8.2. Apache Aries Auto-Enlisting XA Wrapper
Overview
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
One of the features of the Apache Aries transaction module is that it provides support for auto-enlistment of XA transactions in the context of JDBC data sources. As already noted, auto-enlisting is the most practical way of integrating an XA data source with a transaction manager. The basic idea is to wrap the original data source with a data source proxy object that encapsulates the logic to perform auto-enlisting.
An unusual aspect of the Apache Aries' auto-enlisting feature is that the data source proxy is automatically created for you. In order to trigger auto-creation of the data source proxy, it is necessary to export your data source as an OSGi service. The mechanism is illustrated in Figure 8.1, “Creating the Auto-Enlisting XA Wrapper”.
Figure 8.1. Creating the Auto-Enlisting XA Wrapper
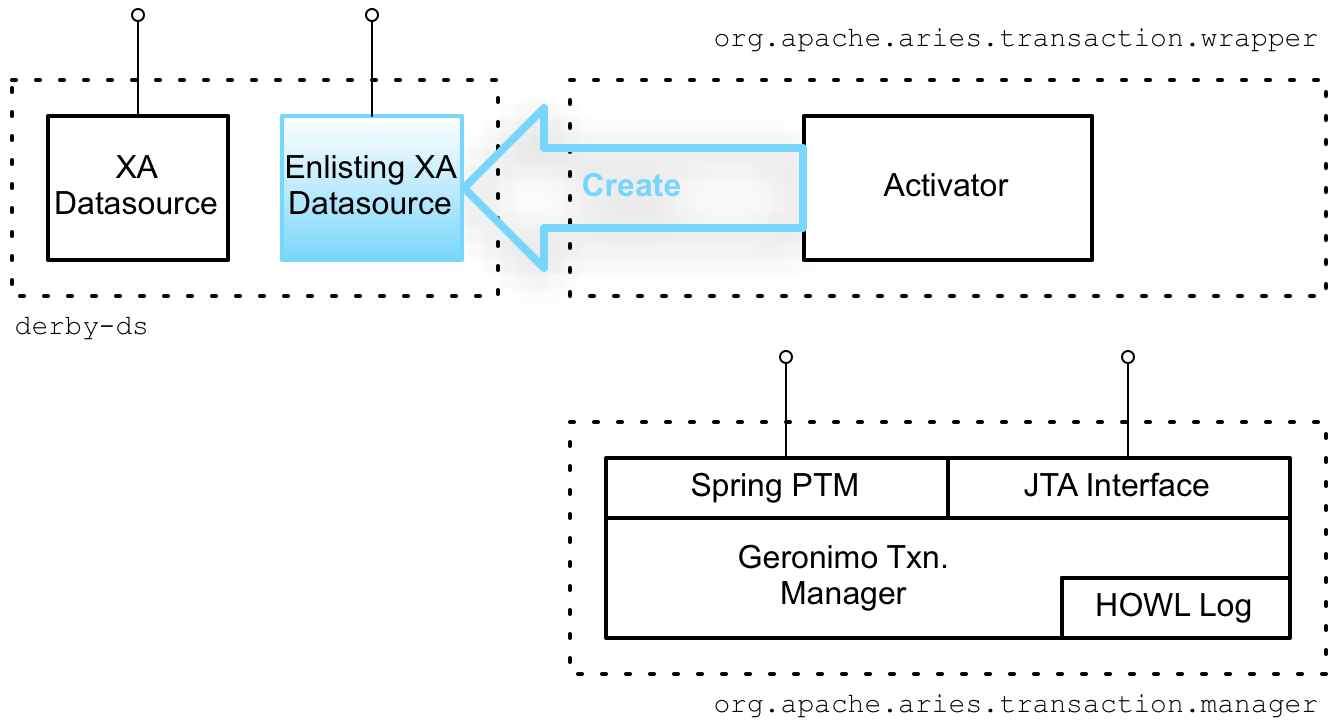
derby-ds bundle
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The
derby-ds bundle shown in Figure 8.1, “Creating the Auto-Enlisting XA Wrapper” encapsulates the code from Example 8.2, “Exposing XA DataSource as an OSGi Service in Blueprint XML”, which defines a Derby XA data source and exports it as an OSGi service.
Also shown wthin the scope of the
derby-ds bundle is the auto-enlisting data source proxy. But this data source proxy is not created by the code in the derby-ds bundle and is initially not part of the bundle.
Automatic wrapper instantiation
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Instantiation of the data source proxy depends on the Aries transaction wrapper bundle (
org.apache.aries.transaction.wrappers bundle). The Aries transaction wrapper bundle defines an activator, which installs hooks into the OSGi runtime, so that it gets notified whenever an OSGi bundle exports a service supporting the javax.sql.XADataSource interface.
XADataSourceEnlistingWrapper
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Upon detecting a new OSGi service supporting the
javax.sql.XADataSource interface, the activator automatically creates a new XADataSourceEnlistingWrapper object, which wraps the original XA data source, effectively acting as a data source proxy. The XADataSourceEnlistingWrapper object also obtains a reference to the JTA transaction manager service (from the org.apache.aries.transaction.manager bundle). Finally, the activator exports the XADataSourceEnlistingWrapper object with the javax.sql.DataSource interface.
JDBC clients now have the option of accessing the XA data source through this newly created data source proxy. Whenever a new database connection is requested from the data source proxy (by calling the
getConnection method), the proxy automatically gets a reference to the underlying XA resource and enlists the XA resource with the JTA transaction manager. This means that the required XA coding steps are automatically performed and the JDBC client does not need to be XA transaction aware.
Note
The
XADataSourceEnlistingWrapper class is not exported from the Aries transaction wrapper bundle, so it is not possible to create the data source proxy explicitly. Instances of this class can only be created automatically by the activator in the transaction wrapper bundle.
Accessing the enlisting wrapper
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
If you deploy the
derby-ds bundle, you can see how the wrapper proxy is automatically created. For example, after following the instructions in Section 10.3, “Define a Derby Datasource” and Section 10.5, “Deploy and Run the Transactional Route” to build and deploy the derby-ds bundle, you can list the OSGi services exported by the derby-ds bundle using the osgi:ls console command. Assuming that derby-ds has the bundle ID, 229, you would then enter:
JBossFuse:karaf@root> osgi:ls 229
JBossFuse:karaf@root> osgi:ls 229
The console produces output similar to the following:
The following OSGi services are exposed:
- An OSGi service with interface
javax.sql.XADataSourceanddatasource.nameequal toderbyXADB—this is the XA data source explicitly exported as an OSGi service in Example 8.2, “Exposing XA DataSource as an OSGi Service in Blueprint XML”. - An OSGi service with interface
javax.sql.DataSourceanddatasource.nameequal toderbyXADB—this is the auto-enlisting data source proxy implicitly created by the Aries wrapper service. The data source proxy copies the user-defined service properties from the original OSGi service and adds the settingaries.xa.aware = true. Thearies.xa.awareproperty enables you to distinguish between the generated proxy and the original data source.
Spring XML
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
In Spring XML, you can access the auto-enlisting data source proxy by defining an
osgi:reference element as shown in Example 8.3, “Importing XA DataSource as an OSGi Service Reference in Spring XML”.
Example 8.3. Importing XA DataSource as an OSGi Service Reference in Spring XML
This example exploits the fact that the data source proxy exposes a different interface to the original data source (
javax.sql.DataSource instead of javax.sql.XADataSource), which enables us to distinguish between the two data sources. In some cases, however, you might need to filter based on the aries.xa.aware property as well. For example:
filter="(&(datasource.name=derbyXADB)(aries.xa.aware=true))"
filter="(&(datasource.name=derbyXADB)(aries.xa.aware=true))"Blueprint
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
In blueprint XML, you can access the auto-enlisting data source proxy by defining an
reference element as shown in Example 8.4, “Importing XA DataSource as an OSGi Service Reference in Blueprint XML”.
Example 8.4. Importing XA DataSource as an OSGi Service Reference in Blueprint XML