Chapter 6. Managing virtual machines in the web console
To manage virtual machines in a graphical interface on a RHEL 8 host, you can use the Virtual Machines pane in the RHEL 8 web console.
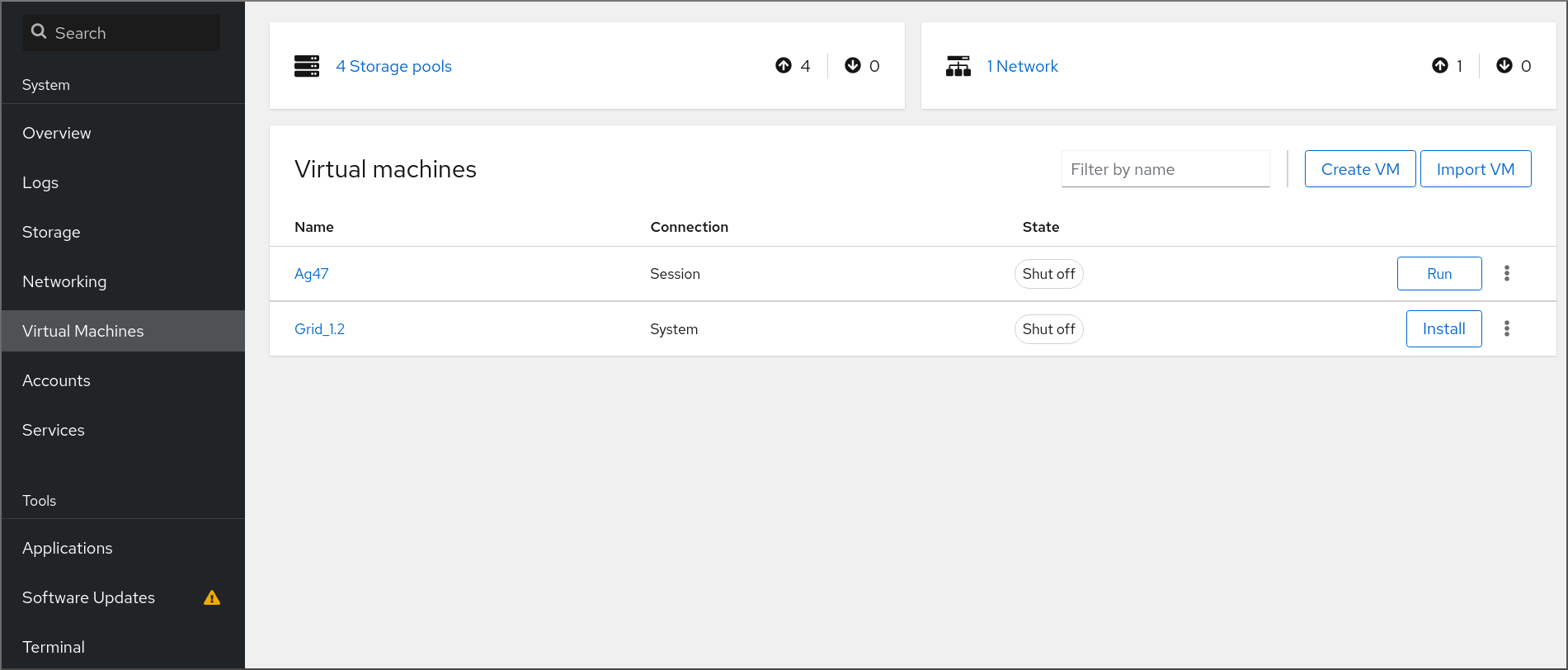
6.1. Overview of virtual machine management by using the web console
The RHEL 8 web console is a web-based interface for system administration. As one of its features, the web console provides a graphical view of virtual machines (VMs) on the host system, and makes it possible to create, access, and configure these VMs.
Note that to use the web console to manage your VMs on RHEL 8, you must first install a web console plug-in for virtualization.
Next steps
- For instructions on enabling VMs management in your web console, see Setting up the web console to manage virtual machines.
- For a comprehensive list of VM management actions that the web console provides, see Virtual machine management features available in the web console.
- For a list of features that are currently not available in the web console but can be used in the virt-manager application, see Differences between virtualization features in Virtual Machine Manager and the web console.
6.2. Setting up the web console to manage virtual machines
Before using the RHEL 8 web console to manage virtual machines (VMs), you must install the web console virtual machine plug-in on the host.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the RHEL 8 web console.
- You have enabled the cockpit service.
Your user account is allowed to log in to the web console.
For instructions, see Installing and enabling the web console.
Procedure
Install the
cockpit-machinesplug-in.yum install cockpit-machines
# yum install cockpit-machinesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Log in to the RHEL 8 web console.
For details, see Logging in to the web console.
If the installation was successful, appears in the web console side menu.

6.3. Renaming virtual machines by using the web console
You might require renaming an existing virtual machine (VM) to avoid naming conflicts or assign a new unique name based on your use case. To rename the VM, you can use the RHEL web console.
Prerequisites
- You have installed the RHEL 8 web console.
- You have enabled the cockpit service.
Your user account is allowed to log in to the web console.
For instructions, see Installing and enabling the web console.
- The web console VM plug-in is installed on your system.
- The VM is shut down.
Procedure
In the interface, click the Menu button of the VM that you want to rename.
A drop-down menu appears with controls for various VM operations.
Click .
The Rename a VM dialog appears.
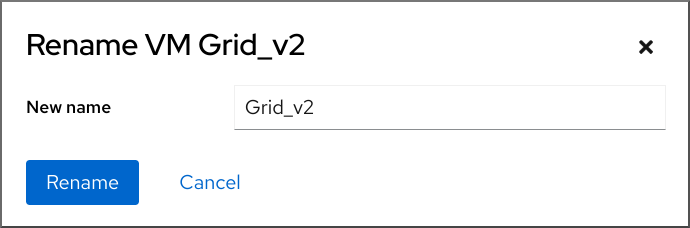
- In the New name field, enter a name for the VM.
- Click .
Verification
- Check that the new VM name has appeared in the interface.
6.4. Virtual machine management features available in the web console
By using the RHEL 8 web console, you can perform the following actions to manage the virtual machines (VMs) on your system.
| Task | For details, see |
|---|---|
| Create a VM and install it with a guest operating system | Creating virtual machines and installing guest operating systems by using the web console |
| Delete a VM | |
| Start, shut down, and restart the VM | Starting virtual machines by using the web console and Shutting down and restarting virtual machines by using the web console |
| Connect to and interact with a VM using a variety of consoles | |
| View a variety of information about the VM | Viewing virtual machine information by using the web console |
| Adjust the host memory allocated to a VM | Adding and removing virtual machine memory by using the web console |
| Manage network connections for the VM | Using the web console for managing virtual machine network interfaces |
| Manage the VM storage available on the host and attach virtual disks to the VM | Managing storage for virtual machines by using the web console |
| Configure the virtual CPU settings of the VM | |
| Live migrate a VM | |
| Manage host devices | |
| Manage virtual optical drives | |
| Attach watchdog device | Attaching a watchdog device to a virtual machine by using the web console |
6.5. Differences between virtualization features in Virtual Machine Manager and the web console
The Virtual Machine Manager (virt-manager) application is supported in RHEL 8, but has been deprecated. The web console is intended to become its replacement in a subsequent major release. It is, therefore, recommended that you get familiar with the web console for managing virtualization in a GUI.
However, in RHEL 8, some VM management tasks can only be performed in virt-manager or the command line. The following table highlights the features that are available in virt-manager but not available in the RHEL 8.0 web console.
If a feature is available in a later minor version of RHEL 8, the minimum RHEL 8 version appears in the Support in web console introduced column.
| Task | Support in web console introduced | Alternative method by using CLI |
|---|---|---|
| Setting a virtual machine to start when the host boots | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Suspending a virtual machine | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Resuming a suspended virtual machine | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Creating file-system directory storage pools | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Creating NFS storage pools | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Creating physical disk device storage pools | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Creating LVM volume group storage pools | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Creating partition-based storage pools | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Creating GlusterFS-based storage pools | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Creating vHBA-based storage pools with SCSI devices | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Creating Multipath-based storage pools | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Creating RBD-based storage pools | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Creating a new storage volume | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Adding a new virtual network | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Deleting a virtual network | RHEL 8.1 |
|
| Creating a bridge from a host machine’s interface to a virtual machine | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Creating a snapshot | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Reverting to a snapshot | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Deleting a snapshot | CURRENTLY UNAVAILABLE |
|
| Cloning a virtual machine | RHEL 8.4 |
|
| Migrating a virtual machine to another host machine | RHEL 8.5 |
|
| Attaching a host device to a VM | RHEL 8.5 |
|
| Removing a host device from a VM | RHEL 8.5 |
|