Chapter 1. Overview
A block is a sequence of bytes (for example, a 512-byte block of data). Block-based storage interfaces are the most common way to store data with rotating media such as hard disks, CDs, floppy disks, and even traditional 9-track tape. The ubiquity of block device interfaces makes a virtual block device an ideal candidate to interact with a mass data storage system like Ceph.
Ceph block devices are thin-provisioned, resizable and store data striped over multiple OSDs in a Ceph cluster. Ceph block devices leverage RADOS (Reliable Autonomic Distributed Object Store) capabilities such as snapshotting, replication and consistency. Ceph’s RADOS (Reliable Autonomic Distributed Object Store) Block Devices (RBD) interact with OSDs using the librbd library.
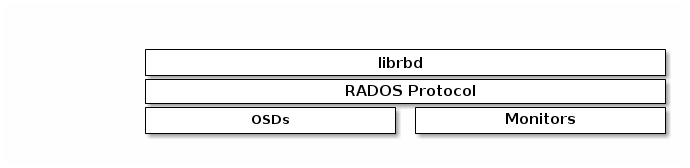
Ceph’s block devices deliver high performance with infinite scalability to KVMs (kernel virtual machines) such as Qemu, and cloud-based computing systems like OpenStack and CloudStack that rely on libvirt and Qemu to integrate with Ceph block devices. You can use the same cluster to operate the Ceph Object Gateway and Ceph block devices simultaneously.
To use Ceph Block Devices, you must have access to a running Ceph cluster.