Chapter 10. Metrics
A metrics endpoint, /api/controller/v2/metrics/ is available in the API that produces instantaneous metrics about automation controller, which can be consumed by system monitoring software such as the open source project Prometheus.
The types of data shown at the metrics/ endpoint are Content-type: text/plain and application/json.
This endpoint has useful information, such as counts of how many active user sessions there are, or how many jobs are actively running on each automation controller node.
You can configure Prometheus to scrape these metrics from automation controller by hitting the automation controller metrics endpoint and storing this data in a time-series database.
Clients can later use Prometheus in conjunction with other software such as Grafana or Metricbeat to visualize that data and set up alerts.
10.1. Setting up Prometheus
To set up and use Prometheus, you must install Prometheus on a virtual machine or container.
For more information, see the First steps with Prometheus documentation.
Procedure
In the Prometheus configuration file (typically
prometheus.yml), specify a<token_value>, a valid username and password for an automation controller user that you have created, and a<controller_host>.NoteAlternatively, you can provide an OAuth2 token (which can be generated at
/api/v2/users/N/personal_tokens/). By default, the configuration assumes a user with username=adminand password=password.Using an OAuth2 Token, created at the
/api/v2/tokensendpoint to authenticate Prometheus with automation controller, the following example provides a valid scrape configuration if the URL for your automation controller’s metrics endpoint is/https://controller_host:443/metrics.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For help configuring other aspects of Prometheus, such as alerts and service discovery configurations, see the Prometheus configuration documentation.
If Prometheus is already running, you must restart it to apply the configuration changes by making a POST to the reload endpoint, or by killing the Prometheus process or service.
Use a browser to navigate to your graph in the Prometheus UI at
/http://<your_prometheus>:9090/graphand test out some queries. For example, you can query the current number of active automation controller user sessions by executing:awx_sessions_total{type="user"}.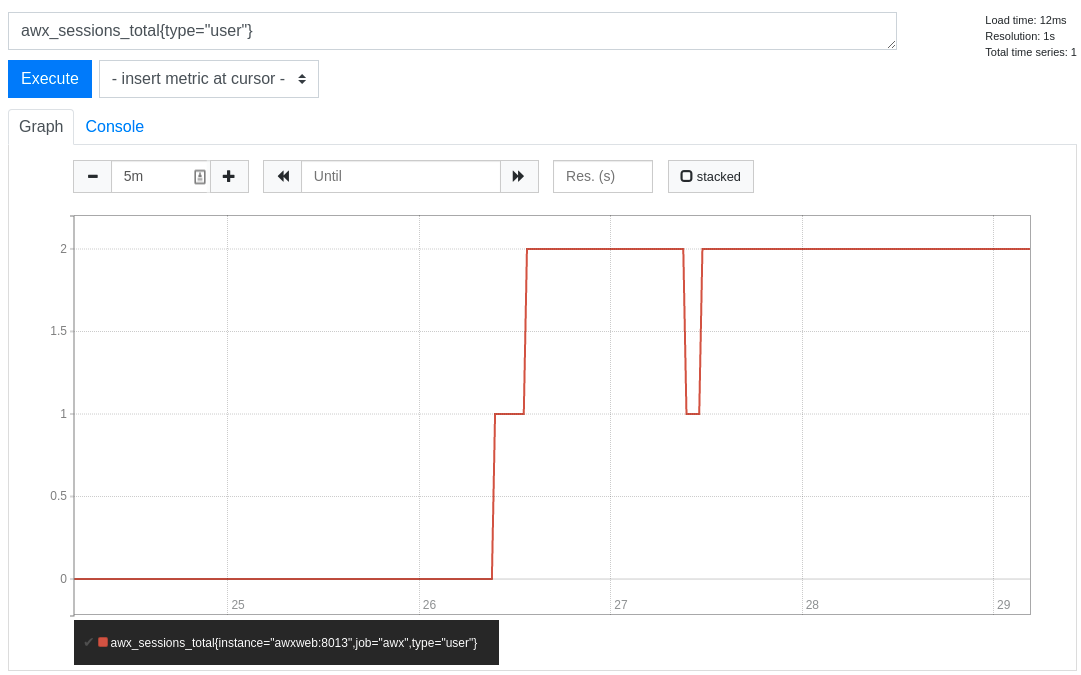
Next steps
Refer to the metrics endpoint in the automation controller API for your instance (api/v2/metrics) for more ways to query.