Chapter 8. WS-Trust
Abstract
WS-Trust provides the necessary security infrastructure for supporting advanced authentication and authorization requirements. In particular, WS-Trust enables you to store security data in a central location (in the Security Token Service) and support various single sign-on scenarios.
8.1. Introduction to WS-Trust
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Overview
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The WS-Trust standard is based around a centralized security server (the Security Token Service), which is capable of authenticating clients and can issue tokens containing various kinds of authentication and authorization data.
WS-Trust specification
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The WS-Trust features of Apache CXF are based on the WS-Trust standard from Oasis:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-sx/ws-trust/v1.4/ws-trust.html
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-sx/ws-trust/v1.4/ws-trust.htmlSupporting specifications
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
Apart from the WS-Trust specification itself, several other specifications play an important role in the WS-Trust architecture, as follows:
WS-Trust architecture
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
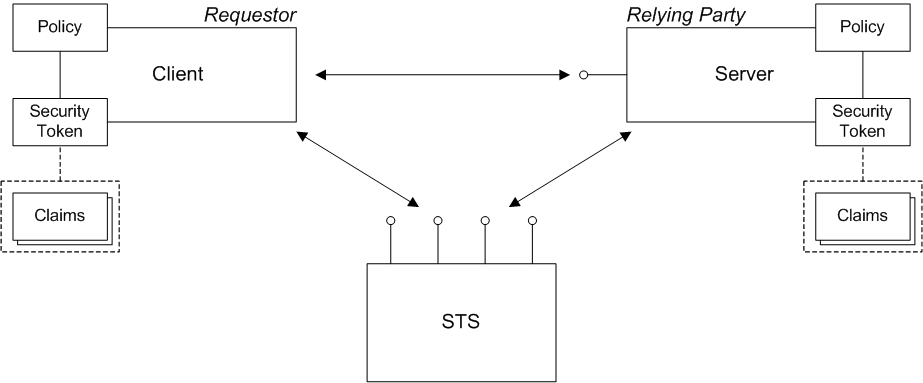
Figure 8.1, “WS-Trust Architecture” shows a general overview of the WS-Trust architecture.
Figure 8.1. WS-Trust Architecture
Requestor
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A requestor is an entity that tries to invoke a secure operation over a network connection. In practice, a requestor is typically a Web service client.
Relying party
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A relying party refers to an entity that has some services or resources that must be secured against unauthorized access. In practice, a relying party is typically a Web service.
Note
This is a term defined by the SAML specification, not by WS-Trust.
Security token
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A security token is a collection of security data that a requestor sends inside a request (typically embedded in the message header) in order to invoke a secure operation or to gain access to a secure resource. In the WS-Trust framework, the notion of a security token is quite general and can be used to describe any block of security data that might accompany a request.
In principle, WS-Trust can be used with the following kinds of security token:
- SAML token.
- UsernameToken token.
- X.509 certificate token.
- Kerberos token.
SAML token
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A SAML token is a particularly flexible kind of security token. The SAML specification defines a general-purpose XML schema that enables you to wrap almost any kind of security data and enables you to sign and encrypt part or all of the token.
SAML is a popular choice of token to use in the context of WS-Trust, because SAML has all of the necessary features to support typical WS-Trust authentication scenarios.
Claims
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
A SAML security token is formally defined to consist of a collection of claims. Each claim typically contains a particular kind of security data.
Policy
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
In WS-Trust scenarios, a policy can represent the security configuration of a participant in a secure application. The requestor, the relying party, and the security token service are all configured by policies. For example, a policy can be used to configure what kinds of authentication are supported and required.
Security token service
Copy linkLink copied to clipboard!
The security token service (STS) lies at the heart of the WS-Trust security architecture. In the WS-Trust standard, the following bindings are defined (not all of which are supported by Apache CXF):
- Issue binding—the specification defines this binding as follows: Based on the credential provided/proven in the request, a new token is issued, possibly with new proof information.
- Validate binding—the specification defines this binding as follows: The validity of the specified security token is evaluated and a result is returned. The result may be a status, a new token, or both.
- Renew binding—the specification defines this binding as follows: A previously issued token with expiration is presented (and possibly proven) and the same token is returned with new expiration semantics.
- Cancel binding—the specification defines this binding as follows: When a previously issued token is no longer needed, the Cancel binding can be used to cancel the token, terminating its use.