | |
| listeners | Configures listeners of Kafka brokers. |
|
| |
| config | Kafka broker config properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: listeners, advertised., broker., listener., host.name, port, inter.broker.listener.name, sasl., ssl., security., password., log.dir, zookeeper.connect, zookeeper.set.acl, zookeeper.ssl, zookeeper.clientCnxnSocket, authorizer., super.user, cruise.control.metrics.topic, cruise.control.metrics.reporter.bootstrap.servers,node.id, process.roles, controller. (with the exception of: zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms, sasl.server.max.receive.size,ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols, ssl.secure.random.implementation,cruise.control.metrics.topic.num.partitions, cruise.control.metrics.topic.replication.factor, cruise.control.metrics.topic.retention.ms,cruise.control.metrics.topic.auto.create.retries, cruise.control.metrics.topic.auto.create.timeout.ms,cruise.control.metrics.topic.min.insync.replicas,controller.quorum.election.backoff.max.ms, controller.quorum.election.timeout.ms, controller.quorum.fetch.timeout.ms). |
| map | |
| storage |
Storage configuration (disk). Cannot be updated. The type depends on the value of the |
| authorization |
Authorization configuration for Kafka brokers. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| rack |
Configuration of the |
| brokerRackInitImage |
The image of the init container used for initializing the |
| string | |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
| jmxOptions | JMX Options for Kafka brokers. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| metricsConfig |
Metrics configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
| logging |
Logging configuration for Kafka. The type depends on the value of the |
| template |
Template for Kafka cluster resources. The template allows users to specify how the |
6.2.4. GenericKafkaListener schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
Full list of GenericKafkaListener schema properties
Configures listeners to connect to Kafka brokers within and outside OpenShift.
You configure the listeners in the Kafka resource.
Example Kafka resource showing listener configuration
6.2.4.1. listeners
You configure Kafka broker listeners using the listeners property in the Kafka resource. Listeners are defined as an array.
Example listener configuration
listeners:
- name: plain
port: 9092
type: internal
tls: false
listeners:
- name: plain
port: 9092
type: internal
tls: falseThe name and port must be unique within the Kafka cluster. The name can be up to 25 characters long, comprising lower-case letters and numbers. Allowed port numbers are 9092 and higher with the exception of ports 9404 and 9999, which are already used for Prometheus and JMX.
By specifying a unique name and port for each listener, you can configure multiple listeners.
6.2.4.2. type
The type is set as internal, or for external listeners, as route, loadbalancer, nodeport, ingress or cluster-ip. You can also configure a cluster-ip listener, a type of internal listener you can use to build custom access mechanisms.
- internal
You can configure internal listeners with or without encryption using the
tlsproperty.Example
internallistener configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - route
Configures an external listener to expose Kafka using OpenShift
Routesand the HAProxy router.A dedicated
Routeis created for every Kafka broker pod. An additionalRouteis created to serve as a Kafka bootstrap address. Kafka clients can use theseRoutesto connect to Kafka on port 443. The client connects on port 443, the default router port, but traffic is then routed to the port you configure, which is9094in this example.Example
routelistener configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - ingress
Configures an external listener to expose Kafka using Kubernetes
Ingressand the Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes.A dedicated
Ingressresource is created for every Kafka broker pod. An additionalIngressresource is created to serve as a Kafka bootstrap address. Kafka clients can use theseIngressresources to connect to Kafka on port 443. The client connects on port 443, the default controller port, but traffic is then routed to the port you configure, which is9095in the following example.You must specify the hostnames used by the bootstrap and per-broker services using
GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBootstrapandGenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBrokerproperties.Example
ingresslistener configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteExternal listeners using
Ingressare currently only tested with the Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes.- loadbalancer
Configures an external listener to expose Kafka using a
LoadbalancertypeService.A new loadbalancer service is created for every Kafka broker pod. An additional loadbalancer is created to serve as a Kafka bootstrap address. Loadbalancers listen to the specified port number, which is port
9094in the following example.You can use the
loadBalancerSourceRangesproperty to configure source ranges to restrict access to the specified IP addresses.Example
loadbalancerlistener configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - nodeport
Configures an external listener to expose Kafka using a
NodePorttypeService.Kafka clients connect directly to the nodes of OpenShift. An additional
NodePorttype of service is created to serve as a Kafka bootstrap address.When configuring the advertised addresses for the Kafka broker pods, AMQ Streams uses the address of the node on which the given pod is running. You can use
preferredNodePortAddressTypeproperty to configure the first address type checked as the node address.Example
nodeportlistener configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteTLS hostname verification is not currently supported when exposing Kafka clusters using node ports.
- cluster-ip
Configures an internal listener to expose Kafka using a per-broker
ClusterIPtypeService.The listener does not use a headless service and its DNS names to route traffic to Kafka brokers. You can use this type of listener to expose a Kafka cluster when using the headless service is unsuitable. You might use it with a custom access mechanism, such as one that uses a specific Ingress controller or the OpenShift Gateway API.
A new
ClusterIPservice is created for each Kafka broker pod. The service is assigned aClusterIPaddress to serve as a Kafka bootstrap address with a per-broker port number. For example, you can configure the listener to expose a Kafka cluster over an Nginx Ingress Controller with TCP port configuration.Example
cluster-iplistener configurationCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.2.4.3. port
The port number is the port used in the Kafka cluster, which might not be the same port used for access by a client.
-
loadbalancerlisteners use the specified port number, as dointernalandcluster-iplisteners -
ingressandroutelisteners use port 443 for access -
nodeportlisteners use the port number assigned by OpenShift
For client connection, use the address and port for the bootstrap service of the listener. You can retrieve this from the status of the Kafka resource.
Example command to retrieve the address and port for client connection
oc get kafka <kafka_cluster_name> -o=jsonpath='{.status.listeners[?(@.name=="<listener_name>")].bootstrapServers}{"\n"}'
oc get kafka <kafka_cluster_name> -o=jsonpath='{.status.listeners[?(@.name=="<listener_name>")].bootstrapServers}{"\n"}'Listeners cannot be configured to use the ports set aside for interbroker communication (9090 and 9091) and metrics (9404).
6.2.4.4. tls
The TLS property is required.
By default, TLS encryption is not enabled. To enable it, set the tls property to true.
For route and ingress type listeners, TLS encryption must be enabled.
6.2.4.5. authentication
Authentication for the listener can be specified as:
-
mTLS (
tls) -
SCRAM-SHA-512 (
scram-sha-512) -
Token-based OAuth 2.0 (
oauth) -
Custom (
custom)
6.2.4.6. networkPolicyPeers
Use networkPolicyPeers to configure network policies that restrict access to a listener at the network level. The following example shows a networkPolicyPeers configuration for a plain and a tls listener.
In the following example:
-
Only application pods matching the labels
app: kafka-sasl-consumerandapp: kafka-sasl-producercan connect to theplainlistener. The application pods must be running in the same namespace as the Kafka broker. -
Only application pods running in namespaces matching the labels
project: myprojectandproject: myproject2can connect to thetlslistener.
The syntax of the networkPolicyPeers property is the same as the from property in NetworkPolicy resources.
Exanmple network policy configuration
6.2.4.7. GenericKafkaListener schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Name of the listener. The name will be used to identify the listener and the related OpenShift objects. The name has to be unique within given a Kafka cluster. The name can consist of lowercase characters and numbers and be up to 11 characters long. |
| string | |
| port | Port number used by the listener inside Kafka. The port number has to be unique within a given Kafka cluster. Allowed port numbers are 9092 and higher with the exception of ports 9404 and 9999, which are already used for Prometheus and JMX. Depending on the listener type, the port number might not be the same as the port number that connects Kafka clients. |
| integer | |
| type |
Type of the listener. Currently the supported types are
|
| string (one of [ingress, internal, route, loadbalancer, cluster-ip, nodeport]) | |
| tls | Enables TLS encryption on the listener. This is a required property. |
| boolean | |
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for this listener. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| configuration | Additional listener configuration. |
| networkPolicyPeers | List of peers which should be able to connect to this listener. Peers in this list are combined using a logical OR operation. If this field is empty or missing, all connections will be allowed for this listener. If this field is present and contains at least one item, the listener only allows the traffic which matches at least one item in this list. For more information, see the external documentation for networking.k8s.io/v1 networkpolicypeer. |
| NetworkPolicyPeer array |
6.2.5. KafkaListenerAuthenticationTls schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListener
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaListenerAuthenticationTls type from KafkaListenerAuthenticationScramSha512, KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth, KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom. It must have the value tls for the type KafkaListenerAuthenticationTls.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.6. KafkaListenerAuthenticationScramSha512 schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListener
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaListenerAuthenticationScramSha512 type from KafkaListenerAuthenticationTls, KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth, KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom. It must have the value scram-sha-512 for the type KafkaListenerAuthenticationScramSha512.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.7. KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListener
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth type from KafkaListenerAuthenticationTls, KafkaListenerAuthenticationScramSha512, KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom. It must have the value oauth for the type KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| accessTokenIsJwt |
Configure whether the access token is treated as JWT. This must be set to |
| boolean | |
| checkAccessTokenType |
Configure whether the access token type check is performed or not. This should be set to |
| boolean | |
| checkAudience |
Enable or disable audience checking. Audience checks identify the recipients of tokens. If audience checking is enabled, the OAuth Client ID also has to be configured using the |
| boolean | |
| checkIssuer |
Enable or disable issuer checking. By default issuer is checked using the value configured by |
| boolean | |
| clientAudience |
The audience to use when making requests to the authorization server’s token endpoint. Used for inter-broker authentication and for configuring OAuth 2.0 over PLAIN using the |
| string | |
| clientId | OAuth Client ID which the Kafka broker can use to authenticate against the authorization server and use the introspect endpoint URI. |
| string | |
| clientScope |
The scope to use when making requests to the authorization server’s token endpoint. Used for inter-broker authentication and for configuring OAuth 2.0 over PLAIN using the |
| string | |
| clientSecret | Link to OpenShift Secret containing the OAuth client secret which the Kafka broker can use to authenticate against the authorization server and use the introspect endpoint URI. |
| connectTimeoutSeconds | The connect timeout in seconds when connecting to authorization server. If not set, the effective connect timeout is 60 seconds. |
| integer | |
| customClaimCheck | JsonPath filter query to be applied to the JWT token or to the response of the introspection endpoint for additional token validation. Not set by default. |
| string | |
| disableTlsHostnameVerification |
Enable or disable TLS hostname verification. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| enableECDSA |
The |
| boolean | |
| enableMetrics |
Enable or disable OAuth metrics. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| enableOauthBearer |
Enable or disable OAuth authentication over SASL_OAUTHBEARER. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| enablePlain |
Enable or disable OAuth authentication over SASL_PLAIN. There is no re-authentication support when this mechanism is used. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| failFast |
Enable or disable termination of Kafka broker processes due to potentially recoverable runtime errors during startup. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| fallbackUserNameClaim |
The fallback username claim to be used for the user id if the claim specified by |
| string | |
| fallbackUserNamePrefix |
The prefix to use with the value of |
| string | |
| groupsClaim | JsonPath query used to extract groups for the user during authentication. Extracted groups can be used by a custom authorizer. By default no groups are extracted. |
| string | |
| groupsClaimDelimiter | A delimiter used to parse groups when they are extracted as a single String value rather than a JSON array. Default value is ',' (comma). |
| string | |
| httpRetries | The maximum number of retries to attempt if an initial HTTP request fails. If not set, the default is to not attempt any retries. |
| integer | |
| httpRetryPauseMs | The pause to take before retrying a failed HTTP request. If not set, the default is to not pause at all but to immediately repeat a request. |
| integer | |
| introspectionEndpointUri | URI of the token introspection endpoint which can be used to validate opaque non-JWT tokens. |
| string | |
| jwksEndpointUri | URI of the JWKS certificate endpoint, which can be used for local JWT validation. |
| string | |
| jwksExpirySeconds |
Configures how often are the JWKS certificates considered valid. The expiry interval has to be at least 60 seconds longer then the refresh interval specified in |
| integer | |
| jwksIgnoreKeyUse |
Flag to ignore the 'use' attribute of |
| boolean | |
| jwksMinRefreshPauseSeconds | The minimum pause between two consecutive refreshes. When an unknown signing key is encountered the refresh is scheduled immediately, but will always wait for this minimum pause. Defaults to 1 second. |
| integer | |
| jwksRefreshSeconds |
Configures how often are the JWKS certificates refreshed. The refresh interval has to be at least 60 seconds shorter then the expiry interval specified in |
| integer | |
| maxSecondsWithoutReauthentication |
Maximum number of seconds the authenticated session remains valid without re-authentication. This enables Apache Kafka re-authentication feature, and causes sessions to expire when the access token expires. If the access token expires before max time or if max time is reached, the client has to re-authenticate, otherwise the server will drop the connection. Not set by default - the authenticated session does not expire when the access token expires. This option only applies to SASL_OAUTHBEARER authentication mechanism (when |
| integer | |
| readTimeoutSeconds | The read timeout in seconds when connecting to authorization server. If not set, the effective read timeout is 60 seconds. |
| integer | |
| tlsTrustedCertificates | Trusted certificates for TLS connection to the OAuth server. |
|
| |
| tokenEndpointUri |
URI of the Token Endpoint to use with SASL_PLAIN mechanism when the client authenticates with |
| string | |
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| userInfoEndpointUri | URI of the User Info Endpoint to use as a fallback to obtaining the user id when the Introspection Endpoint does not return information that can be used for the user id. |
| string | |
| userNameClaim |
Name of the claim from the JWT authentication token, Introspection Endpoint response or User Info Endpoint response which will be used to extract the user id. Defaults to |
| string | |
| validIssuerUri | URI of the token issuer used for authentication. |
| string | |
| validTokenType |
Valid value for the |
| string |
6.2.8. GenericSecretSource schema reference
Used in: KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth, KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom, KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| key | The key under which the secret value is stored in the OpenShift Secret. |
| string | |
| secretName | The name of the OpenShift Secret containing the secret value. |
| string |
6.2.9. CertSecretSource schema reference
Used in: ClientTls, KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak, KafkaAuthorizationOpa, KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth, KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| certificate | The name of the file certificate in the Secret. |
| string | |
| secretName | The name of the Secret containing the certificate. |
| string |
6.2.10. KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListener
Full list of KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom schema properties
To configure custom authentication, set the type property to custom.
Custom authentication allows for any type of kafka-supported authentication to be used.
Example custom OAuth authentication configuration
A protocol map is generated that uses the sasl and tls values to determine which protocol to map to the listener.
-
SASL = True, TLS = True
SASL_SSL -
SASL = False, TLS = True
SSL -
SASL = True, TLS = False
SASL_PLAINTEXT -
SASL = False, TLS = False
PLAINTEXT
6.2.10.1. listenerConfig
Listener configuration specified using listenerConfig is prefixed with listener.name.<listener_name>-<port>. For example, sasl.enabled.mechanisms becomes listener.name.<listener_name>-<port>.sasl.enabled.mechanisms.
6.2.10.2. secrets
Secrets are mounted to /opt/kafka/custom-authn-secrets/custom-listener-<listener_name>-<port>/<secret_name> in the Kafka broker nodes' containers.
For example, the mounted secret (example) in the example configuration would be located at /opt/kafka/custom-authn-secrets/custom-listener-oauth-bespoke-9093/example.
6.2.10.3. Principal builder
You can set a custom principal builder in the Kafka cluster configuration. However, the principal builder is subject to the following requirements:
- The specified principal builder class must exist on the image. Before building your own, check if one already exists. You’ll need to rebuild the AMQ Streams images with the required classes.
-
No other listener is using
oauthtype authentication. This is because an OAuth listener appends its own principle builder to the Kafka configuration. - The specified principal builder is compatible with AMQ Streams.
Custom principal builders must support peer certificates for authentication, as AMQ Streams uses these to manage the Kafka cluster.
Kafka’s default principal builder class supports the building of principals based on the names of peer certificates. The custom principal builder should provide a principal of type user using the name of the SSL peer certificate.
The following example shows a custom principal builder that satisfies the OAuth requirements of AMQ Streams.
Example principal builder for custom OAuth configuration
6.2.10.4. KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom type from KafkaListenerAuthenticationTls, KafkaListenerAuthenticationScramSha512, KafkaListenerAuthenticationOAuth. It must have the value custom for the type KafkaListenerAuthenticationCustom.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| listenerConfig | Configuration to be used for a specific listener. All values are prefixed with listener.name.<listener_name>. |
| map | |
| sasl | Enable or disable SASL on this listener. |
| boolean | |
| secrets | Secrets to be mounted to /opt/kafka/custom-authn-secrets/custom-listener-<listener_name>-<port>/<secret_name>. |
|
| |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.11. GenericKafkaListenerConfiguration schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListener
Full list of GenericKafkaListenerConfiguration schema properties
Configuration for Kafka listeners.
6.2.11.1. brokerCertChainAndKey
The brokerCertChainAndKey property is only used with listeners that have TLS encryption enabled. You can use the property to provide your own Kafka listener certificates.
Example configuration for a loadbalancer external listener with TLS encryption enabled
6.2.11.2. externalTrafficPolicy
The externalTrafficPolicy property is used with loadbalancer and nodeport listeners. When exposing Kafka outside of OpenShift you can choose Local or Cluster. Local avoids hops to other nodes and preserves the client IP, whereas Cluster does neither. The default is Cluster.
6.2.11.3. loadBalancerSourceRanges
The loadBalancerSourceRanges property is only used with loadbalancer listeners. When exposing Kafka outside of OpenShift use source ranges, in addition to labels and annotations, to customize how a service is created.
Example source ranges configured for a loadbalancer listener
6.2.11.4. class
The class property is only used with ingress listeners. You can configure the Ingress class using the class property.
Example of an external listener of type ingress using Ingress class nginx-internal
6.2.11.5. preferredNodePortAddressType
The preferredNodePortAddressType property is only used with nodeport listeners.
Use the preferredNodePortAddressType property in your listener configuration to specify the first address type checked as the node address. This property is useful, for example, if your deployment does not have DNS support, or you only want to expose a broker internally through an internal DNS or IP address. If an address of this type is found, it is used. If the preferred address type is not found, AMQ Streams proceeds through the types in the standard order of priority:
- ExternalDNS
- ExternalIP
- Hostname
- InternalDNS
- InternalIP
Example of an external listener configured with a preferred node port address type
6.2.11.6. useServiceDnsDomain
The useServiceDnsDomain property is only used with internal and cluster-ip listeners. It defines whether the fully-qualified DNS names that include the cluster service suffix (usually .cluster.local) are used. With useServiceDnsDomain set as false, the advertised addresses are generated without the service suffix; for example, my-cluster-kafka-0.my-cluster-kafka-brokers.myproject.svc. With useServiceDnsDomain set as true, the advertised addresses are generated with the service suffix; for example, my-cluster-kafka-0.my-cluster-kafka-brokers.myproject.svc.cluster.local. Default is false.
Example of an internal listener configured to use the Service DNS domain
If your OpenShift cluster uses a different service suffix than .cluster.local, you can configure the suffix using the KUBERNETES_SERVICE_DNS_DOMAIN environment variable in the Cluster Operator configuration.
6.2.11.7. GenericKafkaListenerConfiguration schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| brokerCertChainAndKey |
Reference to the |
| externalTrafficPolicy |
Specifies whether the service routes external traffic to node-local or cluster-wide endpoints. |
| string (one of [Local, Cluster]) | |
| loadBalancerSourceRanges |
A list of CIDR ranges (for example |
| string array | |
| bootstrap | Bootstrap configuration. |
| brokers | Per-broker configurations. |
| ipFamilyPolicy |
Specifies the IP Family Policy used by the service. Available options are |
| string (one of [RequireDualStack, SingleStack, PreferDualStack]) | |
| ipFamilies |
Specifies the IP Families used by the service. Available options are |
| string (one or more of [IPv6, IPv4]) array | |
| createBootstrapService |
Whether to create the bootstrap service or not. The bootstrap service is created by default (if not specified differently). This field can be used with the |
| boolean | |
| class |
Configures a specific class for |
| string | |
| finalizers |
A list of finalizers which will be configured for the |
| string array | |
| maxConnectionCreationRate | The maximum connection creation rate we allow in this listener at any time. New connections will be throttled if the limit is reached. |
| integer | |
| maxConnections | The maximum number of connections we allow for this listener in the broker at any time. New connections are blocked if the limit is reached. |
| integer | |
| preferredNodePortAddressType |
Defines which address type should be used as the node address. Available types are:
This field is used to select the preferred address type, which is checked first. If no address is found for this address type, the other types are checked in the default order. This field can only be used with |
| string (one of [ExternalDNS, ExternalIP, Hostname, InternalIP, InternalDNS]) | |
| useServiceDnsDomain |
Configures whether the OpenShift service DNS domain should be used or not. If set to |
| boolean |
6.2.12. CertAndKeySecretSource schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListenerConfiguration, KafkaClientAuthenticationTls
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| certificate | The name of the file certificate in the Secret. |
| string | |
| key | The name of the private key in the Secret. |
| string | |
| secretName | The name of the Secret containing the certificate. |
| string |
6.2.13. GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBootstrap schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListenerConfiguration
Full list of GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBootstrap schema properties
Broker service equivalents of nodePort, host, loadBalancerIP and annotations properties are configured in the GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBroker schema.
6.2.13.1. alternativeNames
You can specify alternative names for the bootstrap service. The names are added to the broker certificates and can be used for TLS hostname verification. The alternativeNames property is applicable to all types of listeners.
Example of an external route listener configured with an additional bootstrap address
6.2.13.2. host
The host property is used with route and ingress listeners to specify the hostnames used by the bootstrap and per-broker services.
A host property value is mandatory for ingress listener configuration, as the Ingress controller does not assign any hostnames automatically. Make sure that the hostnames resolve to the Ingress endpoints. AMQ Streams will not perform any validation that the requested hosts are available and properly routed to the Ingress endpoints.
Example of host configuration for an ingress listener
By default, route listener hosts are automatically assigned by OpenShift. However, you can override the assigned route hosts by specifying hosts.
AMQ Streams does not perform any validation that the requested hosts are available. You must ensure that they are free and can be used.
Example of host configuration for a route listener
6.2.13.3. nodePort
By default, the port numbers used for the bootstrap and broker services are automatically assigned by OpenShift. You can override the assigned node ports for nodeport listeners by specifying the requested port numbers.
AMQ Streams does not perform any validation on the requested ports. You must ensure that they are free and available for use.
Example of an external listener configured with overrides for node ports
6.2.13.4. loadBalancerIP
Use the loadBalancerIP property to request a specific IP address when creating a loadbalancer. Use this property when you need to use a loadbalancer with a specific IP address. The loadBalancerIP field is ignored if the cloud provider does not support the feature.
Example of an external listener of type loadbalancer with specific loadbalancer IP address requests
6.2.13.5. annotations
Use the annotations property to add annotations to OpenShift resources related to the listeners. You can use these annotations, for example, to instrument DNS tooling such as External DNS, which automatically assigns DNS names to the loadbalancer services.
Example of an external listener of type loadbalancer using annotations
6.2.13.6. GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBootstrap schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| alternativeNames | Additional alternative names for the bootstrap service. The alternative names will be added to the list of subject alternative names of the TLS certificates. |
| string array | |
| host |
The bootstrap host. This field will be used in the Ingress resource or in the Route resource to specify the desired hostname. This field can be used only with |
| string | |
| nodePort |
Node port for the bootstrap service. This field can be used only with |
| integer | |
| loadBalancerIP |
The loadbalancer is requested with the IP address specified in this field. This feature depends on whether the underlying cloud provider supports specifying the |
| string | |
| annotations |
Annotations that will be added to the |
| map | |
| labels |
Labels that will be added to the |
| map |
6.2.14. GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBroker schema reference
Used in: GenericKafkaListenerConfiguration
Full list of GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBroker schema properties
You can see example configuration for the nodePort, host, loadBalancerIP and annotations properties in the GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBootstrap schema, which configures bootstrap service overrides.
Advertised addresses for brokers
By default, AMQ Streams tries to automatically determine the hostnames and ports that your Kafka cluster advertises to its clients. This is not sufficient in all situations, because the infrastructure on which AMQ Streams is running might not provide the right hostname or port through which Kafka can be accessed.
You can specify a broker ID and customize the advertised hostname and port in the configuration property of the listener. AMQ Streams will then automatically configure the advertised address in the Kafka brokers and add it to the broker certificates so it can be used for TLS hostname verification. Overriding the advertised host and ports is available for all types of listeners.
Example of an external route listener configured with overrides for advertised addresses
6.2.14.1. GenericKafkaListenerConfigurationBroker schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| broker | ID of the kafka broker (broker identifier). Broker IDs start from 0 and correspond to the number of broker replicas. |
| integer | |
| advertisedHost |
The host name which will be used in the brokers' |
| string | |
| advertisedPort |
The port number which will be used in the brokers' |
| integer | |
| host |
The broker host. This field will be used in the Ingress resource or in the Route resource to specify the desired hostname. This field can be used only with |
| string | |
| nodePort |
Node port for the per-broker service. This field can be used only with |
| integer | |
| loadBalancerIP |
The loadbalancer is requested with the IP address specified in this field. This feature depends on whether the underlying cloud provider supports specifying the |
| string | |
| annotations |
Annotations that will be added to the |
| map | |
| labels |
Labels that will be added to the |
| map |
6.2.15. EphemeralStorage schema reference
Used in: JbodStorage, KafkaClusterSpec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the EphemeralStorage type from PersistentClaimStorage. It must have the value ephemeral for the type EphemeralStorage.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| id | Storage identification number. It is mandatory only for storage volumes defined in a storage of type 'jbod'. |
| integer | |
| sizeLimit | When type=ephemeral, defines the total amount of local storage required for this EmptyDir volume (for example 1Gi). |
| string | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.16. PersistentClaimStorage schema reference
Used in: JbodStorage, KafkaClusterSpec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the PersistentClaimStorage type from EphemeralStorage. It must have the value persistent-claim for the type PersistentClaimStorage.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| size | When type=persistent-claim, defines the size of the persistent volume claim (i.e 1Gi). Mandatory when type=persistent-claim. |
| string | |
| selector | Specifies a specific persistent volume to use. It contains key:value pairs representing labels for selecting such a volume. |
| map | |
| deleteClaim | Specifies if the persistent volume claim has to be deleted when the cluster is un-deployed. |
| boolean | |
| class | The storage class to use for dynamic volume allocation. |
| string | |
| id | Storage identification number. It is mandatory only for storage volumes defined in a storage of type 'jbod'. |
| integer | |
| overrides |
Overrides for individual brokers. The |
6.2.17. PersistentClaimStorageOverride schema reference
Used in: PersistentClaimStorage
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| class | The storage class to use for dynamic volume allocation for this broker. |
| string | |
| broker | Id of the kafka broker (broker identifier). |
| integer |
6.2.18. JbodStorage schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the JbodStorage type from EphemeralStorage, PersistentClaimStorage. It must have the value jbod for the type JbodStorage.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| volumes | List of volumes as Storage objects representing the JBOD disks array. |
6.2.19. KafkaAuthorizationSimple schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
Full list of KafkaAuthorizationSimple schema properties
Simple authorization in AMQ Streams uses the AclAuthorizer plugin, the default Access Control Lists (ACLs) authorization plugin provided with Apache Kafka. ACLs allow you to define which users have access to which resources at a granular level.
Configure the Kafka custom resource to use simple authorization. Set the type property in the authorization section to the value simple, and configure a list of super users.
Access rules are configured for the KafkaUser, as described in the ACLRule schema reference.
6.2.19.1. superUsers
A list of user principals treated as super users, so that they are always allowed without querying ACL rules.
An example of simple authorization configuration
The super.user configuration option in the config property in Kafka.spec.kafka is ignored. Designate super users in the authorization property instead. For more information, see Kafka broker configuration.
6.2.19.2. KafkaAuthorizationSimple schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaAuthorizationSimple type from KafkaAuthorizationOpa, KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak, KafkaAuthorizationCustom. It must have the value simple for the type KafkaAuthorizationSimple.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| superUsers | List of super users. Should contain list of user principals which should get unlimited access rights. |
| string array |
6.2.20. KafkaAuthorizationOpa schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
Full list of KafkaAuthorizationOpa schema properties
To use Open Policy Agent authorization, set the type property in the authorization section to the value opa, and configure OPA properties as required. AMQ Streams uses Open Policy Agent plugin for Kafka authorization as the authorizer. For more information about the format of the input data and policy examples, see Open Policy Agent plugin for Kafka authorization.
6.2.20.1. url
The URL used to connect to the Open Policy Agent server. The URL has to include the policy which will be queried by the authorizer. Required.
6.2.20.2. allowOnError
Defines whether a Kafka client should be allowed or denied by default when the authorizer fails to query the Open Policy Agent, for example, when it is temporarily unavailable. Defaults to false - all actions will be denied.
6.2.20.3. initialCacheCapacity
Initial capacity of the local cache used by the authorizer to avoid querying the Open Policy Agent for every request. Defaults to 5000.
6.2.20.4. maximumCacheSize
Maximum capacity of the local cache used by the authorizer to avoid querying the Open Policy Agent for every request. Defaults to 50000.
6.2.20.5. expireAfterMs
The expiration of the records kept in the local cache to avoid querying the Open Policy Agent for every request. Defines how often the cached authorization decisions are reloaded from the Open Policy Agent server. In milliseconds. Defaults to 3600000 milliseconds (1 hour).
6.2.20.6. tlsTrustedCertificates
Trusted certificates for TLS connection to the OPA server.
6.2.20.7. superUsers
A list of user principals treated as super users, so that they are always allowed without querying the open Policy Agent policy.
An example of Open Policy Agent authorizer configuration
6.2.20.8. KafkaAuthorizationOpa schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaAuthorizationOpa type from KafkaAuthorizationSimple, KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak, KafkaAuthorizationCustom. It must have the value opa for the type KafkaAuthorizationOpa.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| url | The URL used to connect to the Open Policy Agent server. The URL has to include the policy which will be queried by the authorizer. This option is required. |
| string | |
| allowOnError |
Defines whether a Kafka client should be allowed or denied by default when the authorizer fails to query the Open Policy Agent, for example, when it is temporarily unavailable). Defaults to |
| boolean | |
| initialCacheCapacity |
Initial capacity of the local cache used by the authorizer to avoid querying the Open Policy Agent for every request Defaults to |
| integer | |
| maximumCacheSize |
Maximum capacity of the local cache used by the authorizer to avoid querying the Open Policy Agent for every request. Defaults to |
| integer | |
| expireAfterMs |
The expiration of the records kept in the local cache to avoid querying the Open Policy Agent for every request. Defines how often the cached authorization decisions are reloaded from the Open Policy Agent server. In milliseconds. Defaults to |
| integer | |
| tlsTrustedCertificates | Trusted certificates for TLS connection to the OPA server. |
|
| |
| superUsers | List of super users, which is specifically a list of user principals that have unlimited access rights. |
| string array | |
| enableMetrics |
Defines whether the Open Policy Agent authorizer plugin should provide metrics. Defaults to |
| boolean |
6.2.21. KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak type from KafkaAuthorizationSimple, KafkaAuthorizationOpa, KafkaAuthorizationCustom. It must have the value keycloak for the type KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| clientId | OAuth Client ID which the Kafka client can use to authenticate against the OAuth server and use the token endpoint URI. |
| string | |
| tokenEndpointUri | Authorization server token endpoint URI. |
| string | |
| tlsTrustedCertificates | Trusted certificates for TLS connection to the OAuth server. |
|
| |
| disableTlsHostnameVerification |
Enable or disable TLS hostname verification. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| delegateToKafkaAcls |
Whether authorization decision should be delegated to the 'Simple' authorizer if DENIED by Red Hat Single Sign-On Authorization Services policies. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| grantsRefreshPeriodSeconds | The time between two consecutive grants refresh runs in seconds. The default value is 60. |
| integer | |
| grantsRefreshPoolSize | The number of threads to use to refresh grants for active sessions. The more threads, the more parallelism, so the sooner the job completes. However, using more threads places a heavier load on the authorization server. The default value is 5. |
| integer | |
| superUsers | List of super users. Should contain list of user principals which should get unlimited access rights. |
| string array | |
| connectTimeoutSeconds | The connect timeout in seconds when connecting to authorization server. If not set, the effective connect timeout is 60 seconds. |
| integer | |
| readTimeoutSeconds | The read timeout in seconds when connecting to authorization server. If not set, the effective read timeout is 60 seconds. |
| integer | |
| httpRetries | The maximum number of retries to attempt if an initial HTTP request fails. If not set, the default is to not attempt any retries. |
| integer | |
| enableMetrics |
Enable or disable OAuth metrics. Default value is |
| boolean |
6.2.22. KafkaAuthorizationCustom schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
Full list of KafkaAuthorizationCustom schema properties
To use custom authorization in AMQ Streams, you can configure your own Authorizer plugin to define Access Control Lists (ACLs).
ACLs allow you to define which users have access to which resources at a granular level.
Configure the Kafka custom resource to use custom authorization. Set the type property in the authorization section to the value custom, and the set following properties.
The custom authorizer must implement the org.apache.kafka.server.authorizer.Authorizer interface, and support configuration of super.users using the super.users configuration property.
6.2.22.1. authorizerClass
(Required) Java class that implements the org.apache.kafka.server.authorizer.Authorizer interface to support custom ACLs.
6.2.22.2. superUsers
A list of user principals treated as super users, so that they are always allowed without querying ACL rules.
You can add configuration for initializing the custom authorizer using Kafka.spec.kafka.config.
An example of custom authorization configuration under Kafka.spec
In addition to the Kafka custom resource configuration, the JAR file containing the custom authorizer class along with its dependencies must be available on the classpath of the Kafka broker.
The AMQ Streams Maven build process provides a mechanism to add custom third-party libraries to the generated Kafka broker container image by adding them as dependencies in the pom.xml file under the docker-images/kafka/kafka-thirdparty-libs directory. The directory contains different folders for different Kafka versions. Choose the appropriate folder. Before modifying the pom.xml file, the third-party library must be available in a Maven repository, and that Maven repository must be accessible to the AMQ Streams build process.
The super.user configuration option in the config property in Kafka.spec.kafka is ignored. Designate super users in the authorization property instead. For more information, see Kafka broker configuration.
Custom authorization can make use of group membership information extracted from the JWT token during authentication when using oauth authentication and configuring groupsClaim configuration attribute. Groups are available on the OAuthKafkaPrincipal object during authorize() call as follows:
6.2.22.3. KafkaAuthorizationCustom schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaAuthorizationCustom type from KafkaAuthorizationSimple, KafkaAuthorizationOpa, KafkaAuthorizationKeycloak. It must have the value custom for the type KafkaAuthorizationCustom.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| authorizerClass | Authorization implementation class, which must be available in classpath. |
| string | |
| superUsers | List of super users, which are user principals with unlimited access rights. |
| string array | |
| supportsAdminApi |
Indicates whether the custom authorizer supports the APIs for managing ACLs using the Kafka Admin API. Defaults to |
| boolean |
6.2.23. Rack schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec
Full list of Rack schema properties
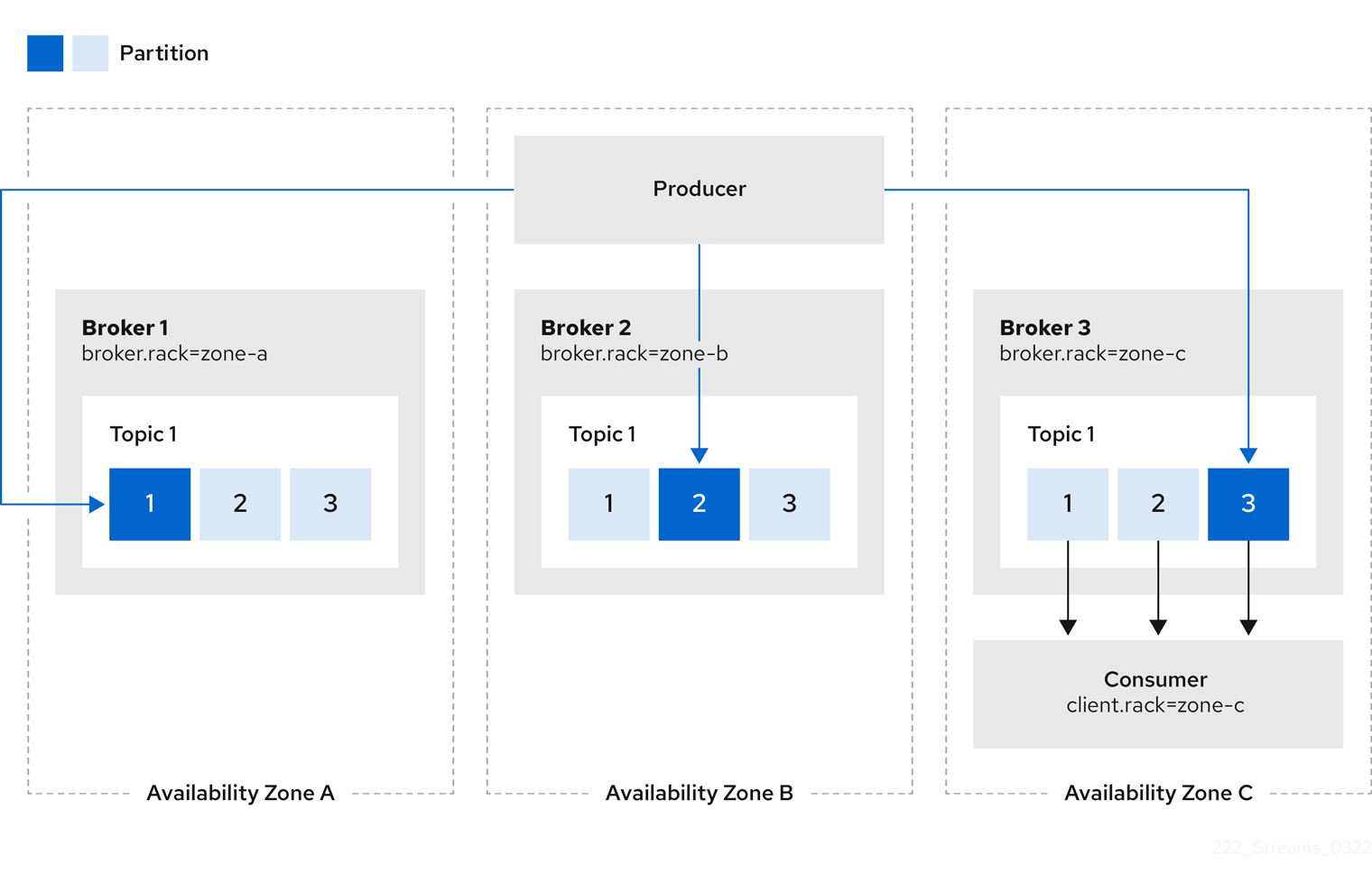
The rack option configures rack awareness. A rack can represent an availability zone, data center, or an actual rack in your data center. The rack is configured through a topologyKey. topologyKey identifies a label on OpenShift nodes that contains the name of the topology in its value. An example of such a label is topology.kubernetes.io/zone (or failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone on older OpenShift versions), which contains the name of the availability zone in which the OpenShift node runs. You can configure your Kafka cluster to be aware of the rack in which it runs, and enable additional features such as spreading partition replicas across different racks or consuming messages from the closest replicas.
For more information about OpenShift node labels, see Well-Known Labels, Annotations and Taints. Consult your OpenShift administrator regarding the node label that represents the zone or rack into which the node is deployed.
6.2.23.1. Spreading partition replicas across racks
When rack awareness is configured, AMQ Streams will set broker.rack configuration for each Kafka broker. The broker.rack configuration assigns a rack ID to each broker. When broker.rack is configured, Kafka brokers will spread partition replicas across as many different racks as possible. When replicas are spread across multiple racks, the probability that multiple replicas will fail at the same time is lower than if they would be in the same rack. Spreading replicas improves resiliency, and is important for availability and reliability. To enable rack awareness in Kafka, add the rack option to the .spec.kafka section of the Kafka custom resource as shown in the example below.
Example rack configuration for Kafka
The rack in which brokers are running can change in some cases when the pods are deleted or restarted. As a result, the replicas running in different racks might then share the same rack. Use Cruise Control and the KafkaRebalance resource with the RackAwareGoal to make sure that replicas remain distributed across different racks.
When rack awareness is enabled in the Kafka custom resource, AMQ Streams will automatically add the OpenShift preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution affinity rule to distribute the Kafka brokers across the different racks. However, the preferred rule does not guarantee that the brokers will be spread. Depending on your exact OpenShift and Kafka configurations, you should add additional affinity rules or configure topologySpreadConstraints for both ZooKeeper and Kafka to make sure the nodes are properly distributed accross as many racks as possible. For more information see Section 2.8, “Configuring pod scheduling”.
6.2.23.2. Consuming messages from the closest replicas
Rack awareness can also be used in consumers to fetch data from the closest replica. This is useful for reducing the load on your network when a Kafka cluster spans multiple datacenters and can also reduce costs when running Kafka in public clouds. However, it can lead to increased latency.
In order to be able to consume from the closest replica, rack awareness has to be configured in the Kafka cluster, and the RackAwareReplicaSelector has to be enabled. The replica selector plugin provides the logic that enables clients to consume from the nearest replica. The default implementation uses LeaderSelector to always select the leader replica for the client. Specify RackAwareReplicaSelector for the replica.selector.class to switch from the default implementation.
Example rack configuration with enabled replica-aware selector
In addition to the Kafka broker configuration, you also need to specify the client.rack option in your consumers. The client.rack option should specify the rack ID in which the consumer is running. RackAwareReplicaSelector associates matching broker.rack and client.rack IDs, to find the nearest replica and consume from it. If there are multiple replicas in the same rack, RackAwareReplicaSelector always selects the most up-to-date replica. If the rack ID is not specified, or if it cannot find a replica with the same rack ID, it will fall back to the leader replica.
Figure 6.1. Example showing client consuming from replicas in the same availability zone
You can also configure Kafka Connect, MirrorMaker 2 and Kafka Bridge so that connectors consume messages from the closest replicas. You enable rack awareness in the KafkaConnect, KafkaMirrorMaker2, and KafkaBridge custom resources. The configuration does does not set affinity rules, but you can also configure affinity or topologySpreadConstraints. For more information see Section 2.8, “Configuring pod scheduling”.
When deploying Kafka Connect using AMQ Streams, you can use the rack section in the KafkaConnect custom resource to automatically configure the client.rack option.
Example rack configuration for Kafka Connect
When deploying MirrorMaker 2 using AMQ Streams, you can use the rack section in the KafkaMirrorMaker2 custom resource to automatically configure the client.rack option.
Example rack configuration for MirrorMaker 2
When deploying Kafka Bridge using AMQ Streams, you can use the rack section in the KafkaBridge custom resource to automatically configure the client.rack option.
Example rack configuration for Kafka Bridge
6.2.23.3. Rack schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| topologyKey |
A key that matches labels assigned to the OpenShift cluster nodes. The value of the label is used to set a broker’s |
| string |
6.2.24. Probe schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec, EntityTopicOperatorSpec, EntityUserOperatorSpec, KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaExporterSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec, TlsSidecar, ZookeeperClusterSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| failureThreshold | Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded. Defaults to 3. Minimum value is 1. |
| integer | |
| initialDelaySeconds | The initial delay before first the health is first checked. Default to 15 seconds. Minimum value is 0. |
| integer | |
| periodSeconds | How often (in seconds) to perform the probe. Default to 10 seconds. Minimum value is 1. |
| integer | |
| successThreshold | Minimum consecutive successes for the probe to be considered successful after having failed. Defaults to 1. Must be 1 for liveness. Minimum value is 1. |
| integer | |
| timeoutSeconds | The timeout for each attempted health check. Default to 5 seconds. Minimum value is 1. |
| integer |
6.2.25. JvmOptions schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec, EntityTopicOperatorSpec, EntityUserOperatorSpec, KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| -XX | A map of -XX options to the JVM. |
| map | |
| -Xms | -Xms option to to the JVM. |
| string | |
| -Xmx | -Xmx option to to the JVM. |
| string | |
| gcLoggingEnabled | Specifies whether the Garbage Collection logging is enabled. The default is false. |
| boolean | |
| javaSystemProperties |
A map of additional system properties which will be passed using the |
|
|
6.2.26. SystemProperty schema reference
Used in: JvmOptions
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| name | The system property name. |
| string | |
| value | The system property value. |
| string |
6.2.27. KafkaJmxOptions schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
Full list of KafkaJmxOptions schema properties
Configures JMX connection options.
Get JMX metrics from Kafka brokers, ZooKeeper nodes, Kafka Connect, and MirrorMaker 2. by connecting to port 9999. Use the jmxOptions property to configure a password-protected or an unprotected JMX port. Using password protection prevents unauthorized pods from accessing the port.
You can then obtain metrics about the component.
For example, for each Kafka broker you can obtain bytes-per-second usage data from clients, or the request rate of the network of the broker.
To enable security for the JMX port, set the type parameter in the authentication field to password.
Example password-protected JMX configuration for Kafka brokers and ZooKeeper nodes
You can then deploy a pod into a cluster and obtain JMX metrics using the headless service by specifying which broker you want to address.
For example, to get JMX metrics from broker 0 you specify:
"CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-0.CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-brokers"
"CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-0.CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-brokers"
CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-0 is name of the broker pod, and CLUSTER-NAME-kafka-brokers is the name of the headless service to return the IPs of the broker pods.
If the JMX port is secured, you can get the username and password by referencing them from the JMX Secret in the deployment of your pod.
For an unprotected JMX port, use an empty object {} to open the JMX port on the headless service. You deploy a pod and obtain metrics in the same way as for the protected port, but in this case any pod can read from the JMX port.
Example open port JMX configuration for Kafka brokers and ZooKeeper nodes
6.2.27.1. KafkaJmxOptions schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for connecting to the JMX port. The type depends on the value of the |
6.2.28. KafkaJmxAuthenticationPassword schema reference
Used in: KafkaJmxOptions
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaJmxAuthenticationPassword type from other subtypes which may be added in the future. It must have the value password for the type KafkaJmxAuthenticationPassword.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.29. JmxPrometheusExporterMetrics schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec, KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the JmxPrometheusExporterMetrics type from other subtypes which may be added in the future. It must have the value jmxPrometheusExporter for the type JmxPrometheusExporterMetrics.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| valueFrom | ConfigMap entry where the Prometheus JMX Exporter configuration is stored. For details of the structure of this configuration, see the Prometheus JMX Exporter. |
6.2.30. ExternalConfigurationReference schema reference
Used in: ExternalLogging, JmxPrometheusExporterMetrics
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| configMapKeyRef | Reference to the key in the ConfigMap containing the configuration. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 configmapkeyselector. |
6.2.31. InlineLogging schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec, EntityTopicOperatorSpec, EntityUserOperatorSpec, KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the InlineLogging type from ExternalLogging. It must have the value inline for the type InlineLogging.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| loggers | A Map from logger name to logger level. |
| map |
6.2.32. ExternalLogging schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec, EntityTopicOperatorSpec, EntityUserOperatorSpec, KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaClusterSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec, ZookeeperClusterSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the ExternalLogging type from InlineLogging. It must have the value external for the type ExternalLogging.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| valueFrom |
|
6.2.33. KafkaClusterTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| statefulset |
Template for Kafka |
| pod |
Template for Kafka |
| bootstrapService |
Template for Kafka bootstrap |
| brokersService |
Template for Kafka broker |
| externalBootstrapService |
Template for Kafka external bootstrap |
| perPodService |
Template for Kafka per-pod |
| externalBootstrapRoute |
Template for Kafka external bootstrap |
| perPodRoute |
Template for Kafka per-pod |
| externalBootstrapIngress |
Template for Kafka external bootstrap |
| perPodIngress |
Template for Kafka per-pod |
| persistentVolumeClaim |
Template for all Kafka |
| podDisruptionBudget |
Template for Kafka |
| kafkaContainer | Template for the Kafka broker container. |
| initContainer | Template for the Kafka init container. |
| clusterCaCert | Template for Secret with Kafka Cluster certificate public key. |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Kafka service account. |
| jmxSecret | Template for Secret of the Kafka Cluster JMX authentication. |
| clusterRoleBinding | Template for the Kafka ClusterRoleBinding. |
| podSet |
Template for Kafka |
6.2.34. StatefulSetTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaClusterTemplate, ZookeeperClusterTemplate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata | Metadata applied to the resource. |
| podManagementPolicy |
PodManagementPolicy which will be used for this StatefulSet. Valid values are |
| string (one of [OrderedReady, Parallel]) |
6.2.35. MetadataTemplate schema reference
Used in: BuildConfigTemplate, DeploymentTemplate, InternalServiceTemplate, PodDisruptionBudgetTemplate, PodTemplate, ResourceTemplate, StatefulSetTemplate
Full list of MetadataTemplate schema properties
Labels and Annotations are used to identify and organize resources, and are configured in the metadata property.
For example:
The labels and annotations fields can contain any labels or annotations that do not contain the reserved string strimzi.io. Labels and annotations containing strimzi.io are used internally by AMQ Streams and cannot be configured.
6.2.35.1. MetadataTemplate schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| labels |
Labels added to the resource template. Can be applied to different resources such as |
| map | |
| annotations |
Annotations added to the resource template. Can be applied to different resources such as |
| map |
6.2.36. PodTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlTemplate, EntityOperatorTemplate, KafkaBridgeTemplate, KafkaClusterTemplate, KafkaConnectTemplate, KafkaExporterTemplate, KafkaMirrorMakerTemplate, ZookeeperClusterTemplate
Full list of PodTemplate schema properties
Configures the template for Kafka pods.
Example PodTemplate configuration
6.2.36.1. hostAliases
Use the hostAliases property to a specify a list of hosts and IP addresses, which are injected into the /etc/hosts file of the pod.
This configuration is especially useful for Kafka Connect or MirrorMaker when a connection outside of the cluster is also requested by users.
Example hostAliases configuration
6.2.36.2. PodTemplate schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata | Metadata applied to the resource. |
| imagePullSecrets |
List of references to secrets in the same namespace to use for pulling any of the images used by this Pod. When the |
| LocalObjectReference array | |
| securityContext | Configures pod-level security attributes and common container settings. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 podsecuritycontext. |
| terminationGracePeriodSeconds | The grace period is the duration in seconds after the processes running in the pod are sent a termination signal, and the time when the processes are forcibly halted with a kill signal. Set this value to longer than the expected cleanup time for your process. Value must be a non-negative integer. A zero value indicates delete immediately. You might need to increase the grace period for very large Kafka clusters, so that the Kafka brokers have enough time to transfer their work to another broker before they are terminated. Defaults to 30 seconds. |
| integer | |
| affinity | The pod’s affinity rules. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 affinity. |
| tolerations | The pod’s tolerations. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 toleration. |
| Toleration array | |
| priorityClassName | The name of the priority class used to assign priority to the pods. For more information about priority classes, see Pod Priority and Preemption. |
| string | |
| schedulerName |
The name of the scheduler used to dispatch this |
| string | |
| hostAliases | The pod’s HostAliases. HostAliases is an optional list of hosts and IPs that will be injected into the Pod’s hosts file if specified. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 hostalias. |
| HostAlias array | |
| tmpDirSizeLimit |
Defines the total amount (for example |
| string | |
| enableServiceLinks | Indicates whether information about services should be injected into Pod’s environment variables. |
| boolean | |
| topologySpreadConstraints | The pod’s topology spread constraints. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 topologyspreadconstraint. |
| TopologySpreadConstraint array |
6.2.37. InternalServiceTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlTemplate, KafkaBridgeTemplate, KafkaClusterTemplate, KafkaConnectTemplate, ZookeeperClusterTemplate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata | Metadata applied to the resource. |
| ipFamilyPolicy |
Specifies the IP Family Policy used by the service. Available options are |
| string (one of [RequireDualStack, SingleStack, PreferDualStack]) | |
| ipFamilies |
Specifies the IP Families used by the service. Available options are |
| string (one or more of [IPv6, IPv4]) array |
6.2.38. ResourceTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlTemplate, EntityOperatorTemplate, KafkaBridgeTemplate, KafkaClusterTemplate, KafkaConnectTemplate, KafkaExporterTemplate, KafkaMirrorMakerTemplate, KafkaUserTemplate, ZookeeperClusterTemplate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata | Metadata applied to the resource. |
6.2.39. PodDisruptionBudgetTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlTemplate, KafkaBridgeTemplate, KafkaClusterTemplate, KafkaConnectTemplate, KafkaMirrorMakerTemplate, ZookeeperClusterTemplate
Full list of PodDisruptionBudgetTemplate schema properties
AMQ Streams creates a PodDisruptionBudget for every new StrimziPodSet, StatefulSet, or Deployment. By default, pod disruption budgets only allow a single pod to be unavailable at a given time. You can increase the amount of unavailable pods allowed by changing the default value of the maxUnavailable property.
An example of PodDisruptionBudget template
6.2.39.1. PodDisruptionBudgetTemplate schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata |
Metadata to apply to the |
| maxUnavailable |
Maximum number of unavailable pods to allow automatic Pod eviction. A Pod eviction is allowed when the |
| integer |
6.2.40. ContainerTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlTemplate, EntityOperatorTemplate, KafkaBridgeTemplate, KafkaClusterTemplate, KafkaConnectTemplate, KafkaExporterTemplate, KafkaMirrorMakerTemplate, ZookeeperClusterTemplate
Full list of ContainerTemplate schema properties
You can set custom security context and environment variables for a container.
The environment variables are defined under the env property as a list of objects with name and value fields. The following example shows two custom environment variables and a custom security context set for the Kafka broker containers:
Environment variables prefixed with KAFKA_ are internal to AMQ Streams and should be avoided. If you set a custom environment variable that is already in use by AMQ Streams, it is ignored and a warning is recorded in the log.
6.2.40.1. ContainerTemplate schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| env | Environment variables which should be applied to the container. |
|
| |
| securityContext | Security context for the container. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 securitycontext. |
6.2.41. ContainerEnvVar schema reference
Used in: ContainerTemplate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| name | The environment variable key. |
| string | |
| value | The environment variable value. |
| string |
6.2.42. ZookeeperClusterSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaSpec
Full list of ZookeeperClusterSpec schema properties
Configures a ZooKeeper cluster.
6.2.42.1. config
Use the config properties to configure ZooKeeper options as keys.
Standard Apache ZooKeeper configuration may be provided, restricted to those properties not managed directly by AMQ Streams.
Configuration options that cannot be configured relate to:
- Security (Encryption, Authentication, and Authorization)
- Listener configuration
- Configuration of data directories
- ZooKeeper cluster composition
The values can be one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
You can specify and configure the options listed in the ZooKeeper documentation with the exception of those managed directly by AMQ Streams. Specifically, all configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
server. -
dataDir -
dataLogDir -
clientPort -
authProvider -
quorum.auth -
requireClientAuthScheme
When a forbidden option is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message is printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other supported options are passed to ZooKeeper.
There are exceptions to the forbidden options. For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties.
Example ZooKeeper configuration
6.2.42.2. logging
ZooKeeper has a configurable logger:
-
zookeeper.root.logger
ZooKeeper uses the Apache log4j logger implementation.
Use the logging property to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.42.3. ZookeeperClusterSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| replicas | The number of pods in the cluster. |
| integer | |
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| storage |
Storage configuration (disk). Cannot be updated. The type depends on the value of the |
| config | The ZooKeeper broker config. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: server., dataDir, dataLogDir, clientPort, authProvider, quorum.auth, requireClientAuthScheme, snapshot.trust.empty, standaloneEnabled, reconfigEnabled, 4lw.commands.whitelist, secureClientPort, ssl., serverCnxnFactory, sslQuorum (with the exception of: ssl.protocol, ssl.quorum.protocol, ssl.enabledProtocols, ssl.quorum.enabledProtocols, ssl.ciphersuites, ssl.quorum.ciphersuites, ssl.hostnameVerification, ssl.quorum.hostnameVerification). |
| map | |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
| jmxOptions | JMX Options for Zookeeper nodes. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| metricsConfig |
Metrics configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
| logging |
Logging configuration for ZooKeeper. The type depends on the value of the |
| template |
Template for ZooKeeper cluster resources. The template allows users to specify how the |
6.2.43. ZookeeperClusterTemplate schema reference
Used in: ZookeeperClusterSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| statefulset |
Template for ZooKeeper |
| pod |
Template for ZooKeeper |
| clientService |
Template for ZooKeeper client |
| nodesService |
Template for ZooKeeper nodes |
| persistentVolumeClaim |
Template for all ZooKeeper |
| podDisruptionBudget |
Template for ZooKeeper |
| zookeeperContainer | Template for the ZooKeeper container. |
| serviceAccount | Template for the ZooKeeper service account. |
| jmxSecret | Template for Secret of the Zookeeper Cluster JMX authentication. |
| podSet |
Template for ZooKeeper |
6.2.44. EntityOperatorSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| topicOperator | Configuration of the Topic Operator. |
| userOperator | Configuration of the User Operator. |
| tlsSidecar | TLS sidecar configuration. |
| template |
Template for Entity Operator resources. The template allows users to specify how a |
6.2.45. EntityTopicOperatorSpec schema reference
Used in: EntityOperatorSpec
Full list of EntityTopicOperatorSpec schema properties
Configures the Topic Operator.
6.2.45.1. logging
The Topic Operator has a configurable logger:
-
rootLogger.level
The Topic Operator uses the Apache log4j2 logger implementation.
Use the logging property in the entityOperator.topicOperator field of the Kafka resource Kafka resource to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j2.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.45.2. EntityTopicOperatorSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| watchedNamespace | The namespace the Topic Operator should watch. |
| string | |
| image | The image to use for the Topic Operator. |
| string | |
| reconciliationIntervalSeconds | Interval between periodic reconciliations. |
| integer | |
| zookeeperSessionTimeoutSeconds | Timeout for the ZooKeeper session. |
| integer | |
| startupProbe | Pod startup checking. |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| topicMetadataMaxAttempts | The number of attempts at getting topic metadata. |
| integer | |
| logging |
Logging configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
6.2.46. EntityUserOperatorSpec schema reference
Used in: EntityOperatorSpec
Full list of EntityUserOperatorSpec schema properties
Configures the User Operator.
6.2.46.1. logging
The User Operator has a configurable logger:
-
rootLogger.level
The User Operator uses the Apache log4j2 logger implementation.
Use the logging property in the entityOperator.userOperator field of the Kafka resource to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j2.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.46.2. EntityUserOperatorSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| watchedNamespace | The namespace the User Operator should watch. |
| string | |
| image | The image to use for the User Operator. |
| string | |
| reconciliationIntervalSeconds | Interval between periodic reconciliations. |
| integer | |
| zookeeperSessionTimeoutSeconds |
The |
| integer | |
| secretPrefix | The prefix that will be added to the KafkaUser name to be used as the Secret name. |
| string | |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| logging |
Logging configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
6.2.47. TlsSidecar schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec, EntityOperatorSpec
Full list of TlsSidecar schema properties
Configures a TLS sidecar, which is a container that runs in a pod, but serves a supporting purpose. In AMQ Streams, the TLS sidecar uses TLS to encrypt and decrypt communication between components and ZooKeeper.
The TLS sidecar is used in the Entity Operator.
The TLS sidecar is configured using the tlsSidecar property in Kafka.spec.entityOperator.
The TLS sidecar supports the following additional options:
-
image -
resources -
logLevel -
readinessProbe -
livenessProbe
The resources property specifies the memory and CPU resources allocated for the TLS sidecar.
The image property configures the container image which will be used.
The readinessProbe and livenessProbe properties configure healthcheck probes for the TLS sidecar.
The logLevel property specifies the logging level. The following logging levels are supported:
- emerg
- alert
- crit
- err
- warning
- notice
- info
- debug
The default value is notice.
Example TLS sidecar configuration
6.2.47.1. TlsSidecar schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| image | The docker image for the container. |
| string | |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| logLevel |
The log level for the TLS sidecar. Default value is |
| string (one of [emerg, debug, crit, err, alert, warning, notice, info]) | |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
6.2.48. EntityOperatorTemplate schema reference
Used in: EntityOperatorSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment |
Template for Entity Operator |
| pod |
Template for Entity Operator |
| topicOperatorContainer | Template for the Entity Topic Operator container. |
| userOperatorContainer | Template for the Entity User Operator container. |
| tlsSidecarContainer | Template for the Entity Operator TLS sidecar container. |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Entity Operator service account. |
| entityOperatorRole | Template for the Entity Operator Role. |
| topicOperatorRoleBinding | Template for the Entity Topic Operator RoleBinding. |
| userOperatorRoleBinding | Template for the Entity Topic Operator RoleBinding. |
6.2.49. DeploymentTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlTemplate, EntityOperatorTemplate, KafkaBridgeTemplate, KafkaConnectTemplate, KafkaExporterTemplate, KafkaMirrorMakerTemplate
Full list of DeploymentTemplate schema properties
Use deploymentStrategy to specify the strategy used to replace old pods with new ones when deployment configuration changes.
Use one of the following values:
-
RollingUpdate: Pods are restarted with zero downtime. -
Recreate: Pods are terminated before new ones are created.
Using the Recreate deployment strategy has the advantage of not requiring spare resources, but the disadvantage is the application downtime.
Example showing the deployment strategy set to Recreate.
# ...
template:
deployment:
deploymentStrategy: Recreate
# ...
# ...
template:
deployment:
deploymentStrategy: Recreate
# ...This configuration change does not cause a rolling update.
6.2.49.1. DeploymentTemplate schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata | Metadata applied to the resource. |
| deploymentStrategy |
Pod replacement strategy for deployment configuration changes. Valid values are |
| string (one of [RollingUpdate, Recreate]) |
6.2.50. CertificateAuthority schema reference
Used in: KafkaSpec
Configuration of how TLS certificates are used within the cluster. This applies to certificates used for both internal communication within the cluster and to certificates used for client access via Kafka.spec.kafka.listeners.tls.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| generateCertificateAuthority | If true then Certificate Authority certificates will be generated automatically. Otherwise the user will need to provide a Secret with the CA certificate. Default is true. |
| boolean | |
| generateSecretOwnerReference |
If |
| boolean | |
| validityDays | The number of days generated certificates should be valid for. The default is 365. |
| integer | |
| renewalDays |
The number of days in the certificate renewal period. This is the number of days before the a certificate expires during which renewal actions may be performed. When |
| integer | |
| certificateExpirationPolicy |
How should CA certificate expiration be handled when |
| string (one of [replace-key, renew-certificate]) |
6.2.51. CruiseControlSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaSpec
Full list of CruiseControlSpec schema properties
Configures a Cruise Control cluster.
Configuration options relate to:
- Goals configuration
- Capacity limits for resource distribution goals
6.2.51.1. config
Use the config properties to configure Cruise Control options as keys.
Standard Cruise Control configuration may be provided, restricted to those properties not managed directly by AMQ Streams.
Configuration options that cannot be configured relate to the following:
- Security (Encryption, Authentication, and Authorization)
- Connection to the Kafka cluster
- Client ID configuration
- ZooKeeper connectivity
- Web server configuration
- Self healing
The values can be one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Cruise Control documentation with the exception of those options that are managed directly by AMQ Streams. See the description of the config property for a list of forbidden prefixes.
When a forbidden option is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message is printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other supported options are passed to Cruise Control.
There are exceptions to the forbidden options. For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties. You can also configure webserver properties to enable Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS).
Example Cruise Control configuration
6.2.51.2. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a HTTP mechanism for controlling access to REST APIs. Restrictions can be on access methods or originating URLs of client applications. You can enable CORS with Cruise Control using the webserver.http.cors.enabled property in the config. When enabled, CORS permits read access to the Cruise Control REST API from applications that have different originating URLs than AMQ Streams. This allows applications from specified origins to use GET requests to fetch information about the Kafka cluster through the Cruise Control API. For example, applications can fetch information on the current cluster load or the most recent optimization proposal. POST requests are not permitted.
For more information on using CORS with Cruise Control, see REST APIs in the Cruise Control Wiki.
Enabling CORS for Cruise Control
You enable and configure CORS in Kafka.spec.cruiseControl.config.
- 1
- Enables CORS.
- 2
- Specifies permitted origins for the
Access-Control-Allow-OriginHTTP response header. You can use a wildcard or specify a single origin as a URL. If you use a wildcard, a response is returned following requests from any origin. - 3
- Exposes specified header names for the
Access-Control-Expose-HeadersHTTP response header. Applications in permitted origins can read responses with the specified headers.
6.2.51.3. Cruise Control REST API security
The Cruise Control REST API is secured with HTTP Basic authentication and SSL to protect the cluster against potentially destructive Cruise Control operations, such as decommissioning Kafka brokers. We recommend that Cruise Control in AMQ Streams is only used with these settings enabled.
However, it is possible to disable these settings by specifying the following Cruise Control configuration:
-
To disable the built-in HTTP Basic authentication, set
webserver.security.enabletofalse. -
To disable the built-in SSL, set
webserver.ssl.enabletofalse.
Cruise Control configuration to disable API authorization, authentication, and SSL
6.2.51.4. brokerCapacity
Cruise Control uses capacity limits to determine if optimization goals for resource distribution are being broken. There are four goals of this type:
-
DiskUsageDistributionGoal- Disk utilization distribution -
CpuUsageDistributionGoal- CPU utilization distribution -
NetworkInboundUsageDistributionGoal- Network inbound utilization distribution -
NetworkOutboundUsageDistributionGoal- Network outbound utilization distribution
You specify capacity limits for Kafka broker resources in the brokerCapacity property in Kafka.spec.cruiseControl . They are enabled by default and you can change their default values. Capacity limits can be set for the following broker resources:
-
cpu- CPU resource in millicores or CPU cores (Default: 1) -
inboundNetwork- Inbound network throughput in byte units per second (Default: 10000KiB/s) -
outboundNetwork- Outbound network throughput in byte units per second (Default: 10000KiB/s)
For network throughput, use an integer value with standard OpenShift byte units (K, M, G) or their bibyte (power of two) equivalents (Ki, Mi, Gi) per second.
Disk and CPU capacity limits are automatically generated by AMQ Streams, so you do not need to set them. In order to guarantee accurate rebalance proposals when using CPU goals, you can set CPU requests equal to CPU limits in Kafka.spec.kafka.resources. That way, all CPU resources are reserved upfront and are always available. This configuration allows Cruise Control to properly evaluate the CPU utilization when preparing the rebalance proposals based on CPU goals. In cases where you cannot set CPU requests equal to CPU limits in Kafka.spec.kafka.resources, you can set the CPU capacity manually for the same accuracy.
Example Cruise Control brokerCapacity configuration using bibyte units
6.2.51.5. Capacity overrides
Brokers might be running on nodes with heterogeneous network or CPU resources. If that’s the case, specify overrides that set the network capacity and CPU limits for each broker. The overrides ensure an accurate rebalance between the brokers. Override capacity limits can be set for the following broker resources:
-
cpu- CPU resource in millicores or CPU cores (Default: 1) -
inboundNetwork- Inbound network throughput in byte units per second (Default: 10000KiB/s) -
outboundNetwork- Outbound network throughput in byte units per second (Default: 10000KiB/s)
An example of Cruise Control capacity overrides configuration using bibyte units
For more information, refer to the BrokerCapacity schema reference.
6.2.51.6. Logging configuration
Cruise Control has its own configurable logger:
-
rootLogger.level
Cruise Control uses the Apache log4j2 logger implementation.
Use the logging property to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.51.7. CruiseControlSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| tlsSidecar |
The |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve for the Cruise Control container. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking for the Cruise Control container. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking for the Cruise Control container. |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for the Cruise Control container. |
| logging |
Logging configuration (Log4j 2) for Cruise Control. The type depends on the value of the |
| template |
Template to specify how Cruise Control resources, |
| brokerCapacity |
The Cruise Control |
| config | The Cruise Control configuration. For a full list of configuration options refer to https://github.com/linkedin/cruise-control/wiki/Configurations. Note that properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: bootstrap.servers, client.id, zookeeper., network., security., failed.brokers.zk.path,webserver.http., webserver.api.urlprefix, webserver.session.path, webserver.accesslog., two.step., request.reason.required,metric.reporter.sampler.bootstrap.servers, capacity.config.file, self.healing., ssl., kafka.broker.failure.detection.enable, topic.config.provider.class (with the exception of: ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols, webserver.http.cors.enabled, webserver.http.cors.origin, webserver.http.cors.exposeheaders, webserver.security.enable, webserver.ssl.enable). |
| map | |
| metricsConfig |
Metrics configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
6.2.52. CruiseControlTemplate schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment |
Template for Cruise Control |
| pod |
Template for Cruise Control |
| apiService |
Template for Cruise Control API |
| podDisruptionBudget |
Template for Cruise Control |
| cruiseControlContainer | Template for the Cruise Control container. |
| tlsSidecarContainer |
The |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Cruise Control service account. |
6.2.53. BrokerCapacity schema reference
Used in: CruiseControlSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| disk |
The |
| string | |
| cpuUtilization |
The |
| integer | |
| cpu | Broker capacity for CPU resource in cores or millicores. For example, 1, 1.500, 1500m. For more information on valid CPU resource units see https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#meaning-of-cpu. |
| string | |
| inboundNetwork | Broker capacity for inbound network throughput in bytes per second. Use an integer value with standard OpenShift byte units (K, M, G) or their bibyte (power of two) equivalents (Ki, Mi, Gi) per second. For example, 10000KiB/s. |
| string | |
| outboundNetwork | Broker capacity for outbound network throughput in bytes per second. Use an integer value with standard OpenShift byte units (K, M, G) or their bibyte (power of two) equivalents (Ki, Mi, Gi) per second. For example, 10000KiB/s. |
| string | |
| overrides |
Overrides for individual brokers. The |
|
|
6.2.54. BrokerCapacityOverride schema reference
Used in: BrokerCapacity
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| brokers | List of Kafka brokers (broker identifiers). |
| integer array | |
| cpu | Broker capacity for CPU resource in cores or millicores. For example, 1, 1.500, 1500m. For more information on valid CPU resource units see https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#meaning-of-cpu. |
| string | |
| inboundNetwork | Broker capacity for inbound network throughput in bytes per second. Use an integer value with standard OpenShift byte units (K, M, G) or their bibyte (power of two) equivalents (Ki, Mi, Gi) per second. For example, 10000KiB/s. |
| string | |
| outboundNetwork | Broker capacity for outbound network throughput in bytes per second. Use an integer value with standard OpenShift byte units (K, M, G) or their bibyte (power of two) equivalents (Ki, Mi, Gi) per second. For example, 10000KiB/s. |
| string |
6.2.55. KafkaExporterSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| groupRegex |
Regular expression to specify which consumer groups to collect. Default value is |
| string | |
| topicRegex |
Regular expression to specify which topics to collect. Default value is |
| string | |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| logging |
Only log messages with the given severity or above. Valid levels: [ |
| string | |
| enableSaramaLogging | Enable Sarama logging, a Go client library used by the Kafka Exporter. |
| boolean | |
| template | Customization of deployment templates and pods. |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness check. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness check. |
6.2.56. KafkaExporterTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaExporterSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment |
Template for Kafka Exporter |
| pod |
Template for Kafka Exporter |
| service |
The |
| container | Template for the Kafka Exporter container. |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Kafka Exporter service account. |
6.2.57. KafkaStatus schema reference
Used in: Kafka
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| listeners | Addresses of the internal and external listeners. |
|
| |
| clusterId | Kafka cluster Id. |
| string |
6.2.58. Condition schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeStatus, KafkaConnectorStatus, KafkaConnectStatus, KafkaMirrorMaker2Status, KafkaMirrorMakerStatus, KafkaRebalanceStatus, KafkaStatus, KafkaTopicStatus, KafkaUserStatus
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type | The unique identifier of a condition, used to distinguish between other conditions in the resource. |
| string | |
| status | The status of the condition, either True, False or Unknown. |
| string | |
| lastTransitionTime | Last time the condition of a type changed from one status to another. The required format is 'yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ', in the UTC time zone. |
| string | |
| reason | The reason for the condition’s last transition (a single word in CamelCase). |
| string | |
| message | Human-readable message indicating details about the condition’s last transition. |
| string |
6.2.59. ListenerStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaStatus
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
The |
| string | |
| name | The name of the listener. |
| string | |
| addresses | A list of the addresses for this listener. |
|
| |
| bootstrapServers |
A comma-separated list of |
| string | |
| certificates |
A list of TLS certificates which can be used to verify the identity of the server when connecting to the given listener. Set only for |
| string array |
6.2.60. ListenerAddress schema reference
Used in: ListenerStatus
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| host | The DNS name or IP address of the Kafka bootstrap service. |
| string | |
| port | The port of the Kafka bootstrap service. |
| integer |
6.2.61. KafkaConnect schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the Kafka Connect cluster. |
| status | The status of the Kafka Connect cluster. |
6.2.62. KafkaConnectSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnect
Full list of KafkaConnectSpec schema properties
Configures a Kafka Connect cluster.
6.2.62.1. config
Use the config properties to configure Kafka options as keys.
Standard Apache Kafka Connect configuration may be provided, restricted to those properties not managed directly by AMQ Streams.
Configuration options that cannot be configured relate to:
- Kafka cluster bootstrap address
- Security (Encryption, Authentication, and Authorization)
- Listener / REST interface configuration
- Plugin path configuration
The values can be one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Apache Kafka documentation with the exception of those options that are managed directly by AMQ Streams. Specifically, configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
ssl. -
sasl. -
security. -
listeners -
plugin.path -
rest. -
bootstrap.servers
When a forbidden option is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message is printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other options are passed to Kafka Connect.
The Cluster Operator does not validate keys or values in the config object provided. When an invalid configuration is provided, the Kafka Connect cluster might not start or might become unstable. In this circumstance, fix the configuration in the KafkaConnect.spec.config object, then the Cluster Operator can roll out the new configuration to all Kafka Connect nodes.
Certain options have default values:
-
group.idwith default valueconnect-cluster -
offset.storage.topicwith default valueconnect-cluster-offsets -
config.storage.topicwith default valueconnect-cluster-configs -
status.storage.topicwith default valueconnect-cluster-status -
key.converterwith default valueorg.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter -
value.converterwith default valueorg.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
These options are automatically configured in case they are not present in the KafkaConnect.spec.config properties.
There are exceptions to the forbidden options. You can use three allowed ssl configuration options for client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version. A cipher suite combines algorithms for secure connection and data transfer. You can also configure the ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm property to enable or disable hostname verification.
Example Kafka Connect configuration
For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties. You can also configure the ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm property to enable or disable hostname verification.
6.2.62.2. logging
Kafka Connect has its own configurable loggers:
-
connect.root.logger.level -
log4j.logger.org.reflections
Further loggers are added depending on the Kafka Connect plugins running.
Use a curl request to get a complete list of Kafka Connect loggers running from any Kafka broker pod:
curl -s http://<connect-cluster-name>-connect-api:8083/admin/loggers/
curl -s http://<connect-cluster-name>-connect-api:8083/admin/loggers/
Kafka Connect uses the Apache log4j logger implementation.
Use the logging property to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Any available loggers that are not configured have their level set to OFF.
If Kafka Connect was deployed using the Cluster Operator, changes to Kafka Connect logging levels are applied dynamically.
If you use external logging, a rolling update is triggered when logging appenders are changed.
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.62.3. KafkaConnectSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The Kafka Connect version. Defaults to 3.4.0. Consult the user documentation to understand the process required to upgrade or downgrade the version. |
| string | |
| replicas | The number of pods in the Kafka Connect group. |
| integer | |
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| bootstrapServers | Bootstrap servers to connect to. This should be given as a comma separated list of <hostname>:_<port>_ pairs. |
| string | |
| tls | TLS configuration. |
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for Kafka Connect. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| config | The Kafka Connect configuration. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: ssl., sasl., security., listeners, plugin.path, rest., bootstrap.servers, consumer.interceptor.classes, producer.interceptor.classes (with the exception of: ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm, ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols). |
| map | |
| resources | The maximum limits for CPU and memory resources and the requested initial resources. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
| jmxOptions | JMX Options. |
| logging |
Logging configuration for Kafka Connect. The type depends on the value of the |
| clientRackInitImage |
The image of the init container used for initializing the |
| string | |
| rack |
Configuration of the node label which will be used as the |
| tracing |
The configuration of tracing in Kafka Connect. The type depends on the value of the |
| template |
Template for Kafka Connect and Kafka Mirror Maker 2 resources. The template allows users to specify how the |
| externalConfiguration | Pass data from Secrets or ConfigMaps to the Kafka Connect pods and use them to configure connectors. |
| build | Configures how the Connect container image should be built. Optional. |
| metricsConfig |
Metrics configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
6.2.63. ClientTls schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Full list of ClientTls schema properties
Configures TLS trusted certificates for connecting KafkaConnect, KafkaBridge, KafkaMirror, KafkaMirrorMaker2 to the cluster.
6.2.63.1. trustedCertificates
Provide a list of secrets using the trustedCertificates property.
6.2.63.2. ClientTls schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| trustedCertificates | Trusted certificates for TLS connection. |
|
|
6.2.64. KafkaClientAuthenticationTls schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Full list of KafkaClientAuthenticationTls schema properties
To configure mTLS authentication, set the type property to the value tls. mTLS uses a TLS certificate to authenticate.
6.2.64.1. certificateAndKey
The certificate is specified in the certificateAndKey property and is always loaded from an OpenShift secret. In the secret, the certificate must be stored in X509 format under two different keys: public and private.
You can use the secrets created by the User Operator, or you can create your own TLS certificate file, with the keys used for authentication, then create a Secret from the file:
oc create secret generic MY-SECRET \ --from-file=MY-PUBLIC-TLS-CERTIFICATE-FILE.crt \ --from-file=MY-PRIVATE.key
oc create secret generic MY-SECRET \
--from-file=MY-PUBLIC-TLS-CERTIFICATE-FILE.crt \
--from-file=MY-PRIVATE.keymTLS authentication can only be used with TLS connections.
Example mTLS configuration
6.2.64.2. KafkaClientAuthenticationTls schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaClientAuthenticationTls type from KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512, KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain, KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth. It must have the value tls for the type KafkaClientAuthenticationTls.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| certificateAndKey |
Reference to the |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.65. KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256 schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Full list of KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256 schema properties
To configure SASL-based SCRAM-SHA-256 authentication, set the type property to scram-sha-256. The SCRAM-SHA-256 authentication mechanism requires a username and password.
6.2.65.1. username
Specify the username in the username property.
6.2.65.2. passwordSecret
In the passwordSecret property, specify a link to a Secret containing the password.
You can use the secrets created by the User Operator.
If required, you can create a text file that contains the password, in cleartext, to use for authentication:
echo -n PASSWORD > MY-PASSWORD.txt
echo -n PASSWORD > MY-PASSWORD.txt
You can then create a Secret from the text file, setting your own field name (key) for the password:
oc create secret generic MY-CONNECT-SECRET-NAME --from-file=MY-PASSWORD-FIELD-NAME=./MY-PASSWORD.txt
oc create secret generic MY-CONNECT-SECRET-NAME --from-file=MY-PASSWORD-FIELD-NAME=./MY-PASSWORD.txtExample Secret for SCRAM-SHA-256 client authentication for Kafka Connect
The secretName property contains the name of the Secret, and the password property contains the name of the key under which the password is stored inside the Secret.
Do not specify the actual password in the password property.
Example SASL-based SCRAM-SHA-256 client authentication configuration for Kafka Connect
6.2.65.3. KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256 schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| passwordSecret |
Reference to the |
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| username | Username used for the authentication. |
| string |
6.2.66. PasswordSecretSource schema reference
Used in: KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth, KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| password | The name of the key in the Secret under which the password is stored. |
| string | |
| secretName | The name of the Secret containing the password. |
| string |
6.2.67. KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512 schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Full list of KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512 schema properties
To configure SASL-based SCRAM-SHA-512 authentication, set the type property to scram-sha-512. The SCRAM-SHA-512 authentication mechanism requires a username and password.
6.2.67.1. username
Specify the username in the username property.
6.2.67.2. passwordSecret
In the passwordSecret property, specify a link to a Secret containing the password.
You can use the secrets created by the User Operator.
If required, you can create a text file that contains the password, in cleartext, to use for authentication:
echo -n PASSWORD > MY-PASSWORD.txt
echo -n PASSWORD > MY-PASSWORD.txt
You can then create a Secret from the text file, setting your own field name (key) for the password:
oc create secret generic MY-CONNECT-SECRET-NAME --from-file=MY-PASSWORD-FIELD-NAME=./MY-PASSWORD.txt
oc create secret generic MY-CONNECT-SECRET-NAME --from-file=MY-PASSWORD-FIELD-NAME=./MY-PASSWORD.txtExample Secret for SCRAM-SHA-512 client authentication for Kafka Connect
The secretName property contains the name of the Secret, and the password property contains the name of the key under which the password is stored inside the Secret.
Do not specify the actual password in the password property.
Example SASL-based SCRAM-SHA-512 client authentication configuration for Kafka Connect
6.2.67.3. KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512 schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| passwordSecret |
Reference to the |
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| username | Username used for the authentication. |
| string |
6.2.68. KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Full list of KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain schema properties
To configure SASL-based PLAIN authentication, set the type property to plain. SASL PLAIN authentication mechanism requires a username and password.
The SASL PLAIN mechanism will transfer the username and password across the network in cleartext. Only use SASL PLAIN authentication if TLS encryption is enabled.
6.2.68.1. username
Specify the username in the username property.
6.2.68.2. passwordSecret
In the passwordSecret property, specify a link to a Secret containing the password.
You can use the secrets created by the User Operator.
If required, create a text file that contains the password, in cleartext, to use for authentication:
echo -n PASSWORD > MY-PASSWORD.txt
echo -n PASSWORD > MY-PASSWORD.txt
You can then create a Secret from the text file, setting your own field name (key) for the password:
oc create secret generic MY-CONNECT-SECRET-NAME --from-file=MY-PASSWORD-FIELD-NAME=./MY-PASSWORD.txt
oc create secret generic MY-CONNECT-SECRET-NAME --from-file=MY-PASSWORD-FIELD-NAME=./MY-PASSWORD.txtExample Secret for PLAIN client authentication for Kafka Connect
The secretName property contains the name of the Secret and the password property contains the name of the key under which the password is stored inside the Secret.
Do not specify the actual password in the password property.
An example SASL based PLAIN client authentication configuration
6.2.68.3. KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain type from KafkaClientAuthenticationTls, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512, KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth. It must have the value plain for the type KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| passwordSecret |
Reference to the |
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| username | Username used for the authentication. |
| string |
6.2.69. KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec, KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Full list of KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth schema properties
To configure OAuth client authentication, set the type property to oauth.
OAuth authentication can be configured using one of the following options:
- Client ID and secret
- Client ID and refresh token
- Access token
- Username and password
- TLS
Client ID and secret
You can configure the address of your authorization server in the tokenEndpointUri property together with the client ID and client secret used in authentication. The OAuth client will connect to the OAuth server, authenticate using the client ID and secret and get an access token which it will use to authenticate with the Kafka broker. In the clientSecret property, specify a link to a Secret containing the client secret.
An example of OAuth client authentication using client ID and client secret
Optionally, scope and audience can be specified if needed.
Client ID and refresh token
You can configure the address of your OAuth server in the tokenEndpointUri property together with the OAuth client ID and refresh token. The OAuth client will connect to the OAuth server, authenticate using the client ID and refresh token and get an access token which it will use to authenticate with the Kafka broker. In the refreshToken property, specify a link to a Secret containing the refresh token.
An example of OAuth client authentication using client ID and refresh token
Access token
You can configure the access token used for authentication with the Kafka broker directly. In this case, you do not specify the tokenEndpointUri. In the accessToken property, specify a link to a Secret containing the access token.
An example of OAuth client authentication using only an access token
authentication:
type: oauth
accessToken:
secretName: my-access-token-secret
key: access-token
authentication:
type: oauth
accessToken:
secretName: my-access-token-secret
key: access-tokenUsername and password
OAuth username and password configuration uses the OAuth Resource Owner Password Grant mechanism. The mechanism is deprecated, and is only supported to enable integration in environments where client credentials (ID and secret) cannot be used. You might need to use user accounts if your access management system does not support another approach or user accounts are required for authentication.
A typical approach is to create a special user account in your authorization server that represents your client application. You then give the account a long randomly generated password and a very limited set of permissions. For example, the account can only connect to your Kafka cluster, but is not allowed to use any other services or login to the user interface.
Consider using a refresh token mechanism first.
You can configure the address of your authorization server in the tokenEndpointUri property together with the client ID, username and the password used in authentication. The OAuth client will connect to the OAuth server, authenticate using the username, the password, the client ID, and optionally even the client secret to obtain an access token which it will use to authenticate with the Kafka broker.
In the passwordSecret property, specify a link to a Secret containing the password.
Normally, you also have to configure a clientId using a public OAuth client. If you are using a confidential OAuth client, you also have to configure a clientSecret.
An example of OAuth client authentication using username and a password with a public client
An example of OAuth client authentication using a username and a password with a confidential client
Optionally, scope and audience can be specified if needed.
TLS
Accessing the OAuth server using the HTTPS protocol does not require any additional configuration as long as the TLS certificates used by it are signed by a trusted certification authority and its hostname is listed in the certificate.
If your OAuth server is using certificates which are self-signed or are signed by a certification authority which is not trusted, you can configure a list of trusted certificates in the custom resource. The tlsTrustedCertificates property contains a list of secrets with key names under which the certificates are stored. The certificates must be stored in X509 format.
An example of TLS certificates provided
The OAuth client will by default verify that the hostname of your OAuth server matches either the certificate subject or one of the alternative DNS names. If it is not required, you can disable the hostname verification.
An example of disabled TLS hostname verification
6.2.69.1. KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth schema properties
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth type from KafkaClientAuthenticationTls, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha256, KafkaClientAuthenticationScramSha512, KafkaClientAuthenticationPlain. It must have the value oauth for the type KafkaClientAuthenticationOAuth.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| accessToken | Link to OpenShift Secret containing the access token which was obtained from the authorization server. |
| accessTokenIsJwt |
Configure whether access token should be treated as JWT. This should be set to |
| boolean | |
| audience |
OAuth audience to use when authenticating against the authorization server. Some authorization servers require the audience to be explicitly set. The possible values depend on how the authorization server is configured. By default, |
| string | |
| clientId | OAuth Client ID which the Kafka client can use to authenticate against the OAuth server and use the token endpoint URI. |
| string | |
| clientSecret | Link to OpenShift Secret containing the OAuth client secret which the Kafka client can use to authenticate against the OAuth server and use the token endpoint URI. |
| connectTimeoutSeconds | The connect timeout in seconds when connecting to authorization server. If not set, the effective connect timeout is 60 seconds. |
| integer | |
| disableTlsHostnameVerification |
Enable or disable TLS hostname verification. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| enableMetrics |
Enable or disable OAuth metrics. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| httpRetries | The maximum number of retries to attempt if an initial HTTP request fails. If not set, the default is to not attempt any retries. |
| integer | |
| httpRetryPauseMs | The pause to take before retrying a failed HTTP request. If not set, the default is to not pause at all but to immediately repeat a request. |
| integer | |
| maxTokenExpirySeconds | Set or limit time-to-live of the access tokens to the specified number of seconds. This should be set if the authorization server returns opaque tokens. |
| integer | |
| passwordSecret |
Reference to the |
| readTimeoutSeconds | The read timeout in seconds when connecting to authorization server. If not set, the effective read timeout is 60 seconds. |
| integer | |
| refreshToken | Link to OpenShift Secret containing the refresh token which can be used to obtain access token from the authorization server. |
| scope |
OAuth scope to use when authenticating against the authorization server. Some authorization servers require this to be set. The possible values depend on how authorization server is configured. By default |
| string | |
| tlsTrustedCertificates | Trusted certificates for TLS connection to the OAuth server. |
|
| |
| tokenEndpointUri | Authorization server token endpoint URI. |
| string | |
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| username | Username used for the authentication. |
| string |
6.2.70. JaegerTracing schema reference
The type JaegerTracing has been deprecated.
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the JaegerTracing type from OpenTelemetryTracing. It must have the value jaeger for the type JaegerTracing.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.71. OpenTelemetryTracing schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec, KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec, KafkaMirrorMakerSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the OpenTelemetryTracing type from JaegerTracing. It must have the value opentelemetry for the type OpenTelemetryTracing.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.72. KafkaConnectTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment |
Template for Kafka Connect |
| podSet |
Template for Kafka Connect |
| pod |
Template for Kafka Connect |
| apiService |
Template for Kafka Connect API |
| headlessService |
Template for Kafka Connect headless |
| connectContainer | Template for the Kafka Connect container. |
| initContainer | Template for the Kafka init container. |
| podDisruptionBudget |
Template for Kafka Connect |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Kafka Connect service account. |
| clusterRoleBinding | Template for the Kafka Connect ClusterRoleBinding. |
| buildPod |
Template for Kafka Connect Build |
| buildContainer | Template for the Kafka Connect Build container. The build container is used only on OpenShift. |
| buildConfig | Template for the Kafka Connect BuildConfig used to build new container images. The BuildConfig is used only on OpenShift. |
| buildServiceAccount | Template for the Kafka Connect Build service account. |
| jmxSecret | Template for Secret of the Kafka Connect Cluster JMX authentication. |
6.2.73. BuildConfigTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectTemplate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| metadata |
Metadata to apply to the |
| pullSecret | Container Registry Secret with the credentials for pulling the base image. |
| string |
6.2.74. ExternalConfiguration schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec
Full list of ExternalConfiguration schema properties
Configures external storage properties that define configuration options for Kafka Connect connectors.
You can mount ConfigMaps or Secrets into a Kafka Connect pod as environment variables or volumes. Volumes and environment variables are configured in the externalConfiguration property in KafkaConnect.spec.
When applied, the environment variables and volumes are available for use when developing your connectors.
6.2.74.1. env
Use the env property to specify one or more environment variables. These variables can contain a value from either a ConfigMap or a Secret.
Example Secret containing values for environment variables
The names of user-defined environment variables cannot start with KAFKA_ or STRIMZI_.
To mount a value from a Secret to an environment variable, use the valueFrom property and the secretKeyRef.
Example environment variables set to values from a Secret
A common use case for mounting Secrets is for a connector to communicate with Amazon AWS. The connector needs to be able to read the AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY.
To mount a value from a ConfigMap to an environment variable, use configMapKeyRef in the valueFrom property as shown in the following example.
Example environment variables set to values from a ConfigMap
6.2.74.2. volumes
Use volumes to mount ConfigMaps or Secrets to a Kafka Connect pod.
Using volumes instead of environment variables is useful in the following scenarios:
- Mounting a properties file that is used to configure Kafka Connect connectors
- Mounting truststores or keystores with TLS certificates
Volumes are mounted inside the Kafka Connect containers on the path /opt/kafka/external-configuration/<volume-name>. For example, the files from a volume named connector-config will appear in the directory /opt/kafka/external-configuration/connector-config.
Configuration providers load values from outside the configuration. Use a provider mechanism to avoid passing restricted information over the Kafka Connect REST interface.
-
FileConfigProviderloads configuration values from properties in a file. -
DirectoryConfigProviderloads configuration values from separate files within a directory structure.
Use a comma-separated list if you want to add more than one provider, including custom providers. You can use custom providers to load values from other file locations.
Using FileConfigProvider to load property values
In this example, a Secret named mysecret contains connector properties that specify a database name and password:
Example Secret with database properties
The Secret and the FileConfigProvider configuration provider are specified in the Kafka Connect configuration.
-
The Secret is mounted to a volume named
connector-config. -
FileConfigProvideris given the aliasfile.
Example external volumes set to values from a Secret
- 1
- The alias for the configuration provider is used to define other configuration parameters.
- 2
FileConfigProviderprovides values from properties files. The parameter uses the alias fromconfig.providers, taking the formconfig.providers.${alias}.class.- 3
- The name of the volume containing the Secret. Each volume must specify a name in the
nameproperty and a reference to a ConfigMap or Secret. - 4
- The name of the Secret.
Placeholders for the property values in the Secret are referenced in the connector configuration. The placeholder structure is file:PATH-AND-FILE-NAME:PROPERTY. FileConfigProvider reads and extracts the database username and password property values from the mounted Secret in connector configurations.
Example connector configuration showing placeholders for external values
Using DirectoryConfigProvider to load property values from separate files
In this example, a Secret contains TLS truststore and keystore user credentials in separate files.
Example Secret with user credentials
The Secret and the DirectoryConfigProvider configuration provider are specified in the Kafka Connect configuration.
-
The Secret is mounted to a volume named
connector-config. -
DirectoryConfigProvideris given the aliasdirectory.
Example external volumes set for user credentials files
- 1
- The
DirectoryConfigProviderprovides values from files in a directory. The parameter uses the alias fromconfig.providers, taking the formconfig.providers.${alias}.class.
Placeholders for the credentials are referenced in the connector configuration. The placeholder structure is directory:PATH:FILE-NAME. DirectoryConfigProvider reads and extracts the credentials from the mounted Secret in connector configurations.
Example connector configuration showing placeholders for external values
6.2.74.3. ExternalConfiguration schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| env | Makes data from a Secret or ConfigMap available in the Kafka Connect pods as environment variables. |
|
| |
| volumes | Makes data from a Secret or ConfigMap available in the Kafka Connect pods as volumes. |
6.2.75. ExternalConfigurationEnv schema reference
Used in: ExternalConfiguration
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| name |
Name of the environment variable which will be passed to the Kafka Connect pods. The name of the environment variable cannot start with |
| string | |
| valueFrom | Value of the environment variable which will be passed to the Kafka Connect pods. It can be passed either as a reference to Secret or ConfigMap field. The field has to specify exactly one Secret or ConfigMap. |
6.2.76. ExternalConfigurationEnvVarSource schema reference
Used in: ExternalConfigurationEnv
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| configMapKeyRef | Reference to a key in a ConfigMap. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 configmapkeyselector. |
| secretKeyRef | Reference to a key in a Secret. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 secretkeyselector. |
6.2.77. ExternalConfigurationVolumeSource schema reference
Used in: ExternalConfiguration
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| configMap | Reference to a key in a ConfigMap. Exactly one Secret or ConfigMap has to be specified. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 configmapvolumesource. |
| name | Name of the volume which will be added to the Kafka Connect pods. |
| string | |
| secret | Reference to a key in a Secret. Exactly one Secret or ConfigMap has to be specified. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 secretvolumesource. |
6.2.78. Build schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectSpec
Full list of Build schema properties
Configures additional connectors for Kafka Connect deployments.
6.2.78.1. output
To build new container images with additional connector plugins, AMQ Streams requires a container registry where the images can be pushed to, stored, and pulled from. AMQ Streams does not run its own container registry, so a registry must be provided. AMQ Streams supports private container registries as well as public registries such as Quay or Docker Hub. The container registry is configured in the .spec.build.output section of the KafkaConnect custom resource. The output configuration, which is required, supports two types: docker and imagestream.
Using Docker registry
To use a Docker registry, you have to specify the type as docker, and the image field with the full name of the new container image. The full name must include:
- The address of the registry
- Port number (if listening on a non-standard port)
- The tag of the new container image
Example valid container image names:
-
docker.io/my-org/my-image/my-tag -
quay.io/my-org/my-image/my-tag -
image-registry.image-registry.svc:5000/myproject/kafka-connect-build:latest
Each Kafka Connect deployment must use a separate image, which can mean different tags at the most basic level.
If the registry requires authentication, use the pushSecret to set a name of the Secret with the registry credentials. For the Secret, use the kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson type and a .dockerconfigjson file to contain the Docker credentials. For more information on pulling an image from a private registry, see Create a Secret based on existing Docker credentials.
Example output configuration
Using OpenShift ImageStream
Instead of Docker, you can use OpenShift ImageStream to store a new container image. The ImageStream has to be created manually before deploying Kafka Connect. To use ImageStream, set the type to imagestream, and use the image property to specify the name of the ImageStream and the tag used. For example, my-connect-image-stream:latest.
Example output configuration
6.2.78.2. plugins
Connector plugins are a set of files that define the implementation required to connect to certain types of external system. The connector plugins required for a container image must be configured using the .spec.build.plugins property of the KafkaConnect custom resource. Each connector plugin must have a name which is unique within the Kafka Connect deployment. Additionally, the plugin artifacts must be listed. These artifacts are downloaded by AMQ Streams, added to the new container image, and used in the Kafka Connect deployment. The connector plugin artifacts can also include additional components, such as (de)serializers. Each connector plugin is downloaded into a separate directory so that the different connectors and their dependencies are properly sandboxed. Each plugin must be configured with at least one artifact.
Example plugins configuration with two connector plugins
- 1
- (Required) List of connector plugins and their artifacts.
AMQ Streams supports the following types of artifacts:
- JAR files, which are downloaded and used directly
- TGZ archives, which are downloaded and unpacked
- ZIP archives, which are downloaded and unpacked
- Maven artifacts, which uses Maven coordinates
- Other artifacts, which are downloaded and used directly
AMQ Streams does not perform any security scanning of the downloaded artifacts. For security reasons, you should first verify the artifacts manually, and configure the checksum verification to make sure the same artifact is used in the automated build and in the Kafka Connect deployment.
Using JAR artifacts
JAR artifacts represent a JAR file that is downloaded and added to a container image. To use a JAR artifacts, set the type property to jar, and specify the download location using the url property.
Additionally, you can specify a SHA-512 checksum of the artifact. If specified, AMQ Streams will verify the checksum of the artifact while building the new container image.
Example JAR artifact
Using TGZ artifacts
TGZ artifacts are used to download TAR archives that have been compressed using Gzip compression. The TGZ artifact can contain the whole Kafka Connect connector, even when comprising multiple different files. The TGZ artifact is automatically downloaded and unpacked by AMQ Streams while building the new container image. To use TGZ artifacts, set the type property to tgz, and specify the download location using the url property.
Additionally, you can specify a SHA-512 checksum of the artifact. If specified, AMQ Streams will verify the checksum before unpacking it and building the new container image.
Example TGZ artifact
Using ZIP artifacts
ZIP artifacts are used to download ZIP compressed archives. Use ZIP artifacts in the same way as the TGZ artifacts described in the previous section. The only difference is you specify type: zip instead of type: tgz.
Using Maven artifacts
maven artifacts are used to specify connector plugin artifacts as Maven coordinates. The Maven coordinates identify plugin artifacts and dependencies so that they can be located and fetched from a Maven repository.
The Maven repository must be accessible for the connector build process to add the artifacts to the container image.
Example Maven artifact
Using other artifacts
other artifacts represent any kind of file that is downloaded and added to a container image. If you want to use a specific name for the artifact in the resulting container image, use the fileName field. If a file name is not specified, the file is named based on the URL hash.
Additionally, you can specify a SHA-512 checksum of the artifact. If specified, AMQ Streams will verify the checksum of the artifact while building the new container image.
Example other artifact
6.2.78.3. Build schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| output |
Configures where should the newly built image be stored. Required. The type depends on the value of the |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve for the build. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| plugins | List of connector plugins which should be added to the Kafka Connect. Required. |
|
|
6.2.79. DockerOutput schema reference
Used in: Build
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the DockerOutput type from ImageStreamOutput. It must have the value docker for the type DockerOutput.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| image |
The full name which should be used for tagging and pushing the newly built image. For example |
| string | |
| pushSecret | Container Registry Secret with the credentials for pushing the newly built image. |
| string | |
| additionalKanikoOptions | Configures additional options which will be passed to the Kaniko executor when building the new Connect image. Allowed options are: --customPlatform, --insecure, --insecure-pull, --insecure-registry, --log-format, --log-timestamp, --registry-mirror, --reproducible, --single-snapshot, --skip-tls-verify, --skip-tls-verify-pull, --skip-tls-verify-registry, --verbosity, --snapshotMode, --use-new-run. These options will be used only on OpenShift where the Kaniko executor is used. They will be ignored on OpenShift. The options are described in the Kaniko GitHub repository. Changing this field does not trigger new build of the Kafka Connect image. |
| string array | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.80. ImageStreamOutput schema reference
Used in: Build
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the ImageStreamOutput type from DockerOutput. It must have the value imagestream for the type ImageStreamOutput.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| image |
The name and tag of the ImageStream where the newly built image will be pushed. For example |
| string | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.81. Plugin schema reference
Used in: Build
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| name |
The unique name of the connector plugin. Will be used to generate the path where the connector artifacts will be stored. The name has to be unique within the KafkaConnect resource. The name has to follow the following pattern: |
| string | |
| artifacts | List of artifacts which belong to this connector plugin. Required. |
|
|
6.2.82. JarArtifact schema reference
Used in: Plugin
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| url |
URL of the artifact which will be downloaded. AMQ Streams does not do any security scanning of the downloaded artifacts. For security reasons, you should first verify the artifacts manually and configure the checksum verification to make sure the same artifact is used in the automated build. Required for |
| string | |
| sha512sum |
SHA512 checksum of the artifact. Optional. If specified, the checksum will be verified while building the new container. If not specified, the downloaded artifact will not be verified. Not applicable to the |
| string | |
| insecure |
By default, connections using TLS are verified to check they are secure. The server certificate used must be valid, trusted, and contain the server name. By setting this option to |
| boolean | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.83. TgzArtifact schema reference
Used in: Plugin
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| url |
URL of the artifact which will be downloaded. AMQ Streams does not do any security scanning of the downloaded artifacts. For security reasons, you should first verify the artifacts manually and configure the checksum verification to make sure the same artifact is used in the automated build. Required for |
| string | |
| sha512sum |
SHA512 checksum of the artifact. Optional. If specified, the checksum will be verified while building the new container. If not specified, the downloaded artifact will not be verified. Not applicable to the |
| string | |
| insecure |
By default, connections using TLS are verified to check they are secure. The server certificate used must be valid, trusted, and contain the server name. By setting this option to |
| boolean | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.84. ZipArtifact schema reference
Used in: Plugin
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| url |
URL of the artifact which will be downloaded. AMQ Streams does not do any security scanning of the downloaded artifacts. For security reasons, you should first verify the artifacts manually and configure the checksum verification to make sure the same artifact is used in the automated build. Required for |
| string | |
| sha512sum |
SHA512 checksum of the artifact. Optional. If specified, the checksum will be verified while building the new container. If not specified, the downloaded artifact will not be verified. Not applicable to the |
| string | |
| insecure |
By default, connections using TLS are verified to check they are secure. The server certificate used must be valid, trusted, and contain the server name. By setting this option to |
| boolean | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.85. MavenArtifact schema reference
Used in: Plugin
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the MavenArtifact type from JarArtifact, TgzArtifact, ZipArtifact, OtherArtifact. It must have the value maven for the type MavenArtifact.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| repository |
Maven repository to download the artifact from. Applicable to the |
| string | |
| group |
Maven group id. Applicable to the |
| string | |
| artifact |
Maven artifact id. Applicable to the |
| string | |
| version |
Maven version number. Applicable to the |
| string | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.86. OtherArtifact schema reference
Used in: Plugin
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| url |
URL of the artifact which will be downloaded. AMQ Streams does not do any security scanning of the downloaded artifacts. For security reasons, you should first verify the artifacts manually and configure the checksum verification to make sure the same artifact is used in the automated build. Required for |
| string | |
| sha512sum |
SHA512 checksum of the artifact. Optional. If specified, the checksum will be verified while building the new container. If not specified, the downloaded artifact will not be verified. Not applicable to the |
| string | |
| fileName | Name under which the artifact will be stored. |
| string | |
| insecure |
By default, connections using TLS are verified to check they are secure. The server certificate used must be valid, trusted, and contain the server name. By setting this option to |
| boolean | |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.87. KafkaConnectStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnect
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| url | The URL of the REST API endpoint for managing and monitoring Kafka Connect connectors. |
| string | |
| connectorPlugins | The list of connector plugins available in this Kafka Connect deployment. |
|
| |
| labelSelector | Label selector for pods providing this resource. |
| string | |
| replicas | The current number of pods being used to provide this resource. |
| integer |
6.2.88. ConnectorPlugin schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectStatus, KafkaMirrorMaker2Status
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
The type of the connector plugin. The available types are |
| string | |
| version | The version of the connector plugin. |
| string | |
| class | The class of the connector plugin. |
| string |
6.2.89. KafkaTopic schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the topic. |
| status | The status of the topic. |
6.2.90. KafkaTopicSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaTopic
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| partitions |
The number of partitions the topic should have. This cannot be decreased after topic creation. It can be increased after topic creation, but it is important to understand the consequences that has, especially for topics with semantic partitioning. When absent this will default to the broker configuration for |
| integer | |
| replicas |
The number of replicas the topic should have. When absent this will default to the broker configuration for |
| integer | |
| config | The topic configuration. |
| map | |
| topicName | The name of the topic. When absent this will default to the metadata.name of the topic. It is recommended to not set this unless the topic name is not a valid OpenShift resource name. |
| string |
6.2.91. KafkaTopicStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaTopic
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| topicName | Topic name. |
| string |
6.2.92. KafkaUser schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the user. |
| status | The status of the Kafka User. |
6.2.93. KafkaUserSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaUser
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| authentication |
Authentication mechanism enabled for this Kafka user. The supported authentication mechanisms are
Authentication is optional. If authentication is not configured, no credentials are generated. ACLs and quotas set for the user are configured in the |
|
| |
| authorization |
Authorization rules for this Kafka user. The type depends on the value of the |
| quotas | Quotas on requests to control the broker resources used by clients. Network bandwidth and request rate quotas can be enforced.Kafka documentation for Kafka User quotas can be found at http://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#design_quotas. |
| template |
Template to specify how Kafka User |
6.2.94. KafkaUserTlsClientAuthentication schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaUserTlsClientAuthentication type from KafkaUserTlsExternalClientAuthentication, KafkaUserScramSha512ClientAuthentication. It must have the value tls for the type KafkaUserTlsClientAuthentication.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.95. KafkaUserTlsExternalClientAuthentication schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaUserTlsExternalClientAuthentication type from KafkaUserTlsClientAuthentication, KafkaUserScramSha512ClientAuthentication. It must have the value tls-external for the type KafkaUserTlsExternalClientAuthentication.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.96. KafkaUserScramSha512ClientAuthentication schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaUserScramSha512ClientAuthentication type from KafkaUserTlsClientAuthentication, KafkaUserTlsExternalClientAuthentication. It must have the value scram-sha-512 for the type KafkaUserScramSha512ClientAuthentication.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| password | Specify the password for the user. If not set, a new password is generated by the User Operator. |
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.97. Password schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserScramSha512ClientAuthentication
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| valueFrom | Secret from which the password should be read. |
6.2.98. PasswordSource schema reference
Used in: Password
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| secretKeyRef | Selects a key of a Secret in the resource’s namespace. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 secretkeyselector. |
6.2.99. KafkaUserAuthorizationSimple schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserSpec
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the KafkaUserAuthorizationSimple type from other subtypes which may be added in the future. It must have the value simple for the type KafkaUserAuthorizationSimple.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| acls | List of ACL rules which should be applied to this user. |
|
|
6.2.100. AclRule schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserAuthorizationSimple
Full list of AclRule schema properties
Configures access control rules for a KafkaUser when brokers are using the AclAuthorizer.
Example KafkaUser configuration with authorization
6.2.100.1. resource
Use the resource property to specify the resource that the rule applies to.
Simple authorization supports four resource types, which are specified in the type property:
-
Topics (
topic) -
Consumer Groups (
group) -
Clusters (
cluster) -
Transactional IDs (
transactionalId)
For Topic, Group, and Transactional ID resources you can specify the name of the resource the rule applies to in the name property.
Cluster type resources have no name.
A name is specified as a literal or a prefix using the patternType property.
-
Literal names are taken exactly as they are specified in the
namefield. -
Prefix names use the
namevalue as a prefix and then apply the rule to all resources with names starting with that value.
When patternType is set as literal, you can set the name to * to indicate that the rule applies to all resources.
Example ACL rule that allows the user to read messages from all topics
6.2.100.2. type
The type of rule, which is to allow or deny (not currently supported) an operations.
The type field is optional. If type is unspecified, the ACL rule is treated as an allow rule.
6.2.100.3. operations
Specify a list of operations for the rule to allow or deny.
The following operations are supported:
- Read
- Write
- Delete
- Alter
- Describe
- All
- IdempotentWrite
- ClusterAction
- Create
- AlterConfigs
- DescribeConfigs
Only certain operations work with each resource.
For more details about AclAuthorizer, ACLs and supported combinations of resources and operations, see Authorization and ACLs.
6.2.100.4. host
Use the host property to specify a remote host from which the rule is allowed or denied.
Use an asterisk (*) to allow or deny the operation from all hosts. The host field is optional. If host is unspecified, the * value is used by default.
6.2.100.5. AclRule schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| host | The host from which the action described in the ACL rule is allowed or denied. |
| string | |
| operation |
The |
| string (one of [Read, Write, Delete, Alter, Describe, All, IdempotentWrite, ClusterAction, Create, AlterConfigs, DescribeConfigs]) | |
| operations | List of operations which will be allowed or denied. Supported operations are: Read, Write, Create, Delete, Alter, Describe, ClusterAction, AlterConfigs, DescribeConfigs, IdempotentWrite and All. |
| string (one or more of [Read, Write, Delete, Alter, Describe, All, IdempotentWrite, ClusterAction, Create, AlterConfigs, DescribeConfigs]) array | |
| resource |
Indicates the resource for which given ACL rule applies. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| type |
The type of the rule. Currently the only supported type is |
| string (one of [allow, deny]) |
6.2.101. AclRuleTopicResource schema reference
Used in: AclRule
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the AclRuleTopicResource type from AclRuleGroupResource, AclRuleClusterResource, AclRuleTransactionalIdResource. It must have the value topic for the type AclRuleTopicResource.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| name |
Name of resource for which given ACL rule applies. Can be combined with |
| string | |
| patternType |
Describes the pattern used in the resource field. The supported types are |
| string (one of [prefix, literal]) |
6.2.102. AclRuleGroupResource schema reference
Used in: AclRule
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the AclRuleGroupResource type from AclRuleTopicResource, AclRuleClusterResource, AclRuleTransactionalIdResource. It must have the value group for the type AclRuleGroupResource.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| name |
Name of resource for which given ACL rule applies. Can be combined with |
| string | |
| patternType |
Describes the pattern used in the resource field. The supported types are |
| string (one of [prefix, literal]) |
6.2.103. AclRuleClusterResource schema reference
Used in: AclRule
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the AclRuleClusterResource type from AclRuleTopicResource, AclRuleGroupResource, AclRuleTransactionalIdResource. It must have the value cluster for the type AclRuleClusterResource.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string |
6.2.104. AclRuleTransactionalIdResource schema reference
Used in: AclRule
The type property is a discriminator that distinguishes use of the AclRuleTransactionalIdResource type from AclRuleTopicResource, AclRuleGroupResource, AclRuleClusterResource. It must have the value transactionalId for the type AclRuleTransactionalIdResource.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
Must be |
| string | |
| name |
Name of resource for which given ACL rule applies. Can be combined with |
| string | |
| patternType |
Describes the pattern used in the resource field. The supported types are |
| string (one of [prefix, literal]) |
6.2.105. KafkaUserQuotas schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserSpec
Full list of KafkaUserQuotas schema properties
Kafka allows a user to set quotas to control the use of resources by clients.
6.2.105.1. quotas
You can configure your clients to use the following types of quotas:
- Network usage quotas specify the byte rate threshold for each group of clients sharing a quota.
- CPU utilization quotas specify a window for broker requests from clients. The window is the percentage of time for clients to make requests. A client makes requests on the I/O threads and network threads of the broker.
- Partition mutation quotas limit the number of partition mutations which clients are allowed to make per second.
A partition mutation quota prevents Kafka clusters from being overwhelmed by concurrent topic operations. Partition mutations occur in response to the following types of user requests:
- Creating partitions for a new topic
- Adding partitions to an existing topic
- Deleting partitions from a topic
You can configure a partition mutation quota to control the rate at which mutations are accepted for user requests.
Using quotas for Kafka clients might be useful in a number of situations. Consider a wrongly configured Kafka producer which is sending requests at too high a rate. Such misconfiguration can cause a denial of service to other clients, so the problematic client ought to be blocked. By using a network limiting quota, it is possible to prevent this situation from significantly impacting other clients.
AMQ Streams supports user-level quotas, but not client-level quotas.
Example Kafka user quota configuration
For more information about Kafka user quotas, refer to the Apache Kafka documentation.
6.2.105.2. KafkaUserQuotas schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| consumerByteRate | A quota on the maximum bytes per-second that each client group can fetch from a broker before the clients in the group are throttled. Defined on a per-broker basis. |
| integer | |
| controllerMutationRate | A quota on the rate at which mutations are accepted for the create topics request, the create partitions request and the delete topics request. The rate is accumulated by the number of partitions created or deleted. |
| number | |
| producerByteRate | A quota on the maximum bytes per-second that each client group can publish to a broker before the clients in the group are throttled. Defined on a per-broker basis. |
| integer | |
| requestPercentage | A quota on the maximum CPU utilization of each client group as a percentage of network and I/O threads. |
| integer |
6.2.106. KafkaUserTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaUserSpec
Full list of KafkaUserTemplate schema properties
Specify additional labels and annotations for the secret created by the User Operator.
An example showing the KafkaUserTemplate
6.2.106.1. KafkaUserTemplate schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| secret |
Template for KafkaUser resources. The template allows users to specify how the |
6.2.107. KafkaUserStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaUser
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| username | Username. |
| string | |
| secret |
The name of |
| string |
6.2.108. KafkaMirrorMaker schema reference
The type KafkaMirrorMaker has been deprecated. Please use KafkaMirrorMaker2 instead.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of Kafka MirrorMaker. |
| status | The status of Kafka MirrorMaker. |
6.2.109. KafkaMirrorMakerSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker
Full list of KafkaMirrorMakerSpec schema properties
Configures Kafka MirrorMaker.
6.2.109.1. include
Use the include property to configure a list of topics that Kafka MirrorMaker mirrors from the source to the target Kafka cluster.
The property allows any regular expression from the simplest case with a single topic name to complex patterns. For example, you can mirror topics A and B using A|B or all topics using *. You can also pass multiple regular expressions separated by commas to the Kafka MirrorMaker.
6.2.109.2. KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec and KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec
Use the KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec and KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec to configure source (consumer) and target (producer) clusters.
Kafka MirrorMaker always works together with two Kafka clusters (source and target). To establish a connection, the bootstrap servers for the source and the target Kafka clusters are specified as comma-separated lists of HOSTNAME:PORT pairs. Each comma-separated list contains one or more Kafka brokers or a Service pointing to Kafka brokers specified as a HOSTNAME:PORT pair.
6.2.109.3. logging
Kafka MirrorMaker has its own configurable logger:
-
mirrormaker.root.logger
MirrorMaker uses the Apache log4j logger implementation.
Use the logging property to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j.properties. Both logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. A ConfigMap using the exact logging configuration specified is created with the custom resource when the Cluster Operator is running, then recreated after each reconciliation. If you do not specify a custom ConfigMap, default logging settings are used. If a specific logger value is not set, upper-level logger settings are inherited for that logger. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging:
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.109.4. KafkaMirrorMakerSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The Kafka MirrorMaker version. Defaults to 3.4.0. Consult the documentation to understand the process required to upgrade or downgrade the version. |
| string | |
| replicas |
The number of pods in the |
| integer | |
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| consumer | Configuration of source cluster. |
| producer | Configuration of target cluster. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| whitelist |
The |
| string | |
| include |
List of topics which are included for mirroring. This option allows any regular expression using Java-style regular expressions. Mirroring two topics named A and B is achieved by using the expression |
| string | |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
| logging |
Logging configuration for MirrorMaker. The type depends on the value of the |
| metricsConfig |
Metrics configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
| tracing |
The configuration of tracing in Kafka MirrorMaker. The type depends on the value of the |
| template |
Template to specify how Kafka MirrorMaker resources, |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
6.2.110. KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMakerSpec
Full list of KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec schema properties
Configures a MirrorMaker consumer.
6.2.110.1. numStreams
Use the consumer.numStreams property to configure the number of streams for the consumer.
You can increase the throughput in mirroring topics by increasing the number of consumer threads. Consumer threads belong to the consumer group specified for Kafka MirrorMaker. Topic partitions are assigned across the consumer threads, which consume messages in parallel.
6.2.110.2. offsetCommitInterval
Use the consumer.offsetCommitInterval property to configure an offset auto-commit interval for the consumer.
You can specify the regular time interval at which an offset is committed after Kafka MirrorMaker has consumed data from the source Kafka cluster. The time interval is set in milliseconds, with a default value of 60,000.
6.2.110.3. config
Use the consumer.config properties to configure Kafka options for the consumer.
The config property contains the Kafka MirrorMaker consumer configuration options as keys, with values set in one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties. You can also configure the ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm property to enable or disable hostname verification.
Exceptions
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Apache Kafka configuration documentation for consumers.
However, there are exceptions for options automatically configured and managed directly by AMQ Streams related to:
- Kafka cluster bootstrap address
- Security (encryption, authentication, and authorization)
- Consumer group identifier
- Interceptors
Specifically, all configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
bootstrap.servers -
group.id -
interceptor.classes -
ssl.(not including specific exceptions) -
sasl. -
security.
When a forbidden option is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message is printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other options are passed to Kafka MirrorMaker.
The Cluster Operator does not validate keys or values in the provided config object. When an invalid configuration is provided, the Kafka MirrorMaker might not start or might become unstable. In such cases, the configuration in the KafkaMirrorMaker.spec.consumer.config object should be fixed and the Cluster Operator will roll out the new configuration for Kafka MirrorMaker.
6.2.110.4. groupId
Use the consumer.groupId property to configure a consumer group identifier for the consumer.
Kafka MirrorMaker uses a Kafka consumer to consume messages, behaving like any other Kafka consumer client. Messages consumed from the source Kafka cluster are mirrored to a target Kafka cluster. A group identifier is required, as the consumer needs to be part of a consumer group for the assignment of partitions.
6.2.110.5. KafkaMirrorMakerConsumerSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| numStreams | Specifies the number of consumer stream threads to create. |
| integer | |
| offsetCommitInterval | Specifies the offset auto-commit interval in ms. Default value is 60000. |
| integer | |
| bootstrapServers | A list of host:port pairs for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster. |
| string | |
| groupId | A unique string that identifies the consumer group this consumer belongs to. |
| string | |
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for connecting to the cluster. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| config | The MirrorMaker consumer config. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: ssl., bootstrap.servers, group.id, sasl., security., interceptor.classes (with the exception of: ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm, ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols). |
| map | |
| tls | TLS configuration for connecting MirrorMaker to the cluster. |
6.2.111. KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMakerSpec
Full list of KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec schema properties
Configures a MirrorMaker producer.
6.2.111.1. abortOnSendFailure
Use the producer.abortOnSendFailure property to configure how to handle message send failure from the producer.
By default, if an error occurs when sending a message from Kafka MirrorMaker to a Kafka cluster:
- The Kafka MirrorMaker container is terminated in OpenShift.
- The container is then recreated.
If the abortOnSendFailure option is set to false, message sending errors are ignored.
6.2.111.2. config
Use the producer.config properties to configure Kafka options for the producer.
The config property contains the Kafka MirrorMaker producer configuration options as keys, with values set in one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties. You can also configure the ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm property to enable or disable hostname verification.
Exceptions
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Apache Kafka configuration documentation for producers.
However, there are exceptions for options automatically configured and managed directly by AMQ Streams related to:
- Kafka cluster bootstrap address
- Security (encryption, authentication, and authorization)
- Interceptors
Specifically, all configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
bootstrap.servers -
interceptor.classes -
ssl.(not including specific exceptions) -
sasl. -
security.
When a forbidden option is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message is printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other options are passed to Kafka MirrorMaker.
The Cluster Operator does not validate keys or values in the provided config object. When an invalid configuration is provided, the Kafka MirrorMaker might not start or might become unstable. In such cases, the configuration in the KafkaMirrorMaker.spec.producer.config object should be fixed and the Cluster Operator will roll out the new configuration for Kafka MirrorMaker.
6.2.111.3. KafkaMirrorMakerProducerSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| bootstrapServers | A list of host:port pairs for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster. |
| string | |
| abortOnSendFailure |
Flag to set the MirrorMaker to exit on a failed send. Default value is |
| boolean | |
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for connecting to the cluster. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| config | The MirrorMaker producer config. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: ssl., bootstrap.servers, sasl., security., interceptor.classes (with the exception of: ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm, ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols). |
| map | |
| tls | TLS configuration for connecting MirrorMaker to the cluster. |
6.2.112. KafkaMirrorMakerTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMakerSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment |
Template for Kafka MirrorMaker |
| pod |
Template for Kafka MirrorMaker |
| podDisruptionBudget |
Template for Kafka MirrorMaker |
| mirrorMakerContainer | Template for Kafka MirrorMaker container. |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Kafka MirrorMaker service account. |
6.2.113. KafkaMirrorMakerStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| labelSelector | Label selector for pods providing this resource. |
| string | |
| replicas | The current number of pods being used to provide this resource. |
| integer |
6.2.114. KafkaBridge schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the Kafka Bridge. |
| status | The status of the Kafka Bridge. |
6.2.115. KafkaBridgeSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridge
Full list of KafkaBridgeSpec schema properties
Configures a Kafka Bridge cluster.
Configuration options relate to:
- Kafka cluster bootstrap address
- Security (Encryption, Authentication, and Authorization)
- Consumer configuration
- Producer configuration
- HTTP configuration
6.2.115.1. logging
Kafka Bridge has its own configurable loggers:
-
logger.bridge -
logger.<operation-id>
You can replace <operation-id> in the logger.<operation-id> logger to set log levels for specific operations:
-
createConsumer -
deleteConsumer -
subscribe -
unsubscribe -
poll -
assign -
commit -
send -
sendToPartition -
seekToBeginning -
seekToEnd -
seek -
healthy -
ready -
openapi
Each operation is defined according OpenAPI specification, and has a corresponding API endpoint through which the bridge receives requests from HTTP clients. You can change the log level on each endpoint to create fine-grained logging information about the incoming and outgoing HTTP requests.
Each logger has to be configured assigning it a name as http.openapi.operation.<operation-id>. For example, configuring the logging level for the send operation logger means defining the following:
logger.send.name = http.openapi.operation.send logger.send.level = DEBUG
logger.send.name = http.openapi.operation.send
logger.send.level = DEBUG
Kafka Bridge uses the Apache log4j2 logger implementation. Loggers are defined in the log4j2.properties file, which has the following default configuration for healthy and ready endpoints:
logger.healthy.name = http.openapi.operation.healthy logger.healthy.level = WARN logger.ready.name = http.openapi.operation.ready logger.ready.level = WARN
logger.healthy.name = http.openapi.operation.healthy
logger.healthy.level = WARN
logger.ready.name = http.openapi.operation.ready
logger.ready.level = WARN
The log level of all other operations is set to INFO by default.
Use the logging property to configure loggers and logger levels.
You can set the log levels by specifying the logger and level directly (inline) or use a custom (external) ConfigMap. If a ConfigMap is used, you set logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name property to the name of the ConfigMap containing the external logging configuration. The logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.name and logging.valueFrom.configMapKeyRef.key properties are mandatory. Default logging is used if the name or key is not set. Inside the ConfigMap, the logging configuration is described using log4j.properties. For more information about log levels, see Apache logging services.
Here we see examples of inline and external logging.
Inline logging
External logging
Any available loggers that are not configured have their level set to OFF.
If the Kafka Bridge was deployed using the Cluster Operator, changes to Kafka Bridge logging levels are applied dynamically.
If you use external logging, a rolling update is triggered when logging appenders are changed.
Garbage collector (GC)
Garbage collector logging can also be enabled (or disabled) using the jvmOptions property.
6.2.115.2. KafkaBridgeSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| replicas |
The number of pods in the |
| integer | |
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| bootstrapServers | A list of host:port pairs for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster. |
| string | |
| tls | TLS configuration for connecting Kafka Bridge to the cluster. |
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for connecting to the cluster. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| http | The HTTP related configuration. |
| adminClient | Kafka AdminClient related configuration. |
| consumer | Kafka consumer related configuration. |
| producer | Kafka producer related configuration. |
| resources | CPU and memory resources to reserve. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| jvmOptions | Currently not supported JVM Options for pods. |
| logging |
Logging configuration for Kafka Bridge. The type depends on the value of the |
| clientRackInitImage |
The image of the init container used for initializing the |
| string | |
| rack | Configuration of the node label which will be used as the client.rack consumer configuration. |
| enableMetrics | Enable the metrics for the Kafka Bridge. Default is false. |
| boolean | |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| template |
Template for Kafka Bridge resources. The template allows users to specify how a |
| tracing |
The configuration of tracing in Kafka Bridge. The type depends on the value of the |
6.2.116. KafkaBridgeHttpConfig schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec
Full list of KafkaBridgeHttpConfig schema properties
Configures HTTP access to a Kafka cluster for the Kafka Bridge.
The default HTTP configuration is for the Kafka Bridge to listen on port 8080.
6.2.116.1. cors
As well as enabling HTTP access to a Kafka cluster, HTTP properties provide the capability to enable and define access control for the Kafka Bridge through Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). CORS is a HTTP mechanism that allows browser access to selected resources from more than one origin. To configure CORS, you define a list of allowed resource origins and HTTP access methods. For the origins, you can use a URL or a Java regular expression.
Example Kafka Bridge HTTP configuration
6.2.116.2. KafkaBridgeHttpConfig schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| port | The port which is the server listening on. |
| integer | |
| cors | CORS configuration for the HTTP Bridge. |
6.2.117. KafkaBridgeHttpCors schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeHttpConfig
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| allowedOrigins | List of allowed origins. Java regular expressions can be used. |
| string array | |
| allowedMethods | List of allowed HTTP methods. |
| string array |
6.2.118. KafkaBridgeAdminClientSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| config | The Kafka AdminClient configuration used for AdminClient instances created by the bridge. |
| map |
6.2.119. KafkaBridgeConsumerSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec
Full list of KafkaBridgeConsumerSpec schema properties
Configures consumer options for the Kafka Bridge as keys.
The values can be one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Apache Kafka configuration documentation for consumers with the exception of those options which are managed directly by AMQ Streams. Specifically, all configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
ssl. -
sasl. -
security. -
bootstrap.servers -
group.id
When one of the forbidden options is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message will be printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other options will be passed to Kafka
The Cluster Operator does not validate keys or values in the config object. If an invalid configuration is provided, the Kafka Bridge cluster might not start or might become unstable. Fix the configuration so that the Cluster Operator can roll out the new configuration to all Kafka Bridge nodes.
There are exceptions to the forbidden options. For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties.
Example Kafka Bridge consumer configuration
6.2.119.1. KafkaBridgeConsumerSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| config | The Kafka consumer configuration used for consumer instances created by the bridge. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: ssl., bootstrap.servers, group.id, sasl., security. (with the exception of: ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm, ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols). |
| map |
6.2.120. KafkaBridgeProducerSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec
Full list of KafkaBridgeProducerSpec schema properties
Configures producer options for the Kafka Bridge as keys.
The values can be one of the following JSON types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
You can specify and configure the options listed in the Apache Kafka configuration documentation for producers with the exception of those options which are managed directly by AMQ Streams. Specifically, all configuration options with keys equal to or starting with one of the following strings are forbidden:
-
ssl. -
sasl. -
security. -
bootstrap.servers
When one of the forbidden options is present in the config property, it is ignored and a warning message will be printed to the Cluster Operator log file. All other options will be passed to Kafka
The Cluster Operator does not validate keys or values in the config object. If an invalid configuration is provided, the Kafka Bridge cluster might not start or might become unstable. Fix the configuration so that the Cluster Operator can roll out the new configuration to all Kafka Bridge nodes.
There are exceptions to the forbidden options. For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties.
Example Kafka Bridge producer configuration
6.2.120.1. KafkaBridgeProducerSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| config | The Kafka producer configuration used for producer instances created by the bridge. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: ssl., bootstrap.servers, sasl., security. (with the exception of: ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm, ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols). |
| map |
6.2.121. KafkaBridgeTemplate schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridgeSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deployment |
Template for Kafka Bridge |
| pod |
Template for Kafka Bridge |
| apiService |
Template for Kafka Bridge API |
| podDisruptionBudget |
Template for Kafka Bridge |
| bridgeContainer | Template for the Kafka Bridge container. |
| clusterRoleBinding | Template for the Kafka Bridge ClusterRoleBinding. |
| serviceAccount | Template for the Kafka Bridge service account. |
| initContainer | Template for the Kafka Bridge init container. |
6.2.122. KafkaBridgeStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaBridge
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| url | The URL at which external client applications can access the Kafka Bridge. |
| string | |
| labelSelector | Label selector for pods providing this resource. |
| string | |
| replicas | The current number of pods being used to provide this resource. |
| integer |
6.2.123. KafkaConnector schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the Kafka Connector. |
| status | The status of the Kafka Connector. |
6.2.124. KafkaConnectorSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnector
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| class | The Class for the Kafka Connector. |
| string | |
| tasksMax | The maximum number of tasks for the Kafka Connector. |
| integer | |
| autoRestart | Automatic restart of connector and tasks configuration. |
| config | The Kafka Connector configuration. The following properties cannot be set: connector.class, tasks.max. |
| map | |
| pause | Whether the connector should be paused. Defaults to false. |
| boolean |
6.2.125. AutoRestart schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectorSpec, KafkaMirrorMaker2ConnectorSpec
Full list of AutoRestart schema properties
Configures automatic restarts for connectors and tasks that are in a FAILED state.
When enabled, a back-off algorithm applies the automatic restart to each failed connector and its tasks.
The operator attempts an automatic restart on reconciliation. If the first attempt fails, the operator makes up to six more attempts. The duration between each restart attempt increases from 2 to 30 minutes. After each restart, failed connectors and tasks transit from FAILED to RESTARTING. If the restart fails after the final attempt, there is likely to be a problem with the connector configuration. The connector and tasks remain in a FAILED state and you have to restart them manually. You can do this by annotating the KafKaConnector custom resource with strimzi.io/restart: "true".
For Kafka Connect connectors, use the autoRestart property of the KafkaConnector resource to enable automatic restarts of failed connectors and tasks.
Enabling automatic restarts of failed connectors for Kafka Connect
For MirrorMaker 2, use the autoRestart property of connectors in the KafkaMirrorMaker2 resource to enable automatic restarts of failed connectors and tasks.
Enabling automatic restarts of failed connectors for MirrorMaker 2
6.2.125.1. AutoRestart schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled | Whether automatic restart for failed connectors and tasks should be enabled or disabled. |
| boolean |
6.2.126. KafkaConnectorStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnector
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| autoRestart | The auto restart status. |
| connectorStatus | The connector status, as reported by the Kafka Connect REST API. |
| map | |
| tasksMax | The maximum number of tasks for the Kafka Connector. |
| integer | |
| topics | The list of topics used by the Kafka Connector. |
| string array |
6.2.127. AutoRestartStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaConnectorStatus, KafkaMirrorMaker2Status
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| count | The number of times the connector or task is restarted. |
| integer | |
| connectorName | The name of the connector being restarted. |
| string | |
| lastRestartTimestamp | The last time the automatic restart was attempted. The required format is 'yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ' in the UTC time zone. |
| string |
6.2.128. KafkaMirrorMaker2 schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 cluster. |
| status | The status of the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 cluster. |
6.2.129. KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker2
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The Kafka Connect version. Defaults to 3.4.0. Consult the user documentation to understand the process required to upgrade or downgrade the version. |
| string | |
| replicas | The number of pods in the Kafka Connect group. |
| integer | |
| image | The docker image for the pods. |
| string | |
| connectCluster |
The cluster alias used for Kafka Connect. The alias must match a cluster in the list at |
| string | |
| clusters | Kafka clusters for mirroring. |
| mirrors | Configuration of the MirrorMaker 2 connectors. |
| resources | The maximum limits for CPU and memory resources and the requested initial resources. For more information, see the external documentation for core/v1 resourcerequirements. |
| livenessProbe | Pod liveness checking. |
| readinessProbe | Pod readiness checking. |
| jvmOptions | JVM Options for pods. |
| jmxOptions | JMX Options. |
| logging |
Logging configuration for Kafka Connect. The type depends on the value of the |
| clientRackInitImage |
The image of the init container used for initializing the |
| string | |
| rack |
Configuration of the node label which will be used as the |
| tracing |
The configuration of tracing in Kafka Connect. The type depends on the value of the |
| template |
Template for Kafka Connect and Kafka Mirror Maker 2 resources. The template allows users to specify how the |
| externalConfiguration | Pass data from Secrets or ConfigMaps to the Kafka Connect pods and use them to configure connectors. |
| metricsConfig |
Metrics configuration. The type depends on the value of the |
6.2.130. KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec
Full list of KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec schema properties
Configures Kafka clusters for mirroring.
6.2.130.1. config
Use the config properties to configure Kafka options.
Standard Apache Kafka configuration may be provided, restricted to those properties not managed directly by AMQ Streams.
For client connection using a specific cipher suite for a TLS version, you can configure allowed ssl properties. You can also configure the ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm property to enable or disable hostname verification.
6.2.130.2. KafkaMirrorMaker2ClusterSpec schema properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| alias | Alias used to reference the Kafka cluster. |
| string | |
| bootstrapServers |
A comma-separated list of |
| string | |
| tls | TLS configuration for connecting MirrorMaker 2 connectors to a cluster. |
| authentication |
Authentication configuration for connecting to the cluster. The type depends on the value of the |
|
| |
| config | The MirrorMaker 2 cluster config. Properties with the following prefixes cannot be set: ssl., sasl., security., listeners, plugin.path, rest., bootstrap.servers, consumer.interceptor.classes, producer.interceptor.classes (with the exception of: ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm, ssl.cipher.suites, ssl.protocol, ssl.enabled.protocols). |
| map |
6.2.131. KafkaMirrorMaker2MirrorSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker2Spec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| sourceCluster |
The alias of the source cluster used by the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 connectors. The alias must match a cluster in the list at |
| string | |
| targetCluster |
The alias of the target cluster used by the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 connectors. The alias must match a cluster in the list at |
| string | |
| sourceConnector | The specification of the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 source connector. |
| heartbeatConnector | The specification of the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 heartbeat connector. |
| checkpointConnector | The specification of the Kafka MirrorMaker 2 checkpoint connector. |
| topicsPattern | A regular expression matching the topics to be mirrored, for example, "topic1|topic2|topic3". Comma-separated lists are also supported. |
| string | |
| topicsBlacklistPattern |
The |
| string | |
| topicsExcludePattern | A regular expression matching the topics to exclude from mirroring. Comma-separated lists are also supported. |
| string | |
| groupsPattern | A regular expression matching the consumer groups to be mirrored. Comma-separated lists are also supported. |
| string | |
| groupsBlacklistPattern |
The |
| string | |
| groupsExcludePattern | A regular expression matching the consumer groups to exclude from mirroring. Comma-separated lists are also supported. |
| string |
6.2.132. KafkaMirrorMaker2ConnectorSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker2MirrorSpec
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| tasksMax | The maximum number of tasks for the Kafka Connector. |
| integer | |
| config | The Kafka Connector configuration. The following properties cannot be set: connector.class, tasks.max. |
| map | |
| autoRestart | Automatic restart of connector and tasks configuration. |
| pause | Whether the connector should be paused. Defaults to false. |
| boolean |
6.2.133. KafkaMirrorMaker2Status schema reference
Used in: KafkaMirrorMaker2
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| url | The URL of the REST API endpoint for managing and monitoring Kafka Connect connectors. |
| string | |
| autoRestartStatuses | List of MirrorMaker 2 connector auto restart statuses. |
|
| |
| connectorPlugins | The list of connector plugins available in this Kafka Connect deployment. |
|
| |
| connectors | List of MirrorMaker 2 connector statuses, as reported by the Kafka Connect REST API. |
| map array | |
| labelSelector | Label selector for pods providing this resource. |
| string | |
| replicas | The current number of pods being used to provide this resource. |
| integer |
6.2.134. KafkaRebalance schema reference
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| spec | The specification of the Kafka rebalance. |
| status | The status of the Kafka rebalance. |
6.2.135. KafkaRebalanceSpec schema reference
Used in: KafkaRebalance
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| mode |
Mode to run the rebalancing. The supported modes are
|
| string (one of [remove-brokers, full, add-brokers]) | |
| brokers |
The list of newly added brokers in case of scaling up or the ones to be removed in case of scaling down to use for rebalancing. This list can be used only with rebalancing mode |
| integer array | |
| goals | A list of goals, ordered by decreasing priority, to use for generating and executing the rebalance proposal. The supported goals are available at https://github.com/linkedin/cruise-control#goals. If an empty goals list is provided, the goals declared in the default.goals Cruise Control configuration parameter are used. |
| string array | |
| skipHardGoalCheck | Whether to allow the hard goals specified in the Kafka CR to be skipped in optimization proposal generation. This can be useful when some of those hard goals are preventing a balance solution being found. Default is false. |
| boolean | |
| rebalanceDisk | Enables intra-broker disk balancing, which balances disk space utilization between disks on the same broker. Only applies to Kafka deployments that use JBOD storage with multiple disks. When enabled, inter-broker balancing is disabled. Default is false. |
| boolean | |
| excludedTopics | A regular expression where any matching topics will be excluded from the calculation of optimization proposals. This expression will be parsed by the java.util.regex.Pattern class; for more information on the supported format consult the documentation for that class. |
| string | |
| concurrentPartitionMovementsPerBroker | The upper bound of ongoing partition replica movements going into/out of each broker. Default is 5. |
| integer | |
| concurrentIntraBrokerPartitionMovements | The upper bound of ongoing partition replica movements between disks within each broker. Default is 2. |
| integer | |
| concurrentLeaderMovements | The upper bound of ongoing partition leadership movements. Default is 1000. |
| integer | |
| replicationThrottle | The upper bound, in bytes per second, on the bandwidth used to move replicas. There is no limit by default. |
| integer | |
| replicaMovementStrategies | A list of strategy class names used to determine the execution order for the replica movements in the generated optimization proposal. By default BaseReplicaMovementStrategy is used, which will execute the replica movements in the order that they were generated. |
| string array |
6.2.136. KafkaRebalanceStatus schema reference
Used in: KafkaRebalance
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| conditions | List of status conditions. |
|
| |
| observedGeneration | The generation of the CRD that was last reconciled by the operator. |
| integer | |
| sessionId | The session identifier for requests to Cruise Control pertaining to this KafkaRebalance resource. This is used by the Kafka Rebalance operator to track the status of ongoing rebalancing operations. |
| string | |
| optimizationResult | A JSON object describing the optimization result. |
| map |