Managing replication in Identity Management
Preparing and verifying replication environments
Abstract
Providing feedback on Red Hat documentation
We are committed to providing high-quality documentation and value your feedback. To help us improve, you can submit suggestions or report errors through the Red Hat Jira tracking system.
Procedure
Log in to the Jira website.
If you do not have an account, select the option to create one.
- Click Create in the top navigation bar.
- Enter a descriptive title in the Summary field.
- Enter your suggestion for improvement in the Description field. Include links to the relevant parts of the documentation.
- Click Create at the bottom of the dialogue.
Chapter 1. Managing replication topology
You can manage replication between servers in an Identity Management (IdM) domain. When you create a replica, Identity Management (IdM) creates a replication agreement between the initial server and the replica. The data that is replicated is then stored in topology suffixes and when two replicas have a replication agreement between their suffixes, the suffixes form a topology segment.
1.1. Replication agreements between IdM replicas
When an administrator creates a replica based on an existing server, Identity Management (IdM) creates a replication agreement between the initial server and the replica. The replication agreement ensures that the data and configuration is continuously replicated between the two servers.
IdM uses multiple read/write replica replication. In this configuration, all replicas joined in a replication agreement receive and provide updates, and are therefore considered suppliers and consumers. Replication agreements are always bilateral.
Figure 1.1. Server and replica agreements
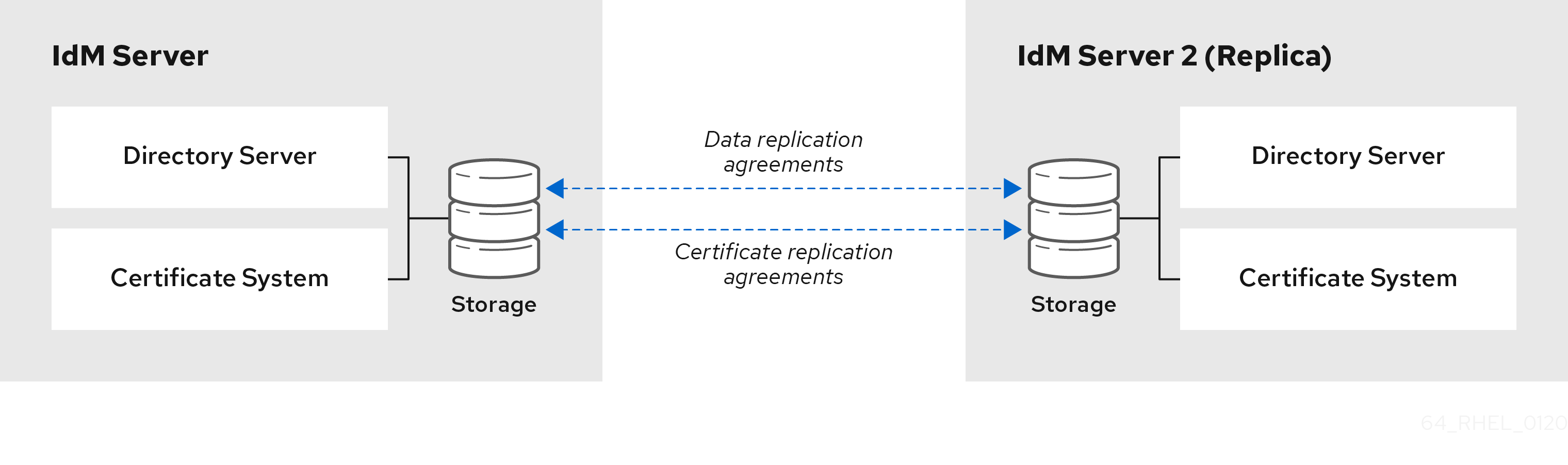
IdM uses two types of replication agreements:
- Domain replication agreements replicate the identity information.
- Certificate replication agreements replicate the certificate information.
Both replication channels are independent. Two servers can have one or both types of replication agreements configured between them. For example, when server A and server B have only domain replication agreement configured, only identity information is replicated between them, not the certificate information.
1.2. Topology suffixes
Topology suffixes store the data that is replicated. IdM supports two types of topology suffixes: domain and ca. Each suffix represents a separate server, a separate replication topology.
When a replication agreement is configured, it joins two topology suffixes of the same type on two different servers.
- The
domainsuffix: dc=example,dc=com The
domainsuffix contains all domain-related data.When two replicas have a replication agreement between their
domainsuffixes, they share directory data, such as users, groups, and policies.- The
casuffix: o=ipaca The
casuffix contains data for the Certificate System component. It is only present on servers with a certificate authority (CA) installed.When two replicas have a replication agreement between their
casuffixes, they share certificate data.
Figure 1.2. Topology suffixes
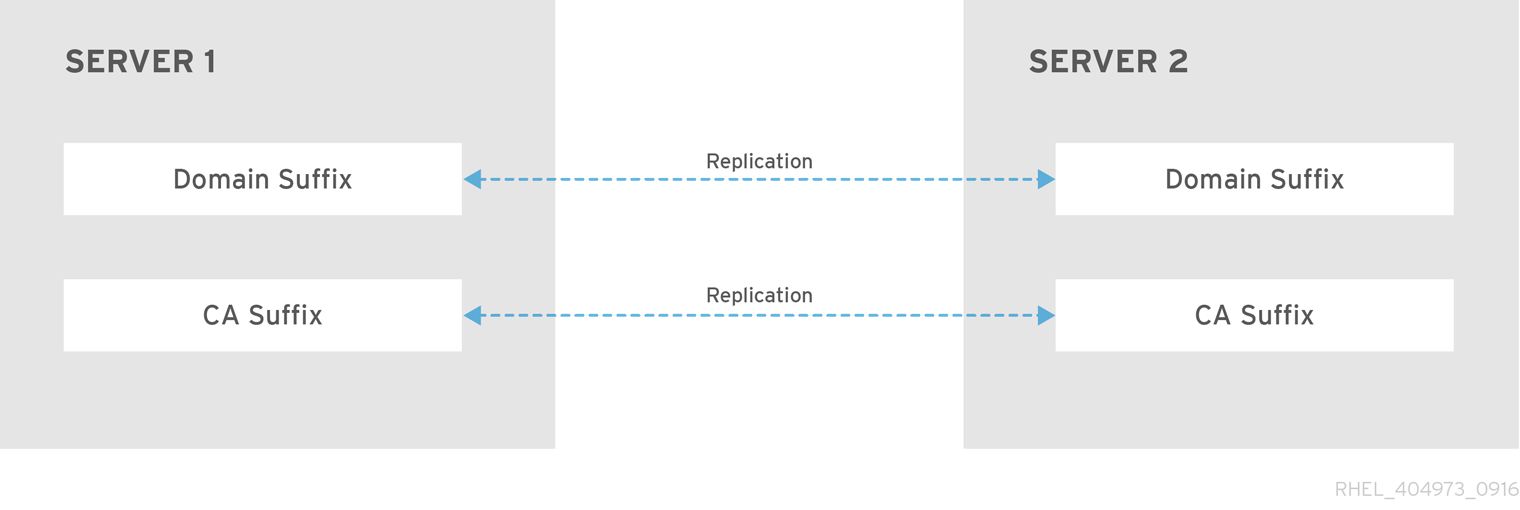
An initial topology replication agreement is set up between two servers by the ipa-replica-install script when installing a new replica.
1.3. Topology segments
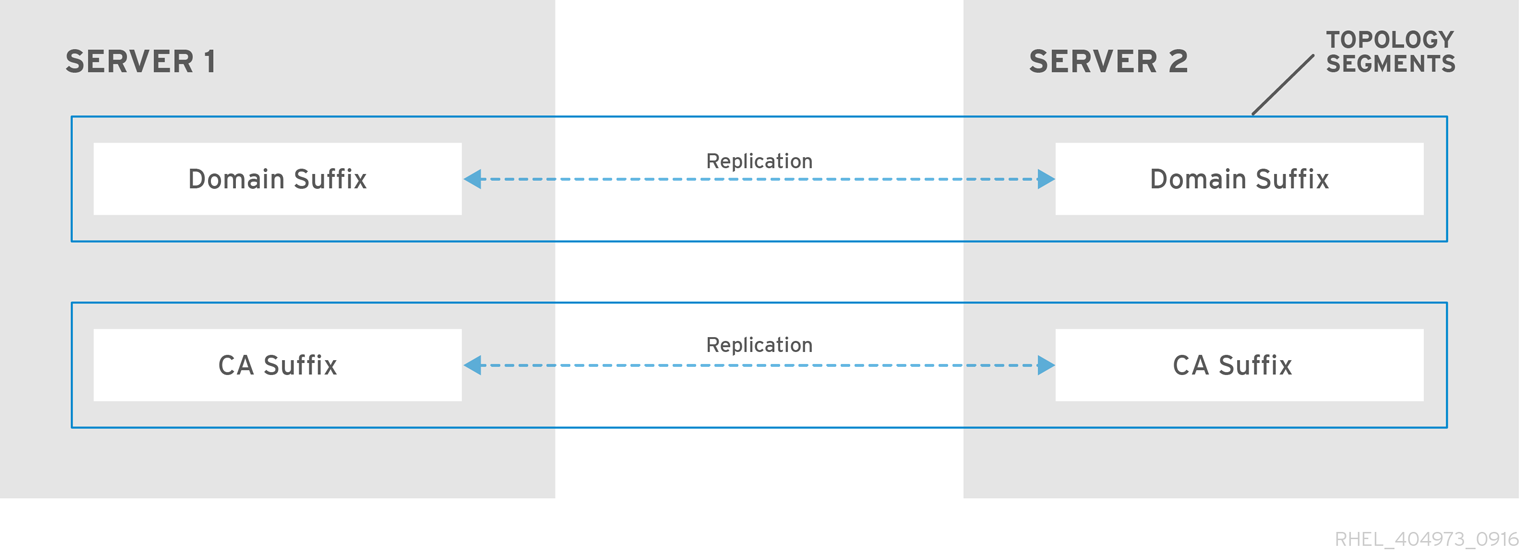
When two replicas have a replication agreement between their suffixes, the suffixes form a topology segment. Each topology segment consists of a left node and a right node. The nodes represent the servers joined in the replication agreement.
Topology segments in IdM are always bidirectional. Each segment represents two replication agreements: from server A to server B, and from server B to server A. The data is therefore replicated in both directions.
Figure 1.3. Topology segments
1.4. Viewing and modifying the visual representation of the replication topology using the WebUI
Using the Web UI, you can view, manipulate, and transform the representation of the replication topology. The topology graph in the web UI shows the relationships between the servers in the domain. You can move individual topology nodes by holding and dragging the mouse.
Interpreting the topology graph
Servers joined in a domain replication agreement are connected by an orange arrow. Servers joined in a CA replication agreement are connected by a blue arrow.
- Topology graph example: recommended topology
The recommended topology example below shows one of the possible recommended topologies for four servers: each server is connected to at least two other servers, and more than one server is a CA server.
Figure 1.4. Recommended topology example

- Topology graph example: discouraged topology
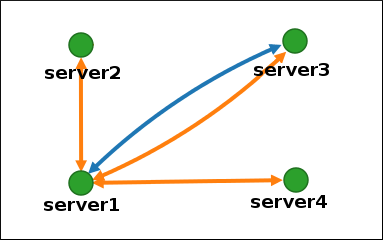
In the discouraged topology example below,
server1is a single point of failure. All the other servers have replication agreements with this server, but not with any of the other servers. Therefore, ifserver1fails, all the other servers will become isolated.Avoid creating topologies like this.
Figure 1.5. Discouraged topology example: Single Point of Failure
Prerequisites
- You are logged in as an IdM administrator.
Procedure
- Select → → .
Make changes to the topology:
You can move the topology graph nodes using the left mouse button:
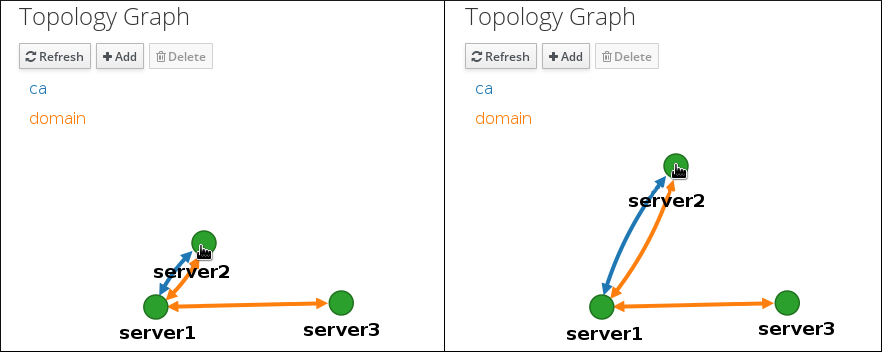
You can zoom in and zoom out the topology graph using the mouse wheel:
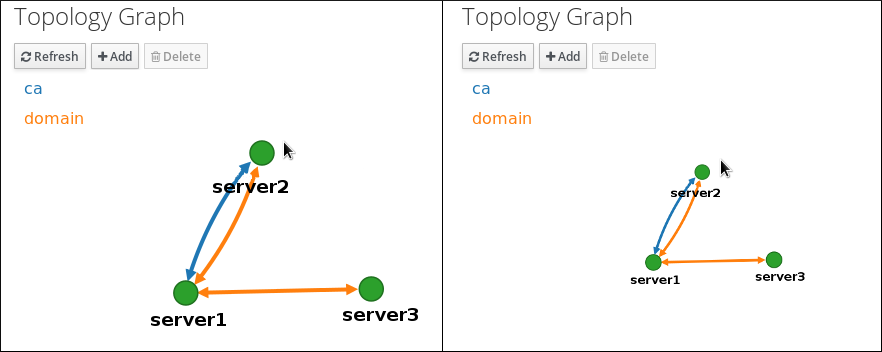
You can move the canvas of the topology graph by holding the left mouse button:
- If you make any changes to the topology that are not immediately reflected in the graph, click .
1.5. Viewing topology suffixes using the CLI
In a replication agreement, topology suffixes store the data that is replicated. You can view topology suffixes using the CLI.
Procedure
Enter the
ipa topologysuffix-findcommand to display a list of topology suffixes:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.6. Viewing topology segments using the CLI
In a replication agreement, when two replicas have a replication agreement between their suffixes, the suffixes form a topology segments. You can view topology segments using the CLI.
Procedure
Enter the
ipa topologysegment-findcommand to show the current topology segments configured for the domain or CA suffixes. For example, for the domain suffix:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In this example, domain-related data is only replicated between two servers:
server1.example.comandserver2.example.com.Optional: To display details for a particular segment only, enter the
ipa topologysegment-showcommand:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.7. Setting up replication between two servers using the Web UI
Using the Identity Management (IdM) Web UI, you can choose two servers and create a new replication agreement between them.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in as an IdM administrator.
Procedure
In the topology graph, hover your mouse over one of the server nodes.
Figure 1.6. Domain or CA options
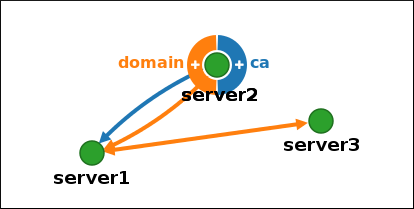
-
Click on the
domainor thecapart of the circle depending on what type of topology segment you want to create. A new arrow representing the new replication agreement appears under your mouse pointer. Move your mouse to the other server node, and click on it.
Figure 1.7. Creating a new segment

-
In the
Add topology segmentwindow, click to confirm the properties of the new segment.
The new topology segment between the two servers joins them in a replication agreement. The topology graph now shows the updated replication topology:
Figure 1.8. New segment created
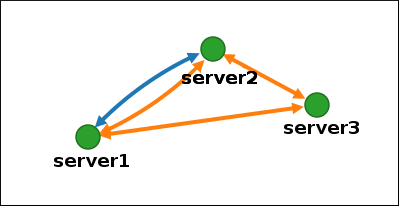
1.8. Stopping replication between two servers using the Web UI
Using the Identity Management (IdM) Web UI, you can remove a replication agreement from servers.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in as an IdM administrator.
Procedure
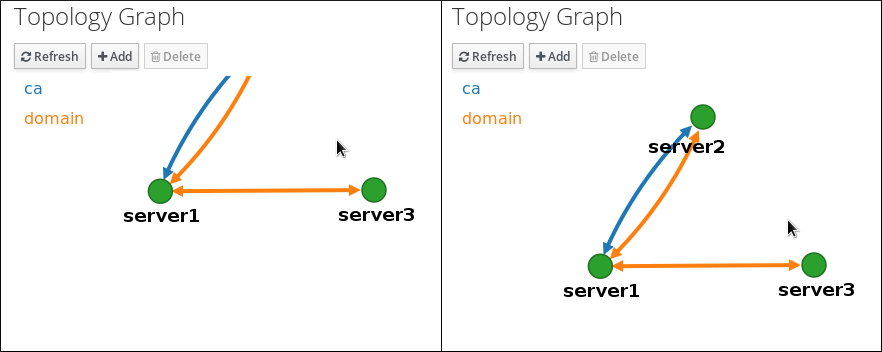
Click on an arrow representing the replication agreement you want to remove. This highlights the arrow.
Figure 1.9. Topology segment highlighted
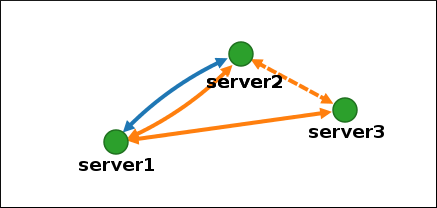
- Click .
In the
Confirmationwindow, click .IdM removes the topology segment between the two servers, which deletes their replication agreement. The topology graph now shows the updated replication topology:
Figure 1.10. Topology segment deleted
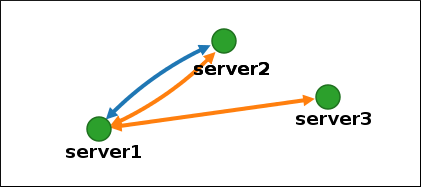
1.9. Setting up replication between two servers using the CLI
You can configure replication agreements between two servers using the ipa topologysegment-add command.
Prerequisites
- You have the IdM administrator credentials.
Procedure
Create a topology segment for the two servers. When prompted, provide:
-
The required topology suffix:
domainorca - The left node and the right node, representing the two servers
Optional: A custom name for the segment
For example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Adding the new segment joins the servers in a replication agreement.
-
The required topology suffix:
Verification
Verify that the new segment is configured:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.10. Stopping replication between two servers using the CLI
You can terminate replication agreements from command line using the ipa topology segment-del command.
Prerequisites
- You have the IdM administrator credentials.
Procedure
Optional: If you do not know the name of the specific replication segment that you want to remove, display all segments available. Use the
ipa topologysegment-findcommand. When prompted, provide the required topology suffix:domainorca. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Locate the required segment in the output.
Remove the topology segment joining the two servers:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deleting the segment removes the replication agreement.
Verification
Verify that the segment is no longer listed:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.11. Removing server from topology using the Web UI
You can use Identity Management (IdM) web interface to remove a server from the topology. This action does not uninstall the server components from the host.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in as an IdM administrator.
- The server you want to remove is not the only server connecting other servers with the rest of the topology; this would cause the other servers to become isolated, which is not allowed.
- The server you want to remove is not your last CA or DNS server.
Removing a server is an irreversible action. If you remove a server, the only way to introduce it back into the topology is to install a new replica on the machine.
Procedure
- Select → → .
Click on the name of the server you want to delete.
Figure 1.11. Selecting a server
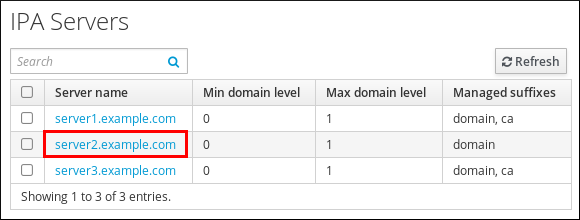
- Click .
Additional resources
1.12. Removing server from topology using the CLI
You can use the command line to remove an Identity Management (IdM) server from the topology.
Prerequisites
- You have the IdM administrator credentials.
- The server you want to remove is not the only server connecting other servers with the rest of the topology; this would cause the other servers to become isolated, which is not allowed.
- The server you want to remove is not your last CA or DNS server.
Removing a server is an irreversible action. If you remove a server, the only way to introduce it back into the topology is to install a new replica on the machine.
Procedure
To remove server1.example.com:
On another server, run the
ipa server-delcommand to removeserver1.example.com. The command removes all topology segments pointing to the server:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: On
server1.example.com, run theipa server-install --uninstallcommand to uninstall the server components from the machine.ipa server-install --uninstall
[root@server1 ~]# ipa server-install --uninstallCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.13. Removing obsolete RUV records
If you remove a server from the IdM topology without properly removing its replication agreements, obsolete replica update vector (RUV) records will remain on one or more remaining servers in the topology. This can happen, for example, due to automation. These servers will then expect to receive updates from the now removed server. In this case, you need to clean the obsolete RUV records from the remaining servers.
Prerequisites
- You have the IdM administrator credentials.
- You know which replicas are corrupted or have been improperly removed.
Procedure
List the details about RUVs using the
ipa-replica-manage list-ruvcommand. The command displays the replica IDs:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantThe
ipa-replica-manage list-ruvcommand lists ALL replicas in the topology, not only the malfunctioning or improperly removed ones.Remove obsolete RUVs associated with a specified replica using the
ipa-replica-manage clean-ruvcommand. Repeat the command for every replica ID with obsolete RUVs. For example, if you knowserver1.example.comandserver2.example.comare the malfunctioning or improperly removed replicas:ipa-replica-manage clean-ruv 6 ipa-replica-manage clean-ruv 5
ipa-replica-manage clean-ruv 6 ipa-replica-manage clean-ruv 5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Proceed with extreme caution when using ipa-replica-manage clean-ruv. Running the command against a valid replica ID will corrupt all the data associated with that replica in the replication database.
If this happens, re-initialize the replica from another replica using $ ipa-replica-manage re-initialize --from server1.example.com.
Verification
-
Run
ipa-replica-manage list-ruvagain. If the command no longer displays any corrupt RUVs, the records have been successfully cleaned. If the command still displays corrupt RUVs, clear them manually using this task:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.14. Viewing available server roles in the IdM topology using the IdM Web UI
Based on the services installed on an IdM server, it can perform various server roles. For example:
- CA server
- DNS server
- Key recovery authority (KRA) server.
Procedure
For a complete list of the supported server roles, see → → .
Note-
Role status
absentmeans that no server in the topology is performing the role. -
Role status
enabledmeans that one or more servers in the topology are performing the role.
Figure 1.12. Server roles in the web UI

-
Role status
1.15. Viewing available server roles in the IdM topology using the IdM CLI
Based on the services installed on an IdM server, it can perform various server roles. For example:
- CA server
- DNS server
- Key recovery authority (KRA) server.
Procedure
To display all CA servers in the topology and the current CA renewal server:
ipa config-show ... IPA masters: server1.example.com, server2.example.com, server3.example.com IPA CA servers: server1.example.com, server2.example.com IPA CA renewal master: server1.example.com
$ ipa config-show ... IPA masters: server1.example.com, server2.example.com, server3.example.com IPA CA servers: server1.example.com, server2.example.com IPA CA renewal master: server1.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, to display a list of roles enabled on a particular server, for example server.example.com:
ipa server-show Server name: server.example.com ... Enabled server roles: CA server, DNS server, KRA server
$ ipa server-show Server name: server.example.com ... Enabled server roles: CA server, DNS server, KRA serverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, use the
ipa server-find --servrolecommand to search for all servers with a particular server role enabled. For example, to search for all CA servers:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
1.16. Promoting a replica to a CA renewal server and CRL publisher server
If your IdM deployment uses an embedded certificate authority (CA), one of the IdM CA servers acts as the CA renewal server, a server that manages the renewal of CA subsystem certificates. One of the IdM CA servers also acts as the IdM CRL publisher server, a server that generates certificate revocation lists.
By default, the CA renewal server and CRL publisher server roles are installed on the first server on which the system administrator installed the CA role using the ipa-server-install or ipa-ca-install command. You can, however, transfer either of the two roles to any other IdM server on which the CA role is enabled.
Prerequisites
- You have the IdM administrator credentials.
Chapter 2. Preparing your environment for managing IdM using Ansible playbooks
As a system administrator managing Identity Management (IdM), when working with Red Hat Ansible Engine, it is good practice to do the following:
- Create a subdirectory dedicated to Ansible playbooks in your home directory, for example ~/MyPlaybooks.
-
Copy and adapt sample Ansible playbooks from the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/*and/usr/share/doc/rhel-system-roles/*directories and subdirectories into your ~/MyPlaybooks directory. - Include your inventory file in your ~/MyPlaybooks directory.
Using this practice, you can find all your playbooks in one place and you can run your playbooks without invoking root privileges.
You only need root privileges on the managed nodes to execute the ipaserver, ipareplica, ipaclient and ipabackup ansible-freeipa roles. These roles require privileged access to directories and the dnf software package manager.
Follow this procedure to create the ~/MyPlaybooks directory and configure it so that you can use it to store and run Ansible playbooks.
Prerequisites
- You have installed an IdM server on your managed nodes, server.idm.example.com and replica.idm.example.com.
- You have configured DNS and networking so you can log in to the managed nodes, server.idm.example.com and replica.idm.example.com, directly from the control node.
-
You know the IdM
adminpassword.
Procedure
Create a directory for your Ansible configuration and playbooks in your home directory:
mkdir ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ mkdir ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change into the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooksCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the ~/MyPlaybooks/ansible.cfg file with the following content:
[defaults] inventory = /home/your_username/MyPlaybooks/inventory [privilege_escalation] become=True
[defaults] inventory = /home/your_username/MyPlaybooks/inventory [privilege_escalation] become=TrueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the ~/MyPlaybooks/inventory file with the following content:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This configuration defines two host groups, eu and us, for hosts in these locations. Additionally, this configuration defines the ipaserver host group, which contains all hosts from the eu and us groups.
Optional: Create an SSH public and private key. To simplify access in your test environment, do not set a password on the private key:
ssh-keygen
$ ssh-keygenCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the SSH public key to the IdM
adminaccount on each managed node:ssh-copy-id admin@server.idm.example.com ssh-copy-id admin@replica.idm.example.com
$ ssh-copy-id admin@server.idm.example.com $ ssh-copy-id admin@replica.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow These commands require that you enter the IdM
adminpassword.
Chapter 3. Using Ansible to manage the replication topology in IdM
You can maintain multiple Identity Management (IdM) servers and let them replicate each other for redundancy purposes to mitigate or prevent server loss. For example, if one server fails, the other servers keep providing services to the domain. You can also recover the lost server by creating a new replica based on one of the remaining servers.
Data stored on an IdM server is replicated based on replication agreements: when two servers have a replication agreement configured, they share their data. The data that is replicated is stored in the topology suffixes. When two replicas have a replication agreement between their suffixes, the suffixes form a topology segment.
This chapter describes how to use Ansible to manage IdM replication agreements, topology segments, and topology suffixes.
3.1. Using Ansible to ensure a replication agreement exists in IdM
Data stored on an Identity Management (IdM) server is replicated based on replication agreements: when two servers have a replication agreement configured, they share their data. Replication agreements are always bilateral: the data is replicated from the first replica to the other one as well as from the other replica to the first one.
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure that a replication agreement of the domain type exists between server.idm.example.com and replica.idm.example.com.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you understand the recommendations for designing your IdM topology listed in Guidelines for connecting IdM replicas in a topology.
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_passwordand that you have access to a file that stores the password protecting the secret.yml file.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Navigate to your ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
add-topologysegment.ymlAnsible playbook file provided by theansible-freeipapackage:cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/add-topologysegment.yml add-topologysegment-copy.yml
$ cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/add-topologysegment.yml add-topologysegment-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
add-topologysegment-copy.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables in the
ipatopologysegmenttask section:-
Indicate that the value of the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable is defined in the secret.yml Ansible vault file. -
Set the
suffixvariable to eitherdomainorca, depending on what type of segment you want to add. -
Set the
leftvariable to the name of the IdM server that you want to be the left node of the replication agreement. -
Set the
rightvariable to the name of the IdM server that you want to be the right node of the replication agreement. -
Ensure that the
statevariable is set topresent.
This is the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Indicate that the value of the
- Save the file.
Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory add-topologysegment-copy.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory add-topologysegment-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.2. Using Ansible to ensure replication agreements exist between multiple IdM replicas
Data stored on an Identity Management (IdM) server is replicated based on replication agreements: when two servers have a replication agreement configured, they share their data. Replication agreements are always bilateral: the data is replicated from the first replica to the other one as well as from the other replica to the first one.
Follow this procedure to ensure replication agreements exist between multiple pairs of replicas in IdM.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you understand the recommendations for designing your IdM topology listed in Connecting the replicas in a topology.
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_passwordand that you have access to a file that stores the password protecting the secret.yml file.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Navigate to your ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
add-topologysegments.ymlAnsible playbook file provided by theansible-freeipapackage:cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/add-topologysegments.yml add-topologysegments-copy.yml
$ cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/add-topologysegments.yml add-topologysegments-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
add-topologysegments-copy.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables in the
varssection:-
Indicate that the value of the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable is defined in the secret.yml Ansible vault file. For every topology segment, add a line in the
ipatopology_segmentssection and set the following variables:-
Set the
suffixvariable to eitherdomainorca, depending on what type of segment you want to add. -
Set the
leftvariable to the name of the IdM server that you want to be the left node of the replication agreement. -
Set the
rightvariable to the name of the IdM server that you want to be the right node of the replication agreement.
-
Set the
-
Indicate that the value of the
In the
taskssection of theadd-topologysegments-copy.ymlfile, ensure that thestatevariable is set topresent.This is the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file.
Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory add-topologysegments-copy.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory add-topologysegments-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.3. Using Ansible to check if a replication agreement exists between two replicas
Data stored on an Identity Management (IdM) server is replicated based on replication agreements: when two servers have a replication agreement configured, they share their data. Replication agreements are always bilateral: the data is replicated from the first replica to the other one as well as from the other replica to the first one.
Follow this procedure to verify that replication agreements exist between multiple pairs of replicas in IdM. In contrast to Using Ansible to ensure a replication agreement exists in IdM, this procedure does not modify the existing configuration.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you understand the recommendations for designing your Identity Management (IdM) topology listed in Connecting the replicas in a topology.
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_passwordand that you have access to a file that stores the password protecting the secret.yml file.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Navigate to your ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
check-topologysegments.ymlAnsible playbook file provided by theansible-freeipapackage:cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/check-topologysegments.yml check-topologysegments-copy.yml
$ cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/check-topologysegments.yml check-topologysegments-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
check-topologysegments-copy.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables in the
varssection:-
Indicate that the value of the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable is defined in the secret.yml Ansible vault file. For every topology segment, add a line in the
ipatopology_segmentssection and set the following variables:-
Set the
suffixvariable to eitherdomainorca, depending on the type of segment you are adding. -
Set the
leftvariable to the name of the IdM server that you want to be the left node of the replication agreement. -
Set the
rightvariable to the name of the IdM server that you want to be the right node of the replication agreement.
-
Set the
-
Indicate that the value of the
In the
taskssection of thecheck-topologysegments-copy.ymlfile, ensure that thestatevariable is set topresent.This is the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file.
Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory check-topologysegments-copy.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory check-topologysegments-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.4. Using Ansible to verify that a topology suffix exists in IdM
In the context of replication agreements in Identity Management (IdM), topology suffixes store the data that is replicated. IdM supports two types of topology suffixes: domain and ca. Each suffix represents a separate back end, a separate replication topology. When a replication agreement is configured, it joins two topology suffixes of the same type on two different servers.
The domain suffix contains all domain-related data, such as data about users, groups, and policies. The ca suffix contains data for the Certificate System component. It is only present on servers with a certificate authority (CA) installed.
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure that a topology suffix exists in IdM. The example describes how to ensure that the domain suffix exists in IdM.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_passwordand that you have access to a file that stores the password protecting the secret.yml file.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Navigate to your ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
verify-topologysuffix.ymlAnsible playbook file provided by theansible-freeipapackage:cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/ verify-topologysuffix.yml verify-topologysuffix-copy.yml
$ cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/ verify-topologysuffix.yml verify-topologysuffix-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
verify-topologysuffix-copy.ymlAnsible playbook file for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables in the
ipatopologysuffixsection:-
Indicate that the value of the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable is defined in the secret.yml Ansible vault file. -
Set the
suffixvariable todomain. If you are verifying the presence of thecasuffix, set the variable toca. -
Ensure that the
statevariable is set toverified. No other option is possible.
This is the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Indicate that the value of the
- Save the file.
Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory verify-topologysuffix-copy.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory verify-topologysuffix-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.5. Using Ansible to reinitialize an IdM replica
If a replica has been offline for a long period of time or its database has been corrupted, you can reinitialize it. Reinitialization refreshes the replica with an updated set of data. Reinitialization can, for example, be used if an authoritative restore from backup is required.
In contrast to replication updates, during which replicas only send changed entries to each other, reinitialization refreshes the whole database.
The local host on which you run the command is the reinitialized replica. To specify the replica from which the data is obtained, use the direction option.
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to reinitialize the domain data on replica.idm.example.com from server.idm.example.com.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_passwordand that you have access to a file that stores the password protecting the secret.yml file.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Navigate to your ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
reinitialize-topologysegment.ymlAnsible playbook file provided by theansible-freeipapackage:cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/reinitialize-topologysegment.yml reinitialize-topologysegment-copy.yml
$ cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/reinitialize-topologysegment.yml reinitialize-topologysegment-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
reinitialize-topologysegment-copy.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables in the
ipatopologysegmentsection:-
Indicate that the value of the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable is defined in the secret.yml Ansible vault file. -
Set the
suffixvariable todomain. If you are reinitializing thecadata, set the variable toca. -
Set the
leftvariable to the left node of the replication agreement. -
Set the
rightvariable to the right node of the replication agreement. -
Set the
directionvariable to the direction of the reinitializing data. Theleft-to-rightdirection means that data flows from the left node to the right node. Ensure that the
statevariable is set toreinitialized.This is the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Indicate that the value of the
- Save the file.
Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory reinitialize-topologysegment-copy.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory reinitialize-topologysegment-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.6. Using Ansible to ensure a replication agreement is absent in IdM
Data stored on an Identity Management (IdM) server is replicated based on replication agreements: when two servers have a replication agreement configured, they share their data. Replication agreements are always bilateral: the data is replicated from the first replica to the other one as well as from the other replica to the first one.
Follow this procedure to ensure a replication agreement between two replicas does not exist in IdM. The example describes how to ensure a replication agreement of the domain type does not exist between the replica01.idm.example.com and replica02.idm.example.com IdM servers.
Prerequisites
- You understand the recommendations for designing your IdM topology listed in Connecting the replicas in a topology.
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_passwordand that you have access to a file that stores the password protecting the secret.yml file.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica.
Procedure
Navigate to your ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory:
cd ~/MyPlaybooks/
$ cd ~/MyPlaybooks/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
delete-topologysegment.ymlAnsible playbook file provided by theansible-freeipapackage:cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/delete-topologysegment.yml delete-topologysegment-copy.yml
$ cp /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/topology/delete-topologysegment.yml delete-topologysegment-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
delete-topologysegment-copy.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables in the
ipatopologysegmenttask section:-
Indicate that the value of the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable is defined in the secret.yml Ansible vault file. -
Set the
suffixvariable todomain. Alternatively, if you are ensuring that thecadata are not replicated between the left and right nodes, set the variable toca. -
Set the
leftvariable to the name of the IdM server that is the left node of the replication agreement. -
Set the
rightvariable to the name of the IdM server that is the right node of the replication agreement. -
Ensure that the
statevariable is set toabsent.
This is the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Indicate that the value of the
- Save the file.
Run the Ansible playbook. Specify the playbook file, the file storing the password protecting the secret.yml file, and the inventory file:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory delete-topologysegment-copy.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory delete-topologysegment-copy.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 5. Checking IdM replication using Healthcheck
You can test Identity Management (IdM) replication using the Healthcheck tool.
Prerequisites
- You are using RHEL version 8.1 or newer.
5.1. The IdM replication and topology Healthcheck tests
The Healthcheck tool includes tests of the Identity Management (IdM) topology configuration. The tests search for replication conflict issues.
You can find the IPATopologyDomainCheck and ReplicationConflictCheck tests under the ipahealthcheck.ipa.topology and ipahealthcheck.ds.replication sources of the output of the ipa-healthcheck --list-sources command.
- IPATopologyDomainCheck
Tests the following configuration:
- No IdM server is disconnected from the topology.
- The IdM servers do not have more than the recommended number of replication agreements.
If the test succeeds, the test returns the configured domains. Otherwise, specific connection errors are reported.
NoteThe test runs the
ipa topologysuffix-verifycommand for thedomainsuffix. It also runs the command for thecasuffix if the IdM Certificate Authority server role is configured on this server.- ReplicationConflictCheck
-
Searches for entries in LDAP matching
(&(!(objectclass=nstombstone))(nsds5ReplConflict=*)).
5.2. Screening replication using Healthcheck
Follow this procedure to run a standalone manual test of your Identity Management (IdM) replication and topology configuration using the Healthcheck tool.
Prerequisites
-
You have
rootprivileges.
Procedure
Enter:
ipa-healthcheck --source=ipahealthcheck.ds.replication --source=ipahealthcheck.ipa.topology
# ipa-healthcheck --source=ipahealthcheck.ds.replication --source=ipahealthcheck.ipa.topologyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
The
--source=ipahealthcheck.ds.replicationand--source=ipahealthcheck.ipa.topologyoptions ensure that IdM Healthcheck only performs the replication conflict and topology tests.
Four different results are possible:
SUCCESS — the test passed successfully.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - WARNING — the test passed but there might be a problem.
ERROR — the test failed.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - CRITICAL — the test failed and it affects the IdM server functionality.
-
The
Run these tests on all IdM servers when trying to check for issues.