Chapter 4. Quickstarts
4.1. Quickstart
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The quickstarts are sample projects. Each one demonstrates how to use a specific piece of functionality in order to aid you in building services. There are several dozen quickstarts included in the
SOA_ROOT/jboss-as/samples/quickstarts/ directory. Build and deploy every quickstart by using Apache Ant.
4.2. Important Notes About Quickstarts
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
When intending to run a quickstart, remember the following points:
- Each quickstart needs to be built and deployed using Apache Ant.
- Each quickstart uses the
samples/quickstarts/conf/quickstarts.propertiesfile to store environment-specific configuration options such as the directory where the server was installed. You must create aquickstarts.propertiesfile that matches your server installation. An example properties file (quickstarts.properties-example) is included. - Each quickstart has different requirements. These are documented in their individual
readme.txtfiles. - Not every quickstart can run under every server profile.
- The jBPM quickstarts require a valid jBPM Console user name and password. Supply these by adding them as properties in the
SOA_ROOT/jboss-as/samples/quickstarts/conf/quickstarts.propertiesfile:jBPM console security credentials jbpm.console.username=admin jbpm.console.password=adminpassword
# jBPM console security credentials jbpm.console.username=admin jbpm.console.password=adminpasswordCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The quickstarts that are affected by this requirement arebpm_orchestration1,bpm_orchestration2,bpm_orchestration3andbpm_orchestration4. - You can only execute some of the quickstarts (such as groovy_gateway) if the server is not running in headless mode. (The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform is configured to launch in headless mode by default.)
Important
Red Hat recommends that you run production servers in headless mode only.
4.3. Learn More About a Quickstart
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
To learn more about a particular quickstart:
Procedure 4.1. Task
- Study the quickstart's
readme.txtfile. - Run the
ant helpcommand in the quickstart's directory.
4.4. Overview of How the "Hello World" Quickstart Works
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
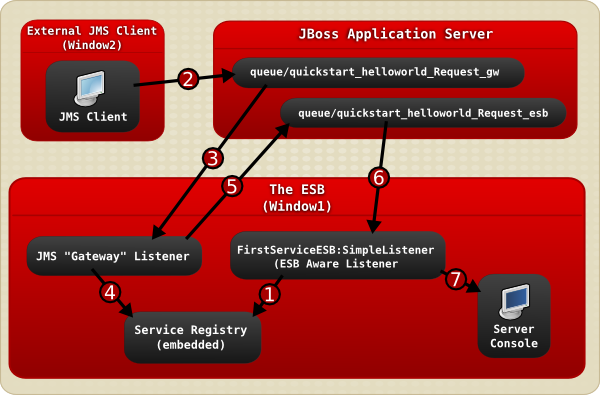
Figure 4.1. Image
- The JBoss Enterprise SOA Platform server is launched in
Window1and then theFirstServiceESB:SimpleListenerservice is added to the Service Registry service when the helloworld quickstart is deployed. - A JMS client sends an ESB-unaware "Hello World" message, (it is a plain
Stringobject), to the JMS Queue (queue/quickstart_helloworld_Request_gw). - The JMS Gateway Listener receives the ESB-unaware message and creates from it an ESB-aware message for use by ESB-aware end-points.
- The
JMS Gateway Listeneruses theservice registryto find theFirstServiceESB:SimpleListenerservice's end-point reference (EPR). In this case, the EPR is thequeue/quickstart_helloworld_Request_esbJMS queue. - The
JMS Gateway Listenertakes the new ESB-aware message and sends it to thequeue/quickstart_helloworld_Request_esbJMS queue. - The
FirstServiceESB:SimpleListenerservice receives the message. - The
FirstServiceESB:SimpleListenerservice extracts the payload from the message and outputs it to the console.