Chapter 9. Configuring high availability for Knative services
9.1. High availability for Knative services
High availability (HA) is a standard feature of Kubernetes APIs that helps to ensure that APIs stay operational if a disruption occurs. In an HA deployment, if an active controller crashes or is deleted, another controller is readily available. This controller takes over processing of the APIs that were being serviced by the controller that is now unavailable.
HA in OpenShift Serverless is available through leader election, which is enabled by default after the Knative Serving or Eventing control plane is installed. When using a leader election HA pattern, instances of controllers are already scheduled and running inside the cluster before they are required. These controller instances compete to use a shared resource, known as the leader election lock. The instance of the controller that has access to the leader election lock resource at any given time is called the leader.
9.2. High availability for Knative services
High availability (HA) is available by default for the Knative Serving activator, autoscaler, autoscaler-hpa, controller, webhook, kourier-control, and kourier-gateway components, which are configured to have two replicas each by default. You can change the number of replicas for these components by modifying the spec.high-availability.replicas value in the KnativeServing custom resource (CR).
9.2.1. Configuring high availability replicas for Knative Serving
To specify three minimum replicas for the eligible deployment resources, set the value of the field spec.high-availability.replicas in the custom resource to 3.
Prerequisites
- You have cluster administrator permissions on OpenShift Container Platform, or you have cluster or dedicated administrator permissions on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS or OpenShift Dedicated.
- The OpenShift Serverless Operator and Knative Serving are installed on your cluster.
Procedure
-
In the OpenShift Container Platform web console Administrator perspective, navigate to OperatorHub
Installed Operators. -
Select the
knative-servingnamespace. - Click Knative Serving in the list of Provided APIs for the OpenShift Serverless Operator to go to the Knative Serving tab.
Click knative-serving, then go to the YAML tab in the knative-serving page.
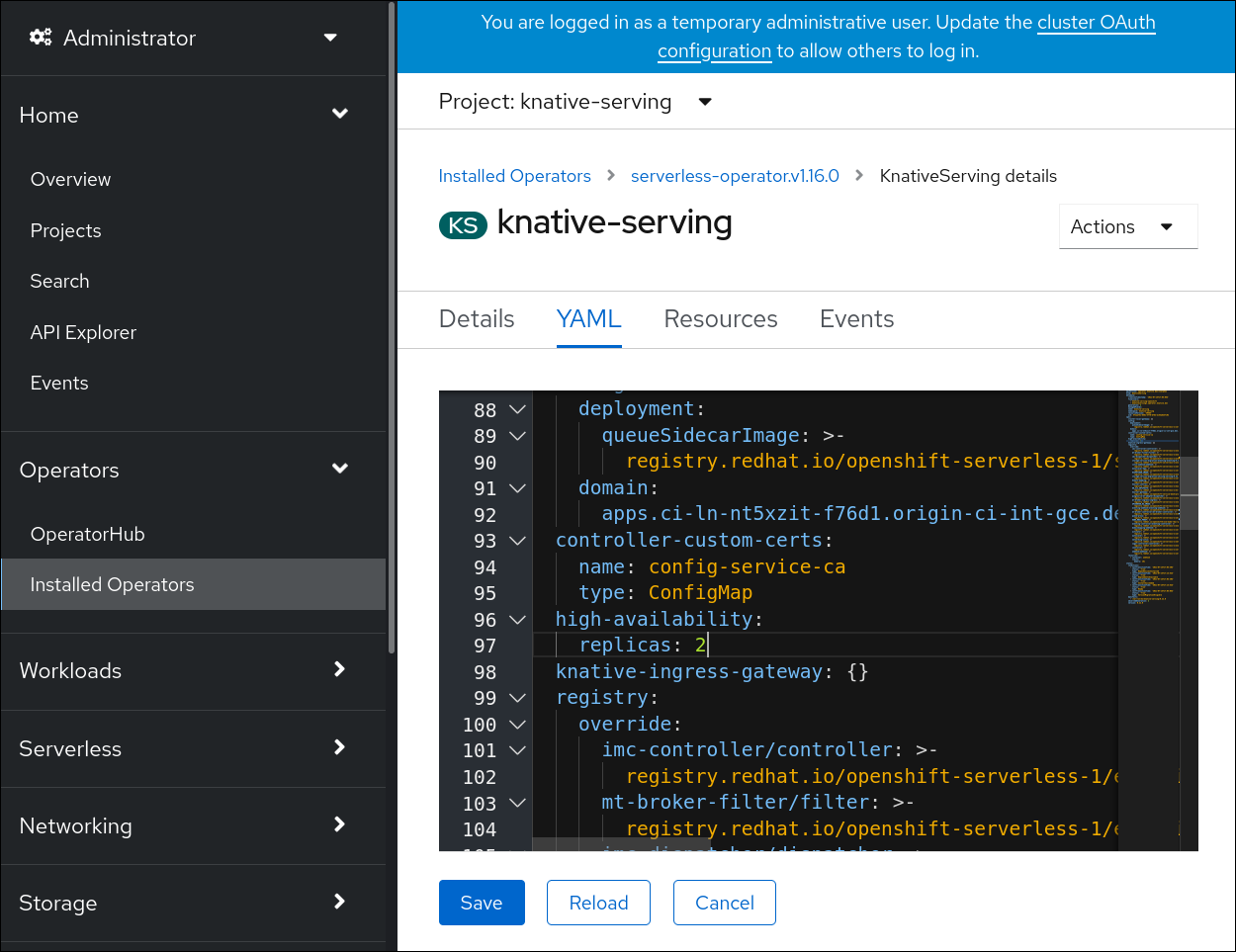
Modify the number of replicas in the
KnativeServingCR:Example YAML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow