Chapter 2. Instance boot source
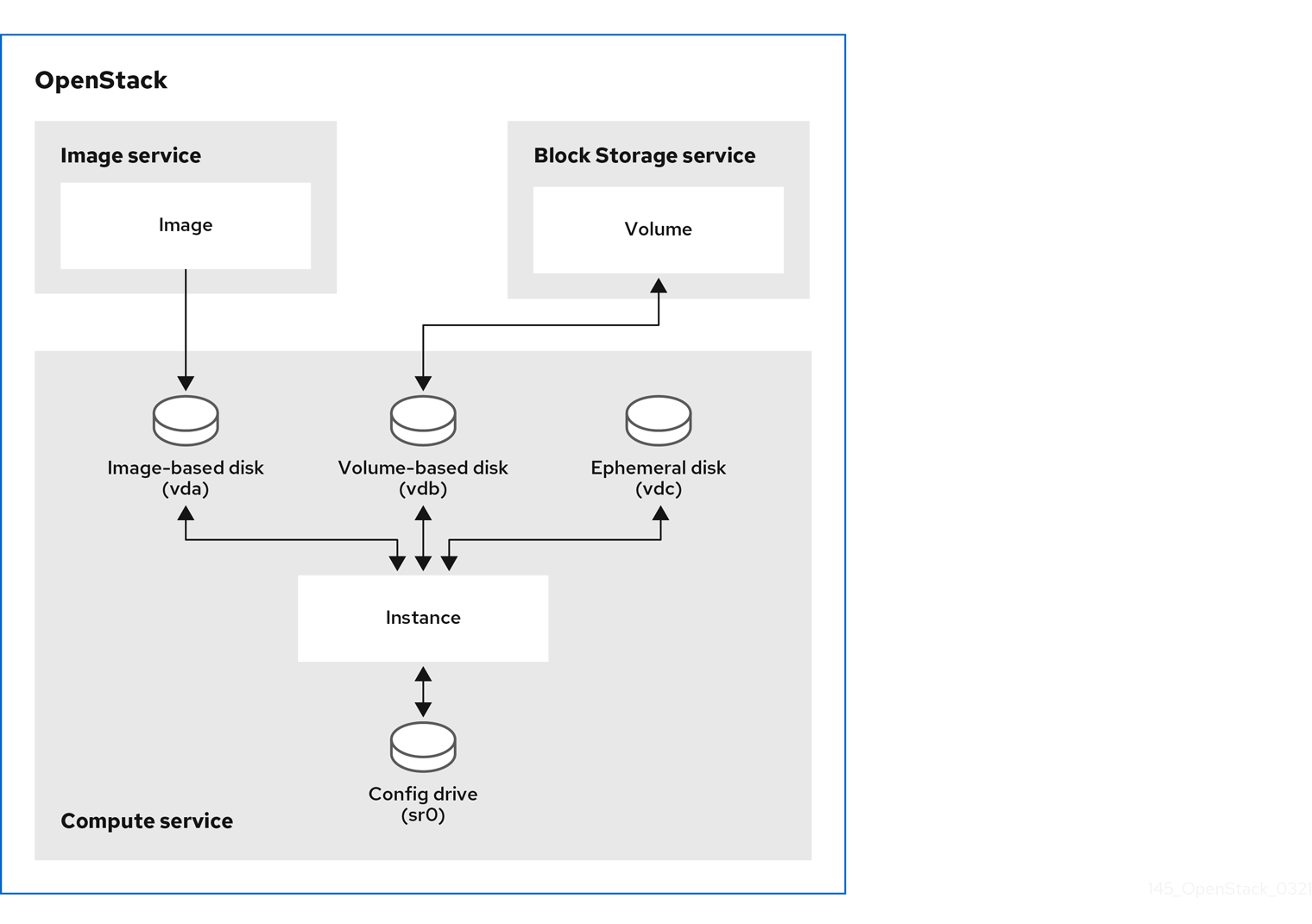
The boot source for an instance can be an image or a bootable volume. The instance disk of an instance that you boot from an image is controlled by the Compute service and deleted when the instance is deleted. The instance disk of an instance that you boot from a volume is controlled by the Block Storage service and is stored remotely.
An image contains a bootable operating system. The Image Service (glance) controls image storage and management. You can launch any number of instances from the same base image. Each instance runs from a copy of the base image. Any changes that you make to the instance do not affect the base image.
A bootable volume is a block storage volume created from an image that contains a bootable operating system. The instance can use the bootable volume to persist instance data when the instance is deleted. You can use an existing persistent root volume when you launch an instance. You can also create persistent storage when you launch an instance from an image, so that you can save the instance data when the instance is deleted. A new persistent storage volume is created automatically when you create an instance from a volume snapshot.
The following diagram shows the instance disks and storage that you can create when you launch an instance. The actual instance disks and storage created depend on the boot source and flavor used.