Fuse 6 is no longer supported
As of February 2025, Red Hat Fuse 6 is no longer supported. If you are using Fuse 6, please upgrade to Red Hat build of Apache Camel.Chapter 3. Application Basics
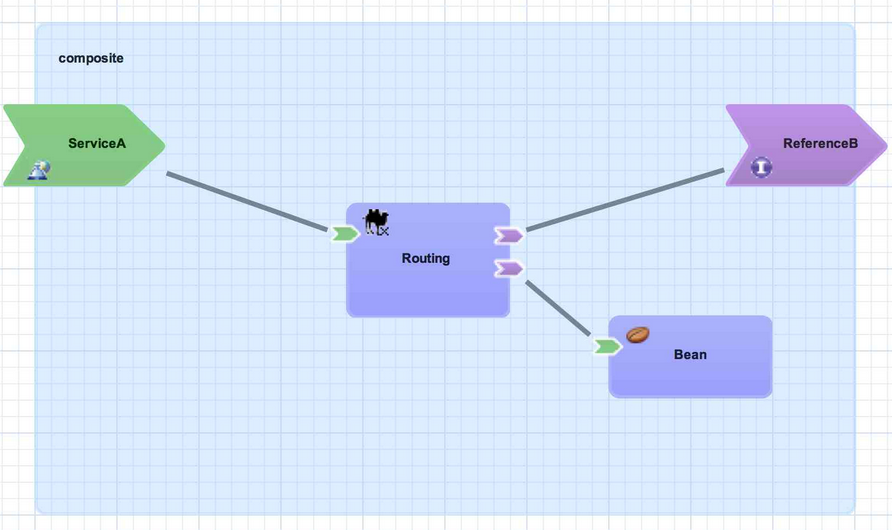
This section introduces the basic building blocks of a SwitchYard application starting from an empty application and building up to the complete application as shown below:
Figure 3.1. Composite
Each topic includes a visual representation of the
switchyard.xml configuration file as designed in the SwitchYard graphical editor and the corresponding source XML which is automatically generated from the visual design.
3.1. Composite
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A composite is displayed as a light blue rectangle and represents the boundary between what is inside your application and what is outside your application. A SwitchYard application consists of exactly one composite that has a
name and a targetNamespace. The targetNamespace value is important as it allows names defined locally in the application (for example, service names) to be qualified and unique within a SwitchYard runtime.
Figure 3.2. Composite
Example 3.1. Sample Corresponding XML
<sca:composite name="example" targetNamespace="urn:example:switchyard:1.0"> </sca:composite>
<sca:composite name="example" targetNamespace="urn:example:switchyard:1.0">
</sca:composite>