Chapter 2. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform Architecture
As a modular platform, Ansible Automation Platform provides the flexibility to easily integrate components and customize your deployment to best meet your automation requirements. The following section provides a comprehensive architectural example of an Ansible Automation Platform deployment.
2.1. Example Ansible Automation Platform architecture
The Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform 2.5 reference architecture provides an example setup of a standard deployment of Ansible Automation Platform using automation mesh on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. The deployment shown takes advantage of the following components to provide a simple, secure and flexible method of handling your automation workloads, a central location for content collections, and automated resolution of IT requests.
- Automation controller
- Provides the control plane for automation through its UI, Restful API, RBAC workflows and CI/CD integrations.
- Automation mesh
- Is an overlay network that provides the ability to ease the distribution of work across a large and dispersed collection of workers through nodes that establish peer-to-peer connections with each other using existing networks.
- Private automation hub
- Provides automation developers the ability to collaborate and publish their own automation content and streamline delivery of Ansible code within their organization.
- Event-Driven Ansible
- Provides the event-handling capability needed to automate time-consuming tasks and respond to changing conditions in any IT domain.
The architecture for this example consists of the following:
- A two node automation controller cluster
- An optional hop node to connect automation controller to execution nodes
- A two node automation hub cluster
- A single node Event-Driven Ansible controller cluster
- A single PostgreSQL database connected to the automation controller, automation hub, and Event-Driven Ansible controller clusters
- Two execution nodes per automation controller cluster
Figure 2.1. Example Ansible Automation Platform 2.5 architecture

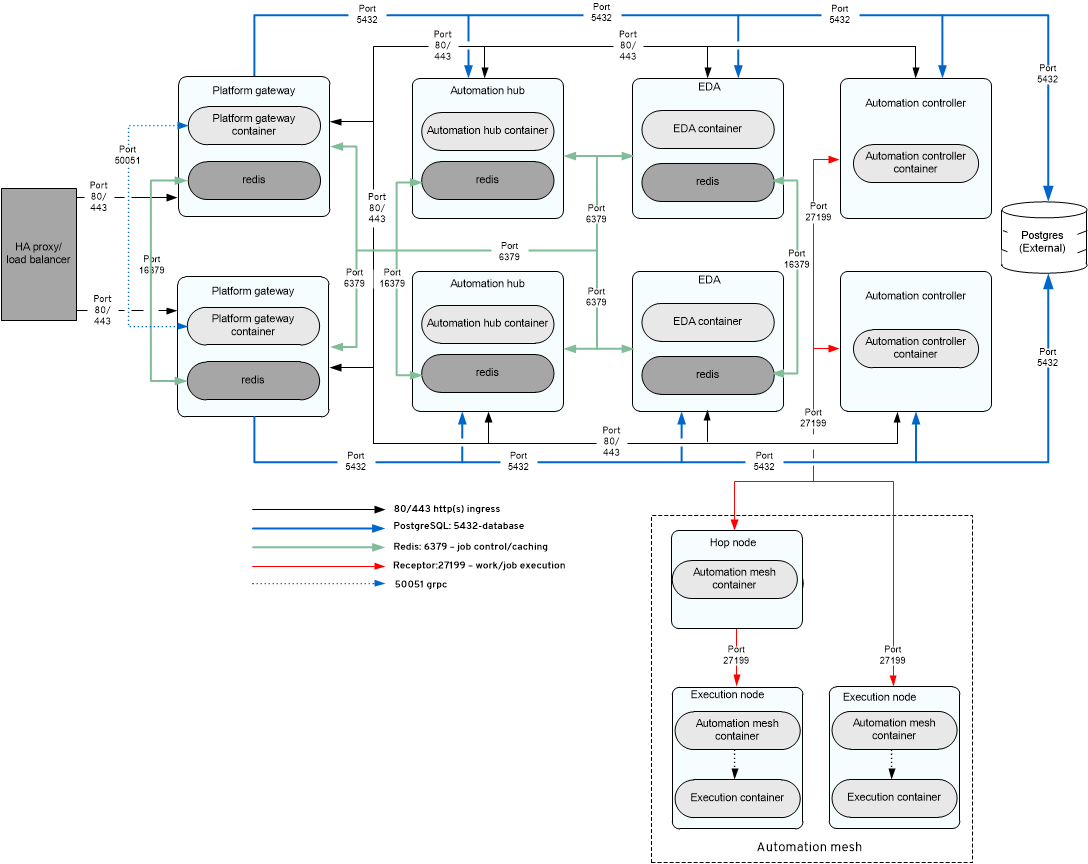
2.2. Example containerized deployment architecture
The following reference architecture provides an example setup of an enterprise deployment of containerized Ansible Automation Platform.
Figure 2.2. Example enterprise containerized deployment architecture
2.3. Example Operator-based deployment architecture
The following reference architecture provides an example setup of an enterprise deployment of Ansible Automation Platform on OpenShift Container Platform.
Figure 2.3. Example enterprise Operator-based deployment architecture
