36.5. Generating Responses Using Templates
Overview
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
One of the simplest and quickest approaches to generating a response message is to use a velocity template. Figure 36.3, “Response Generated by Velocity” shows the outline of a general template-based route. At the start of the route is a Camel CXF endpoint in PAYLOAD mode, which is the appropriate mode to use for processing the message as an XML document. After doing the work required to process the message and stashing some intermediate results in message headers, the route generates the response message using a Velocity template.
Figure 36.3. Response Generated by Velocity
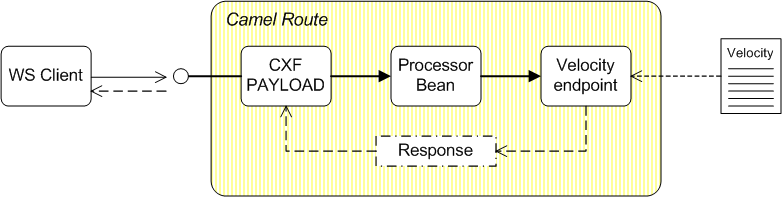
Sample template-based route
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
For example, you could define a template-based route specifically for the
getCustoemrStatus operation, as follows:
Route processing steps
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Given the preceding route definition, any message whose operation name matches
getCustomerStatus would be processed as follows:
- To facilitate processing the payload body, the first step uses
convertBodyToto convert the body type fromorg.apache.camel.component.cxf.CxfPayload(the default payload type) toorg.w3c.dom.Node. - The route then applies an XPath expression to the message in order to extract the customer ID value and then stashes it in the
customerIdheader. - The next step sends the message to the
getCustomerStatusbean, which does whatever processing is required to get the customer status for the specified customer ID. The results from this step are stashed in message headers. - Finally, a response is generated using a velocity template.
Note
A common pattern when implementing Apache Camel routes is to use message headers as a temporary stash to hold intermediate results (you could also use exchange properties in the same way).
Converting XPath result to a string
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Because the default return type of XPath is a node list, you must explicitly convert the result to a string, if you want to obtain the string contents of an element. There are two alternative ways of obtaining the string value of an element:
- Specify the result type explicitly using the
resultTypeattribute, as follows:<xpath resultType="java.lang.String">/cus:getCustomerStatus/customerId</xpath>
<xpath resultType="java.lang.String">/cus:getCustomerStatus/customerId</xpath>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Modify the expression so that it returns a
text()node, which automatically converts to string:<xpath>/cus:getCustomerStatus/customerId/text()</xpath>
<xpath>/cus:getCustomerStatus/customerId/text()</xpath>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
getCustomerStatus processor bean
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The
getCustomerStatus processor bean is an instance of the GetCustomerStatus processor class, which is defined as follows:
The implementation shown here is just a placeholder. In a realistic application you would perform some sort of checks or database lookup to obtain the customer status. In the demonstration code, however, the
status and statusMessage are simply set to constant values and stashed in message headers.
In the preceding code, we make the modifications directly to the In message. When the exchange's Out message is
null, the next processor in the route gets a copy of the current In message instead
Note
An exceptional case occurs when the message exchange pattern is inOnly, in which case the Out message value is always copied into the In message, even if it is
null.
getCustomerStatusResponse.vm Velocity template
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
You can generate a response message very simply using a Velocity template. The Velocity template consists of a message in plain text, where specific pieces of data can be inserted using expressions—for example, the expression
${header.HeaderName} substitutes the value of a named header.
The Velocity template for generating the
getCustomerStatus reponse is located in the customer-ws-camel-cxf-payload/src/main/resources directory and it contains the following template script:
<ns2:getCustomerStatusResponse xmlns:ns2="http://demo.fusesource.com/wsdl/CustomerService/">
<status>${headers.status}</status>
<statusMessage>${headers.statusMessage}</statusMessage>
</ns2:getCustomerStatusResponse>
<ns2:getCustomerStatusResponse xmlns:ns2="http://demo.fusesource.com/wsdl/CustomerService/">
<status>${headers.status}</status>
<statusMessage>${headers.statusMessage}</statusMessage>
</ns2:getCustomerStatusResponse>