Chapter 9. Examples
Use the following examples to understand how to launch a compute instance post-deployment with various network configurations.
9.1. Example 1: Launching an instance with one NIC on the project and provider networks
Use this example to understand how to launch an instance with the private project network and the provider network after you deploy the all-in-one Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment. This example is based on a single NIC configuration and requires at least three IP addresses.
Prerequisites
To complete this example successfully, you must have the following IP addresses available in your environment:
- One IP address for the OpenStack services.
- One IP address for the virtual router to provide connectivity to the project network. This IP address is assigned automatically in this example.
- At least one IP address for floating IPs on the provider network.
Procedure
Create configuration helper variables:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a basic flavor:
openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tiny
$ openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tinyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download CirrOS and create an OpenStack image:
wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img
$ wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img $ openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.imgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure SSH:
ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem.pub default
$ ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem $ openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem.pub defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a simple network security group:
openstack security group create basic
$ openstack security group create basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the new network security group:
Enable SSH:
openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
$ openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable ping:
openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable DNS:
openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create Neutron networks:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a virtual router:
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. openstack router create vrouter openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public openstack router add subnet vrouter private-net
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. $ openstack router create vrouter $ openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public $ openstack router add subnet vrouter private-netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a floating IP:
openstack floating ip create public
$ openstack floating ip create publicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the instance:
openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserver
$ openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Assign the floating IP:
openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>
$ openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.Test SSH:
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.
Network Architecture
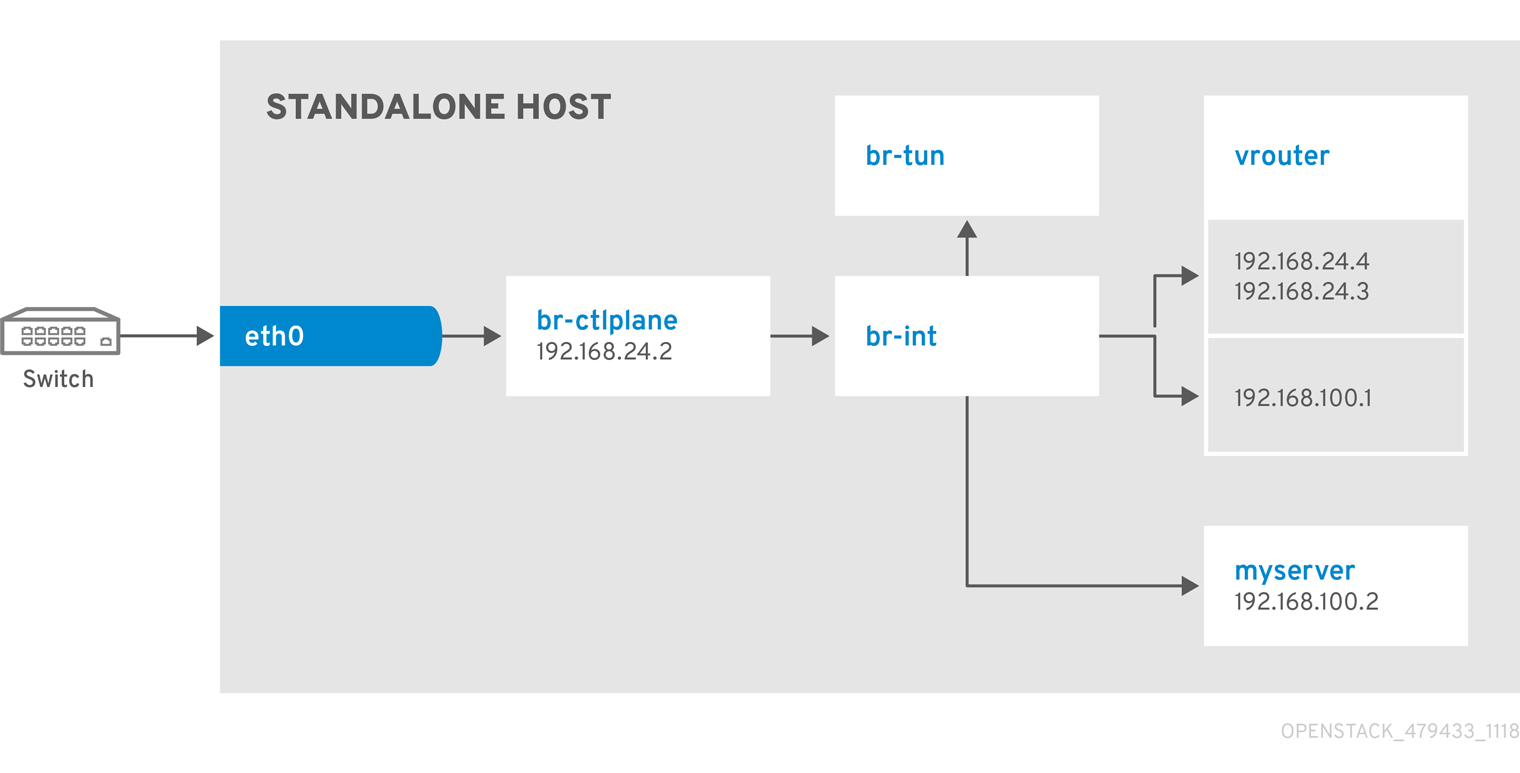
9.2. Example 2: Launching an instance with one NIC on the provider network
Use this example to understand how to launch an instance with the provider network after you deploy the all-in-one Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment. This example is based on a single NIC configuration and requires at least four IP addresses.
Prerequisites
To complete this example successfully, you must have the following IP addresses available in your environment:
- One IP address for the OpenStack services.
- One IP address for the virtual router to provide connectivity to the project network. This IP address is assigned automatically in this example.
- One IP address for DHCP on the provider network.
- At least one IP address for floating IPs on the provider network.
Procedure
Create configuration helper variables:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a basic flavor:
openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tiny
$ openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tinyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download CirrOS and create an OpenStack image:
wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img
$ wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img $ openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.imgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure SSH:
ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem.pub default
$ ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem $ openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem.pub defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a simple network security group:
openstack security group create basic
$ openstack security group create basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the new network security group:
Enable SSH:
openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
$ openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable ping:
openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create Neutron networks:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the instance:
openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network public --security-group basic myserver
$ openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network public --security-group basic myserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Test SSH:
ssh cirros@<VM_IP>
ssh cirros@<VM_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
VM_IPwith the address of the virtual machine that you create in the previous step.
Network Architecture
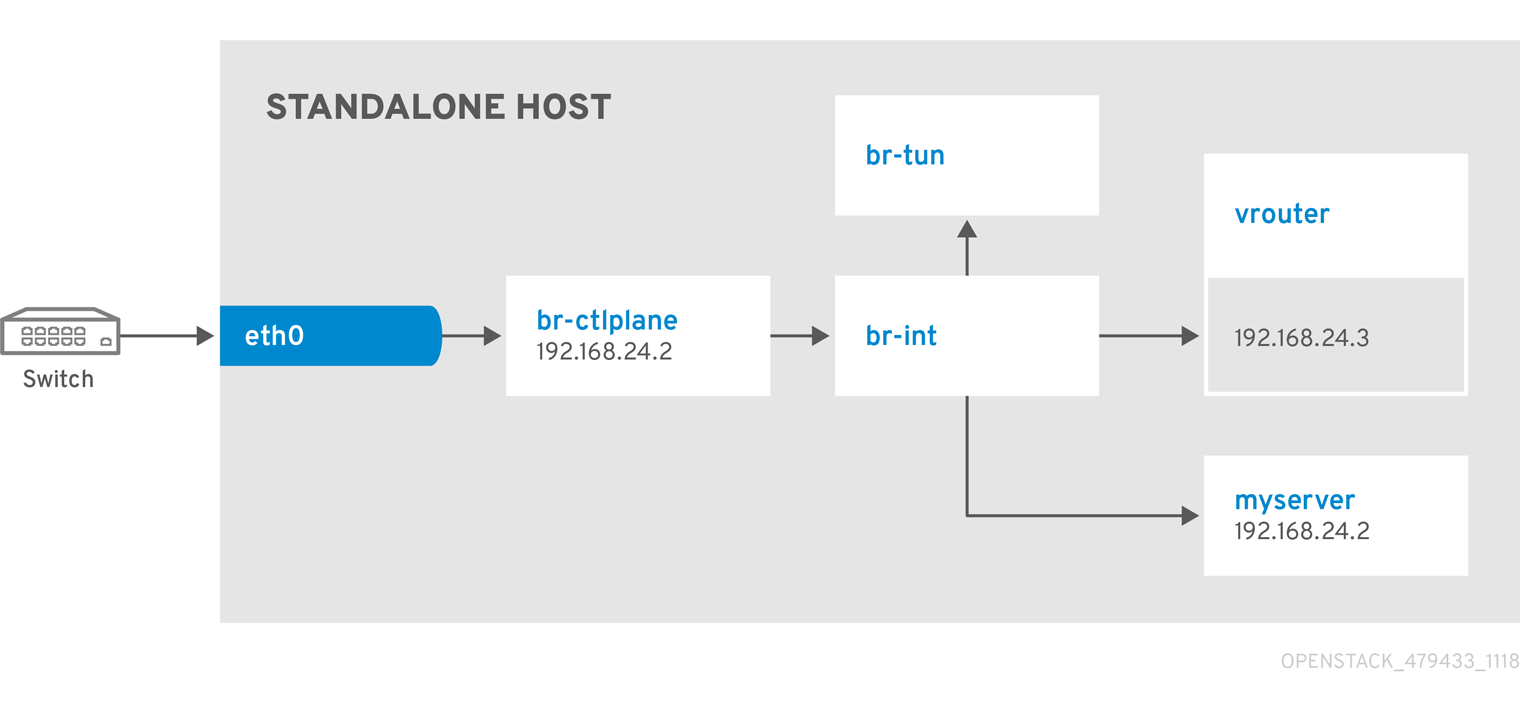
9.3. Example 3: Launching an instance with two NICs on the project and provider networks
Use this example to understand how to launch an instance with the private project network and the provider network after you deploy the all-in-one Red Hat OpenStack Platform environment. This example is based on a dual NIC configuration and requires at least four IP addresses on the provider network.
Prerequisites
- One IP address for a gateway on the provider network.
- One IP address for OpenStack endpoints.
- One IP address for the virtual router to provide connectivity to the project network. This IP address is assigned automatically in this example.
- At least one IP address for floating IPs on the provider network.
Procedure
Create configuration helper variables:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a basic flavor:
openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tiny
$ openstack flavor create --ram 512 --disk 1 --vcpu 1 --public tinyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Download CirrOS and create an OpenStack image:
wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img
$ wget https://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img $ openstack image create cirros --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --public --file cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.imgCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure SSH:
ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem.pub default
$ ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem $ openstack keypair create --public-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa_pem.pub defaultCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a simple network security group:
openstack security group create basic
$ openstack security group create basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the new network security group:
Enable SSH:
openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0
$ openstack security group rule create basic --protocol tcp --dst-port 22:22 --remote-ip 0.0.0.0/0Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable ping:
openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol icmp basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable DNS:
openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basic
$ openstack security group rule create --protocol udp --dst-port 53:53 basicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create Neutron networks:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a virtual router:
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. openstack router create vrouter openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public openstack router add subnet vrouter private-net
# NOTE: In this case an IP will be automatically assigned # from the allocation pool for the subnet. $ openstack router create vrouter $ openstack router set vrouter --external-gateway public $ openstack router add subnet vrouter private-netCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a floating IP:
openstack floating ip create public
$ openstack floating ip create publicCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Launch the instance:
openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserver
$ openstack server create --flavor tiny --image cirros --key-name default --network private --security-group basic myserverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Assign the floating IP:
openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>
$ openstack server add floating ip myserver <FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.Test SSH:
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>
ssh cirros@<FLOATING_IP>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
FLOATING_IPwith the address of the floating IP that you create in a previous step.
Network Architecture
