Chapter 2. Che-Theia IDE basics
This section describes basics workflows and commands for Che-Theia: the native integrated development environment for Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.
2.1. Defining custom commands for Che-Theia
The Che-Theia IDE allows users to define custom commands in a devfile that are then available when working in a workspace.
The following is an example of the commands section of a devfile.
- CodeReady Workspaces commands
theia:build-
The
exectype implies that the CodeReady Workspaces runner is used for command execution. The user can specify the component in whose container the command is executed. -
The
commandfield contains the command line for execution. -
The
workdiris the working directory in which the command is executed.
-
The
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code) tasks
run-
The type is
vscode-task. -
For this type of command, the
referenceContentfield must contain content with task configurations in the VS Code format. - For more information about VS Code tasks, see the Task section on the Visual Studio User Guide page.
-
The type is
- VS Code launch configurations
debug-
The type is
vscode-launch. - It contains the launch configurations in the VS Code format.
- For more information about VS Code launch configurations, see the Debugging section on the Visual Studio documentation page.
-
The type is
For a list of available tasks and launch configurations, see the:
-
tasks.jsonfile in the/projects/.theiadirectory launch.jsonfile in the/home/theia/.theiadirectoryof the
theia-idecontainer.
2.1.1. Che-Theia task types
The commands section in a devfile allows a user to automate certain actions when running a CodeReady Workspaces workspace.
There are three types of CodeReady Workspaces commands:
-
exec: Each command of typeexecis translated into a Che-Theia task of typecodeready. Acodereadycommand executes a shell command, but in contrast to regular Che-Theia shell-type tasks, a user can choose a workspace container for the command execution. -
vscode-task:vscode-taskis a single command type that copies the contents of thereferenceContentfieldof the specific command directly to the user-level task configurations in Che-Theia. -
vscode-launch: Functions like avscode-taskcommand, but instead of being copied into the task configurations, the content of thereferenceContentfield is copied into thelaunch.jsonconfiguration file.
Tasks of type codeready, also known as exec commands, can be executed from the Terminal→Run Task menu or by clicking them in the My Workspace panel. Other tasks are only available via Terminal→Run Task. Launch configurations are available in the Che-Theia debugger.
Example:
The following example contains a codeready task and vscode-task task sample.
The configuration in Defining custom commands for Che-Theia sets up the theia:watch and theia:build tasks in the theia workspace:
-
theia:watch, which runs thetheiaproject inwatchmode. -
theia:build, which builds thetheiaproject in theche-devcomponent.
Descriptions of used codeready commands in the above-mentioned example theia:build
-
The
exectype implies that the CodeReady Workspaces runner is used for command execution. - The user can specify the component in whose container the command is executed.
-
The
commandfield contains the command line for execution. -
The
workdiris the working directory in which the command is executed.
These tasks are available for running in a workspace from the Terminal→Run Task menu or by clicking them in the My Workspace panel.
Additional examples
2.1.2. Running and debugging
Che-Theia supports the Debug Adapter Protocol. This protocol defines a generic way for how a development tool can communicate with a debugger. It means Che-Theia works with all implementations.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see Installing CodeReady Workspaces on OpenShift Container Platform.
Procedure
To debug an application:
Click Debug
Add Configuration to add debugging or launch configuration to the project. 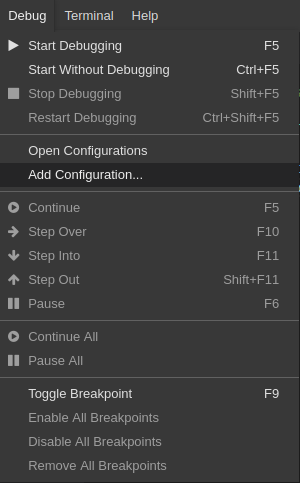
From the pop-up menu, select the appropriate configuration for the application that you want to debug.
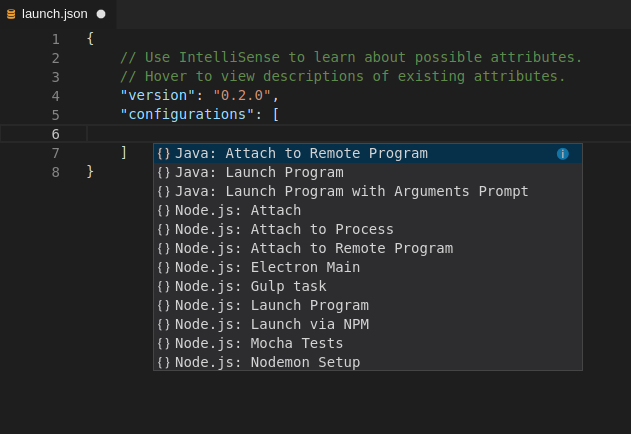
Update the configuration by modifying or adding attributes.
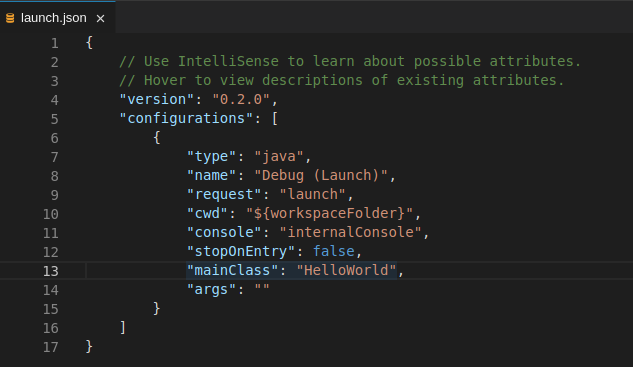
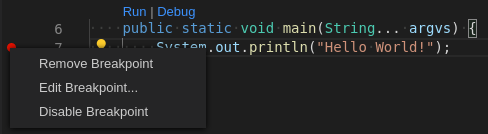
Breakpoints can be toggled by clicking the editor margin.
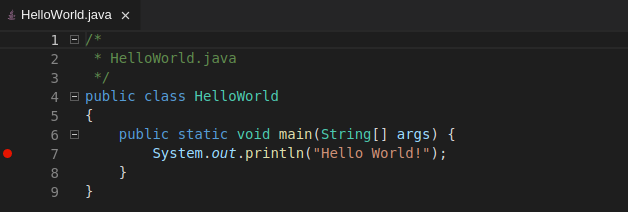
After opening a context menu, use the Edit Breakpoint command to add conditions.
The IDE then displays the
Expresioninput field.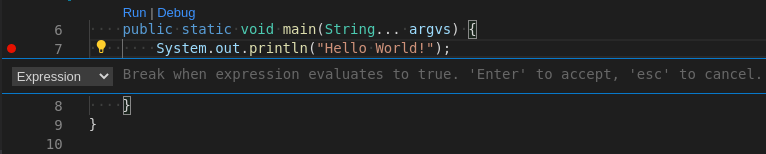
To start debugging, click View→Debug.
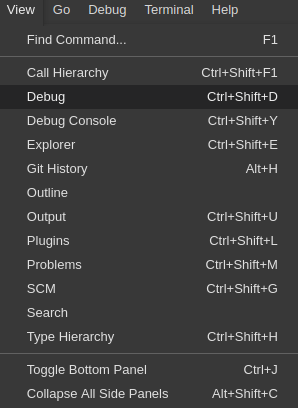
In the Debug view, select the configuration and press F5 to debug the application. Or, start the application without debugging by pressing Ctrl+F5.
2.1.3. Editing a task and launch configuration
Procedure
To customize the configuration file:
-
Edit the
tasks.jsonorlaunch.jsonconfiguration files. Add new definitions to the configuration file or modify the existing ones.
NoteThe changes are stored in the configuration file.
-
To customize the task configuration provided by plug-ins, select the Terminal
Configure Tasks menu option, and choose the task to configure. The configuration is then copied to the tasks.jsonfile and is available for editing.
2.2. Version Control
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces natively supports the VS Code SCM model. By default, Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces includes the native VS Code Git extension as a Source Code Management (SCM) provider.
2.2.1. Managing Git configuration: identity
The first thing to do before starting to use Git is to set a user name and email address. This is important because every Git commit uses this information.
Prerequisites
- The Visual Studio Code Git extension installed.
Procedure
To configure Git identity using the CodeReady Workspaces user interface, go to in Preferences.
Open File > Settings > Open Preferences:
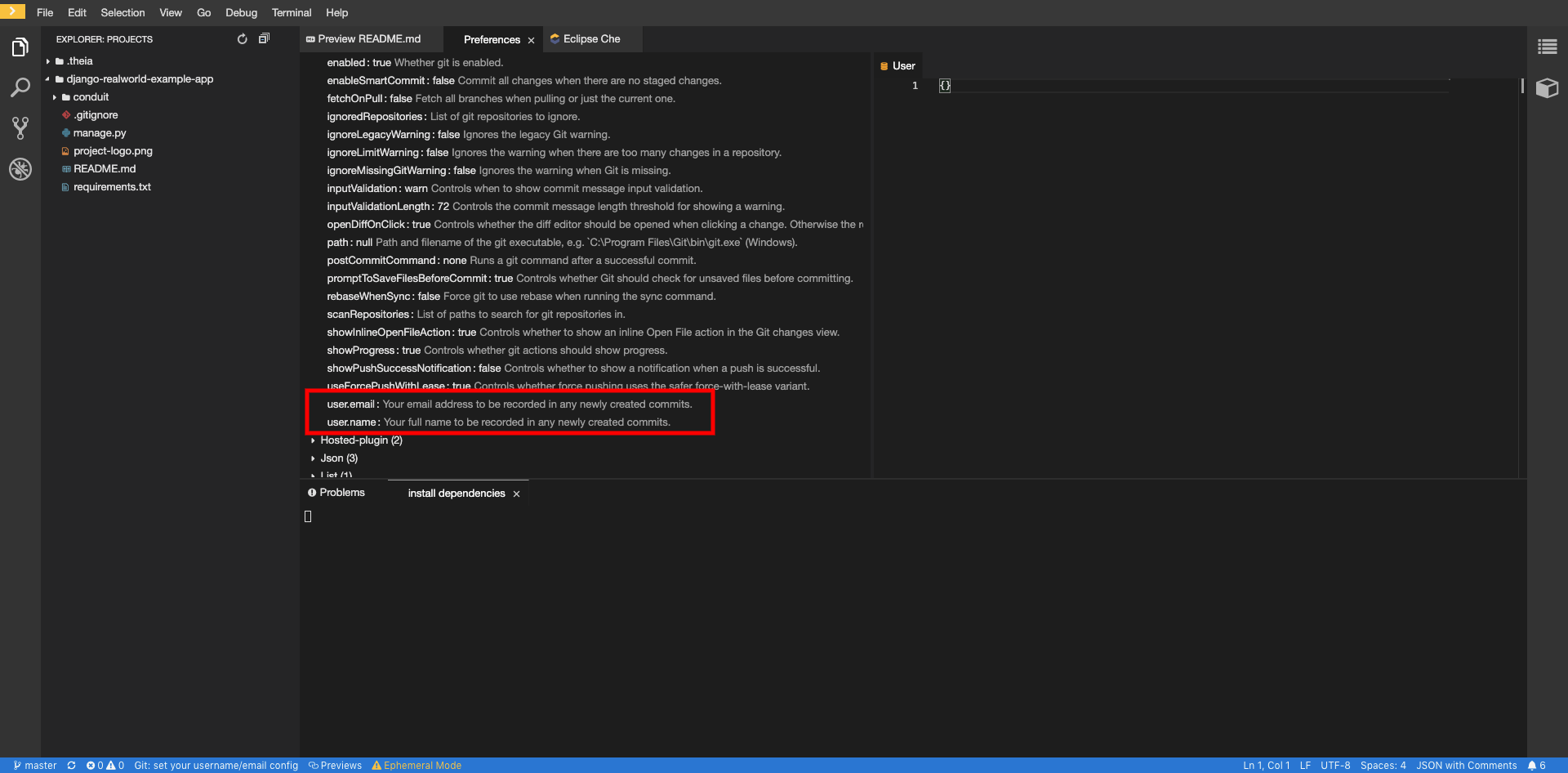
In the opened window, navigate to the Git section, and find:
user.name user.email
user.name user.emailCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the identity.
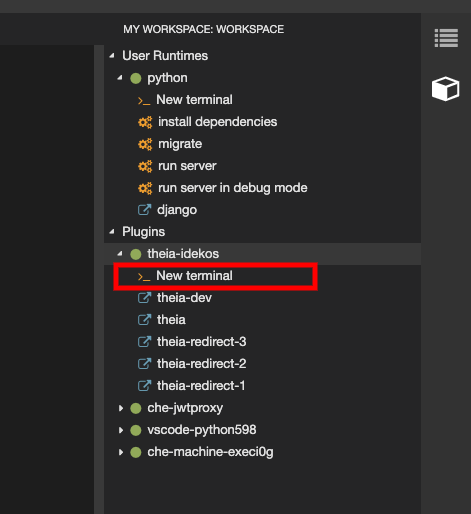
To configure Git identity using the command line, open the terminal of the Che-Theia container.
Navigate to the My Workspace view, and open Plugins > theia-ide… > New terminal:
Execute the following commands:
git config --global user.name "John Doe" git config --global user.email johndoe@example.com
$ git config --global user.name "John Doe" $ git config --global user.email johndoe@example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Che-Theia permanently stores this information and restores it on future workspace starts.
2.2.2. Accessing a Git repository using HTTPS
Prerequisites
-
The
gittool is available. See: Getting Started - Installing Git.
Procedure
To clone a repository using HTTPS:
- Use the clone command provided by the Visual Studio Code Git extension.
Alternatively, use the native Git commands in the terminal to clone a project.
-
Navigate to destination folder using the
cdcommand. Use
git cloneto clone a repository:git clone <link>
$ git clone <link>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces supports Git self-signed TLS certificates. See the Installation Guide to learn more.
2.2.3. Accessing a Git repository using a generated SSH key pair
2.2.3.1. Generating an SSH key using the CodeReady Workspaces command palette
The following section describes a generation of an SSH key using the CodeReady Workspaces command palette and its further use in Git provider communication. This SSH key restricts permissions for the specific Git provider; therefore, the user has to create a unique SSH key for each Git provider in use.
Prerequisites
- A running instance of CodeReady Workspaces. To install an instance of Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces, see the CodeReady Workspaces 2.3 Installation Guide.
- An existing workspace defined on this instance of CodeReady Workspaces Creating a workspace from user dashboard.
- Personal GitHub account or other Git provider account created.
Procedure
A common SSH key pair that works with all the Git providers is present by default. To start using it, add the public key to the Git provider.
Generate an SSH key pair that only works with a particular Git provider:
In the CodeReady Workspaces IDE, press F1 to open the Command Palette, or navigate to View
Find Command in the top menu. The command palette can be also activated by pressing Ctrl+Shift+p (or Cmd+Shift+p on macOS).
-
Search for SSH: generate key pair for particular host by entering
generateinto the search box and pressing Enter once filled. Provide the hostname for the SSH key pair such as, for example,
github.com.The SSH key pair is generated.
Click the button and copy the public key from the editor and add it to the Git provider.
Because of this action, the user can now use another command from the command palette: Clone git repository by providing an SSH secured URL.
2.2.3.2. Adding the associated public key to a repository or account on GitHub
To add the associated public key to a repository or account on GitHub:
- Navigate to github.com.
- Click the drop-down arrow next to the user icon in the upper right corner of the window.
-
Click Settings
SSH and GPG keys and then click the button. - In the Title field, type a title for the key, and in the Key field, paste the public key copied from CodeReady Workspaces.
- Click the button.
2.2.3.3. Adding the associated public key to a Git repository or account on GitLab
To add the associated public key to a Git repository or account on GitLab:
- Navigate to gitlab.com.
- Click the user icon in the upper right corner of the window.
-
Click Settings
SSH Keys. - In the Title field, type a title for the key and in the Key field, paste the public key copied from CodeReady Workspaces.
- Click the button.
2.2.4. Managing pull requests using the GitHub PR plug-in
To manage GitHub pull requests, the VS Code GitHub Pull Request plug-in is available in the list of plug-ins of the workspace.
2.2.4.1. Using the GitHub Pull Requests plug-in
Prerequisites
- GitHub OAuth is configured. See Configuring GitHub OAuth.
Procedure
- Authenticate by running the GitHub authenticate command.
- You will be redirected to GitHub to authorize CodeReady Workspaces.
- When CodeReady Workspaces is authorized, refresh the browser page where CodeReady Workspaces is running to update the plug-in with the GitHub token.
Alternatively, manually fetch the GitHub token and paste it to the plug-in by running the GitHub Pull Requests: Manually Provide Authentication Response command.
2.2.4.2. Creating a new pull request
- Open the GitHub repository. To be able to execute remote operations, the repository must have a remote with an SSH URL.
- Checkout a new branch and make changes that you want to publish.
- Run the GitHub Pull Requests: Create Pull Request command.
2.3. Che-Theia Troubleshooting
This section describes some of the most frequent issues with the Che-Theia IDE.
- Che-Theia shows a notification with the following message:
Plugin runtime crashed unexpectedly, all plugins are not working, please reload the page. Probably there is not enough memory for the plugins. This means that one of the Che-Theia plug-ins that are running in the Che-Theia IDE container requires more memory than the container has. To fix this problem, increase the amount of memory for the Che-Theia IDE container:
- Navigate to the CodeReady Workspaces Dashboard.
- Select the workspace in which the problem happened.
- Switch to the Devfile tab.
-
In the
componentssection of the devfile, find a component of thecheEditortype. -
Add a new property,
memoryLimit: 1024M(or increase the value if it already exists). - Save changes and restart the workspace.
Additional resources
- Asking the community for help: Mattermost channel dedicated to Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces.
- Reporting a bug: Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces repository issues.