Chapter 6. Service Catalog Components
6.1. Service Catalog
6.1.1. Overview
Enabling the service catalog is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information on Red Hat Technology Preview features support scope, see https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/.
To opt-in during installation, see Advanced Installation.
When developing microservices-based applications to run on cloud native platforms, there are many ways to provision different resources and share their coordinates, credentials, and configuration, depending on the service provider and the platform.
To give developers a more seamless experience, OpenShift Container Platform includes a service catalog, an implementation of the Open Service Broker API (OSB API) for Kubernetes. This allows users to connect any of their applications deployed in OpenShift Container Platform to a wide variety of service brokers.
The service catalog allows cluster administrators to integrate multiple platforms using a single API specification. The OpenShift Container Platform web console displays the service classes offered by brokers in the service catalog, allowing users to discover and instantiate those services for use with their applications.
As a result, service users benefit from ease and consistency of use across different types of services from different providers, while service providers benefit from having one integration point that gives them access to multiple platforms.
6.1.2. Design
The design of the service catalog follows this basic workflow:
New terms in the following are defined further in Concepts and Terminology.
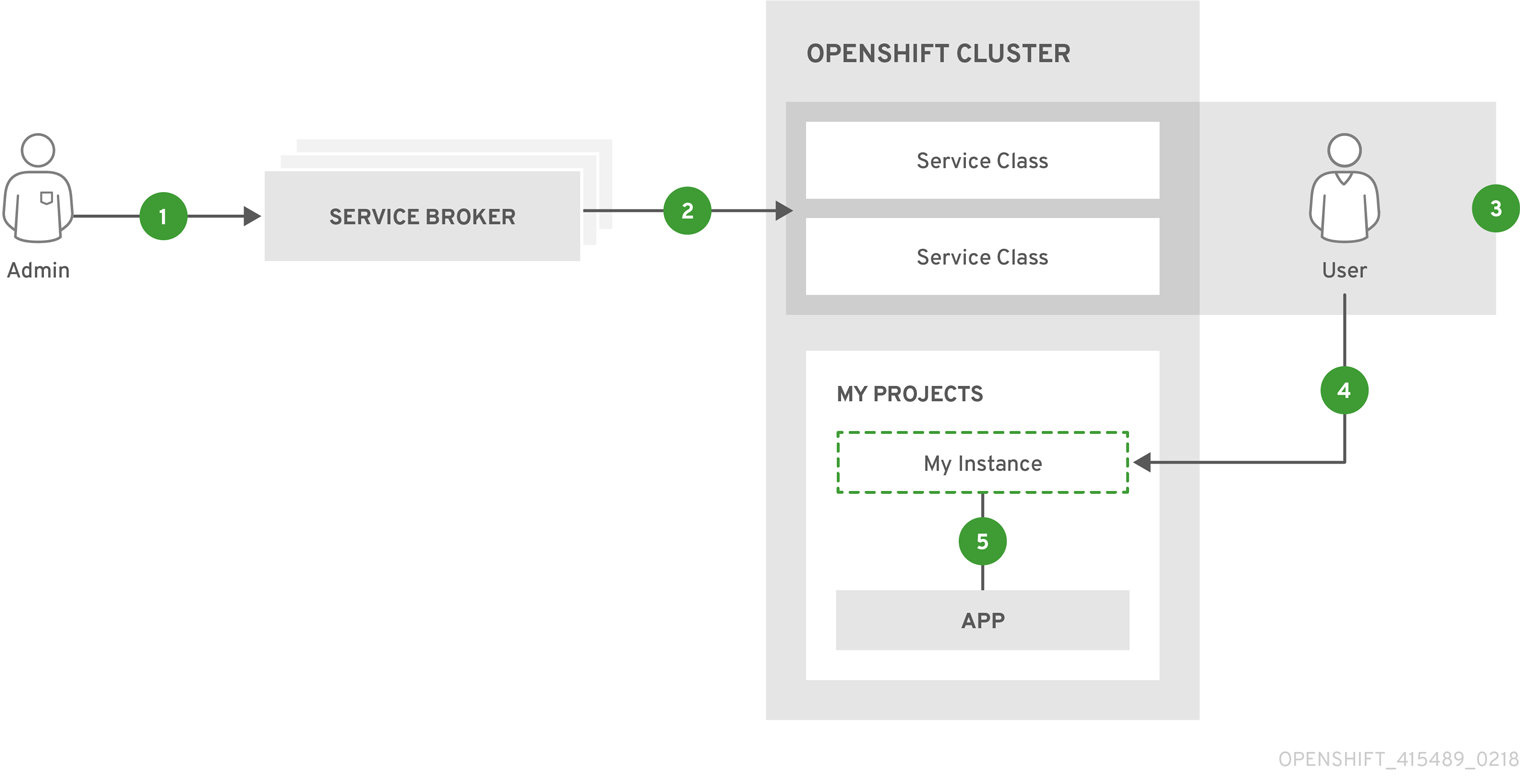
- A cluster administrator registers one or more service brokers with their OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This can be done automatically during installation for some default-provided service brokers or manually.
- Each service broker specifies a set of service classes and variations of those services (service plans) to OpenShift Container Platform that should be made available to users.
- Using the OpenShift Container Platform web console or CLI, users discover the services that are available. For example, a service class may be available that is a database-as-a-service called BestDataBase.
- A user chooses a service class and requests a new instance of their own. For example, a service instance may be a BestDataBase instance named
my_db. - A user links, or binds, their service instance to a set of pods (their application). For example, the
my_dbservice instance may be bound to the user’s application calledmy_app.
This infrastructure allows a loose coupling between applications running in OpenShift Container Platform and the services they use. This allows the application that uses those services to focus on its own business logic while leaving the management of these services to the provider.
6.1.3. Concepts and Terminology
- Service Broker
A service broker is a server that conforms to the OSB API specification and manages a set of one or more services. The software could be hosted within your own OpenShift Container Platform cluster or elsewhere.
Cluster administrators can create
BrokerAPI resources representing service brokers and register them with their OpenShift Container Platform cluster. This allows cluster administrators to make new types of managed services using that service broker available within their cluster.A
Brokerresource specifies connection details for a service broker and the set of services (and variations of those services) to OpenShift Container Platform that should then be made available to users.Example
BrokerResourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Service Class
Also synonymous with "service" in the context of the service catalog, a service class is a type of managed service offered by a particular broker. Each time a new broker resource is added to the cluster, the service catalog controller connects to the corresponding service broker to obtain a list of service offerings. A new
ServiceClassresource is automatically created for each.NoteOpenShift Container Platform also has a core concept called services, which are separate Kubernetes resources related to internal load balancing. These resources are not to be confused with how the term is used in the context of the service catalog and OSB API.
Example
ServiceClassResourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Service Plan
- A service plan is represents tiers of a service class. For example, a service class may expose a set of plans that offer varying degrees of quality-of-service (QoS), each with a different cost associated with it.
- Service Instance
A service instance is a provisioned instance of a service class. When a user wants to use the capability provided by a service class, they can create a new instance.
When a new
Instanceresource is created, the service catalog controller connects to the appropriate service broker and instructs it to provision the service instance.Example
InstanceResourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Application
- The term application refers to the OpenShift Container Platform deployment artifacts, for example pods running in a user’s project, that will use a service instance.
- Credentials
- Credentials are information needed by an application to communicate with a service instance.
- Service Binding
A service binding is a link between a service instance and an application. These are created by cluster users who wish for their applications to reference and use a service instance.
Upon creation, the service catalog controller creates a Kubernetes secret containing connection details and credentials for the service instance. Such secrets can be mounted into pods as usual. There is also integration with
PodPresets, which allow you to express how the secret should be consumed, and in which pods.Example
BindingResourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.4. Provided Service Brokers
OpenShift Container Platform provides the following service brokers for use with the service catalog.
Because the service catalog is currently Technology Preview, the provided service brokers are also currently Technology Preview.
6.2. Template Service Broker
Enabling the template service broker is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information on Red Hat Technology Preview features support scope, see https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/.
To opt-in during installation, see Configuring the Template Service Broker.
The template service broker (TSB) gives the service catalog visibility into the default Instant App and Quickstart templates that have shipped with OpenShift Container Platform since its initial release. The TSB can also make available as a service anything for which an OpenShift Container Platform template has been written, whether provided by Red Hat, a cluster administrator or user, or a third party vendor.
By default, the TSB shows the objects that are globally available from the openshift project. It can also be configured to watch any other project that a cluster administrator chooses.
6.3. Ansible Service Broker
6.3.1. Overview
Enabling the Ansible service broker is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information on Red Hat Technology Preview features support scope, see https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/.
To opt-in during installation, see Advanced Installation.
The Ansible service broker (ASB) is an implementation of the OSB API that manages applications defined by Ansible playbook bundles (APBs). APBs provide a new method for defining and distributing container applications in OpenShift Container Platform, consisting of a bundle of Ansible playbooks built into a container image with an Ansible runtime. APBs leverage Ansible to create a standard mechanism for automating complex deployments.
The design of the ASB follows this basic workflow:
- A user requests list of available applications from the service catalog using the OpenShift Container Platform web console.
- The service catalog requests the ASB for available applications.
- The ASB communicates with a defined container registry to learn which APBs are available.
- The user issues a request to provision a specific APB.
- The provision request makes its way to the ASB, which fulfills the user’s request by invoking the provision method on the APB.
6.3.2. Ansible Playbook Bundles
An Ansible playbook bundle (APB) is a lightweight application definition that allows you to leverage existing investment in Ansible roles and playbooks.
APBs use a simple directory with named playbooks to perform OSB API actions, such as provision and bind. Metadata defined in apb.yml spec file contains a list of required and optional parameters for use during deployment.
6.3.2.1. Directory Structure
The following shows an example directory structure of an APB:
6.3.2.2. Spec File
An APB spec file (apb.yml) must be edited for your specific application. For example, the etherpad-apb spec file looks as follows:
For an APB that does not have any parameters, the parameters field should be blank:
parameters: []
parameters: []6.3.2.3. Actions
The following are the actions for an APB. At a minimum, an APB must implement the provision and deprovision actions.
- provision.yml
- Playbook called to handle installing application to the cluster.
- deprovision.yml
- Playbook called to handle uninstalling.
- bind.yml
- Playbook to grant access to another service to use this service. For example, generating credentials.
- unbind.yml
- Playbook to revoke access to this service.
The required named playbooks correspond to methods defined by the OSB API. For example, when the ASB needs to provision an APB, it will execute the provision.yml.
After the required named playbooks have been generated, the files can be used directly to test management of the application. A developer may want to work with this directory of files, make changes, run, and repeat until they are satisfied with the behavior. They can test the playbooks by invoking Ansible directly with the playbook and any required variables.