このコンテンツは選択した言語では利用できません。
Release Notes
JBoss Operations Network 3.0
for release information
Copyright © 2011 Red Hat, Inc.
December 7, 2011
Abstract
These release notes contain important information about new features, known issues, and other technical notes available at the time that JBoss Operations Network 3.0 was released.
These release notes contain feature information, changed support, and structural changes in JBoss Operations Network 3.0.
JBoss Operations Network provides an integrated solution for managing JBoss middleware, applications deployed on Red Hat products, and related middleware infrastructure. JBoss ON provides central configuration and visibility and local management and monitoring. This results in simplified maintenance and lower costs. Vigorous monitoring, versioned application deployment, auditable configuration management, and controlled software patching through JBoss ON reduce the risk of large JBoss deployments.
This version of JBoss Operations Network contains new features, enhancements, and bug fixes. It is recommended that all JBoss Operations Network users upgrade to JBoss Operations Network 3.0.
1. New Features in JBoss Operations Network 3.0
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
This version of JBoss ON introduces both new features and feature enhancements that improve JBoss ON's performance for managing resources.
1.1. Rewritten UI
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
The GUI has been redesigned in JBoss ON 3.0, moving from an older JavaScript/Struts design to GWT 2.0.4 and SmartGWT 2.4. The new GUI includes new stylesheets and a more efficient Ajax architecture, preserving a familiar layout with a cleaner and more responsive experience.
The top navigation menu has been updated to focus on clearer and more relevant tasks, adding new Bundles and Reporting tabs. Additionally, the previous top-level menus have been removed and replaced with context-specific task panes in the left navigation area. This makes it simpler to locate configuration areas. Even tables are now easier to manage, with improved sort and the ability to change the information displayed in the table columns.

Figure 1. New UI: Menus, Tables, and Navigation
One of the key features for administrative management is a more dynamic dashboard, including the ability to have multiple, user-customized dashboards in the primary Dashboard area and customizable resource-level dashboards on resource Summary tabs.
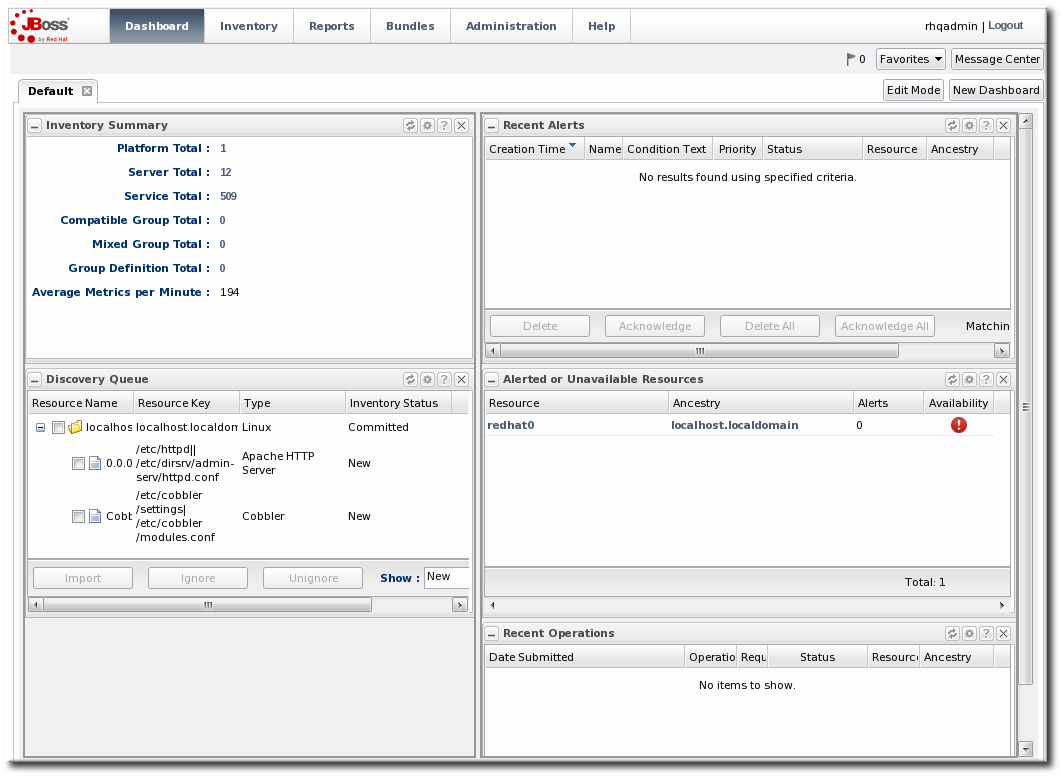
Figure 2. New UI: Default Dashboard
The new design brings other benefits:
- A new message center which provides a stream of errors, notifications, and system messages that have been generated during the current session
- Support for cron expressions when scheduling operations
- Support for editing simple properties in the configuration editor for resources
1.2. New: Managing Configuration Drift
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
Much of the JBoss ON configuration management is designed around implementing changes for resources by editing configuration files or updating files and packages. But another aspect of managing configuration is detecting unplanned, unapproved changes. The ideal configuration for a server includes defining file settings, software versions, and system settings. Resource configuration will change naturally over time, but administrators need to track those changes that could impact performance or availability. Defining a baseline configuration and tracking changes helps systems remain resilient, compliant, and understandable.
Unplanned changes to a resource's configuration are called drift, the movement away from the designated configuration baseline. JBoss Operations Network's drift management offers a way to identify and track these changes and to revert to previous versions if necessary. Drift management is a blend between JBoss ON's configuration management (which manages file settings), its content management (package lists, individual files, and versions), and monitoring.
Drift management is driven by a drift definition that defines:
- The directory to monitor
- Any files and subdirectories within the base directory to include or exclude from monitoring
- The interval or schedule which the agent uses to check the drift base directory
Along with resource-level drift definitions, JBoss ON also supports drift definition templates, which allows default settings that can be applied to multiple resources.
Once a drift definition is created, JBoss ON schedules an ongoing comparison between definitions and the current state of a directory. Every time a file is added, edited, or deleted from the monitored directory, the changes are tracked in snapshots.
When the drift definition is first set up, the current state of the resource can be compared against the last snapshot. This is a rolling snapshot. A specific snapshot can be selected as a baseline; this snapshot is pinned to the definition and then every subsequent change is compared against that snapshot. Pinning allows administrators to select a standard configuration. If it is pinned to a resource-level definition, the resource changes are compared to that. If a resource snapshot is pinned to a drift template, then changes for all resources of a type can be compared against the selected snapshot.
Finally, a new alert condition has been added to enable alerting, notifications, and responsiveness to drift on resources. Additionally, any drift changes show up on resources in the events timeline.
The JBoss ON remote API has been expanded to include a drift methods, so that drift configuration and monitoring can be automated.
Drift Requirements
- Drift is enabled as a server-side plug-in. If this plug-in is disabled, the drift monitoring is disabled and drift detection will not run. Any drift events will not be recorded in the events timeline, and any drift alerts will not be fired.This behavior is different than disabling other server-side plug-ins. For example, if an alert sender plug-in is disabled, the alert scans still run and any alerts are still recorded in the server, but the notification based on that sender is not sent.
- Drift is not supported on embedded web applications, such as an embedded WAR under an EAR application.
Drift Documentation
For more information on drift, see Managing Resource Configuration.
1.3. Enhanced: Provisioning to Allow Bundles on Non-Platform Resources
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
Beginning in JBoss Operations Network 2.4, the server was able to deploy bundles. Bundles are complete application servers, configuration, packages, or patches which are installed on remote resources. Each bundle definition allows multiple versions and destinations, so it is easy to manage what versions are deployed on what resources. It is a simplified and flexible content delivery mechanism.
In JBoss ON 2.4, bundles could be deployed only to platform resources. In JBoss ON 3.0, the bundle system has been expanded so that bundles can be deployed to server resources along with platform resources. Resource plug-ins can now define a new
<bundle-target> element, which sets a base directory or directories for the provisioning process to use. Of the default resources, three resource types support provisioning:
- All supported platform types
- JBoss AS 4 servers
- JBoss AS 5 servers and any server which uses the JBoss AS 5 resource plug-in
Note
Supporting non-platform resources for bundle provisioning has required some changes to how resources are selected when configuring provisioning. In JBoss ON 2.4, any platform group was automatically available for provisioning while all others were ignored. The group could be a mixed group, so long as all the resources in it were platforms. In JBoss ON 3.0, only compatible groups can be used for provisioning, and the groups can only contain a resource type which supports provisioning.
Different platforms are considered different resource types. So a group of Linux, Windows, and Solaris resources is considered a mixed group, even though they are all platform resources. Any platform groups created for provisioning in JBoss ON 2.4 will have to be re-created in JBoss ON 3.0, and each platform type must have its own group.
1.4. New: Synchronization (Import/Export) for Server and Monitoring Settings
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
A local network may have several separate environments — development, staging, production — which all use similar resources and JBoss ON server settings. Server synchronization allows administrators to export configuration settings from one JBoss ON server, make any necessary edits, and import them into another JBoss ON server.
Two configuration areas can be synchronized:
- System settings
- Metric templates
When the configuration is exported, it is sent to an XML file. Administrators can edit the settings, if necessary. The JBoss ON server validates the file before importing it, which mitigates some risk on importing data.
Note
There is always a risk of importing inconsistent data, and administrators should back up all existing databases before any import operation.
Server synchronization is performed using the JBoss ON CLI. Example scripts are available as part of the JBoss ON installation in the installDir
/rhq-remoting-cli-version#/samples/ directory. Documentation with usage examples is available in Configuring JBoss ON Servers and Agents.
1.5. New: Launching Server-side CLI Scripts in Response to Alerts
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
JBoss ON has its own command-line client that can be used to manage server instances in the same way that the web UI manages servers. Much like running a script resource or launching an operation in response to an alert condition, a server CLI script can be run in response to an alert condition.
The JBoss ON script is added to a content repository as an available package. The script (JavaScript file) can then be selected when configuring an alert notification.
An example CLI alert script is included in the server files, in serverInstallDir
/alert-scripts/.
1.6. New: Configuring Alert Conditions Based on Call-Time Data
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
Certain resource types (session beans and web servers) deliver call time or response time data. This information contains pre-aggregated measurements for the maximum, minimum, or average results for the responses.
Resources which collect call time data can use that pre-processed information as the basis for alert notifications, the same as other monitoring data. The call-time data condition can be set to issue an alert when it changes, increases, or decreases in value or when it crosses a defined threshold. It can also be filtered using regular expressions, so only certain measurements or values are considered as part of the condition.
Two types of resources support call-time data:
- Session bean methods
- Web servers with response time monitoring configured
1.7. New: Alert Conditions Based on Ranges
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
JBoss ON alert definitions have long supported both AND and OR operators. If a resource encountered one condition and then another, an alert would be issued. This allows administrators to get both detailed information and to create detailed responses through scripts and operations. For example, if a JBoss server had a high thread count and a low free memory, then administrators could run a particular script or start another JBoss resource.
However, while the AND operator was effective with different metrics, it could trigger unexpected alerts when it was used with the same metric in an attempt to create a range.
JBoss ON 3.0 introduces a new range condition, which triggers an alert only if a measurement is between two values.
1.8. Enhanced: Authorization Controls for Content Repositories
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
Previously, any user with global inventory permissions could create and manage content repositories. This method had granted very broad access permissions, where a user had global access to the inventory in order to manage content.
JBoss Operations Network 3.0 defines a new access control scheme for repositories and the content within them. Every user has the ability to create repositories and to upload packages to them. Additionally, repositories have two new settings which control access to them:
- Owner, which assigns the repository to belong to a specific user; this sets write access to the repository.
- Private, which sets whether the repository can be accessed by anyone or only by the owner. This sets read/download access to the repository.
JBoss Operations Network 3.0 also introduces a new access control permission, repositories. Any user with that permission can manage any configured repository, regardless of who the repository's owner is. Repositories without an owner can only be managed by users with the repositories permission. Lastly, only users with this permission can associated a content source with a repository; all other users must add packages manually.
As part of the upgrade process, all existing repositories are automatically assigned to be private with no owner. This restricts all access to the repositories to administrative users, which is similar to the behavior in JBoss ON 2.4. All users with the inventory permission are automatically assigned the repositories permission.
1.9. New: Deleting and Purging Agent Resource Plug-ins
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
In previous versions of JBoss ON it was not possible to remove any agent resource plug-ins from the JBoss ON configuration. Now, agent plug-ins can be deleted (removed and blocked) or purged (removed and allowed to be reloaded) from the JBoss ON configuration.
1.10. New: Support for PostgreSQL 9.0
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
PostgreSQL 9.0 can now be used as the backend database for the JBoss ON server.
1.11. Tech Preview: JBoss Resource Plug-ins for mod_cluster Domains
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
JBoss ON 3.0 introduces a new resource plug-in for
mod_cluster domains. This is for mod_cluster version 1.1.2[1].
The
mod_cluster plug-in will be one of the new standard resource plug-ins with JBoss ON.
Note
The
mod_cluster domain resources are tech preview in JBoss Operations Network 3.0. These resource types are not fully-supported.
If you configure a
mod_cluster resource in JBoss ON 3.0, it must be uninventoried and re-added in later versions of JBoss Operations Network. It cannot be migrated. This means that you can lose monitoring data and configuration.
For more information on how JBoss ON manages
mod_cluster is in Manage JBoss Servers with JBoss ON.
1.12. Tech Preview: JBoss Resource Plug-ins for JBoss AS 7.1
リンクのコピーリンクがクリップボードにコピーされました!
JBoss ON 3.0 includes a JBoss AS 7.1 resource plug-in which adds early support for individual servers, host controllers, domain controllers, server groups, and managed servers.
Note
The JBoss AS 7.1 standalone, host controller, and manager server resources are tech preview in JBoss Operations Network 3.0. These resource types are not fully-supported.
If you configure a JBoss AS 7.1 resource in JBoss ON 3.0, it must be uninventoried and re-added in later versions of JBoss Operations Network. It cannot be migrated. This means that you can lose monitoring data and configuration.
This is included in a special Tech Preview Plug-in Pack. More information on the managed resources is in the Resource Reference.
[1]
The latest
mod_cluster version supported in JBoss EAP and the httpd service in Red Hat Enterprise Linux is 1.0.10.