Chapter 6. Managing DNS forwarding in IdM
Follow these procedures to configure DNS global forwarders and DNS forward zones in the Identity Management (IdM) Web UI, the IdM CLI, and using Ansible:
- The two roles of an IdM DNS server
- DNS forward policies in IdM
- Adding a global forwarder in the IdM Web UI
- Adding a global forwarder in the CLI
- Adding a DNS Forward Zone in the IdM Web UI
- Adding a DNS Forward Zone in the CLI
- Establishing a DNS Global Forwarder in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring the presence of a DNS global forwarder in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring the absence of a DNS global forwarder in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring DNS Global Forwarders are disabled in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring the presence of a DNS Forward Zone in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring a DNS Forward Zone has multiple forwarders in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring a DNS Forward Zone is disabled in IdM using Ansible
- Ensuring the absence of a DNS Forward Zone in IdM using Ansible
6.1. The two roles of an IdM DNS server
DNS forwarding affects how a DNS service answers DNS queries. By default, the Berkeley Internet Name Domain (BIND) service integrated with IdM acts as both an authoritative and a recursive DNS server:
- Authoritative DNS server
- When a DNS client queries a name belonging to a DNS zone for which the IdM server is authoritative, BIND replies with data contained in the configured zone. Authoritative data always takes precedence over any other data.
- Recursive DNS server
- When a DNS client queries a name for which the IdM server is not authoritative, BIND attempts to resolve the query using other DNS servers. If forwarders are not defined, BIND asks the root servers on the Internet and uses a recursive resolution algorithm to answer the DNS query.
In some cases, it is not desirable to let BIND contact other DNS servers directly and perform the recursion based on data available on the Internet. You can configure BIND to use another DNS server, a forwarder, to resolve the query.
When you configure BIND to use a forwarder, queries and answers are forwarded back and forth between the IdM server and the forwarder, and the IdM server acts as the DNS cache for non-authoritative data.
6.2. DNS forward policies in IdM
IdM supports the first and only standard BIND forward policies, as well as the none IdM-specific forward policy.
- Forward first (default)
-
The IdM BIND service forwards DNS queries to the configured forwarder. If a query fails because of a server error or timeout, BIND falls back to the recursive resolution using servers on the Internet. The
forward firstpolicy is the default policy, and it is suitable for optimizing DNS traffic. - Forward only
-
The IdM BIND service forwards DNS queries to the configured forwarder. If a query fails because of a server error or timeout, BIND returns an error to the client. The
forward onlypolicy is recommended for environments with split DNS configuration. - None (forwarding disabled)
-
DNS queries are not forwarded with the
noneforwarding policy. Disabling forwarding is only useful as a zone-specific override for global forwarding configuration. This option is the IdM equivalent of specifying an empty list of forwarders in BIND configuration.
You cannot use forwarding to combine data in IdM with data from other DNS servers. You can only forward queries for specific subzones of the primary zone in IdM DNS.
By default, the BIND service does not forward queries to another server if the queried DNS name belongs to a zone for which the IdM server is authoritative. In such a situation, if the queried DNS name cannot be found in the IdM database, the NXDOMAIN answer is returned. Forwarding is not used.
Example 6.1. Example Scenario
The IdM server is authoritative for the test.example. DNS zone. BIND is configured to forward queries to the DNS server with the 192.0.2.254 IP address.
When a client sends a query for the nonexistent.test.example. DNS name, BIND detects that the IdM server is authoritative for the test.example. zone and does not forward the query to the 192.0.2.254. server. As a result, the DNS client receives the NXDomain error message, informing the user that the queried domain does not exist.
6.3. Adding a global forwarder in the IdM Web UI
Follow this procedure to add a global DNS forwarder in the Identity Management (IdM) Web UI.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the IdM WebUI as IdM administrator.
- You know the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the DNS server to forward queries to.
Procedure
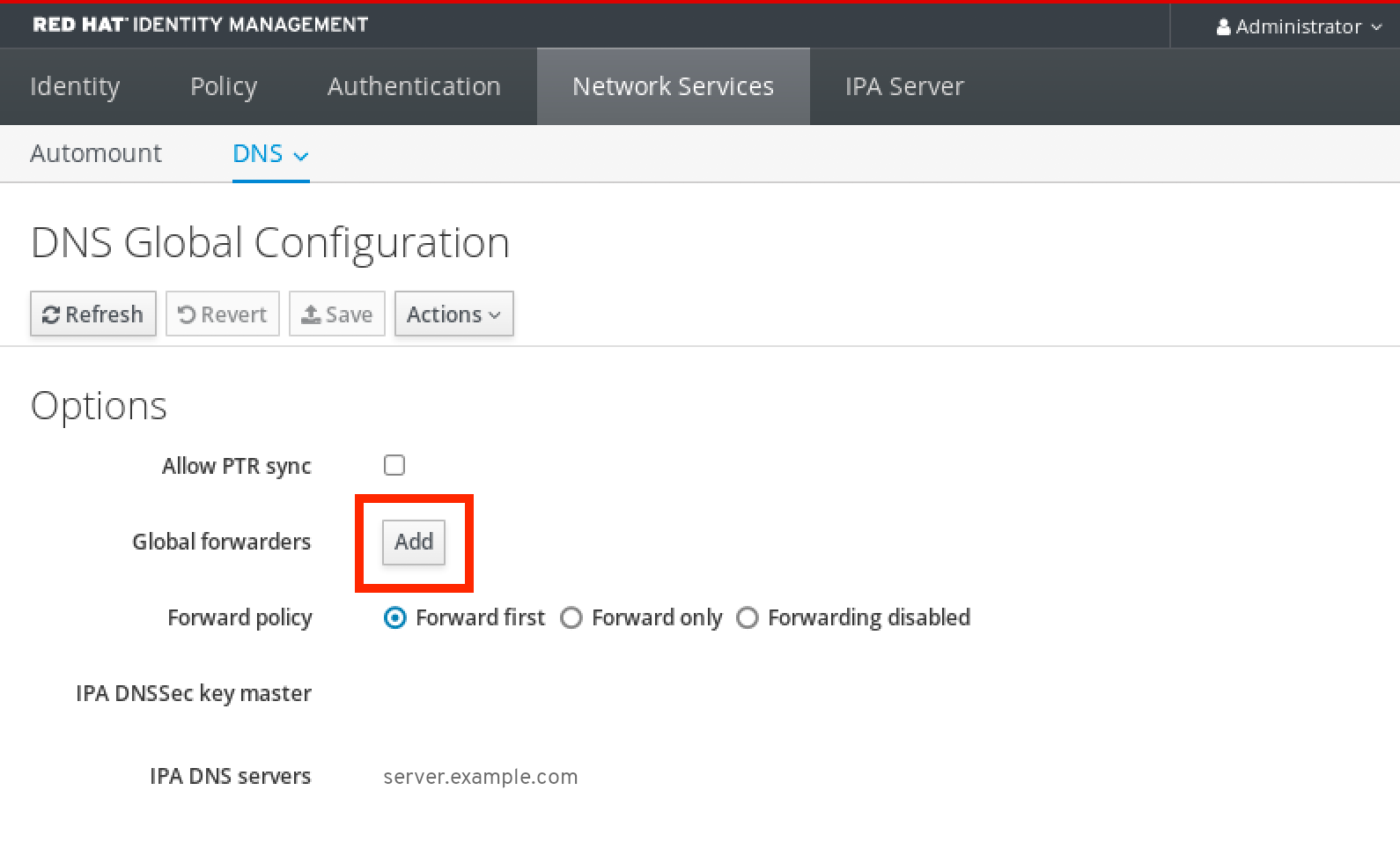
In the IdM Web UI, select
Network ServicesDNS Global ConfigurationDNS.In the
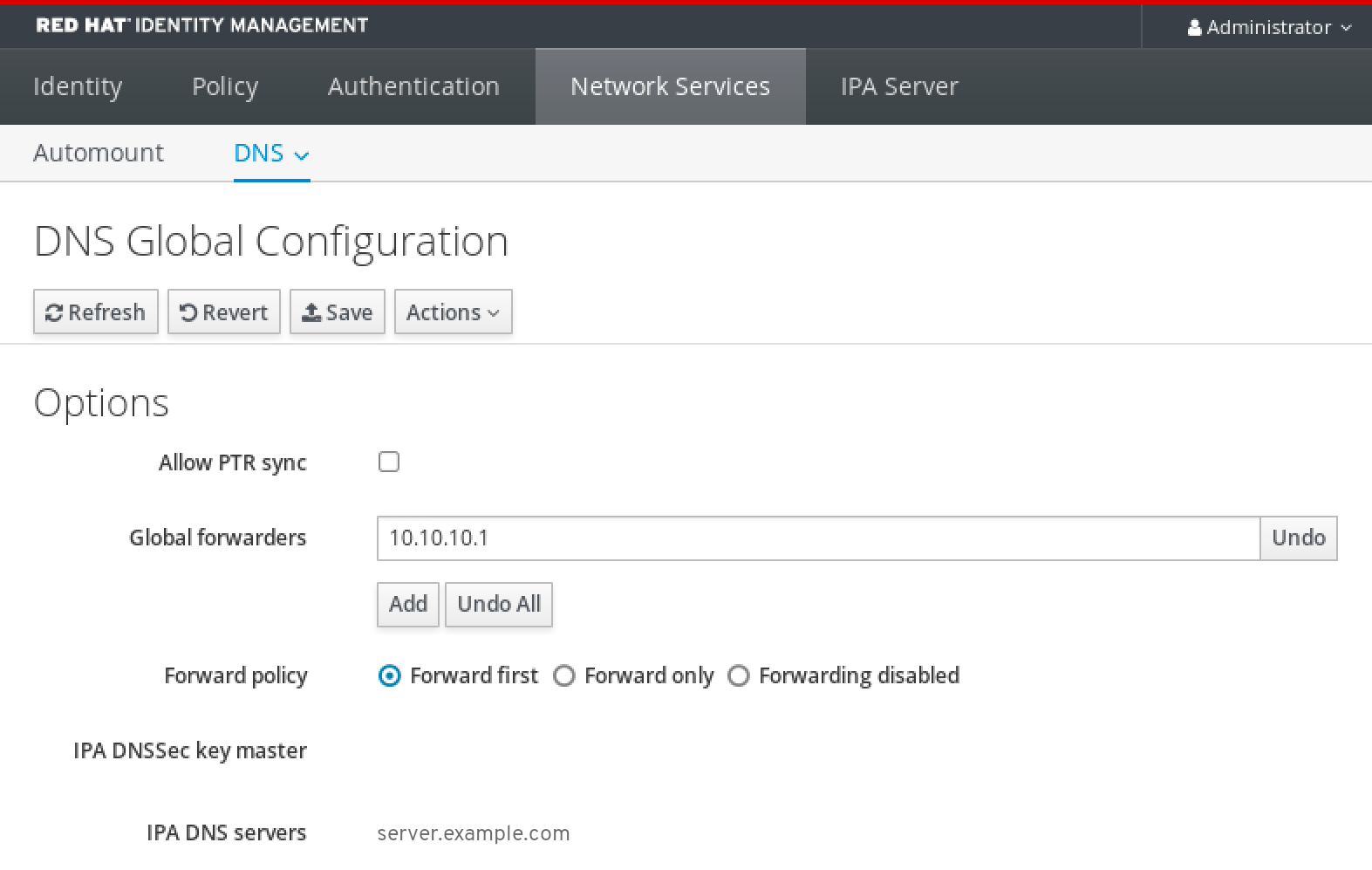
DNS Global Configurationsection, clickAdd.Specify the IP address of the DNS server that will receive forwarded DNS queries.
Select the
Forward policy.-
Click
Saveat the top of the window.
Verification
Select
Network ServicesDNS Global ConfigurationDNS.Verify that the global forwarder, with the forward policy you specified, is present and enabled in the IdM Web UI.
6.4. Adding a global forwarder in the CLI
Follow this procedure to add a global DNS forwarder by using the command line (CLI).
Prerequisites
- You are logged in as IdM administrator.
- You know the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the DNS server to forward queries to.
Procedure
Use the
ipa dnsconfig-modcommand to add a new global forwarder. Specify the IP address of the DNS forwarder with the--forwarderoption.ipa dnsconfig-mod --forwarder=10.10.0.1
[user@server ~]$ ipa dnsconfig-mod --forwarder=10.10.0.1 Server will check DNS forwarder(s). This may take some time, please wait ... Global forwarders: 10.10.0.1 IPA DNS servers: server.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Use the
dnsconfig-showcommand to display global forwarders.ipa dnsconfig-show
[user@server ~]$ ipa dnsconfig-show Global forwarders: 10.10.0.1 IPA DNS servers: server.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
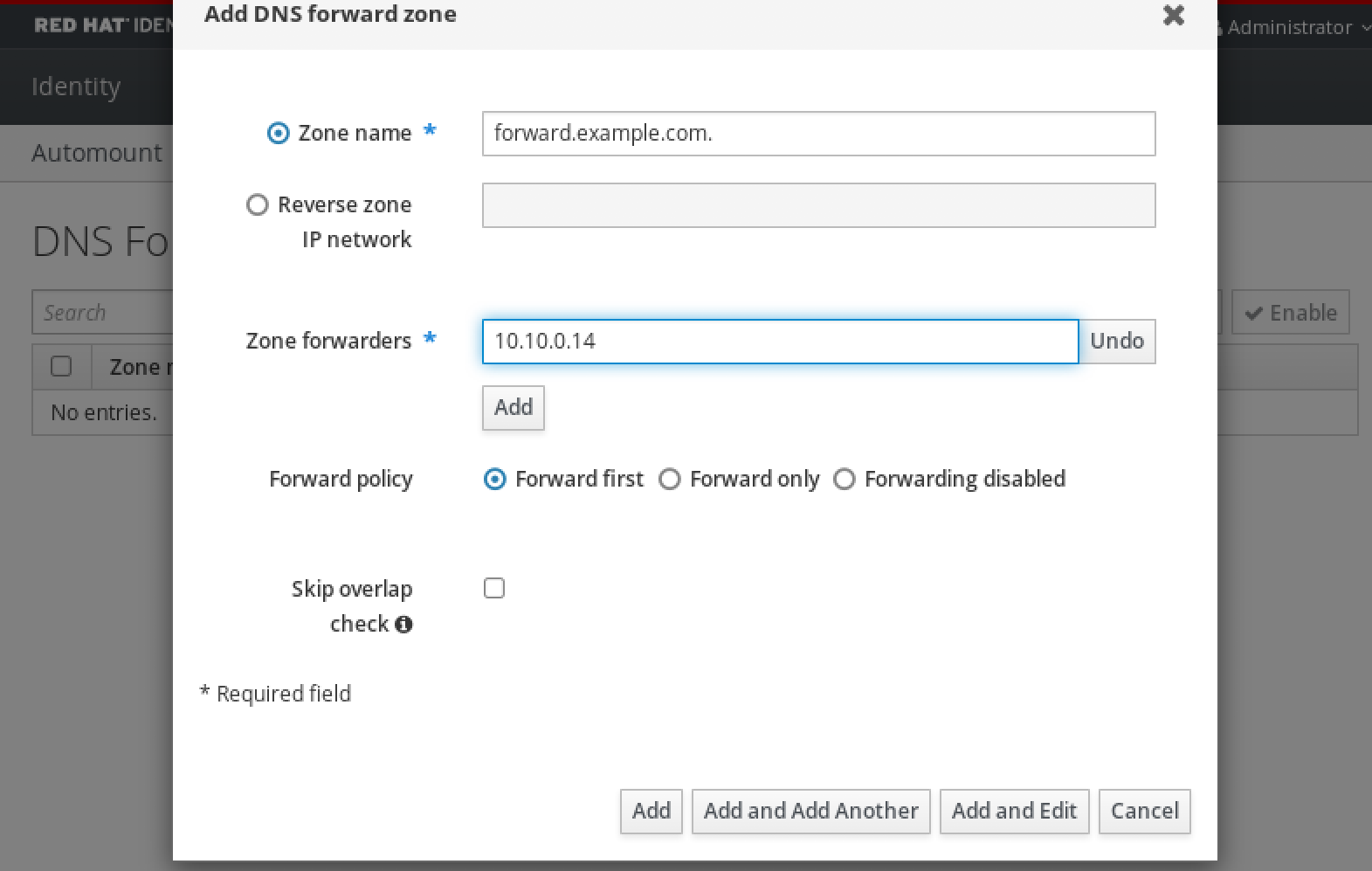
6.5. Adding a DNS Forward Zone in the IdM Web UI
Follow this procedure to add a DNS forward zone in the Identity Management (IdM) Web UI.
Do not use forward zones unless absolutely required. Forward zones are not a standard solution, and using them can lead to unexpected and problematic behavior. If you must use forward zones, limit their use to overriding a global forwarding configuration.
When creating a new DNS zone, Red Hat recommends to always use standard DNS delegation using nameserver (NS) records and to avoid forward zones. In most cases, using a global forwarder is sufficient, and forward zones are not necessary.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in to the IdM WebUI as IdM administrator.
- You know the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the DNS server to forward queries to.
Procedure
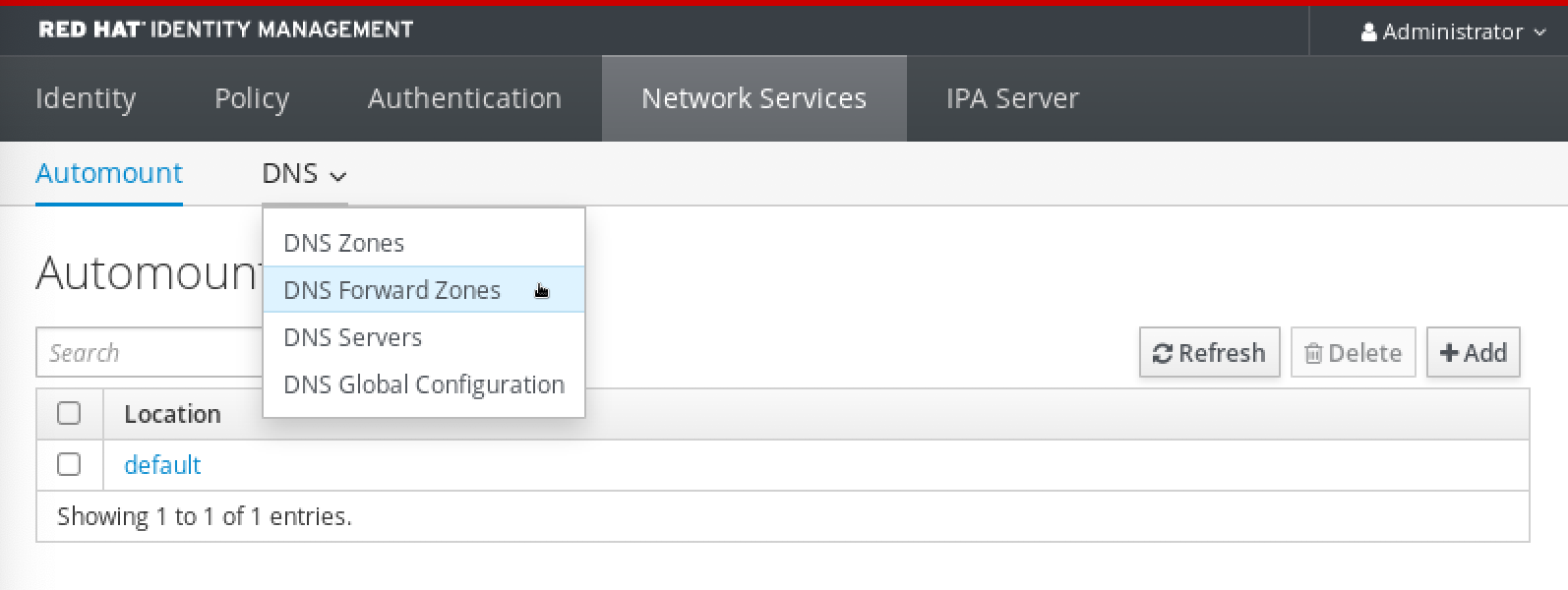
In the IdM Web UI, select
Network ServicesDNS Forward ZonesDNS.In the
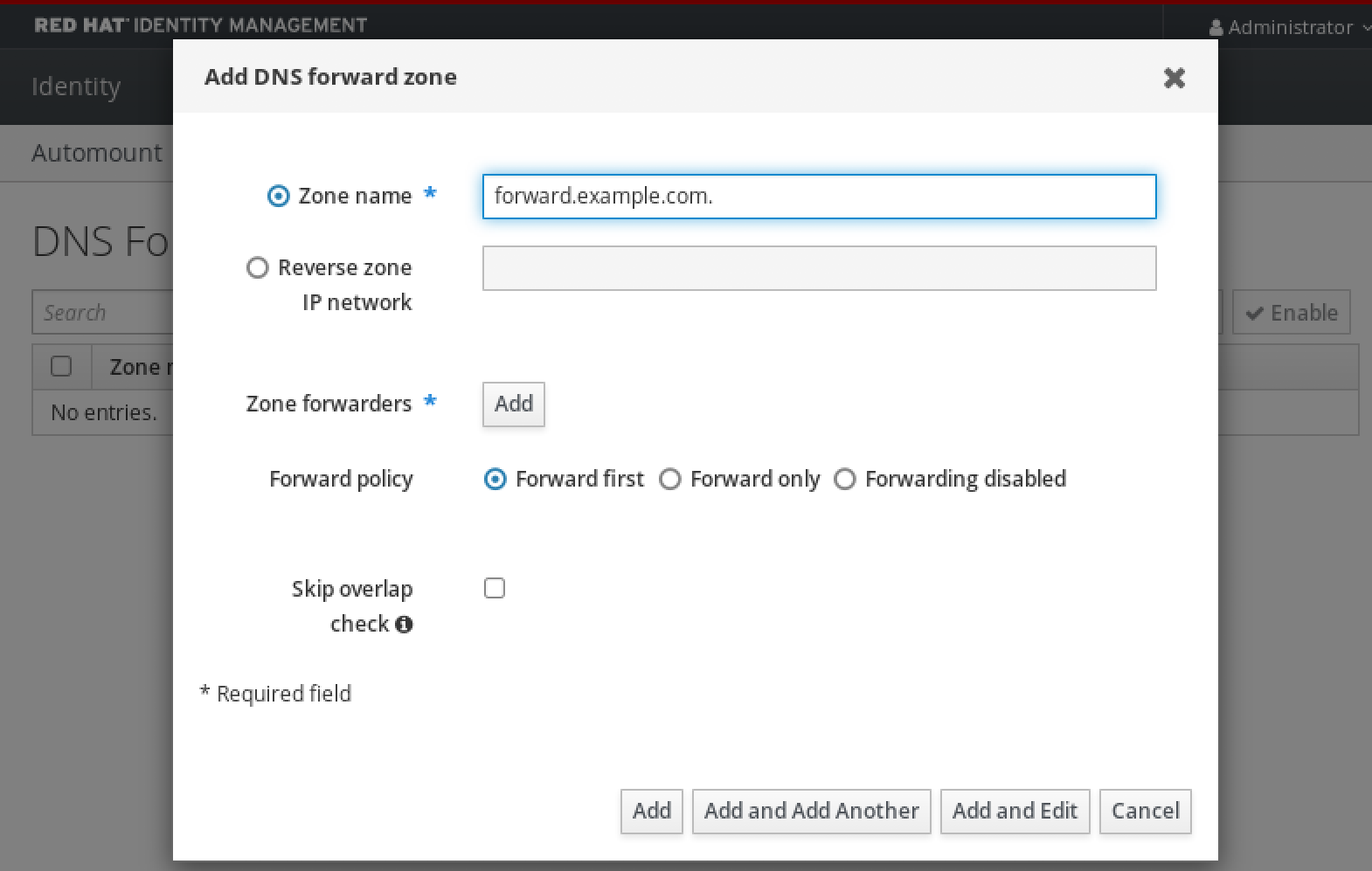
DNS Forward Zonessection, clickAdd.In the
Add DNS forward zonewindow, specify the forward zone name.Click the
Addbutton and specify the IP address of a DNS server to receive the forwarding request. You can specify multiple forwarders per forward zone.Select the
Forward policy.-
Click
Addat the bottom of the window to add the new forward zone.
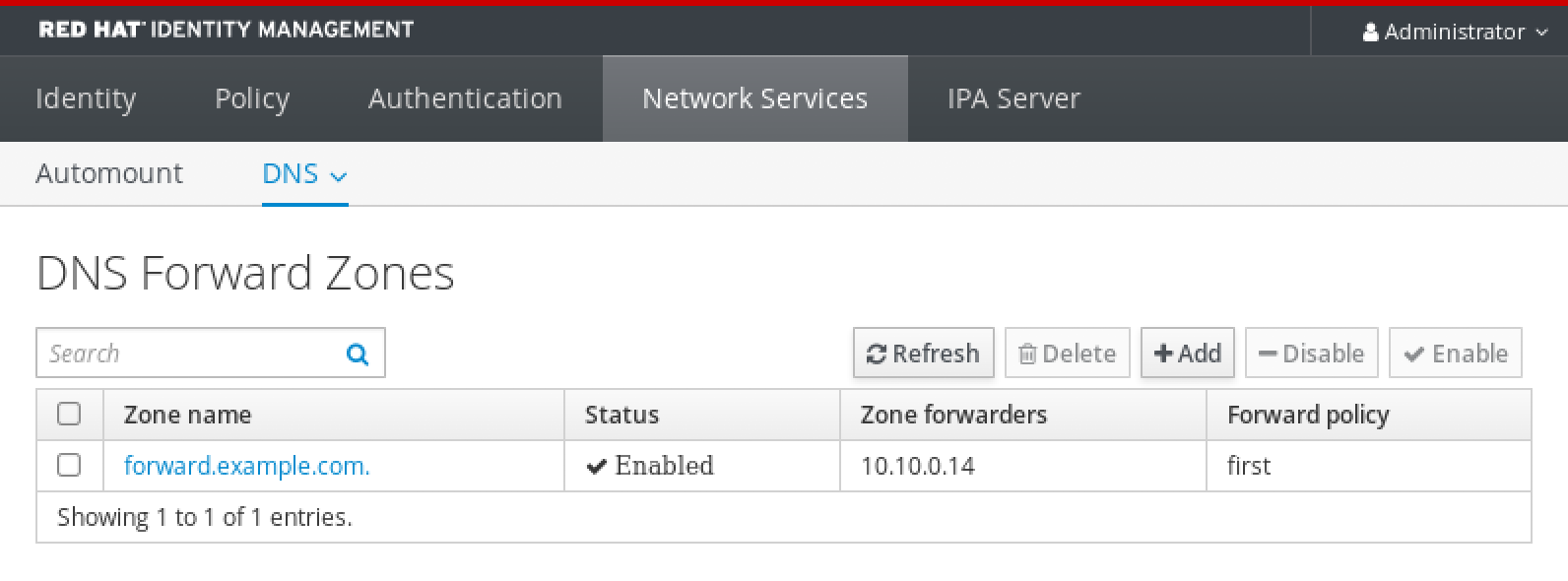
Verification
In the IdM Web UI, select
Network ServicesDNS Forward ZonesDNS.Verify that the forward zone you created, with the forwarders and forward policy you specified, is present and enabled in the IdM Web UI.
6.6. Adding a DNS Forward Zone in the CLI
Follow this procedure to add a DNS forward zone by using the command line (CLI).
Do not use forward zones unless absolutely required. Forward zones are not a standard solution, and using them can lead to unexpected and problematic behavior. If you must use forward zones, limit their use to overriding a global forwarding configuration.
When creating a new DNS zone, Red Hat recommends to always use standard DNS delegation using nameserver (NS) records and to avoid forward zones. In most cases, using a global forwarder is sufficient, and forward zones are not necessary.
Prerequisites
- You are logged in as IdM administrator.
- You know the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the DNS server to forward queries to.
Procedure
Use the
dnsforwardzone-addcommand to add a new forward zone. Specify at least one forwarder with the--forwarderoption if the forward policy is notnone, and specify the forward policy with the--forward-policyoption.ipa dnsforwardzone-add forward.example.com. --forwarder=10.10.0.14 --forwarder=10.10.1.15 --forward-policy=first
[user@server ~]$ ipa dnsforwardzone-add forward.example.com. --forwarder=10.10.0.14 --forwarder=10.10.1.15 --forward-policy=first Zone name: forward.example.com. Zone forwarders: 10.10.0.14, 10.10.1.15 Forward policy: firstCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Use the
dnsforwardzone-showcommand to display the DNS forward zone you just created.ipa dnsforwardzone-show forward.example.com.
[user@server ~]$ ipa dnsforwardzone-show forward.example.com. Zone name: forward.example.com. Zone forwarders: 10.10.0.14, 10.10.1.15 Forward policy: firstCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.7. Establishing a DNS Global Forwarder in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to establish a DNS Global Forwarder in IdM.
In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator creates a DNS global forwarder to a DNS server with an Internet Protocol (IP) v4 address of 8.8.6.6 and IPv6 address of 2001:4860:4860::8800 on port 53.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
set-configuration.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp set-configuration.yml establish-global-forwarder.yml
$ cp set-configuration.yml establish-global-forwarder.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
establish-global-forwarder.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to establish a global forwarder in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toCreate a DNS global forwarder to 8.8.6.6 and 2001:4860:4860::8800. In the
forwarderssection of theipadnsconfigportion:-
Change the first
ip_addressvalue to the IPv4 address of the global forwarder:8.8.6.6. -
Change the second
ip_addressvalue to the IPv6 address of the global forwarder:2001:4860:4860::8800. -
Verify the
portvalue is set to53.
-
Change the first
Change the
forward_policytofirst.This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file establish-global-forwarder.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file establish-global-forwarder.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.8. Ensuring the presence of a DNS global forwarder in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure the presence of a DNS global forwarder in IdM. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures the presence of a DNS global forwarder to a DNS server with an Internet Protocol (IP) v4 address of 7.7.9.9 and IP v6 address of 2001:db8::1:0 on port 53.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
forwarders-absent.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-presence-of-a-global-forwarder.yml
$ cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-presence-of-a-global-forwarder.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
ensure-presence-of-a-global-forwarder.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to ensure the presence of a global forwarder in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toEnsure the presence of a DNS global forwarder to 7.7.9.9 and 2001:db8::1:0 on port 53. In the
forwarderssection of theipadnsconfigportion:-
Change the first
ip_addressvalue to the IPv4 address of the global forwarder:7.7.9.9. -
Change the second
ip_addressvalue to the IPv6 address of the global forwarder:2001:db8::1:0. -
Verify the
portvalue is set to53.
-
Change the first
Change the
statetopresent.This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-presence-of-a-global-forwarder.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-presence-of-a-global-forwarder.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.9. Ensuring the absence of a DNS global forwarder in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure the absence of a DNS global forwarder in IdM. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures the absence of a DNS global forwarder with an Internet Protocol (IP) v4 address of 8.8.6.6 and IP v6 address of 2001:4860:4860::8800 on port 53.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
forwarders-absent.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-absence-of-a-global-forwarder.yml
$ cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-absence-of-a-global-forwarder.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
ensure-absence-of-a-global-forwarder.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to ensure the absence of a global forwarder in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toEnsure the absence of a DNS global forwarder to 8.8.6.6 and 2001:4860:4860::8800 on port 53. In the
forwarderssection of theipadnsconfigportion:-
Change the first
ip_addressvalue to the IPv4 address of the global forwarder:8.8.6.6. -
Change the second
ip_addressvalue to the IPv6 address of the global forwarder:2001:4860:4860::8800. -
Verify the
portvalue is set to53.
-
Change the first
-
Set the
actionvariable tomember. -
Verify the
stateis set toabsent.
This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantIf you only use the
state: absentoption in your playbook without also usingaction: member, the playbook fails.-
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-absence-of-a-global-forwarder.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-absence-of-a-global-forwarder.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.10. Ensuring DNS Global Forwarders are disabled in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure DNS Global Forwarders are disabled in IdM. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures that the forwarding policy for the global forwarder is set to none, which effectively disables the global forwarder.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verify the contents of the
disable-global-forwarders.ymlAnsible playbook file which is already configured to disable all DNS global forwarders. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file disable-global-forwarders.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file disable-global-forwarders.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.11. Ensuring the presence of a DNS Forward Zone in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure the presence of a DNS Forward Zone in IdM. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures the presence of a DNS forward zone for example.com to a DNS server with an Internet Protocol (IP) address of 8.8.8.8.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
forwarders-absent.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-presence-forwardzone.yml
$ cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-presence-forwardzone.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
ensure-presence-forwardzone.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to ensure the presence of a dnsforwardzone in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toEnsure presence of a dnsforwardzone for example.com to 8.8.8.8. -
In the
taskssection, change theipadnsconfigheading toipadnsforwardzone. In the
ipadnsforwardzonesection:-
Add the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable and set it to your IdM administrator password. -
Add the
namevariable and set it toexample.com. In the
forwarderssection:-
Remove the
ip_addressandportlines. Add the IP address of the DNS server to receive forwarded requests by specifying it after a dash:
- 8.8.8.8
- 8.8.8.8Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Remove the
-
Add the
forwardpolicyvariable and set it tofirst. -
Add the
skip_overlap_checkvariable and set it totrue. -
Change the
statevariable topresent.
This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
-
Add the
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-presence-forwardzone.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-presence-forwardzone.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.12. Ensuring a DNS Forward Zone has multiple forwarders in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure a DNS Forward Zone in IdM has multiple forwarders. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures the DNS forward zone for example.com is forwarding to 8.8.8.8 and 4.4.4.4.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
forwarders-absent.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-presence-multiple-forwarders.yml
$ cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-presence-multiple-forwarders.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
ensure-presence-multiple-forwarders.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to ensure the presence of multiple forwarders in a dnsforwardzone in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toEnsure presence of 8.8.8.8 and 4.4.4.4 forwarders in dnsforwardzone for example.com. -
In the
taskssection, change theipadnsconfigheading toipadnsforwardzone. In the
ipadnsforwardzonesection:-
Add the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable and set it to your IdM administrator password. -
Add the
namevariable and set it toexample.com. In the
forwarderssection:-
Remove the
ip_addressandportlines. Add the IP address of the DNS servers you want to ensure are present, preceded by a dash:
- 8.8.8.8 - 4.4.4.4
- 8.8.8.8 - 4.4.4.4Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Remove the
- Change the state variable to present.
This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
-
Add the
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-presence-multiple-forwarders.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-presence-multiple-forwarders.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.13. Ensuring a DNS Forward Zone is disabled in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure a DNS Forward Zone is disabled in IdM. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures the DNS forward zone for example.com is disabled.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
forwarders-absent.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-disabled-forwardzone.yml
$ cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-disabled-forwardzone.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
ensure-disabled-forwardzone.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to ensure a dnsforwardzone is disabled in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toEnsure a dnsforwardzone for example.com is disabled. -
In the
taskssection, change theipadnsconfigheading toipadnsforwardzone. In the
ipadnsforwardzonesection:-
Add the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable and set it to your IdM administrator password. -
Add the
namevariable and set it toexample.com. -
Remove the entire
forwarderssection. -
Change the
statevariable todisabled.
This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
-
Add the
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-disabled-forwardzone.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-disabled-forwardzone.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.14. Ensuring the absence of a DNS Forward Zone in IdM using Ansible
Follow this procedure to use an Ansible playbook to ensure the absence of a DNS Forward Zone in IdM. In the example procedure below, the IdM administrator ensures the absence of a DNS forward zone for example.com.
Prerequisites
You have configured your Ansible control node to meet the following requirements:
- You are using Ansible version 2.14 or later.
-
You have installed the
ansible-freeipapackage. - The example assumes that in the ~/MyPlaybooks/ directory, you have created an Ansible inventory file with the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the IdM server.
-
The example assumes that the secret.yml Ansible vault stores your
ipaadmin_password.
-
The target node, that is the node on which the
ansible-freeipamodule is executed, is part of the IdM domain as an IdM client, server or replica. - You know the IdM administrator password.
Procedure
Navigate to the
/usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigdirectory:cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfig
$ cd /usr/share/doc/ansible-freeipa/playbooks/dnsconfigCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Open your inventory file and make sure that the IdM server that you want to configure is listed in the
[ipaserver]section. For example, to instruct Ansible to configureserver.idm.example.com, enter:[ipaserver] server.idm.example.com
[ipaserver] server.idm.example.comCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Make a copy of the
forwarders-absent.ymlAnsible playbook file. For example:cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-absence-forwardzone.yml
$ cp forwarders-absent.yml ensure-absence-forwardzone.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Open the
ensure-absence-forwardzone.ymlfile for editing. Adapt the file by setting the following variables:
-
Change the
namevariable for the playbook toPlaybook to ensure the absence of a dnsforwardzone in IdM DNS. -
In the
taskssection, change thenameof the task toEnsure the absence of a dnsforwardzone for example.com. -
In the
taskssection, change theipadnsconfigheading toipadnsforwardzone. In the
ipadnsforwardzonesection:-
Add the
ipaadmin_passwordvariable and set it to your IdM administrator password. -
Add the
namevariable and set it toexample.com. -
Remove the entire
forwarderssection. -
Leave the
statevariable asabsent.
This the modified Ansible playbook file for the current example:
-
Add the
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Change the
- Save the file.
Run the playbook:
ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-absence-forwardzone.yml
$ ansible-playbook --vault-password-file=password_file -v -i inventory.file ensure-absence-forwardzone.ymlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow