1.2. Overview of DM Multipath
DM Multipath can be used to provide:
- RedundancyDM Multipath can provide failover in an active/passive configuration. In an active/passive configuration, only half the paths are used at any time for I/O. If any element of an I/O path (the cable, switch, or controller) fails, DM Multipath switches to an alternate path.
- Improved PerformanceDM Multipath can be configured in active/active mode, where I/O is spread over the paths in a round-robin fashion. In some configurations, DM Multipath can detect loading on the I/O paths and dynamically rebalance the load.
Figure 1.1, “Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device” shows an active/passive configuration with two I/O paths from the server to a RAID device. There are 2 HBAs on the server, 2 SAN switches, and 2 RAID controllers.
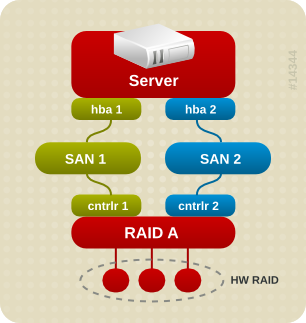
Figure 1.1. Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device
In this configuration, there is one I/O path that goes through hba1, SAN1, and controller 1 and a second I/O path that goes through hba2, SAN2, and controller2. There are many points of possible failure in this configuration:
- HBA failure
- FC cable failure
- SAN switch failure
- Array controller port failure
With DM Multipath configured, a failure at any of these points will cause DM Multipath to switch to the alternate I/O path.
Figure 1.2, “Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with Two RAID Devices” shows a more complex active/passive configuration with 2 HBAs on the server, 2 SAN switches, and 2 RAID devices with 2 RAID controllers each.
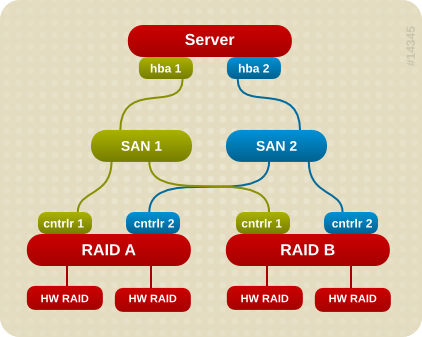
Figure 1.2. Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with Two RAID Devices
In the example shown in Figure 1.2, “Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with Two RAID Devices”, there are two I/O paths to each RAID device (just as there are in the example shown in Figure 1.1, “Active/Passive Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device”). With DM Multipath configured, a failure at any of the points of the I/O path to either of the RAID devices will cause DM Multipath to switch to the alternate I/O path for that device.
Figure 1.3, “Active/Active Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device” shows an active/active configuration with 2 HBAs on the server, 1 SAN switch, and 2 RAID controllers. There are four I/O paths from the server to a storage device:
- hba1 to controller1
- hba1 to controller2
- hba2 to controller1
- hba2 to controller2
In this configuration, I/O can be spread among those four paths.
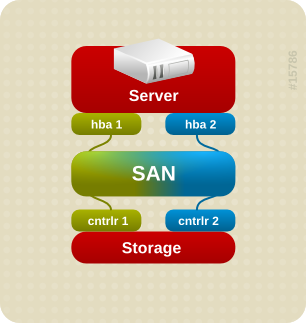
Figure 1.3. Active/Active Multipath Configuration with One RAID Device