This documentation is for a release that is no longer maintained
See documentation for the latest supported version 3 or the latest supported version 4.Authentication
Configuring user authentication, encryption, and access controls for users and services
Abstract
Chapter 1. Understanding authentication
For users to interact with OpenShift Container Platform, they must first authenticate to the cluster. The authentication layer identifies the user associated with requests to the OpenShift Container Platform API. The authorization layer then uses information about the requesting user to determine if the request is allowed.
As an administrator, you can configure authentication for OpenShift Container Platform.
1.1. Users
A user in OpenShift Container Platform is an entity that can make requests to the OpenShift Container Platform API. An OpenShift Container Platform user object represents an actor which can be granted permissions in the system by adding roles to them or to their groups. Typically, this represents the account of a developer or administrator that is interacting with OpenShift Container Platform.
Several types of users can exist:
|
|
This is the way most interactive OpenShift Container Platform users are represented. Regular users are created automatically in the system upon first login or can be created via the API. Regular users are represented with the |
|
|
Many of these are created automatically when the infrastructure is defined, mainly for the purpose of enabling the infrastructure to interact with the API securely. They include a cluster administrator (with access to everything), a per-node user, users for use by routers and registries, and various others. Finally, there is an |
|
|
These are special system users associated with projects; some are created automatically when the project is first created, while project administrators can create more for the purpose of defining access to the contents of each project. Service accounts are represented with the |
Each user must authenticate in some way in order to access OpenShift Container Platform. API requests with no authentication or invalid authentication are authenticated as requests by the anonymous system user. Once authenticated, policy determines what the user is authorized to do.
1.2. Groups
A user can be assigned to one or more groups, each of which represent a certain set of users. Groups are useful when managing authorization policies to grant permissions to multiple users at once, for example allowing access to objects within a project, versus granting them to users individually.
In addition to explicitly defined groups, there are also system groups, or virtual groups, that are automatically provisioned by the cluster.
The following default virtual groups are most important:
| Virtual group | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Automatically associated with all authenticated users. |
|
| Automatically associated with all users authenticated with an OAuth access token. |
|
| Automatically associated with all unauthenticated users. |
1.3. API authentication
Requests to the OpenShift Container Platform API are authenticated using the following methods:
- OAuth Access Tokens
-
Obtained from the OpenShift Container Platform OAuth server using the
<namespace_route>/oauth/authorizeand<namespace_route>/oauth/tokenendpoints. -
Sent as an
Authorization: Bearer…header. -
Sent as a websocket subprotocol header in the form
base64url.bearer.authorization.k8s.io.<base64url-encoded-token>for websocket requests.
-
Obtained from the OpenShift Container Platform OAuth server using the
- X.509 Client Certificates
- Requires an HTTPS connection to the API server.
- Verified by the API server against a trusted certificate authority bundle.
- The API server creates and distributes certificates to controllers to authenticate themselves.
Any request with an invalid access token or an invalid certificate is rejected by the authentication layer with a 401 error.
If no access token or certificate is presented, the authentication layer assigns the system:anonymous virtual user and the system:unauthenticated virtual group to the request. This allows the authorization layer to determine which requests, if any, an anonymous user is allowed to make.
1.3.1. OpenShift Container Platform OAuth server
The OpenShift Container Platform master includes a built-in OAuth server. Users obtain OAuth access tokens to authenticate themselves to the API.
When a person requests a new OAuth token, the OAuth server uses the configured identity provider to determine the identity of the person making the request.
It then determines what user that identity maps to, creates an access token for that user, and returns the token for use.
1.3.1.1. OAuth token requests
Every request for an OAuth token must specify the OAuth client that will receive and use the token. The following OAuth clients are automatically created when starting the OpenShift Container Platform API:
| OAuth Client | Usage |
|---|---|
|
|
Requests tokens at |
|
|
Requests tokens with a user-agent that can handle |
<namespace_route> refers to the namespace’s route. This is found by running the following command.
oc get route oauth-openshift -n openshift-authentication -o json | jq .spec.host
oc get route oauth-openshift -n openshift-authentication -o json | jq .spec.host
All requests for OAuth tokens involve a request to <namespace_route>/oauth/authorize. Most authentication integrations place an authenticating proxy in front of this endpoint, or configure OpenShift Container Platform to validate credentials against a backing identity provider. Requests to <namespace_route>/oauth/authorize can come from user-agents that cannot display interactive login pages, such as the CLI. Therefore, OpenShift Container Platform supports authenticating using a WWW-Authenticate challenge in addition to interactive login flows.
If an authenticating proxy is placed in front of the <namespace_route>/oauth/authorize endpoint, it sends unauthenticated, non-browser user-agents WWW-Authenticate challenges rather than displaying an interactive login page or redirecting to an interactive login flow.
To prevent cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks against browser clients, only send Basic authentication challenges with if a X-CSRF-Token header is on the request. Clients that expect to receive Basic WWW-Authenticate challenges must set this header to a non-empty value.
If the authenticating proxy cannot support WWW-Authenticate challenges, or if OpenShift Container Platform is configured to use an identity provider that does not support WWW-Authenticate challenges, you must use a browser to manually obtain a token from <namespace_route>/oauth/token/request.
1.3.1.2. API impersonation
You can configure a request to the OpenShift Container Platform API to act as though it originated from another user. For more information, see User impersonation in the Kubernetes documentation.
1.3.1.3. Authentication metrics for Prometheus
OpenShift Container Platform captures the following Prometheus system metrics during authentication attempts:
-
openshift_auth_basic_password_countcounts the number ofoc loginuser name and password attempts. -
openshift_auth_basic_password_count_resultcounts the number ofoc loginuser name and password attempts by result,successorerror. -
openshift_auth_form_password_countcounts the number of web console login attempts. -
openshift_auth_form_password_count_resultcounts the number of web console login attempts by result,successorerror. -
openshift_auth_password_totalcounts the total number ofoc loginand web console login attempts.
Chapter 2. Certificate types and descriptions
2.1. Certificate validation
OpenShift Container Platform monitors certificates for proper validity, for the cluster certificates it issues and manages. The OpenShift Container Platform alerting framework has rules to help identify when a certificate issue is about to occur. These rules consist of the following checks:
- API server client certificate expiration is less than five minutes.
2.2. User-provided certificates for the API server
Purpose
The API server is accessible by clients external to the cluster at api.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. You might want clients to access the API server at a different host name or without the need to distribute the cluster-managed certificate authority (CA) certificates to the clients. The administrator must set a custom default certificate to be used by the API server when serving content.
Location
The user-provided certificates must be provided in a kubernetes.io/tls type Secret in the openshift-config namespace. Update the API server cluster configuration, the apiserver/cluster resource, to enable the use of the user-provided certificate.
Management
User-provided certificates are managed by the user.
Expiration
User-provided certificates are managed by the user.
Customization
Update the secret containing the user-managed certificate as needed.
2.3. Proxy certificates
Purpose
Proxy certificates allow users to specify one or more custom certificate authority (CA) certificates used by platform components when making egress connections.
The trustedCA field of the Proxy object is a reference to a ConfigMap that contains a user-provided trusted certificate authority (CA) bundle. This bundle is merged with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) trust bundle and injected into the trust store of platform components that make egress HTTPS calls. For example, image-registry-operator calls an external image registry to download images. If trustedCA is not specified, only the RHCOS trust bundle is used for proxied HTTPS connections. Provide custom CA certificates to the RHCOS trust bundle if you want to use your own certificate infrastructure.
The trustedCA field should only be consumed by a proxy validator. The validator is responsible for reading the certificate bundle from required key ca-bundle.crt and copying it to a ConfigMap named trusted-ca-bundle in the openshift-config-managed namespace. The namespace for the ConfigMap referenced by trustedCA is openshift-config:
Managing proxy certificates during installation
The additionalTrustBundle value of the installer configuration is used to specify any proxy-trusted CA certificates during installation. For example:
Location
The user-provided trust bundle is represented as a ConfigMap. The ConfigMap is mounted into the file system of platform components that make egress HTTPS calls. Typically, Operators mount the ConfigMap to /etc/pki/ca-trust/extracted/pem/tls-ca-bundle.pem, but this is not required by the proxy. A proxy can modify or inspect the HTTPS connection. In either case, the proxy must generate and sign a new certificate for the connection.
Complete proxy support means connecting to the specified proxy and trusting any signatures it has generated. Therefore, it is necessary to let the user specify a trusted root, such that any certificate chain connected to that trusted root is also trusted.
If using the RHCOS trust bundle, place CA certificates in /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors.
See Using shared system certificates in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux documentation for more information.
Expiration
The user sets the expiration term of the user-provided trust bundle.
The default expiration term is defined by the CA certificate itself. It is up to the CA administrator to configure this for the certificate before it can be used by OpenShift Container Platform or RHCOS.
Red Hat does not monitor for when CAs expire. However, due to the long life of CAs, this is generally not an issue. However, you might need to periodically update the trust bundle.
Services
By default, all platform components that make egress HTTPS calls will use the RHCOS trust bundle. If trustedCA is defined, it will also be used.
Any service that is running on the RHCOS node is able to use the trust bundle of the node.
Management
These certificates are managed by the system and not the user.
Customization
Updating the user-provided trust bundle consists of either:
-
updating the PEM-encoded certificates in the ConfigMap referenced by
trustedCA,or -
creating a ConfigMap in the namespace
openshift-configthat contains the new trust bundle and updatingtrustedCAto reference the name of the new ConfigMap.
The mechanism for writing CA certificates to the RHCOS trust bundle is exactly the same as writing any other file to RHCOS, which is done through the use of MachineConfigs. When the Machine Config Operator (MCO) applies the new MachineConfig that contains the new CA certificates, the node is rebooted. During the next boot, the service coreos-update-ca-trust.service runs on the RHCOS nodes, which automatically update the trust bundle with the new CA certificates. For example:
The trust store of machines must also support updating the trust store of nodes.
Renewal
There are no Operators that can auto-renew certificates on the RHCOS nodes.
Red Hat does not monitor for when CAs expire. However, due to the long life of CAs, this is generally not an issue. However, you might need to periodically update the trust bundle.
2.4. Service CA certificates
Purpose
service-ca is an Operator that creates a self-signed CA when an OpenShift Container Platform cluster is deployed.
Expiration
A custom expiration term is not supported. The self-signed CA is stored in a secret with qualified name service-ca/signing-key in fields tls.crt (certificate(s)), tls.key (private key), and ca-bundle.crt (CA bundle).
Other services can request a service serving certificate by annotating a service resource with service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name: <secret name>. In response, the Operator generates a new certificate, as tls.crt, and private key, as tls.key to the named secret. The certificate is valid for two years.
Other services can request that the CA bundle for the service CA be injected into APIService or ConfigMap resources by annotating with service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle: true to support validating certificates generated from the service CA. In response, the Operator writes its current CA bundle to the CABundle field of APIService or as service-ca.crt to a ConfigMap.
As of OpenShift Container Platform 4.3.5, automated rotation is supported and is backported to some 4.2.z and 4.3.z releases. For any release supporting automated rotation, the service CA is valid for 26 months and is automatically refreshed when there is less than 13 months validity left. If necessary, you can manually refresh the service CA.
The service CA expiration of 26 months is longer than the expected upgrade interval for a supported OpenShift Container Platform cluster, such that non-control plane consumers of service CA certificates will be refreshed after CA rotation and prior to the expiration of the pre-rotation CA.
A manually-rotated service CA does not maintain trust with the previous service CA. You might experience a temporary service disruption until the Pods in the cluster are restarted, which ensures that Pods are using service serving certificates issued by the new service CA.
Management
These certificates are managed by the system and not the user.
Services
Services that use service CA certificates include:
- cluster-autoscaler-operator
- cluster-monitoring-operator
- cluster-authentication-operator
- cluster-image-registry-operator
- cluster-ingress-operator
- cluster-kube-apiserver-operator
- cluster-kube-controller-manager-operator
- cluster-kube-scheduler-operator
- cluster-networking-operator
- cluster-openshift-apiserver-operator
- cluster-openshift-controller-manager-operator
- cluster-samples-operator
- cluster-svcat-apiserver-operator
- cluster-svcat-controller-manager-operator
- machine-config-operator
- console-operator
- insights-operator
- machine-api-operator
- operator-lifecycle-manager
This is not a comprehensive list.
2.5. Node certificates
Purpose
Node certificates are signed by the cluster; they come from a certificate authority (CA) that is generated by the bootstrap process. Once the cluster is installed, the node certificates are auto-rotated.
Management
These certificates are managed by the system and not the user.
2.6. Bootstrap certificates
Purpose
The kubelet, in OpenShift Container Platform 4 and later, uses the bootstrap certificate located in /etc/kubernetes/kubeconfig to initially bootstrap. This is followed by the bootstrap initialization process and authorization of the kubelet to create a CSR.
In that process, the kubelet generates a CSR while communicating over the bootstrap channel. The controller manager signs the CSR, resulting in a certificate that the kubelet manages.
Management
These certificates are managed by the system and not the user.
Expiration
This bootstrap CA is valid for 10 years.
The kubelet-managed certificate is valid for one year and rotates automatically at around the 80 percent mark of that one year.
Customization
You cannot customize the bootstrap certificates.
2.7. etcd certificates
Purpose
etcd certificates are signed by the etcd-signer; they come from a certificate authority (CA) that is generated by the bootstrap process.
Location
CA certificates:
-
etcd CA certificate:
/etc/ssl/etcd/ca.crt -
etcd metric CA certificate:
/etc/ssl/etcd/metric-ca.crt
-
etcd CA certificate:
-
Server certificates:
/etc/ssl/etcd/system:etcd-server -
Client certificates:
<api_server_pod_directory>/secrets/etcd-client/ -
Peer certificates:
/etc/ssl/etcd/system:etcd-peer -
Metric certificates:
/etc/ssl/etcd/metric-signer
Expiration
The CA certificates are valid for 10 years. The peer, client, and server certificates are valid for three years.
Management
These certificates are managed by the system and not the user.
Services
etcd certificates are used for encrypted communication between etcd member peers, as well as encrypted client traffic. The following certificates are generated and used by etcd and other processes that communicate with etcd:
- Peer certificates: Used for communication between etcd members.
-
Client certificates: Used for encrypted server-client communication. Client certificates are currently used by the API server only, and no other service should connect to etcd directly except for the proxy. Client secrets (
etcd-client,etcd-metric-client,etcd-metric-signer, andetcd-signer) are added to theopenshift-config,openshift-monitoring, andopenshift-kube-apiservernamespaces. - Server certificates: Used by the etcd server for authenticating client requests.
- Metric certificates: All metric consumers connect to proxy with metric-client certificates.
2.8. OLM certificates
Management
All certificates for OpenShift Lifecycle Manager (OLM) components (olm-operator, catalog-operator, packageserver, and marketplace-operator) are managed by the system.
Operators installed via OLM can have certificates generated for them if they are providing API services. packageserver is one example.
Certificates in the openshift-operator-lifecycle-manager namespace are managed by OLM with the exception of certificates used by Operators that require a validating or mutating webhook.
Operators that install validating or mutating webhooks must currently manage those certificates themselves. They do not require the user to manage the certificates.
OLM will not update the certificates of Operators that it manages in proxy environments. These certificates must be managed by the user via the subscription config.
2.9. User-provided certificates for default ingress
Purpose
Applications are usually exposed at <route_name>.apps.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>. The <cluster_name> and <base_domain> come from the installation config file. <route_name> is the host field of the route, if specified, or the route name. For example, hello-openshift-default.apps.username.devcluster.openshift.com. hello-openshift is the name of the route and the route is in the default namespace. You might want clients to access the applications without the need to distribute the cluster-managed CA certificates to the clients. The administrator must set a custom default certificate when serving application content.
The Ingress Operator generates a default certificate for an Ingress Controller to serve as a placeholder until you configure a custom default certificate. Do not use operator-generated default certificates in production clusters.
Location
The user-provided certificates must be provided in a kubernetes.io/tls type Secret in the openshift-config namespace. Update the ingresscontroller.operator/default resource in the openshift-ingress-operator namespace to enable the use of the user-provided certificate.
Management
User-provided certificates are managed by the user.
Expiration
User-provided certificates are managed by the user.
Services
Applications deployed on the cluster use user-provided certificates for default ingress.
Customization
Update the secret containing the user-managed certificate as needed.
2.10. Ingress certificates
Purpose
The Ingress Operator uses certificates for:
- Securing access to metrics for Prometheus.
- Securing access to routes.
Location
To secure access to Ingress Operator and Ingress Controller metrics, the Ingress Operator uses service serving certificates. The Operator requests a certificate from the service-ca controller for its own metrics, and the service-ca controller puts the certificate in a secret named metrics-tls in the openshift-ingress-operator namespace. Additionally, the Ingress Operator requests a certificate for each Ingress Controller, and the service-ca controller puts the certificate in a secret named router-metrics-certs-<name>, where <name> is the name of the Ingress Controller, in the openshift-ingress namespace.
Each Ingress Controller has a default certificate that it uses for secured routes that do not specify their own certificates. Unless you specify a custom certificate, the Operator uses a self-signed certificate by default. The Operator uses its own self-signed signing certificate to sign any default certificate that it generates. The Operator generates this signing certificate and puts it in a secret named router-ca in the openshift-ingress-operator namespace. When the Operator generates a default certificate, it puts the default certificate in a secret named router-certs-<name> (where <name> is the name of the Ingress Controller) in the openshift-ingress namespace.
The Ingress Operator generates a default certificate for an Ingress Controller to serve as a placeholder until you configure a custom default certificate. Do not use Operator-generated default certificates in production clusters.
Workflow
Figure 2.1. Custom certificate workflow
Figure 2.2. Default certificate workflow
![]() An empty
An empty defaultCertificate field causes the Ingress Operator to use its self-signed CA to generate a serving certificate for the specified domain.
![]() The default CA certificate and key generated by the Ingress Operator. Used to sign Operator-generated default serving certificates.
The default CA certificate and key generated by the Ingress Operator. Used to sign Operator-generated default serving certificates.
![]() In the default workflow, the wildcard default serving certificate, created by the Ingress Operator and signed using the generated default CA certificate. In the custom workflow, this is the user-provided certificate.
In the default workflow, the wildcard default serving certificate, created by the Ingress Operator and signed using the generated default CA certificate. In the custom workflow, this is the user-provided certificate.
![]() The router deployment. Uses the certificate in
The router deployment. Uses the certificate in secrets/router-certs-default as its default front-end server certificate.
![]() In the default workflow, the contents of the wildcard default serving certificate (public and private parts) are copied here to enable OAuth integration. In the custom workflow, this is the user-provided certificate.
In the default workflow, the contents of the wildcard default serving certificate (public and private parts) are copied here to enable OAuth integration. In the custom workflow, this is the user-provided certificate.
![]() Transitional resource containing the certificate (public part) of the Operator-generated default CA certificate; read by OAuth and the web console to establish trust. This object will be removed in a future release.
Transitional resource containing the certificate (public part) of the Operator-generated default CA certificate; read by OAuth and the web console to establish trust. This object will be removed in a future release.
![]() The public (certificate) part of the default serving certificate. Replaces the
The public (certificate) part of the default serving certificate. Replaces the configmaps/router-ca resource.
![]() The user updates the cluster proxy configuration with the CA certificate that signed the
The user updates the cluster proxy configuration with the CA certificate that signed the ingresscontroller serving certificate. This enables components like auth, console, and the registry to trust the serving certificate.
![]() The cluster-wide trusted CA bundle containing the combined Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) and user-provided CA bundles or an RHCOS-only bundle if a user bundle is not provided.
The cluster-wide trusted CA bundle containing the combined Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) and user-provided CA bundles or an RHCOS-only bundle if a user bundle is not provided.
![]() The custom CA certificate bundle, which instructs other components (for example,
The custom CA certificate bundle, which instructs other components (for example, auth and console) to trust an ingresscontroller configured with a custom certificate.
![]() The
The trustedCA field is used to reference the user-provided CA bundle.
![]() The Cluster Network Operator injects the trusted CA bundle into the
The Cluster Network Operator injects the trusted CA bundle into the proxy-ca ConfigMap.
![]() OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 and earlier versions use
OpenShift Container Platform 4.3 and earlier versions use router-ca.
Expiration
The expiration terms for the Ingress Operator’s certificates are as follows:
-
The expiration date for metrics certificates that the
service-cacontroller creates is two years after the date of creation. - The expiration date for the Operator’s signing certificate is two years after the date of creation.
- The expiration date for default certificates that the Operator generates is two years after the date of creation.
You cannot specify custom expiration terms on certificates that the Ingress Operator or service-ca controller creates.
You cannot specify expiration terms when installing OpenShift Container Platform for certificates that the Ingress Operator or service-ca controller creates.
Services
Prometheus uses the certificates that secure metrics.
The Ingress Operator uses its signing certificate to sign default certificates that it generates for Ingress Controllers for which you do not set custom default certificates.
Cluster components that use secured routes may use the default Ingress Controller’s default certificate.
Ingress to the cluster via a secured route uses the default certificate of the Ingress Controller by which the route is accessed unless the route specifies its own certificate.
Management
Ingress certificates are managed by the user. See Replacing the default ingress certificate for more information.
Renewal
The service-ca controller automatically rotates the certificates that it issues. However, it is possible to use oc delete secret <secret> to manually rotate service serving certificates.
The Ingress Operator does not rotate its own signing certificate or the default certificates that it generates. Operator-generated default certificates are intended as placeholders for custom default certificates that you configure.
Chapter 3. Monitoring and cluster logging Operator component certificates
Monitoring components secure their traffic with service CA certificates. These certificates are valid for 2 years and are replaced automatically on rotation of the service CA, which is every 13 months.
If the certificate lives in the openshift-monitoring or openshift-logging namespace, it is system managed and rotated automatically.
Management
These certificates are managed by the system and not the user.
Chapter 4. Control plane certificates
Location
Control plane certificates are included in these namespaces:
- openshift-config-managed
- openshift-kube-apiserver
- openshift-kube-apiserver-operator
- openshift-kube-controller-manager
- openshift-kube-controller-manager-operator
- openshift-kube-scheduler
Management
Control plane certificates are managed by the system and rotated automatically.
In the rare case that your control plane certificates expired, see Recovering from expired control plane certificates
Additional resources
- Manually rotate service serving certificates
- Securing service traffic using service serving certificate secrets
- Recovering from expired control plane certificates
- Configuring the cluster-wide proxy
- Adding API server certificates
- Replacing the default ingress certificate
- Working with nodes
- Recovering from lost master hosts
Chapter 5. Configuring the internal OAuth server
5.1. OpenShift Container Platform OAuth server
The OpenShift Container Platform master includes a built-in OAuth server. Users obtain OAuth access tokens to authenticate themselves to the API.
When a person requests a new OAuth token, the OAuth server uses the configured identity provider to determine the identity of the person making the request.
It then determines what user that identity maps to, creates an access token for that user, and returns the token for use.
5.2. OAuth token request flows and responses
The OAuth server supports standard authorization code grant and the implicit grant OAuth authorization flows.
When requesting an OAuth token using the implicit grant flow (response_type=token) with a client_id configured to request WWW-Authenticate challenges (like openshift-challenging-client), these are the possible server responses from /oauth/authorize, and how they should be handled:
| Status | Content | Client response |
|---|---|---|
| 302 |
|
Use the |
| 302 |
|
Fail, optionally surfacing the |
| 302 |
Other | Follow the redirect, and process the result using these rules |
| 401 |
|
Respond to challenge if type is recognized (e.g. |
| 401 |
| No challenge authentication is possible. Fail and show response body (which might contain links or details on alternate methods to obtain an OAuth token) |
| Other | Other | Fail, optionally surfacing response body to the user |
5.3. Options for the internal OAuth server
Several configuration options are available for the internal OAuth server.
5.3.1. OAuth token duration options
The internal OAuth server generates two kinds of tokens:
| Access tokens | Longer-lived tokens that grant access to the API. |
| Authorize codes | Short-lived tokens whose only use is to be exchanged for an access token. |
You can configure the default duration for both types of token. If necessary, you can override the duration of the access token by using an OAuthClient object definition.
5.3.2. OAuth grant options
When the OAuth server receives token requests for a client to which the user has not previously granted permission, the action that the OAuth server takes is dependent on the OAuth client’s grant strategy.
The OAuth client requesting token must provide its own grant strategy.
You can apply the following default methods:
|
| Auto-approve the grant and retry the request. |
|
| Prompt the user to approve or deny the grant. |
5.4. Configuring the internal OAuth server’s token duration
You can configure default options for the internal OAuth server’s token duration.
By default, tokens are only valid for 24 hours. Existing sessions expire after this time elapses.
If the default time is insufficient, then this can be modified using the following procedure.
Procedure
Create a configuration file that contains the token duration options. The following file sets this to 48 hours, twice the default.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Set
accessTokenMaxAgeSecondsto control the lifetime of access tokens. The default lifetime is 24 hours, or 86400 seconds. This attribute cannot be negative.
Apply the new configuration file:
NoteBecause you update the existing OAuth server, you must use the
oc applycommand to apply the change.oc apply -f </path/to/file.yaml>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/file.yaml>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the changes are in effect:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.5. Register an additional OAuth client
If you need an additional OAuth client to manage authentication for your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, you can register one.
Procedure
To register additional OAuth clients:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
nameof the OAuth client is used as theclient_idparameter when making requests to<namespace_route>/oauth/authorizeand<namespace_route>/oauth/token. - 2
- The
secretis used as theclient_secretparameter when making requests to<namespace_route>/oauth/token. - 3
- The
redirect_uriparameter specified in requests to<namespace_route>/oauth/authorizeand<namespace_route>/oauth/tokenmust be equal to or prefixed by one of the URIs listed in theredirectURIsparameter value. - 4
- The
grantMethodis used to determine what action to take when this client requests tokens and has not yet been granted access by the user. Specifyautoto automatically approve the grant and retry the request, orpromptto prompt the user to approve or deny the grant.
5.6. OAuth server metadata
Applications running in OpenShift Container Platform might have to discover information about the built-in OAuth server. For example, they might have to discover what the address of the <namespace_route> is without manual configuration. To aid in this, OpenShift Container Platform implements the IETF OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server Metadata draft specification.
Thus, any application running inside the cluster can issue a GET request to https://openshift.default.svc/.well-known/oauth-authorization-server to fetch the following information:
- 1
- The authorization server’s issuer identifier, which is a URL that uses the
httpsscheme and has no query or fragment components. This is the location where.well-knownRFC 5785 resources containing information about the authorization server are published. - 2
- URL of the authorization server’s authorization endpoint. See RFC 6749.
- 3
- URL of the authorization server’s token endpoint. See RFC 6749.
- 4
- JSON array containing a list of the OAuth 2.0 RFC 6749 scope values that this authorization server supports. Note that not all supported scope values are advertised.
- 5
- JSON array containing a list of the OAuth 2.0
response_typevalues that this authorization server supports. The array values used are the same as those used with theresponse_typesparameter defined by "OAuth 2.0 Dynamic Client Registration Protocol" in RFC 7591. - 6
- JSON array containing a list of the OAuth 2.0 grant type values that this authorization server supports. The array values used are the same as those used with the
grant_typesparameter defined byOAuth 2.0 Dynamic Client Registration Protocolin RFC 7591. - 7
- JSON array containing a list of PKCE RFC 7636 code challenge methods supported by this authorization server. Code challenge method values are used in the
code_challenge_methodparameter defined in Section 4.3 of RFC 7636. The valid code challenge method values are those registered in the IANAPKCE Code Challenge Methodsregistry. See IANA OAuth Parameters.
5.7. Troubleshooting OAuth API events
In some cases the API server returns an unexpected condition error message that is difficult to debug without direct access to the API master log. The underlying reason for the error is purposely obscured in order to avoid providing an unauthenticated user with information about the server’s state.
A subset of these errors is related to service account OAuth configuration issues. These issues are captured in events that can be viewed by non-administrator users. When encountering an unexpected condition server error during OAuth, run oc get events to view these events under ServiceAccount.
The following example warns of a service account that is missing a proper OAuth redirect URI:
oc get events | grep ServiceAccount 1m 1m 1 proxy ServiceAccount Warning NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs service-account-oauth-client-getter system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>
$ oc get events | grep ServiceAccount
1m 1m 1 proxy ServiceAccount Warning NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs service-account-oauth-client-getter system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>
Running oc describe sa/<service-account-name> reports any OAuth events associated with the given service account name.
oc describe sa/proxy | grep -A5 Events Events: FirstSeen LastSeen Count From SubObjectPath Type Reason Message --------- -------- ----- ---- ------------- -------- ------ ------- 3m 3m 1 service-account-oauth-client-getter Warning NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>
$ oc describe sa/proxy | grep -A5 Events
Events:
FirstSeen LastSeen Count From SubObjectPath Type Reason Message
--------- -------- ----- ---- ------------- -------- ------ -------
3m 3m 1 service-account-oauth-client-getter Warning NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>The following is a list of the possible event errors:
No redirect URI annotations or an invalid URI is specified
Reason Message NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>
Reason Message
NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>Invalid route specified
Reason Message NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs [routes.route.openshift.io "<name>" not found, system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>]
Reason Message
NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs [routes.route.openshift.io "<name>" not found, system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>]Invalid reference type specified
Reason Message NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs [no kind "<name>" is registered for version "v1", system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>]
Reason Message
NoSAOAuthRedirectURIs [no kind "<name>" is registered for version "v1", system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no redirectURIs; set serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<some-value>=<redirect> or create a dynamic URI using serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.<some-value>=<reference>]Missing SA tokens
Reason Message NoSAOAuthTokens system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no tokens
Reason Message
NoSAOAuthTokens system:serviceaccount:myproject:proxy has no tokensChapter 6. Understanding identity provider configuration
The OpenShift Container Platform master includes a built-in OAuth server. Developers and administrators obtain OAuth access tokens to authenticate themselves to the API.
As an administrator, you can configure OAuth to specify an identity provider after you install your cluster.
6.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
6.2. Supported identity providers
You can configure the following types of identity providers:
| Identity provider | Description |
|---|---|
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure the | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure a | |
|
Configure an |
Once an identity provider has been defined, you can use RBAC to define and apply permissions.
6.3. Removing the kubeadmin user
After you define an identity provider and create a new cluster-admin user, you can remove the kubeadmin to improve cluster security.
If you follow this procedure before another user is a cluster-admin, then OpenShift Container Platform must be reinstalled. It is not possible to undo this command.
Prerequisites
- You must have configured at least one identity provider.
-
You must have added the
cluster-adminrole to a user. - You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Remove the
kubeadminsecrets:oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-system
$ oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4. Identity provider parameters
The following parameters are common to all identity providers:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
| The provider name is prefixed to provider user names to form an identity name. |
|
| Defines how new identities are mapped to users when they log in. Enter one of the following values:
|
When adding or changing identity providers, you can map identities from the new provider to existing users by setting the mappingMethod parameter to add.
6.5. Sample identity provider CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and default values that you use to configure an identity provider. This example uses the HTPasswd identity provider.
Sample identity provider CR
Chapter 7. Configuring identity providers
7.1. Configuring an HTPasswd identity provider
7.1.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
To define an HTPasswd identity provider you must perform the following steps:
-
Create an
htpasswdfile to store the user and password information. Instructions are provided for Linux and Windows. -
Create an OpenShift Container Platform secret to represent the
htpasswdfile. - Define the HTPasswd identity provider resource.
- Apply the resource to the default OAuth configuration.
7.1.2. Creating an HTPasswd file using Linux
To use the HTPasswd identity provider, you must generate a flat file that contains the user names and passwords for your cluster by using htpasswd.
Prerequisites
-
Have access to the
htpasswdutility. On Red Hat Enterprise Linux this is available by installing thehttpd-toolspackage.
Procedure
Create or update your flat file with a user name and hashed password:
htpasswd -c -B -b </path/to/users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>
$ htpasswd -c -B -b </path/to/users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command generates a hashed version of the password.
For example:
htpasswd -c -B -b users.htpasswd user1 MyPassword! Adding password for user user1
$ htpasswd -c -B -b users.htpasswd user1 MyPassword! Adding password for user user1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Continue to add or update credentials to the file:
htpasswd -B -b </path/to/users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>
$ htpasswd -B -b </path/to/users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.1.3. Creating an HTPasswd file using Windows
To use the HTPasswd identity provider, you must generate a flat file that contains the user names and passwords for your cluster by using htpasswd.
Prerequisites
-
Have access to
htpasswd.exe. This file is included in the\bindirectory of many Apache httpd distributions.
Procedure
Create or update your flat file with a user name and hashed password:
> htpasswd.exe -c -B -b <\path\to\users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>
> htpasswd.exe -c -B -b <\path\to\users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command generates a hashed version of the password.
For example:
> htpasswd.exe -c -B -b users.htpasswd user1 MyPassword! Adding password for user user1
> htpasswd.exe -c -B -b users.htpasswd user1 MyPassword! Adding password for user user1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Continue to add or update credentials to the file:
> htpasswd.exe -b <\path\to\users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>
> htpasswd.exe -b <\path\to\users.htpasswd> <user_name> <password>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.1.4. Creating the HTPasswd Secret
To use the HTPasswd identity provider, you must define a secret that contains the HTPasswd user file.
Prerequisites
- Create an HTPasswd file.
Procedure
Create an OpenShift Container Platform Secret that contains the HTPasswd users file.
oc create secret generic htpass-secret --from-file=htpasswd=</path/to/users.htpasswd> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic htpass-secret --from-file=htpasswd=</path/to/users.htpasswd> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe secret key containing the users file for the
--from-fileargument must be namedhtpasswd, as shown in the above command.
7.1.5. Sample HTPasswd CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for an HTPasswd identity provider.
HTPasswd CR
7.1.6. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Log in to the cluster as a user from your identity provider, entering the password when prompted.
oc login -u <username>
$ oc login -u <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.1.7. Updating users for an HTPasswd identity provider
You can add or remove users from an existing HTPasswd identity provider.
Prerequisites
-
You have created a secret that contains the HTPasswd user file. This procedure assumes that it is named
htpass-secret. -
You have configured an HTPasswd identity provider. This procedure assumes that it is named
my_htpasswd_provider. -
You have access to the
htpasswdutility. On Red Hat Enterprise Linux this is available by installing thehttpd-toolspackage. - You have cluster administrator privileges.
Procedure
Retrieve the HTPasswd file from the
htpass-secretsecret and save the file to your file system:oc get secret htpass-secret -ojsonpath={.data.htpasswd} -n openshift-config | base64 -d > users.htpasswd$ oc get secret htpass-secret -ojsonpath={.data.htpasswd} -n openshift-config | base64 -d > users.htpasswdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add or remove users from the
users.htpasswdfile.To add a new user:
htpasswd -bB users.htpasswd <username> <password> Adding password for user <username>
$ htpasswd -bB users.htpasswd <username> <password> Adding password for user <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove an existing user:
htpasswd -D users.htpasswd <username> Deleting password for user <username>
$ htpasswd -D users.htpasswd <username> Deleting password for user <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Replace the
htpass-secretsecret with the updated users in theusers.htpasswdfile:oc create secret generic htpass-secret --from-file=htpasswd=users.htpasswd --dry-run -o yaml -n openshift-config | oc replace -f -
$ oc create secret generic htpass-secret --from-file=htpasswd=users.htpasswd --dry-run -o yaml -n openshift-config | oc replace -f -Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you removed one or more users, you must additionally remove existing resources for each user.
Delete the user:
oc delete user <username> user.user.openshift.io "<username>" deleted
$ oc delete user <username> user.user.openshift.io "<username>" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Be sure to remove the user, otherwise the user can continue using their token as long as it has not expired.
Delete the identity for the user:
oc delete identity my_htpasswd_provider:<username> identity.user.openshift.io "my_htpasswd_provider:<username>" deleted
$ oc delete identity my_htpasswd_provider:<username> identity.user.openshift.io "my_htpasswd_provider:<username>" deletedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.1.8. Configuring identity providers using the web console
Configure your identity provider (IDP) through the web console instead of the CLI.
Prerequisites
- You must be logged in to the web console as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
- Navigate to Administration → Cluster Settings.
- Under the Global Configuration tab, click OAuth.
- Under the Identity Providers section, select your identity provider from the Add drop-down menu.
You can specify multiple IDPs through the web console without overwriting existing IDPs.
7.2. Configuring a Keystone identity provider
Configure the keystone identity provider to integrate your OpenShift Container Platform cluster with Keystone to enable shared authentication with an OpenStack Keystone v3 server configured to store users in an internal database. This configuration allows users to log in to OpenShift Container Platform with their Keystone credentials.
Keystone is an OpenStack project that provides identity, token, catalog, and policy services.
You can configure the integration with Keystone so that the new OpenShift Container Platform users are based on either the Keystone user names or unique Keystone IDs. With both methods, users log in by entering their Keystone user name and password. Basing the OpenShift Container Platform users off of the Keystone ID is more secure. If you delete a Keystone user and create a new Keystone user with that user name, the new user might have access to the old user’s resources.
7.2.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.2.2. Creating the Secret
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform Secrets in the openshift-config namespace to contain the client secret, client certificates, and keys.
You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing a string by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the contents of a file, such as a certificate file, by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.2.3. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.2.4. Sample Keystone CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for a Keystone identity provider.
Keystone CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to provider user names to form an identity name.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- Keystone domain name. In Keystone, usernames are domain-specific. Only a single domain is supported.
- 4
- The URL to use to connect to the Keystone server (required). This must use https.
- 5
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the PEM-encoded certificate authority bundle to use in validating server certificates for the configured URL.
- 6
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the client certificate to present when making requests to the configured URL.
- 7
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the key for the client certificate. Required if
tlsClientCertis specified.
7.2.5. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Log in to the cluster as a user from your identity provider, entering the password when prompted.
oc login -u <username>
$ oc login -u <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3. Configuring an LDAP identity provider
Configure the ldap identity provider to validate user names and passwords against an LDAPv3 server, using simple bind authentication.
7.3.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.3.2. About LDAP authentication
During authentication, the LDAP directory is searched for an entry that matches the provided user name. If a single unique match is found, a simple bind is attempted using the distinguished name (DN) of the entry plus the provided password.
These are the steps taken:
-
Generate a search filter by combining the attribute and filter in the configured
urlwith the user-provided user name. - Search the directory using the generated filter. If the search does not return exactly one entry, deny access.
- Attempt to bind to the LDAP server using the DN of the entry retrieved from the search, and the user-provided password.
- If the bind is unsuccessful, deny access.
- If the bind is successful, build an identity using the configured attributes as the identity, email address, display name, and preferred user name.
The configured url is an RFC 2255 URL, which specifies the LDAP host and search parameters to use. The syntax of the URL is:
ldap://host:port/basedn?attribute?scope?filter
ldap://host:port/basedn?attribute?scope?filterFor this URL:
| URL Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
For regular LDAP, use the string |
|
|
The name and port of the LDAP server. Defaults to |
|
| The DN of the branch of the directory where all searches should start from. At the very least, this must be the top of your directory tree, but it could also specify a subtree in the directory. |
|
|
The attribute to search for. Although RFC 2255 allows a comma-separated list of attributes, only the first attribute will be used, no matter how many are provided. If no attributes are provided, the default is to use |
|
|
The scope of the search. Can be either |
|
|
A valid LDAP search filter. If not provided, defaults to |
If you are using an insecure LDAP connection (ldap:// or port 389), then you must check the Insecure option in the configuration wizard.
When doing searches, the attribute, filter, and provided user name are combined to create a search filter that looks like:
(&(<filter>)(<attribute>=<username>))
(&(<filter>)(<attribute>=<username>))For example, consider a URL of:
ldap://ldap.example.com/o=Acme?cn?sub?(enabled=true)
ldap://ldap.example.com/o=Acme?cn?sub?(enabled=true)
When a client attempts to connect using a user name of bob, the resulting search filter will be (&(enabled=true)(cn=bob)).
If the LDAP directory requires authentication to search, specify a bindDN and bindPassword to use to perform the entry search.
7.3.3. Creating the LDAP Secret
To use the identity provider, you must define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret that contains the bindPassword.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret that contains the bindPassword.
oc create secret generic ldap-secret --from-literal=bindPassword=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic ldap-secret --from-literal=bindPassword=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe secret key containing the bindPassword for the
--from-literalargument must be calledbindPassword, as shown in the above command.
7.3.4. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.3.5. Sample LDAP CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for an LDAP identity provider.
LDAP CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the returned user ID to form an identity name.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- List of attributes to use as the identity. First non-empty attribute is used. At least one attribute is required. If none of the listed attribute have a value, authentication fails. Defined attributes are retrieved as raw, allowing for binary values to be used.
- 4
- List of attributes to use as the email address. First non-empty attribute is used.
- 5
- List of attributes to use as the display name. First non-empty attribute is used.
- 6
- List of attributes to use as the preferred user name when provisioning a user for this identity. First non-empty attribute is used.
- 7
- Optional DN to use to bind during the search phase. Must be set if
bindPasswordis defined. - 8
- Optional reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the bind password. Must be set if
bindDNis defined. - 9
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the PEM-encoded certificate authority bundle to use in validating server certificates for the configured URL. Only used when
insecureisfalse. - 10
- When
true, no TLS connection is made to the server. Whenfalse,ldaps://URLs connect using TLS, andldap://URLs are upgraded to TLS. This should be set tofalsewhenldaps://URLs are in use, as these URLs always attempt to connect using TLS. - 11
- An RFC 2255 URL which specifies the LDAP host and search parameters to use.
To whitelist users for an LDAP integration, use the lookup mapping method. Before a login from LDAP would be allowed, a cluster administrator must create an identity and user object for each LDAP user.
7.3.6. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Log in to the cluster as a user from your identity provider, entering the password when prompted.
oc login -u <username>
$ oc login -u <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4. Configuring an basic authentication identity provider
Configure a basic-authentication identity provider for users to log in to OpenShift Container Platform with credentials validated against a remote identity provider. Basic authentication is a generic backend integration mechanism.
7.4.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.4.2. About basic authentication
Basic authentication is a generic backend integration mechanism that allows users to log in to OpenShift Container Platform with credentials validated against a remote identity provider.
Because basic authentication is generic, you can use this identity provider for advanced authentication configurations.
Basic authentication must use an HTTPS connection to the remote server to prevent potential snooping of the user ID and password and man-in-the-middle attacks.
With basic authentication configured, users send their user name and password to OpenShift Container Platform, which then validates those credentials against a remote server by making a server-to-server request, passing the credentials as a basic authentication header. This requires users to send their credentials to OpenShift Container Platform during login.
This only works for user name/password login mechanisms, and OpenShift Container Platform must be able to make network requests to the remote authentication server.
User names and passwords are validated against a remote URL that is protected by basic authentication and returns JSON.
A 401 response indicates failed authentication.
A non-200 status, or the presence of a non-empty "error" key, indicates an error:
{"error":"Error message"}
{"error":"Error message"}
A 200 status with a sub (subject) key indicates success:
{"sub":"userid"}
{"sub":"userid"} - 1
- The subject must be unique to the authenticated user and must not be able to be modified.
A successful response can optionally provide additional data, such as:
A display name using the
namekey. For example:{"sub":"userid", "name": "User Name", ...}{"sub":"userid", "name": "User Name", ...}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow An email address using the
emailkey. For example:{"sub":"userid", "email":"user@example.com", ...}{"sub":"userid", "email":"user@example.com", ...}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A preferred user name using the
preferred_usernamekey. This is useful when the unique, unchangeable subject is a database key or UID, and a more human-readable name exists. This is used as a hint when provisioning the OpenShift Container Platform user for the authenticated identity. For example:{"sub":"014fbff9a07c", "preferred_username":"bob", ...}{"sub":"014fbff9a07c", "preferred_username":"bob", ...}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4.3. Creating the Secret
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform Secrets in the openshift-config namespace to contain the client secret, client certificates, and keys.
You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing a string by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the contents of a file, such as a certificate file, by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4.4. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4.5. Sample basic authentication CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for an basic authentication identity provider.
Basic authentication CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the returned user ID to form an identity name.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- URL accepting credentials in Basic authentication headers.
- 4
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the PEM-encoded certificate authority bundle to use in validating server certificates for the configured URL.
- 5
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the client certificate to present when making requests to the configured URL.
- 6
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the key for the client certificate. Required if
tlsClientCertis specified.
7.4.6. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Log in to the cluster as a user from your identity provider, entering the password when prompted.
oc login -u <username>
$ oc login -u <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.4.7. Example Apache HTTPD configuration for basic identity providers
The basic identify provider (IDP) configuration in OpenShift Container Platform 4 requires that the IDP server respond with JSON for success and failures. You can use CGI scripting in Apache HTTPD to accomplish this. This section provides examples.
/etc/httpd/conf.d/login.conf
/var/www/cgi-bin/login.cgi
#!/bin/bash
echo "Content-Type: application/json"
echo ""
echo '{"sub":"userid", "name":"'$REMOTE_USER'"}'
exit 0
#!/bin/bash
echo "Content-Type: application/json"
echo ""
echo '{"sub":"userid", "name":"'$REMOTE_USER'"}'
exit 0/var/www/cgi-bin/fail.cgi
#!/bin/bash
echo "Content-Type: application/json"
echo ""
echo '{"error": "Login failure"}'
exit 0
#!/bin/bash
echo "Content-Type: application/json"
echo ""
echo '{"error": "Login failure"}'
exit 07.4.7.1. File requirements
These are the requirements for the files you create on an Apache HTTPD web server:
-
login.cgiandfail.cgimust be executable (chmod +x). -
login.cgiandfail.cgimust have proper SELinux contexts if SELinux is enabled:restorecon -RFv /var/www/cgi-bin, or ensure that the context ishttpd_sys_script_exec_tusingls -laZ. -
login.cgiis only executed if your user successfully logs in perRequire and Authdirectives. -
fail.cgiis executed if the user fails to log in, resulting in anHTTP 401response.
7.4.8. Basic authentication troubleshooting
The most common issue relates to network connectivity to the backend server. For simple debugging, run curl commands on the master. To test for a successful login, replace the <user> and <password> in the following example command with valid credentials. To test an invalid login, replace them with false credentials.
curl --cacert /path/to/ca.crt --cert /path/to/client.crt --key /path/to/client.key -u <user>:<password> -v https://www.example.com/remote-idp
curl --cacert /path/to/ca.crt --cert /path/to/client.crt --key /path/to/client.key -u <user>:<password> -v https://www.example.com/remote-idpSuccessful responses
A 200 status with a sub (subject) key indicates success:
{"sub":"userid"}
{"sub":"userid"}The subject must be unique to the authenticated user, and must not be able to be modified.
A successful response can optionally provide additional data, such as:
A display name using the
namekey:{"sub":"userid", "name": "User Name", ...}{"sub":"userid", "name": "User Name", ...}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow An email address using the
emailkey:{"sub":"userid", "email":"user@example.com", ...}{"sub":"userid", "email":"user@example.com", ...}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A preferred user name using the
preferred_usernamekey:{"sub":"014fbff9a07c", "preferred_username":"bob", ...}{"sub":"014fbff9a07c", "preferred_username":"bob", ...}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
preferred_usernamekey is useful when the unique, unchangeable subject is a database key or UID, and a more human-readable name exists. This is used as a hint when provisioning the OpenShift Container Platform user for the authenticated identity.
Failed responses
-
A
401response indicates failed authentication. -
A non-
200status or the presence of a non-empty "error" key indicates an error:{"error":"Error message"}
7.5. Configuring a request header identity provider
Configure a request-header identity provider to identify users from request header values, such as X-Remote-User. It is typically used in combination with an authenticating proxy, which sets the request header value.
7.5.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.5.2. About request header authentication
A request header identity provider identifies users from request header values, such as X-Remote-User. It is typically used in combination with an authenticating proxy, which sets the request header value.
You can also use the request header identity provider for advanced configurations such as the community-supported SAML authentication. Note that this solution is not supported by Red Hat.
For users to authenticate using this identity provider, they must access https://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize (and subpaths) via an authenticating proxy. To accomplish this, configure the OAuth server to redirect unauthenticated requests for OAuth tokens to the proxy endpoint that proxies to https://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize.
To redirect unauthenticated requests from clients expecting browser-based login flows:
-
Set the
provider.loginURLparameter to the authenticating proxy URL that will authenticate interactive clients and then proxy the request tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize.
To redirect unauthenticated requests from clients expecting WWW-Authenticate challenges:
-
Set the
provider.challengeURLparameter to the authenticating proxy URL that will authenticate clients expectingWWW-Authenticatechallenges and then proxy the request tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize.
The provider.challengeURL and provider.loginURL parameters can include the following tokens in the query portion of the URL:
${url}is replaced with the current URL, escaped to be safe in a query parameter.For example:
https://www.example.com/sso-login?then=${url}${query}is replaced with the current query string, unescaped.For example:
https://www.example.com/auth-proxy/oauth/authorize?${query}
As of OpenShift Container Platform 4.1, your proxy must support mutual TLS.
7.5.2.1. SSPI connection support on Microsoft Windows
Using SSPI connection support on Microsoft Windows is a Technology Preview feature. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
For more information on Red Hat Technology Preview features support scope, see https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview/.
oc supports the Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) to allow for SSO flows on Microsft Windows. If you use the request header identity provider with a GSSAPI-enabled proxy to connect an Active Directory server to OpenShift Container Platform, users can automatically authenticate to OpenShift Container Platform by using the oc command line interface from a domain-joined Microsoft Windows computer.
7.5.3. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.5.4. Sample request header CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for a request header identity provider.
Request header CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the user name in the request header to form an identity name.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- Optional: URL to redirect unauthenticated
/oauth/authorizerequests to, that will authenticate browser-based clients and then proxy their request tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize. The URL that proxies tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorizemust end with/authorize(with no trailing slash), and also proxy subpaths, in order for OAuth approval flows to work properly.${url}is replaced with the current URL, escaped to be safe in a query parameter.${query}is replaced with the current query string. If this attribute is not defined, thenloginURLmust be used. - 4
- Optional: URL to redirect unauthenticated
/oauth/authorizerequests to, that will authenticate clients which expectWWW-Authenticatechallenges, and then proxy them tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize.${url}is replaced with the current URL, escaped to be safe in a query parameter.${query}is replaced with the current query string. If this attribute is not defined, thenchallengeURLmust be used. - 5
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing a PEM-encoded certificate bundle. Used as a trust anchor to validate the TLS certificates presented by the remote server.Important
As of OpenShift Container Platform 4.1, the
cafield is required for this identity provider. This means that your proxy must support mutual TLS. - 6
- Optional: list of common names (
cn). If set, a valid client certificate with a Common Name (cn) in the specified list must be presented before the request headers are checked for user names. If empty, any Common Name is allowed. Can only be used in combination withca. - 7
- Header names to check, in order, for the user identity. The first header containing a value is used as the identity. Required, case-insensitive.
- 8
- Header names to check, in order, for an email address. The first header containing a value is used as the email address. Optional, case-insensitive.
- 9
- Header names to check, in order, for a display name. The first header containing a value is used as the display name. Optional, case-insensitive.
- 10
- Header names to check, in order, for a preferred user name, if different than the immutable identity determined from the headers specified in
headers. The first header containing a value is used as the preferred user name when provisioning. Optional, case-insensitive.
7.5.5. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Log in to the cluster as a user from your identity provider, entering the password when prompted.
oc login -u <username>
$ oc login -u <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.5.6. Example Apache authentication configuration using request header
This example configures an Apache authentication proxy for the OpenShift Container Platform using the request header identity provider.
Custom proxy configuration
Using the mod_auth_gssapi module is a popular way to configure the Apache authentication proxy using the request header identity provider; however, it is not required. Other proxies can easily be used if the following requirements are met:
-
Block the
X-Remote-Userheader from client requests to prevent spoofing. -
Enforce client certificate authentication in the
RequestHeaderIdentityProviderconfiguration. -
Require the
X-Csrf-Tokenheader be set for all authentication requests using the challenge flow. -
Make sure only the
/oauth/authorizeendpoint and its subpaths are proxied; redirects must be rewritten to allow the backend server to send the client to the correct location. -
The URL that proxies to
https://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorizemust end with/authorizewith no trailing slash. For example,https://proxy.example.com/login-proxy/authorize?…must proxy tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize?…. -
Subpaths of the URL that proxies to
https://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorizemust proxy to subpaths ofhttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize. For example,https://proxy.example.com/login-proxy/authorize/approve?…must proxy tohttps://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize/approve?….
The https://<namespace_route> address is the Route to the OAuth server and can be obtained by running oc get route -n openshift-authentication.
Configuring Apache authentication using request header
This example uses the mod_auth_gssapi module to configure an Apache authentication proxy using the request header identity provider.
Prerequisites
Obtain the
mod_auth_gssapimodule from the Optional channel. You must have the following packages installed on your local machine:-
httpd -
mod_ssl -
mod_session -
apr-util-openssl -
mod_auth_gssapi
-
Generate a CA for validating requests that submit the trusted header. Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the CA. This is done by running:
oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The CA must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.- Generate a client certificate for the proxy. You can generate this certificate by using any x509 certificate tooling. The client certificate must be signed by the CA you generated for validating requests that submit the trusted header.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
Procedure
This proxy uses a client certificate to connect to the OAuth server, which is configured to trust the X-Remote-User header.
-
Create the certificate for the Apache configuration. The certificate that you specify as the
SSLProxyMachineCertificateFileparameter value is the proxy’s client certificate that is used to authenticate the proxy to the server. It must useTLS Web Client Authenticationas the extended key type. Create the Apache configuration. Use the following template to provide your required settings and values:
ImportantCarefully review the template and customize its contents to fit your environment.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe
https://<namespace_route>address is the Route to the OAuth server and can be obtained by runningoc get route -n openshift-authentication.Update the
identityProvidersstanza in the Custom Resource (CR):Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the configuration.
Confirm that you can bypass the proxy by requesting a token by supplying the correct client certificate and header:
curl -L -k -H "X-Remote-User: joe" \ --cert /etc/pki/tls/certs/authproxy.pem \ https://<namespace_route>/oauth/token/request
# curl -L -k -H "X-Remote-User: joe" \ --cert /etc/pki/tls/certs/authproxy.pem \ https://<namespace_route>/oauth/token/requestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that requests that do not supply the client certificate fail by requesting a token without the certificate:
curl -L -k -H "X-Remote-User: joe" \ https://<namespace_route>/oauth/token/request
# curl -L -k -H "X-Remote-User: joe" \ https://<namespace_route>/oauth/token/requestCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the
challengeURLredirect is active:curl -k -v -H 'X-Csrf-Token: 1' \ https://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize?client_id=openshift-challenging-client&response_type=token
# curl -k -v -H 'X-Csrf-Token: 1' \ https://<namespace_route>/oauth/authorize?client_id=openshift-challenging-client&response_type=tokenCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
challengeURLredirect to use in the next step.Run this command to show a 401 response with a
WWW-Authenticatebasic challenge, a negotiate challenge, or both challenges:curl -k -v -H 'X-Csrf-Token: 1' \ <challengeURL_redirect + query>
# curl -k -v -H 'X-Csrf-Token: 1' \ <challengeURL_redirect + query>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Test logging in to the OpenShift CLI (
oc) with and without using a Kerberos ticket:If you generated a Kerberos ticket by using
kinit, destroy it:kdestroy -c cache_name
# kdestroy -c cache_name1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Make sure to provide the name of your Kerberos cache.
Log in to the
octool by using your Kerberos credentials:oc login
# oc loginCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter your Kerberos user name and password at the prompt.
Log out of the
octool:oc logout
# oc logoutCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use your Kerberos credentials to get a ticket:
kinit
# kinitCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter your Kerberos user name and password at the prompt.
Confirm that you can log in to the
octool:oc login
# oc loginCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If your configuration is correct, you are logged in without entering separate credentials.
7.6. Configuring a GitHub or GitHub Enterprise identity provider
Configure a github identity provider to validate user names and passwords against GitHub or GitHub Enterprise’s OAuth authentication server. OAuth facilitates a token exchange flow between OpenShift Container Platform and GitHub or GitHub Enterprise.
You can use the GitHub integration to connect to either GitHub or GitHub Enterprise. For GitHub Enterprise integrations, you must provide the hostname of your instance and can optionally provide a ca certificate bundle to use in requests to the server.
The following steps apply to both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise unless noted.
Configuring GitHub authentication allows users to log in to OpenShift Container Platform with their GitHub credentials. To prevent anyone with any GitHub user ID from logging in to your OpenShift Container Platform cluster, you can restrict access to only those in specific GitHub organizations.
7.6.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.6.2. Registering a GitHub application
To use GitHub or GitHub Enterprise as an identity provider, you must register an application to use.
Procedure
Register an application on GitHub:
- For GitHub, click Settings → Developer settings → OAuth Apps → Register a new OAuth application.
- For GitHub Enterprise, go to your GitHub Enterprise home page and then click Settings → Developer settings → Register a new application.
-
Enter an application name, for example
My OpenShift Install. -
Enter a homepage URL, such as
https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster-name>.<cluster-domain>. - Optional: Enter an application description.
Enter the authorization callback URL, where the end of the URL contains the identity provider
name:https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster-name>.<cluster-domain>/oauth2callback/<idp-provider-name>
https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster-name>.<cluster-domain>/oauth2callback/<idp-provider-name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
https://oauth-openshift.apps.example-openshift-cluster.com/oauth2callback/github/
https://oauth-openshift.apps.example-openshift-cluster.com/oauth2callback/github/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Click Register application. GitHub provides a Client ID and a Client Secret. You need these values to complete the identity provider configuration.
7.6.3. Creating the Secret
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform Secrets in the openshift-config namespace to contain the client secret, client certificates, and keys.
You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing a string by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the contents of a file, such as a certificate file, by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.6.4. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.6.5. Sample GitHub CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for a GitHub identity provider.
GitHub CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the GitHub numeric user ID to form an identity name. It is also used to build the callback URL.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the PEM-encoded certificate authority bundle to use in validating server certificates for the configured URL. Only for use in GitHub Enterprise with a non-publicly trusted root certificate.
- 4
- The client ID of a registered GitHub OAuth application. The application must be configured with a callback URL of
https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster-name>.<cluster-domain>/oauth2callback/<idp-provider-name>. - 5
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the client secret issued by GitHub.
- 6
- For GitHub Enterprise, you must provide the host name of your instance, such as
example.com. This value must match the GitHub Enterprisehostnamevalue in in the /setup/settings file and cannot include a port number. If this value is not set, then eitherteamsororganizationsmust be defined. For GitHub, omit this parameter. - 7
- The list of organizations. Either the
organizationsorteamsfield must be set unless thehostnamefield is set, or ifmappingMethodis set tolookup. Cannot be used in combination with theteamsfield. - 8
- The list of teams. Either the
teamsororganizationsfield must be set unless thehostnamefield is set, or ifmappingMethodis set tolookup. Cannot be used in combination with theorganizationsfield.
If organizations or teams is specified, only GitHub users that are members of at least one of the listed organizations will be allowed to log in. If the GitHub OAuth application configured in clientID is not owned by the organization, an organization owner must grant third-party access in order to use this option. This can be done during the first GitHub login by the organization’s administrator, or from the GitHub organization settings.
7.6.6. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Obtain a token from the OAuth server.
As long as the
kubeadminuser has been removed, theoc logincommand provides instructions on how to access a web page where you can retrieve the token.You can also access this page from the web console by navigating to (?) Help → Command Line Tools → Copy Login Command.
Log in to the cluster, passing in the token to authenticate.
oc login --token=<token>
$ oc login --token=<token>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis identity provider does not support logging in with a user name and password.
Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.7. Configuring a GitLab identity provider
Configure a gitlab identity provider to use GitLab.com or any other GitLab instance as an identity provider. If you use GitLab version 7.7.0 to 11.0, you connect using the OAuth integration. If you use GitLab version 11.1 or later, you can use OpenID Connect (OIDC) to connect instead of OAuth.
7.7.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.7.2. Creating the Secret
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform Secrets in the openshift-config namespace to contain the client secret, client certificates, and keys.
You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing a string by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the contents of a file, such as a certificate file, by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.7.3. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.7.4. Sample GitLab CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for a GitLab identity provider.
GitLab CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the GitLab numeric user ID to form an identity name. It is also used to build the callback URL.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- The client ID of a registered GitLab OAuth application. The application must be configured with a callback URL of
https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster-name>.<cluster-domain>/oauth2callback/<idp-provider-name>. - 4
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the client secret issued by GitLab.
- 5
- The host URL of a GitLab provider. This could either be
https://gitlab.com/or any other self hosted instance of GitLab. - 6
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the PEM-encoded certificate authority bundle to use in validating server certificates for the configured URL.
7.7.5. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Log in to the cluster as a user from your identity provider, entering the password when prompted.
oc login -u <username>
$ oc login -u <username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8. Configuring a Google identity provider
Configure a google identity provider using Google’s OpenID Connect integration.
Using Google as an identity provider requires users to get a token using <master>/oauth/token/request to use with command-line tools.
Using Google as an identity provider allows any Google user to authenticate to your server. You can limit authentication to members of a specific hosted domain with the hostedDomain configuration attribute.
7.8.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.8.2. Creating the Secret
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform Secrets in the openshift-config namespace to contain the client secret, client certificates, and keys.
You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing a string by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the contents of a file, such as a certificate file, by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.8.3. Sample Google CR
The following Custom Resource (CR) shows the parameters and acceptable values for a Google identity provider.
Google CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the Google numeric user ID to form an identity name. It is also used to build the redirect URL.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- The client ID of a registered Google project. The project must be configured with a redirect URI of
https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster-name>.<cluster-domain>/oauth2callback/<idp-provider-name>. - 4
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the client secret issued by Google.
- 5
- A hosted domain used to restrict sign-in accounts. Optional if the
lookupmappingMethodis used. If empty, any Google account is allowed to authenticate.
7.8.4. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Obtain a token from the OAuth server.
As long as the
kubeadminuser has been removed, theoc logincommand provides instructions on how to access a web page where you can retrieve the token.You can also access this page from the web console by navigating to (?) Help → Command Line Tools → Copy Login Command.
Log in to the cluster, passing in the token to authenticate.
oc login --token=<token>
$ oc login --token=<token>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis identity provider does not support logging in with a user name and password.
Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.9. Configuring a OpenID Connect identity provider
Configure an oidc identity provider to integrate with an OpenID Connect identity provider using an Authorization Code Flow.
You can configure Red Hat Single Sign-On as an OpenID Connect identity provider for OpenShift Container Platform.
The Authentication Operator in OpenShift Container Platform requires that the configured OpenID Connect identity provider implements the OpenID Connect Discovery specification.
ID Token and UserInfo decryptions are not supported.
By default, the openid scope is requested. If required, extra scopes can be specified in the extraScopes field.
Claims are read from the JWT id_token returned from the OpenID identity provider and, if specified, from the JSON returned by the UserInfo URL.
At least one claim must be configured to use as the user’s identity. The standard identity claim is sub.
You can also indicate which claims to use as the user’s preferred user name, display name, and email address. If multiple claims are specified, the first one with a non-empty value is used. The standard claims are:
|
| Short for "subject identifier." The remote identity for the user at the issuer. |
|
|
The preferred user name when provisioning a user. A shorthand name that the user wants to be referred to as, such as |
|
| Email address. |
|
| Display name. |
See the OpenID claims documentation for more information.
Using an OpenID Connect identity provider requires users to get a token using <master>/oauth/token/request to use with command-line tools.
7.9.1. About identity providers in OpenShift Container Platform
By default, only a kubeadmin user exists on your cluster. To specify an identity provider, you must create a Custom Resource (CR) that describes that identity provider and add it to the cluster.
OpenShift Container Platform user names containing /, :, and % are not supported.
7.9.2. Creating the Secret
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform Secrets in the openshift-config namespace to contain the client secret, client certificates, and keys.
You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing a string by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-literal=clientSecret=<secret> -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the contents of a file, such as a certificate file, by using the following command.
oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-config
$ oc create secret generic <secret_name> --from-file=/path/to/file -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.9.3. Creating a ConfigMap
Identity providers use OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMaps in the openshift-config namespace to contain the certificate authority bundle. These are primarily used to contain certificate bundles needed by the identity provider.
Define an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the certificate authority by using the following command. The certificate authority must be stored in the
ca.crtkey of the ConfigMap.oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-config
$ oc create configmap ca-config-map --from-file=ca.crt=/path/to/ca -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.9.4. Sample OpenID Connect CRs
The following Custom Resources (CRs) show the parameters and acceptable values for an OpenID Connect identity provider.
If you must specify a custom certificate bundle, extra scopes, extra authorization request parameters, or a userInfo URL, use the full OpenID Connect CR.
Standard OpenID Connect CR
- 1
- This provider name is prefixed to the value of the identity claim to form an identity name. It is also used to build the redirect URL.
- 2
- Controls how mappings are established between this provider’s identities and user objects.
- 3
- The client ID of a client registered with the OpenID provider. The client must be allowed to redirect to
https://oauth-openshift.apps.<cluster_name>.<cluster_domain>/oauth2callback/<idp_provider_name>. - 4
- Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform Secret containing the client secret.
- 5
- List of claims to use as the identity. First non-empty claim is used. At least one claim is required. If none of the listed claims have a value, authentication fails. For example, this uses the value of the
subclaim in the returnedid_tokenas the user’s identity. - 6
- Issuer Identifier described in the OpenID spec. Must use
httpswithout query or fragment component.
Full OpenID Connect CR
- 1
- Optional: Reference to an OpenShift Container Platform ConfigMap containing the PEM-encoded certificate authority bundle to use in validating server certificates for the configured URL.
- 2
- Optional list of scopes to request, in addition to the
openidscope, during the authorization token request. - 3
- Optional map of extra parameters to add to the authorization token request.
- 4
- List of claims to use as the preferred user name when provisioning a user for this identity. First non-empty claim is used.
- 5
- List of claims to use as the display name. First non-empty claim is used.
- 6
- List of claims to use as the email address. First non-empty claim is used.
7.9.5. Adding an identity provider to your clusters
After you install your cluster, add an identity provider to it so your users can authenticate.
Prerequisites
- Create an OpenShift Container Platform cluster.
- Create the Custom Resource (CR) for your identity providers.
- You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Apply the defined CR:
oc apply -f </path/to/CR>
$ oc apply -f </path/to/CR>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf a CR does not exist,
oc applycreates a new CR and might trigger the following warning:Warning: oc apply should be used on resources created by either oc create --save-config or oc apply. In this case you can safely ignore this warning.Obtain a token from the OAuth server.
As long as the
kubeadminuser has been removed, theoc logincommand provides instructions on how to access a web page where you can retrieve the token.You can also access this page from the web console by navigating to (?) Help → Command Line Tools → Copy Login Command.
Log in to the cluster, passing in the token to authenticate.
oc login --token=<token>
$ oc login --token=<token>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThis identity provider does not support logging in with a user name and password.
Confirm that the user logged in successfully, and display the user name.
oc whoami
$ oc whoamiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.9.6. Configuring identity providers using the web console
Configure your identity provider (IDP) through the web console instead of the CLI.
Prerequisites
- You must be logged in to the web console as a cluster administrator.
Procedure
- Navigate to Administration → Cluster Settings.
- Under the Global Configuration tab, click OAuth.
- Under the Identity Providers section, select your identity provider from the Add drop-down menu.
You can specify multiple IDPs through the web console without overwriting existing IDPs.
Chapter 8. Configuring certificates
8.1. Replacing the default ingress certificate
8.1.1. Understanding the default ingress certificate
By default OpenShift Container Platform uses the Ingress Operator to create an internal CA and issue a wildcard certificate that is valid for applications under the .apps sub-domain. Both the web console and CLI use this certificate as well.
The internal infrastructure CA certificates are self-signed. While this process might be perceived as bad practice by some security or PKI teams, any risk here is minimal. The only clients that implicitly trust these certificates are other components within the cluster. Replacing the default wildcard certificate with one that is issued by a public CA already included in the CA bundle as provided by the container userspace allows external clients to connect securely to applications running under the .apps sub-domain.
8.1.2. Replacing the default ingress certificate
You can replace the default ingress certificate for all applications under the .apps subdomain. After you replace the certificate, all applications, including the web console and CLI, will have encryption provided by specified certificate.
Prerequisites
-
You must have a wildcard certificate for the fully qualified
.appssubdomain and its corresponding private key. Each should be in a separate PEM format file. - The private key must be unencrypted. If your key is encrypted, decrypt it before importing it into OpenShift Container Platform.
-
The certificate must include the
subjectAltNameextension showing*.apps.<clustername>.<domain>. - The certificate file can contain one or more certificates in a chain. The wildcard certificate must be the first certificate in the file. It can then be followed with any intermediate certificates, and the file should end with the root CA certificate.
- Copy the root CA certificate into an additional PEM format file.
Procedure
Create a ConfigMap that includes only the root CA certificate used to sign the wildcard certificate:
oc create configmap custom-ca \ --from-file=ca-bundle.crt=</path/to/example-ca.crt> \ -n openshift-config$ oc create configmap custom-ca \ --from-file=ca-bundle.crt=</path/to/example-ca.crt> \1 -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
</path/to/example-ca.crt>is the path to the root CA certificate file on your local file system.
Update the cluster-wide proxy configuration with the newly created ConfigMap:
oc patch proxy/cluster \ --type=merge \ --patch='{"spec":{"trustedCA":{"name":"custom-ca"}}}'$ oc patch proxy/cluster \ --type=merge \ --patch='{"spec":{"trustedCA":{"name":"custom-ca"}}}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a secret that contains the wildcard certificate chain and key:
oc create secret tls <secret> \ --cert=</path/to/cert.crt> \ --key=</path/to/cert.key> \ -n openshift-ingress$ oc create secret tls <secret> \1 --cert=</path/to/cert.crt> \2 --key=</path/to/cert.key> \3 -n openshift-ingressCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the Ingress Controller configuration with the newly created secret:
oc patch ingresscontroller.operator default \ --type=merge -p \ '{"spec":{"defaultCertificate": {"name": "<secret>"}}}' \ -n openshift-ingress-operator$ oc patch ingresscontroller.operator default \ --type=merge -p \ '{"spec":{"defaultCertificate": {"name": "<secret>"}}}' \1 -n openshift-ingress-operatorCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<secret>with the name used for the secret in the previous step.
8.2. Adding API server certificates
The default API server certificate is issued by an internal OpenShift Container Platform cluster CA. Clients outside of the cluster will not be able to verify the API server’s certificate by default. This certificate can be replaced by one that is issued by a CA that clients trust.
8.2.1. Add an API server named certificate
The default API server certificate is issued by an internal OpenShift Container Platform cluster CA. You can add one or more alternative certificates that the API server will return based on the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) requested by the client, for example when a reverse proxy or load balancer is used.
Prerequisites
- You must have a certificate for the FQDN and its corresponding private key. Each should be in a separate PEM format file.
- The private key must be unencrypted. If your key is encrypted, decrypt it before importing it into OpenShift Container Platform.
-
The certificate must include the
subjectAltNameextension showing the FQDN. - The certificate file can contain one or more certificates in a chain. The certificate for the API server FQDN must be the first certificate in the file. It can then be followed with any intermediate certificates, and the file should end with the root CA certificate.
Do not provide a named certificate for the internal load balancer (host name api-int.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>). Doing so will leave your cluster in a degraded state.
Procedure
Create a secret that contains the certificate chain and private key in the
openshift-confignamespace.oc create secret tls <secret> \ --cert=</path/to/cert.crt> \ --key=</path/to/cert.key> \ -n openshift-config$ oc create secret tls <secret> \1 --cert=</path/to/cert.crt> \2 --key=</path/to/cert.key> \3 -n openshift-configCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the API server to reference the created secret.
oc patch apiserver cluster \ --type=merge -p \ '{"spec":{"servingCerts": {"namedCertificates": [{"names": ["<FQDN>"], "servingCertificate": {"name": "<secret>"}}]}}}'$ oc patch apiserver cluster \ --type=merge -p \ '{"spec":{"servingCerts": {"namedCertificates": [{"names": ["<FQDN>"],1 "servingCertificate": {"name": "<secret>"}}]}}}'2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Examine the
apiserver/clusterobject and confirm the secret is now referenced.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3. Securing service traffic using service serving certificate secrets
8.3.1. Understanding service serving certificates
Service serving certificates are intended to support complex middleware applications that require encryption. These certificates are issued as TLS web server certificates.
The service-ca controller uses the x509.SHA256WithRSA signature algorithm to generate service certificates.
The generated certificate and key are in PEM format, stored in tls.crt and tls.key respectively, within a created secret. The certificate and key are automatically replaced when they get close to expiration.
The service CA certificate, which issues the service certificates, is valid for 26 months and is automatically rotated when there is less than six months validity left. After rotation, the previous service CA configuration is still trusted until its expiration. This allows a grace period for all affected services to refresh their key material before the expiration. If you do not upgrade your cluster during this grace period, which restarts services and refreshes their key material, you might need to manually restart services to avoid failures after the previous service CA expires.
You can use the following command to manually restart all Pods in the cluster. Be aware that running this command causes a service interruption, because it deletes every running Pod in every namespace. These Pods will automatically restart after they are deleted.
for I in $(oc get ns -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]} {.metadata.name}{"\n"} {end}'); \
do oc delete pods --all -n $I; \
sleep 1; \
done
$ for I in $(oc get ns -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]} {.metadata.name}{"\n"} {end}'); \
do oc delete pods --all -n $I; \
sleep 1; \
done8.3.2. Add a service certificate
To secure communication to your service, generate a signed serving certificate and key pair into a secret in the same namespace as the service.
The generated certificate is only valid for the internal service DNS name <service.name>.<service.namespace>.svc, and are only valid for internal communications.
Prerequisites:
- You must have a service defined.
Procedure
Annotate the service with
service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name.oc annotate service <service-name> \ service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name=<secret-name>$ oc annotate service <service-name> \1 service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name=<secret-name>2 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For instance, use the following command to annotate the service
foo:oc annotate service foo service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name=foo
$ oc annotate service foo service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name=fooCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Examine the service to confirm the annotations are present.
oc describe service <service-name> ... Annotations: service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name: <service-name> service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-signed-by: openshift-service-serving-signer@1556850837 ...$ oc describe service <service-name> ... Annotations: service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name: <service-name> service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-signed-by: openshift-service-serving-signer@1556850837 ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - After the cluster generates a secret for your service, your PodSpec can mount it, and the Pod will run after it becomes available.
8.3.3. Add a service certificate to a ConfigMap
A Pod can access the service CA certificate by mounting a ConfigMap that is annotated with service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=true. Once annotated, the cluster automatically injects the service CA certificate into the service-ca.crt key on the ConfigMap. Access to this CA certificate allows TLS clients to verify connections to services using service serving certificates.
After adding this annotation to a ConfigMap all existing data in it is deleted. It is recommended to use a separate ConfigMap to contain the service-ca.crt, instead of using the same ConfigMap that stores your Pod’s configuration.
Procedure
Annotate the ConfigMap with
service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=true.oc annotate configmap <configmap-name> \ service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=true$ oc annotate configmap <configmap-name> \1 service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<configmap-name>with the name of the ConfigMap to annotate.
NoteExplicitly referencing the
service-ca.crtkey in a volumeMount will prevent a Pod from starting until the ConfigMap has been injected with the CA bundle.For instance, to annotate the ConfigMap
foothe following command would be used:oc annotate configmap foo service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=true
$ oc annotate configmap foo service.beta.openshift.io/inject-cabundle=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the ConfigMap to ensure the certificate has been generated. This appears as a
service-ca.crtin the YAML output.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3.4. Manually rotate the generated service certificate
You can rotate the service certificate by deleting the associated secret. Deleting the secret results in a new one being automatically created, resulting in a new certificate.
Prerequisites
- A secret containing the certificate and key pair must have been generated for the service.
Procedure
Examine the service to determine the secret containing the certificate. This is found in the
serving-cert-secret-nameannotation, as seen below.oc describe service <service-name> ... service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name: <secret> ...
$ oc describe service <service-name> ... service.beta.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name: <secret> ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete the generated secret for the service. This process will automatically recreate the secret.
oc delete secret <secret>
$ oc delete secret <secret>1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- Replace
<secret>with the name of the secret from the previous step.
Confirm that the certificate has been recreated by obtaining the new secret and examining the
AGE.oc get secret <service-name> NAME TYPE DATA AGE <service.name> kubernetes.io/tls 2 1s
$ oc get secret <service-name> NAME TYPE DATA AGE <service.name> kubernetes.io/tls 2 1sCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
8.3.5. Manually rotate the service CA certificate
The service CA is valid for 26 months and is automatically refreshed when there is less than six months validity left.
If necessary, you can manually refresh the service CA by using the following procedure.
A manually-rotated service CA does not maintain trust with the previous service CA. You might experience a temporary service disruption until the Pods in the cluster are restarted, which ensures that Pods are using service serving certificates issued by the new service CA.
Prerequisites
- You must be logged in as a cluster admin.
Procedure
View the expiration date of the current service CA certificate by using the following command.
oc get secrets/signing-key -n openshift-service-ca \ -o template='{{index .data "tls.crt"}}' \ | base64 -d \ | openssl x509 -noout -enddate$ oc get secrets/signing-key -n openshift-service-ca \ -o template='{{index .data "tls.crt"}}' \ | base64 -d \ | openssl x509 -noout -enddateCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Manually rotate the service CA. This process generates a new service CA which will be used to sign the new service certificates.
oc delete secret/signing-key -n openshift-service-ca
$ oc delete secret/signing-key -n openshift-service-caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To apply the new certificates to all services, restart all the Pods in your cluster. This command ensures that all services use the updated certificates.
for I in $(oc get ns -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]} {.metadata.name}{"\n"} {end}'); \ do oc delete pods --all -n $I; \ sleep 1; \ done$ for I in $(oc get ns -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]} {.metadata.name}{"\n"} {end}'); \ do oc delete pods --all -n $I; \ sleep 1; \ doneCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningThis command will cause a service interruption, as it goes through and deletes every running pod in every namespace. These pods will automatically restart after they are deleted.
Chapter 9. Using RBAC to define and apply permissions
9.1. RBAC overview
Role-based access control (RBAC) objects determine whether a user is allowed to perform a given action within a project.
Cluster administrators can use the cluster roles and bindings to control who has various access levels to the OpenShift Container Platform platform itself and all projects.
Developers can use local roles and bindings to control who has access to their projects. Note that authorization is a separate step from authentication, which is more about determining the identity of who is taking the action.
Authorization is managed using:
| Rules |
Sets of permitted verbs on a set of objects. For example, whether a user or service account can |
| Roles | Collections of rules. You can associate, or bind, users and groups to multiple roles. |
| Bindings | Associations between users and/or groups with a role. |
There are two levels of RBAC roles and bindings that control authorization:
| Cluster RBAC | Roles and bindings that are applicable across all projects. Cluster roles exist cluster-wide, and cluster role bindings can reference only cluster roles. |
| Local RBAC | Roles and bindings that are scoped to a given project. While local roles exist only in a single project, local role bindings can reference both cluster and local roles. |
A cluster role binding is a binding that exists at the cluster level. A role binding exists at the project level. The cluster role view must be bound to a user using a local role binding for that user to view the project. Create local roles only if a cluster role does not provide the set of permissions needed for a particular situation.
This two-level hierarchy allows reuse across multiple projects through the cluster roles while allowing customization inside of individual projects through local roles.
During evaluation, both the cluster role bindings and the local role bindings are used. For example:
- Cluster-wide "allow" rules are checked.
- Locally-bound "allow" rules are checked.
- Deny by default.
9.1.1. Default cluster roles
OpenShift Container Platform includes a set of default cluster roles that you can bind to users and groups cluster-wide or locally. You can manually modify the default cluster roles, if required, but you must take extra steps each time you restart a master node.
| Default Cluster Role | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A project manager. If used in a local binding, an |
|
| A user that can get basic information about projects and users. |
|
| A super-user that can perform any action in any project. When bound to a user with a local binding, they have full control over quota and every action on every resource in the project. |
|
| A user that can get basic cluster status information. |
|
| A user that can modify most objects in a project but does not have the power to view or modify roles or bindings. |
|
| A user that can create their own projects. |
|
| A user who cannot make any modifications, but can see most objects in a project. They cannot view or modify roles or bindings. |
Be mindful of the difference between local and cluster bindings. For example, if you bind the cluster-admin role to a user by using a local role binding, it might appear that this user has the privileges of a cluster administrator. This is not the case. Binding the cluster-admin to a user in a project grants super administrator privileges for only that project to the user. That user has the permissions of the cluster role admin, plus a few additional permissions like the ability to edit rate limits, for that project. This binding can be confusing via the web console UI, which does not list cluster role bindings that are bound to true cluster administrators. However, it does list local role bindings that you can use to locally bind cluster-admin.
The relationships between cluster roles, local roles, cluster role bindings, local role bindings, users, groups and service accounts are illustrated below.
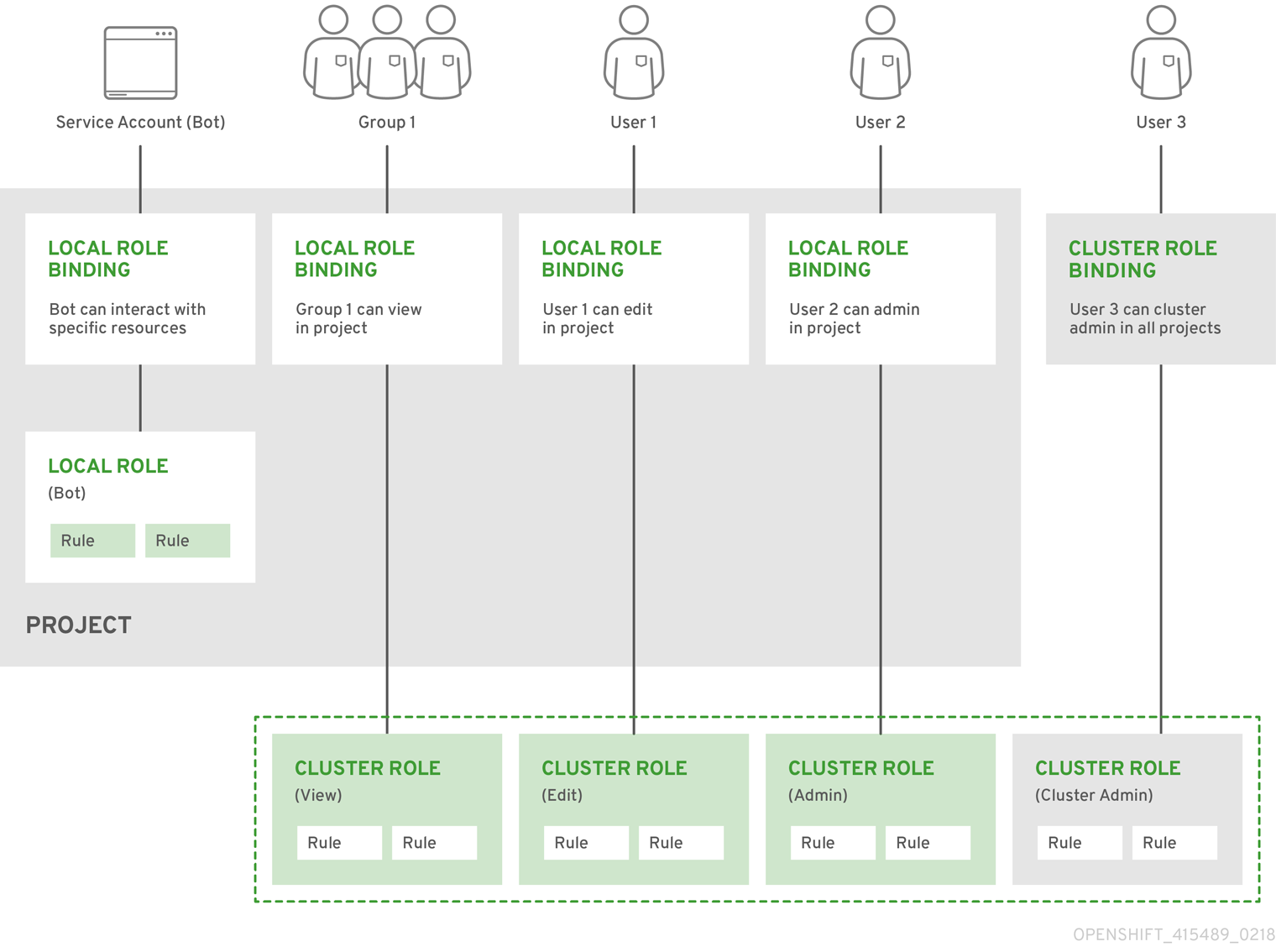
9.1.2. Evaluating authorization
OpenShift Container Platform evaluates authorization by using:
- Identity
- The user name and list of groups that the user belongs to.
- Action
The action you perform. In most cases, this consists of:
- Project: The project you access. A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations that allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities.
-
Verb : The action itself:
get,list,create,update,delete,deletecollection, orwatch. - Resource Name: The API endpoint that you access.
- Bindings
- The full list of bindings, the associations between users or groups with a role.
OpenShift Container Platform evaluates authorization by using the following steps:
- The identity and the project-scoped action is used to find all bindings that apply to the user or their groups.
- Bindings are used to locate all the roles that apply.
- Roles are used to find all the rules that apply.
- The action is checked against each rule to find a match.
- If no matching rule is found, the action is then denied by default.
Remember that users and groups can be associated with, or bound to, multiple roles at the same time.
Project administrators can use the CLI to view local roles and bindings, including a matrix of the verbs and resources each are associated with.
The cluster role bound to the project administrator is limited in a project through a local binding. It is not bound cluster-wide like the cluster roles granted to the cluster-admin or system:admin.
Cluster roles are roles defined at the cluster level but can be bound either at the cluster level or at the project level.
9.1.2.1. Cluster Role Aggregation
The default admin, edit, view, and cluster-reader cluster roles support cluster role aggregation, where the cluster rules for each role are dynamically updated as new rules are created. This feature is relevant only if you extend the Kubernetes API by creating custom resources.
9.2. Projects and namespaces
A Kubernetes namespace provides a mechanism to scope resources in a cluster. The Kubernetes documentation has more information on namespaces.
Namespaces provide a unique scope for:
- Named resources to avoid basic naming collisions.
- Delegated management authority to trusted users.
- The ability to limit community resource consumption.
Most objects in the system are scoped by namespace, but some are excepted and have no namespace, including nodes and users.
A project is a Kubernetes namespace with additional annotations and is the central vehicle by which access to resources for regular users is managed. A project allows a community of users to organize and manage their content in isolation from other communities. Users must be given access to projects by administrators, or if allowed to create projects, automatically have access to their own projects.
Projects can have a separate name, displayName, and description.
-
The mandatory
nameis a unique identifier for the project and is most visible when using the CLI tools or API. The maximum name length is 63 characters. -
The optional
displayNameis how the project is displayed in the web console (defaults toname). -
The optional
descriptioncan be a more detailed description of the project and is also visible in the web console.
Each project scopes its own set of:
|
| Pods, services, replication controllers, etc. |
|
| Rules for which users can or cannot perform actions on objects. |
|
| Quotas for each kind of object that can be limited. |
|
| Service accounts act automatically with designated access to objects in the project. |
Cluster administrators can create projects and delegate administrative rights for the project to any member of the user community. Cluster administrators can also allow developers to create their own projects.
Developers and administrators can interact with projects the CLI or the web console.
9.3. Default projects
OpenShift Container Platform comes with a number of default projects, and projects starting with openshift- are the most essential to users. These projects host master components that run as pods and other infrastructure components. The pods created in these namespaces that have a critical pod annotation are considered critical, and the have guaranteed admission by kubelet. Pods created for master components in these namespaces are already marked as critical.
9.4. Viewing cluster roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view cluster roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. - Obtain permission to view the cluster roles and bindings.
Users with the cluster-admin default cluster role bound cluster-wide can perform any action on any resource, including viewing cluster roles and bindings.
Procedure
To view the cluster roles and their associated rule sets:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the current set of cluster role bindings, which shows the users and groups that are bound to various roles:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.5. Viewing local roles and bindings
You can use the oc CLI to view local roles and bindings by using the oc describe command.
Prerequisites
-
Install the
ocCLI. Obtain permission to view the local roles and bindings:
-
Users with the
cluster-admindefault cluster role bound cluster-wide can perform any action on any resource, including viewing local roles and bindings. -
Users with the
admindefault cluster role bound locally can view and manage roles and bindings in that project.
-
Users with the
Procedure
To view the current set of local role bindings, which show the users and groups that are bound to various roles for the current project:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbacCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To view the local role bindings for a different project, add the
-nflag to the command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.6. Adding roles to users
You can use the oc adm administrator CLI to manage the roles and bindings.
Binding, or adding, a role to users or groups gives the user or group the access that is granted by the role. You can add and remove roles to and from users and groups using oc adm policy commands.
You can bind any of the default cluster roles to local users or groups in your project.
Procedure
Add a role to a user in a specific project:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user <role> <user> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, you can add the
adminrole to thealiceuser injoeproject by running:oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joe
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user admin alice -n joeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow View the local role bindings and verify the addition in the output:
oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>
$ oc describe rolebinding.rbac -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, to view the local role bindings for the
joeproject:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aliceuser has been added to theadminsRoleBinding.
9.7. Creating a local role
You can create a local role for a project and then bind it to a user.
Procedure
To create a local role for a project, run the following command:
oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>
$ oc create role <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource> -n <project>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role -
<resource>, the resources that the role applies to -
<project>, the project name
For example, to create a local role that allows a user to view pods in the
blueproject, run the following command:oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blue
$ oc create role podview --verb=get --resource=pod -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To bind the new role to a user, run the following command:
oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blue
$ oc adm policy add-role-to-user podview user2 --role-namespace=blue -n blueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.8. Creating a cluster role
You can create a cluster role.
Procedure
To create a cluster role, run the following command:
oc create clusterrole <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource>
$ oc create clusterrole <name> --verb=<verb> --resource=<resource>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this command, specify:
-
<name>, the local role’s name -
<verb>, a comma-separated list of the verbs to apply to the role <resource>, the resources that the role applies toFor example, to create a cluster role that allows a user to view pods, run the following command:
oc create clusterrole podviewonly --verb=get --resource=pod
$ oc create clusterrole podviewonly --verb=get --resource=podCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
9.9. Local role binding commands
When you manage a user or group’s associated roles for local role bindings using the following operations, a project may be specified with the -n flag. If it is not specified, then the current project is used.
You can use the following commands for local RBAC management.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Indicates which users can perform an action on a resource. |
|
| Binds a specified role to specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified users and all of their roles in the current project. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups in the current project. |
|
| Removes specified groups and all of their roles in the current project. |
9.10. Cluster role binding commands
You can also manage cluster role bindings using the following operations. The -n flag is not used for these operations because cluster role bindings use non-namespaced resources.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Binds a given role to specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified users for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Binds a given role to specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
|
| Removes a given role from specified groups for all projects in the cluster. |
9.11. Creating a cluster admin
The cluster-admin role is required to perform administrator level tasks on the OpenShift Container Platform cluster, such as modifying cluster resources.
Prerequisites
- You must have created a user to define as the cluster admin.
Procedure
Define the user as a cluster admin:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user>
$ oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin <user>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 10. Removing the kubeadmin user
10.1. The kubeadmin user
OpenShift Container Platform creates a cluster administrator, kubeadmin, after the installation process completes.
This user has the cluster-admin role automatically applied and is treated as the root user for the cluster. The password is dynamically generated and unique to your OpenShift Container Platform environment. After installation completes the password is provided in the installation program’s output. For example:
INFO Install complete! INFO Run 'export KUBECONFIG=<your working directory>/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI. INFO The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p <provided>' succeeds (wait a few minutes). INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.demo1.openshift4-beta-abcorp.com INFO Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: <provided>
INFO Install complete!
INFO Run 'export KUBECONFIG=<your working directory>/auth/kubeconfig' to manage the cluster with 'oc', the OpenShift CLI.
INFO The cluster is ready when 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p <provided>' succeeds (wait a few minutes).
INFO Access the OpenShift web-console here: https://console-openshift-console.apps.demo1.openshift4-beta-abcorp.com
INFO Login to the console with user: kubeadmin, password: <provided>10.2. Removing the kubeadmin user
After you define an identity provider and create a new cluster-admin user, you can remove the kubeadmin to improve cluster security.
If you follow this procedure before another user is a cluster-admin, then OpenShift Container Platform must be reinstalled. It is not possible to undo this command.
Prerequisites
- You must have configured at least one identity provider.
-
You must have added the
cluster-adminrole to a user. - You must be logged in as an administrator.
Procedure
Remove the
kubeadminsecrets:oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-system
$ oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-systemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 11. Configuring the user agent
11.1. About the user agent
OpenShift Container Platform implements a user agent that can be used to prevent an application developer’s CLI accessing the OpenShift Container Platform API. If a client uses a particular library or binary file, they cannot access the OpenShift Container Platform API.
You construct user agents for the OpenShift Container Platform CLI from a set of values within OpenShift Container Platform:
<command>/<version> (<platform>/<architecture>) <client>/<git_commit>
<command>/<version> (<platform>/<architecture>) <client>/<git_commit>For example, when:
-
<command> =
oc -
<version> = The client version. For example,
v4.3.0. Requests made against the Kubernetes API at/apireceive the Kubernetes version, while requests made against the OpenShift Container Platform API at/oapireceive the OpenShift Container Platform version (as specified byoc version) -
<platform> =
linux -
<architecture> =
amd64 -
<client> =
openshift, orkubernetesdepending on if the request is made against the Kubernetes API at/api, or the OpenShift Container Platform API at/oapi -
<git_commit> = The Git commit of the client version (for example,
f034127)
the user agent is:
oc/v3.3.0 (linux/amd64) openshift/f034127
oc/v3.3.0 (linux/amd64) openshift/f03412711.2. Configuring the user agent
As an administrator, you can prevent clients from accessing the API with the userAgentMatching configuration setting of a master configuration.
Procedure
Modify the master configuration file to include the user agent configuration. For example, the following user agent denies the Kubernetes 1.2 client binary, OKD 1.1.3 binary, and the POST and PUT
httpVerbs:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example denies clients that do not exactly match an expected client:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 12. Understanding and creating service accounts
12.1. Service accounts overview
A service account is an OpenShift Container Platform account that allows a component to directly access the API. Service accounts are API objects that exist within each project. Service accounts provide a flexible way to control API access without sharing a regular user’s credentials.
When you use the OpenShift Container Platform CLI or web console, your API token authenticates you to the API. You can associate a component with a service account so that they can access the API without using a regular user’s credentials. For example, service accounts can allow:
- Replication controllers to make API calls to create or delete pods.
- Applications inside containers to make API calls for discovery purposes.
- External applications to make API calls for monitoring or integration purposes.
Each service account’s user name is derived from its project and name:
system:serviceaccount:<project>:<name>
system:serviceaccount:<project>:<name>Every service account is also a member of two groups:
- system:serviceaccounts
- Includes all service accounts in the system.
- system:serviceaccounts:<project>
- Includes all service accounts in the specified project.
Each service account automatically contains two secrets:
- An API token
- Credentials for the OpenShift Container Registry
The generated API token and registry credentials do not expire, but you can revoke them by deleting the secret. When you delete the secret, a new one is automatically generated to take its place.
12.2. Creating service accounts
You can create a service account in a project and grant it permissions by binding it to a role.
Procedure
Optional: To view the service accounts in the current project:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a new service account in the current project:
oc create sa <service_account_name> serviceaccount "robot" created
$ oc create sa <service_account_name>1 serviceaccount "robot" createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- To create a service account in a different project, specify
-n <project_name>.
Optional: View the secrets for the service account:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
12.3. Examples of granting roles to service accounts
You can grant roles to service accounts in the same way that you grant roles to a regular user account.
You can modify the service accounts for the current project. For example, to add the
viewrole to therobotservice account in thetop-secretproject:oc policy add-role-to-user view system:serviceaccount:top-secret:robot
$ oc policy add-role-to-user view system:serviceaccount:top-secret:robotCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also grant access to a specific service account in a project. For example, from the project to which the service account belongs, use the
-zflag and specify the<serviceaccount_name>oc policy add-role-to-user <role_name> -z <serviceaccount_name>
$ oc policy add-role-to-user <role_name> -z <serviceaccount_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantIf you want to grant access to a specific service account in a project, use the
-zflag. Using this flag helps prevent typos and ensures that access is granted to only the specified service account.To modify a different namespace, you can use the
-noption to indicate the project namespace it applies to, as shown in the following examples.For example, to allow all service accounts in all projects to view resources in the
top-secretproject:oc policy add-role-to-group view system:serviceaccounts -n top-secret
$ oc policy add-role-to-group view system:serviceaccounts -n top-secretCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To allow all service accounts in the
managersproject to edit resources in thetop-secretproject:oc policy add-role-to-group edit system:serviceaccounts:managers -n top-secret
$ oc policy add-role-to-group edit system:serviceaccounts:managers -n top-secretCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 13. Using service accounts in applications
13.1. Service accounts overview
A service account is an OpenShift Container Platform account that allows a component to directly access the API. Service accounts are API objects that exist within each project. Service accounts provide a flexible way to control API access without sharing a regular user’s credentials.
When you use the OpenShift Container Platform CLI or web console, your API token authenticates you to the API. You can associate a component with a service account so that they can access the API without using a regular user’s credentials. For example, service accounts can allow:
- Replication controllers to make API calls to create or delete pods.
- Applications inside containers to make API calls for discovery purposes.
- External applications to make API calls for monitoring or integration purposes.
Each service account’s user name is derived from its project and name:
system:serviceaccount:<project>:<name>
system:serviceaccount:<project>:<name>Every service account is also a member of two groups:
- system:serviceaccounts
- Includes all service accounts in the system.
- system:serviceaccounts:<project>
- Includes all service accounts in the specified project.
Each service account automatically contains two secrets:
- An API token
- Credentials for the OpenShift Container Registry
The generated API token and registry credentials do not expire, but you can revoke them by deleting the secret. When you delete the secret, a new one is automatically generated to take its place.
13.2. Default service accounts
Your OpenShift Container Platform cluster contains default service accounts for cluster management and generates more service accounts for each project.
13.2.1. Default cluster service accounts
Several infrastructure controllers run using service account credentials. The following service accounts are created in the OpenShift Container Platform infrastructure project (openshift-infra) at server start, and given the following roles cluster-wide:
| Service Account | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Assigned the |
|
|
Assigned the |
|
|
Assigned the |
13.2.2. Default project service accounts and roles
Three service accounts are automatically created in each project:
| Service Account | Usage |
|---|---|
|
|
Used by build pods. It is given the |
|
|
Used by deployment pods and given the |
|
| Used to run all other pods unless they specify a different service account. |
All service accounts in a project are given the system:image-puller role, which allows pulling images from any imagestream in the project using the internal container image registry.
13.3. Creating service accounts
You can create a service account in a project and grant it permissions by binding it to a role.
Procedure
Optional: To view the service accounts in the current project:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To create a new service account in the current project:
oc create sa <service_account_name> serviceaccount "robot" created
$ oc create sa <service_account_name>1 serviceaccount "robot" createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- To create a service account in a different project, specify
-n <project_name>.
Optional: View the secrets for the service account:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
13.4. Using a service account’s credentials externally
You can distribute a service account’s token to external applications that must authenticate to the API.
In order to pull an image, the authenticated user must have get rights on the requested imagestreams/layers. In order to push an image, the authenticated user must have update rights on the requested imagestreams/layers.
By default, all service accounts in a project have rights to pull any image in the same project, and the builder service account has rights to push any image in the same project.
Procedure
View the service account’s API token:
oc describe secret <secret-name>
$ oc describe secret <secret-name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in using the token that you obtained:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Confirm that you logged in as the service account:
oc whoami system:serviceaccount:top-secret:robot
$ oc whoami system:serviceaccount:top-secret:robotCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 14. Using a service account as an OAuth client
14.1. Service accounts as OAuth clients
You can use a service account as a constrained form of OAuth client. Service accounts can request only a subset of scopes that allow access to some basic user information and role-based power inside of the service account’s own namespace:
-
user:info -
user:check-access -
role:<any_role>:<serviceaccount_namespace> -
role:<any_role>:<serviceaccount_namespace>:!
When using a service account as an OAuth client:
-
client_idissystem:serviceaccount:<serviceaccount_namespace>:<serviceaccount_name>. client_secretcan be any of the API tokens for that service account. For example:oc sa get-token <serviceaccount_name>
$ oc sa get-token <serviceaccount_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To get
WWW-Authenticatechallenges, set anserviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-want-challengesannotation on the service account totrue. -
redirect_urimust match an annotation on the service account.
14.1.1. Redirect URIs for Service Accounts as OAuth Clients
Annotation keys must have the prefix serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi. or serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference. such as:
serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<name>
serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.<name>In its simplest form, the annotation can be used to directly specify valid redirect URIs. For example:
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.first": "https://example.com" "serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.second": "https://other.com"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.first": "https://example.com"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.second": "https://other.com"
The first and second postfixes in the above example are used to separate the two valid redirect URIs.
In more complex configurations, static redirect URIs may not be enough. For example, perhaps you want all Ingresses for a route to be considered valid. This is where dynamic redirect URIs via the serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference. prefix come into play.
For example:
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"Since the value for this annotation contains serialized JSON data, it is easier to see in an expanded format:
Now you can see that an OAuthRedirectReference allows us to reference the route named jenkins. Thus, all Ingresses for that route will now be considered valid. The full specification for an OAuthRedirectReference is:
- 1
kindrefers to the type of the object being referenced. Currently, onlyrouteis supported.- 2
namerefers to the name of the object. The object must be in the same namespace as the service account.- 3
grouprefers to the group of the object. Leave this blank, as the group for a route is the empty string.
Both annotation prefixes can be combined to override the data provided by the reference object. For example:
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.first": "custompath"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.first": "custompath"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
The first postfix is used to tie the annotations together. Assuming that the jenkins route had an Ingress of https://example.com, now https://example.com/custompath is considered valid, but https://example.com is not. The format for partially supplying override data is as follows:
| Type | Syntax |
|---|---|
| Scheme | "https://" |
| Hostname | "//website.com" |
| Port | "//:8000" |
| Path | "examplepath" |
Specifying a host name override will replace the host name data from the referenced object, which is not likely to be desired behavior.
Any combination of the above syntax can be combined using the following format:
<scheme:>//<hostname><:port>/<path>
The same object can be referenced more than once for more flexibility:
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.first": "custompath"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.second": "//:8000"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.second": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.first": "custompath"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.second": "//:8000"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.second": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
Assuming that the route named jenkins has an Ingress of https://example.com, then both https://example.com:8000 and https://example.com/custompath are considered valid.
Static and dynamic annotations can be used at the same time to achieve the desired behavior:
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.second": "https://other.com"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.first": "{\"kind\":\"OAuthRedirectReference\",\"apiVersion\":\"v1\",\"reference\":{\"kind\":\"Route\",\"name\":\"jenkins\"}}"
"serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirecturi.second": "https://other.com"Chapter 15. Scoping tokens
15.1. About scoping tokens
You can created scoped tokens to delegate some of your permissions to another user or service account. For example, a project administrator might want to delegate the power to create pods.
A scoped token is a token that identifies as a given user but is limited to certain actions by its scope. Only a user with the cluster-admin role can create scoped tokens.
Scopes are evaluated by converting the set of scopes for a token into a set of PolicyRules. Then, the request is matched against those rules. The request attributes must match at least one of the scope rules to be passed to the "normal" authorizer for further authorization checks.
15.1.1. User scopes
User scopes are focused on getting information about a given user. They are intent-based, so the rules are automatically created for you:
-
user:full- Allows full read/write access to the API with all of the user’s permissions. -
user:info- Allows read-only access to information about the user, such as name and groups. -
user:check-access- Allows access toself-localsubjectaccessreviewsandself-subjectaccessreviews. These are the variables where you pass an empty user and groups in your request object. -
user:list-projects- Allows read-only access to list the projects the user has access to.
15.1.2. Role scope
The role scope allows you to have the same level of access as a given role filtered by namespace.
role:<cluster-role name>:<namespace or * for all>- Limits the scope to the rules specified by the cluster-role, but only in the specified namespace .NoteCaveat: This prevents escalating access. Even if the role allows access to resources like secrets, rolebindings, and roles, this scope will deny access to those resources. This helps prevent unexpected escalations. Many people do not think of a role like
editas being an escalating role, but with access to a secret it is.-
role:<cluster-role name>:<namespace or * for all>:!- This is similar to the example above, except that including the bang causes this scope to allow escalating access.
Chapter 16. Managing Security Context Constraints
16.1. About Security Context Constraints
Similar to the way that RBAC resources control user access, administrators can use Security Context Constraints (SCCs) to control permissions for pods. These permissions include actions that a pod, a collection of containers, can perform and what resources it can access. You can use SCCs to define a set of conditions that a pod must run with in order to be accepted into the system.
SCCs allow an administrator to control:
- Whether a pod can run privileged containers.
- The capabilities that a container can request.
- The use of host directories as volumes.
- The SELinux context of the container.
- The container user ID.
- The use of host namespaces and networking.
-
The allocation of an
FSGroupthat owns the pod’s volumes. - The configuration of allowable supplemental groups.
- Whether a container requires the use of a read only root file system.
- The usage of volume types.
-
The configuration of allowable
seccompprofiles.
Docker has a default list of capabilities that are allowed for each container of a pod. The containers use the capabilities from this default list, but pod manifest authors can alter it by requesting additional capabilities or removing some of the default behaviors. Use the allowedCapabilities, defaultAddCapabilities, and requiredDropCapabilities parameters to control such requests from the pods and to dictate which capabilities can be requested, which ones must be added to each container, and which ones must be forbidden.
The cluster contains eight default SCCs:
-
anyuid -
hostaccess -
hostmount-anyuid hostnetworkWarningIf additional workloads are run on master hosts, use caution when providing access to
hostnetwork. A workload that runshostnetworkon a master host is effectively root on the cluster and must be trusted accordingly.-
node-exporter -
nonroot -
privileged -
restricted
Do not modify the default SCCs. Customizing the default SCCs can lead to issues when OpenShift Container Platform is upgraded. Instead, create new SCCs.
The privileged SCC allows:
- Users to run privileged pods
- Pods to mount host directories as volumes
- Pods to run as any user
- Pods to run with any MCS label
- Pods to use the host’s IPC namespace
- Pods to use the host’s PID namespace
- Pods to use any FSGroup
- Pods to use any supplemental group
- Pods to use any seccomp profiles
- Pods to request any capabilities
The restricted SCC:
- Ensures that pods cannot run as privileged.
- Ensures that pods cannot mount host directory volumes.
- Requires that a pod run as a user in a pre-allocated range of UIDs.
- Requires that a pod run with a pre-allocated MCS label.
- Allows pods to use any FSGroup.
- Allows pods to use any supplemental group.
For more information about each SCC, see the kubernetes.io/description annotation available on the SCC.
SCCs are composed of settings and strategies that control the security features a pod has access to. These settings fall into three categories:
| Controlled by a boolean |
Fields of this type default to the most restrictive value. For example, |
| Controlled by an allowable set | Fields of this type are checked against the set to ensure their value is allowed. |
| Controlled by a strategy | Items that have a strategy to generate a value provide:
|
16.1.1. SCC Strategies
RunAsUser
-
MustRunAs- Requires arunAsUserto be configured. Uses the configuredrunAsUseras the default. Validates against the configuredrunAsUser. -
MustRunAsRange- Requires minimum and maximum values to be defined if not using pre-allocated values. Uses the minimum as the default. Validates against the entire allowable range. -
MustRunAsNonRoot- Requires that the pod be submitted with a non-zerorunAsUseror have theUSERdirective defined in the image. No default provided. -
RunAsAny- No default provided. Allows anyrunAsUserto be specified.
SELinuxContext
-
MustRunAs- RequiresseLinuxOptionsto be configured if not using pre-allocated values. UsesseLinuxOptionsas the default. Validates againstseLinuxOptions. -
RunAsAny- No default provided. Allows anyseLinuxOptionsto be specified.
SupplementalGroups
-
MustRunAs- Requires at least one range to be specified if not using pre-allocated values. Uses the minimum value of the first range as the default. Validates against all ranges. -
RunAsAny- No default provided. Allows anysupplementalGroupsto be specified.
FSGroup
-
MustRunAs- Requires at least one range to be specified if not using pre-allocated values. Uses the minimum value of the first range as the default. Validates against the first ID in the first range. -
RunAsAny- No default provided. Allows anyfsGroupID to be specified.
16.1.2. Controlling volumes
The usage of specific volume types can be controlled by setting the volumes field of the SCC. The allowable values of this field correspond to the volume sources that are defined when creating a volume:
-
azureFile -
azureDisk -
flocker -
flexVolume -
hostPath -
emptyDir -
gcePersistentDisk -
awsElasticBlockStore -
gitRepo -
secret -
nfs -
iscsi -
glusterfs -
persistentVolumeClaim -
rbd -
cinder -
cephFS -
downwardAPI -
fc -
configMap -
vsphereVolume -
quobyte -
photonPersistentDisk -
projected -
portworxVolume -
scaleIO -
storageos - * (a special value to allow the use of all volume types)
-
none(a special value to disallow the use of all volumes types. Exist only for backwards compatibility)
The recommended minimum set of allowed volumes for new SCCs are configMap, downwardAPI, emptyDir, persistentVolumeClaim, secret, and projected.
The list of allowable volume types is not exhaustive because new types are added with each release of OpenShift Container Platform.
For backwards compatibility, the usage of allowHostDirVolumePlugin overrides settings in the volumes field. For example, if allowHostDirVolumePlugin is set to false but allowed in the volumes field, then the hostPath value will be removed from volumes.
16.1.3. Admission
Admission control with SCCs allows for control over the creation of resources based on the capabilities granted to a user.
In terms of the SCCs, this means that an admission controller can inspect the user information made available in the context to retrieve an appropriate set of SCCs. Doing so ensures the pod is authorized to make requests about its operating environment or to generate a set of constraints to apply to the pod.
The set of SCCs that admission uses to authorize a pod are determined by the user identity and groups that the user belongs to. Additionally, if the pod specifies a service account, the set of allowable SCCs includes any constraints accessible to the service account.
Admission uses the following approach to create the final security context for the pod:
- Retrieve all SCCs available for use.
- Generate field values for security context settings that were not specified on the request.
- Validate the final settings against the available constraints.
If a matching set of constraints is found, then the pod is accepted. If the request cannot be matched to an SCC, the pod is rejected.
A pod must validate every field against the SCC. The following are examples for just two of the fields that must be validated:
These examples are in the context of a strategy using the preallocated values.
A FSGroup SCC strategy of MustRunAs
If the pod defines a fsGroup ID, then that ID must equal the default fsGroup ID. Otherwise, the pod is not validated by that SCC and the next SCC is evaluated.
If the SecurityContextConstraints.fsGroup field has value RunAsAny and the pod specification omits the Pod.spec.securityContext.fsGroup, then this field is considered valid. Note that it is possible that during validation, other SCC settings will reject other pod fields and thus cause the pod to fail.
A SupplementalGroups SCC strategy of MustRunAs
If the pod specification defines one or more supplementalGroups IDs, then the pod’s IDs must equal one of the IDs in the namespace’s openshift.io/sa.scc.supplemental-groups annotation. Otherwise, the pod is not validated by that SCC and the next SCC is evaluated.
If the SecurityContextConstraints.supplementalGroups field has value RunAsAny and the pod specification omits the Pod.spec.securityContext.supplementalGroups, then this field is considered valid. Note that it is possible that during validation, other SCC settings will reject other pod fields and thus cause the pod to fail.
16.1.4. SCC prioritization
SCCs have a priority field that affects the ordering when attempting to validate a request by the admission controller. A higher priority SCC is moved to the front of the set when sorting. When the complete set of available SCCs are determined they are ordered by:
- Highest priority first, nil is considered a 0 priority
- If priorities are equal, the SCCs will be sorted from most restrictive to least restrictive
- If both priorities and restrictions are equal the SCCs will be sorted by name
By default, the anyuid SCC granted to cluster administrators is given priority in their SCC set. This allows cluster administrators to run pods as any user by without specifying a RunAsUser on the pod’s SecurityContext. The administrator may still specify a RunAsUser if they wish.
16.2. About pre-allocated Security Context Constraints values
The admission controller is aware of certain conditions in the Security Context Constraints (SCCs) that trigger it to look up pre-allocated values from a namespace and populate the SCC before processing the pod. Each SCC strategy is evaluated independently of other strategies, with the pre-allocated values, where allowed, for each policy aggregated with pod specification values to make the final values for the various IDs defined in the running pod.
The following SCCs cause the admission controller to look for pre-allocated values when no ranges are defined in the pod specification:
-
A
RunAsUserstrategy ofMustRunAsRangewith no minimum or maximum set. Admission looks for theopenshift.io/sa.scc.uid-rangeannotation to populate range fields. -
An
SELinuxContextstrategy ofMustRunAswith no level set. Admission looks for theopenshift.io/sa.scc.mcsannotation to populate the level. -
A
FSGroupstrategy ofMustRunAs. Admission looks for theopenshift.io/sa.scc.supplemental-groupsannotation. -
A
SupplementalGroupsstrategy ofMustRunAs. Admission looks for theopenshift.io/sa.scc.supplemental-groupsannotation.
During the generation phase, the security context provider uses default values for any parameter values that are not specifically set in the pod. Default values are based on the selected strategy:
-
RunAsAnyandMustRunAsNonRootstrategies do not provide default values. If the pod needs a parameter value, such as a group ID, you must define the value in the pod specification. -
MustRunAs(single value) strategies provide a default value that is always used. For example, for group IDs, even if the pod specification defines its own ID value, the namespace’s default parameter value also appears in the pod’s groups. -
MustRunAsRangeandMustRunAs(range-based) strategies provide the minimum value of the range. As with a single valueMustRunAsstrategy, the namespace’s default parameter value appears in the running pod. If a range-based strategy is configurable with multiple ranges, it provides the minimum value of the first configured range.
FSGroup and SupplementalGroups strategies fall back to the openshift.io/sa.scc.uid-range annotation if the openshift.io/sa.scc.supplemental-groups annotation does not exist on the namespace. If neither exists, the SCC is not created.
By default, the annotation-based FSGroup strategy configures itself with a single range based on the minimum value for the annotation. For example, if your annotation reads 1/3, the FSGroup strategy configures itself with a minimum and maximum value of 1. If you want to allow more groups to be accepted for the FSGroup field, you can configure a custom SCC that does not use the annotation.
The openshift.io/sa.scc.supplemental-groups annotation accepts a comma-delimited list of blocks in the format of <start>/<length or <start>-<end>. The openshift.io/sa.scc.uid-range annotation accepts only a single block.
16.3. Example Security Context Constraints
The following examples show the Security Context Constraint (SCC) format and annotations:
Annotated priviledged SCC
- 1
- A list of capabilities that a pod can request. An empty list means that none of capabilities can be requested while the special symbol
*allows any capabilities. - 2
- A list of additional capabilities that are added to any pod.
- 3
- The
FSGroupstrategy, which dictates the allowable values for the Security Context. - 4
- The groups that can access this SCC.
- 5
- A list of capabilities that are be dropped from a pod.
- 6
- The
runAsUserstrategy type, which dictates the allowable values for the Security Context. - 7
- The
seLinuxContextstrategy type, which dictates the allowable values for the Security Context. - 8
- The
supplementalGroupsstrategy, which dictates the allowable supplemental groups for the Security Context. - 9
- The users who can access this SCC.
The users and groups fields on the SCC control which users can access the SCC. By default, cluster administrators, nodes, and the build controller are granted access to the privileged SCC. All authenticated users are granted access to the restricted SCC.
Without explicit runAsUser setting
- 1
- When a container or pod does not request a user ID under which it should be run, the effective UID depends on the SCC that emits this pod. Because restricted SCC is granted to all authenticated users by default, it will be available to all users and service accounts and used in most cases. The restricted SCC uses
MustRunAsRangestrategy for constraining and defaulting the possible values of thesecurityContext.runAsUserfield. The admission plug-in will look for theopenshift.io/sa.scc.uid-rangeannotation on the current project to populate range fields, as it does not provide this range. In the end, a container will haverunAsUserequal to the first value of the range that is hard to predict because every project has different ranges.
With explicit runAsUser setting
- 1
- A container or pod that requests a specific user ID will be accepted by OpenShift Container Platform only when a service account or a user is granted access to a SCC that allows such a user ID. The SCC can allow arbitrary IDs, an ID that falls into a range, or the exact user ID specific to the request.
This configuration is valid for SELinux, fsGroup, and Supplemental Groups.
16.4. Creating Security Context Constraints
You can create a Security Context Constraint (SCC) by using the CLI.
Prerequisites
-
You must install the
occommand line. -
Your account must have
cluster-adminprivileges to create SCCs.
Procedure
Define the SCC in a JSON or YAML file:
Security Context Constraint Object Definition
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optionally, you can add drop capabilities to an SCC by setting the
requiredDropCapabilitiesfield with the desired values. Any specified capabilities will be dropped from the container. For example, to create an SCC with theKILL,MKNOD, andSYS_CHROOTrequired drop capabilities, add the following to the SCC object:requiredDropCapabilities: - KILL - MKNOD - SYS_CHROOT
requiredDropCapabilities: - KILL - MKNOD - SYS_CHROOTCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can see the list of possible values in the Docker documentation.
TipBecause capabilities are passed to the Docker, you can use a special
ALLvalue to drop all possible capabilities.Then, run
oc createpassing the file to create it:oc create -f scc_admin.yaml securitycontextconstraints "scc-admin" created
$ oc create -f scc_admin.yaml securitycontextconstraints "scc-admin" createdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the SCC was created:
oc get scc scc-admin NAME PRIV CAPS SELINUX RUNASUSER FSGROUP SUPGROUP PRIORITY READONLYROOTFS VOLUMES scc-admin true [] RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny <none> false [awsElasticBlockStore azureDisk azureFile cephFS cinder configMap downwardAPI emptyDir fc flexVolume flocker gcePersistentDisk gitRepo glusterfs iscsi nfs persistentVolumeClaim photonPersistentDisk quobyte rbd secret vsphere]
$ oc get scc scc-admin NAME PRIV CAPS SELINUX RUNASUSER FSGROUP SUPGROUP PRIORITY READONLYROOTFS VOLUMES scc-admin true [] RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny <none> false [awsElasticBlockStore azureDisk azureFile cephFS cinder configMap downwardAPI emptyDir fc flexVolume flocker gcePersistentDisk gitRepo glusterfs iscsi nfs persistentVolumeClaim photonPersistentDisk quobyte rbd secret vsphere]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.5. Role-based access to Security Context Constraints
You can specify SCCs as resources that are handled by RBAC. This allows you to scope access to your SCCs to a certain project or to the entire cluster. Assigning users, groups, or service accounts directly to an SCC retains cluster-wide scope.
You cannot assign a SCC to pods created in one of the default namespaces: default, kube-system, kube-public, openshift-node, openshift-infra, openshift. These namespaces should not be used for running pods or services.
To include access to SCCs for your role, specify the scc resource when creating a role.
oc create role <role-name> --verb=use --resource=scc --resource-name=<scc-name> -n <namespace>
$ oc create role <role-name> --verb=use --resource=scc --resource-name=<scc-name> -n <namespace>This results in the following role definition:
- 1
- The role’s name.
- 2
- Namespace of the defined role. Defaults to
defaultif not specified. - 3
- The API group that includes the SecurityContextConstraint resource. Automatically defined when
sccis specified as a resource. - 4
- An example name for an SCC you want to have access.
- 5
- Name of the resource group that allows users to specify SCC names in the
resourceNamesfield. - 6
- A list of verbs to apply to the role.
A local or cluster role with such a rule allows the subjects that are bound to it with a RoleBinding or a ClusterRoleBinding to use the user-defined SCC called scc-name.
Because RBAC is designed to prevent escalation, even project administrators will be unable to grant access to an SCC. By defualt, they are not allowed to use the verb use on SCC resources, including the restricted SCC.
16.6. Security Context Constraints reference commands
You can manage SCCs in your instance as normal API objects using the CLI.
You must have cluster-admin privileges to manage SCCs.
Do not modify the default SCCs. Customizing the default SCCs can lead to issues when upgrading. Instead, create new SCCs.
16.6.1. Listing SCCs
To get a current list of SCCs:
16.6.2. Examining an SCC
You can view information about a particular SCC, including which users, service accounts, and groups the SCC is applied to.
For example, to examine the restricted SCC:
To preserve customized SCCs during upgrades, do not edit settings on the default SCCs.
16.6.3. Deleting an SCC
To delete an SCC:
oc delete scc <scc_name>
$ oc delete scc <scc_name>If you delete a default SCC, it will regenerate when you restart the cluster.
16.6.4. Updating an SCC
To update an existing SCC:
oc edit scc <scc_name>
$ oc edit scc <scc_name>To preserve customized SCCs during upgrades, do not edit settings on the default SCCs.
Chapter 17. Impersonating the system:admin user
17.1. API impersonation
You can configure a request to the OpenShift Container Platform API to act as though it originated from another user. For more information, see User impersonation in the Kubernetes documentation.
17.2. Impersonating the system:admin user
You can grant a user permission to impersonate system:admin, which grants them cluster administrator permissions.
Procedure
To grant a user permission to impersonate
system:admin, run the following command:oc create clusterrolebinding <any_valid_name> --clusterrole=sudoer --user=<username>
$ oc create clusterrolebinding <any_valid_name> --clusterrole=sudoer --user=<username>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.3. Impersonating the system:admin group
When a system:admin user is granted cluster administration permissions through a group, you must include the --as=<user> --as-group=<group1> --as-group=<group2> parameters in the command to impersonate the associated groups.
Procedure
To grant a user permission to impersonate a
system:adminby impersonating the associated cluster administration groups, run the following command:oc create clusterrolebinding <any_valid_name> --clusterrole=sudoer --as=<user> \ --as-group=<group1> --as-group=<group2>
$ oc create clusterrolebinding <any_valid_name> --clusterrole=sudoer --as=<user> \ --as-group=<group1> --as-group=<group2>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 18. Syncing LDAP groups
As an administrator, you can use groups to manage users, change their permissions, and enhance collaboration. Your organization may have already created user groups and stored them in an LDAP server. OpenShift Container Platform can sync those LDAP records with internal OpenShift Container Platform records, enabling you to manage your groups in one place. OpenShift Container Platform currently supports group sync with LDAP servers using three common schemas for defining group membership: RFC 2307, Active Directory, and augmented Active Directory.
For more information on configuring LDAP, see Configuring an LDAP identity provider.
You must have cluster-admin privileges to sync groups.
18.1. About configuring LDAP sync
Before you can run LDAP sync, you need a sync configuration file. This file contains the following LDAP client configuration details:
- Configuration for connecting to your LDAP server.
- Sync configuration options that are dependent on the schema used in your LDAP server.
- An administrator-defined list of name mappings that maps OpenShift Container Platform group names to groups in your LDAP server.
The format of the configuration file depends upon the schema you are using: RFC 2307, Active Directory, or augmented Active Directory.
- LDAP client configuration
- The LDAP client configuration section of the configuration defines the connections to your LDAP server.
The LDAP client configuration section of the configuration defines the connections to your LDAP server.
LDAP client configuration
url: ldap://10.0.0.0:389 bindDN: cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com bindPassword: password insecure: false ca: my-ldap-ca-bundle.crt
url: ldap://10.0.0.0:389
bindDN: cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com
bindPassword: password
insecure: false
ca: my-ldap-ca-bundle.crt - 1
- The connection protocol, IP address of the LDAP server hosting your database, and the port to connect to, formatted as
scheme://host:port. - 2
- Optional distinguished name (DN) to use as the Bind DN. OpenShift Container Platform uses this if elevated privilege is required to retrieve entries for the sync operation.
- 3
- Optional password to use to bind. OpenShift Container Platform uses this if elevated privilege is necessary to retrieve entries for the sync operation. This value may also be provided in an environment variable, external file, or encrypted file.
- 4
- When
false, secure LDAP (ldaps://) URLs connect using TLS, and insecure LDAP (ldap://) URLs are upgraded to TLS. Whentrue, no TLS connection is made to the server unless you specify anldaps://URL, in which case URLs still attempt to connect by using TLS. - 5
- The certificate bundle to use for validating server certificates for the configured URL. If empty, OpenShift Container Platform uses system-trusted roots. This only applies if
insecureis set tofalse.
- LDAP query definition
- Sync configurations consist of LDAP query definitions for the entries that are required for synchronization. The specific definition of an LDAP query depends on the schema used to store membership information in the LDAP server.
LDAP query definition
- 1
- The distinguished name (DN) of the branch of the directory where all searches will start from. It is required that you specify the top of your directory tree, but you can also specify a subtree in the directory.
- 2
- The scope of the search. Valid values are
base,one, orsub. If this is left undefined, then a scope ofsubis assumed. Descriptions of the scope options can be found in the table below. - 3
- The behavior of the search with respect to aliases in the LDAP tree. Valid values are
never,search,base, oralways. If this is left undefined, then the default is toalwaysdereference aliases. Descriptions of the dereferencing behaviors can be found in the table below. - 4
- The time limit allowed for the search by the client, in seconds. A value of
0imposes no client-side limit. - 5
- A valid LDAP search filter. If this is left undefined, then the default is
(objectClass=*). - 6
- The optional maximum size of response pages from the server, measured in LDAP entries. If set to
0, no size restrictions will be made on pages of responses. Setting paging sizes is necessary when queries return more entries than the client or server allow by default.
| LDAP search scope | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Only consider the object specified by the base DN given for the query. |
|
| Consider all of the objects on the same level in the tree as the base DN for the query. |
|
| Consider the entire subtree rooted at the base DN given for the query. |
| Dereferencing behavior | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Never dereference any aliases found in the LDAP tree. |
|
| Only dereference aliases found while searching. |
|
| Only dereference aliases while finding the base object. |
|
| Always dereference all aliases found in the LDAP tree. |
- User-defined name mapping
- A user-defined name mapping explicitly maps the names of OpenShift Container Platform groups to unique identifiers that find groups on your LDAP server. The mapping uses normal YAML syntax. A user-defined mapping can contain an entry for every group in your LDAP server or only a subset of those groups. If there are groups on the LDAP server that do not have a user-defined name mapping, the default behavior during sync is to use the attribute specified as the OpenShift Container Platform group’s name.
User-defined name mapping
groupUIDNameMapping: "cn=group1,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com": firstgroup "cn=group2,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com": secondgroup "cn=group3,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com": thirdgroup
groupUIDNameMapping:
"cn=group1,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com": firstgroup
"cn=group2,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com": secondgroup
"cn=group3,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com": thirdgroup18.1.1. About the RFC 2307 configuration file
The RFC 2307 schema requires you to provide an LDAP query definition for both user and group entries, as well as the attributes with which to represent them in the internal OpenShift Container Platform records.
For clarity, the group you create in OpenShift Container Platform should use attributes other than the distinguished name whenever possible for user- or administrator-facing fields. For example, identify the users of an OpenShift Container Platform group by their e-mail, and use the name of the group as the common name. The following configuration file creates these relationships:
If using user-defined name mappings, your configuration file will differ.
LDAP sync configuration that uses RFC 2307 schema: rfc2307_config.yaml
- 1
- The IP address and host of the LDAP server where this group’s record is stored.
- 2
- When
false, secure LDAP (ldaps://) URLs connect using TLS, and insecure LDAP (ldap://) URLs are upgraded to TLS. Whentrue, no TLS connection is made to the server unless you specify anldaps://URL, in which case URLs still attempt to connect by using TLS. - 3
- The attribute that uniquely identifies a group on the LDAP server. You cannot specify
groupsQueryfilters when using DN forgroupUIDAttribute. For fine-grained filtering, use the whitelist / blacklist method. - 4
- The attribute to use as the name of the group.
- 5
- The attribute on the group that stores the membership information.
- 6
- The attribute that uniquely identifies a user on the LDAP server. You cannot specify
usersQueryfilters when using DN for userUIDAttribute. For fine-grained filtering, use the whitelist / blacklist method. - 7
- The attribute to use as the name of the user in the OpenShift Container Platform group record.
18.1.2. About the Active Directory configuration file
The Active Directory schema requires you to provide an LDAP query definition for user entries, as well as the attributes to represent them with in the internal OpenShift Container Platform group records.
For clarity, the group you create in OpenShift Container Platform should use attributes other than the distinguished name whenever possible for user- or administrator-facing fields. For example, identify the users of an OpenShift Container Platform group by their e-mail, but define the name of the group by the name of the group on the LDAP server. The following configuration file creates these relationships:
LDAP sync configuration that uses Active Directory schema: active_directory_config.yaml
18.1.3. About the augmented Active Directory configuration file
The augmented Active Directory schema requires you to provide an LDAP query definition for both user entries and group entries, as well as the attributes with which to represent them in the internal OpenShift Container Platform group records.
For clarity, the group you create in OpenShift Container Platform should use attributes other than the distinguished name whenever possible for user- or administrator-facing fields. For example, identify the users of an OpenShift Container Platform group by their e-mail, and use the name of the group as the common name. The following configuration file creates these relationships.
LDAP sync configuration that uses augmented Active Directory schema: augmented_active_directory_config.yaml
- 1
- The attribute that uniquely identifies a group on the LDAP server. You cannot specify
groupsQueryfilters when using DN for groupUIDAttribute. For fine-grained filtering, use the whitelist / blacklist method. - 2
- The attribute to use as the name of the group.
- 3
- The attribute to use as the name of the user in the OpenShift Container Platform group record.
- 4
- The attribute on the user that stores the membership information.
18.2. Running LDAP sync
Once you have created a sync configuration file, you can begin to sync. OpenShift Container Platform allows administrators to perform a number of different sync types with the same server.
18.2.1. Syncing the LDAP server with OpenShift Container Platform
You can sync all groups from the LDAP server with OpenShift Container Platform.
Prerequisites
- Create a sync configuration file.
Procedure
To sync all groups from the LDAP server with OpenShift Container Platform:
oc adm groups sync --sync-config=config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --sync-config=config.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, all group synchronization operations are dry-run, so you must set the
--confirmflag on theoc adm groups synccommand in order to make changes to OpenShift Container Platform group records.
18.2.2. Syncing OpenShift Container Platform groups with the LDAP server
You can sync all groups already in OpenShift Container Platform that correspond to groups in the LDAP server specified in the configuration file.
Prerequisites
- Create a sync configuration file.
Procedure
To sync OpenShift Container Platform groups with the LDAP server:
oc adm groups sync --type=openshift --sync-config=config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --type=openshift --sync-config=config.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, all group synchronization operations are dry-run, so you must set the
--confirmflag on theoc adm groups synccommand in order to make changes to OpenShift Container Platform group records.
18.2.3. Syncing subgroups from the LDAP server with OpenShift Container Platform
You can sync a subset of LDAP groups with OpenShift Container Platform using whitelist files, blacklist files, or both.
You can use any combination of blacklist files, whitelist files, or whitelist literals. Whitelist and blacklist files must contain one unique group identifier per line, and you can include whitelist literals directly in the command itself. These guidelines apply to groups found on LDAP servers as well as groups already present in OpenShift Container Platform.
Prerequisite
- Create a sync configuration file.
Procedure
To sync a subset of LDAP groups with OpenShift Container Platform, use any the following commands:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteBy default, all group synchronization operations are dry-run, so you must set the
--confirmflag on theoc adm groups synccommand in order to make changes to OpenShift Container Platform group records.
18.3. Running a group pruning job
An administrator can also choose to remove groups from OpenShift Container Platform records if the records on the LDAP server that created them are no longer present. The prune job will accept the same sync configuration file and whitelists or blacklists as used for the sync job.
For example:
oc adm prune groups --sync-config=/path/to/ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm oc adm prune groups --whitelist=/path/to/whitelist.txt --sync-config=/path/to/ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm oc adm prune groups --blacklist=/path/to/blacklist.txt --sync-config=/path/to/ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm prune groups --sync-config=/path/to/ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm prune groups --whitelist=/path/to/whitelist.txt --sync-config=/path/to/ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm prune groups --blacklist=/path/to/blacklist.txt --sync-config=/path/to/ldap-sync-config.yaml --confirm18.4. LDAP group sync examples
This section contains examples for the RFC 2307, Active Directory, and augmented Active Directory schemas.
These examples assume that all users are direct members of their respective groups. Specifically, no groups have other groups as members. See the Nested Membership Sync Example for information on how to sync nested groups.
18.4.1. Syncing groups using the RFC 2307 schema
For the RFC 2307 schema, the following examples synchronize a group named admins that has two members: Jane and Jim. The examples explain:
- How the group and users are added to the LDAP server.
- What the resulting group record in OpenShift Container Platform will be after synchronization.
These examples assume that all users are direct members of their respective groups. Specifically, no groups have other groups as members. See the Nested Membership Sync Example for information on how to sync nested groups.
In the RFC 2307 schema, both users (Jane and Jim) and groups exist on the LDAP server as first-class entries, and group membership is stored in attributes on the group. The following snippet of ldif defines the users and group for this schema:
LDAP entries that use RFC 2307 schema: rfc2307.ldif
Prerequisites
- Create the configuration file.
Procedure
Run the sync with the
rfc2307_config.yamlfile:oc adm groups sync --sync-config=rfc2307_config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --sync-config=rfc2307_config.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform creates the following group record as a result of the above sync operation:
OpenShift Container Platform group created by using the
rfc2307_config.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The last time this OpenShift Container Platform group was synchronized with the LDAP server, in ISO 6801 format.
- 2
- The unique identifier for the group on the LDAP server.
- 3
- The IP address and host of the LDAP server where this group’s record is stored.
- 4
- The name of the group as specified by the sync file.
- 5
- The users that are members of the group, named as specified by the sync file.
18.4.2. Syncing groups using the RFC2307 schema with user-defined name mappings
When syncing groups with user-defined name mappings, the configuration file changes to contain these mappings as shown below.
LDAP sync configuration that uses RFC 2307 schema with user-defined name mappings: rfc2307_config_user_defined.yaml
- 1
- The user-defined name mapping.
- 2
- The unique identifier attribute that is used for the keys in the user-defined name mapping. You cannot specify
groupsQueryfilters when using DN for groupUIDAttribute. For fine-grained filtering, use the whitelist / blacklist method. - 3
- The attribute to name OpenShift Container Platform groups with if their unique identifier is not in the user-defined name mapping.
- 4
- The attribute that uniquely identifies a user on the LDAP server. You cannot specify
usersQueryfilters when using DN for userUIDAttribute. For fine-grained filtering, use the whitelist / blacklist method.
Prerequisites
- Create the configuration file.
Procedure
Run the sync with the
rfc2307_config_user_defined.yamlfile:oc adm groups sync --sync-config=rfc2307_config_user_defined.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --sync-config=rfc2307_config_user_defined.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform creates the following group record as a result of the above sync operation:
OpenShift Container Platform group created by using the
rfc2307_config_user_defined.yamlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The name of the group as specified by the user-defined name mapping.
18.4.3. Syncing groups using RFC 2307 with user-defined error tolerances
By default, if the groups being synced contain members whose entries are outside of the scope defined in the member query, the group sync fails with an error:
Error determining LDAP group membership for "<group>": membership lookup for user "<user>" in group "<group>" failed because of "search for entry with dn="<user-dn>" would search outside of the base dn specified (dn="<base-dn>")".
Error determining LDAP group membership for "<group>": membership lookup for user "<user>" in group "<group>" failed because of "search for entry with dn="<user-dn>" would search outside of the base dn specified (dn="<base-dn>")".
This often indicates a misconfigured baseDN in the usersQuery field. However, in cases where the baseDN intentionally does not contain some of the members of the group, setting tolerateMemberOutOfScopeErrors: true allows the group sync to continue. Out of scope members will be ignored.
Similarly, when the group sync process fails to locate a member for a group, it fails outright with errors:
Error determining LDAP group membership for "<group>": membership lookup for user "<user>" in group "<group>" failed because of "search for entry with base dn="<user-dn>" refers to a non-existent entry". Error determining LDAP group membership for "<group>": membership lookup for user "<user>" in group "<group>" failed because of "search for entry with base dn="<user-dn>" and filter "<filter>" did not return any results".
Error determining LDAP group membership for "<group>": membership lookup for user "<user>" in group "<group>" failed because of "search for entry with base dn="<user-dn>" refers to a non-existent entry".
Error determining LDAP group membership for "<group>": membership lookup for user "<user>" in group "<group>" failed because of "search for entry with base dn="<user-dn>" and filter "<filter>" did not return any results".
This often indicates a misconfigured usersQuery field. However, in cases where the group contains member entries that are known to be missing, setting tolerateMemberNotFoundErrors: true allows the group sync to continue. Problematic members will be ignored.
Enabling error tolerances for the LDAP group sync causes the sync process to ignore problematic member entries. If the LDAP group sync is not configured correctly, this could result in synced OpenShift Container Platform groups missing members.
LDAP entries that use RFC 2307 schema with problematic group membership: rfc2307_problematic_users.ldif
In order to tolerate the errors in the above example, the following additions to your sync configuration file must be made:
LDAP sync configuration that uses RFC 2307 schema tolerating errors: rfc2307_config_tolerating.yaml
- 1
- The attribute that uniquely identifies a user on the LDAP server. You cannot specify
usersQueryfilters when using DN for userUIDAttribute. For fine-grained filtering, use the whitelist / blacklist method. - 2
- When
true, the sync job tolerates groups for which some members were not found, and members whose LDAP entries are not found are ignored. The default behavior for the sync job is to fail if a member of a group is not found. - 3
- When
true, the sync job tolerates groups for which some members are outside the user scope given in theusersQuerybase DN, and members outside the member query scope are ignored. The default behavior for the sync job is to fail if a member of a group is out of scope.
Prerequisites
- Create the configuration file.
Procedure
Run the sync with the rfc2307_config_tolerating.yaml file:
oc adm groups sync --sync-config=rfc2307_config_tolerating.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --sync-config=rfc2307_config_tolerating.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform creates the following group record as a result of the above sync operation:
OpenShift Container Platform group created by using the rfc2307_config.yaml file
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The users that are members of the group, as specified by the sync file. Members for which lookup encountered tolerated errors are absent.
18.4.4. Syncing groups using the Active Directory schema
In the Active Directory schema, both users (Jane and Jim) exist in the LDAP server as first-class entries, and group membership is stored in attributes on the user. The following snippet of ldif defines the users and group for this schema:
LDAP entries that use Active Directory schema: active_directory.ldif
- 1
- The user’s group memberships are listed as attributes on the user, and the group does not exist as an entry on the server. The
memberOfattribute does not have to be a literal attribute on the user; in some LDAP servers, it is created during search and returned to the client, but not committed to the database.
Prerequisites
- Create the configuration file.
Procedure
Run the sync with the active_directory_config.yaml file:
oc adm groups sync --sync-config=active_directory_config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --sync-config=active_directory_config.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform creates the following group record as a result of the above sync operation:
OpenShift Container Platform group created by using the active_directory_config.yaml file
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The last time this OpenShift Container Platform group was synchronized with the LDAP server, in ISO 6801 format.
- 2
- The unique identifier for the group on the LDAP server.
- 3
- The IP address and host of the LDAP server where this group’s record is stored.
- 4
- The name of the group as listed in the LDAP server.
- 5
- The users that are members of the group, named as specified by the sync file.
18.4.5. Syncing groups using the augmented Active Directory schema
In the augmented Active Directory schema, both users (Jane and Jim) and groups exist in the LDAP server as first-class entries, and group membership is stored in attributes on the user. The following snippet of ldif defines the users and group for this schema:
LDAP entries that use augmented Active Directory schema: augmented_active_directory.ldif
Prerequisites
- Create the configuration file.
Procedure
Run the sync with the augmented_active_directory_config.yaml file:
oc adm groups sync --sync-config=augmented_active_directory_config.yaml --confirm
$ oc adm groups sync --sync-config=augmented_active_directory_config.yaml --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow OpenShift Container Platform creates the following group record as a result of the above sync operation:
OpenShift group created by using the augmented_active_directory_config.yaml file
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The last time this OpenShift Container Platform group was synchronized with the LDAP server, in ISO 6801 format.
- 2
- The unique identifier for the group on the LDAP server.
- 3
- The IP address and host of the LDAP server where this group’s record is stored.
- 4
- The name of the group as specified by the sync file.
- 5
- The users that are members of the group, named as specified by the sync file.
18.4.5.1. LDAP nested membership sync example
Groups in OpenShift Container Platform do not nest. The LDAP server must flatten group membership before the data can be consumed. Microsoft’s Active Directory Server supports this feature via the LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_IN_CHAIN rule, which has the OID 1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941. Furthermore, only explicitly whitelisted groups can be synced when using this matching rule.
This section has an example for the augmented Active Directory schema, which synchronizes a group named admins that has one user Jane and one group otheradmins as members. The otheradmins group has one user member: Jim. This example explains:
- How the group and users are added to the LDAP server.
- What the LDAP sync configuration file looks like.
- What the resulting group record in OpenShift Container Platform will be after synchronization.
In the augmented Active Directory schema, both users (Jane and Jim) and groups exist in the LDAP server as first-class entries, and group membership is stored in attributes on the user or the group. The following snippet of ldif defines the users and groups for this schema:
LDAP entries that use augmented Active Directory schema with nested members: augmented_active_directory_nested.ldif
When syncing nested groups with Active Directory, you must provide an LDAP query definition for both user entries and group entries, as well as the attributes with which to represent them in the internal OpenShift Container Platform group records. Furthermore, certain changes are required in this configuration:
-
The
oc adm groups synccommand must explicitly whitelist groups. -
The user’s
groupMembershipAttributesmust include"memberOf:1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941:"to comply with theLDAP_MATCHING_RULE_IN_CHAINrule. -
The
groupUIDAttributemust be set todn. The
groupsQuery:-
Must not set
filter. -
Must set a valid
derefAliases. -
Should not set
baseDNas that value is ignored. -
Should not set
scopeas that value is ignored.
-
Must not set
For clarity, the group you create in OpenShift Container Platform should use attributes other than the distinguished name whenever possible for user- or administrator-facing fields. For example, identify the users of an OpenShift Container Platform group by their e-mail, and use the name of the group as the common name. The following configuration file creates these relationships:
LDAP sync configuration that uses augmented Active Directory schema with nested members: augmented_active_directory_config_nested.yaml
- 1
groupsQueryfilters cannot be specified. ThegroupsQuerybase DN and scope values are ignored.groupsQuerymust set a validderefAliases.- 2
- The attribute that uniquely identifies a group on the LDAP server. It must be set to
dn. - 3
- The attribute to use as the name of the group.
- 4
- The attribute to use as the name of the user in the OpenShift Container Platform group record.
mailorsAMAccountNameare preferred choices in most installations. - 5
- The attribute on the user that stores the membership information. Note the use of
LDAP_MATCHING_RULE_IN_CHAIN.
Prerequisites
- Create the configuration file.
Procedure
Run the sync with the augmented_active_directory_config_nested.yaml file:
oc adm groups sync \ 'cn=admins,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com' \ --sync-config=augmented_active_directory_config_nested.yaml \ --confirm$ oc adm groups sync \ 'cn=admins,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com' \ --sync-config=augmented_active_directory_config_nested.yaml \ --confirmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou must explicitly whitelist the
cn=admins,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=comgroup.OpenShift Container Platform creates the following group record as a result of the above sync operation:
OpenShift group created by using the augmented_active_directory_config_nested.yaml file
- 1
- The last time this OpenShift Container Platform group was synchronized with the LDAP server, in ISO 6801 format.
- 2
- The unique identifier for the group on the LDAP server.
- 3
- The IP address and host of the LDAP server where this group’s record is stored.
- 4
- The name of the group as specified by the sync file.
- 5
- The users that are members of the group, named as specified by the sync file. Note that members of nested groups are included since the group membership was flattened by the Microsoft Active Directory Server.
18.5. LDAP sync configuration specification
The object specification for the configuration file is below. Note that the different schema objects have different fields. For example, v1.ActiveDirectoryConfig has no groupsQuery field whereas v1.RFC2307Config and v1.AugmentedActiveDirectoryConfig both do.
There is no support for binary attributes. All attribute data coming from the LDAP server must be in the format of a UTF-8 encoded string. For example, never use a binary attribute, such as objectGUID, as an ID attribute. You must use string attributes, such as sAMAccountName or userPrincipalName, instead.
18.5.1. v1.LDAPSyncConfig
LDAPSyncConfig holds the necessary configuration options to define an LDAP group sync.
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
|
| String value representing the REST resource this object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds | string |
|
| Defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources | string |
|
|
Host is the scheme, host and port of the LDAP server to connect to: | string |
|
| Optional DN to bind to the LDAP server with. | string |
|
| Optional password to bind with during the search phase. | v1.StringSource |
|
|
If | boolean |
|
| Optional trusted certificate authority bundle to use when making requests to the server. If empty, the default system roots are used. | string |
|
| Optional direct mapping of LDAP group UIDs to OpenShift Container Platform group names. | object |
|
| Holds the configuration for extracting data from an LDAP server set up in a fashion similar to RFC2307: first-class group and user entries, with group membership determined by a multi-valued attribute on the group entry listing its members. | v1.RFC2307Config |
|
| Holds the configuration for extracting data from an LDAP server set up in a fashion similar to that used in Active Directory: first-class user entries, with group membership determined by a multi-valued attribute on members listing groups they are a member of. | v1.ActiveDirectoryConfig |
|
| Holds the configuration for extracting data from an LDAP server set up in a fashion similar to that used in Active Directory as described above, with one addition: first-class group entries exist and are used to hold metadata but not group membership. | v1.AugmentedActiveDirectoryConfig |
18.5.2. v1.StringSource
StringSource allows specifying a string inline, or externally via environment variable or file. When it contains only a string value, it marshals to a simple JSON string.
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the cleartext value, or an encrypted value if | string |
|
|
Specifies an environment variable containing the cleartext value, or an encrypted value if the | string |
|
|
References a file containing the cleartext value, or an encrypted value if a | string |
|
| References a file containing the key to use to decrypt the value. | string |
18.5.3. v1.LDAPQuery
LDAPQuery holds the options necessary to build an LDAP query.
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
|
| DN of the branch of the directory where all searches should start from. | string |
|
|
The optional scope of the search. Can be | string |
|
|
The optional behavior of the search with regards to alisases. Can be | string |
|
|
Holds the limit of time in seconds that any request to the server can remain outstanding before the wait for a response is given up. If this is | integer |
|
| A valid LDAP search filter that retrieves all relevant entries from the LDAP server with the base DN. | string |
|
|
Maximum preferred page size, measured in LDAP entries. A page size of | integer |
18.5.4. v1.RFC2307Config
RFC2307Config holds the necessary configuration options to define how an LDAP group sync interacts with an LDAP server using the RFC2307 schema.
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
|
| Holds the template for an LDAP query that returns group entries. | v1.LDAPQuery |
|
|
Defines which attribute on an LDAP group entry will be interpreted as its unique identifier. ( | string |
|
| Defines which attributes on an LDAP group entry will be interpreted as its name to use for an OpenShift Container Platform group. | string array |
|
|
Defines which attributes on an LDAP group entry will be interpreted as its members. The values contained in those attributes must be queryable by your | string array |
|
| Holds the template for an LDAP query that returns user entries. | v1.LDAPQuery |
|
|
Defines which attribute on an LDAP user entry will be interpreted as its unique identifier. It must correspond to values that will be found from the | string |
|
|
Defines which attributes on an LDAP user entry will be used, in order, as its OpenShift Container Platform user name. The first attribute with a non-empty value is used. This should match your | string array |
|
|
Determines the behavior of the LDAP sync job when missing user entries are encountered. If | boolean |
|
|
Determines the behavior of the LDAP sync job when out-of-scope user entries are encountered. If | boolean |
18.5.5. v1.ActiveDirectoryConfig
ActiveDirectoryConfig holds the necessary configuration options to define how an LDAP group sync interacts with an LDAP server using the Active Directory schema.
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
|
| Holds the template for an LDAP query that returns user entries. | v1.LDAPQuery |
|
|
Defines which attributes on an LDAP user entry will be interpreted as its OpenShift Container Platform user name. The attribute to use as the name of the user in the OpenShift Container Platform group record. | string array |
|
| Defines which attributes on an LDAP user entry will be interpreted as the groups it is a member of. | string array |
18.5.6. v1.AugmentedActiveDirectoryConfig
AugmentedActiveDirectoryConfig holds the necessary configuration options to define how an LDAP group sync interacts with an LDAP server using the augmented Active Directory schema.
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
|
| Holds the template for an LDAP query that returns user entries. | v1.LDAPQuery |
|
|
Defines which attributes on an LDAP user entry will be interpreted as its OpenShift Container Platform user name. The attribute to use as the name of the user in the OpenShift Container Platform group record. | string array |
|
| Defines which attributes on an LDAP user entry will be interpreted as the groups it is a member of. | string array |
|
| Holds the template for an LDAP query that returns group entries. | v1.LDAPQuery |
|
|
Defines which attribute on an LDAP group entry will be interpreted as its unique identifier. ( | string |
|
| Defines which attributes on an LDAP group entry will be interpreted as its name to use for an OpenShift Container Platform group. | string array |
Chapter 19. Allowing JavaScript-based access to the API server from additional hosts
19.1. Allowing JavaScript-based access to the API server from additional hosts
The default OpenShift Container Platform configuration only allows the OpenShift web console to send requests to the API server.
If you need to access the API server or OAuth server from a JavaScript application using a different host name, you can configure additional host names to allow.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Edit the API servers resource:
oc edit apiserver.config.openshift.io cluster
$ oc edit apiserver.config.openshift.io clusterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
additionalCORSAllowedOriginsfield under thespecsection and specify one or more additional host names:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The host name is specified as a Golang regular expression that matches against CORS headers from HTTP requests against the API server and OAuth server.
NoteThis example uses the following syntax:
-
The
(?i)makes it case-insensitive. -
The
//pins to the beginning of the domain and matches the double slash followinghttp:orhttps:. -
The
\.escapes dots in the domain name. -
The
(:|\z)matches the end of the domain name(\z)or a port separator(:).
- Save the file to apply the changes.
Chapter 20. Encrypting etcd data
20.1. About etcd encryption
By default, etcd data is not encrypted in OpenShift Container Platform. You can enable etcd encryption for your cluster to provide an additional layer of data security. For example, it can help protect the loss of sensitive data if an etcd backup is exposed to the incorrect parties.
When you enable etcd encryption, the following OpenShift API server and Kubernetes API server resources are encrypted:
- Secrets
- ConfigMaps
- Routes
- OAuth access tokens
- OAuth authorize tokens
When you enable etcd encryption, encryption keys are created. These keys are rotated on a weekly basis. You must have these keys in order to restore from an etcd backup.
20.2. Enabling etcd encryption
You can enable etcd encryption to encrypt sensitive resources in your cluster.
It is not recommended to take a backup of etcd until the initial encryption process is complete. If the encryption process has not completed, the backup might be only partially encrypted.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Modify the API server object:
oc edit apiserver
$ oc edit apiserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
encryptionfield type toaescbc:spec: encryption: type: aescbcspec: encryption: type: aescbc1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
aescbctype means that AES-CBC with PKCS#7 padding and a 32 byte key is used to perform the encryption.
Save the file to apply the changes.
The encryption process starts. It can take 20 minutes or longer for this process to complete, depending on the size of your cluster.
Verify that etcd encryption was successful.
Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the OpenShift API server to verify that its resources were successfully encrypted:oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
EncryptionCompletedupon successful encryption:EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: routes.route.openshift.io, oauthaccesstokens.oauth.openshift.io, oauthauthorizetokens.oauth.openshift.io
EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: routes.route.openshift.io, oauthaccesstokens.oauth.openshift.io, oauthauthorizetokens.oauth.openshift.ioCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
EncryptionInProgress, this means that encryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the Kubernetes API server to verify that its resources were successfully encrypted:oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
EncryptionCompletedupon successful encryption:EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: secrets, configmaps
EncryptionCompleted All resources encrypted: secrets, configmapsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
EncryptionInProgress, this means that encryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.
20.3. Disabling etcd encryption
You can disable encryption of etcd data in your cluster.
Prerequisites
-
Access to the cluster as a user with the
cluster-adminrole.
Procedure
Modify the API server object:
oc edit apiserver
$ oc edit apiserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
encryptionfield type toidentity:spec: encryption: type: identityspec: encryption: type: identity1 Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - 1
- The
identitytype is the default value and means that no encryption is performed.
Save the file to apply the changes.
The decryption process starts. It can take 20 minutes or longer for this process to complete, depending on the size of your cluster.
Verify that etcd decryption was successful.
Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the OpenShift API server to verify that its resources were successfully decrypted:oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
DecryptionCompletedupon successful decryption:DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decrypted
DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decryptedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
DecryptionInProgress, this means that decryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.Review the
Encryptedstatus condition for the Kubernetes API server to verify that its resources were successfully decrypted:oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'$ oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output shows
DecryptionCompletedupon successful decryption:DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decrypted
DecryptionCompleted Encryption mode set to identity and everything is decryptedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the output shows
DecryptionInProgress, this means that decryption is still in progress. Wait a few minutes and try again.
Legal Notice
Copyright © Red Hat
OpenShift documentation is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
Modified versions must remove all Red Hat trademarks.
Portions adapted from https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/service-catalog/ with modifications by Red Hat.
Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Red Hat logo, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, OpenShift, Fedora, the Infinity logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries.
Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries.
MySQL® is a registered trademark of MySQL AB in the United States, the European Union and other countries.
Node.js® is an official trademark of the OpenJS Foundation.
The OpenStack® Word Mark and OpenStack logo are either registered trademarks/service marks or trademarks/service marks of the OpenStack Foundation, in the United States and other countries and are used with the OpenStack Foundation’s permission. We are not affiliated with, endorsed or sponsored by the OpenStack Foundation, or the OpenStack community.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.