Chapter 1. Overview of AMQ Streams
AMQ Streams simplifies the process of running Apache Kafka in an OpenShift cluster.
This guide provides instructions for evaluating a working environment of AMQ Streams. The steps describe how to get a AMQ Streams deployment up-and-running as quickly as possible.
Before trying AMQ Streams, it is useful to understand its capabilities and how you might wish to use it. This chapter introduces some of the key concepts behind Kafka, and also provides a brief overview of the AMQ Streams Operators.
Operators are a method of packaging, deploying, and managing an OpenShift application. AMQ Streams Operators extend OpenShift functionality, automating common and complex tasks related to a Kafka deployment. By implementing knowledge of Kafka operations in code, Kafka administration tasks are simplified and require less manual intervention.
1.1. Kafka capabilities
The underlying data stream-processing capabilities and component architecture of Kafka can deliver:
- Microservices and other applications to share data with extremely high throughput and low latency
- Message ordering guarantees
- Message rewind/replay from data storage to reconstruct an application state
- Message compaction to remove old records when using a key-value log
- Horizontal scalability in a cluster configuration
- Replication of data to control fault tolerance
- Retention of high volumes of data for immediate access
1.2. Kafka use cases
Kafka’s capabilities make it suitable for:
- Event-driven architectures
- Event sourcing to capture changes to the state of an application as a log of events
- Message brokering
- Website activity tracking
- Operational monitoring through metrics
- Log collection and aggregation
- Commit logs for distributed systems
- Stream processing so that applications can respond to data in real time
1.3. How AMQ Streams supports Kafka
AMQ Streams provides container images and Operators for running Kafka on OpenShift. AMQ Streams Operators are fundamental to the running of AMQ Streams. The Operators provided with AMQ Streams are purpose-built with specialist operational knowledge to effectively manage Kafka.
Operators simplify the process of:
- Deploying and running Kafka clusters
- Deploying and running Kafka components
- Configuring access to Kafka
- Securing access to Kafka
- Upgrading Kafka
- Managing brokers
- Creating and managing topics
- Creating and managing users
1.4. Operators
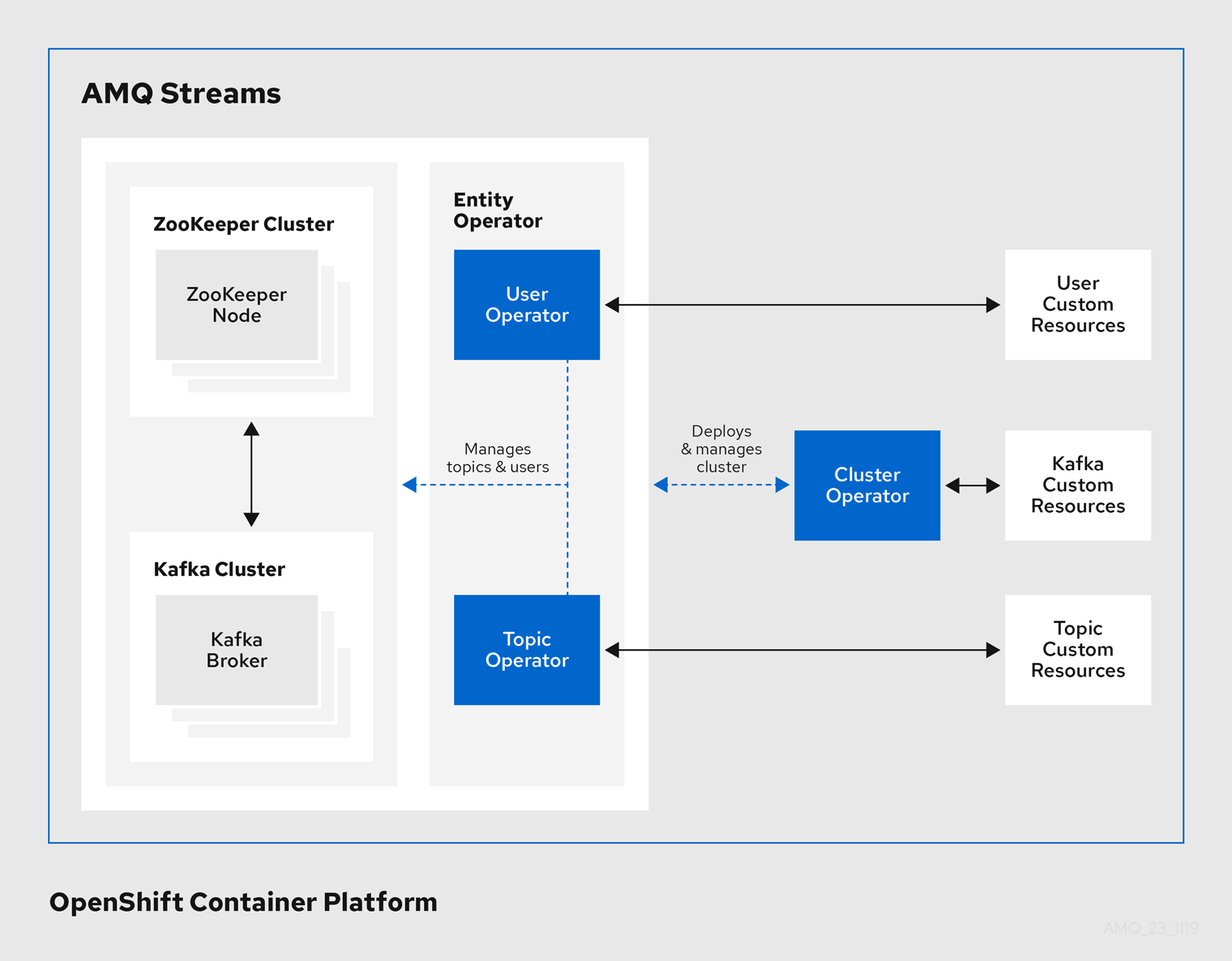
AMQ Streams provides Operators for managing a Kafka cluster running within an OpenShift cluster.
- Cluster Operator
- Deploys and manages Apache Kafka clusters, Kafka Connect, Kafka MirrorMaker, Kafka Bridge, Kafka Exporter, and the Entity Operator
- Entity Operator
- Comprises the Topic Operator and User Operator
- Topic Operator
- Manages Kafka topics
- User Operator
- Manages Kafka users
The Cluster Operator can deploy the Topic Operator and User Operator as part of an Entity Operator configuration at the same time as a Kafka cluster.
Operators within the AMQ Streams architecture
1.5. Document Conventions
Replaceables
In this document, replaceable text is styled in monospace, with italics, uppercase, and hyphens.
For example, in the following code, you will want to replace MY-NAMESPACE with the name of your namespace:
sed -i 's/namespace: .*/namespace: MY-NAMESPACE/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yaml
sed -i 's/namespace: .*/namespace: MY-NAMESPACE/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yaml