Chapter 15. Configure Load Balancing-as-a-Service with the Networking LBaaSv2 API
15.1. Overview of LBaaS
Load Balancing-as-a-Service (LBaaS) enables OpenStack Networking to distribute incoming requests evenly between designated instances. Complete the steps in this section to configure OpenStack Networking to use LBaaS with the Open vSwitch (OVS) plug-in.
Load Balancing-as-a-Service (LBaaS) enables OpenStack Networking to distribute incoming requests evenly between designated instances. This ensures the workload is shared predictably among instances, and allows more effective use of system resources. Incoming requests are distributed using one of the following load balancing methods:
- Round robin - Rotates requests evenly between multiple instances.
- Source IP - Requests from a unique source IP address are consistently directed to the same instance.
- Least connections - Allocates requests to the instance with the least number of active connections.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitors | LBaaS provides availability monitoring with the PING, TCP, HTTP and HTTPS GET methods. Monitors determine whether pool members are available to handle requests. |
| Management | LBaaS is managed using a variety of tool sets. The REST API is available for programmatic administration and scripting. Users perform administrative management of load balancers through either the CLI (neutron) or the OpenStack dashboard. |
| Connection limits | Ingress traffic can be shaped with connection limits. This feature allows workload control and can also assist with mitigating DoS (Denial of Service) attacks. |
| Session persistence | LBaaS supports session persistence by ensuring incoming requests are routed to the same instance within a pool of multiple instances. LBaaS supports routing decisions based on cookies and source IP address. |
LBaaS is currently supported only with IPv4 addressing.
15.2. OpenStack Networking and LBaaS Topology
OpenStack Networking (neutron) services can be broadly classified into two categories.
Neutron API server - This service runs the OpenStack Networking API server, which has the main responsibility of providing an API for end users and services to interact with OpenStack Networking. This server also has the responsibility of interacting with the underlying database to store and retrieve tenant network, router, and loadbalancer details, among others.
Neutron Agents - These are the services that deliver various network functionality for OpenStack Networking.
- neutron-dhcp-agent - manages DHCP IP addressing for tenant private networks.
- neutron-l3-agent - facilitates layer 3 routing between tenant private networks, the external network, and other networks.
The neutron-lbaasv2-agent (with HAProxy) is deprecated. See Chapter 16, Load Balancing-as-a-Service (LBaaS) with Octavia for the preferred load-balancing reference implementation with Octavia.
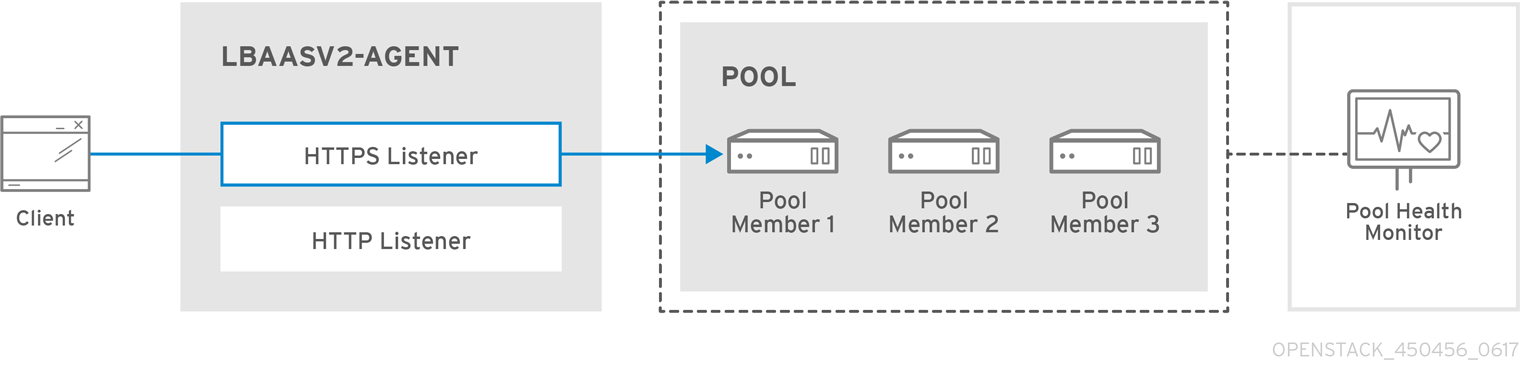
The following diagram shows the flow of HTTPS traffic through to a pool member:
15.2.1. Support Status of LBaaS
- LBaaS v1 API was removed in version 10.
- LBaaS v2 API is deprecated in Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14 and 15, and will be removed in a future release. (Octavia is the replacement.)
- LBaaS deployment is not currently supported in Red Hat OpenStack Platform director.
The neutron-lbaasv2-agent (with HAProxy) is deprecated and no longer supported. See Chapter 16, Load Balancing-as-a-Service (LBaaS) with Octavia for the preferred load-balancing reference implementation with Octavia. The neutron-lbaas RPMs are still available to support the API for third-party plugin support.