Chapter 11. Authentication for enrolling certificates
This chapter covers how to enroll end entity certificates, how to create and manage server certificates, the authentication methods available in the Certificate System to use when enrolling end entity certificates, and how to set up those authentication methods.
Enrollment is the process of issuing certificates to an end entity. The process is creating and submitting the request, authenticating the user requesting it, and then approving the request and issuing the certificate.
The method used to authenticate the end entity determines the entire enrollment process. There are three ways that the Certificate System can authenticate an entity:
- In agent-approved enrollment, end-entity requests are sent to an agent for approval. The agent approves the certificate request.
- In automatic enrollment, end-entity requests are authenticated using a plug-in, and then the certificate request is processed; an agent is not involved in the enrollment process.
- In CMC enrollment, a third party application can create a request that is signed by an agent and then automatically processed.
A Certificate Manager is initially configured for agent-approved enrollment and for CMC authentication. Automated enrollment is enabled by configuring one of the authentication plug-in modules. More than one authentication method can be configured in a single instance of a subsystem.
An email can be automatically sent to an end entity when the certificate is issued for any authentication method by configuring automated notifications. See Chapter 13, Using automated notifications for more information on notifications.
11.1. Configuring agent-approved enrollment
The Certificate Manager is initially configured for agent-approved enrollment. An end entity makes a request which is sent to the agent queue for an agent’s approval. An agent can modify request, change the status of the request, reject the request, or approve the request. Once the request is approved, the signed request is sent to the Certificate Manager for processing. The Certificate Manager processes the request and issues the certificate.
The agent-approved enrollment method is not configurable. If a Certificate Manager is not configured for any other enrollment method, the server automatically sends all certificate-related requests to a queue where they await agent approval. This ensures that all requests that lack authentication credentials are sent to the request queue for agent approval.
To use agent-approved enrollment, leave the authentication method blank in the profile’s
.cfgfile. For example:auth.instance_id=
auth.instance_id=Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.2. Automated enrollment
In automated enrollment, an end-entity enrollment request is processed as soon as the user successfully authenticates by the method set in the authentication plug-in module; no agent approval is necessary. The following authentication plug-in modules are provided:
- Directory-based enrollment. End entities are authenticated against an LDAP directory using their user ID and password or their DN and password. See Section 11.2.1, “Setting up directory-based authentication”.
- PIN-based enrollment. End entities are authenticated against an LDAP directory using their user ID, password, and a PIN set in their directory entry. See Section 11.2.2, “Setting up PIN-based enrollment”.
- Certificate-based authentication. Entities of some kind - both end users and other entities, like servers or tokens - are authenticated to the CA using a certificate issued by the CA which proves their identity. This is most commonly used for renewal, where the original certificate is presented to authenticate the renewal process. See Section 11.2.3, “Using Certificate-Based Authentication”.
AgentCertAuth. This method automatically approves a certificate request if the entity submitting the request is authenticated as a subsystem agent. A user authenticates as an agent by presenting an agent certificate. If the presented certificate is recognized by the subsystem as an agent certificate, then the CA automatically processes the certificate request.
This form of automatic authentication can be associated with the certificate profile for enrolling for server certificates.
This plug-in is enabled by default and has no parameters.
- Flat file-based enrollment. Used exclusively for router (SCEP) enrollments, a text file is used which contains a list of IP addresses, hostnames, or other identifier and a password, which is usually a random PIN. A router authenticates to the CA using its ID and PIN, and then the CA compares the presented credentials to the list of identities in the text file. See Section 11.2.4, “Configuring Flat File Authentication”.
11.2.1. Setting up directory-based authentication
The UidPwdDirAuth and the UdnPwdDirAuth plug-in modules implement directory-based authentication. End users enroll for a certificate by providing their user IDs or DN and password to authenticate to an LDAP directory.
Create an instance of either the
UidPwdDirAuthorUdnPwdDirAuthauthentication plug-in module and configure the instance.Open the CA Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.In the Configuration tab, select Authentication in the navigation tree.
The right pane shows the Authentication Instance tab, which lists the currently configured authentication instances.
NoteThe
UidPwdDirAuthplug-in is enabled by default.Click .
The Select Authentication Plug-in Implementation window appears.
-
Select
UidPwdDirAuthfor user ID and password authentication, or selectUdnPwdDirAuthfor DN and password authentication. Fill in the following fields in the Authentication Instance Editor window:
- Authentication Instance ID. Accept the default instance name, or enter a new name.
- dnpattern. Specifies a string representing a subject name pattern to formulate from the directory attributes and entry DN.
- ldapStringAttributes. Specifies the list of LDAP string attributes that should be considered authentic for the end entity. If specified, the values corresponding to these attributes are copied from the authentication directory into the authentication token and used by the certificate profile to generate the subject name. Entering values for this parameter is optional.
ldapByteAttributes. Specifies the list of LDAP byte (binary) attributes that should be considered authentic for the end entity. If specified, the values corresponding to these attributes will be copied from the authentication directory into the authentication token for use by other modules, such as adding additional information to users' certificates.
Entering values for this parameter is optional.
- ldap.ldapconn.host. Specifies the fully-qualified DNS hostname of the authentication directory.
- ldap.ldapconn.port. Specifies the TCP/IP port on which the authentication directory listens to requests; if the ldap.ldapconn.secureConn. checkbox is selected, this should be the SSL port number.
- ldap.ldapconn.secureConn. Specifies the type, SSL or non-SSL, of the port on which the authentication directory listens to requests from the Certificate System. Select if this is an SSL port.
-
ldap.ldapconn.version. Specifies the LDAP protocol version, either
2or3. The default is3, since all Directory Servers later than version 3.x are LDAPv3. -
ldap.basedn. Specifies the base DN for searching the authentication directory. The server uses the value of the
uidfield from the HTTP input (what a user enters in the enrollment form) and the base DN to construct an LDAP search filter. -
ldap.minConns. Specifies the minimum number of connections permitted to the authentication directory. The permissible values are
1to3. -
ldap.maxConns. Specifies the maximum number of connections permitted to the authentication directory. The permissible values are
3to10.
- Click . The authentication instance is set up and enabled.
Set the certificate profiles to use to enroll users by setting policies for specific certificates. Customize the enrollment forms by configuring the inputs in the certificate profiles, and include inputs for the information needed by the plug-in to authenticate the user. If the default inputs do not contain all of the information that needs to be collected, submit a request created with a third-party tool.
For information on configuring the profiles, see Section 3.7.2, “Inserting LDAP directory attribute values and other information into the subject alt name”.
Setting up bound LDAP connection
Some environments require disallowing an anonymous bind for the LDAP server that is used for authentication. To create a bound connection between a CA and the LDAP server, you need to make the following configuration changes:
Set up directory-based authentication according to the following example in
CS.cfg:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow where bindPWPrompt is the tag or prompt that is used in the
password.conffile; it is also the name used under the cms.passwordlist and authPrefix options.Add the tag or prompt from
CS.cfgwith its password inpassword.conf:externalLDAP=your_password
externalLDAP=your_passwordCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Setting up external authorization
A directory-based authentication plug-in can also be configured to evaluate the group membership of the user for authentication. To set up the plug-in this way, the following options has to be configured in CS.cfg:
-
groupsEnable is a boolean option that enables retrieval of groups. The default value is
false. - groupsBasedn is the base DN of groups. It needs to be specified when it differs from the default basedn.
-
groups is the DN component for groups. The default value is
ou=groups. -
groupObjectClass is one of the following group object classes:
groupofuniquenames,groupofnames. The default value isgroupofuniquenames. -
groupUseridName is the name of the user ID attribute in the group object member attribute. The default value is
cn. -
useridName is the name of the user ID DN component. The default value is
uid. -
searchGroupUserByUserdn is a boolean option that determines whether to search the group object member attribute for the userdn or
${groupUserIdName}=${uid}attributes. The default value istrue.
For example:
Finally, you have to modify the /instance_path/ca/profiles/ca/profile_id.cfg file to configure the profile to use the UserDirEnrollment auth instance defined in CS.cfg, and if appropriate, provide an ACL for authorization based on groups. For example:
auth.instance_id=UserDirEnrollment authz.acl=group="cn=devlab-access,ou=engineering,dc=example,dc=com"
auth.instance_id=UserDirEnrollment
authz.acl=group="cn=devlab-access,ou=engineering,dc=example,dc=com"11.2.2. Setting up PIN-based enrollment
PIN-based authentication involves setting up PINs for each user in the LDAP directory, distributing those PINs to the users, and then having the users provide the PIN along with their user ID and password when filling out a certificate request. Users are then authenticated both against an LDAP directory using their user ID and password and against the PIN in their LDAP entry. When the user successfully authenticates, the request is automatically processed, and a new certificate is issued.
The Certificate System provides a tool, setpin, that adds the necessary schema for PINs to the Directory Server and generates the PINs for each user.
The PIN tool performs the following functions:
- Adds the necessary schema for PINs to the LDAP directory.
- Adds a PIN manager user who has read-write permissions to the PINs that are set up.
- Sets up ACIs to allow for PIN removal once the PIN has been used, giving read-write permissions for PINs to the PIN manager, and preventing users from creating or changing PINs.
- Creates PINs in each user entry.
This tool is documented in the Certificate System Command-Line Tools Guide.
Use the PIN tool to add schema needed for PINs, add PINs to the user entries, and then distribute the PINs to users.
-
Open the
/usr/share/pki/native-tools/directory. -
Open the
setpin.conffile in a text editor. Follow the instructions outlined in the file and make the appropriate changes.
Usually, the parameters which need updated are the Directory Server’s host name, Directory Manager’s bind password, and PIN manager’s password.
Run the
setpincommand with itsoptfileoption pointing to thesetpin.conffile.setpin optfile=/usr/share/pki/native-tools/setpin.conf
setpin optfile=/usr/share/pki/native-tools/setpin.confCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The tool modifies the schema with a new attribute (by default,
pin) and a new object class (by default,pinPerson), creates apinmanageruser, and sets the ACI to allow only thepinmanageruser to modify thepinattribute.To generate PINs for specific user entries or to provide user-defined PINs, create an input file with the DNs of those entries listed. For example:
dn:uid=bjensen,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com dn:uid=jsmith,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com dn:jtyler,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com ...
dn:uid=bjensen,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com dn:uid=jsmith,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com dn:jtyler,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com ...Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For information on constructing an input file, see the PIN generator chapter in the Certificate System Command-Line Tools Guide.
Disable setup mode for the
setpincommand. Either comment out thesetupline or change the value to no.vim /usr/share/pki/native-tools/setpin.conf
# vim /usr/share/pki/native-tools/setpin.conf setup=noCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Setup mode creates the required uers and object classes, but the tool will not generate PINs while in setup mode.
Run the
setpincommand to create PINs in the directory.NoteTest-run the tool first without the write option to generate a list of PINs without actually changing the directory.
For example:
setpin host=yourhost port=9446 length=11 input=infile output=outfile write "binddn=cn=pinmanager,o=example.com" bindpw="password" basedn=o=example.com "filter=(uid=u*)" hash=sha256
setpin host=yourhost port=9446 length=11 input=infile output=outfile write "binddn=cn=pinmanager,o=example.com" bindpw="password" basedn=o=example.com "filter=(uid=u*)" hash=sha256Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningDo not set the hash argument to
none. Running thesetpincommand withhash=noneresults in the pin being stored in the user LDAP entry as plain text.Use the output file for delivering PINs to users after completing setting up the required authentication method.
After confirming that the PIN-based enrollment works, deliver the PINs to users so they can use them during enrollment. To protect the privacy of PINs, use a secure, out-of-band delivery method.
-
Open the
- Set the policies for specific certificates in the certificate profiles to enroll users. See Chapter 3, Certificate profiles (Making Rules for Issuing Certificates) for information about certificate profile policies.
Create and configure an instance of the
UidPwdPinDirAuthauthentication plug-in.Open the CA Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.In the Configuration tab, select Authentication in the navigation tree.
The right pane shows the Authentication Instance tab, which lists the currently configured authentication instances.
Click .
The Select Authentication Plug-in Implementation window appears.
-
Select the
UidPwdPinDirAuthplug-in module. Fill in the following fields in the Authentication Instance Editor window:
- Authentication Instance ID. Accept the default instance name or enter a new name.
- removePin. Sets whether to remove PINs from the authentication directory after end users successfully authenticate. Removing PINs from the directory restricts users from enrolling more than once, and thus prevents them from getting more than one certificate.
-
pinAttr. Specifies the authentication directory attribute for PINs. The
PIN Generatorutility sets the attribute to the value of theobjectclassparameter in thesetpin.conffile; the default value for this parameter ispin. - dnpattern. Specifies a string representing a subject name pattern to formulate from the directory attributes and entry DN.
- ldapStringAttributes. Specifies the list of LDAP string attributes that should be considered authentic for the end entity. Entering values for this parameter is optional.
ldapByteAttributes. Specifies the list of LDAP byte (binary) attributes that should be considered authentic for the end entity. If specified, the values corresponding to these attributes will be copied from the authentication directory into the authentication token for use by other modules, such as adding additional information to users' certificates.
Entering values for this parameter is optional.
- ldap.ldapconn.host. Specifies the fully-qualified DNS host name of the authentication directory.
- ldap.ldapconn.port. Specifies the TCP/IP port on which the authentication directory listens to requests from the Certificate System.
- ldap.ldapconn.secureConn. Specifies the type, SSL or non-SSL, of the port on which the authentication directory listens to requests. Select if this is an SSL port.
-
ldap.ldapconn.version. Specifies the LDAP protocol version, either
2or3. By default, this is3, since all Directory Server versions later than 3.x are LDAPv3. - ldap.ldapAuthentication.bindDN. Specifies the user entry as whom to bind when removing PINs from the authentication directory. Specify this parameter only if the removePin checkbox is selected. It is recommended that a separate user entry that has permission to modify only the PIN attribute in the directory be created and used. For example, do not use the Directory Manager’s entry because it has privileges to modify the entire directory content.
-
password. Gives the password associated with the DN specified by the
ldap.ldapauthbindDNparameter. When saving changes, the server stores the password in the single sign-on password cache and uses it for subsequent start ups. This parameter needs set only if the removePin checkbox is selected. -
ldap.ldapAuthentication.clientCertNickname. Specifies the nickname of the certificate to use for SSL client authentication to the authentication directory to remove PINs. Make sure that the certificate is valid and has been signed by a CA that is trusted in the authentication directory’s certificate database and that the authentication directory’s
certmap.conffile has been configured to map the certificate correctly to a DN in the directory. This is needed for PIN removal only. ldap.ldapAuthentication.authtype. Specifies the authentication type, basic authentication or SSL client authentication, required in order to remove PINs from the authentication directory.
- BasicAuth specifies basic authentication. With this option, enter the correct values for ldap.ldapAuthentication.bindDN and password parameters; the server uses the DN from the ldap.ldapAuthentication.bindDN attribute to bind to the directory.
-
SslClientAuth specifies SSL client authentication. With this option, set the value of the ldap.ldapconn.secureConn parameter to
trueand the value of the ldap.ldapAuthentication.clientCertNickname parameter to the nickname of the certificate to use for SSL client authentication.
-
ldap.basedn. Specifies the base DN for searching the authentication directory; the server uses the value of the
uidfield from the HTTP input (what a user enters in the enrollment form) and the base DN to construct an LDAP search filter. -
ldap.minConns. Specifies the minimum number of connections permitted to the authentication directory. The permissible values are
1to3. -
ldap.maxConns. Specifies the maximum number of connections permitted to the authentication directory. The permissible values are
3to10.
- Click .
- Customize the enrollment forms by configuring the inputs in the certificate profiles. Include the information that will be needed by the plug-in to authenticate the user. If the default inputs do not contain all of the information that needs to be collected, submit a request created with a third-party tool.
11.2.3. Using Certificate-Based Authentication
Certificate-based authentication is when a certificate is presented that verifies the identity of the requester and automatically validates and authenticates the request being submitted. This is most commonly used for renewal processes, when the original certificate is presented by the user, server, and application and that certificate is used to authenticate the request.
There are other circumstances when it may be useful to use certificate-based authentication for initially requesting a certificate. For example, tokens may be bulk-loaded with generic certificates which are then used to authenticate the users when they enroll for their user certificates or, alternatively, users can be issued signing certificates which they then use to authenticate their requests for encryption certificates.
The certificate-based authentication module, SSLclientCertAuth, is enabled by default, and this authentication method can be referenced in any custom certificate profile.
11.2.4. Configuring Flat File Authentication
A router certificate is enrolled and authenticated using a randomly-generated PIN. The CA uses the flatFileAuth authentication module to process a text file which contains the router’s authentication credentials.
11.2.4.1. Configuring the flatFileAuth Module
Flat file authentication is already configured for SCEP enrollments, but the location of the flat file and its authentication parameters can be edited.
Open the CA Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.- In the Configuration tab, select Authentication in the navigation tree.
Select the flatFileAuth authentication module.
- Click .
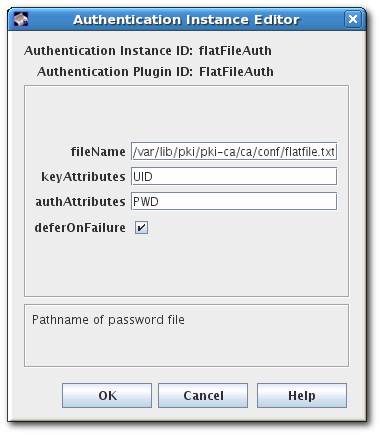
To change the file location and name, reset the fileName field.
To change the authentication name parameter, reset the keyAttributes value to another value submitted in the SCEP enrollment form, like CN. It is also possible to use multiple name parameters by separating them by commas, like
UID,CN. To change the password parameter name, reset theauthAttributesfield.- Save the edits.
11.2.4.2. Editing flatfile.txt
The same flatfile.txt file is used to authenticate every SCEP enrollment. This file must be manually updated every time a new PIN is issued to a router.
By default, this file is in /var/lib/pki/pki-ca/ca/conf/ and specifies two parameters per authentication entry, the UID of the site (usually its IP address, either IPv4 or IPv6) and the PIN issued by the router.
UID:192.168.123.123 PIN:HU89dj
UID:192.168.123.123
PIN:HU89djEach entry must be followed by a blank line. For example:
If the authentication entries are not separated by an empty line, then when the router attempts to authenticate to the CA, it will fail. For example:
11.3. CMC authentication plug-ins
CMC enrollment allows an enrollment client to use a CMC Authentication plug-in for authentication, by which the certificate request is either pre-signed with an agent certificate or a user certificate, depending on the plug-in. The Certificate Manager automatically issues certificates when a CMC request signed with a valid certificate is received.
The CMC authentication plug-ins also provide CMC revocation for the client. CMC revocation allows the client to have the certificate request either signed by the agent certificate, or a verifiable user that owns the certificate, and then send such a request to the Certificate Manager. The Certificate Manager automatically revokes certificates when a CMC revocation request signed with a valid certificate is received.
Certificate System provides the following CMC authentication plug-ins:
CMCAuthUse this plug-in when a CA agent signs CMC requests.
To use the
CMCAuthplug-in, set the following in the enrollment profile:auth.instance_id=CMCAuth
auth.instance_id=CMCAuthCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, the following enrollment profiles use the
CMCAuthplug-in:For system certificates:
-
caCMCauditSigningCert -
caCMCcaCert -
caCMCECserverCert -
caCMCECsubsystemCert -
caCMCECUserCert -
caCMCkraStorageCert -
caCMCkraTransportCert -
caCMCocspCert -
caCMCserverCert -
caCMCsubsystemCert
-
For user certificates:
-
caCMCUserCert -
caECFullCMCUserCert -
caFullCMCUserCert
-
CMCUserSignedAuthUse this plug-in when users submit signed or SharedSecret-based CMC requests.
To use the
CMCUserSignedAuthplug-in, set the following in the enrollment profile:auth.instance_id=CMCUserSignedAuth
auth.instance_id=CMCUserSignedAuthCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A user-signed CMC request must be signed by the user’s certificate which contains the same
subjectDNattribute as the requested certificate. You can only use a user-signed CMC request if the user already obtained a signing certificate which can be used to prove the user’s identity for other certificates.A SharedSecret-based CMC request means that the request was signed by the private key of the request itself. In this case, the CMC request must use the Shared Secret mechanism for authentication. A SharedSecret-based CMC request is typically used to obtain the user’s first signing certificate, which is later used to obtain other certificates. For further details, see Section 11.4, “CMC SharedSecret authentication”.
By default, the following enrollment profiles use the
CMCUserSignedAuthplug-in:-
caFullCMCUserSignedCert -
caECFullCMCUserSignedCert -
caFullCMCSharedTokenCert -
caECFullCMCSharedTokenCert
-
11.5. Testing enrollment
For information on testing enrollment through the profiles, see Chapter 3, Certificate profiles (Making Rules for Issuing Certificates). To test whether end users can successfully enroll for a certificate using the authentication method set:
Open the end-entities page.
https://server.example.com:8443/ca/ee/ca
https://server.example.com:8443/ca/ee/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - In the Enrollment tab, open the customized enrollment form.
- Fill in the values, and submit the request.
- Enter the password to the key database when prompted.
When the correct password is entered, the client generates the key pair.
Do not interrupt the key-generation process. Upon completion of the key generation, the request is submitted to the server to issue the certificate. The server subjects the request to the certificate profile and issues the certificate only if the request meets all the requirements.
When the certificate is issued, install the certificate in the browser.
- Verify that the certificate is installed in the browser’s certificate database.
- If PIN-based directory authentication was configured with PIN removal, re-enroll for another certificate using the same PIN. The request should be rejected.
11.5.1. Registering custom authentication plug-ins
Custom authentication plug-in modules can be registered through the CA Console. Authentication plug-in modules can also be deleted through the CA Console. Before deleting a module, delete instances that are based on that module.
For writing custom plug-ins, refer to the Authentication Plug-in Tutorial.
-
Create the custom authentication class. For this example, the custom authentication plug-in is called
UidPwdDirAuthenticationTestms.java. Compile the new class.
javac -d . -classpath $CLASSPATH UidPwdDirAuthenticationTestms.java
javac -d . -classpath $CLASSPATH UidPwdDirAuthenticationTestms.javaCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a directory in the CA’s
WEB-INFweb directory to hold the custom classes, so that the CA can access them for the enrollment forms.mkdir /usr/share/pki/ca/webapps/ca/WEB-INF/classes
mkdir /usr/share/pki/ca/webapps/ca/WEB-INF/classesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the new plug-in files into the new
classesdirectory, and set the owner to the Certificate System system user (pkiuser).cp -pr com /usr/share/pki/ca/webapps/ca/WEB-INF/classes chown -R pkiuser:pkiuser /usr/share/pki/ca/webapps/ca/WEB-INF/classes
cp -pr com /usr/share/pki/ca/webapps/ca/WEB-INF/classes chown -R pkiuser:pkiuser /usr/share/pki/ca/webapps/ca/WEB-INF/classesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Log into the console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/ca
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:8443/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Notepkiconsoleis being deprecated.Register the plug-in.
- In the Configuration tab, click Authentication in the navigation tree.
In the right pane, click the Authentication Plug-in Registration tab.
The tab lists modules that are already registered.
To register a plug-in, click .
The Register Authentication Plug-in Implementation window appears.
Specify which module to register by filling in the two fields:
- Plugin name. The name for the module.
-
Class name. The full name of the class for this module. This is the path to the implementing Java™ class. If this class is part of a package, include the package name. For example, to register a class named
customAuthin a package namedcom.customplugins, the class name iscom.customplugins.customAuth.
After registering the module, add the module as an active authentication instance.
- In the Configuration tab, click Authentication in the navigation tree.
- In the right pane, click the Authentication Instance tab.
- Click .
-
Select the custom module,
UidPwdDirAuthenticationTestms.java, from the list to add the module. Fill in the appropriate configuration for the module.
Create a new end-entity enrollment form to use the new authentication module.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the new profile to the CA’s
CS.cfgfile.TIPBack up the
CS.cfgfile before editing it.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the CA.
pki-server restart instance_name
pki-server restart instance_nameCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.6. Manually reviewing the certificate status
To review certificate requests, ensure that you are authenticated as an agent with proper permissions to approve certificate requests. For details about configuring the pki command-line interface, see Section 2.5.1.1, “pki CLI initialization”.
11.6.1. Manually reviewing the certificate status using the command line
To review the requests using the CLI:
Display the list of pending certificate requests:
pki agent_authentication_parameters ca-cert-request-find --status pending
$ pki agent_authentication_parameters ca-cert-request-find --status pendingCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command lists all pending certificate requests.
Download a particular certificate request:
pki agent_authentication_parameters ca-cert-request-review id --file request.xml
$ pki agent_authentication_parameters ca-cert-request-review id --file request.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
request.xmlfile in an editor or a separate terminal, and review the contents of the request to ensure it is legitimate. Then answer the prompt: if the request is valid, answerapproveand press Enter. If the request is invalid, answerrejectand press Enter. Organizations can subscribe semantic differences torejectandcancel; both result in no certificate being issued.
11.6.2. Manually reviewing the certificate status using the web interface
To review the requests using Web UI:
Open the following URL in a web browser:
https://server_host_name:8443/ca/agent/ca
https://server_host_name:8443/ca/agent/caCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Authenticate as an agent. For information about authenticating as a user and configuring your browser, see Section 2.4.1, “Browser initialization”.
- On the sidebar on the left, click the List requests link.
-
Filter the requests by selecting
Show all requestsfor Request type andShow pending requestsfor Request status. Click in the lower right corner.
- The results page lists all pending requests waiting for review. Click on the request number to review a request.
Review the request information and ensure that it is a legitimate request. If necessary, modify the policy information to correct any mistakes or make any desired changes to the certificate, such as changing the not valid after field. Optionally, leave an additional note.
The drop down menu includes several review status updates. Select Approve request to approve the request or Reject request to deny it, and click . Organizations can subscribe semantic differences to Reject request and Cancel Request; both result in no certificate being issued.