4.4. GLOBAL SETTINGS
The GLOBAL SETTINGS panel is where the you define the networking details for the primary LVS router's public and private network interfaces.
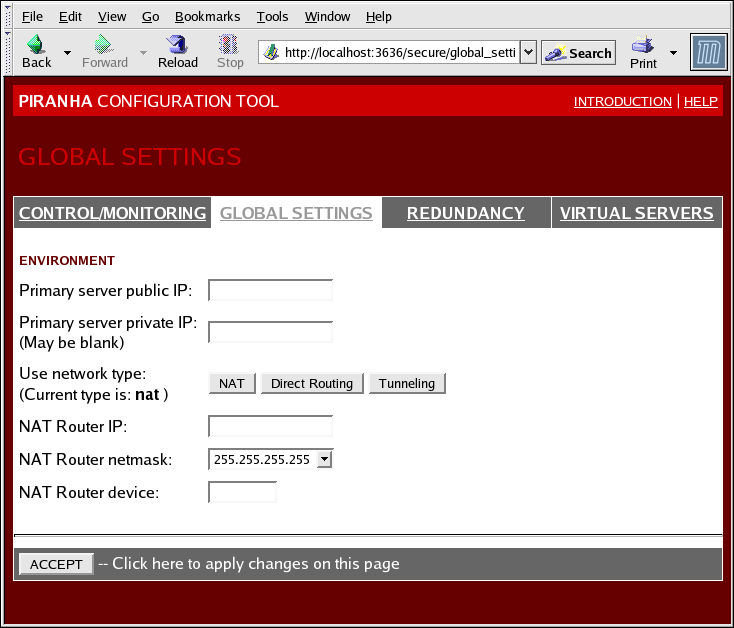
Figure 4.3. The GLOBAL SETTINGS Panel
The top half of this panel sets up the primary LVS router's public and private network interfaces. These are the interfaces already configured in Section 3.1.1, “Configuring Network Interfaces for LVS with NAT”.
- Primary server public IP
- In this field, enter the publicly routable real IP address for the primary LVS node.
- Primary server private IP
- Enter the real IP address for an alternative network interface on the primary LVS node. This address is used solely as an alternative heartbeat channel for the backup router and does not have to correlate to the real private IP address assigned in Section 3.1.1, “Configuring Network Interfaces for LVS with NAT”. You may leave this field blank, but doing so will mean there is no alternate heartbeat channel for the backup LVS router to use and therefore will create a single point of failure.
Note
The private IP address is not needed for configurations, as all real servers as well as the LVS directors share the same virtual IP addresses and should have the same IP route configuration.Note
The primary LVS router's private IP can be configured on any interface that accepts TCP/IP, whether it be an Ethernet adapter or a serial port. - Use network type
- Click the button to select NAT routing.Click the button to select direct routing.
The next three fields deal specifically with the NAT router's virtual network interface connecting the private network with the real servers. These fields do not apply to the direct routing network type.
- NAT Router IP
- Enter the private floating IP in this text field. This floating IP should be used as the gateway for the real servers.
- NAT Router netmask
- If the NAT router's floating IP needs a particular netmask, select it from drop-down list.
- NAT Router device
- Use this text field to define the device name of the network interface for the floating IP address, such as
eth1:1.Note
You should alias the NAT floating IP address to the Ethernet interface connected to the private network. In this example, the private network is on theeth1interface, soeth1:1is the floating IP address.
Warning
After completing this page, click the button to make sure you do not lose any changes when selecting a new panel.