Chapter 1. Firewall policy management with Ansible security automation
As a security operator, you can use Ansible security automation to manage multiple firewall policies. Create and delete firewall rules to block or unblock a source IP address from accessing a destination IP address.
1.1. About firewall policy management
An organization’s network firewall is the first line of defense against an attack and a vital component for maintaining a secure environment. As a security operator, you construct and manage secure networks to ensure that your firewall only allows inbound and outbound network traffic defined by your organization’s firewall policies. A firewall policy consists of security rules that protect the network against harmful incoming and outgoing traffic.
Managing multiple firewall rules across various products and vendors can be both challenging and time consuming for security teams. Manual workflow processes that involve complex tasks can result in errors and ultimately cause delays in investigating an application’s suspicious behavior or stopping an ongoing attack on a server. When every solution in a security portfolio is automated through the same language, both security analysts and operators can perform a series of actions across various products in a fraction of the time. This automated process maximizes the overall efficiency of the security team.
Ansible security automation interacts with a wide variety of security technologies from a range of vendors. Ansible enables security teams to manage different products, interfaces, and workflows in a unified way to produce a successful deployment. For example, your security team can automate tasks such as blocking and unblocking IP and URLs on supported technologies such as enterprise firewalls.
1.2. Automate firewall rules
Ansible security automation enables you to automate various firewall policies that require a series of actions across various products. You can use an Ansible role, such as the acl_manager role to manage your Access Control Lists (ACLs) for many firewall devices such as blocking or unblocking an IP or URL. Roles let you automatically load related vars, files, tasks, handlers, and other Ansible artifacts based on a known file structure. After you group your content in roles, you can easily reuse them and share them with other users.
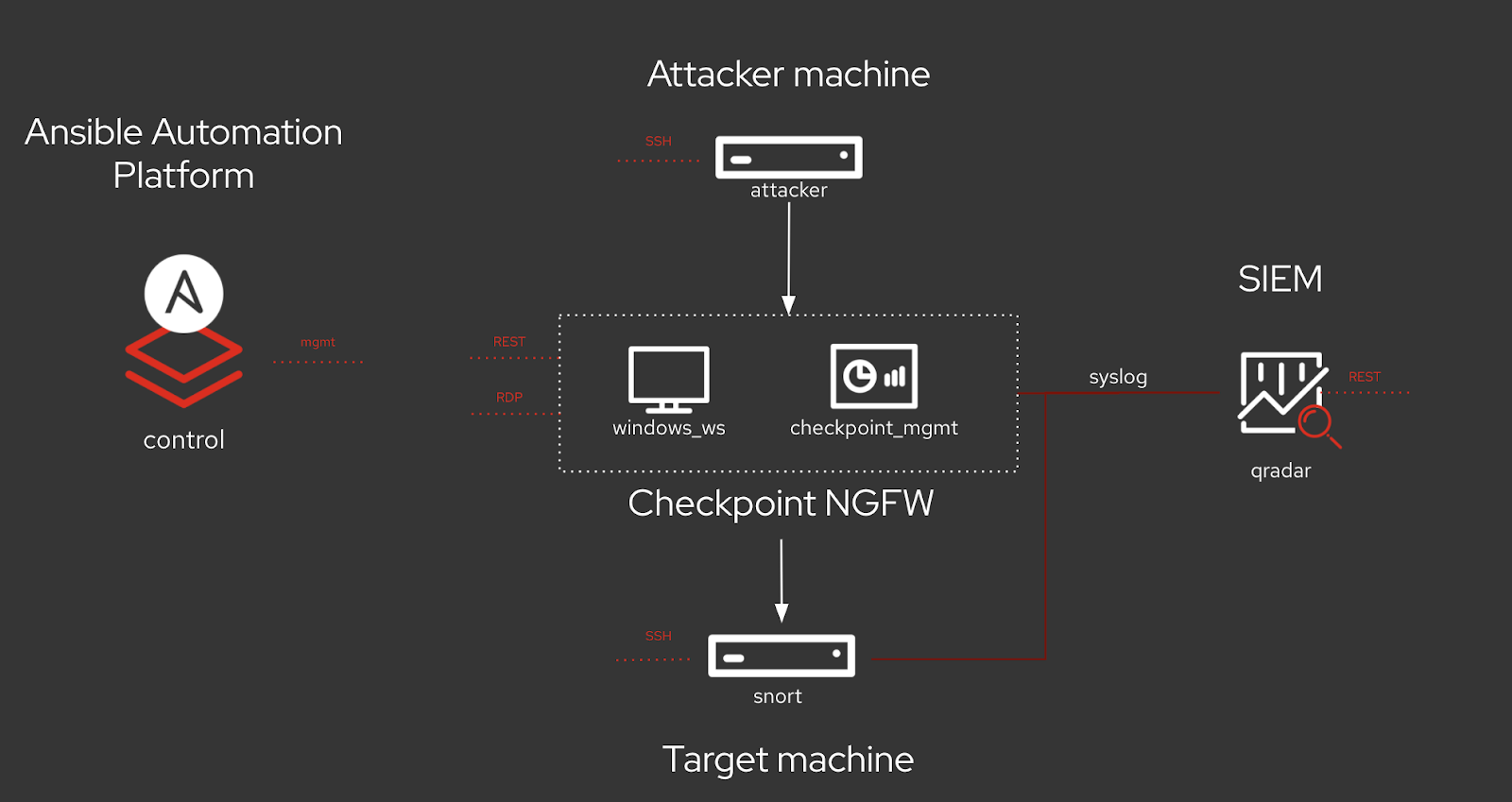
The below lab environment is a simplified example of a real-world enterprise security architecture, which can be more complex and include additional vendor-specific tools. This is a typical incident response scenario where you receive an intrusion alert and immediately execute a playbook with the acl_manger role that blocks the attacker’s IP address.
Your entire team can use Ansible security automation to address investigations, threat hunting, and incident response all on one platform. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform provides you with certified content collections that are easy to consume and reuse within your security team.
Additional resources
For more information on Ansible roles, see roles on docs.ansible.com.
1.2.1. Creating a new firewall rule
Use the acl_manager role to create a new firewall rule for blocking a source IP address from accessing a destination IP address.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the latest version of ansible-core.
- You have access to the Check Point Management server to enforce the new policies
Procedure
Install the acl_manager role using the ansible-galaxy command.
$ ansible-galaxy install ansible_security.acl_manager
Create a new playbook and set the following parameter. For example, source object, destination object, access rule between the two objects and the actual firewall you are managing, such as Check Point:
- name: block IP address hosts: checkpoint connection: httpapi tasks: - include_role: name: acl_manager tasks_from: block_ip vars: source_ip: 172.17.13.98 destination_ip: 192.168.0.10 ansible_network_os: checkpointRun the playbook
$ ansible-navigator run --ee false <playbook.yml>.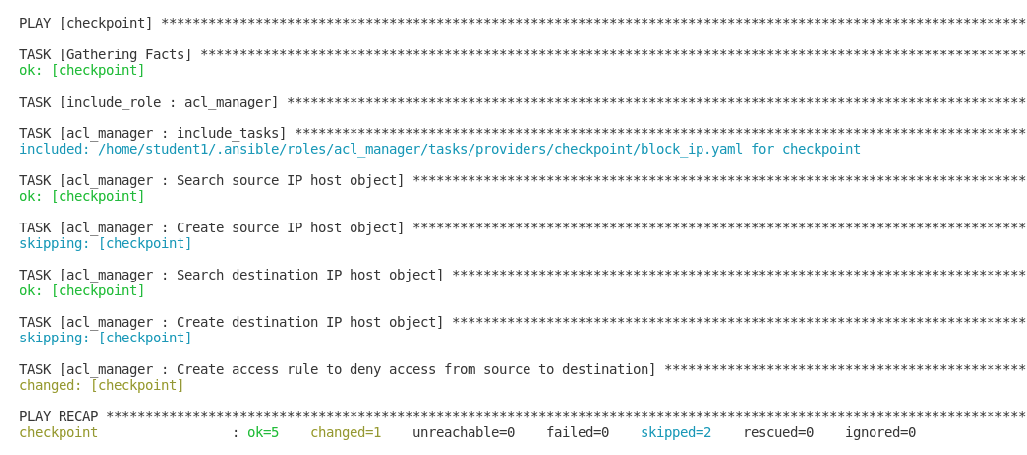
Verification
You have created a new firewall rule that blocks a source IP address from accessing a destination IP address. Access the MGMT server and verify that the new security policy has been created.
Additional resources
For more information on installing roles, see Installing roles from Galaxy.
1.2.2. Deleting a firewall rule
Use the acl_manager role to delete a security rule.
Prerequisites
- You have installed Ansible 2.9 or later
- You have access to the firewall MGMT servers to enforce the new policies
Procedure
Install the acl_manager role using the ansible-galaxy command:
$ ansible-galaxy install ansible_security.acl_manager
Using CLI, create a new playbook with the acl_manger role and set the parameters (e.g., source object, destination object, access rule between the two objects):
- name: delete block list entry hosts: checkpoint connection: httpapi - include_role: name: acl_manager Tasks_from: unblock_ip vars: source_ip: 192.168.0.10 destination_ip: 192.168.0.11 ansible_network_os: checkpointRun the playbook $ ansible-navigator run --ee false <playbook.yml>:

Verification
You have deleted the firewall rule. Access the MGMT server and verify that the new security policy has been removed.
Additional resources
For more information on installing roles, see Installing roles from Galaxy.