Chapter 10. The Ceph iSCSI Gateway (Limited Availability)
As a storage administrator, you can install and configure an iSCSI gateway for the Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster. With Ceph’s iSCSI gateway you can effectively run a fully integrated block-storage infrastructure with all features and benefits of a conventional Storage Area Network (SAN).
This technology is Limited Availability. See the Deprecated functionality chapter for additional information.
SCSI persistent reservations are not supported. Mapping multiple iSCSI initiators to an RBD image is supported, if using a cluster aware file system or clustering software that does not rely on SCSI persistent reservations. For example, VMware vSphere environments using ATS is supported, but using Microsoft’s clustering server (MSCS) is not supported.
10.1. Introduction to the Ceph iSCSI gateway
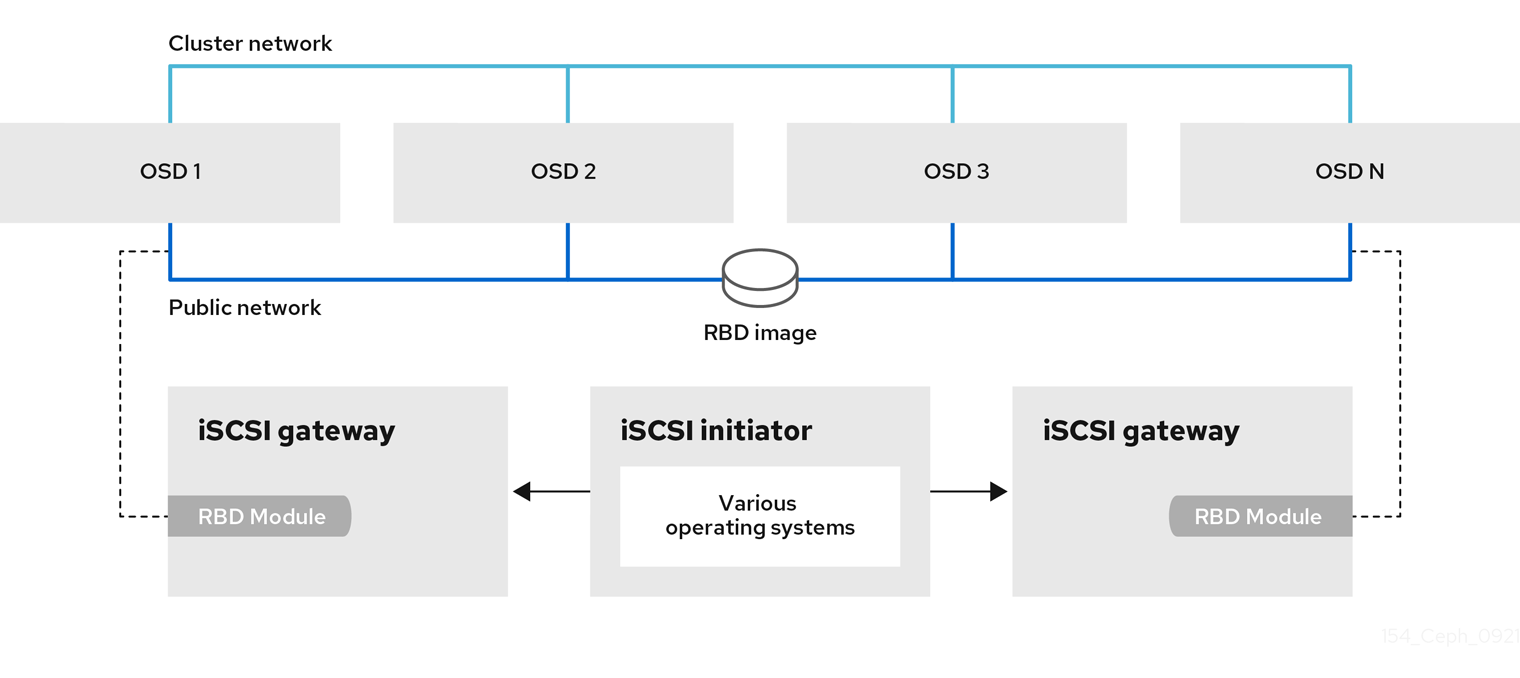
Traditionally, block-level access to a Ceph storage cluster has been limited to QEMU and librbd, which is a key enabler for adoption within OpenStack environments. Block-level access to the Ceph storage cluster can now take advantage of the iSCSI standard to provide data storage.
The iSCSI gateway integrates Red Hat Ceph Storage with the iSCSI standard to provide a highly available (HA) iSCSI target that exports RADOS Block Device (RBD) images as SCSI disks. The iSCSI protocol allows clients, known as initiators, to send SCSI commands to SCSI storage devices, known as targets, over a TCP/IP network. This allows for heterogeneous clients, such as Microsoft Windows, to access the Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster.
Figure 10.1. Ceph iSCSI Gateway
10.2. Requirements for the iSCSI target
The Red Hat Ceph Storage Highly Available (HA) iSCSI gateway solution has requirements for the number of gateway nodes, memory capacity, and timer settings to detect down OSDs.
Required Number of Nodes
Install a minimum of two iSCSI gateway hosts. To increase resiliency and I/O handling, install up to four iSCSI gateway hosts.
Memory Requirements
The memory footprint of the RBD images can grow to a large size. Each RBD image mapped on the iSCSI gateway hosts uses roughly 90 MB of memory. Ensure the iSCSI gateway hosts have enough memory to support each mapped RBD image.
Detecting Down OSDs
There are no specific iSCSI gateway options for the Ceph Monitors or OSDs, but it is important to lower the default timers for detecting down OSDs to reduce the possibility of initiator timeouts.
Additional Resources
- See the Red Hat Ceph Storage Hardware Selection Guide for more information.
10.3. Installing the iSCSI gateway
As a storage administrator, before you can utilize the benefits of the Ceph iSCSI gateway, you must install the required software packages. You can install the Ceph iSCSI gateway by using the command-line interface.
Each iSCSI gateway runs the Linux I/O target kernel subsystem (LIO) to provide iSCSI protocol support. LIO utilizes a user-space passthrough (TCMU) to interact with the Ceph librbd library to expose RBD images to iSCSI clients. With the Ceph iSCSI gateway you can effectively run a fully integrated block-storage infrastructure with all features and benefits of a conventional Storage Area Network (SAN).
10.3.1. Prerequisites
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.4 or higher.
- A running Red Hat Ceph Storage 5 or higher cluster.
10.3.2. Installing the Ceph iSCSI gateway using the command-line interface
The Ceph iSCSI gateway is the iSCSI target node and also a Ceph client node. The Ceph iSCSI gateway can be a standalone node or be colocated on a Ceph Object Store Disk (OSD) node. Complete the following steps to install the Ceph iSCSI gateway.
Prerequisites
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.4 or higher
- A Red Hat Ceph Storage 5 cluster or higher
-
If the Ceph iSCSI gateway is not colocated on an OSD node, copy the Ceph configuration files, located in the
/etc/ceph/directory, from a running Ceph node in the storage cluster to the all iSCSI gateway hosts. The Ceph configuration files must exist on the iSCSI gateway hosts under/etc/ceph/. - On all Ceph iSCSI gateway hosts, enable the Ceph Tools repository.
- On all Ceph iSCSI gateway hosts, install and configure the Ceph command-line interface.
- If needed, open TCP ports 3260 and 5000 on the firewall on all Ceph iSCSI nodes.
- Create a new or use an existing RADOS Block Device (RBD).
Procedure
Retrieve the information of the iSCSI container on the host:
Example
podman ps
[root@iscsigw ~]# podman psCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log into the Cephadm shell:
Example
cephadm shell
[root@iscsigw ~]# cephadm shellCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: On all Ceph iSCSI gateway hosts, install and configure the OpenSSL utility, if needed.
Install the
opensslpackage:Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# yum install openssl
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# yum install opensslCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On the primary iSCSI gateway node, create a directory to hold the SSL keys:
Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# mkdir ~/ssl-keys [ceph: root@iscsigw /]# cd ~/ssl-keys
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# mkdir ~/ssl-keys [ceph: root@iscsigw /]# cd ~/ssl-keysCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On the primary iSCSI gateway node, create the certificate and key files. Enter the environmental information when prompted.
Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout iscsi-gateway.key -x509 -days 365 -out iscsi-gateway.crt
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout iscsi-gateway.key -x509 -days 365 -out iscsi-gateway.crtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On the primary iSCSI gateway node, create a PEM file:
Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# cat iscsi-gateway.crt iscsi-gateway.key > iscsi-gateway.pem
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# cat iscsi-gateway.crt iscsi-gateway.key > iscsi-gateway.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow On the primary iSCSI gateway node, create a public key:
Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# openssl x509 -inform pem -in iscsi-gateway.pem -pubkey -noout > iscsi-gateway-pub.key
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# openssl x509 -inform pem -in iscsi-gateway.pem -pubkey -noout > iscsi-gateway-pub.keyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
From the primary iSCSI gateway node, copy the
iscsi-gateway.crt,iscsi-gateway.pem,iscsi-gateway-pub.key, andiscsi-gateway.keyfiles to the/etc/ceph/directory on the other iSCSI gateway hosts.
Create a pool using the following commands:
Syntax
ceph osd pool create POOL_NAME PG_NUM ceph osd pool application enable POOL_NAME rbd rbd pool init -p POOL_NAME
ceph osd pool create POOL_NAME PG_NUM ceph osd pool application enable POOL_NAME rbd rbd pool init -p POOL_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# ceph osd pool create pool1 100 [ceph: root@iscsigw /]# ceph osd pool application enable pool1 rbd [ceph: root@iscsigw /]# rbd pool init -p pool1
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# ceph osd pool create pool1 100 [ceph: root@iscsigw /]# ceph osd pool application enable pool1 rbd [ceph: root@iscsigw /]# rbd pool init -p pool1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a configuration file on a Ceph iSCSI gateway node.
Create a file named
iscsi-gateway.yamlin the/etc/ceph/directory:Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# touch /etc/ceph/iscsi-gateway.yaml
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# touch /etc/ceph/iscsi-gateway.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Edit the
iscsi-gateway.yamlfile and add the following lines:Syntax
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Change the path to
/etc/ceph/and apply the specification with the following command:Example
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# ceph orch apply -i iscsi-gateway.yaml
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# ceph orch apply -i iscsi-gateway.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Next, configure targets, LUNs, and clients. See the Configuring the iSCSI target using the command-line interface section for details.
10.4. Configuring the iSCSI target
As a storage administrator, you can configure targets, LUNs, and clients, using the gwcli command-line utility. You can also optimize performance of the iSCSI target, use the gwcli reconfigure subcommand.
Red Hat does not support managing Ceph block device images exported by the Ceph iSCSI gateway tools, such as gwcli.. Also, using the rbd command to rename or remove RBD images exported by the Ceph iSCSI gateway, can result in an unstable storage cluster.
Before removing RBD images from the iSCSI gateway configuration, follow the standard procedures for removing a storage device from the operating system. For details, see the Removing a storage device chapter in the Storage Administration Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 or the System Design Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
10.4.1. Prerequisites
- Installation of the Ceph iSCSI gateway software.
10.4.2. Configuring the iSCSI target using the command-line interface
The Ceph iSCSI gateway is the iSCSI target node and also a Ceph client node. Configure the Ceph iSCSI gateway either on a standalone node, or colocate it with a Ceph Object Storage Device (OSD) node.
Do not adjust other options using the gwcli reconfigure subcommand unless specified in this document or Red Hat Support has instructed you to do so.
Prerequisites
- Installation of the Ceph iSCSI gateway software.
Procedure
Retrieve the information of the iSCSI container running on the host:
Example
podman ps podman exec -it 4b5ffb814409 /bin/bash
[root@iscsigw ~]# podman ps [root@iscsigw ~]# podman exec -it 4b5ffb814409 /bin/bashCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the iSCSI gateway command-line interface:
gwcli
[root@iscsigw ~]# gwcliCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the
iscsi-targetsdirectory:Example
/>cd /iscsi-targets
/>cd /iscsi-targetsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the iSCSI gateways using either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses:
Syntax
/>iscsi-targets create iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:_TARGET_NAME_ > goto gateways > create ISCSI_GW_NAME IP_ADDR_OF_GW > create ISCSI_GW_NAME IP_ADDR_OF_GW
/>iscsi-targets create iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:_TARGET_NAME_ > goto gateways > create ISCSI_GW_NAME IP_ADDR_OF_GW > create ISCSI_GW_NAME IP_ADDR_OF_GWCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
/>iscsi-targets create iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw > goto gateways > create ceph-gw-1 10.172.19.21 > create ceph-gw-2 10.172.19.22
/>iscsi-targets create iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw > goto gateways > create ceph-gw-1 10.172.19.21 > create ceph-gw-2 10.172.19.22Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a Ceph block device:
Syntax
> cd /disks />disks/ create POOL_NAME image=IMAGE_NAME size=IMAGE_SIZE_m|g|t
> cd /disks />disks/ create POOL_NAME image=IMAGE_NAME size=IMAGE_SIZE_m|g|tCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
> cd /disks />disks/ create rbd image=disk_1 size=50g
> cd /disks />disks/ create rbd image=disk_1 size=50gCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteDo not use any periods (
.) in the pool or image name.Create a client:
Syntax
> goto hosts > create iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:_client_name_ > auth username=USER_NAME password=PASSWORD
> goto hosts > create iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:_client_name_ > auth username=USER_NAME password=PASSWORDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
> goto hosts > create iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client > auth username=iscsiuser1 password=temp12345678
> goto hosts > create iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client > auth username=iscsiuser1 password=temp12345678Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantRed Hat does not support mixing clients, some with Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) enabled and some CHAP disabled. All clients must have either CHAP enabled or have CHAP disabled. The default behavior is to only authenticate an initiator by its initiator name.
If initiators are failing to log into the target, the CHAP authentication might not be configured correctly for some initiators, for example:
o- hosts ................................ [Hosts: 2: Auth: MISCONFIG]
o- hosts ................................ [Hosts: 2: Auth: MISCONFIG]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the following command at the
hostslevel to reset all the CHAP authentication:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add disks to a client:
Syntax
/>iscsi-target..eph-igw/hosts > cd iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:_CLIENT_NAME_ > disk add POOL_NAME/IMAGE_NAME
/>iscsi-target..eph-igw/hosts > cd iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:_CLIENT_NAME_ > disk add POOL_NAME/IMAGE_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
/>iscsi-target..eph-igw/hosts > cd iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client > disk add rbd/disk_1
/>iscsi-target..eph-igw/hosts > cd iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client > disk add rbd/disk_1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the Ceph ISCSI gateways are working:
/> goto gateways /iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> ls o- gateways ............................ [Up: 2/2, Portals: 2] o- ceph-gw-1 ........................ [ 10.172.19.21 (UP)] o- ceph-gw-2 ........................ [ 10.172.19.22 (UP)]
/> goto gateways /iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> ls o- gateways ............................ [Up: 2/2, Portals: 2] o- ceph-gw-1 ........................ [ 10.172.19.21 (UP)] o- ceph-gw-2 ........................ [ 10.172.19.22 (UP)]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the status is
UNKNOWN, check for network issues and any misconfigurations. If using a firewall, verify that the appropriate TCP port is open. Verify that the iSCSI gateway is listed in thetrusted_ip_listoption. Verify that therbd-target-apiservice is running on the iSCSI gateway node.Optionally, reconfigure the
max_data_area_mboption:Syntax
/>disks/ reconfigure POOL_NAME/IMAGE_NAME max_data_area_mb NEW_BUFFER_SIZE
/>disks/ reconfigure POOL_NAME/IMAGE_NAME max_data_area_mb NEW_BUFFER_SIZECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
/>disks/ reconfigure rbd/disk_1 max_data_area_mb 64
/>disks/ reconfigure rbd/disk_1 max_data_area_mb 64Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe
max_data_area_mboption controls the amount of memory in megabytes that each image can use to pass SCSI command data between the iSCSI target and the Ceph cluster. If this value is too small, it can result in excessive queue full retries which will affect performance. If the value is too large, it can result in one disk using too much of the system memory, which can cause allocation failures for other subsystems. The default value for themax_data_area_mboption is8.- Configure an iSCSI initiator.
Additional Resources
- See Installing the iSCSI gateway for details.
- See Configuring the iSCSI initiator section for more information.
10.4.3. Optimize the performance of the iSCSI Target
There are many settings that control how the iSCSI Target transfers data over the network. These settings can be used to optimize the performance of the iSCSI gateway.
Only change these settings if instructed to by Red Hat Support or as specified in this document.
The gwcli reconfigure subcommand controls the settings that are used to optimize the performance of the iSCSI gateway.
Settings that affect the performance of the iSCSI target
max_data_area_mb- Description
- The size of kernel data ring buffer in megabytes.
- Type
- Integer
- Default
-
8
cmdsn_depth- Description
- Indicates the depth of the queue that controls maximum I/O.
- Type
- Integer
- Default
-
128
immediate_data- Description
-
Indicates if the initiator requests permission from the target to transmit immediate data whenever it establishes a new session. If this value is
Yes, the initiator requests permission from the target to transmit immediate data whenever it establishes a new session. - Type
- Boolean
- Default
-
Yes
initial_r2t- Description
-
Indicates if the host bus adapter (HBA) initiator requests permission from the target to transmit unsolicited SCSI data whenever it establishes a new session. If this member is
Yes, the HBA initiator requests permission from the target to transmit unsolicited SCSI data whenever it establishes a new session. - Type
- Boolean
- Default
-
Yes
max_outstanding_r2t- Description
- The maximum number of outstanding ready to transfer (R2T) requests for each task, excluding the first R2T that initiates the task.
- Type
- Integer
- Default
-
1
first_burst_length- Description
- The maximum amount of unsolicited data an iSCSI initiator can send to the target during the execution of a single SCSI command.
- Type
- Integer in bytes
- Default
-
262144
max_burst_length- Description
- The maximum SCSI data payload in an input PDU sequence or a solicited output PDU sequence.
- Type
- Integer in bytes
- Default
-
524288
max_recv_data_segment_length- Description
- The maximum number of data bytes the initiator can receive in an iSCSI PDU from a target.
- Type
- Integer in bytes
- Default
-
262144
max_xmit_data_segment_length- Description
- The maximum number of data bytes the initiator sends in an iSCSI PDU to the target.
- Type
- Integer in bytes
- Default
-
0
Additional Resources
-
Information about
max_data_area_mb, including an example showing how to adjust it usinggwcli reconfigure, is in the section Configuring the iSCSI Target using the Command Line Interface.
10.4.4. Configuring iSCSI host groups using the command-line interface
The Ceph iSCSI gateway can configure host groups for managing multiple servers that share the same disk configuration. iSCSI host groups creates a logical grouping of hosts and the disks that each host in the group has access to.
The sharing of disk devices to multiple hosts must use a cluster-aware file system.
Prerequisites
- Installation of the Ceph iSCSI gateway software.
- Root-level access to the Ceph iSCSI gateway node.
Procedure
Retrieve the information of the iSCSI container running on the host:
Example
[root@iscsigw ~] podman ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4b5ffb814409 registry.redhat.io/rhceph-alpha/rhceph-5-rhel8:latest 2 hours ago Up 2 hours ago ceph-f838eb7a-597c-11eb-b0a9-525400e2439c-iscsi.iscsi.cephLab2-node-01.anaahg
[root@iscsigw ~] podman ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4b5ffb814409 registry.redhat.io/rhceph-alpha/rhceph-5-rhel8:latest 2 hours ago Up 2 hours ago ceph-f838eb7a-597c-11eb-b0a9-525400e2439c-iscsi.iscsi.cephLab2-node-01.anaahgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the iSCSI container ID to enter into the container:
Example
podman exec -it 4b5ffb814409 /bin/bash
[root@iscsigw ~]# podman exec -it 4b5ffb814409 /bin/bashCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the
gwclicommand:[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# gwcli
[ceph: root@iscsigw /]# gwcliCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a new host group:
Syntax
cd iscsi-targets/ cd IQN/host-groups create group_name=GROUP_NAME
cd iscsi-targets/ cd IQN/host-groups create group_name=GROUP_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
/> cd iscsi-targets/ /iscsi-targets> cd iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw/host-groups/ /iscsi-target.../host-groups> create group_name=igw_grp01
/> cd iscsi-targets/ /iscsi-targets> cd iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw/host-groups/ /iscsi-target.../host-groups> create group_name=igw_grp01Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a host to the host group:
ImportantEnsure that you remove all the disks that are added to the host, before adding the host to the host group otheriwse, a host cannot be added to the hostgroup.
Syntax
cd GROUP_NAME host add client_iqn=CLIENT_IQN
cd GROUP_NAME host add client_iqn=CLIENT_IQNCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
> cd igw_grp01 /iscsi-target.../host-groups/igw_grp01> host add client_iqn=iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh8-client
> cd igw_grp01 /iscsi-target.../host-groups/igw_grp01> host add client_iqn=iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh8-clientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Repeat this step to add additional hosts to the group.
Add a disk to the host group:
Syntax
cd /disks/ /disks> create pool=POOL image=IMAGE_NAME size=SIZE cd /IQN/host-groups/GROUP_NAME disk add POOL/IMAGE_NAME
cd /disks/ /disks> create pool=POOL image=IMAGE_NAME size=SIZE cd /IQN/host-groups/GROUP_NAME disk add POOL/IMAGE_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
> cd /disks/ /disks> create pool=rbd image=rbdimage size=1G /> cd iscsi-targets/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw/host-groups/igw_grp01/ /iscsi-target...s/igw_grp01> disk add rbd/rbdimage
> cd /disks/ /disks> create pool=rbd image=rbdimage size=1G /> cd iscsi-targets/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw/host-groups/igw_grp01/ /iscsi-target...s/igw_grp01> disk add rbd/rbdimageCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Repeat this step to add additional disks to the group.
10.4.5. Additional Resources
- For details on configuring iSCSI targets using the Red Hat Ceph Storage Dashboard, see the Creating iSCSI targets section in the Red Hat Ceph Storage Dashboard Guide.
10.5. Configuring the iSCSI initiator
You can configure the iSCSI initiator to connect to the Ceph iSCSI gateway on the following platforms.
10.5.1. Configuring the iSCSI initiator for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Prerequisites
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.7 or higher.
-
Package
iscsi-initiator-utils-6.2.0.873-35or newer must be installed. -
Package
device-mapper-multipath-0.4.9-99or newer must be installed.
Procedure
Install the iSCSI initiator and multipath tools:
yum install iscsi-initiator-utils yum install device-mapper-multipath
[root@rhel ~]# yum install iscsi-initiator-utils [root@rhel ~]# yum install device-mapper-multipathCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Set the initiator name by editing the
/etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsifile. Note that the initiator name must match the initiator name that was used during the initial setup using thegwclicommand. Configure multipath I/O.
Create the default
/etc/multipath.conffile and enable themultipathdservice:mpathconf --enable --with_multipathd y
[root@rhel ~]# mpathconf --enable --with_multipathd yCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the
/etc/multipath.conffile as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the
multipathdservice:systemctl reload multipathd
[root@rhel ~]# systemctl reload multipathdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Set up CHAP and iSCSI discovery and login.
Provide a CHAP user name and password by updating the
/etc/iscsi/iscsid.conffile accordingly, for example:node.session.auth.authmethod = CHAP node.session.auth.username = user node.session.auth.password = password
node.session.auth.authmethod = CHAP node.session.auth.username = user node.session.auth.password = passwordCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Discover the target portals:
Syntax
iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p IP_ADDR
iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p IP_ADDRCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log in to target:
Syntax
iscsiadm -m node -T TARGET -l
iscsiadm -m node -T TARGET -lCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
View the multipath I/O configuration. The
multipathddaemon sets up devices automatically based on the settings in themultipath.conffile.Use the
multipathcommand to show devices setup in a failover configuration with a priority group for each path, for example:Example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
multipath -lloutputpriovalue indicates the ALUA state, whereprio=50indicates it is the path to the owning iSCSI gateway in the ALUA Active-Optimized state andprio=10indicates it is an Active-non-Optimized path. Thestatusfield indicates which path is being used, whereactiveindicates the currently used path, andenabledindicates the failover path, if theactivefails.To match the device name, for example,
sdein themultipath -lloutput, to the iSCSI gateway:Example
iscsiadm -m session -P 3
[root@rhel ~]# iscsiadm -m session -P 3Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
Persistent Portalvalue is the IP address assigned to the iSCSI gateway listed in thegwcliutility.
10.5.2. Configuring the iSCSI initiator for Red Hat Virtualization
Prerequisites
- Red Hat Virtualization 4.1
- Configured MPIO devices on all Red Hat Virtualization nodes
-
The
iscsi-initiator-utils-6.2.0.873-35package or newer -
The
device-mapper-multipath-0.4.9-99package or newer
Procedure
Configure multipath I/O.
Update the
/etc/multipath/conf.d/DEVICE_NAME.conffile as follows:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the
multipathdservice:systemctl reload multipathd
[root@rhv ~]# systemctl reload multipathdCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- Click the Storage resource tab to list the existing storage domains.
- Click the New Domain button to open the New Domain window.
- Enter the Name of the new storage domain.
- Use the Data Center drop-down menu to select an data center.
- Use the drop-down menus to select the Domain Function and the Storage Type. The storage domain types that are not compatible with the chosen domain function are not available.
- Select an active host in the Use Host field. If this is not the first data domain in a data center, you must select the data center’s SPM host.
The New Domain window automatically displays known targets with unused LUNs when iSCSI is selected as the storage type. If the target that you are adding storage from is not listed then you can use target discovery to find it, otherwise proceed to the next step.
- Click Discover Targets to enable target discovery options. When targets have been discovered and logged in to, the New Domain window automatically displays targets with LUNs unused by the environment. Note that LUNs external to the environment are also displayed. You can use the Discover Targets options to add LUNs on many targets, or multiple paths to the same LUNs.
- Enter the fully qualified domain name or IP address of the iSCSI host in the Address field.
-
Enter the port to connect to the host on when browsing for targets in the Port field. The default is
3260. - If the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is being used to secure the storage, select the User Authentication check box. Enter the CHAP user name and CHAP password.
- Click the Discover button.
Select the target to use from the discovery results and click the Login button. Alternatively, click the Login All to log in to all of the discovered targets.
ImportantIf more than one path access is required, ensure to discover and log in to the target through all the required paths. Modifying a storage domain to add additional paths is currently not supported.
- Click the + button next to the desired target. This will expand the entry and display all unused LUNs attached to the target.
- Select the check box for each LUN that you are using to create the storage domain.
Optionally, you can configure the advanced parameters.
- Click Advanced Parameters.
- Enter a percentage value into the Warning Low Space Indicator field. If the free space available on the storage domain is below this percentage, warning messages are displayed to the user and logged.
- Enter a GB value into the Critical Space Action Blocker field. If the free space available on the storage domain is below this value, error messages are displayed to the user and logged, and any new action that consumes space, even temporarily, will be blocked.
-
Select the Wipe After Delete check box to enable the
wipe after deleteoption. You can edit this option after creating the domain, but doing so does not change thewipe after deleteproperty of disks that already exist. - Select the Discard After Delete check box to enable the discard after delete option. You can edit this option after creating the domain. This option is only available to block storage domains.
- Click OK to create the storage domain and close the window.
10.5.3. Configuring the iSCSI initiator for Microsoft Windows
Prerequisites
- Microsoft Windows Server 2016
Procedure
Install the iSCSI initiator and configure discovery and setup.
- Install the iSCSI initiator driver and MPIO tools.
- Launch the MPIO program, click the Discover Multi-Paths tab, check the Add support for iSCSI devices box, and click Add.
- Reboot the MPIO program.
- On the iSCSI Initiator Properties window, on the Discovery tab, add a target portal. Enter the IP address or DNS name and Port of the Ceph iSCSI gateway.
- On the Targets tab, select the target and click Connect.
- On the Connect To Target window, select the Enable multi-path option, and click the Advanced button.
Under the Connect using section, select the Microsoft ISCSI Intiator as the Local adapter from the drop-down box. Select the Windows client IP address as the Initiator IP from the drop-down box. Select a Target portal IP address. Select Enable CHAP login on and enter the Name and Target secret values from the Ceph iSCSI client credentials section, and click OK.
ImportantWindows Server 2016 does not accept a CHAP secret less than 12 bytes.
- Repeat the previous two steps for each target portal defined when setting up the iSCSI gateway before clicking on the Connecting tab.
- If the initiator name is different than the initiator name used during the initial setup, rename the initiator name. From iSCSI Initiator Properties window, on the Configuration tab, click the Change button to rename the initiator name.
Set up
multipathI/O. In PowerShell, use thePDORemovePeriodcommand to set the MPIO load balancing policy and thempclaimcommand to set the load balancing policy. The iSCSI Initiator Tool configures the remaining options.NoteRed Hat recommends increasing the
PDORemovePeriodoption to 120 seconds from PowerShell. You might need to adjust this value based on the application. When all paths are down, and 120 seconds expires, the operating system starts failing I/O requests.Set-MPIOSetting -NewPDORemovePeriod 120
Set-MPIOSetting -NewPDORemovePeriod 120Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the failover policy
mpclaim.exe -l -m 1
mpclaim.exe -l -m 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the failover policy
mpclaim -s -m MSDSM-wide Load Balance Policy: Fail Over Only
mpclaim -s -m MSDSM-wide Load Balance Policy: Fail Over OnlyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Using the iSCSI Initiator tool, from the Targets tab click on the Devices… button:
- From the Devices window, select a disk and click the MPIO… button:
- The Device Details window displays the paths to each target portal. The Load Balancing Policy Fail Over Only must be selected.
View the
multipathconfiguration from the PowerShell:mpclaim -s -d MPIO_DISK_ID
mpclaim -s -d MPIO_DISK_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace MPIO_DISK_ID with the appropriate disk identifier.
NoteThere is one Active/Optimized path which is the path to the iSCSI gateway node that owns the LUN, and there is an Active/Unoptimized path for each other iSCSI gateway node.
Optionally, tune the settings. Consider using the following registry settings:
Windows Disk Timeout
Key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Disk
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\DiskCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Value
TimeOutValue = 65
TimeOutValue = 65Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Microsoft iSCSI Initiator Driver
Key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\{4D36E97B-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}\<Instance_Number>\ParametersHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\{4D36E97B-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}\<Instance_Number>\ParametersCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Values
LinkDownTime = 25 SRBTimeoutDelta = 15
LinkDownTime = 25 SRBTimeoutDelta = 15Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.5.4. Configuring the iSCSI initiator for VMware ESXi
Prerequisites
- See the iSCSI Gateway (IGW) section in the Customer Portal Knowledgebase article for supported VMware ESXi versions.
- Access to the VMware ESXi web interface.
-
Root access to VMware ESXi host console to execute the
esxclicommand.
Procedure
- Log into the VMware ESXi web interface.
-
Click on Actions
highlight Services click Enable SSH. Log into the VMware ESXi host console, and disable
HardwareAcceleratedMove(XCOPY):> esxcli system settings advanced set --int-value 0 --option /DataMover/HardwareAcceleratedMove
> esxcli system settings advanced set --int-value 0 --option /DataMover/HardwareAcceleratedMoveCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - From the VMware ESXi web interface, on the Navigator pane, click Storage. Click on the Adapters tab. Highlight the adapter, and click on Configure iSCSI.
- Verify the initiator name in the Name & alias field.
If the initiator name is different than the initiator name used when creating the client during the initial setup using the
gwcliutility, then change the initiator name. From the VMware ESXi host console, do the following steps.Get the adapter name for the iSCSI software:
> esxcli iscsi adapter list > Adapter Driver State UID Description > ------- --------- ------ ------------- ---------------------- > vmhba64 iscsi_vmk online iscsi.vmhba64 iSCSI Software Adapter
> esxcli iscsi adapter list > Adapter Driver State UID Description > ------- --------- ------ ------------- ---------------------- > vmhba64 iscsi_vmk online iscsi.vmhba64 iSCSI Software AdapterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the initiator name:
Syntax
esxcli iscsi adapter set -A ADAPTOR_NAME -n INITIATOR_NAME
esxcli iscsi adapter set -A ADAPTOR_NAME -n INITIATOR_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
> esxcli iscsi adapter set -A vmhba64 -n iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh8-client
> esxcli iscsi adapter set -A vmhba64 -n iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh8-clientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Verify the new initiator name from the VMware ESXi web interface. Click Storage in the Navigator pane. Click Software iSCSI. The new initiator name is in the Name & alias field, along with the Ceph Object Gateway node names.
Expand the CHAP authentication section. From the drop-down list, select Do not use CHAP unless required by target. Enter the CHAP Name and Secret credentials that were used in the initial setup. Verify the Mutual CHAP authentication section has Do not use CHAP selected.
ImportantThe usernames/passwords should not be the same for admin and mutual CHAP authentication.
-
The
username/mutual_usernameis 8-64 characters long, containing any alphanumeric in the range of [0-9,a-z,A-Z] and.,:,@,_,-. -
The
password/mutual_passwordis 12-16 characters long, containing any alphanumeric in the range of [0-9,a-z,A-Z] and@,-,_,/.
WarningDue to a bug in the VMware host client, the CHAP settings are not used initially. On the Ceph iSCSI gateway node, the kernel logs include the following errors as an indication of this bug:
> kernel: CHAP user or password not set for Initiator ACL > kernel: Security negotiation failed. > kernel: iSCSI Login negotiation failed.
> kernel: CHAP user or password not set for Initiator ACL > kernel: Security negotiation failed. > kernel: iSCSI Login negotiation failed.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To work around this bug, configure the CHAP settings using the
esxclicommand. Theauthnameargument is the Name in the CHAP authentication section:Syntax
esxcli iscsi adapter auth chap set --direction=uni --authname=ISCSI_USER_NAME --secret=ISCSI_PASSWORD --level=discouraged -A ADAPTOR_NAME
esxcli iscsi adapter auth chap set --direction=uni --authname=ISCSI_USER_NAME --secret=ISCSI_PASSWORD --level=discouraged -A ADAPTOR_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
- Expand Advanced settings section. Set the RecoveryTimeout value to 25.
In the Dynamic targets section, click on Add dynamic target. Under the Address field click to add an IP addresses for one of the Ceph iSCSI gateways. Only one IP address needs to be added. Finally, click the Save configuration button. Click on the Devices tab to see the RBD image.
NoteLUN is configured automatically, using the ALUA SATP and MRU PSP. Do not use other SATPs and PSPs. You can verify this by the
esxclicommand:Syntax
esxcli storage nmp path list -d eui.DEVICE_ID
esxcli storage nmp path list -d eui.DEVICE_IDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace DEVICE_ID with the appropriate device identifier.
From the VMware ESXi host console, verify that multipathing is set up correctly.
List the devices:
Example
> esxcli storage nmp device list | grep iSCSI Device Display Name: LIO-ORG iSCSI Disk (naa.6001405f8d087846e7b4f0e9e3acd44b) Device Display Name: LIO-ORG iSCSI Disk (naa.6001405057360ba9b4c434daa3c6770c)
> esxcli storage nmp device list | grep iSCSI Device Display Name: LIO-ORG iSCSI Disk (naa.6001405f8d087846e7b4f0e9e3acd44b) Device Display Name: LIO-ORG iSCSI Disk (naa.6001405057360ba9b4c434daa3c6770c)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Get the multipath information for the Ceph iSCSI disk from the previous step:
Example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the example output, each path has an iSCSI or SCSI name with the following parts:
Initiator name =
iqn.2005-03.com.ceph:esx1ISID =00023d000002Target name =iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igwTarget port group =2Device id =naa.6001405f8d087846e7b4f0e9e3acd44bThe
Group Statevalue ofactiveindicates this is the Active-Optimized path to the iSCSI gateway. Thegwclicommand lists theactiveas the iSCSI gateway owner. The rest of the paths have theGroup Statevalue ofunoptimizedand are the failover path, if theactivepath goes into adeadstate.To match all paths to their respective iSCSI gateways:
Example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Match the path name with the
ISIDvalue, and theRemoteAddressvalue is the IP address of the owning iSCSI gateway.
- From the VMware ESXi web interface, click on the Devices tab to see the iSCSI disk.
Click on New datastore to start the wizard.
- Provide a name for the new datastore, and click Next.
- Select Use full disk, and click Next.
- Click Finish. A warning message appears about erasing the disk. Click Yes to proceed, and create the new datastore.
- The new datastore will appear on the Datastores tab.
You can check disk usage by selecting the datastore name. You can also check disk usage from Ceph by running the following command:
Syntax
rbd du --pool POOL_NAME
rbd du --pool POOL_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
rbd du --pool rbdpool
[root@rbd-client ~]# rbd du --pool rbdpoolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.6. Adding more iSCSI gateways
As a storage administrator, you can expand the initial two iSCSI gateways to four iSCSI gateways by using the gwcli command-line tool or the Red Hat Ceph Storage Dashboard. Adding more iSCSI gateways provides you more flexibility when using load-balancing and failover options, along with providing more redundancy.
10.6.1. Prerequisites
- A running Red Hat Ceph Storage 5 cluster
- Spare nodes or existing OSD nodes
-
rootpermissions
10.6.2. Using gwcli to add more iSCSI gateways
You can use the gwcli command-line tool to add more iSCSI gateways. This procedure expands the default of two iSCSI gateways to four iSCSI gateways.
Prerequisites
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.7 or later.
- A running Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster.
-
Having
rootuser access to the new nodes or OSD nodes.
Procedure
On the new iSCSI gateway hosts, enable the Red Hat Ceph Storage Tools repository:
Example
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhceph-5-tools-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms
[root@iscsigw ~]# subscription-manager repos --enable=rhceph-5-tools-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpmsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Install the
ceph-iscsi, andtcmu-runnerpackages:Example
dnf install ceph-iscsi tcmu-runner
[root@iscsigw ~]# dnf install ceph-iscsi tcmu-runnerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the specification file:
Syntax
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Add proper rules in firewall for the newly added node/nodes:
Example
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5000/tcp ; firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3260/tcp ; firewall-cmd --reload
[root@host01 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5000/tcp ; firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3260/tcp ; firewall-cmd --reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notecephadmmight open the ports on its own.Mount the YAML file under a directory in the container:
Example
cephadm shell --mount iscsi-gateway.yaml:/var/lib/ceph/iscsi-gateway.yaml
[root@host01 ~]# cephadm shell --mount iscsi-gateway.yaml:/var/lib/ceph/iscsi-gateway.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Navigate to the directory:
Example
[ceph: root@host01 /]# cd /var/lib/ceph
[ceph: root@host01 /]# cd /var/lib/cephCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the Ceph iSCSI service:
Syntax
ceph orch apply -i FILE_NAME.yaml
ceph orch apply -i FILE_NAME.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
[ceph: root@host01 ceph]# ceph orch apply -i iscsi-gateway.yaml
[ceph: root@host01 ceph]# ceph orch apply -i iscsi-gateway.yamlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Deploy the Ceph iSCSI service using the placement specification:
Syntax
ceph orch apply iscsi POOL_NAME --placement="HOSTNAME_1,HOSTNAME_2,HOSTNAME_3,HOSTNAME_4" --trusted_ip_list="IP_ADDRESS_1,IP_ADDRESS_2,IP_ADDRESS_3,IP_ADDRESS_4" admin admin
ceph orch apply iscsi POOL_NAME --placement="HOSTNAME_1,HOSTNAME_2,HOSTNAME_3,HOSTNAME_4" --trusted_ip_list="IP_ADDRESS_1,IP_ADDRESS_2,IP_ADDRESS_3,IP_ADDRESS_4" admin adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
[ceph: root@host01 ceph]# ceph orch apply iscsi iscsipool --placement="ceph-amk5-m0g9z7-node1-installer,ceph-amk5-m0g9z7-node4" --trusted_ip_list="10.0.210.209,10.0.210.153,192.168.0.50,192.168.0.51" admin admin
[ceph: root@host01 ceph]# ceph orch apply iscsi iscsipool --placement="ceph-amk5-m0g9z7-node1-installer,ceph-amk5-m0g9z7-node4" --trusted_ip_list="10.0.210.209,10.0.210.153,192.168.0.50,192.168.0.51" admin adminCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the installation:
Example
[ceph: root@host01 /]# ceph orch ls --service_type=iscsi NAME PORTS RUNNING REFRESHED AGE PLACEMENT iscsi.foo ?:5000 3/3 10m ago 75s host01;host02;host03;host04
[ceph: root@host01 /]# ceph orch ls --service_type=iscsi NAME PORTS RUNNING REFRESHED AGE PLACEMENT iscsi.foo ?:5000 3/3 10m ago 75s host01;host02;host03;host04Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the
ceph orch pscommand, get the hostname on which iSCSI is installed:Example
[ceph: root@host01 /]# ceph orch ps --daemon_type=iscsi NAME HOST PORTS STATUS REFRESHED AGE MEM USE MEM LIM VERSION IMAGE ID CONTAINER ID iscsi.foo.host02 host02 *:9095 running (2h) 8m ago 2h 85.3M - 2.22.2 ac25aac5d567 ad8c7593d7c0
[ceph: root@host01 /]# ceph orch ps --daemon_type=iscsi NAME HOST PORTS STATUS REFRESHED AGE MEM USE MEM LIM VERSION IMAGE ID CONTAINER ID iscsi.foo.host02 host02 *:9095 running (2h) 8m ago 2h 85.3M - 2.22.2 ac25aac5d567 ad8c7593d7c0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enter the container:
Example
[ceph: root@host01 /]# cephadm enter --name iscsi.foo.host02.tetras
[ceph: root@host01 /]# cephadm enter --name iscsi.foo.host02.tetrasCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the gateway using the gwcli from the iSCSI container:
Example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.7. Verifying that the initiator is connected to the iSCSI target
After installing the iSCSI gateway and configuring the iSCSI target and an initiator, verify that the initiator is properly connected to the iSCSI target.
Prerequisites
- Installation of the Ceph iSCSI gateway software.
- Configured the iSCSI target.
- Configured the iSCSI initiator.
Procedure
Start the iSCSI gateway command-line interface:
gwcli
[root@iscsigw ~]# gwcliCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify that the initiator is connected the iSCSI target:
/> goto hosts /iscsi-target...csi-igw/hosts> ls o- hosts .............................. [Hosts: 1: Auth: None] o- iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client [LOGGED-IN, Auth: None, Disks: 0(0.00Y)]
/> goto hosts /iscsi-target...csi-igw/hosts> ls o- hosts .............................. [Hosts: 1: Auth: None] o- iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client [LOGGED-IN, Auth: None, Disks: 0(0.00Y)]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The initiator status is
LOGGED-INif it is connected.Verify that LUNs are balanced across iSCSI gateways:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When creating a disk, the disk is assigned an iSCSI gateway as its
Ownerbased on what gateways have the lowest number of mapped LUNs. If this number is balanced, gateways are assigned based on a round robin allocation. Currently, the balancing of LUNs is not dynamic and cannot be selected by the user.When the initiator is logged into the target, and the
multipathlayer is in a optimized state, the initiator’s operating systemmultipathutilities report the path to theOwnergateway as being in ALUA Active-Optimized (AO) state. Themultipathutilities report the other paths as being in the ALUA Active-non-Optimized (ANO) state.If the AO path fails, one of the other iSCSI gateways is used. The ordering for the failover gateway depends on the initiator’s
multipathlayer, where normally, the order is based on which path was discovered first.
10.8. Monitoring the iSCSI gateways
Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster now incorporates a generic metric gathering framework within the OSDs and MGRs to provide built-in monitoring. The metrics are generated within the Red Hat Ceph Storage cluster and there is no need to access client nodes to scrape metrics.
To monitor the performance of RBD images, Ceph has a built-in MGR Prometheus exporter module to translate individual RADOS object metrics into aggregated RBD image metrics for Input/Output(I/O) operations per second, throughput, and latency. The Ceph iSCSI gateway also provides a Prometheus exporter for Linux-IO (LIO) level performance metrics, supporting monitoring and visualization tools like Grafana. These metrics include the information about defined Target Portal Groups (TPGs) and mapped Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs), per LUN state and the number of Input Output operations per second (IOPS), read bytes and write bytes per LUN per client. By default, the Prometheus exporter is enabled.
You can change the default settings by using the following options in the iscsi-gateway.cfg:
Example
[config] prometheus_exporter = True prometheus_port = 9287 prometheus_host = xx.xx.xx.xxx
[config]
prometheus_exporter = True
prometheus_port = 9287
prometheus_host = xx.xx.xx.xxx
The gwtop tool used for Ceph iSCSI gateway environments to monitor performance of exported Ceph block device (RBD) images is deprecated.
10.9. Removing the iSCSI configuration
To remove the iSCSI configuration, use the gwcli utility to remove hosts and disks.
Prerequisites
Disconnect all iSCSI initiators:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux initiators:
Syntax
iscsiadm -m node -T TARGET_NAME --logout
iscsiadm -m node -T TARGET_NAME --logoutCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
TARGET_NAMEwith the configured iSCSI target name, for example:Example
iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw --logout Logging out of session [sid: 1, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.21,3260] Logging out of session [sid: 2, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.22,3260] Logout of [sid: 1, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.21,3260] successful. Logout of [sid: 2, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.22,3260] successful.
# iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw --logout Logging out of session [sid: 1, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.21,3260] Logging out of session [sid: 2, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.22,3260] Logout of [sid: 1, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.21,3260] successful. Logout of [sid: 2, target: iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw, portal: 10.172.19.22,3260] successful.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Windows initiators:
See the Microsoft documentation for more details.
VMware ESXi initiators:
See the VMware documentation for more details.
Procedure
Run the iSCSI gateway command line utility:
gwcli
[root@iscsigw ~]# gwcliCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the hosts:
Syntax
/> cd /iscsi-target/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:$TARGET_NAME/hosts /> /iscsi-target...TARGET_NAME/hosts> delete CLIENT_NAME
/> cd /iscsi-target/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:$TARGET_NAME/hosts /> /iscsi-target...TARGET_NAME/hosts> delete CLIENT_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
TARGET_NAMEwith the configured iSCSI target name, and replaceCLIENT_NAMEwith iSCSI initiator name, for example:Example
/> cd /iscsi-target/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw/hosts /> /iscsi-target...eph-igw/hosts> delete iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client
/> cd /iscsi-target/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:ceph-igw/hosts /> /iscsi-target...eph-igw/hosts> delete iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-clientCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the disks:
Syntax
/> cd /disks/ /disks> delete POOL_NAME.IMAGE_NAME
/> cd /disks/ /disks> delete POOL_NAME.IMAGE_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
POOL_NAMEwith the name of the pool and theIMAGE_NAMEwith the name of the image, for example:Example
/> cd /disks/ /disks> delete rbd.disk_1
/> cd /disks/ /disks> delete rbd.disk_1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.10. Additional Resources
- For details on managing iSCSI gateway using the Red Hat Ceph Storage Dashboard, see the iSCSI functions section in the Dashboard Guide for Red Hat Ceph Storage 5.