Chapter 1. Overview
Red Hat OpenShift AI is an artificial intelligence (AI) platform that provides tools to rapidly train, serve, and monitor machine learning (ML) models onsite, in the public cloud, or at the edge.
OpenShift AI provides a powerful AI/ML platform for building AI-enabled applications. Data scientists and MLOps engineers can collaborate to move from experiment to production in a consistent environment quickly.
You can deploy OpenShift AI on any supported version of OpenShift, whether on-premise, in the cloud, or in disconnected environments. For details on supported versions, see Red Hat OpenShift AI: Supported Configurations.
1.1. Data science workflow
For the purpose of getting you started with OpenShift AI, Figure 1 illustrates a simplified data science workflow. The real world process of developing ML models is an iterative one.
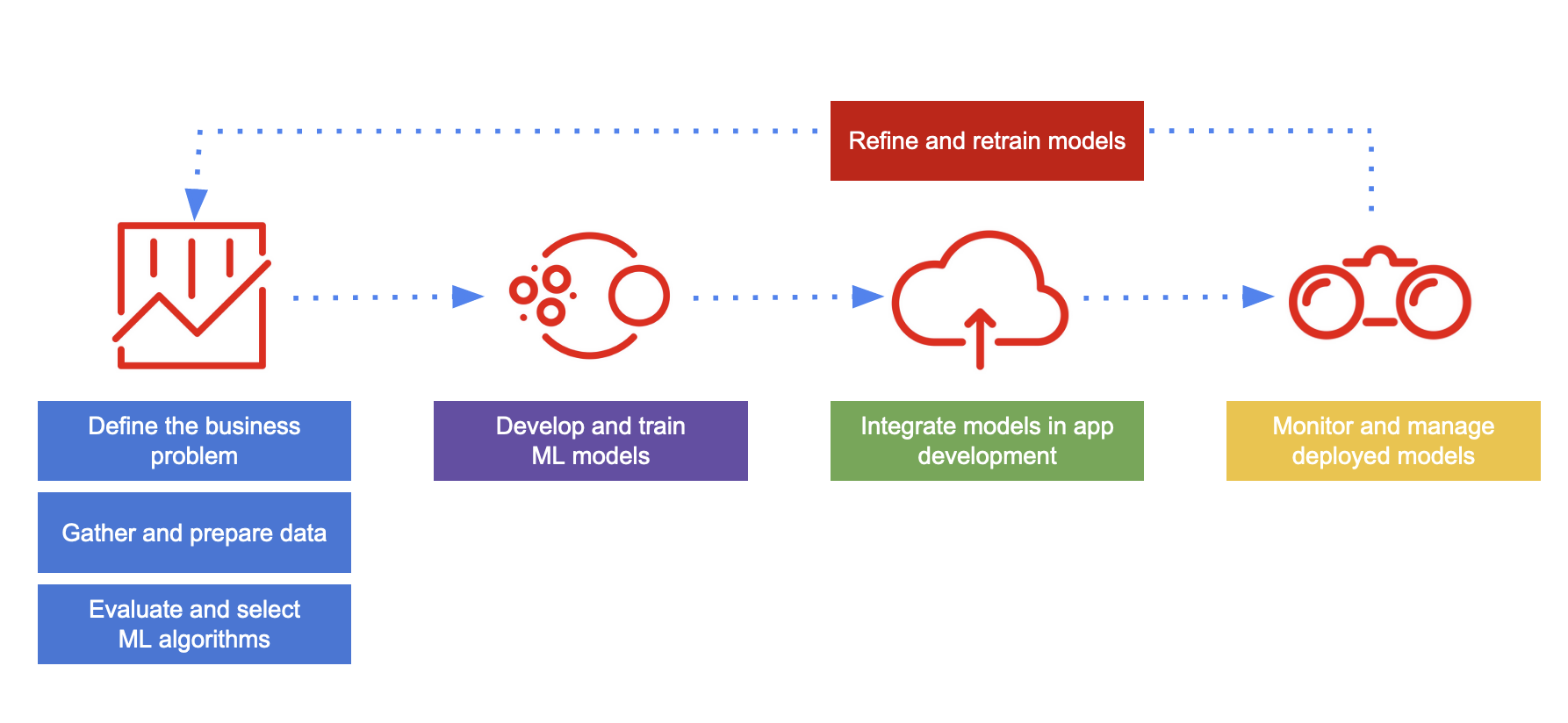
The simplified data science workflow for predictive AI use cases includes the following tasks:
- Defining your business problem and setting goals to solve it.
- Gathering, cleaning, and preparing data. Data often has to be federated from a range of sources, and exploring and understanding data plays a key role in the success of a data science project.
- Evaluating and selecting ML models for your business use case.
- Train models for your business use case by tuning model parameters based on your set of training data. In practice, data scientists train a range of models, and compare performance while considering tradeoffs such as time and memory constraints.
- Integrate models into an application, including deployment and testing. After model training, the next step of the workflow is production. Data scientists are often responsible for putting the model in production and making it accessible so that a developer can integrate the model into an application.
- Monitor and manage deployed models. Depending on the organization, data scientists, data engineers, or ML engineers must monitor the performance of models in production, tracking prediction and performance metrics.
- Refine and retrain models. Data scientists can evaluate model performance results and refine models to improve outcome by excluding or including features, changing the training data, and modifying other configuration parameters.
1.2. About this guide
This guide assumes you are familiar with data science and ML Ops concepts. It describes the following tasks to get you started with using OpenShift AI:
- Log in to the OpenShift AI dashboard
- Create a data science project
- If you have data stored in Object Storage, configure a data connection to more easily access it
- Create a workbench and choose an IDE, such as JupyterLab or code-server, for your data scientist development work
Learn where to get information about the next steps:
- Developing and training a model
- Automating the workflow with pipelines
- Implementing distributed workloads
- Testing your model
- Deploying your model
- Monitoring and managing your model
See also OpenShift AI tutorial: Fraud detection example. It provides step-by-step guidance for using OpenShift AI to develop and train an example model in JupyterLab, deploy the model, and refine the model by using automated pipelines.