Appendix A. Managing Certificates
Abstract
TLS authentication uses X.509 certificates—a common, secure and reliable method of authenticating your application objects. You can create X.509 certificates that identify your Red Hat Fuse applications.
A.1. What is an X.509 Certificate?
Role of certificates
An X.509 certificate binds a name to a public key value. The role of the certificate is to associate a public key with the identity contained in the X.509 certificate.
Integrity of the public key
Authentication of a secure application depends on the integrity of the public key value in the application’s certificate. If an impostor replaces the public key with its own public key, it can impersonate the true application and gain access to secure data.
To prevent this type of attack, all certificates must be signed by a certification authority (CA). A CA is a trusted node that confirms the integrity of the public key value in a certificate.
Digital signatures
A CA signs a certificate by adding its digital signature to the certificate. A digital signature is a message encoded with the CA’s private key. The CA’s public key is made available to applications by distributing a certificate for the CA. Applications verify that certificates are validly signed by decoding the CA’s digital signature with the CA’s public key.
The supplied demonstration certificates are self-signed certificates. These certificates are insecure because anyone can access their private key. To secure your system, you must create new certificates signed by a trusted CA.
Contents of an X.509 certificate
An X.509 certificate contains information about the certificate subject and the certificate issuer (the CA that issued the certificate). A certificate is encoded in Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1), a standard syntax for describing messages that can be sent or received on a network.
The role of a certificate is to associate an identity with a public key value. In more detail, a certificate includes:
- A subject distinguished name (DN) that identifies the certificate owner.
- The public key associated with the subject.
- X.509 version information.
- A serial number that uniquely identifies the certificate.
- An issuer DN that identifies the CA that issued the certificate.
- The digital signature of the issuer.
- Information about the algorithm used to sign the certificate.
- Some optional X.509 v.3 extensions; for example, an extension exists that distinguishes between CA certificates and end-entity certificates.
Distinguished names
A DN is a general purpose X.500 identifier that is often used in the context of security.
See Appendix B, ASN.1 and Distinguished Names for more details about DNs.
A.2. Certification Authorities
A.2.1. Introduction to Certificate Authorities
A CA consists of a set of tools for generating and managing certificates and a database that contains all of the generated certificates. When setting up a system, it is important to choose a suitable CA that is sufficiently secure for your requirements.
There are two types of CA you can use:
- commercial CAs are companies that sign certificates for many systems.
- private CAs are trusted nodes that you set up and use to sign certificates for your system only.
A.2.2. Commercial Certification Authorities
Signing certificates
There are several commercial CAs available. The mechanism for signing a certificate using a commercial CA depends on which CA you choose.
Advantages of commercial CAs
An advantage of commercial CAs is that they are often trusted by a large number of people. If your applications are designed to be available to systems external to your organization, use a commercial CA to sign your certificates. If your applications are for use within an internal network, a private CA might be appropriate.
Criteria for choosing a CA
Before choosing a commercial CA, consider the following criteria:
- What are the certificate-signing policies of the commercial CAs?
- Are your applications designed to be available on an internal network only?
- What are the potential costs of setting up a private CA compared to the costs of subscribing to a commercial CA?
A.2.3. Private Certification Authorities
Choosing a CA software package
If you want to take responsibility for signing certificates for your system, set up a private CA. To set up a private CA, you require access to a software package that provides utilities for creating and signing certificates. Several packages of this type are available.
OpenSSL software package
One software package that allows you to set up a private CA is OpenSSL, http://www.openssl.org. The OpenSSL package includes basic command line utilities for generating and signing certificates. Complete documentation for the OpenSSL command line utilities is available at http://www.openssl.org/docs.
Setting up a private CA using OpenSSL
To set up a private CA, see the instructions in Section A.5, “Creating Your Own Certificates”.
Choosing a host for a private certification authority
Choosing a host is an important step in setting up a private CA. The level of security associated with the CA host determines the level of trust associated with certificates signed by the CA.
If you are setting up a CA for use in the development and testing of Red Hat Fuse applications, use any host that the application developers can access. However, when you create the CA certificate and private key, do not make the CA private key available on any hosts where security-critical applications run.
Security precautions
If you are setting up a CA to sign certificates for applications that you are going to deploy, make the CA host as secure as possible. For example, take the following precautions to secure your CA:
- Do not connect the CA to a network.
- Restrict all access to the CA to a limited set of trusted users.
- Use an RF-shield to protect the CA from radio-frequency surveillance.
A.3. Certificate Chaining
Certificate chain
A certificate chain is a sequence of certificates, where each certificate in the chain is signed by the subsequent certificate.
Figure A.1, “A Certificate Chain of Depth 2” shows an example of a simple certificate chain.
Figure A.1. A Certificate Chain of Depth 2

Self-signed certificate
The last certificate in the chain is normally a self-signed certificate—a certificate that signs itself.
Chain of trust
The purpose of a certificate chain is to establish a chain of trust from a peer certificate to a trusted CA certificate. The CA vouches for the identity in the peer certificate by signing it. If the CA is one that you trust (indicated by the presence of a copy of the CA certificate in your root certificate directory), this implies you can trust the signed peer certificate as well.
Certificates signed by multiple CAs
A CA certificate can be signed by another CA. For example, an application certificate could be signed by the CA for the finance department of Progress Software, which in turn is signed by a self-signed commercial CA.
Figure A.2, “A Certificate Chain of Depth 3” shows what this certificate chain looks like.
Figure A.2. A Certificate Chain of Depth 3
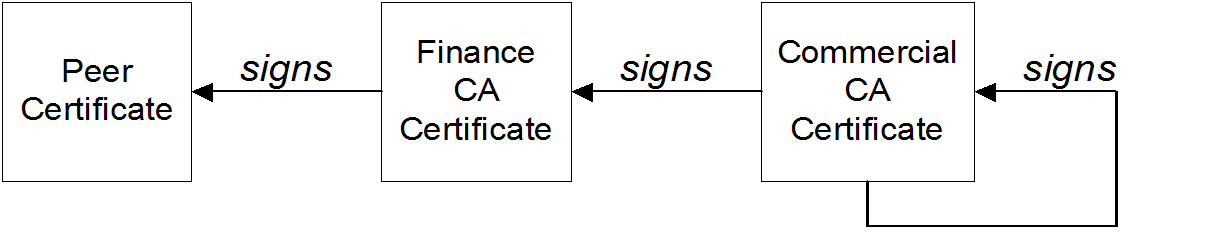
Trusted CAs
An application can accept a peer certificate, provided it trusts at least one of the CA certificates in the signing chain.
A.4. Special Requirements on HTTPS Certificates
Overview
The HTTPS specification mandates that HTTPS clients must be capable of verifying the identity of the server. This can potentially affect how you generate your X.509 certificates. The mechanism for verifying the server identity depends on the type of client. Some clients might verify the server identity by accepting only those server certificates signed by a particular trusted CA. In addition, clients can inspect the contents of a server certificate and accept only the certificates that satisfy specific constraints.
In the absence of an application-specific mechanism, the HTTPS specification defines a generic mechanism, known as the HTTPS URL integrity check, for verifying the server identity. This is the standard mechanism used by Web browsers.
HTTPS URL integrity check
The basic idea of the URL integrity check is that the server certificate’s identity must match the server host name. This integrity check has an important impact on how you generate X.509 certificates for HTTPS: the certificate identity (usually the certificate subject DN’s common name) must match the host name on which the HTTPS server is deployed.
The URL integrity check is designed to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Reference
The HTTPS URL integrity check is specified by RFC 2818, published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2818.txt.
How to specify the certificate identity
The certificate identity used in the URL integrity check can be specified in one of the following ways:
Using commonName
The usual way to specify the certificate identity (for the purpose of the URL integrity check) is through the Common Name (CN) in the subject DN of the certificate.
For example, if a server supports secure TLS connections at the following URL:
https://www.redhat.com/secure
https://www.redhat.com/secureThe corresponding server certificate would have the following subject DN:
C=IE,ST=Co. Dublin,L=Dublin,O=RedHat, OU=System,CN=www.redhat.com
C=IE,ST=Co. Dublin,L=Dublin,O=RedHat,
OU=System,CN=www.redhat.com
Where the CN has been set to the host name, www.redhat.com.
For details of how to set the subject DN in a new certificate, see Section A.5, “Creating Your Own Certificates”.
Using subjectAltName (multi-homed hosts)
Using the subject DN’s Common Name for the certificate identity has the disadvantage that only one host name can be specified at a time. If you deploy a certificate on a multi-homed host, however, you might find it is practical to allow the certificate to be used with any of the multi-homed host names. In this case, it is necessary to define a certificate with multiple, alternative identities, and this is only possible using the subjectAltName certificate extension.
For example, if you have a multi-homed host that supports connections to either of the following host names:
www.redhat.com www.jboss.org
www.redhat.com
www.jboss.org
Then you can define a subjectAltName that explicitly lists both of these DNS host names. If you generate your certificates using the openssl utility, edit the relevant line of your openssl.cnf configuration file to specify the value of the subjectAltName extension, as follows:
subjectAltName=DNS:www.redhat.com,DNS:www.jboss.org
subjectAltName=DNS:www.redhat.com,DNS:www.jboss.org
Where the HTTPS protocol matches the server host name against either of the DNS host names listed in the subjectAltName (the subjectAltName takes precedence over the Common Name).
The HTTPS protocol also supports the wildcard character, \*, in host names. For example, you can define the subjectAltName as follows:
subjectAltName=DNS:*.jboss.org
subjectAltName=DNS:*.jboss.orgThis certificate identity matches any three-component host name in the domain jboss.org.
You must never use the wildcard character in the domain name (and you must take care never to do this accidentally by forgetting to type the dot, ., delimiter in front of the domain name). For example, if you specified *jboss.org, your certificate could be used on *any* domain that ends in the letters jboss.
A.5. Creating Your Own Certificates
Abstract
This chapter describes the techniques and procedures to set up your own private Certificate Authority (CA) and to use this CA to generate and sign your own certificates.
Creating and managing your own certificates requires an expert knowledge of security. While the procedures described in this chapter can be convenient for generating your own certificates for demonstration and testing environments, it is not recommended to use these certificates in a production environment.
A.5.1. Install the OpenSSL Utilities
Installing OpenSSL on RHEL and Fedora platforms
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 5 and 6 and Fedora platforms, are made available as an RPM package. To install OpenSSL, enter the following command (executed with administrator privileges):
yum install openssl
yum install opensslSource code distribution
The source distribution of OpenSSL is available from http://www.openssl.org/docs. The OpenSSL project provides source code distributions only. You cannot download a binary install of the OpenSSL utilities from the OpenSSL Web site.
A.5.2. Set Up a Private Certificate Authority
Overview
If you choose to use a private CA you need to generate your own certificates for your applications to use. The OpenSSL project provides free command-line utilities for setting up a private CA, creating signed certificates, and adding the CA to your Java keystore.
Setting up a private CA for a production environment requires a high level of expertise and extra care must be taken to protect the certificate store from external threats.
Steps to set up a private Certificate Authority
To set up your own private Certificate Authority:
Create the directory structure for the CA, as follows:
X509CA/demoCA X509CA/demoCA/private X509CA/demoCA/certs X509CA/demoCA/newcerts X509CA/demoCA/crl
X509CA/demoCA X509CA/demoCA/private X509CA/demoCA/certs X509CA/demoCA/newcerts X509CA/demoCA/crlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Using a text editor, create the file,
X509CA/openssl.cfg, and add the following contents to this file:Example A.1. OpenSSL Configuration
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantThe preceding
openssl.cfgconfiguration file is provided as a demonstration only. In a production environment, this configuration file would need to be carefully elaborated by an engineer with a high level of security expertise, and actively maintained to protect against evolving security threats.Initialize the
demoCA/serialfile, which must have the initial contents01(zero one). Enter the following command:echo 01 > demoCA/serial
echo 01 > demoCA/serialCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Initialize the
demoCA/index.txt, which must initially be completely empty. Enter the following command:touch demoCA/index.txt
touch demoCA/index.txtCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a new self-signed CA certificate and private key with the command:
openssl req -x509 -new -config openssl.cfg -days 365 -out demoCA/cacert.pem -keyout demoCA/private/cakey.pem
openssl req -x509 -new -config openssl.cfg -days 365 -out demoCA/cacert.pem -keyout demoCA/private/cakey.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You are prompted for a pass phrase for the CA private key and details of the CA distinguished name as shown in Example A.2, “Creating a CA Certificate”.
Example A.2. Creating a CA Certificate
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe security of the CA depends on the security of the private key file and the private key pass phrase used in this step.
You must ensure that the file names and location of the CA certificate and private key,
cacert.pemandcakey.pem, are the same as the values specified inopenssl.cfg.
A.5.3. Create a CA Trust Store File
Overview
A trust store file is commonly required on the client side of an SSL/TLS connection, in order to verify a server’s identity. A trust store file can also be used to check digital signatures (for example, to check that a signature was made using the private key corresponding to one of the trusted certificates in the trust store file).
Steps to create a CA trust store
To add one of more CA certificates to a trust store file:
Assemble the collection of trusted CA certificates that you want to deploy.
The trusted CA certificates can be obtained from public CAs or private CAs. The trusted CA certificates can be in any format that is compatible with the Java
keystoreutility; for example, PEM format. All you need are the certificates themselves—the private keys and passwords are not required.Add a CA certificate to the trust store using the
keytool -importcommand.Enter the following command to add the CA certificate,
cacert.pem, in PEM format, to a JKS trust store.keytool -import -file cacert.pem -alias CAAlias -keystore truststore.ts -storepass StorePass
keytool -import -file cacert.pem -alias CAAlias -keystore truststore.ts -storepass StorePassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where
truststore.tsis a keystore file containing CA certificates. If this file does not already exist, thekeytoolcommand creates it. TheCAAliasis a convenient identifier for the imported CA certificate andStorePassis the password required to access the keystore file.- Repeat the previous step to add all of the CA certificates to the trust store.
A.5.4. Generate and Sign a New Certificate
Overview
In order for a certificate to be useful in the real world, it must be signed by a CA, which vouches for the authenticity of the certificate. This facilitates a scalable solution for certificate verification, because it means that a single CA certificate can be used to verify a large collection of certificates.
Steps to generate and sign a new certificate
To generate and sign a new certificate, using your own private CA, perform the following steps:
Generate a certificate and private key pair using the
keytool -genkeypaircommand, as follows:keytool -genkeypair -keyalg RSA -dname "CN=Alice, OU=Engineering, O=Red Hat, ST=Dublin, C=IE" -validity 365 -alias alice -keypass KeyPass -keystore alice.ks -storepass StorePass
keytool -genkeypair -keyalg RSA -dname "CN=Alice, OU=Engineering, O=Red Hat, ST=Dublin, C=IE" -validity 365 -alias alice -keypass KeyPass -keystore alice.ks -storepass StorePassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Because the specified keystore,
alice.ks, did not exist prior to issuing the command implicitly creates a new keystore and sets its password toStorePass.The
-dnameand-validityflags define the contents of the newly created X.509 certificate.NoteWhen specifying the certificate’s Distinguished Name (through the
-dnameparameter), you must be sure to observe any policy constraints specified in theopenssl.cfgfile. If those policy constraints are not heeded, you will not be able to sign the certificate using the CA (in the next steps).NoteIt is essential to generate the key pair with the
-keyalg RSAoption (or a key algorithm of similar strength). The default key algorithm uses a combination of DSA encryption and SHA-1 signature. But the SHA-1 algorithm is no longer regarded as sufficiently secure and modern Web browsers will reject certificates signed using SHA-1. When you select the RSA key algorithm, thekeytoolutility uses an SHA-2 algorithm instead.Create a certificate signing request using the
keystore -certreqcommand.Create a new certificate signing request for the
alice.kscertificate and export it to thealice_csr.pemfile, as follows:keytool -certreq -alias alice -file alice_csr.pem -keypass KeyPass -keystore alice.ks -storepass StorePass
keytool -certreq -alias alice -file alice_csr.pem -keypass KeyPass -keystore alice.ks -storepass StorePassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sign the CSR using the
openssl cacommand.Sign the CSR for the Alice certificate, using your private CA, as follows:
openssl ca -config openssl.cfg -days 365 -in alice_csr.pem -out alice_signed.pem
openssl ca -config openssl.cfg -days 365 -in alice_csr.pem -out alice_signed.pemCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You will prompted to enter the CA private key pass phrase you used when creating the CA (in the section called “Steps to set up a private Certificate Authority”).
For more details about the
openssl cacommand see http://www.openssl.org/docs/apps/ca.html#.Convert the signed certificate to PEM only format using the
openssl x509command with the-outformoption set toPEM. Enter the following command:openssl x509 -in alice_signed.pem -out alice_signed.pem -outform PEM
openssl x509 -in alice_signed.pem -out alice_signed.pem -outform PEMCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Concatenate the CA certificate file and the converted, signed certificate file to form a certificate chain. For example, on Linux and UNIX platforms, you can concatenate the CA certificate file and the signed Alice certificate,
alice_signed.pem, as follows:cat demoCA/cacert.pem alice_signed.pem > alice.chain
cat demoCA/cacert.pem alice_signed.pem > alice.chainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Import the new certificate’s full certificate chain into the Java keystore using the
keytool -importcommand. Enter the following command:keytool -import -file alice.chain -keypass KeyPass -keystore alice.ks -storepass StorePass
keytool -import -file alice.chain -keypass KeyPass -keystore alice.ks -storepass StorePassCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow