Chapter 1. Introduction to Camel K
This chapter introduces the concepts, features, and cloud-native architecture provided by Red Hat Integration - Camel K:
Red Hat Integration - Camel K is a Technology Preview feature only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs) and might not be functionally complete. Red Hat does not recommend using them in production.
These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process. For more information about the support scope of Red Hat Technology Preview features, see https://access.redhat.com/support/offerings/techpreview.
1.1. Camel K overview
Red Hat Integration - Camel K is a lightweight integration framework built from Apache Camel K that runs natively in the cloud on OpenShift. Camel K is specifically designed for serverless and microservice architectures. You can use Camel K to instantly run your integration code written in Camel Domain Specific Language (DSL) directly on OpenShift. Camel K is a subproject of the Apache Camel open source community: https://github.com/apache/camel-k.
Camel K is implemented in the Go programming language and uses the Kubernetes Operator SDK to automatically deploy integrations in the cloud. For example, this includes automatically creating services and routes on OpenShift. This provides much faster turnaround times when deploying and redeploying integrations in the cloud, such as a few seconds or less instead of minutes.
The Camel K runtime provides significant performance optimizations. The Quarkus cloud-native Java framework is enabled by default to provide faster start up times, and lower memory and CPU footprints. When running Camel K in developer mode, you can make live updates to your integration DSL and view results instantly in the cloud on OpenShift, without waiting for your integration to redeploy.
Using Camel K with OpenShift Serverless and Knative Serving, containers are created only as needed and are autoscaled under load up and down to zero. This reduces cost by removing the overhead of server provisioning and maintenance and enables you to focus on application development instead.
Using Camel K with OpenShift Serverless and Knative Eventing, you can manage how components in your system communicate in an event-driven architecture for serverless applications. This provides flexibility and creates efficiencies through decoupled relationships between event producers and consumers using a publish-subscribe or event-streaming model.
Additional resources
1.2. Camel K Technology Preview features
The Camel K Technology Preview includes the following main platforms and features:
1.2.1. Platform and component versions
- OpenShift Container Platform 4.6
- OpenShift Serverless 1.7
- Quarkus 1.7 Java runtime
- Camel 3.5
- Java 11
1.2.2. Technology Preview features
- Knative Serving for autoscaling and scale-to-zero
- Knative Eventing for event-driven architectures
- Performance optimizations using Quarkus runtime by default
- Camel integrations written in Java, XML, or YAML DSL
- Development tooling with Visual Studio Code
- Monitoring of integrations using Prometheus in OpenShift
- Quickstart tutorials, including new Transformations and SaaS examples
- Kamelet catalog of connectors to external systems such as AWS, Jira, and Salesforce
The Technology Preview includes building Camel K integration images with OpenShift only. Installing Camel K with the Buildah or Kaniko image builder is not included in the Technology Preview and has community-only support.
1.3. Camel K cloud-native architecture
The following diagram shows a simplified view of the Camel K cloud-native architecture:
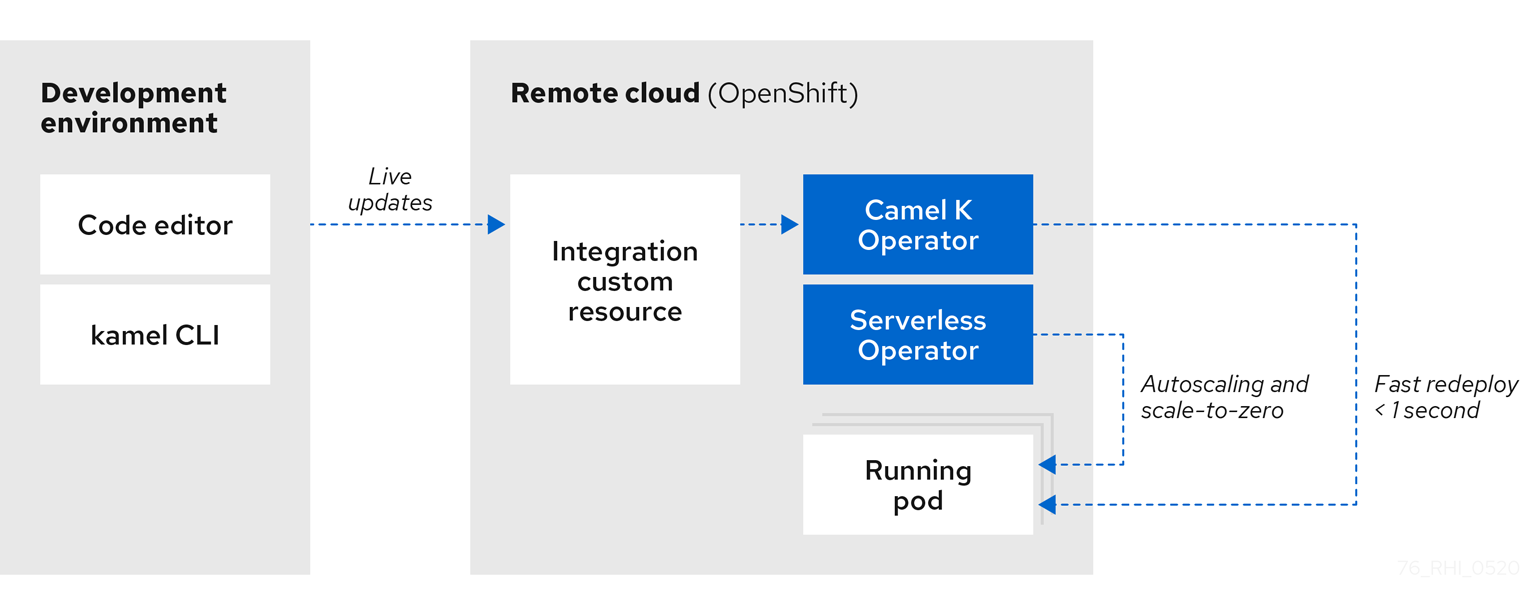
Camel K automatically wraps the Camel integration in a Kubernetes custom resource and uploads it to the cloud. This architecture provides the following benefits:
- Cloud-native integration and developer experience on OpenShift for faster development cycles
- Automatic installation of Camel K and deployment of integrations using the Camel K Operator
- Live code updates using Camel K developer mode, without needing to redeploy
- Autoscaling up and down to zero with Knative using the OpenShift Serverless Operator
Performance optimizations and cost savings using the Quarkus Java runtime:
- Pre-compilation and pre-initialization of code at build time
- Fast start up, deploy, and redeploy times
- Low memory and CPU footprint
- Automatic dependency resolution of Camel integration code
- Configuring advanced features using Camel K traits on the command line and modeline
Additional resources
1.3.1. Kamelets
Kamelets hide the complexity of connecting to external systems behind a simple interface, which contains all the information needed to instantiate them, even for users who are not familiar with Camel.
Kamelets are implemented as custom resources that you can install on an OpenShift cluster and use in Camel K integrations. They contain high-level connectors in the form of route templates. Kamelets abstract the details of connecting to external systems. You can also combine Kamelets to create complex Camel integrations, just like using standard Camel components.
Additional resources
1.4. Camel K development tooling
The Camel K Technology Preview provides development tooling extensions for Visual Studio (VS) Code, Red Hat CodeReady WorkSpaces, and Eclipse Che. The Camel-based tooling extensions include features such as automatic completion of Camel DSL code, Camel K modeline configuration, and Camel K traits. While Didact tutorial tooling extensions provide automatic execution of Camel K quick start tutorial commands.
The following VS Code development tooling extensions are available:
VS Code Extension Pack for Apache Camel by Red Hat
- Tooling for Apache Camel K extension
- Language Support for Apache Camel extension
- Additional extensions for OpenShift, Java, XML, and more
- Didact Tutorial Tools for VS Code extension
For details on how to set up these VS Code extensions for Camel K, see Section 3.1, “Setting up your Camel K development environment”.
Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces and Eclipse Che also provide these features using the vscode-camelk plug-in.
1.5. Camel K distributions
| Distribution | Description | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Operator image |
Container image for the Red Hat Integration - Camel K Operator: |
|
| Maven repository | Maven artifacts for Red Hat Integration - Camel K | |
| Source code | Source code for Red Hat Integration - Camel K | |
| Quickstarts | Quick start tutorials:
|
You must have a subscription for Red Hat Integration and be logged into the Red Hat Customer Portal to access the Red Hat Integration - Camel K distributions.